Abstract
Individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are characterised as having impairments in social-emotional interaction and communication, alongside displaying repetitive behaviours and interests. Additionally, they can frequently experience difficulties in processing sensory information with particular prevalence in the auditory domain. Often triggered by everyday environmental sounds, auditory hypersensitivity can provoke self-regulatory fear responses such as crying and isolation from sounds. This paper presents SoundFields, an interactive virtual reality game designed to address this area by integrating exposure based therapy techniques into game mechanics and delivering target auditory stimuli to the player rendered via binaural based spatial audio. A pilot study was conducted with six participants diagnosed with ASD who displayed hypersensitivity to specific sounds to evaluate the use of SoundFields as a tool to reduce levels of anxiety associated with identified problematic sounds. During the course of the investigation participants played the game weekly over four weeks and all participants actively engaged with the virtual reality (VR) environment and enjoyed playing the game. Following this period, a comparison of pre- and post-study measurements showed a significant decrease in anxiety linked to target auditory stimuli. The study results therefore suggest that SoundFields could be an effective tool for helping individuals with autism manage auditory hypersensitivity.
1. Introduction
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex, pervasive neurological disorder that influences perception, thought and emotion. Characterised through impaired development in social interaction, communication, repetitive behaviours and interests [1]. In addition, atypical responses to sensory stimulation have been documented in individuals with ASD since its original descriptions in the 1940s by Kanner [2] and Asperger [3], with particular prevalence being exhibited within the auditory domain [4,5,6,7,8]. Data collected by the Autism Research Institute from over 17,000 families of children with autism, found that approximately 40% contained parental reports of sound sensitivity [6]. These auditory receptive abnormalities can often provoke atypical self-regulatory behaviours which may be observed as aggressive or autonomic fear responses such as covering ears, crying and self injury from blows to the ears [9].
The cause of sound hypersensitivity has been the focus of much research aiming to detect some physiological evidence that could demonstrate a difference in auditory processing between individuals with ASD and their typically developed peers [10,11,12]. However, at present, there appears to be no indication of any physiological abnormalities within the auditory canal of those with autism. A study conducted by Lucker [13] which involved 50 children with ASD presenting with auditory hypersensitivity, measured tolerance for loud sounds by exposing subjects to narrow band noise and warbled tones ranging from 250 to 8000 Hz. Although prior to testing all children demonstrated negative behavioural reactions to loud sounds in everyday scenarios, 86% of children in the ASD group were found to tolerate sounds at 110 dBHL. This correlates with earlier work [14,15,16], indicating that neurological and neurophysiological issues affect auditory processing.
Rather than a physiological pain response to sound, literature therefore suggests that an individual’s extreme aversion to particular auditory stimulus is a manifestation of an irrational fear of the auditory stimulus [9,13,17,18]. Unfortunately these profound aversions are reported to be provoked by common environmental sounds [17], with individuals on the autistic spectrum reporting, for example, a fear of vacuum cleaners [19], toilet flushing [17] and paper bag popping [20]. By avoiding challenging acoustic environments, children with ASD will experience increased isolation and further impairment in natural and social communications. If left untreated, an individual’s reaction while experiencing an intense aversion to sound may be severe.
1.1. Current Interventions for Auditory Hypersensitivity
With evidence suggesting that auditory hypersensitivity within the ASD population is caused by psycho-emotional problems rather than specific physiological manifestations within the auditory system, interventions have been developed which focus on the neural mechanisms involved with emotional processing, emotional memory and emotional reactions. Such interventions call upon cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) techniques such as systematic desensitisation, a procedure which reduces pathological fear and its related emotions by exposing the patient to the feared stimulus in the presence of relaxation or play activity. However, this does not alter any existing pathological structures, rather it forms completely new and competing structures that contain no pathological associations [21,22].
This approach has been demonstrated to reduce fear in children with ASD who have specific phobias such as eating, dogs and visits to the dentist [23,24,25]. Importantly, desensitisation has been used to treat the hypersensitivity of children with autism to common environmental auditory stimuli. An example of this is shown in research by Koegal et al. [17]. A small group of three children with autism who had severe hypersensitivity to everyday sounds (vacuum cleaner, blender, hand-mixer, toilet flushing, toys), was found to have a noticeable reduction in adverse reactions to auditory stimuli after up to 34 weeks of systematic exposure.
There is extensive literature that supports the use of CBT as an effective intervention to reduce anxieties in autism [26]. However, there are arguments based on the core symptoms of autism that would suggest that traditional CBT techniques are not appropriate for this particular neurological disorder. Firstly, CBT sessions often involve face-to-face verbal exchanges. These aim to teach the child to not only become knowingly aware of their pathological associations with a feared stimulus but also create a challenge for them and develop new positive associations [27]. This would be particularly challenging for a child with cognitive and social impairments, resulting in diminished motivation and engagement in traditional CBT [28]. Secondly, CBT techniques that use imaginal exposure are not contextualised and do not fully characterise the medium in which the patient experiences their anxiety. This is also problematic for ASD, as they need frequent practice and contextualised exposure to increase chances of real life generalisation [29]. Another important consideration of current CBT is a lack of accessibility. A recent systematic review by Ince et al. [30] has noted that the rates of implementation for cognitive behavioural therapy are below the recommended levels for the United Kingdom. This gap in delivering successful mental health interventions has stemmed from a number of influences including lack of resources, limited dedicated therapy time and a lack of specialist training [31].
It is often reported that individuals with ASD have an affinity with technology, and similar to their neuro-typically developed peers, actively engage with and enjoy playing video games. This has led to an increase over the past decade in interventions for this population being delivered through computer driven approaches such as serious games (SG). These applications are capable of combining computer game mechanics and traditional therapeutic mechanisms within engaging virtual environments. Such games allow for full control over sensory information presented to the user, creating a safe environment in which players can practise newly acquired skills. Furthermore, serious games have been observed as a cost effective and accessible approach to interventions for individuals with autism.
At this time there is only one published study examining this area. Sinbad and the Magic Cure [32] is a mobile game in which during game play children are exposed to stereo renders of sounds that are found to be particularly disturbing to those with autism. Audio files were chosen based on an auditory questionnaire completed by ten male children diagnosed with ASD. The game was evaluated using a small cohort of seven participants aged between 8 and 11 with autism and hypersensitivity to sound. The intervention involved playing the game over multiple sessions over a course of seven days, with their responsiveness to the sounds measured daily through an auditory questionnaire. Although testing spanned a shorter time than most exposure therapy methods, the results showed that the children started to develop a tolerance to the sounds.
Despite the positive results, current audio rendering technology, such as head-tracked binaural based audio that is used within virtual reality (VR) applications, could improve SG for auditory hypersensitivity. This can be achieved by accurately simulating the natural movement of a sound stimuli within a 360° acoustic space. Increased realism delivered by VR has been observed as having a positive impact upon the generalisation of newly acquired skills to real-world applications of those with ASD [33].
1.2. Virtual Reality and ASD Therapy
Virtual reality has demonstrated to be another active area of research for interventions for children and adults with ASD [34]. Empirical studies have not only recognised VR as an important support tool for educational and training practices such as disaster awareness [35], driving [36] and independent functioning [37], but virtual environments have also demonstrated effectiveness in fostering the development of social and emotional skills of those with autism [38,39].
Similar to serious games, VR has the facility to control audio and visual stimulus and deliver a consistent error-free learning environment [34]. However, a significant difference between VR and serious games is its specific ability to deliver immersive three-dimensional virtual surroundings based on either real life or simulated environments. These realistic virtual environments (VEs) can be interpreted by young people with ASD, making decisions based on the similarity between the virtual and real world. This rationalisation is further demonstrated in studies that observe generalisation of skills and information learned with VEs to real world context [40,41,42].
1.3. The Use of Binaural-Based Spatial Audio
Primarily, the use of virtual reality to treat anxiety and other psychiatric disorders often relies on the accurate visual representation of the feared stimuli, with sound playing an accompanying and lesser role [43,44]. However, spatial sound can have direct impact on immersion and presence felt within a virtual environment. These are one of the essential psychological functions associated with triggering anxiety in virtual reality exposure therapy (VRET) [45].
