Soil Hg Contamination Impact on Earthworms’ Gut Microbiome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Set-up
2.2. Soil Physico-Chemical Parameters
2.3. Sequencing of Bacterial and Fungal Ribosomal Markers
2.4. Quantitative PCR of Bacterial and Fungal Ribosomal Markers and Mercury Resistance Genes
2.5. Sequence Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physico-Chemical Parameters and Earthworm Biomass
3.2. Bacterial, Fungal and Mercury Reductase Gene Abundance
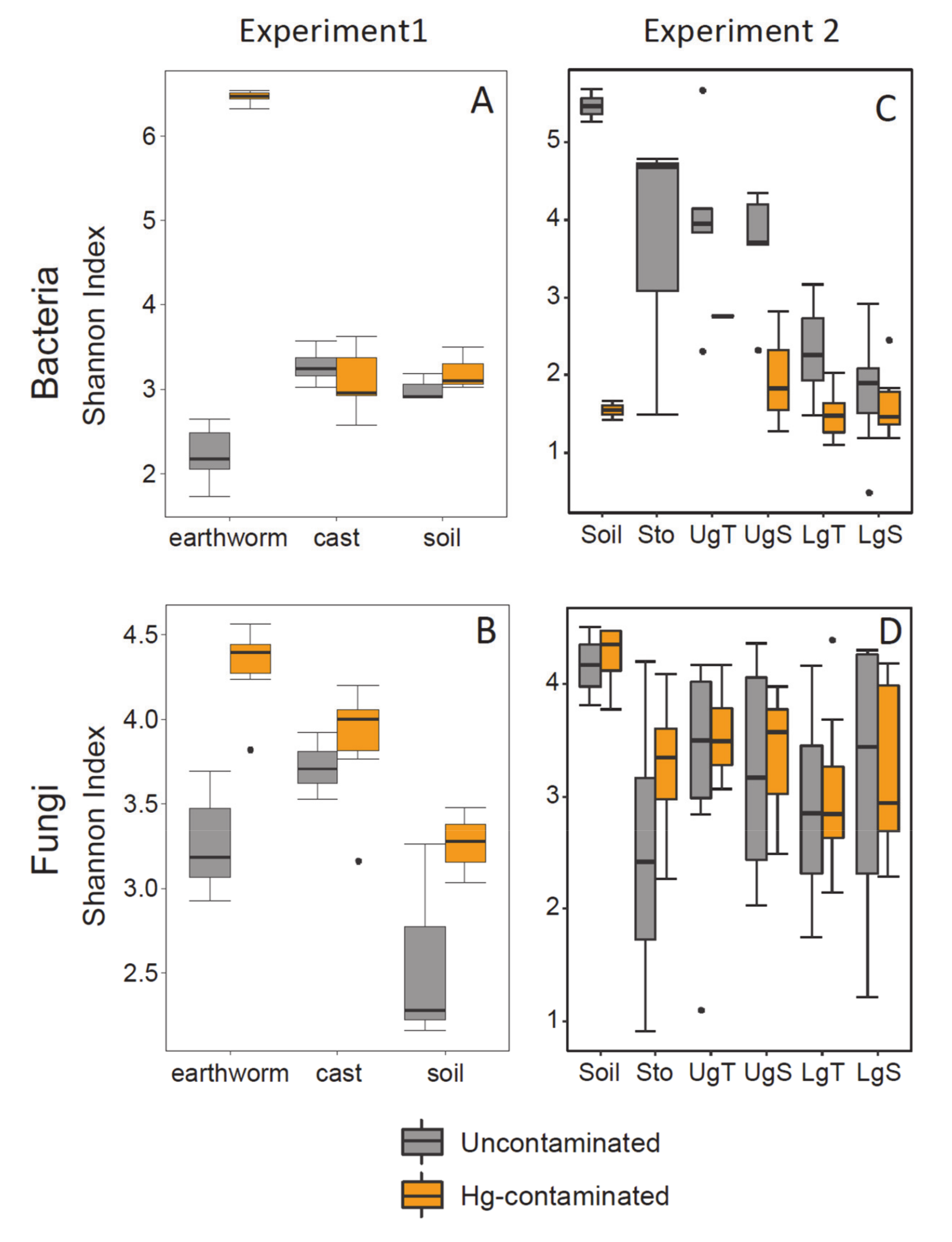
3.3. Alpha Diversity
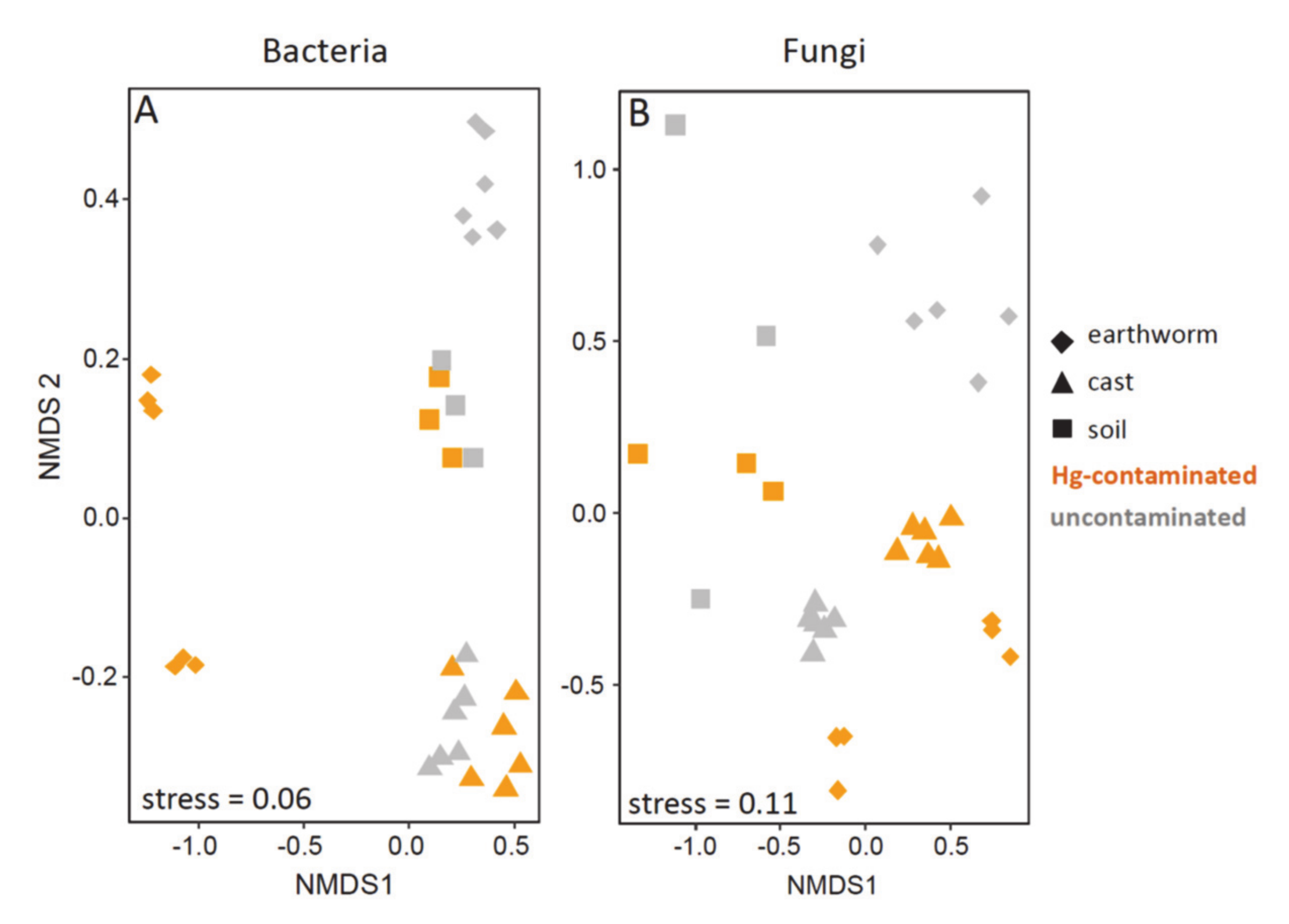
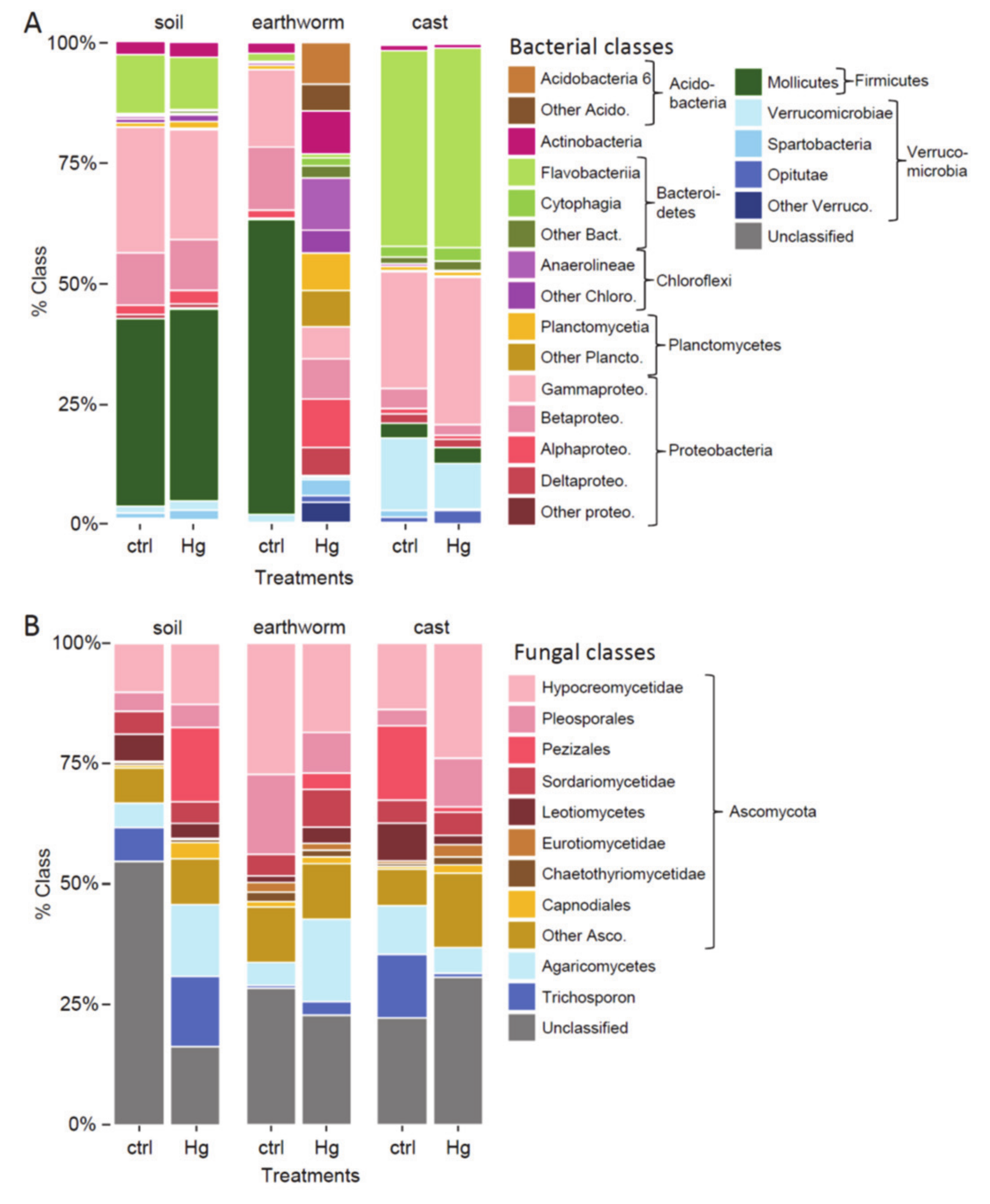
3.4. Beta Diversity in Earthworm, Cast and Soil (Experiment 1)
3.5. Beta Diversity in Earthworms Gut Parts (Experiment 2)
4. Discussion
4.1. Hg Contamination in Soils and Its Effect on Earthworms
4.2. Effect of Hg in Earthworm, Cast and Soil Microbiomes
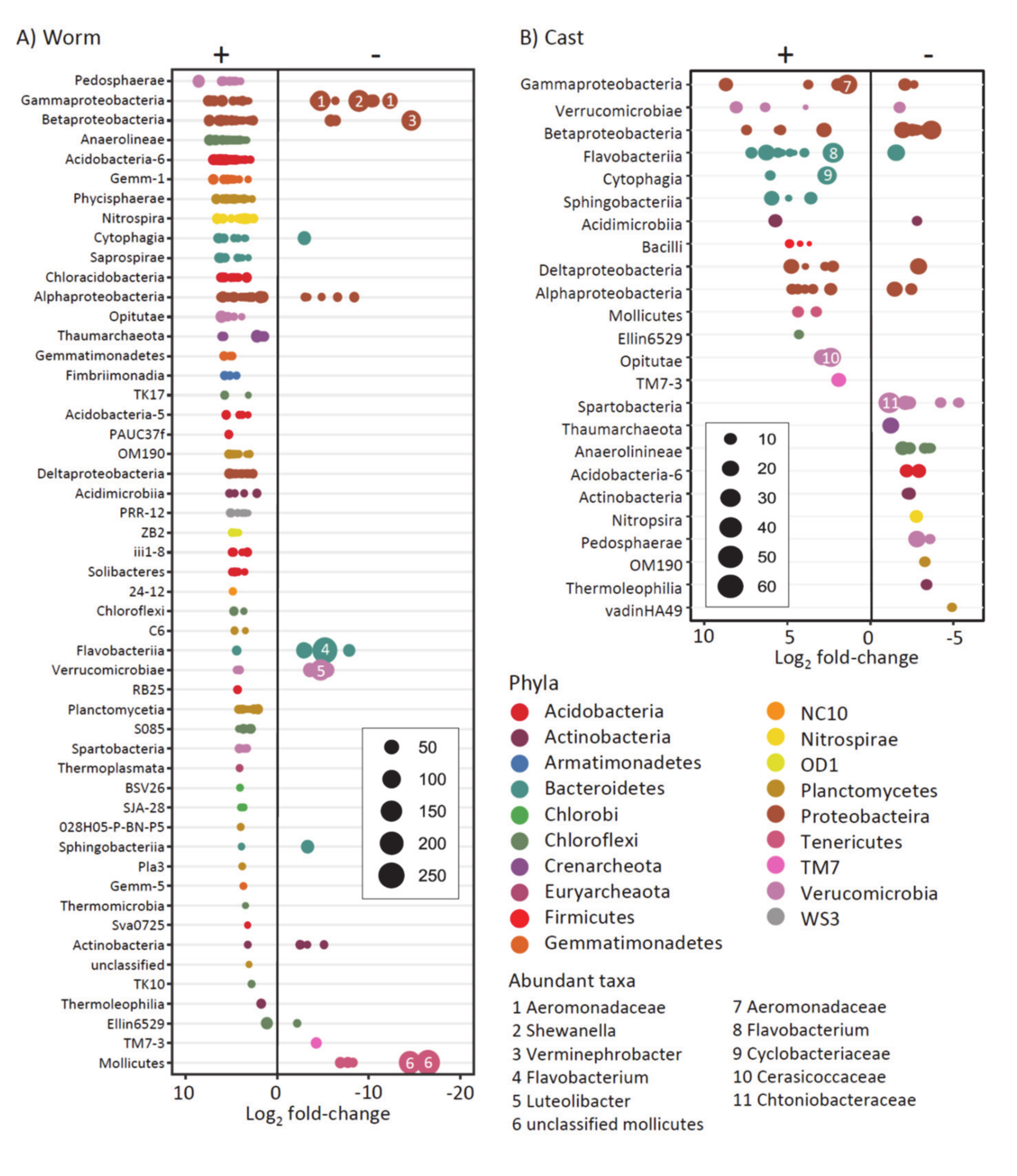
4.3. Effect of Hg on Earthworm Gut Parts
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clarkson, T.W.; Magos, L.; Myers, G.J. The Toxicology of Mercury—Current Exposures and Clinical Manifestations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Organometallic Compounds in the Environment: Principles and Reactions; Craig, P.J. (Ed.) Longman: Harlow, UK, 1986; ISBN 978-0-582-46361-5. [Google Scholar]
- Laffont, L.; Maurice, L.; Amouroux, D.; Navarro, P.; Monperrus, M.; Sonke, J.E.; Behra, P. Mercury speciation analysis in human hair by species-specific isotope-dilution using GC–ICP–MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3001–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahbub, K.R.; Krishnan, K.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Mercury toxicity to Eisenia fetida in three different soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frossard, A.; Hartmann, M.; Frey, B. Tolerance of the forest soil microbiome to increasing mercury concentrations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 105, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, M. Interactions between mercury and dissolved organic matter––A review. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roux, S.; Baker, P.; Crouch, A. Bioaccumulation of total mercury in the earthworm Eisenia andrei. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabriel, M.C.; Williamson, D.G. Principal Biogeochemical Factors Affecting the Speciation and Transport of Mercury through the terrestrial environment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2004, 26, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-S.; Lu, X.-G.; Wang, Q.-C.; Zheng, D.-M. Mercury, Cadmium and Lead Biogeochemistry in the Soil–Plant–Insect System in Huludao City. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, G.G. How do earthworms affect microfloral and faunal community diversity? Plant Soil 1995, 170, 209–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, F.; Zhao, J.; Greenfield, B.K.; Zhong, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, D. Soil geochemistry and digestive solubilization control mercury bioaccumulation in the earthworm Pheretima guillemi. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 292, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, J.J.; Veiga, M.M. Using Earthworms to Assess Hg Distribution and Bioavailability in Gold Mining Soils. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2009, 18, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, S.R.; Brunner, I.; Daniel, O.; Liu, B.; Frey, B. Methylation of Mercury in Earthworms and the Effect of Mercury on the Associated Bacterial Communities. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmour, C.C.; Elias, D.A.; Kucken, A.M.; Brown, S.D.; Palumbo, A.V.; Schadt, C.W.; Wall, J.D. Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium Desulfovibrio desulfuricans ND132 as a Model for Understanding Bacterial Mercury Methylation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3938–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Álvarez, C.R.; Moreno, M.J.; Bernardo, F.G.; Martín-Doimeadios, R.R.; Nevado, J.B. Mercury methylation, uptake and bioaccumulation by the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris (Oligochaeta). Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 84, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Doimeadios, R.C.R.; Mateo, R.; Jiménez-Moreno, M. Is gastrointestinal microbiota relevant for endogenous mercury methylation in terrestrial animals? Environ. Res. 2017, 152, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaschak, E.; Knopf, B.; Petersen, J.H.; Bings, N.H.; König, H. Biotic methylation of mercury by intestinal and sulfate-reducing bacteria and their potential role in mercury accumulation in the tissue of the soil-living Eisenia foetida. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 69, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, J.M.; Johs, A.; Podar, M.; Bridou, R.; Hurt, R.A.; Smith, S.D.; Tomanicek, S.J.; Qian, Y.; Brown, S.D.; Brandt, C.C.; et al. The genetic basis for bacterial mercury methylation. Science 2013, 339, 1332–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Podar, M.; Gilmour, C.C.; Brandt, C.C.; Soren, A.; Brown, S.D.; Crable, B.R.; Palumbo, A.V.; Somenahally, A.C.; Elias, D.A. Global prevalence and distribution of genes and microorganisms involved in mercury methylation. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilmour, C.C.; Podar, M.; Bullock, A.L.; Graham, A.M.; Brown, S.D.; Somenahally, A.C.; Johs, A.; Hurt, R.A.; Bailey, K.L.; Elias, D.A. Mercury Methylation by Novel Microorganisms from New Environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11810–11820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-R.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Bi, L.; Zhu, J.; He, J.-Z. Consistent responses of soil microbial taxonomic and functional attributes to mercury pollution across China. Microbiome 2018, 6, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, E.S.; Barkay, T. The Mercury Resistance Operon: From an Origin in a Geothermal Environment to an Efficient Detoxification Machine. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Takaoka, M.; Sano, A.; Matsuyama, A.; Yanase, R. Vertical Distribution of Total Mercury and Mercury Methylation in a Landfill Site in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2018, 15, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frossard, A.; Donhauser, J.; Mestrot, A.; Gygax, S.; Bååth, E.; Frey, B. Long- and short-term effects of mercury pollution on the soil microbiome. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.M.; Khairalla, A.S.; El-Gendy, A.O.; Elkhatib, W.F. Isolation and characterization of mercury-resistant bacteria from wastewater sources in Egypt. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilli, R.S.; Karlen, C.; Weber, M.; Rüegg, J.; Barmettler, K.; Biester, H.; Boivin, P.; Kretzschmar, R. Speciation and Mobility of Mercury in Soils Contaminated by Legacy Emissions from a Chemical Factory in the Rhône Valley in Canton of Valais, Switzerland. Soil Syst. 2018, 2, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gygax, S.; Gfeller, L.; Wilcke, W.; Mestrot, A. Emerging investigator series: Mercury mobility and methylmercury formation in a contaminated agricultural flood plain: Influence of flooding and manure addition. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 2008–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterwalder, S.; Huang, J.-H.; Shetaya, W.H.; Agnan, Y.; Frossard, A.; Frey, B.; Alewell, C.; Kretzschmar, R.; Biester, H.; Obrist, D. Mercury emission from industrially contaminated soils in relation to chemical, microbial, and meteorological factors. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Particle-size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzaro, A.; Hartmann, M.; Blaser, P.; Widmer, F.; Schulin, R.; Frey, B. Bacterial community structure and activity in different Cd-treated forest soils: Bacterial structure and activity in Cd-treated forest soils. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 58, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frey, B.; Rime, T.; Phillips, M.; Stierli, B.; Hajdas, I.; Widmer, F.; Hartmann, M. Microbial diversity in European alpine permafrost and active layers. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larose, C.; Prestat, E.; Cecillon, S.; Berger, S.; Malandain, C.; Lyon, D.; Ferrari, C.; Schneider, D.; Dommergue, A.; Vogel, T.M. Interactions between Snow Chemistry, Mercury Inputs and Microbial Population Dynamics in an Arctic Snowpack. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frey, B.; Niklaus, P.A.; Kremer, J.; Lüscher, P.; Zimmermann, S. Heavy-machinery traffic impacts methane emissions as well as methanogen abundance and community structure in oxic forest soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6060–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C.; Flyvbjerg, H. Error filtering, pair assembly and error correction for next-generation sequencing reads. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3476–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nikolenko, S.I.; Korobeynikov, A.I.; Alekseyev, M.A. BayesHammer: Bayesian clustering for error correction in single-cell sequencing. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of rRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UNITE Database for Molecular Identification of Fungi–Recent Updates and Future Perspectives—Abarenkov-2010-New Phytologist-Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03160.x (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.r-project.org (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- Gobet, A.; Quince, C.; Ramette, A. Multivariate Cutoff Level Analysis (MultiCoLA) of large community data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Nat. Preced. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahmani, J.; Hodson, M.E.; Black, S. A review of studies performed to assess metal uptake by earthworms. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 402–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhan, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Response mechanism of microbial community to the environmental stress caused by the different mercury concentration in soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Arizono, K.; Ji, H.; Yakushiji, Y.; Zhang, D.; Huang, K.; Ishibashi, Y. Comparison of mercury and methylmercury bioaccumulation in earthworms (Bimastus parvus) native to landfill-leachate-contaminated forest soil. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 43, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Yan, Q.; Wang, X.; Ai, X.; Robin, P.; Matthew, C.; Qiu, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y. Earthworm (Eisenia fetida) behavioral and respiration responses to sublethal mercury concentrations in an artificial soil substrate. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 104, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, J.H. Diversity in Tropical Rain Forests and Coral Reefs. Science 1978, 199, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Lian, B.; Wu, C.; Guo, P. A comparative study of gut microbiota profiles of earthworms fed in three different substrates. Symbiosis 2018, 74, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Drosos, M.; Li, Z.; Hu, Z.; Xi, B. Water-soluble mercury induced by organic amendments affected microbial community assemblage in mercury-polluted paddy soil. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egert, M.; Marhan, S.; Wagner, B.; Scheu, S.; Friedrich, M.W. Molecular profiling of 16S rRNA genes reveals diet-related differences of microbial communities in soil, gut, and casts of Lumbricus terrestris L. (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 48, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schramm, A.; Davidson, S.K.; Dodsworth, J.A.; Drake, H.L.; Stahl, D.A.; Dubilier, N. Acidovorax-like symbionts in the nephridia of earthworms. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pass, D.A.; Morgan, A.J.; Read, D.S.; Field, D.; Weightman, A.J.; Kille, P. The effect of anthropogenic arsenic contamination on the earthworm microbiome. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 176, 1884–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, H.L.; Horn, M.A. As the Worm Turns: The Earthworm Gut as a Transient Habitat for Soil Microbial Biomes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 61, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barois, I.; Lavelle, P. Changes in respiration rate and some physicochemical properties of a tropical soil during transit through Pontoscolex corethrurus (glossoscolecidae, oligochaeta). Soil Biol. Biochem. 1986, 18, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


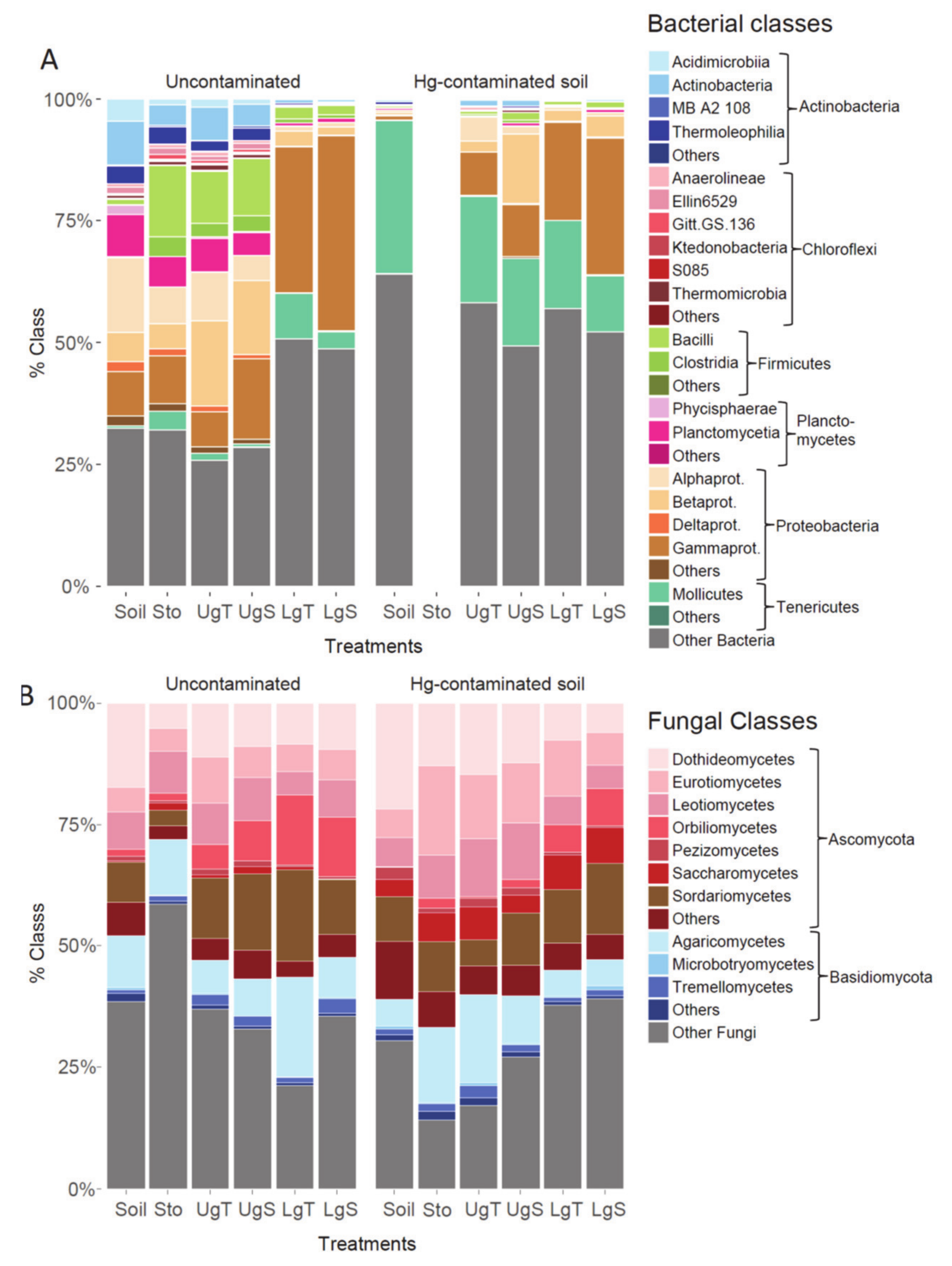
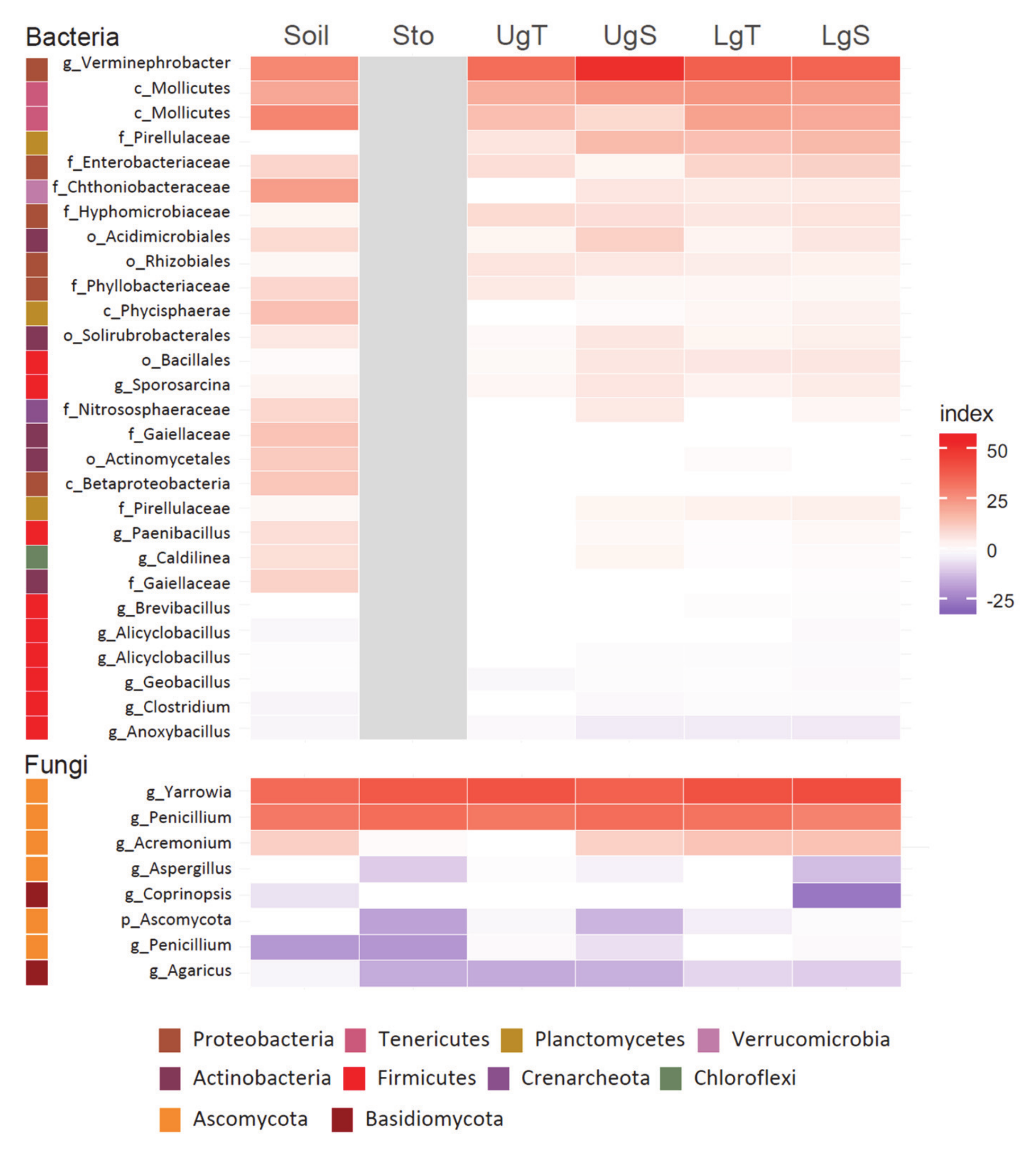
