On the Tortuosity-Connectivity of Cement-Based Porous Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. General Considerations
3. The Transport Equations at the Pore Scale
4. The Transport Equations at the Macroscopic Scale
4.1. The Time Derivative
4.2. The Divergence of the Mass Fluxes
4.3. The Transport Equations at the Macroscopic Scale
4.4. The Mass Fluxes
4.5. The Dispersion Terms
4.6. The Surface Integrals
4.6.1. The Surface Integrals at the Pore Scale
4.6.2. The Surface Integrals in the REV
4.6.3. The Final Transport Equation in the Equivalent Pore
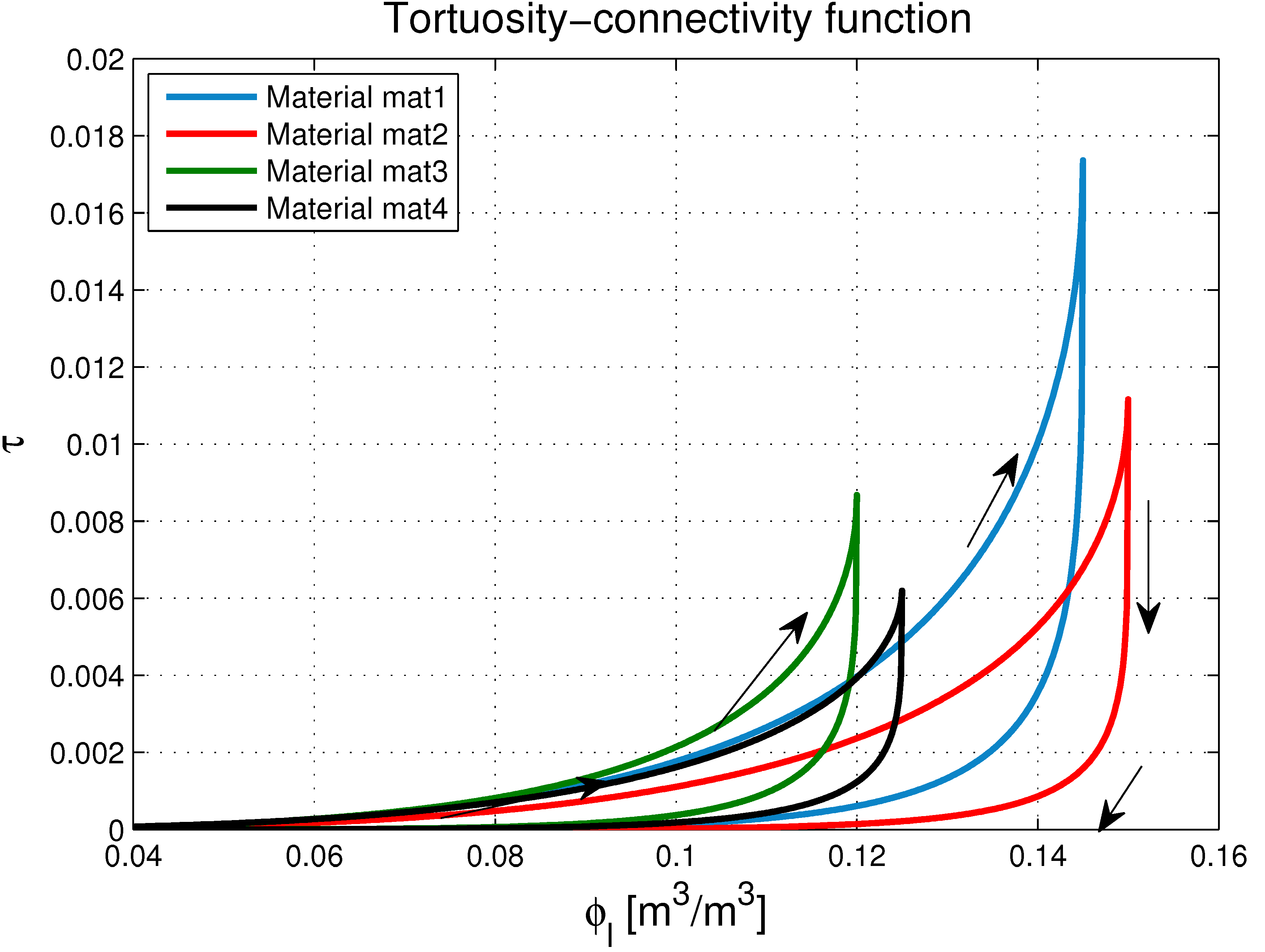