Although 3D sound is important in creating an immersive virtual experience, there is limited research with mixed results investigating its capability to induce feelings of anxiety. Brinkman et al. [46] compared the effects of different audio rendering techniques over headphones and measured the participants self-reported levels of anxiety towards a virtual wasp. The experiment exposed individuals to the sound of the wasp flying around an indoor VR space. Results showed that compared to mono, stereo and 5.1 surround, 3D audio generated significantly higher levels of presence and anxiety. In addition, Argo [47] developed a soundscape exposure therapy that made use of CBT techniques and higher order ambisonics rendered over multiple loudspeaker arrays. The program was built not to tackle a specific phobia but rather aimed at those who experience general feelings of anxiety. The produced soundscapes did not aim to be a realistic reconstruction of an auditory environment. Instead they were designed to be hyperreal, with the use of strange spatial panning and universally anxiety-eliciting sounds. During exposure sessions, participants experienced feelings of anxiety and stress. However, following the intervention program they became habituated to the physical symptoms of anxiety they experienced in everyday life.
Within virtual reality applications, the realistic rendering of three-dimensional auditory environments via headphones is known as binaural-based spatial audio. This is achieved through filters which simulate the free field acoustic path from a sound source to the ear canal. These filters are known as Head Related Transfer Functions (HRTFs) [48]. HRTFs contain direction dependant information such as interaural differences in time and level and spectral shaping caused by the torso, head and pinnae [48]. Binaural rendering can subsequently be achieved via the convolution of a monaural anechoic audio signal with the appropriate HRTF for a given point in space for each ear [49,50].
1.4. This Study
This paper describes SoundFields, a novel virtual reality game designed to address auditory hypersensitivity in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. The system has the capability to present naturalistic representations of feared auditory stimuli to the player using binaural-based spatial audio. Using this audio rendering technique it is possible to realistically simulate the dynamic movement of an averse stimuli and the acoustic environment in which it is commonly experienced. Feared auditory stimuli are incorporated into serious game mechanics established in CBT approaches, in particular exposure based training [17] which has been seen to address auditory hypersensitivity in individuals with ASD in serious game contexts [32,51].
Following the description of SoundFields, a pilot study is presented which evaluates the effectiveness of the game at reducing fear based reactions towards target auditory stimuli. The investigation involved a group of six individuals diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder and observed as having hypersensitivity to particular sounds. Each participant played the virtual reality game once a week over a four week period in which each session they would be exposed to target stimuli delivered using in-game mechanics. It is hypothesised that following the four week study participants will demonstrate an increase in tolerance towards target stimuli, indexed through a decrease in self-reported anxiety scores and an increase in voluntary interactions with target auditory stimuli.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SoundFields: Game Description
SoundFields is the prototype of an individual interactive virtual reality game. It is designed for children and adolescents diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder and who also display auditory hypersensitivity towards particular sounds. It aims to help individuals become habituated to sounds that might ordinarily provoke feelings of irritation or anxiety by integrating principles of exposure therapy into its core game mechanics.
A critical feature of serious games developed for individuals with ASD is the inclusion of story-driven rationale which provides long-term goals [52]. Within SoundFields children are presented with a non-playable character (NPC) named Fabian the wizard (see Figure 1) who acts as a guide within the game. He explains that the player must help him locate and collect virtual characters that are distributed throughout the enchanted forest environment (see Figure 2) using magic, and that some emit sounds that they may find disturbing. For each collected character the player is rewarded with gems that are used as an in-game currency and score system. This method of reward system has been included in SG for people with autism and is used to engage players and encourage them to perform well in the game [53]. This is further reinforced when the player interacts with characters who play target feared stimuli. When these are successfully captured the player is rewarded with additional bonus gems. This extra reward aims to encourage the child to voluntarily interact with averse sounds.

Figure 1.
Nonplayable character Fabian.

Figure 2.
Bird’s-eye view of the SoundFields virtual environment.
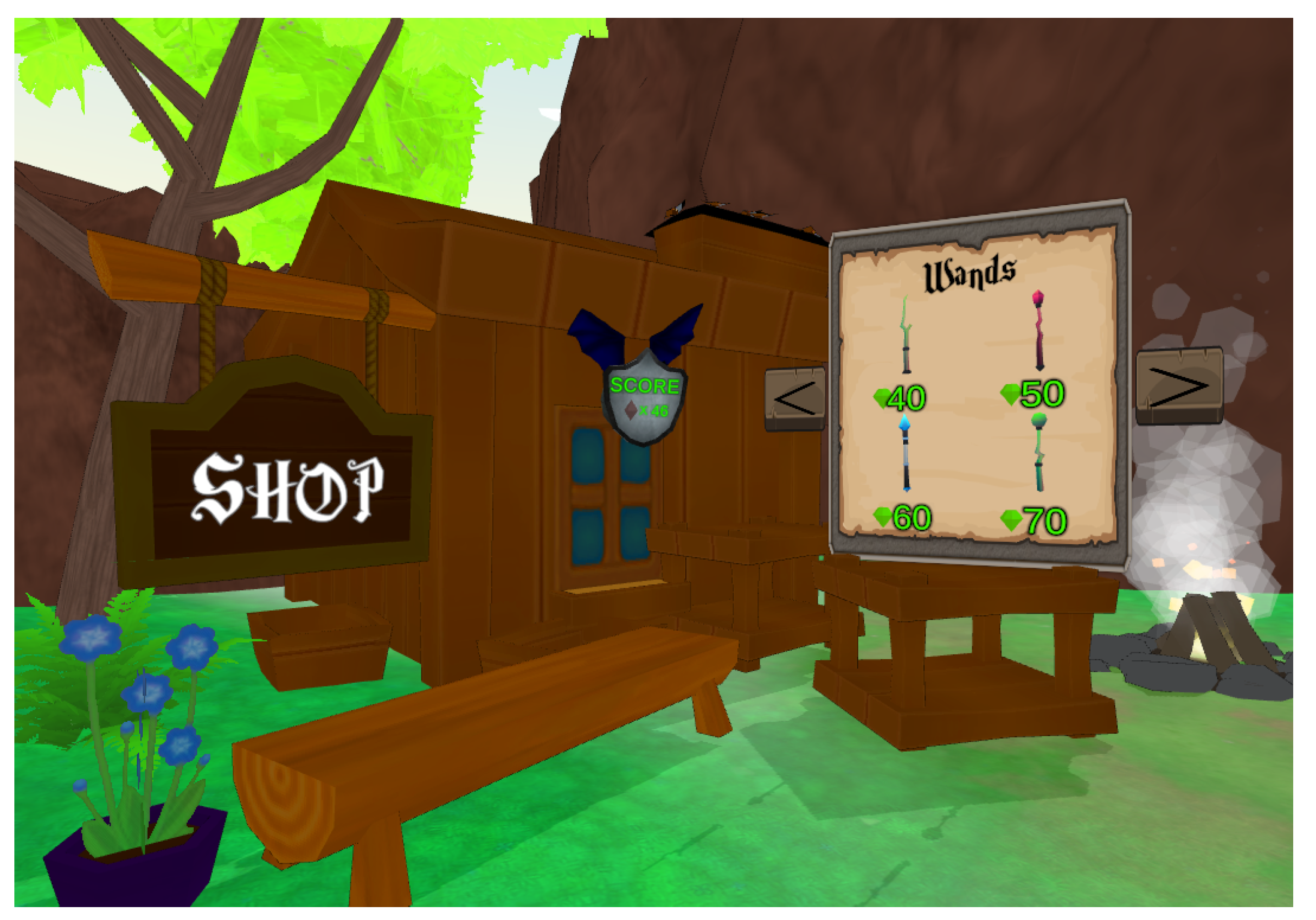
Additional motivation to facilitate engagement with game mechanics comes via the virtual shop (see Figure 3) in which earned currency can be spent. Players are able to customise their avatar through purchasing new magic wands and gloves. Further to motivation, the customisation and personalisation of the player’s virtual aesthetics has demonstrated to improve game experience and enhance immersion in SG developed for people with disabilities [54].

