Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Based Analysis of Cephalometric Radiographs for Differential Diagnosis of Orthognathic Surgery Indications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
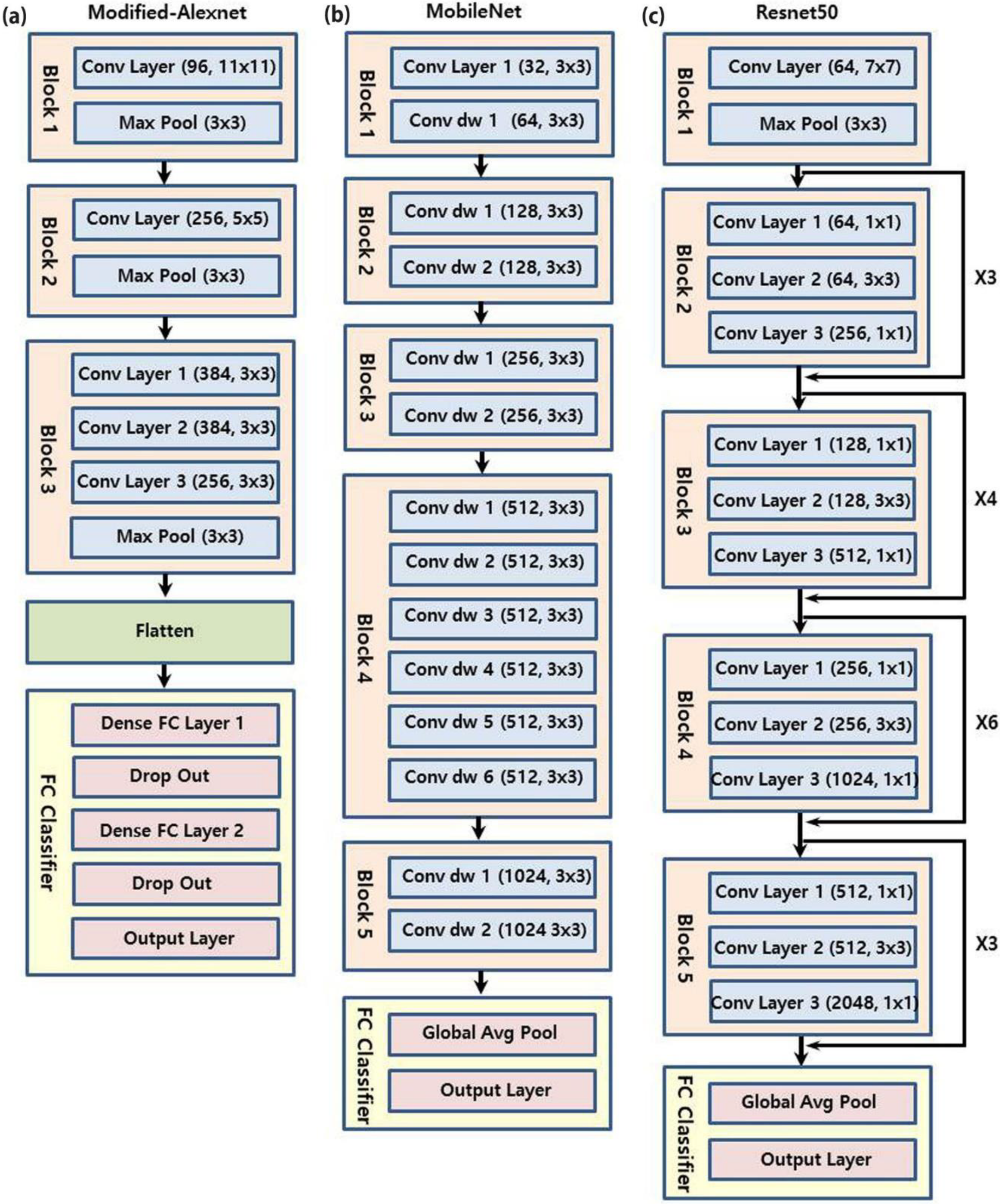
2. Materials and Methods
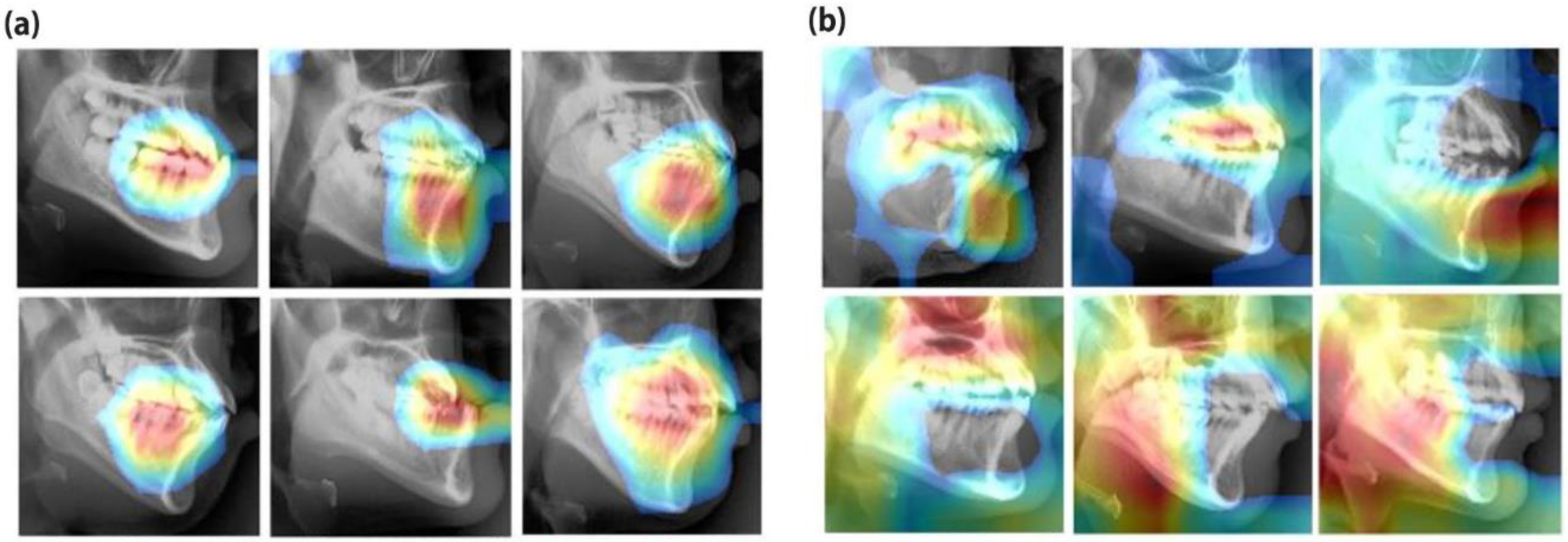
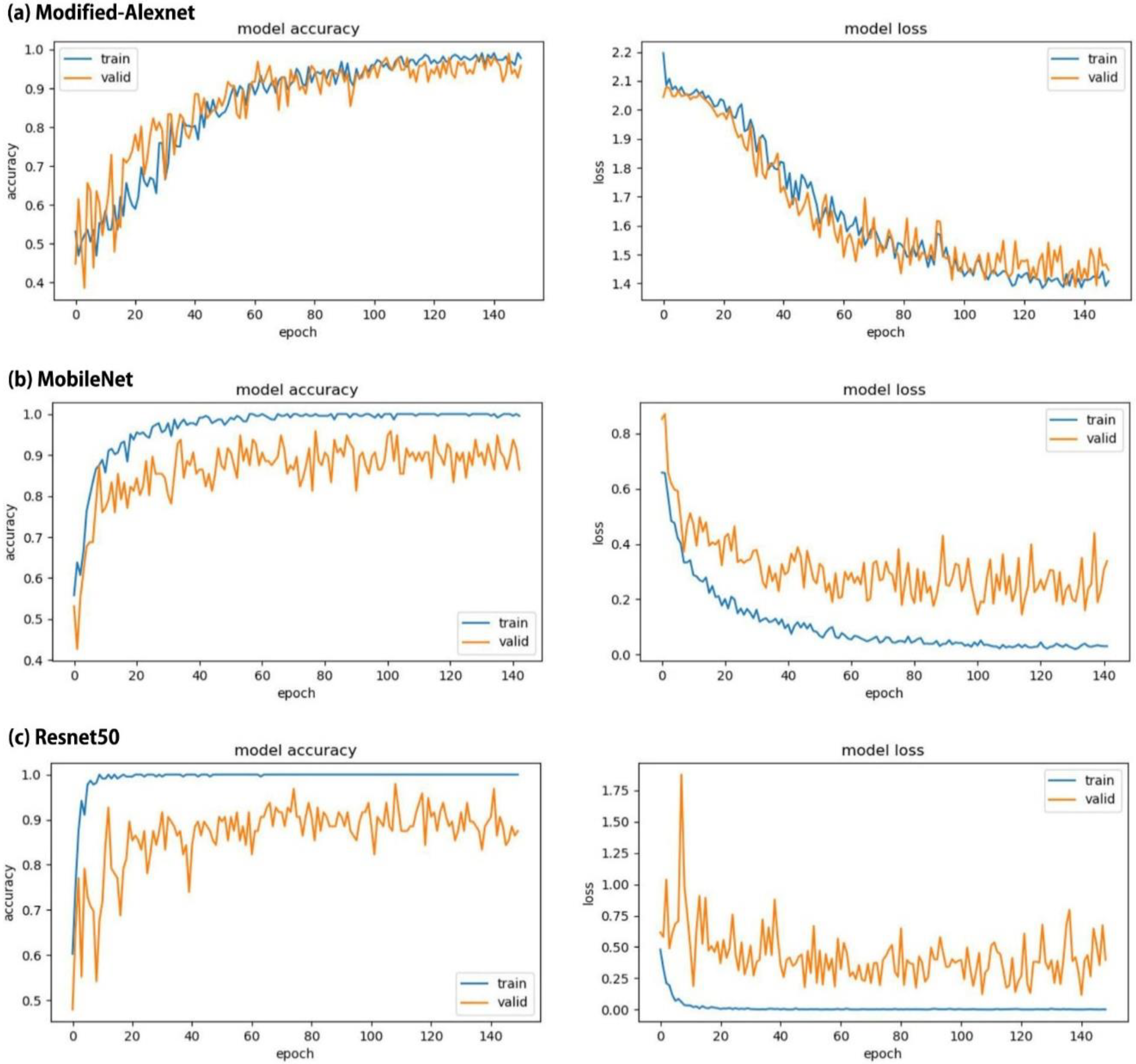
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Proffit, W.R.; Fields, H.W.; Sarver, D.M. Contemporary Orthodontics, 5th ed.; Mosby: St Louis, MO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Veiszenbacher, E.; Wang, J.; Davis, M.; Waite, P.D.; Borbely, P.; Kau, C.H. Virtual surgical planning: Balancing esthetics, practicality, and anticipated stability in a complex Class III patient. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 156, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geramy, A.; Sheikhzadeh, S.; Jalali, Y.F.; Nazarifar, A.M. Anthropometric Facial Changes After Orthognathic Surgery and Their Relation With Oral Health Related Quality of Life. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2019, 30, 1118–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, K.P.; Kaban, L.B.; Masoud, M.I. Orthognathic Surgery and Orthodontics: Inadequate Planning Leading to Complications or Unfavorable Results. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 32, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turpin, D.L. The orthodontic examination. Angle Orthod. 1990, 60, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Heinz, J.; Stewart, K.; Ghoneima, A. Evaluation of two-dimensional lateral cephalometric radiographs and three-dimensional cone beam computed tomography superimpositions: A comparative study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manosudprasit, A.; Haghi, A.; Allareddy, V.; Masoud, M.I. Diagnosis and treatment planning of orthodontic patients with 3-dimensional dentofacial records. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2017, 151, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Yin, D.; Li, C.; Wang, G.; Xu, T. Automated 2-D cephalometric analysis on X-ray images by a model-based approach. IEEE. Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 1615–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Perillo, M.; Beideman, R.; Shofer, F. Effect of landmark identification on cephalometric measurements: Guidelines for cephalometric analyses. Clin. Orthod. Res. 2000, 3, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.W. Variation of the sella-nasion plane and its effect on SNA and SNB. J. Oral Surg. 1976, 34, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.C.; Roth, H.R.; Gao, M.; Lu, L.; Xu, Z.; Nogues, I.; Yao, J.; Mollura, D.; Summers, R.M. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Computer-Aided Detection: CNN Architectures, Dataset Characteristics and Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Huang, Q.; Wang, D.; Gao, L. A CNN-SVM combined model for pattern recognition of knee motion using mechanomyography signals. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2018, 42, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arandjelovic, R.; Gronat, P.; Torii, A.; Pajdla, T.; Sivic, J. NetVLAD: CNN Architecture for Weakly Supervised Place Recognition. IEEE. Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 1437–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Qi, S.; Zhang, B.; Ma, H.; Qian, W.; Yao, Y.; Sun, J. Deep CNN models for pulmonary nodule classification: Model modification, model integration, and transfer learning. J. X-ray Sci. Technol. 2019, 27, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spadea, M.F.; Pileggi, G.; Zaffino, P.; Salome, P.; Catana, C.; Izquierdo-Garcia, D.; Amato, F.; Seco, J. Deep Convolution Neural Network (DCNN) Multiplane Approach to Synthetic CT Generation From MR images-Application in Brain Proton Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Chaudhari, P.; Varghese, K. Runtime Programmable and Memory Bandwidth Optimized FPGA-Based Coprocessor for Deep Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE. Trans. Neural Netw. Learn Syst. 2018, 29, 5922–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03385. [Google Scholar]
- Park, W.J.; Park, J.B. History and application of artificial neural networks in dentistry. Eur. J. Dent. 2018, 12, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miotto, R.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Jiang, X.; Dudley, J.T. Deep learning for healthcare: Review, opportunities and challenges. Brief Bioinform. 2018, 19, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, S.N.; Choi, S.H. Detection and diagnosis of dental caries using a deep learning-based convolutional neural network algorithm. J. Dent. 2018, 77, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.W.; Huang, C.T.; Hsieh, M.C.; Li, C.H.; Chang, S.W.; Li, W.C.; Vandaele, R.; Maree, R.; Jodogne, S.; Geurts, P.; et al. Evaluation and Comparison of Anatomical Landmark Detection Methods for Cephalometric X-Ray Images: A Grand Challenge. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1890–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, E.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Deng, H.; Wu, Y.; Megalooikonomou, V.; Gable, B.; Ling, H. Automatic Dent-landmark detection in 3-D CBCT dental volumes. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; Volume 2011, pp. 6204–6207. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.-K.; Kim, T.-W. New approach for the diagnosis of extractions with neural network machine learning. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2016, 149, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Kong, D.; Tang, T.; Su, D.; Yang, P.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y. Orthodontic Treatment Planning based on Artificial Neural Networks. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 1, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alom, M.Z.; Taha, T.M.; Yakopcic, C.; Westberg, S.; Sidike, P.; Nasrin, M.S.; Esesn, B.C.; Awwal, A.A.; Asari, V.K. The history began from alexnet: A comprehensive survey on deep learning approaches. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.01164. [Google Scholar]
- Bottou, L. Large-scale machine learning with stochastic gradient descent. In Proceedings of the COMPSTAT’2010, Paris, France, 22–27 August 2010; pp. 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, Y.; Hu, J. A K-fold Averaging Cross-validation Procedure. J. Nonparametr. Stat. 2015, 27, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.02391. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.-S.; Jung, S.-K.; Ryu, J.-J.; Shin, S.-W.; Choi, J. Evaluation of Transfer Learning with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Screening Osteoporosis in Dental Panoramic Radiographs. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, H.W.; Park, J.H.; Moon, J.H.; Yu, Y.; Kim, H.; Her, S.B.; Srinivasan, G.; Aljanabi, M.N.A.; Donatelli, R.E.; Lee, S.J. Automated identification of cephalometric landmarks: Part 2-Might it be better than human? Angle Orthod. 2020, 90, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michele, A.; Colin, V.; Santika, D.D. Mobilenet convolutional neural networks and support vector machines for palmprint recognition. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 157, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.I.; Jung, S.K.; Baek, S.H.; Lim, W.H.; Ahn, S.J.; Yang, I.H.; Kim, T.W. Artificial Intelligent Model With Neural Network Machine Learning for the Diagnosis of Orthognathic Surgery. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2019, 30, 1986–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Orthodontic Treatment | Orthognathic Surgery | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 159 | 174 | 333 |
| Number of females/males | 88/71 | 93/81 | 181/152 |
| Mean age (SD) | 22.7 (5.8) | 23.4 (4.9) | 23.1 (5.1) |
| Model | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy (95% CI) | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified-Alexnet | 0.969 (±0.019) | 0.919 (±0.030) | 0.852 (±0.041) | 0.973 (±0.017) |
| MobileNet | 0.908 (±0.032) | 0.838 (±0.429) | 0.761 (±0.051) | 0.931 (±0.028) |
| Resnet50 | 0.923 (±0.030) | 0.838 (±0.429) | 0.750 (±0.052) | 0.944 (±0.025) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.-S.; Ryu, J.-J.; Jang, H.S.; Lee, D.-Y.; Jung, S.-K. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Based Analysis of Cephalometric Radiographs for Differential Diagnosis of Orthognathic Surgery Indications. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062124
Lee K-S, Ryu J-J, Jang HS, Lee D-Y, Jung S-K. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Based Analysis of Cephalometric Radiographs for Differential Diagnosis of Orthognathic Surgery Indications. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(6):2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062124
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ki-Sun, Jae-Jun Ryu, Hyon Seok Jang, Dong-Yul Lee, and Seok-Ki Jung. 2020. "Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Based Analysis of Cephalometric Radiographs for Differential Diagnosis of Orthognathic Surgery Indications" Applied Sciences 10, no. 6: 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062124
APA StyleLee, K.-S., Ryu, J.-J., Jang, H. S., Lee, D.-Y., & Jung, S.-K. (2020). Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Based Analysis of Cephalometric Radiographs for Differential Diagnosis of Orthognathic Surgery Indications. Applied Sciences, 10(6), 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062124