5. Determining the Tortuosity-Connectivity Parameter
5.1. Darcy versus Hagen–Poiseuille Flows
5.2. Calculation of the Tortuosity-Connectivity Parameter
5.3. Closure Equations
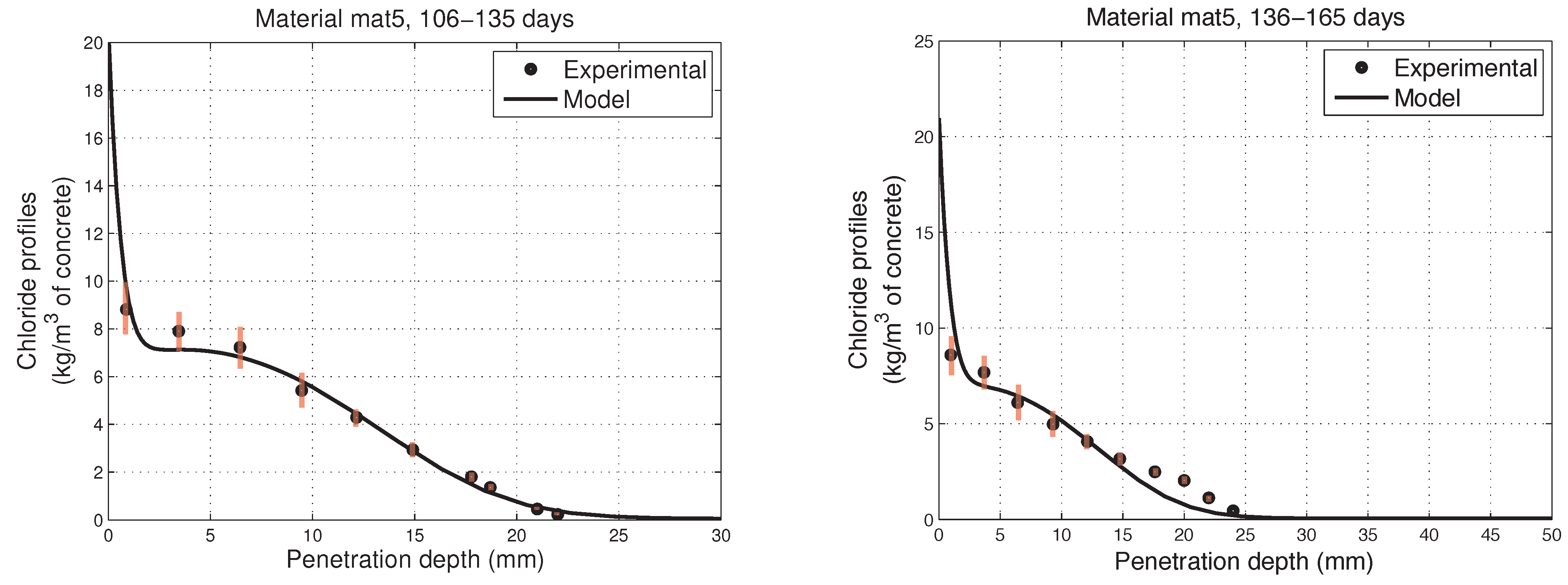
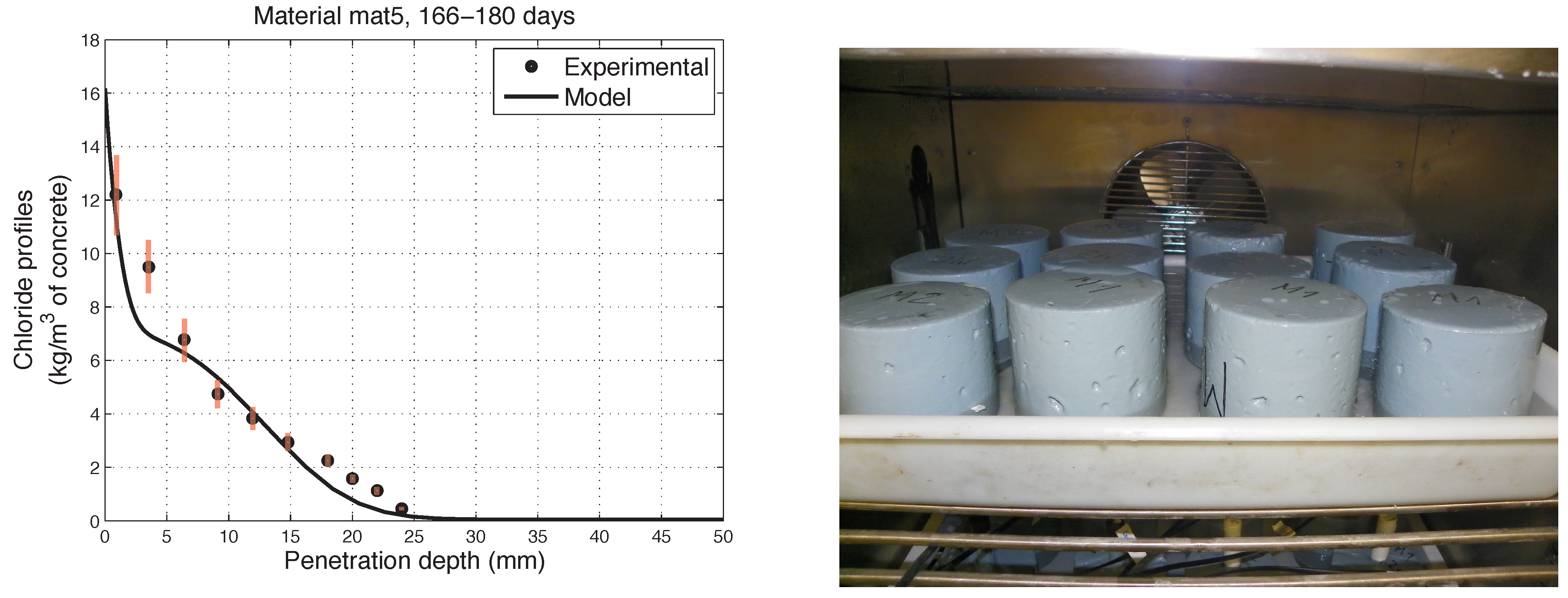
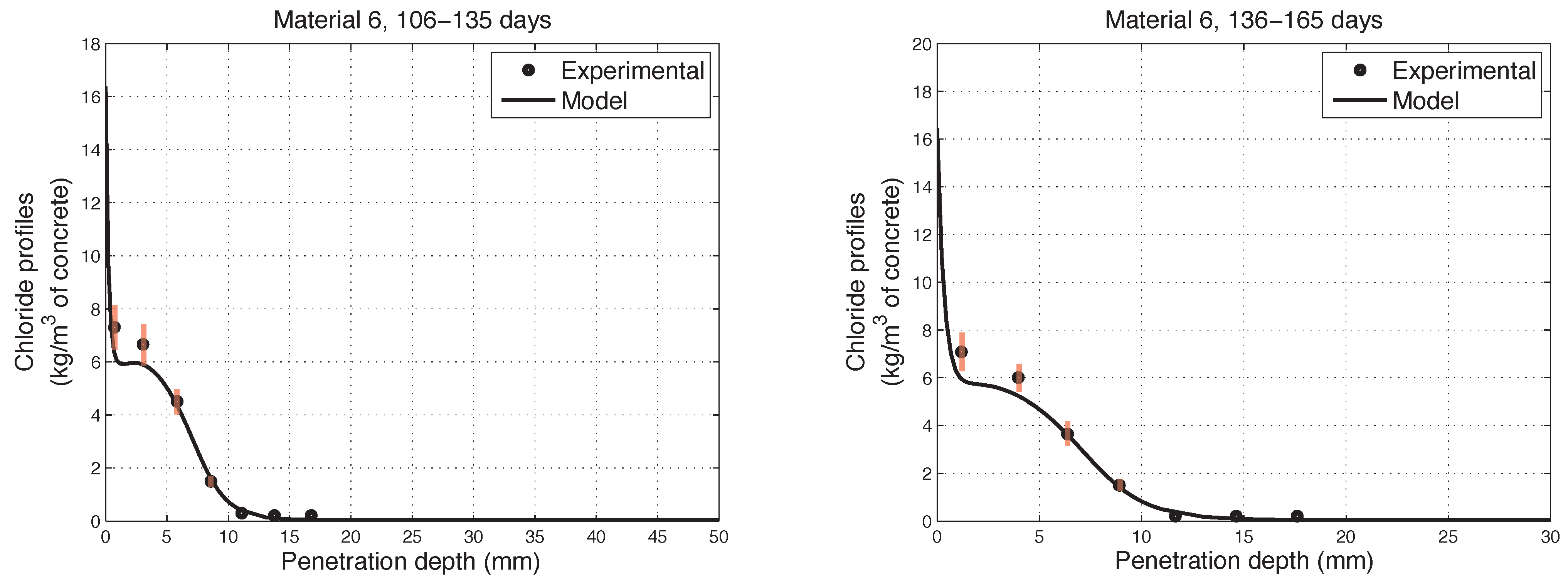
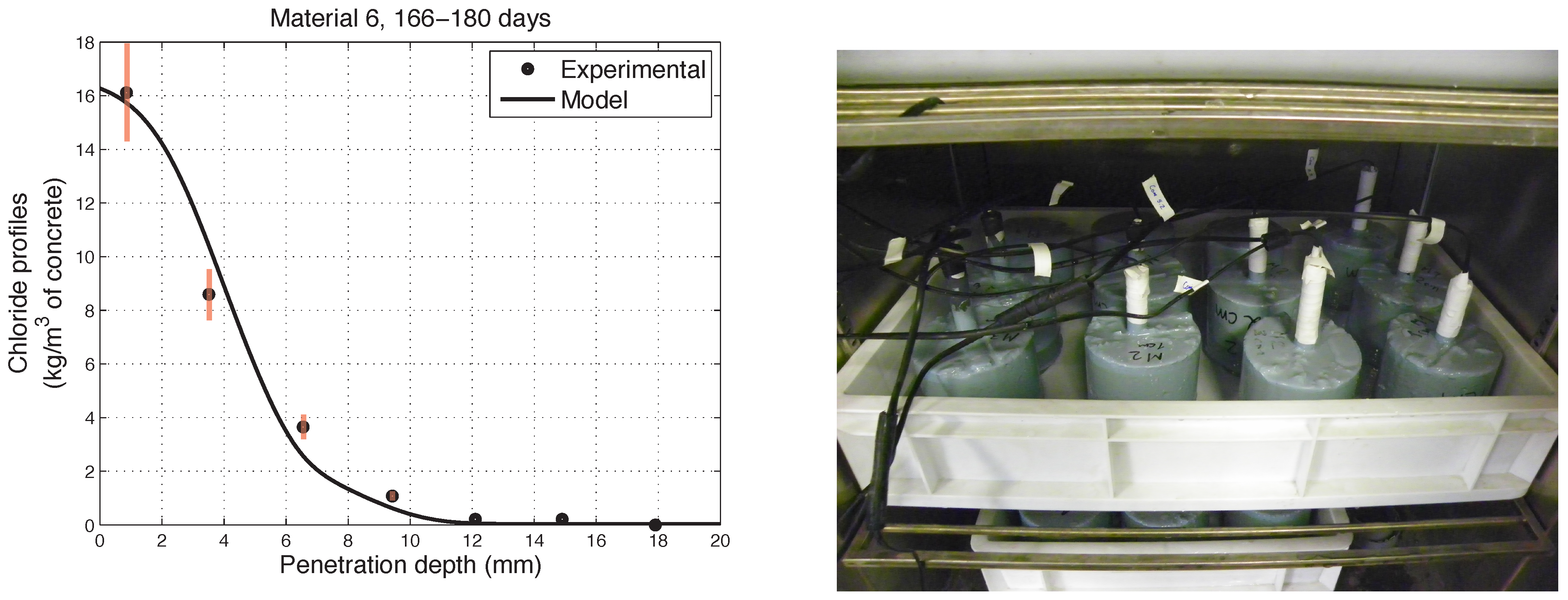
6. Numerical Simulations of Experimental Chloride Profiles
6.1. Overview of the Experimental Programme
6.2. Numerical Modelling
7. Conclusions
- In order to obtain the transport equations at the macroscopic scale, the microscopic equations were integrated over the REV by means of the well known averaging technique.