Figure 3.
SoundFields virtual shop. Here, players are able to spend in-game currency to customise their avatar.
The effective outcome of VRET for phobias is based on the controlled delivery of sensory information, creating a realistic simulation of feared stimulus within the virtual environment. SoundFields accomplishes this by rendering feared auditory stimuli using head-tracked binaural based spatial audio. This sound reproduction technique is capable of simulating the movement of an audio source within a 360 degree space and adapt its movement to compensate for the movement of the players head within the virtual environment. Furthermore, it is also possible to emulate the acoustic parameters of the sound in the environment it is most encountered in. The enhanced perceptual realism of soundscapes experienced whilst using spatial audio [55] aims to address difficulties in contextualisation of the presented stimuli encountered by individuals with ASD during virtual CBT sessions. Finally, by using spatial audio, exposure hierarchies similar to those applied in previous exposure training for auditory hypersensitivity [17] can be recreated inside the virtual environment. This is achieved through simulated distance attenuation properties of sound, moving the virtual sound source closer to the player in a stepped process. The heterogeneous nature of ASD symptoms varying between children necessitates the need to individualise the gaming experience [52]. Within SoundFields, the exposure stimuli can be chosen from a database within the game to individualise the therapeutic experience.
The main gameplay consists of two mini-games in which the player is given opportunities to voluntarily expose themselves to feared target auditory stimuli. Players are able to choose which game they play and can repeat it as many times as they please. This repeatability does not only make SG experiences enjoyable and motivating for those with autism [56] but can also increase generalisation by allowing repeated exposure to stimuli [29].
The first game, shown in Figure 4, requires the player to locate orbs hidden within the virtual game environment. Once found, the player must then capture the orb by using their magic wand which gradually moves it towards them. During game-play orbs will spawn randomly at predetermined locations within the VE. Once active, the orbs will emit speech-like stimuli which aims to attract the player’s spatial attention towards their position and assist them in locating it. When the orb is successfully caught it will play an audio stimuli for positive reinforcement.

Figure 4.
Mini-game one: Orb Hunt.
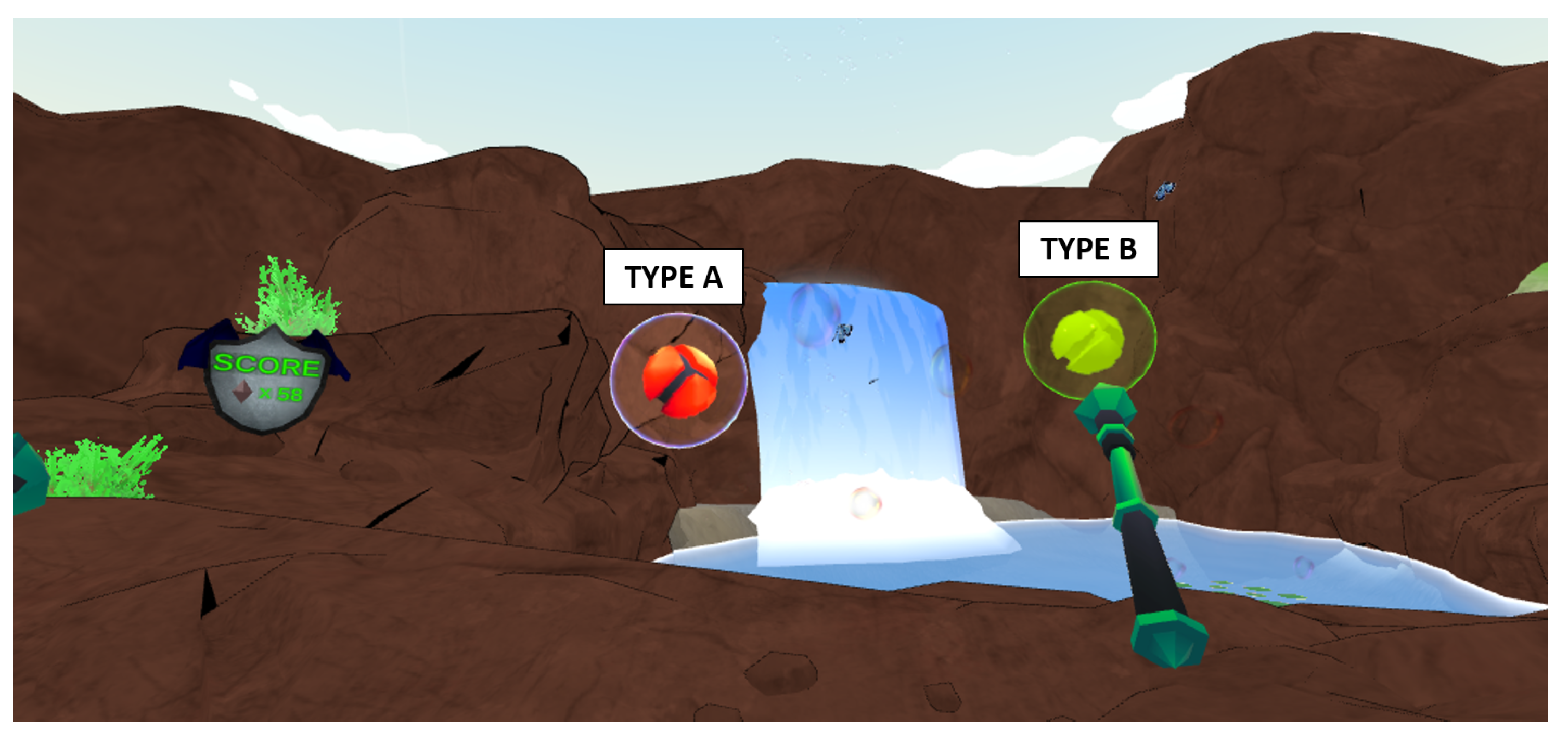
Two variants of the orb are used during this mini-game and are displayed in Figure 4. Type A will only emit speech like stimuli throughout the length of time the player interacts with it; once the player successfully catches the orb they are rewarded with one gem. Type B, which is denoted by its gold colour, will emit speech like stimuli until the player interacts with it. Once interaction commences the orb will play spatialised reproductions of averse target auditory stimuli. In addition, the orb will travel towards the player at a slower speed in order to maximise exposure time. Once the player successfully collects this orb, they are rewarded with 10 gems. As a strategy to optimise the potential therapeutic outcomes, the spawn, locate and collect game mechanic is looped until the player wishes to stop it. This creates multiple chances for the player to be exposed to their target averse stimuli. Furthermore, it is based upon the repeated and predictable game-play that can maintain interest and motivation to engage with SG for those with ASD [56,57]. The objective of mini-game two (see Figure 5) is for the player to rescue orbs trapped within floating bubbles by using their magic wand to pop them. During game-play, bubbles containing the orbs will spawn randomly at predetermined locations within the VE waterfall. Bubbles will float upwards until they have either been popped by the player or they reach a virtual height of 20 m; at this point they will disappear and respawn.
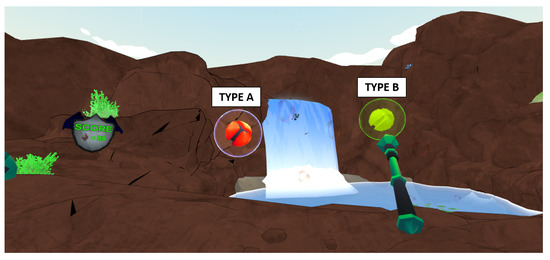
Figure 5.
Mini-game two: Bubble Rescue.
Similar to the orb hunt mini-game, there are two variations of characters the players can interact with; these are highlighted in Figure 5. Type A will only emit speech like stimuli; once the virtual bubble is popped the orb will play a positive reinforcement auditory stimulus and the player is awarded one gem. Type B is represented as a golden bubble; this bubble will emit speech-like stimuli until it is interacted with. Once the player begins interaction, a reproduction of the player’s target averse stimulus will be played at the corresponding exposure hierarchy, if the player ceases interaction the target stimuli will stop. Once the bubble has been popped by the player, the target audio will stop, the positive reinforcement will be played and the player will be awarded ten gems.
