Evaluating the Effect of Tissue Selection on the Characteristics of Extracellular Matrix Hydrogels from Decellularized Porcine Bladders
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Decellularization
2.2. Decellularization Confirmation
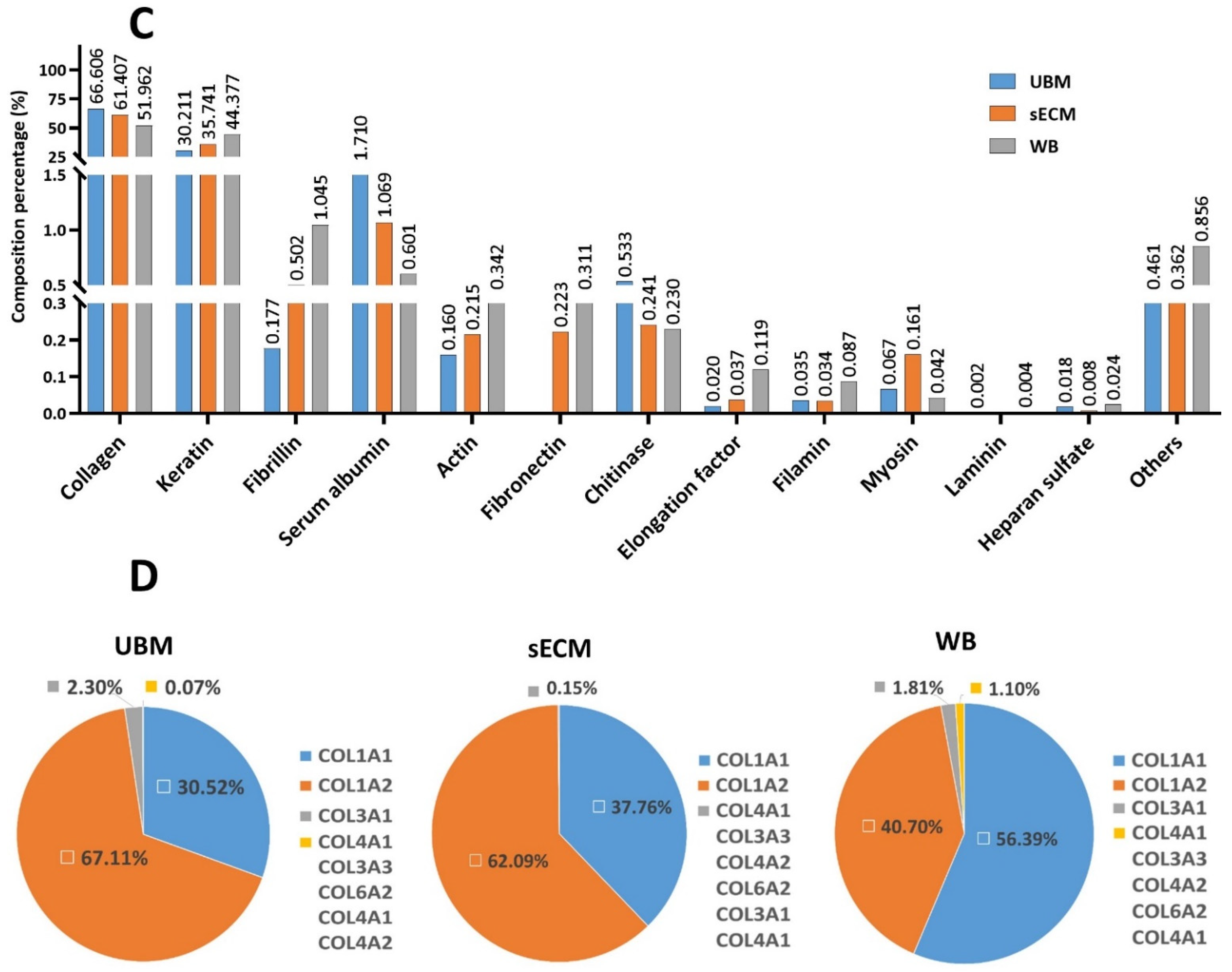
2.3. Biochemical Composition
2.3.1. Collagen and sGAG
2.3.2. Relative Quantification of Protein Profile by Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
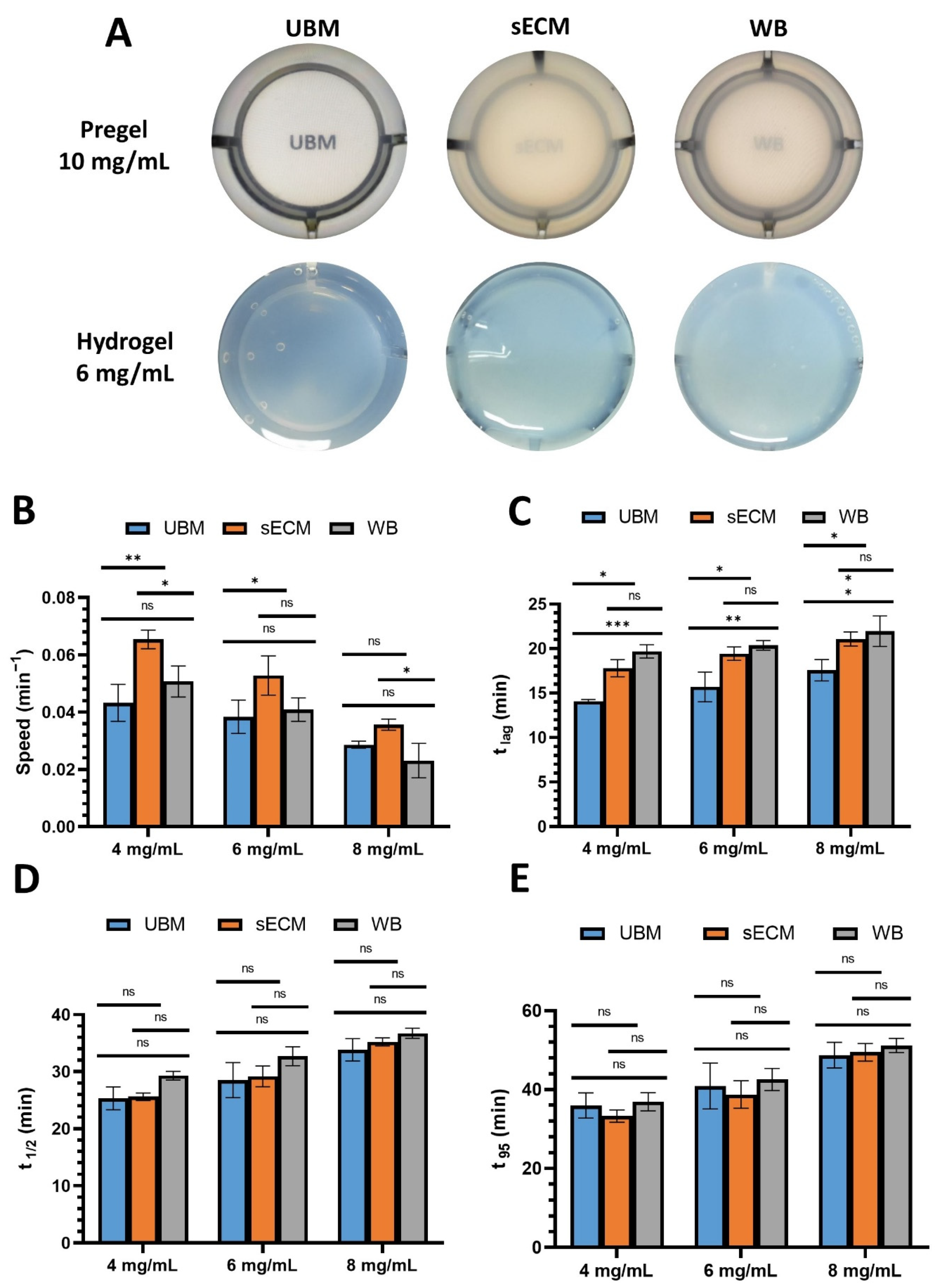
2.4. Turbidity Measurement
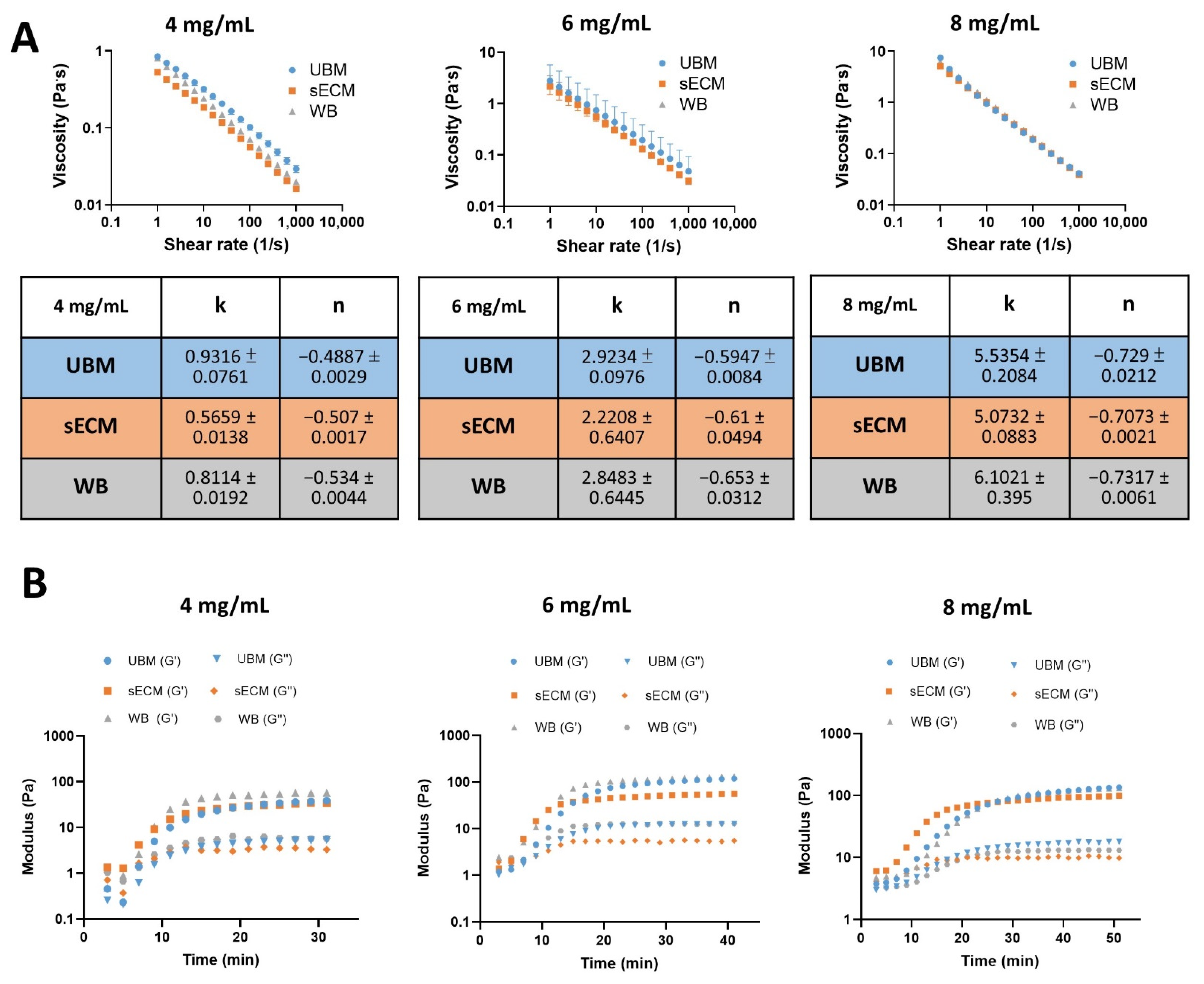
2.5. Rheological Measurements
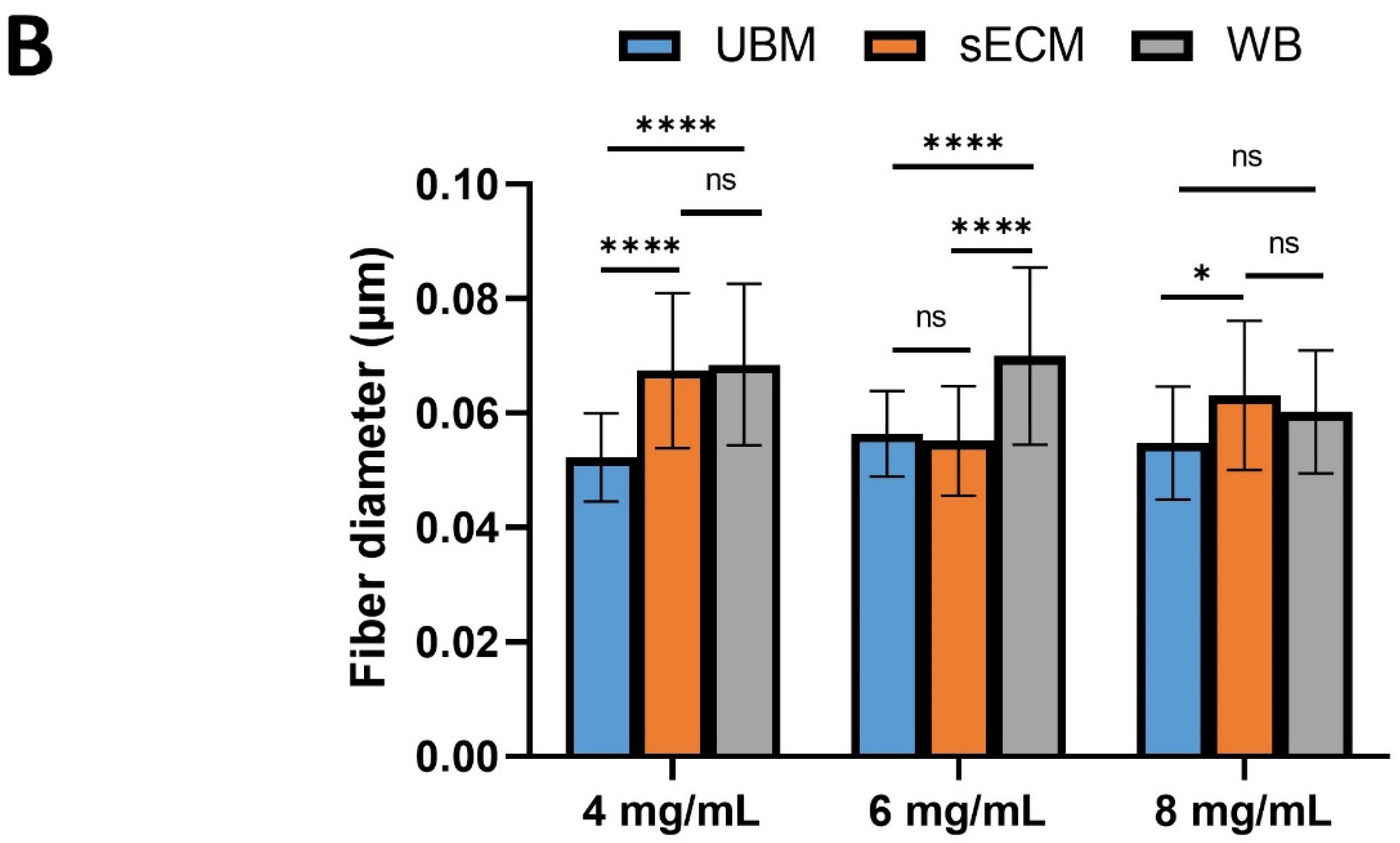
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.7. Effect on L929 Fibroblast In Vitro Cell Viability
2.8. Effect on C2C12 Myogenic Differentiation
2.8.1. C2C12 Cell Culture
2.8.2. Immunocytochemistry
2.8.3. Western Blot
2.9. Effect on C2C12 Osteoblast Differentiation
2.9.1. Osteoblast Differentiation
2.9.2. Alizarin Red Staining (ARS)
2.9.3. Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Activity
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Decellularization Confirmation
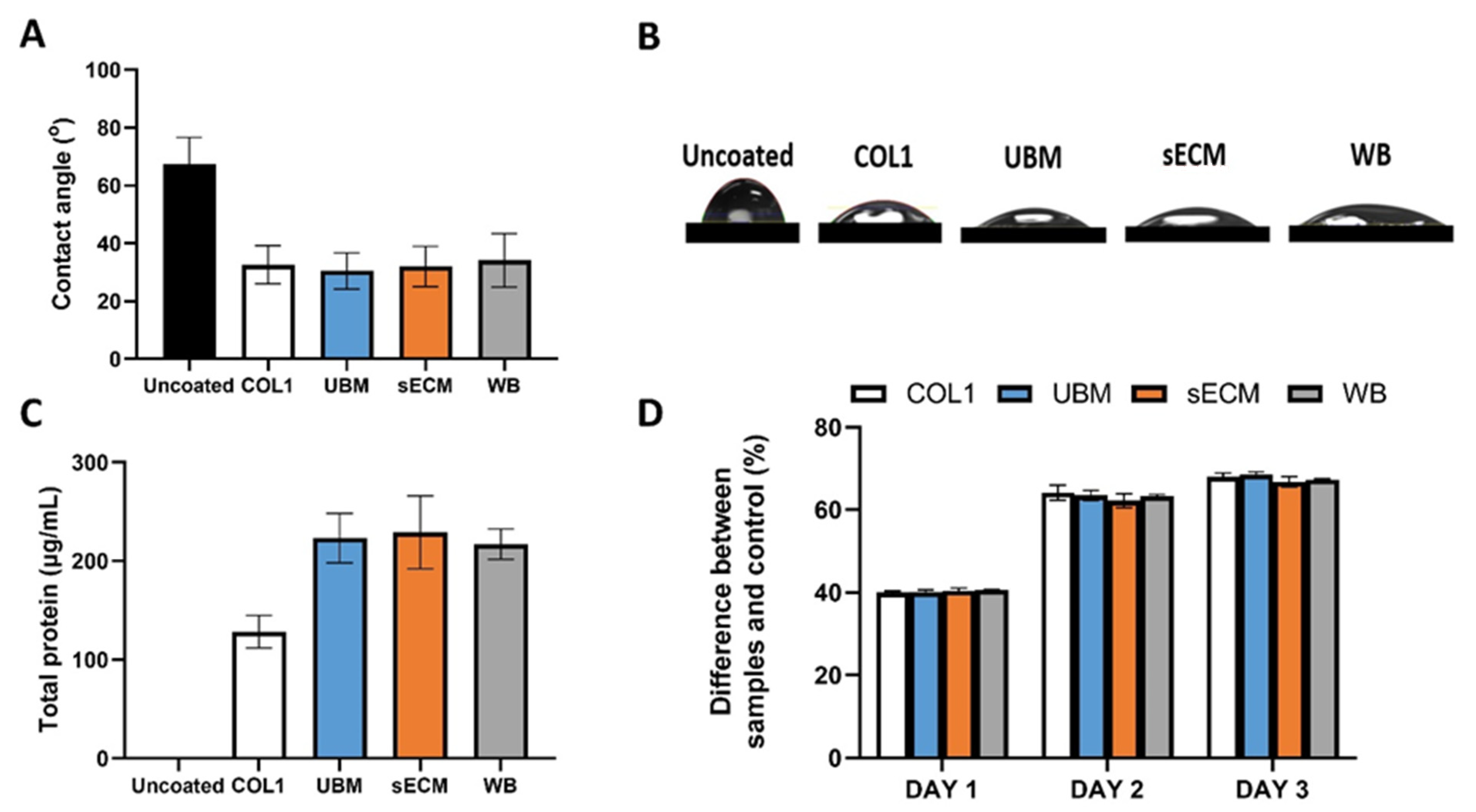
3.2. Biochemical Composition
3.3. Turbidity Measurement
3.4. Rheological Measurements
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
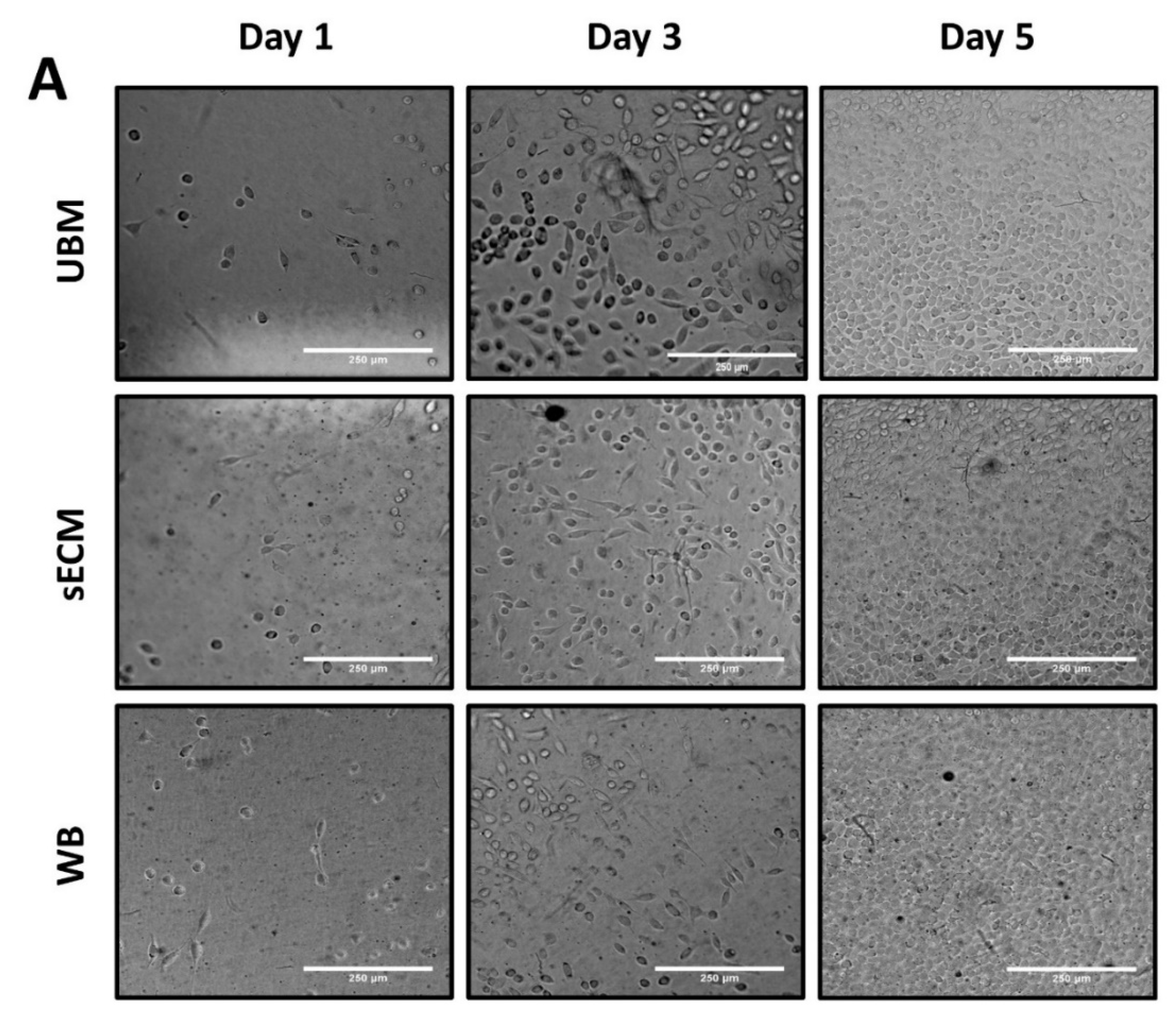
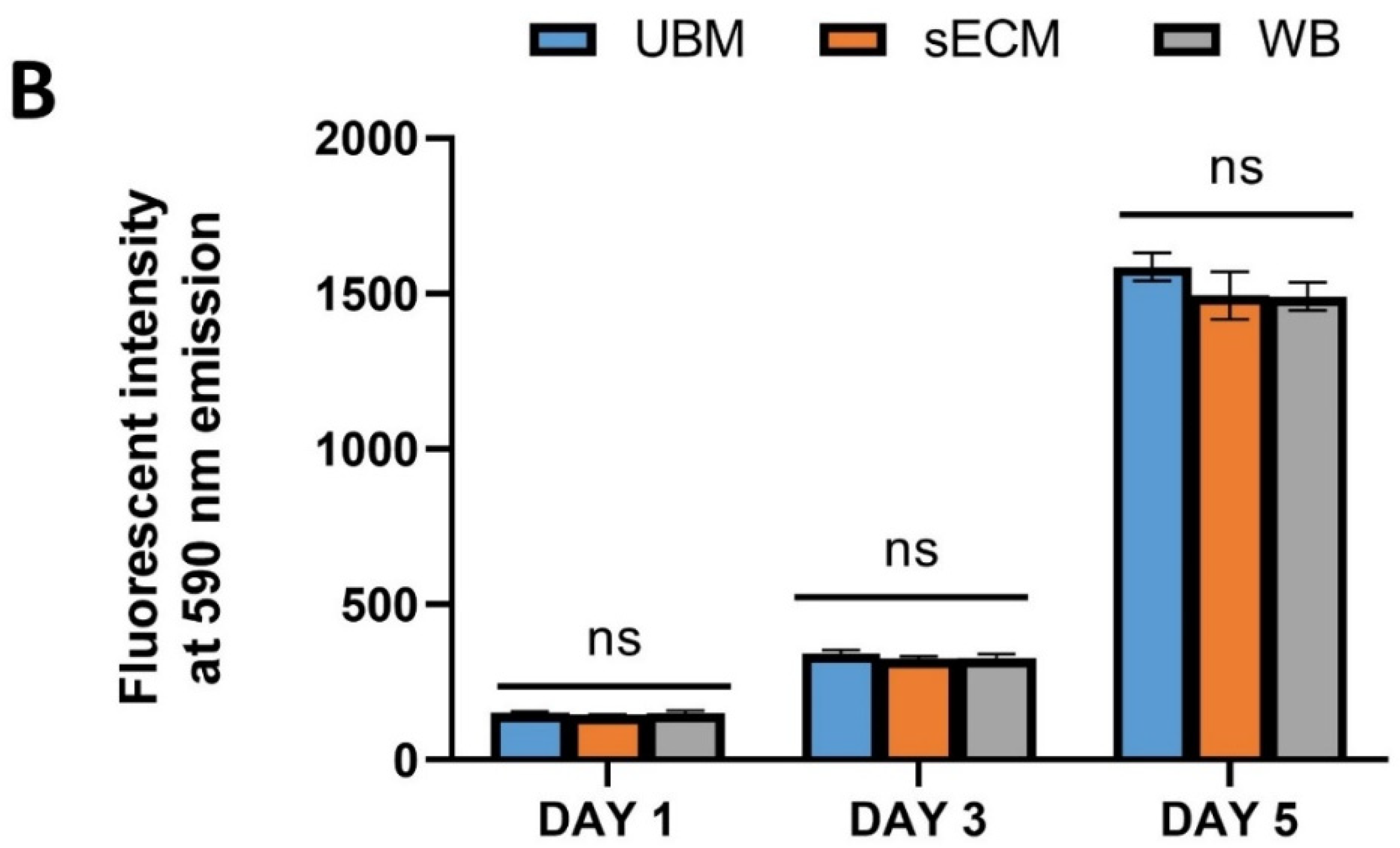
3.6. Effect on L292 Fibroblast In Vitro Cell Viability
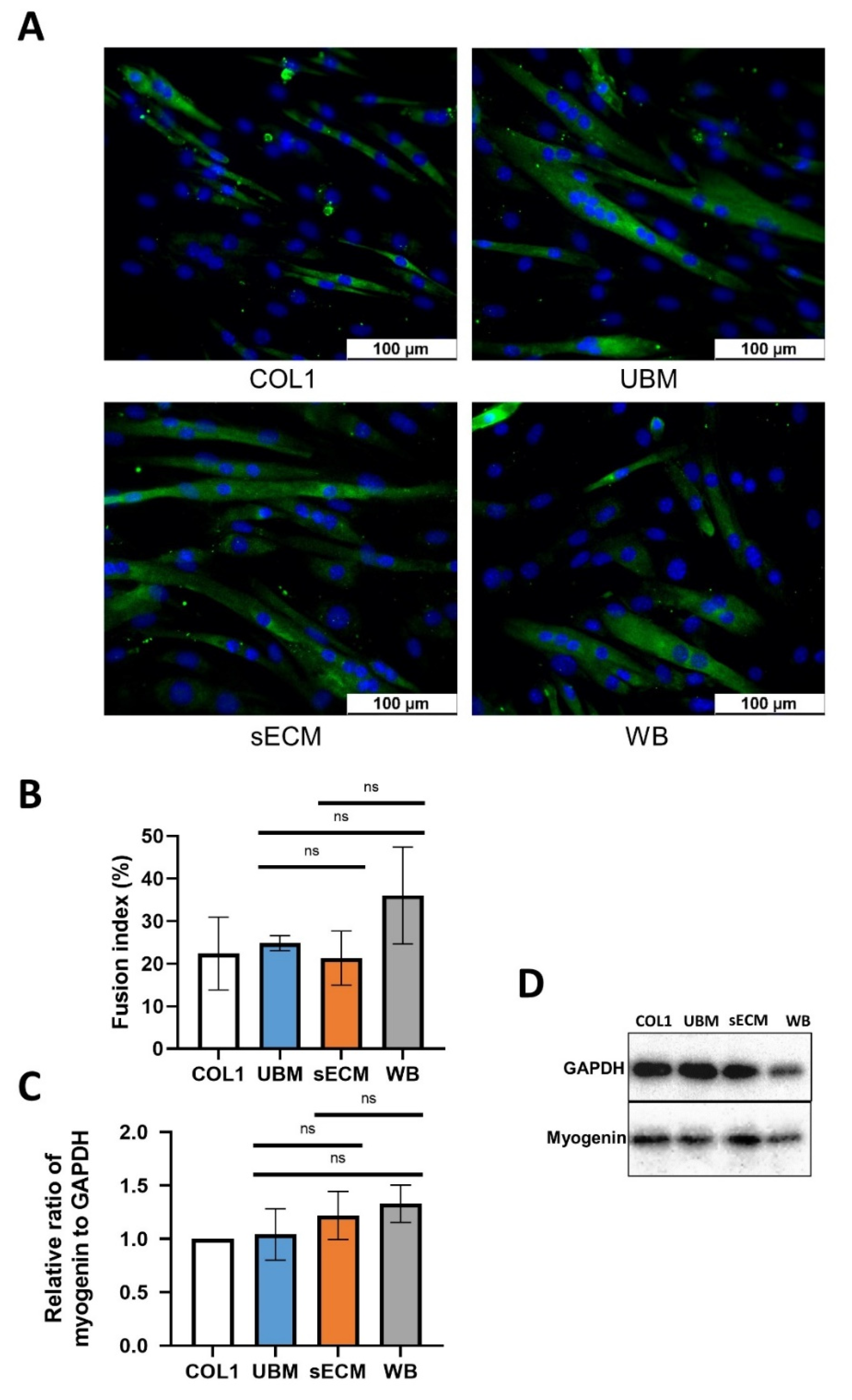
3.7. Effect on C2C12 Myogenic Differentiation
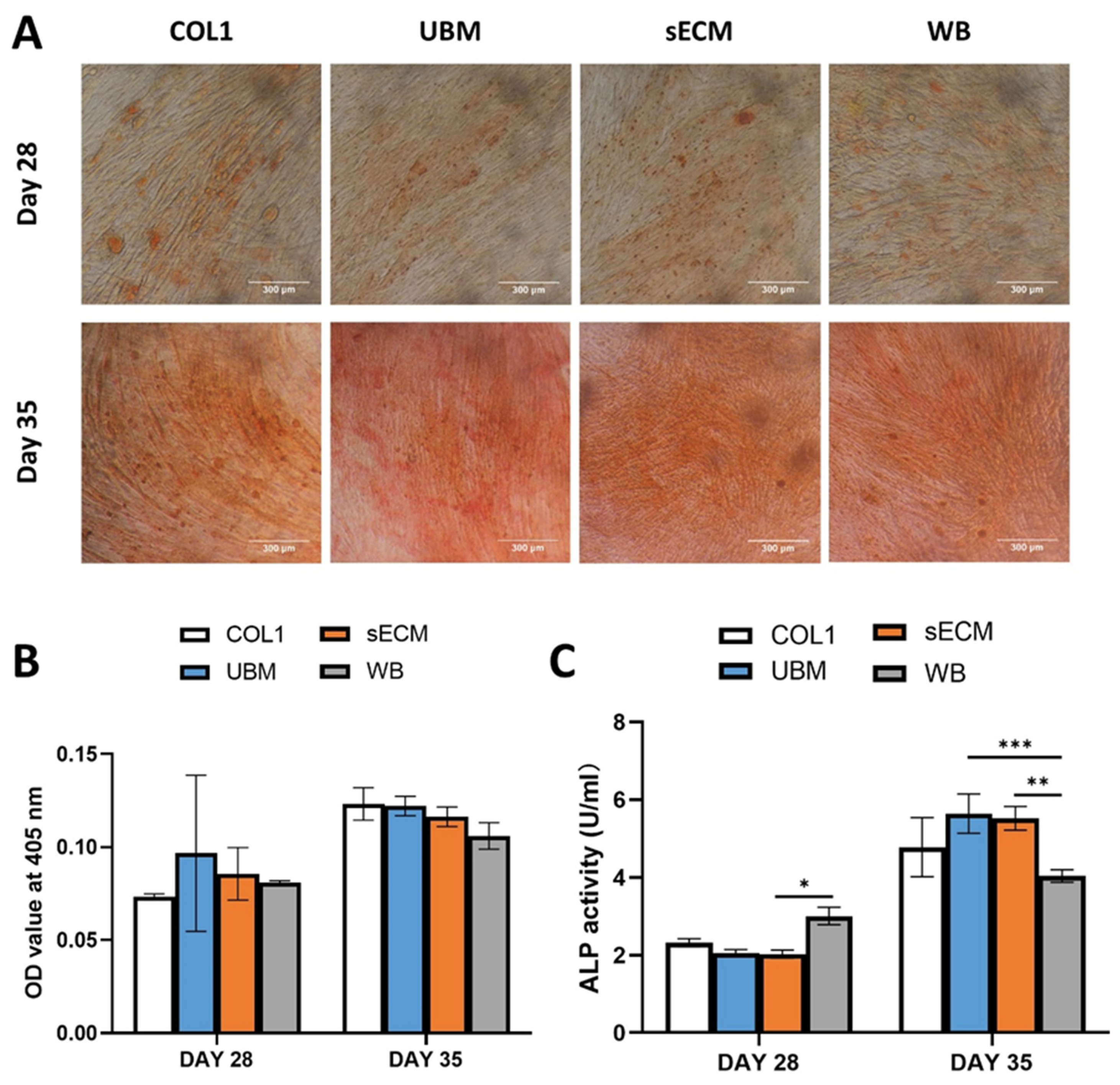
