Shellfish Chitosan Potential in Wine Clarification
Abstract
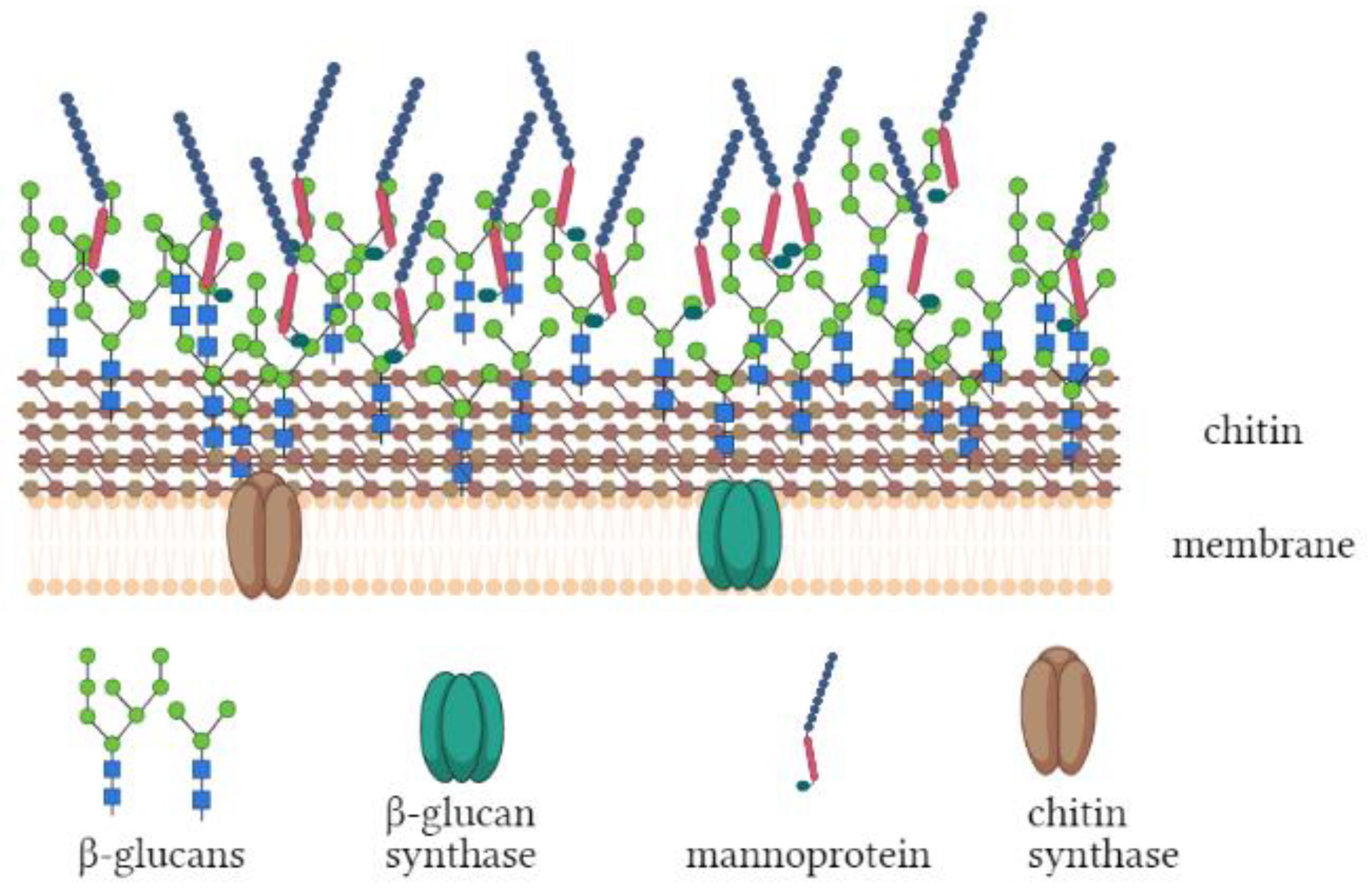
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Chitosan Samples
2.3. Chitosan Deacetylation Degree
2.4. Chitosan Content
2.5. Viscosity
2.6. Molecular Weight Determination
2.7. Wine Clarification
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chitosan Deacetylation
3.2. Chitosan Purity
3.3. Chitosan Viscosity
3.4. Wine Clarification Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santos, V.P.; Marques, N.S.S.; Maia, P.C.S.V.; de Lima, M.A.B.; Franco, L.D.O.; de Campos-Takaki, G.M. Seafood waste as attractive source of chitin and chitosan production and their applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaens, L.; Soetemans, L.; D’Hondt, E.; Elst, K. Sources of chitin and chitosan and their isolation. In Chitin and Chitosan:Properties and Applications; van den Broek, L., Boeriu, C.G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsoud, M.M.A.; El Kady, E.M. Current trends in fungal biosynthesis of chitin and chitosan. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Gawad, K.M.; Hifney, A.F.; Fawzy, M.A.; Gomaa, M. technology optimization of chitosan production from Aspergillus niger biomass and its functional activities. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K. Chitin and chitosan: Functional biopolymers from marine crustaceans. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordoñez, L.; García, J.; Bolaños, G. Producing chitin and chitin-glucan complexes from Aspergillus niger biomass using subcritical water. In Proceedings of the III Iberoamerican Conference on Supercritical Fluids, Cartagena de Indias, Colombia, 1–5 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sietsma, J.H.; Wessels, J.G.H. Evidence for covalent linkages between chitin and β-glucan in a fungal wall. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1979, 114, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riaz Rajoka, M.S.; Mehwish, H.M.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Arfat, Y.; Majeed, K.; Anwaar, S. Chitin/chitosan derivatives and their interactions with microorganisms: A comprehensive review and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.O.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.G. Improving solubility, stability, and cellular uptake of resveratrol by nanoencapsulation with chitosan and γ-poly (glutamic acid). Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 147, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, M.; Morsi, R.E.; Kerch, G.; Elsabee, M.Z.; Kaya, M.; Labidi, J.; Khawar, K.M. Current advancements in chitosan-based film production for food technology; A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagna, G.; Pifferi, P.G.; Rangoni, C.; Mattivi, F.; Nicolini, G.; Palmonari, R. the stabilization of white wines by adsorption of phenolic compounds on chitin and chitosan. Food Res. Int. 1996, 29, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincenzi, S.; Mosconi, S.; Zoccatelli, G.; Pellegrina, C.D.; Veneri, G.; Chignola, R.; Peruffo, A.; Curioni, A.; Rizzi, C. Development of a new procedure for protein recovery and quantification in wine. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2005, 56, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- The Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EU) 53/2011. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, L19/1–L19/6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OIV. Resolution OIV-OENO 338A/2009. Available online: www.oiv.int/public/medias/1082/oiv-oeno-338a-2009-en.pdf (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- OIV. Resolution OIV-OENO 337A/2009. Available online: www.oiv.int/public/medias/1047/oiv-oeno-337a-2009-en.pdf (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- Kou, S.G.; Peters, L.M.; Mucalo, M.R. Chitosan: A review of sources and preparation methods. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Z.; Horev, B.; Rutenberg, R.; Danay, O.; Bilbao, C.; McHugh, T.; Rodov, V.; Poverenov, E. Efficient production of fungal chitosan utilizing an advanced freeze-thawing method; quality and activity studies. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Son, J.H.; Kim, S.; Weller, C.L.; Hanna, M.A. Properties of chitosan films as a function of pH and solvent type. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, E119–E124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romanazzi, G.; Gabler, F.M.; Margosan, D.; MacKey, B.E.; Smilanick, J.L. Effect of chitosan dissolved in different acids on its ability to control postharvest gray mold of table grape. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.S.; Eckmann, D.M.; Lee, D.; Hickok, N.J.; Composto, R.J. Symmetric pH-dependent swelling and antibacterial properties of chitosan brushes. Langmuir 2011, 27, 12458–12465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Czechowska-Biskup, R.; Jarosińska, D.; Rokita, B.; Ulański, P.; Rosiak, J.M. Determination of degree of deacetylation of chitosan—Comparision of methods. Prog. Chem. Appl. Chitin Its Deriv. 2012, 2012, 5–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, K.Y. Characterization of a chitin synthase cDNA and its increased mRNA level associated with decreased chitin synthesis in Anopheles quadrimaculatus exposed to diflubenzuron. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 36, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasaai, M.R.; Arul, J.; Charlet, G. Intrinsic Viscosity-molecular weight relationship for chitosan. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2000, 38, 2591–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Shuai, X.; Unger, F.; Simon, M.; Bi, D.; Kissel, T. The depolymerization of chitosan: Effects on physicochemical and biological properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 281, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.C.; Jabrail, F.H. Effects of degree of deacetylation and cross-linking on physical characteristics, swelling and release behavior of chitosan microspheres. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 66, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, K.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Hu, L.; Li, P. The production of fully deacetylated chitosan by compression method. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2016, 42, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furuike, T.; Komoto, D.; Hashimoto, H.; Tamura, H. Preparation of chitosan hydrogel and its solubility in organic Acids. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwe, N.; Furuike, T.; Tamura, H. Production of fungal chitosan by enzymatic method and applications in plant tissue culture and tissue engineering: 11 years of our progress, present situation and future prospects. Biopolymers 2010, 7, 135–162. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco-Garcia, P.F.; Perez-Gonzalez, A.; Ramos-Flores, A.; Flores-Gonzalez, L.A.; Lopez-Oglesby, J.M.; Gonzalez-Perez, M. Experimental study and calculation of the electron transfer coefficients on the dissolution behavior of chitosan in organic acids. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2017, 3, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajaj, M.; Winter, J.; Gallert, C. Effect of deproteination and deacetylation conditions on viscosity of chitin and chitosan extracted from Crangon crangon shrimp waste. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 56, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Heuzey, M.C.; Bégin, A.; Carreau, P.J. Viscoelastic properties of chitosan solutions: Effect of concentration and ionic strength. J. Food Eng. 2006, 74, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goñi, M.G.; Tomadoni, B.; Roura, S.I.; Moreira, M.D.R. Lactic acid as potential substitute of acetic acid for dissolution of chitosan: Preharvest application to butterhead lettuce. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, P.; Lai, Y.; Kuo, T.; Liu, F. Improving the properties of chitosan membranes using natural organic acid solution as solvent for chitosan dissolution. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2007, 27, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Melro, E.; Antunes, F.E.; da Silva, G.J.; Cruz, I.; Ramos, P.E.; Carvalho, F.; Alves, L. Chitosan films in food applications.tuning film properties by changing acidic dissolution conditions. Polymers 2021, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro Marín, A.; Colangelo, D.; Lambri, M.; Riponi, C.; Chinnici, F. Relevance and perspectives of the use of chitosan in winemaking: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, D.; Wu, C. A New approach for the flocculation mechanism of chitosan. J. Polym. Environ. 2003, 11, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, D.; Torchio, F.; De Faveri, D.M.; Lambri, M. The use of chitosan as alternative to bentonite for wine fining: Effects on heat-stability, proteins, organic acids, colour, and volatile compounds in an aromatic white wine. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagas, R.; Monteiro, S.; Ferreira, R.B. Assessment of potential effects of common fining agents used for white wine protein stabilization. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2012, 63, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample ID | Supplier | Commercial Name/Code | Origin | Other | Calculated MW (kDa) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | Kytozime | Kiofine | A. niger | 33 | |
| F2 | Chibio | GBS009 | A. niger | High density | 84 |
| F3 | Chibio | GBS008 | A. niger | Chitosan oligosaccharide | 30 |
| F4 | Beijing Wisapple Biotech Co. LTD | A. niger | 49 | ||
| A5 | Qingdao Yunzhou Biochemistry Co. LTD | Lot. 150912 | Food Grade (100–200 kDa) | 173 | |
| A6 | Sigma-Aldrich | 48165 | Crab | Highly viscous | 478 |
| A7 | Fluka | 50494 | Shrimp | Low viscous | 51 |
| A8 | Beijing Wisapple Biotech Co. LTD | WA20170522 | Shrimp | 282 | |
| A9 | Qingdao Yunzhou Biochemistry Co. LTD | Lot. 150520-2 | Shrimp | Industry grade (100–200 kDa) | 244 |
| A10 | Qingdao Yunzhou Biochemistry Co. LTD | Lot. 150520-3 | Shrimp | Industry grade (200–300 kDa) | 228 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vendramin, V.; Spinato, G.; Vincenzi, S. Shellfish Chitosan Potential in Wine Clarification. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104417
Vendramin V, Spinato G, Vincenzi S. Shellfish Chitosan Potential in Wine Clarification. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(10):4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104417
Chicago/Turabian StyleVendramin, Veronica, Gaia Spinato, and Simone Vincenzi. 2021. "Shellfish Chitosan Potential in Wine Clarification" Applied Sciences 11, no. 10: 4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104417
APA StyleVendramin, V., Spinato, G., & Vincenzi, S. (2021). Shellfish Chitosan Potential in Wine Clarification. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104417