The system was developed using the Unity3D game engine software [58] and was programmed using C# scripting language. All audio stimuli were recorded or edited using the Reaper digital audio workstation and WWise [59] game audio engine. Stimuli were a combination of original spatial audio recordings extracted from the Eigenscape database [60], the Vocal Interaction in an Immersive Virtual Acoustic (VIIVA) system [61] and recordings obtained from FreeSound.org [62] under the creative commons licence. The 3D binaural-based spatial audio was rendered via the Google Resonance spatial audio SDK [63].
2.2. Participants
A study group consisted of a small cohort of 6 adolescents (4 male and 2 female, mean age = 17.7, SD = 1.03, range of 16–19 years). Participants were recruited from Springwater Special Education School, Harrogate, UK. All participants had a formal diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder obtained from their local national health trust, displaying social, cognitive, and motor functioning associated with moderate to high functioning autism. In addition, all participants experienced auditory hypersensitivities to single or multiple auditory stimuli. Exclusion criteria were self-reported physiological hearing problems; physical disabilities that would limit movement around the experiment space; and an inability to finish the task.
The sessions took place within the school that participants were recruited. This study and methods were approved by the University of York Department of Electronics board of ethical approval, and an information package was provided to the participants parent(s) or legal guardian(s). Participants were admitted into the study after informed consent and assent was obtained from their parent(s) or legal guardian(s).
2.3. Intervention Protocol
All six participants underwent an intervention of 4 sessions of increasing exposure towards a particular auditory stimulus (see Table 1), with a duration of approximately 30 min. Of the six participants recruited, all were able to complete all 4 intervention sessions. During the recruitment, parents of the participants were required to complete a questionnaire which stated the particular auditory stimuli each participant displayed negative behavioural reactions towards.

Table 1.
Participant demographics including identified problematic sounds.
2.3.1. Baseline
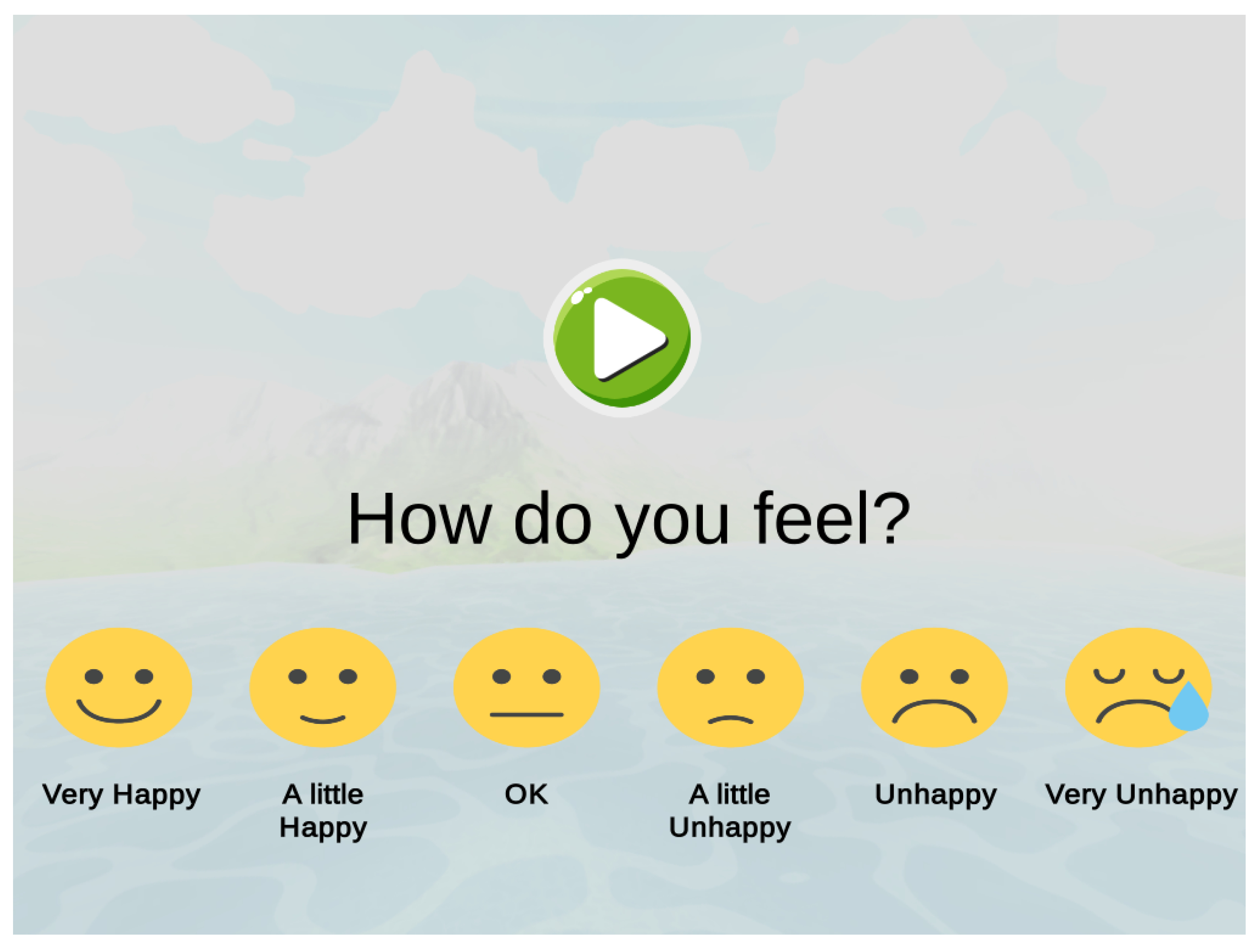
Baseline measurements were recorded one week prior to the beginning of the intervention. Each participant completed an identical audio based questionnaire in which they would rate their perception of specific sounds. A series of emojis were designed to translate an analogue scale into graphical information that could be understood by the participant and bypass any possible communication impairments (see Figure 6). A total of twenty-two types of sounds were included, eleven representing all disturbing sounds provided through parent questionnaires, and eleven “relaxing” soundscapes taken from the Eigenscape database [60]. All audio was presented using binaural based spatial audio. The audio questionnaire was developed in the Unity3D 2018 game engine software. Table 1 provides demographic data for each participant alongside their target auditory stimuli. In addition, all participants played the basic virtual reality tutorial “First Steps” by Oculus [64] to gain practical experience of virtual reality and to learn the associated controls.
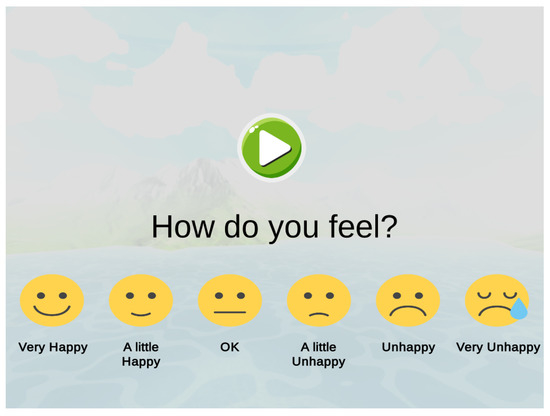
Figure 6.
Audio interactive questionnaire.
2.3.2. Session Procedure
Each participant was given the opportunity to play the SoundFields game for a period of approximately 30 min, once a week over the course of four weeks. At the beginning of each session the investigator would select the target stimuli for the participant from a library of sounds built into the application. The investigator limited interaction with the participants to giving assistance with gaming controls and to provide verbal praise when they successfully interacted with objects that emitted problematic target sounds.
Each stimuli could appear within the game a maximum of twenty times throughout each 30 min session. To simulate exposure hierarchies used in proven desensitisation approaches [17], virtual auditory stimuli were moved closer to the participant at the beginning of each session, see Table 2. After playing the game each participant would complete the same audio questionnaire to record their own perceived level of anxiety towards the target stimuli.

Table 2.