3.8. Effect on C2C12 Osteoblast Differentiation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Catoira, M.C.; Fusaro, L.; Di Francesco, D.; Ramella, M.; Boccafoschi, F. Overview of natural hydrogels for regenerative medicine applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varaprasad, K.; Raghavendra, G.M.; Jayaramudu, T.; Yallapu, M.M.; Sadiku, R. A mini review on hydrogels classification and recent developments in miscellaneous applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 79, 958–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurila, P.; Leivo, I. Basement membrane and interstitial matrix components form separate matrices in heterokaryons of PYS-2 cells and fibroblasts. J. Cell Sci. 1993, 104, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matrix, Extracellular and Interstitial. In Reviews in Cell Biology and Molecular Medicine; Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/3527600906.mcb.200400091 (accessed on 20 June 2021). [CrossRef]
- Frantz, C.; Stewart, K.M.; Weaver, V.M. The extracellular matrix at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123 Pt 24, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pokrywczyńska, M.; Gubanska, I.; Drewa, G.; Drewa, T. Application of Bladder Acellular Matrix in Urinary Bladder Regen-Eration: The State of the Art and Future Directions. BioMed Res. Int. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhout, S.; Rousseau, A.; Chabaud, S.; Morissette, A.; Bolduc, S. Potential of Different Tissue Engineering Strategies in the Bladder Reconstruction. Regen. Med. Tissue Eng. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grounds, M.D. Complexity of Extracellular Matrix and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. In Skeletal Muscle Repair and Regeneration; Schiaffino, S., Partridge, T., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 269–302. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, C.-Y.; Nguyen, H.-Q.-D.; Weng, Y.-C. Characterization of Porcine Urinary Bladder Matrix Hydrogels from Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Decellularization Method. Polymers 2020, 12, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuman, H.; Massensini, A.R.; Donnelly, J.; Kim, S.-M.; Medberry, C.J.; Badylak, S.F.; Modo, M. ECM hydrogel for the treatment of stroke: Characterization of the host cell infiltrate. Biomaterials 2016, 91, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loneker, A.E.; Faulk, D.M.; Hussey, G.S.; D’Amore, A.; Badylak, S.F. Solubilized liver extracellular matrix maintains primary rat hepatocyte phenotype in-vitro. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2016, 104, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukmachev, D.; Forostyak, S.; Koci, Z.; Zaviskova, K.; Vackova, I.; Vyborny, K.; Sandvig, I.; Sandvig, A.; Medberry, C.J.; Badylak, S.F.; et al. Injectable Extracellular Matrix Hydrogels as Scaffolds for Spinal Cord Injury Repair. Tissue Eng. Part A 2016, 22, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allbritton-King, J.D.; Kimicata, M.; Fisher, J.P. Incorporating a structural extracellular matrix gradient into a porcine urinary bladder matrix -based hydrogel dermal scaffold. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, A.; Kandakatla, A.; Van Der Merwe, Y.; Ren, T.; Huleihel, L.; Hussey, G.; Naranjo, J.D.; Johnson, S.; Badylak, S.; Steketee, M. Urinary bladder extracellular matrix hydrogels and matrix-bound vesicles differentially regulate central nervous system neuron viability and axon growth and branching. J. Biomater. Appl. 2017, 31, 1277–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, K.; Bägli, D.J. The bladder extracellular matrix. Part I: Architecture, development and disease. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2009, 6, 596–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, B.N.; Buckenmeyer, M.J.; Prest, T.A. Preparation of Decellularized Biological Scaffolds for 3D Cell Culture. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1612, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freytes, D.O.; Martin, J.; Velankar, S.S.; Lee, A.S.; Badylak, S.F. Preparation and rheological characterization of a gel form of the porcine urinary bladder matrix. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Pérez, J.; Ahearne, M. The impact of decellularization methods on extracellular matrix derived hydrogels. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolf, M.T.; Daly, K.A.; Brennan-Pierce, E.P.; Johnson, S.A.; Carruthers, C.A.; D’Amore, A.; Nagarkar, S.P.; Velankar, S.S.; Badylak, S.F. A hydrogel derived from decellularized dermal extracellular matrix. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7028–7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.S.; Shin, J.; Park, H.-M.; Kim, Y.-G.; Kim, B.-G.; Oh, J.-W.; Cho, S.-W. Liver Extracellular Matrix Providing Dual Functions of Two-Dimensional Substrate Coating and Three-Dimensional Injectable Hydrogel Platform for Liver Tissue Engineering. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeQuach, J.A.; Yuan, S.H.; Goldstein, L.S.; Christman, K.L. Decellularized Porcine Brain Matrix for Cell Culture and Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part A 2011, 17, 2583–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rauch, C.; Brunet, A.-C.; Deleule, J.; Farge, E. C2C12 myoblast/osteoblast transdifferentiation steps enhanced by epigenetic inhibition of BMP2 endocytosis. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2002, 283, C235–C243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Andrea, P.; Civita, D.; Cok, M.; Severino, L.U.; Vita, F.; Scaini, D.; Casalis, L.; Lorenzon, P.; Donati, I.; Bandiera, A. Myoblast Adhesion, Proliferation and Differentiation on Human Elastin-Like Polypeptide (HELP) Hydrogels. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2017, 15, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yang, G.; Hong, Y. Rap1A Regulates Osteoblastic Differentiation via the ERK and p38 Mediated Signaling. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Long, X.; Hayashi, T.; Mizuno, K.; Hattori, S.; Fujisaki, H.; Ogura, T.; Wang, D.O.; Ikejima, T. Type I collagen promotes the migration and myogenic differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts via the release of interleukin-6 mediated by FAK/NF-κB p65 activation. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, F.; Nowald, C.; Pflieger, K.; Boettcher, K.; Zahler, S.; Lieleg, O. The Biophysical Properties of Basal Lamina Gels Depend on the Biochemical Composition of the Gel. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldin, L.T.; Cramer, M.C.; Velankar, S.S.; White, L.J.; Badylak, S.F. Extracellular matrix hydrogels from decellularized tissues: Structure and function. Acta Biomater. 2017, 49, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aurora, A.; McCarron, J.; Iannotti, J.P.; Derwin, K. Commercially available extracellular matrix materials for rotator cuff repairs: State of the art and future trends. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2007, 16, S171–S178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurchenco, P.D. Basement Membranes: Cell Scaffoldings and Signaling Platforms. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oegema, T.R.; Laidlaw, J.; Hascall, V.C.; Dziewiatkowski, D.D. The effect of proteoglycans on the formation of fibrils from collagen solutions. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1975, 170, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, C.; Altunbas, A.; Yucel, T.; Nagarkar, R.P.; Schneider, J.P.; Pochan, D.J. Injectable solid hydrogel: Mechanism of shear-thinning and immediate recovery of injectable β-hairpin peptide hydrogels. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 5143–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bual, R.P.; Ijima, H. Intact extracellular matrix component promotes maintenance of liver-specific functions and larger aggregates formation of primary rat hepatocytes. Regen. Ther. 2019, 11, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutolf, M.P.; Hubbell, J. Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alom, N.; Peto, H.; Kirkham, G.R.; Shakesheff, K.M.; White, L.J. Bone extracellular matrix hydrogel enhances osteogenic differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts and mouse primary calvarial cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeQuach, J.A.; Mezzano, V.; Miglani, A.; Lange, S.; Keller, G.; Sheikh, F.; Christman, K.L. Simple and High Yielding Method for Preparing Tissue Specific Extracellular Matrix Coatings for Cell Culture. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Agostino, M.; Torcinaro, A.; Madaro, L.; Marchetti, L.; Sileno, S.; Beji, S.; Salis, C.; Proietti, D.; Imeneo, G.; Capogrossi, M.C.; et al. Role of miR-200c in Myogenic Differentiation Impairment via p66Shc: Implication in Skeletal Muscle Regeneration of Dystrophic mdx Mice. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4814696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willkomm, L.; Schubert, S.; Jung, R.; Elsen, M.; Borde, J.; Gehlert, S.; Suhr, F.; Bloch, W. Lactate regulates myogenesis in C2C12 myoblasts in vitro. Stem Cell Res. 2014, 12, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillies, A.R.; Lieber, R.L. Structure and function of the skeletal muscle extracellular matrix. Muscle Nerve 2011, 44, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaturvedi, V.; Dye, D.E.; Kinnear, B.F.; Van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Grounds, M.; Coombe, D.R. Interactions between Skeletal Muscle Myoblasts and their Extracellular Matrix Revealed by a Serum Free Culture System. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundharrajan, I.; Kim, D.H.; Kuppusamy, P.; Choi, K.C. Modulation of osteogenic and myogenic differentiation by a phytoestrogen formononetin via p38MAPK-dependent JAK-STAT and Smad-1/5/8 signaling pathways in mouse myogenic pro-genitor cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Shi, Z.