| Physico-Chemical Characteristics | Uncontaminated Soil | Hg-Contaminated Soil | Diff. between Soils/ Hg Treatments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | |||
| Soil THg (µg g−1) | 0.25 ± 0.09 | 36.10 ± 4.80 | 609.8 | <0.001 |
| Soil water-extractable Hg (µg kg−1) | <LOD | 13.11 ± 4.76 | NA | NA |
| Soil MeHg (µg kg−1) | <LOD | 4.59 ± 0.51 | NA | NA |
| pH | 8.30 ± 0.20 | 7.98 ± 0.08 | 9.6 | 0.021 |
| Total C (%) | 2.71 ± 0.32 | 3.88 ± 0.94 | 5.6 | 0.056 |
| Total N (%) | 0.17 ± 0.04 | 0.31 ± 0.08 | 8.9 | 0.025 |
| Sand (%) | 44.40 ± 12.44 | 29.35 ± 3.20 | 5.5 | 0.057 |
| Silt (%) | 48.73 ± 12.05 | 61.18 ± 1.95 | 4.1 | 0.088 |
| Clay (%) | 7.00 ± 1.16 | 9.48 ± 1.47 | 7.1 | 0.037 |
| Exp. 1—earthworm biomass difference (g) | +0.67 ± 3.13 | +0.64 ± 4.56 | 0.0 | 0.975 |
| Exp. 1—earthworm total Hg (µg g−1) | 0.39 ± 0.10 | 12.55 ± 5.46 | 6.3 | 0.030 |
| Exp. 1—earthworm MeHg (µg kg−1) | 6.41 ± 5.82 | 172.54 ± 42.15 | 4.7 | 0.055 |
| Exp. 2—earthworm biomass difference (g) | −1.45 ± 0.65 | −1.35 ± 0.82 | 0.2 | 0.681 |
| Exp. 2—earthworm total Hg (µg g−1) | 0.46 ± 0.09 | 6.88 ± 2.91 | 24.7 | 0.003 |
| Variable | Richness | Shannon Index | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sample subset | Bacteria | Fungi | Bacteria | Fungi | |||||
| DF | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| Experiment 1 | |||||||||
| Type of sample | 2, 29 | 7.5 | 0.003 | 22.24 | <0.001 | 3.8 | 0.036 | 5.2 | 0.124 |
| Treatment | 1, 29 | 13.7 | 0.001 | 31.49 | <0.001 | 15.4 | <0.001 | 3.8 | 0.062 |
| earthworm samples | 1, 11 | 107 | <0.001 | 246.9 | <0.001 | 868.5 | <0.001 | 41.5 | <0.001 |
| cast samples | 1, 11 | 4.4 | 0.062 | 12.23 | 0.006 | 1.0 | 0.339 | 0.0 | 0.862 |
| soil samples | 1, 5 | 9.7 | 0.036 | 3.51 | 0.134 | 1.4 | 0.303 | 1.3 | 0.313 |
| Experiment 2 | |||||||||
| Hg treatment | 1, 49/87 * | 22.1 | <0.001 | 0.4 | 0.531 | 34.0 | <0.001 | 2.4 | 0.127 |
| soil samples | 1, 3/7 * | 18.6 | 0.050 | 0.1 | 0.718 | 259.9 | 0.004 | 0.1 | 0.743 |
| stomach samples | 1, NA/15 * | NA | NA | 0.5 | 0.500 | NA | NA | 3.0 | 0.103 |
| UgT samples | 1, 5/15 * | 0.6 | 0.500 | 0.1 | 0.729 | 0.9 | 0.401 | 0.5 | 0.480 |
| UgS samples | 1, 7/15 * | 9.5 | 0.022 | 0.3 | 0.609 | 8.4 | 0.027 | 0.2 | 0.650 |