Exposure hierarchy. Each exposure level corresponds to the distance between the participant and the virtual sound source; distance is represented in metres.
2.4. Equipment Setup
All visual stimuli was rendered using the Oculus Rift CV1 head mounted display (HMD). Head tracking was also achieved using the HMD, with motion tracking of participant position calculated by the Oculus Rift sensors. Player input was achieved using the Oculus Touch controllers [64]. Throughout each session participants were permitted to move freely around a predefined tracked experimental space of 1.6 m × 1.6 m while wearing the HMD. Audio was presented to the participant using Sennheiser HD-650 headphones.
2.5. Assessments
2.5.1. Primary Outcome
Modified Smiley-Face Assessment Scale: A self-reported analogue scale using a picture response approach with six faces representing emotional expressions was used and accompanied by short descriptive text. Participants were required to rate their perceived anxiety towards the presented auditory stimuli giving a score of 1–6, where 1 represents “very happy” and 6 represents “very unhappy” (see Figure 6). This instrument has been used in the assessment of the Sinbad and the Magic Cure project [32], a serious game developed to address auditory hypersensitivity in children with autism.
2.5.2. Secondary Outcome
Tracked Voluntary Participant Interaction with Target Auditory Stimuli: Participant interaction with feared stimulus was tracked throughout each intervention session. The data recorded the total time each participant was exposed to sound. As each target stimulus was presented to participants a maximum of 20 times, the highest possible value recording is ≈200 s. This data collection technique was used in order to bypass any communication and emotional recognition problems that may occur as a result of the core symptoms associated with autism during the participant’s self report of anxiety.
3. Results
3.1. Modified Smiley-Face Assessment Scale
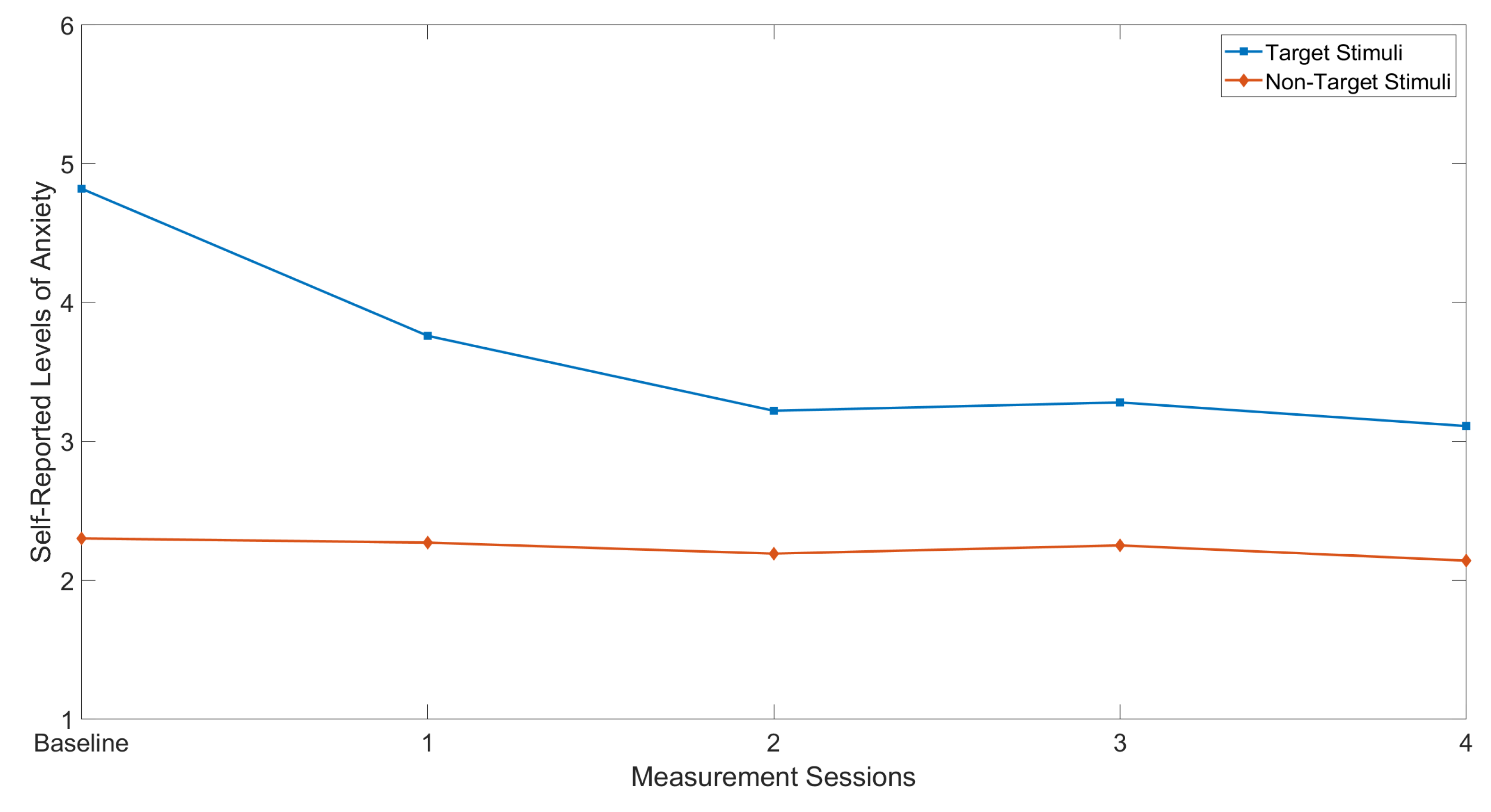
Table 3 shows each of the six participants problematic auditory stimuli alongside the pre- and post-intervention self-reported anxiety scores. Baseline measurements for all participants ranged from 4 to 6, whilst post intervention measurements ranged from 3 to 5. All participants experienced a decrease in their SUD following the 4 week intervention. The average decrease in self-reported anxiety was 1.7 points, with a minimum decrease of 1 point and a maximum of 3 points. In addition, non-target stimuli were played to each participant during each measurement session, the average decrease in anxiety scale points for these was 0.2 points. The mean self reported levels of anxiety across all participants for both target and non-target stimuli are displayed in Figure 7. Finally, a pairwise comparison of pre- and post-smiley face assessment scores was conducted using the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test [65]. This test was chosen due to the small sample size of the study group. Statistical analysis indicated that the score means significantly decreased between the baseline and Week 4 measurement ( , ).

Table 3.
Participant self-reported levels of anxiety scores.
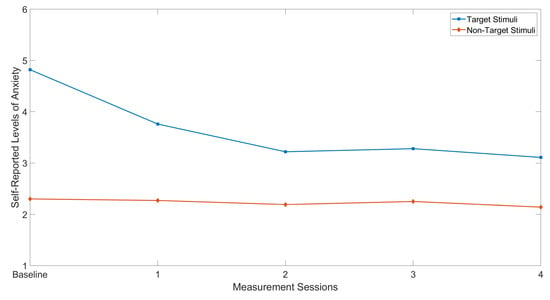
Figure 7.
Calculated mean of all participants’ self-reported levels of anxiety for both target and nontarget auditory stimuli.