-D.; Ji, X.; Morales, J.; Zhang, J.; Kaur, N.; Wang, S. Enhanced Osteogenesis of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Periodic Heat Shock in Self-Assembling Peptide Hydrogel. Tissue Eng. Part A 2013, 19, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kao, C.-Y.; Nguyen, H.-Q.-D.; Weng, Y.-C.; Hung, Y.-H.; Lo, C.-M. Evaluating the Effect of Tissue Selection on the Characteristics of Extracellular Matrix Hydrogels from Decellularized Porcine Bladders. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135820
Kao C-Y, Nguyen H-Q-D, Weng Y-C, Hung Y-H, Lo C-M. Evaluating the Effect of Tissue Selection on the Characteristics of Extracellular Matrix Hydrogels from Decellularized Porcine Bladders. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(13):5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135820
Chicago/Turabian StyleKao, Chen-Yu, Huynh-Quang-Dieu Nguyen, Yu-Chuan Weng, Yu-Han Hung, and Chun-Min Lo. 2021. "Evaluating the Effect of Tissue Selection on the Characteristics of Extracellular Matrix Hydrogels from Decellularized Porcine Bladders" Applied Sciences 11, no. 13: 5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135820
APA StyleKao, C.-Y., Nguyen, H.-Q.-D., Weng, Y.-C., Hung, Y.-H., & Lo, C.-M. (2021). Evaluating the Effect of Tissue Selection on the Characteristics of Extracellular Matrix Hydrogels from Decellularized Porcine Bladders. Applied Sciences, 11(13), 5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135820