- It was shown that the dispersion terms which arose from the averaging procedure can be ignored.
- The surface integrals which arose from the averaging technique were interpreted. It was shown not only how they are related to the tortuosity-connectivity of the porous network, but also how they influence the mass fluxes of the ionic species.
- The transport equations in the REV were compared with the equations in an equivalent pore, oriented in the direction of the net mass flux.
- An explicit expression of the tortuosity-connectivity parameter was obtained by comparing Darcy’s law and the Hagen–Poiseuille equations for the equivalent pore.
- The proposed model accurately fits the results obtained from experimental tests performed on concretes in non-saturated conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guzmán, S.; Gálvez, J.; Sancho, J. Cover cracking of reinforced concrete due to rebar corrosion induced by chloride penetration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzmán, S.; Gálvez, J.C.; Sancho, J.M. Modelling of corrosion-induced cover cracking in reinforced concrete by an embedded cohesive crack finite element. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2012, 93, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EHE—Code on Structural Concrete; Ministry of the Presidency: Madrid, Spain, August 2008.
- Bertolini, L.; Elsener, B.; Pedeferri, P.; Polder, R. Corrosion of Steel in Concrete, 2nd ed.; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; 436p. [Google Scholar]
- Fenaux, M. Modelling of Chloride Transport in Non-Saturated Concrete. From Microscale to Macroscale. Ph.D. Thesis, Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingenieros de Caminos, Canales y Puertos, Madrid, Spain, May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Samson, E.; Marchand, J. Numerical Solution of the Extended Nernst-Planck Model. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 215, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, E.; Marchand, J. Modeling the effect of temperature on ionic transport in cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussy, O.; Ulm, F. Elements of durability mechanics of concrete structures. In Creep, Shrinkage and Durability Mechanics of Concrete and Other Quasi-Brittle Materials; Ulm, F., Bažant, Z., Wittmann, F., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 393–409. [Google Scholar]
- Marchand, J.; Gérard, B.; Delagrave, A. Ion transport mechanisms in cement-based materials. In Materials Science of Concrete; American Ceramic Society: Columbus, OH, USA, 1998; Volume 5, pp. 307–400. [Google Scholar]
- Marchand, J.; Maltais, Y.; Samson, E.; Johansen, V.; Hazrati, K. Modeling interaction mechanisms in cement-based materials—An overview. In Sidney Diamond Symposium on Materials Science of Concrete and Cementitious-Based Composites; American Ceramic Society: Columbus, OH, USA, 1998; pp. 143–162. [Google Scholar]
- Page, C.; Short, N.; Tarras, A.E. Diffusion of chloride ions in hardened cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1981, 11, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, S.; Roy, D. Diffusion of Ions Through Hardened Cement Pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1981, 11, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saetta, A.; Scotta, R.; Vitaliani, R. Analysis of Chloride Diffusion into Partially Saturated Concrete. Mater. J. 1993, 90, 441–451. [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Pérez, B.; Zibara, H.; Hooton, R.; Thomas, M. A study of the effect of chloride binding on service life predictions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Jiang, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, J. Influence of cation type on diffusion behavior of chloride ions in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 99, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ožbolt, J.; Oršanić, F.; Balabanixcx, G. Modelling processes related to corrosion of reinforcement in concrete: Coupled 3d finite element model. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2017, 13, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luzio, G.D.; Alnaggar, M. Coupled multi-physics simulation of chloride diffusion in saturated and unsaturated concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 292, 123394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdette, B.; Ringot, E.; Ollivier, J. Modelling of the transition zone porosity. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Azad, A.; Loughlin, K. Effect of the key mixture parameters on tortuosity and permeability of concrete. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2012, 10, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karger, J.; Ruthven, D.M. Diffusion in Zeolites and Other Microporous Solids; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1992; 605p, ISBN 0-471-50907-8. [Google Scholar]