3.2. Tracked Interaction Time
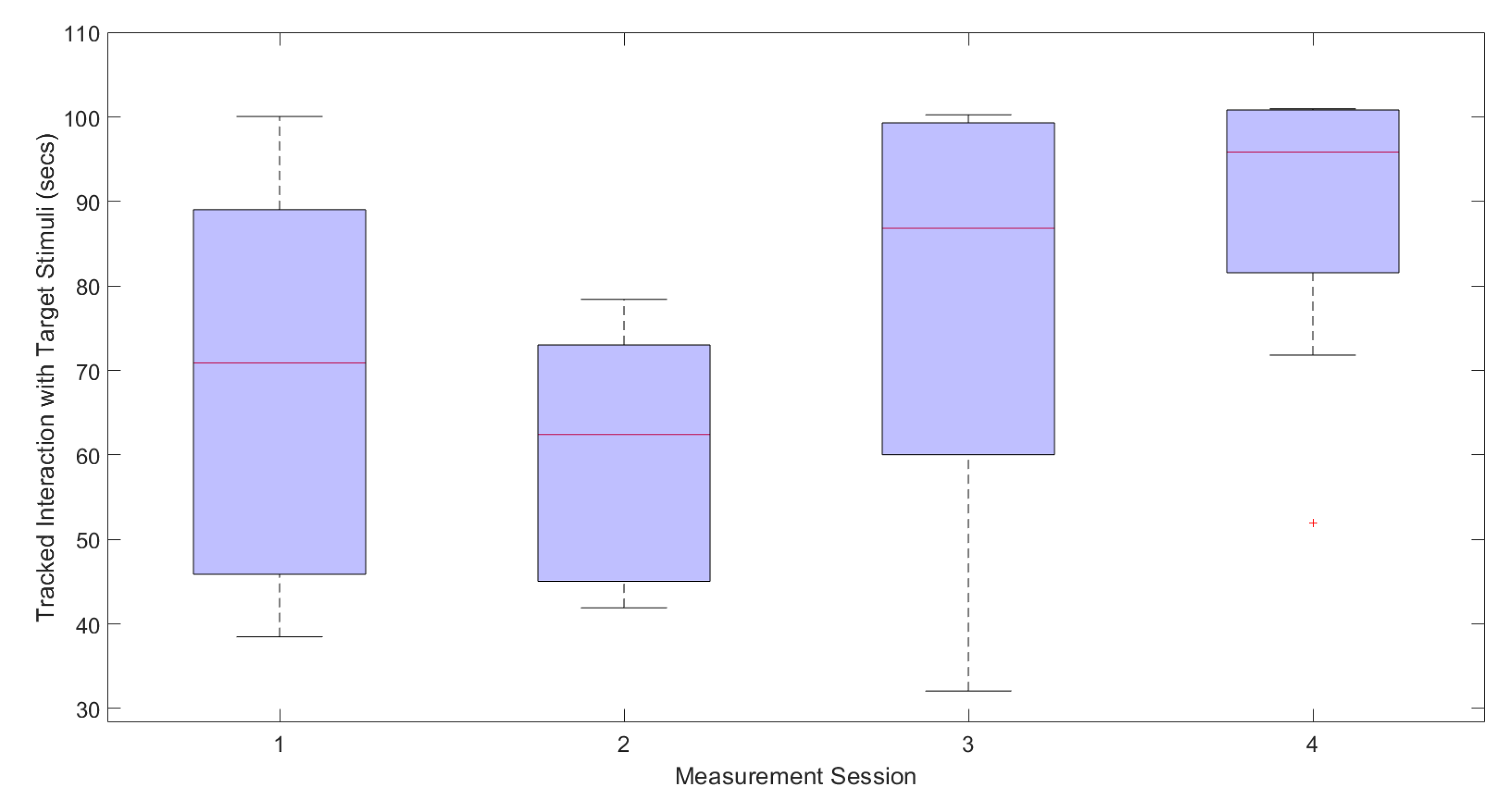
Table 4 displays the total amount of time each participant voluntarily interacted with target auditory stimuli across all four intervention sessions. Despite a gradual increase shown during sessions one, three and four, times are diminished during session two. Statistical comparison between the first and last sessions using the Wilcoxon pairwise test indicated a significant increase (, ) in the mean amount of tracked interaction time for each participant’s target stimuli. Figure 8 shows the total tracked exposure times for all participants across the four week intervention period.

Table 4.
Participant tracked interaction time for each target stimuli across all four experimental sessions, represented in seconds.
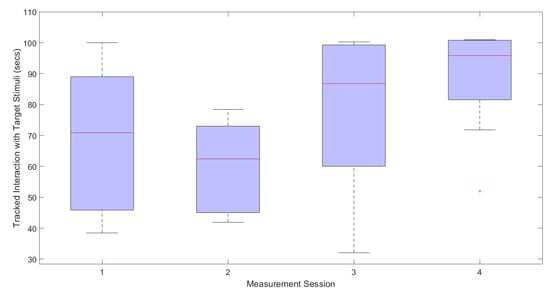
Figure 8.
Box plot displaying the tracked interaction time with target stimuli for all participants across each session.
4. Discussion
This pilot study evaluated the potential of a novel virtual reality based serious game as an intervention tool for auditory hypersensitivity in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. SoundFields is the first application of this type to combine VR and game mechanics to deliver an exposure therapy framework for this issue. Another novel aspect is the use of head tracked binaural based spatial audio as a rendering technique to present feared auditory stimuli to the user.
Similar to the use of realistic visual three-dimensional stimuli rendered in VR for desensitisation to specific phobias and environments that may provoke anxiety in individuals with autism [66,67,68], SoundFields produces realistic three-dimensional auditory stimuli that can simulate the movement and acoustic environments of feared sounds. For any form of VRET to be considered successful, the virtual environment must be capable of eliciting emotions such as anxiety in order for new positive associations with the stimuli to be formed through controlled and graduated exposure [69]. The current study found that all of the target stimuli activated a level of anxiety in participants during baseline measurements which resulted in the lower scores reported in the “Smiley-Face” assessment scale. These results are consistent with similar research conducted with neurologically healthy participants, reporting that the use of spatialised sound can activate the anxiety provoking structure [46,47]. Furthermore, with the addition of the positive emotional response to non-target stimuli during measurements (see Figure 7), these results support the use of spatial audio in VR based therapy for auditory hypersensitivity.
The presented intervention was successful in reducing the participants’ perceived anxiety towards target auditory stimuli over four weekly playing sessions. This was evident from the significant decrease in the self-reported levels of anxiety scores in the pre- and post-study measurement sessions, which was the main outcome measure highlighted in Table 3 and Figure 7. This falls in line with similar research that reveals a reduction in stress associated with presented audio stimuli within a computer game environment [32]. Additionally, the increase in time participants voluntarily interacted with target stimuli can also be interpreted as an increase in tolerance. Results show a significant increase in tracked interaction time between sessions one and four. This is further supported by the implemented exposure hierarchy which moves the virtual sound stimuli closer to the participant. However, interestingly there is a drop in the amount of tracked interaction during session two (see Figure 8). This could be explained by the reduction in virtual distance between the participant and the target stimuli from 25 to 15 m, which would result in a perceptible rise in loudness after the first session.
Research has observed that much like their typically developing peers, children with autism often enjoy playing computer games during their spare time [70,71]. This has been echoed in the reported effectiveness of serious game interventions used to improve sensory integration [72], social communication [73], emotional recognition [74] and auditory hypersensitivity [32,51]. By integrating therapy frameworks into computer game mechanics it is possible to motivate participants to engage with the intervention repeatedly over time. This was experienced during the present study with all six participants playing the game for the 30 min session across the entire four week period, creating an opportunity for the experimental group to have repeated graduated exposure to averse stimuli. However, future developments of the game should see the inclusion of additional mini-games with new mechanics which would increase in difficulty. By challenging the player they will stay motivated to interact with the game and therefore be exposed to any therapeutic outcomes for a longer period [75].
In addition, the mechanism by which participants were exposed to target stimuli is also an important consideration. Whilst playing the game, it is possible for each participant to complete all sessions with little to no exposure to target stimuli. However, the extrinsic motivator system that rewards players with in-game currency motivates them to interact with the game mechanics which would expose them to perceptually abhorrent sounds, potentially developing new and positive associations with the stimulus. Throughout the experiment, participants were driven to collect the currency in order to customise their avatar within the in-game shop.
Finally, another meaningful observation was the shared anxiety associated with particular stimuli between several of the participants. Work investigating phobias in children with autism has also noted common themes such as a fear of buses, toilets, weather and social situations [76,77]. This supports the inclusion of a library of sounds within SoundFields, therefore negating the need for bespoke variants which increases the accessibility of this approach to therapy.