| LgT samples | 1, 14/15 * | 18.0 | 0.001 | 0.0 | 0.828 | 9.6 | 0.008 | 0.0 | 0.896 |
| LgS samples | 1, 14/15 * | 1.9 | 0.192 | 0.0 | 0.869 | 0.3 | 0.618 | 0.1 | 0.736 |
| Earthworm gut part | 5, 49/87 * | 7.4 | <0.001 | 6.7 | <0.001 | 8.4 | <0.001 | 3.3 | 0.009 |
| Variable | Bacteria | Fungi | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample subset | DF | F | P | F | P |
| Experiment 1 | |||||
| Type of sample | 2, 29 | 8.3 | <0.001 | 4.6 | <0.001 |
| Hg Treatment | 1, 29 | 5.9 | <0.001 | 3.6 | 0.001 |
| earthworm samples | 1, 11 | 21.5 | 0.002 | 5.0 | 0.002 |
| cast samples | 1, 11 | 4.4 | 0.002 | 12.3 | 0.002 |
| soil samples | 1, 5 | 1.0 | 0.400 | 0.9 | 0.700 |
| Experiment 2 | |||||
| Hg treatments | 1, 49/87 * | 6.5 | <0.001 | 4.0 | <0.001 |
| soil samples | 1, 3/7 * | 2.5 | 0.333 | 1.4 | 0.028 |
| stomach samples | 1, NA/15 * | NA | NA | 1.2 | 0.114 |
| UgT samples | 1, 5/15 * | 1.3 | 0.333 | 2.5 | 0.003 |
| UgS samples | 1, 7/15 * | 1.5 | 0.168 | 1.7 | 0.045 |
| LgT samples | 1, 14/15 * | 1.2 | 0.307 | 1.8 | 0.007 |
| LgS samples | 1, 14/15 * | 1.0 | 0.406 | 1.0 | 0.379 |
| Earthworm gut part | 5, 49/87 * | 2.8 | <0.001 | 2.1 | <0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brantschen, J.; Gygax, S.; Mestrot, A.; Frossard, A. Soil Hg Contamination Impact on Earthworms’ Gut Microbiome. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2565. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072565
Brantschen J, Gygax S, Mestrot A, Frossard A. Soil Hg Contamination Impact on Earthworms’ Gut Microbiome. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(7):2565. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072565
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrantschen, Jeanine, Sebastian Gygax, Adrien Mestrot, and Aline Frossard. 2020. "Soil Hg Contamination Impact on Earthworms’ Gut Microbiome" Applied Sciences 10, no. 7: 2565. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072565
APA StyleBrantschen, J., Gygax, S., Mestrot, A., & Frossard, A. (2020). Soil Hg Contamination Impact on Earthworms’ Gut Microbiome. Applied Sciences, 10(7), 2565. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10072565