- Dullien, F. Porous Media, Fluid Transport and Pore Structure; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, W.G. A derivation of the equations for multi-phase transport. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1975, 30, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, F.A.; Whitaker, S. The spatial averaging theorem revisited. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1985, 40, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmat, Y.; Bear, J. Macroscopic modelling of transport phenomena in porous media. 1: The continuum approach. Transp. Porous Media 1986, 1, 213–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulaine, C.; Debenest, G.; Quintard, M. Upscaling multi-component two-phase flow in porous media with partitioning coefficient. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 6180–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mainguy, M.; Coussy, O.; Baroghel-Bouny, V. Role of Air Pressure in Drying of Weakly Permeable Materials. J. Eng. Mech. 2001, 127, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenaux, M.; Reyes, E.; Gálvez, J.; Moragues, A. Modelling the transport of chloride and other ions in cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 97, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimar aes, A.; Climent, M.; de Vera, G.; Vicente, F.; Rodrigues, F.; Andrade, C. Determination of chloride diffusivity through partially saturated portland cement concrete by a simplified procedure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, M.A.; de Vera, G.; López, J.F.; Viqueira, E.; Andrade, C. A test method for measuring chloride diffusion coefficients through nonsaturated concrete. Part I. the instantaneous plane source diffusion case. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vera, G.; Climent, M.A.; Viqueira, E.; Antón, C.; Andrade, C. A test method for measuring chloride diffusion coefficients through partially saturated concrete. Part II: The instantaneous plane source diffusion case with chloride binding consideration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEN, En ISO 12571. Hygrothermal Performance of Building Materials and Products. Determination of Hygroscopic Sorption Properties; Standard; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2003.
- CEN, En 197-1. Composition, Specifications and Conformity for Common Cements; Standard; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2011.
- Abdelkader, S.M.; Pozo, E.R.; Terrades, A.M. Evolution of microstructure and mechanical behavior of concretes utilized in marine environments. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 3412–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Dosages (kg/m3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | mat1 | mat2 | mat3 | mat4 |
| Cement | 380 | 357 | 380 | 304 |
| Water | 171 | 194 | 171 | 154 |
| Fly ash | 0 | 76 | 0 | 0 |
| Silica fume | 0 | 0 | 0 | 38 |
| Aggregate | 787 | 770 | 787 | 800 |
| Sand | 1022 | 966 | 1022 | 1067 |
| Superplasticizer * | 0.97 | 0.70 | 1.30 | 1.80 |
| Dosages (kg/m3) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Material | mat5 | mat6 |
| Cement | 400 | 320 |
| Water | 160 | 180 |
| Silica fume | 0 | 40 |
| Ratio water/cementitious materials | 0.40 | 0.45 |
| Aggregate | 970 | 1015.73 |
| Sand | 846 | 861.08 |
| Superplasticizer * | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Aggressive Environments | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Days | Chloride Concentration (g/L) | Relative Humidity (%) | Temperature (°C) |
| 1–75 | 100 | 100 | 1 |
| 76–105 | 0 (at day 76) | 100 | 10 |
| 106–135 | - | 75 | 16 |
| 136–165 | - | 75 | 5 |
| 166–180 | 100 | 100 | 3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fenaux, M.; Reyes, E.; Gálvez, J.C.; Moragues, A.; Bernal, J. On the Tortuosity-Connectivity of Cement-Based Porous Materials. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5812. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135812
Fenaux M, Reyes E, Gálvez JC, Moragues A, Bernal J. On the Tortuosity-Connectivity of Cement-Based Porous Materials. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(13):5812. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135812
Chicago/Turabian StyleFenaux, Michiel, Encarnacion Reyes, Jaime C. Gálvez, Amparo Moragues, and Jesús Bernal. 2021. "On the Tortuosity-Connectivity of Cement-Based Porous Materials" Applied Sciences 11, no. 13: 5812. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135812
APA StyleFenaux, M., Reyes, E., Gálvez, J. C., Moragues, A., & Bernal, J. (2021). On the Tortuosity-Connectivity of Cement-Based Porous Materials. Applied Sciences, 11(13), 5812. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135812