Despite positive results, the evaluation of SoundFields does however have caveats that will need to be addressed. For this study, it is not possible to determine if the use of binaural based spatial audio specifically had a positive impact on the outcomes of this study. Consequently, any future investigations would require two experimental groups with a larger sample to compare the use of spatialised sound to traditional audio rendering techniques such as stereo. Furthermore, without a crossed carry-over randomised controlled design, it is not possible to distinguish if the repeated exposure to stimuli during measurement sessions had an impact on the final results. Finally, there are no measurements to determine if any increase in tolerance towards target sounds were generalised to outside of the experimental conditions. This could be evaluated in further studies comparing pre- and post-intervention measurements using the Short Sensory Profile [78] and parental questionnaires such as the Parent Stress Index [79]. Furthermore, additional follow up measurements subsequent to any intervention period would provide data to assess generalisation of any newly acquired tolerance.
5. Conclusions
This paper presented the virtual reality application SoundFields, a serious game developed as an intervention tool to address auditory hypersensitivities in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. The system is designed to expose participants to common environmental sounds which often cause distress in everyday scenarios within a safe, controlled and engaging virtual environment using head-tracked binaural based spatial audio. Pilot study experiments observed a decrease in participants’ self reported levels of anxiety towards target stimuli after just four 30 min sessions playing the game. In addition, despite the increase of exposure levels as the intervention progressed, the time each participant exposed themselves to target stimuli also increased. Although the engagement with the game by participants and the experimental results are positive, future studies are required with larger intervention groups to replicate these findings and to test the validity of binaural based spatial audio as a rendering technique for graduated exposure therapy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, D.J. and G.K.; Methodology, D.J.; Software, D.J.; Validation, D.J., H.E. and G.K.; Formal Analysis, D.J., H.E.; Investigation, D.J.; Resources, D.J.; Data Curation, D.J.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, D.J.; Writing—Review & Editing, D.J., H.E. and G.K.; Visualisation, D.J.; Supervision, H.E. and G.K.; Project Administration, D.J.; Funding Acquisition, G.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding was provided by a UK Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) Doctoral Training Award, via the Department of Electronic Engineering at the University of York, EPSRC Grant Number: EP/N509802/1.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Springwater School (Harrogate, UK) for their participation and support of this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ASD | Autism Spectrum Disorders |
| HMD | Head Mounted Display |
| NPC | Non-Playable Character |
| SG | Serious Game |
| VE | Virtual Environment |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
| VRET | Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy |
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®); American Psychiatric Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kanner, L. Autistic disturbances of affective contact. Nerv. Child 1943, 2, 217–250. [Google Scholar]
- Frith, U.; Mira, M. Autism and Asperger syndrome. Focus Autistic Behav. 1992, 7, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettison, S. The long-term effects of auditory training on children with autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1996, 26, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelson, S.M.; Arin, D.; Bauman, M.; Lukas, S.E.; Rudy, J.H.; Sholar, M.; Rimland, B. Auditory integration training: A double-blind study of behavioral and electrophysiological effects in people with autism. Focus Autism Other Dev. Disabil. 1999, 14, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimland, B.; Edelson, S.M. Brief report: A pilot study of auditory integration training in autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1995, 25, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, S.J.; Hepburn, S.; Wehner, E. Parent reports of sensory symptoms in toddlers with autism and those with other developmental disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2003, 33, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranek, G.T.; Boyd, B.A.; Poe, M.D.; David, F.J.; Watson, L.R. Hyperresponsive sensory patterns in young children with autism, developmental delay, and typical development. Am. J. Ment. Retard. 2007, 112, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiegler, L.N.; Davis, R. Understanding sound sensitivity in individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Focus Autism Other Dev. Disabil. 2010, 25, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, E.; Pedroso, F.S.; Wagner, M.B. Auditory hypersensitivity in the autistic spectrum disorder. Pró-Fono Revista de Atualizaç Ao Científica 2008, 20, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.C.; Parham, L.D.; Blanche, E.I.; Schell, A.; Chou, C.P.; Dawson, M.; Clark, F. Autonomic and behavioral responses of children with autism to auditory stimuli. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2012, 66, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargas, N.; López, B.; Reddy, V.; Morris, P. The relationship between auditory processing and restricted, repetitive behaviors in adults with autism spectrum disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucker, J.R. Auditory hypersensitivity in children with autism spectrum disorders. Focus Autism Other Dev. Disabil. 2013, 28, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, E.; Rotta, N.T.; Pedroso, F.S.; Sleifer, P.; Danesi, M.C. Auditory hypersensitivity in children and teenagers with autistic spectrum disorder. Arq. De Neuro Psiquiatr. 2004, 62, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenhall, U.; Nordin, V.; Brantberg, K.; Gillberg, C. Autism and auditory brain stem responses. Ear Hear. 2003, 24, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.R.; Happé, F.; Baird, G.; Simonoff, E.; Marsden, A.J.; Tregay, J.; Phillips, R.J.; Goswami, U.; Thomson, J.M.; Charman, T. Auditory discrimination and auditory sensory behaviours in autism spectrum disorders. Neuropsychologia 2009, 47, 2850–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koegel, R.L.; Openden, D.; Koegel, L.K. A systematic desensitization paradigm to treat hypersensitivity to auditory stimuli in children with autism in family contexts. Res. Pract. Pers. Sev. Disabil. 2004, 29, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigner, J.; Ruhlin, S.U. Systematic Desensitization of Hyperacusis and Vocal Pitch Disorder Treatment in a Patient with Autism. Internet J. Allied Health Sci. Pract. 2014, 12, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Jolliffe, T.; Lansdown, R.; Robinson, C. Autism: A Personal Account; EduCare, National Bureau for Handicapped Students: London, UK, 1993; 8p. [Google Scholar]
- Grandin, T. A personal perspective of autism. Handb. Autism Pervasive Dev. Disord. 2005, 2, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donohue, W.T. Cognitive Behavior Therapy: Core Principles for Practice; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, J.; Hill, R.J.; Dodrill, P. A survey of practice for clinicians working with children with autism spectrum disorders and feeding difficulties. Int. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2013, 15, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.; Ware, R.; Ziviani, J.; Hill, R.; Dodrill, P. Efficacy of interventions to improve feeding difficulties in children with autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Child Care Health Dev. 2015, 41, 278–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyner, S.; Brewer, A.; Helman, M.; Leon, Y.; Pritchard, J.; Schlund, M. Nice Doggie! Contact Desensitization Plus Reinforcement Decreases Dog Phobias for Children with Autism. Behav. Anal. Pract. 2016, 9, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullen, V.; Mahfood, S.L.; Francis, G.L.; Bubenik, J. Using Prediction and Desensitization Techniques to Treat Dental Anxiety: A Case Example. Behav. Interv. 2017, 32, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Steensel, F.; Bögels, S. CBT for anxiety disorders in children with and without ASD. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2015, 83, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnhoven, L.A.; Creemers, D.H.; Engels, R.C.; Granic, I. The effect of the video game Mindlight on anxiety symptoms in children with an Autism Spectrum Disorder. BMC Psychiatry 2015, 15, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, M.; Oakes, P. Evaluation of a new computer intervention to teach people with autism or Asperger syndrome to recognize and predict emotions in others. Autism 2001, 5, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.W.; Oswald, D.; Ollendick, T.; Scahill, L. Anxiety in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2009, 29, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, P.; Haddock, G.; Tai, S. A systematic review of the implementation of recommended psychological interventions for schizophrenia: Rates, barriers, and improvement strategies. Psychol. Psychother. Theory Res. Pract. 2016, 89, 324–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Krieke, L.; Wunderink, L.; Emerencia, A.C.; De Jonge, P.; Sytema, S. E–mental health self-management for psychotic disorders: State of the art and future perspectives. Psychiatr. Serv. 2014, 65, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakari, H.M.; Poyade, M.; Simmons, D. Sinbad and the Magic Cure: A Serious Game for Children with ASD and Auditory Hypersensitivity. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Games and Learning Alliance, Lisbon, Portugal, 5–7 December 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Newbutt, N.; Sung, C.; Kuo, H.J.; Leahy, M.J.; Lin, C.C.; Tong, B. Brief report: A pilot study of the use of a virtual reality headset in autism populations. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2016, 46, 3166–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, S.; Cobb, S. State-of-the-art of virtual reality technologies for children on the autism spectrum. Eur. J. Spec. Needs Educ. 2011, 26, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fino, R.; Lin, M.J.; Caballero, A.; Balahadia, F.F. Disaster Awareness Simulation for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Android Virtual Reality. J. Telecommun. Electron. Comput. Eng. (JTEC) 2017, 9, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, D.J.; Brown, T.; Ross, V.; Moncrief, M.; Schmitt, R.; Gaffney, G.; Reeve, R. Can youth with autism spectrum disorder use virtual reality driving simulation training to evaluate and improve driving performance? An exploratory study. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 2544–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamash, L.; Klinger, E.; Josman, N. Using a virtual supermarket to promote independent functioning among adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2017 International Conference on Virtual Rehabilitation (ICVR), Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–22 June 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, H.L.; Bugnariu, N.L. Level of immersion in virtual environments impacts the ability to assess and teach social skills in autism spectrum disorder. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2016, 19, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, G.; Lledó, A.; Pomares, J.; Roig, R. Design and application of an immersive virtual reality system to enhance emotional skills for children with autism spectrum disorders. Comput. Educ. 2016, 98, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, D.C.; McAllister, D.; Coles, C.D.; Osborne, S. An evolution of virtual reality training designs for children with autism and fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Top. Lang. Disord. 2007, 27, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charitos, D.; Karadanos, G.; Sereti, E.; Triantafillou, S.; Koukouvinou, S.; Martakos, D. Employing virtual reality for aiding the organisation of autistic children behaviour in everyday tasks. In Proceedings of the ICDVRAT, Alghero, Italy, 23–25 September 2000; pp. 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Anagnostou, E. Virtual reality as treatment tool for children with autism. In Comprehensive Guide to Autism; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 2125–2141. [Google Scholar]
- Maples-Keller, J.L.; Bunnell, B.E.; Kim, S.J.; Rothbaum, B.O. The Use of Virtual Reality Technology in the Treatment of Anxiety and Other Psychiatric Disorders. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2017, 25, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemer, J.; Alpers, G.W.; Peperkorn, H.M.; Shiban, Y.; Mühlberger, A. The impact of perception and presence on emotional reactions: A review of research in virtual reality. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.; Anderson, P. The role of presence in virtual reality exposure therapy. J. Anxiety Disord. 2007, 21, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, W.P.; Hoekstra, A.R.; van EGMOND, R. The effect of 3D audio and other audio techniques on virtual reality experience. In Annual Review Of Cybertherapy and Telemedicine 2015; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Argo, J. Immersive Soundscapes to Elicit Anxiety in Exposure Therapy: Physical Desensitization and Mental Catharsis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Begault, D.R.; Trejo, L.J. 3-D Sound for Virtual Reality and Multimedia; NASA: Hanovcr, MD, USA, 2000.
- Potisk, T. Head-Related Transfer Function; Seminar Ia; Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, University of Ljubljana: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.I.; Wakefield, G.H. Introduction to head-related transfer functions (HRTFs): Representations of HRTFs in time, frequency, and space. In Proceedings of the 107th Audio Engineering Society Convention, New York, NY, USA, 24–27 September 1999; Audio Engineering Society: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, R. Managing Sound Sensitivity in Autism Spectrum Disorder: New Technologies for Customized Intervention. Master’s Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Whyte, E.M.; Smyth, J.M.; Scherf, K.S. Designing serious game interventions for individuals with autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 3820–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerns, K.A.; Macoun, S.; MacSween, J.; Pei, J.; Hutchison, M. Attention and working memory training: A feasibility study in children with neurodevelopmental disorders. Appl. Neuropsychol. Child 2017, 6, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikinas, S.; Xinogalos, S. Designing effective serious games for people with intellectual disabilities. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON), Tenerife, Spain, 17–20 April 2018; pp. 1896–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Algazi, V.R.; Duda, R.O. Headphone-based spatial sound. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2011, 28, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Lee, Y. Serious games for the job training of persons with developmental disabilities. Comput. Educ. 2016, 95, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovannone, R.; Dunlap, G.; Huber, H.; Kincaid, D. Effective educational practices for students with autism spectrum disorders. Focus Autism Other Dev. Disabil. 2003, 18, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unity3D—Game Engine. Available online: https://unity3d.com (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- AudioKinetic-Wwise. Available online: https://www.audiokinetic.com/products/wwise (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Green, M.; Murphy, D. EigenScape: A database of spatial acoustic scene recordings. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daffern, H.; Camlin, D.; Egermann, H.; Gully, A.J.; Kearney, G.; Neale, C.; Rees-Jones, J. Exploring the potential of virtual reality technology to investigate the health and well being benefits of group singing. Int. J. Perform. Arts Digit. Media 2019, 15, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freesound—Audio Database. Available online: https://freesound.org/home/ (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Google Resonance—Spatial Audio SDK. Available online: https://developers.google.com/resonance-audio/ (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Oculus Rift Head Mounted Display. Available online: https://www.oculus.com/rift/ (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Wilcoxon, F. Individual comparisons by ranking methods. In Breakthroughs in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- Maskey, M.; Rodgers, J.; Grahame, V.; Glod, M.; Honey, E.; Kinnear, J.; Labus, M.; Milne, J.; Minos, D.; McConachie, H.; et al. A Randomised Controlled Feasibility Trial of Immersive Virtual Reality Treatment with Cognitive Behaviour Therapy for Specific Phobias in Young People with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 49, 1912–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim oes, M.; Bernardes, M.; Barros, F.; Castelo-Branco, M. Virtual travel training for autism spectrum disorder: Proof-of-concept interventional study. JMIR Serious Games 2018, 6, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyade, M.; Morris, G.; Taylor, I.; Portela, V. Using mobile virtual reality to empower people with hidden disabilities to overcome their barriers. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Glasgow, UK, 13–17 November 2017; pp. 504–505. [Google Scholar]
- Krijn, M.; Emmelkamp, P.M.; Olafsson, R.P.; Biemond, R. Virtual reality exposure therapy of anxiety disorders: A review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2004, 24, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.H.; Orsmond, G.I.; Cohn, E.S.; Coster, W.J. Friendship characteristics and activity patterns of adolescents with an autism spectrum disorder. Autism 2013, 17, 481–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsmond, G.I.; Kuo, H.Y. The daily lives of adolescents with an autism spectrum disorder: Discretionary time use and activity partners. Autism 2011, 15, 579–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.H.; Lou, S.J.; Tsai, H.Y.; Shih, R.C. The Effects of Applying Game-Based Learning to Webcam Motion Sensor Games for Autistic Students’ Sensory Integration Training. Turk. Online J. Educ. Technol. TOJET 2012, 11, 451–459. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini, S.; Porayska-Pomsta, K.; Smith, T.J. ECHOES: An intelligent serious game for fostering social communication in children with autism. Inf. Sci. 2014, 264, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.M.; da Silva, D.P.; Theodório, D.P.; Silva, W.W.; Rodrigues, S.C.M.; Scardovelli, T.A.; da Silva, A.P.; Bissaco, M.A.S. ALTRIRAS: A Computer Game for Training Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder in the Recognition of Basic Emotions. Int. J. Comput. Games Technol. 2019, 2019, 4384896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikinas, S.; Xinogalos, S. Design guidelines for serious games targeted to people with autism. In Smart Education and e-Learning 2019; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 489–499. [Google Scholar]
- Maskey, M.; Lowry, J.; Rodgers, J.; McConachie, H.; Parr, J.R. Reducing specific phobia/fear in young people with autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) through a virtual reality environment intervention. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayes, S.D.; Calhoun, S.L.; Aggarwal, R.; Baker, C.; Mathapati, S.; Molitoris, S.; Mayes, R.D. Unusual fears in children with autism. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2013, 7, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomchek, S.D.; Dunn, W. Sensory processing in children with and without autism: A comparative study using the short sensory profile. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2007, 61, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, J.O.; Jones, W.H. The parental stress scale: Initial psychometric evidence. J. Soc. Pers. Relatsh. 1995, 12, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).