Effect of the Rolling Friction on the Heap Formation of Dry and Wet Coarse Discs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
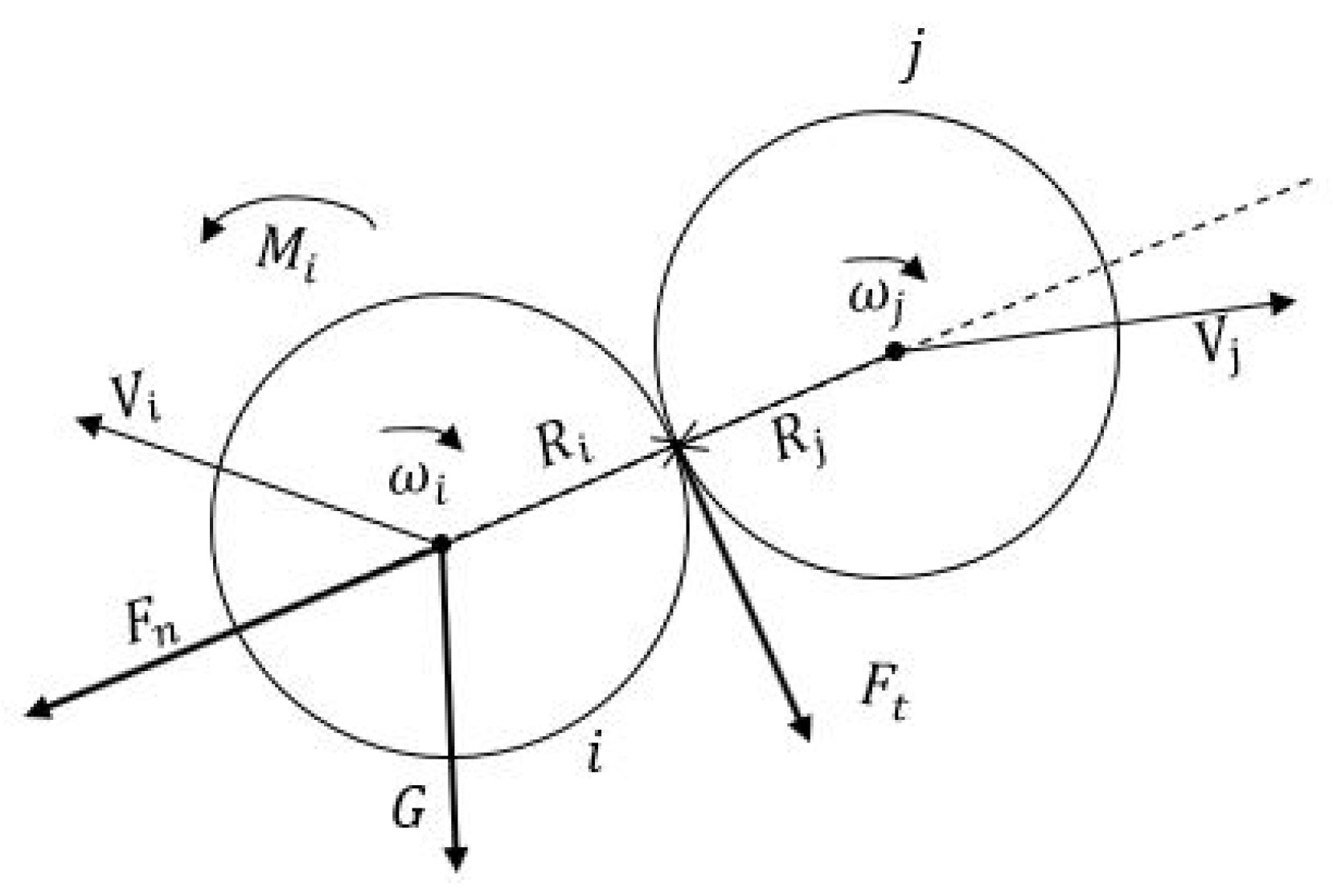
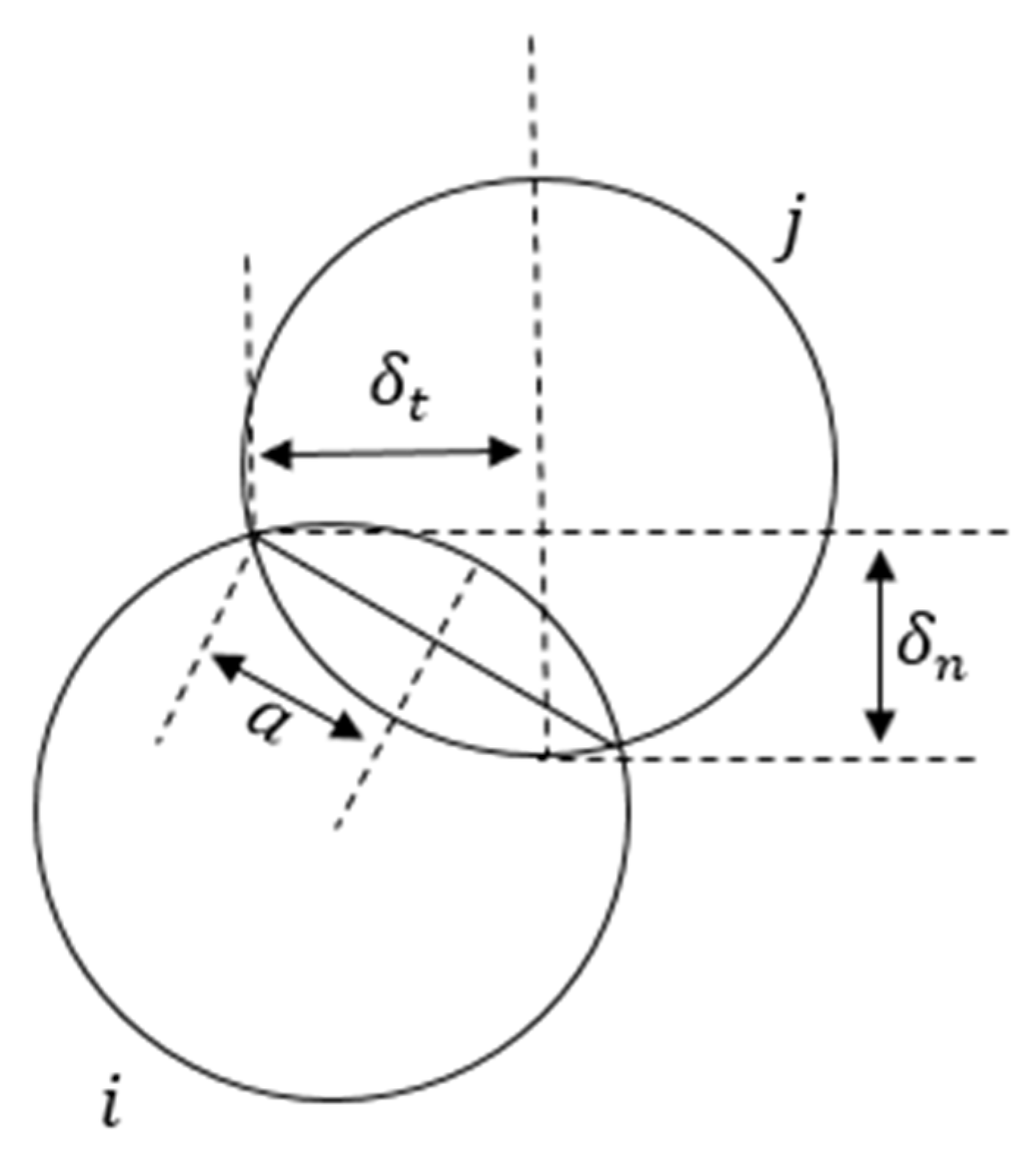
2.1. Contact Force Model
2.2. Cohesion Force Model
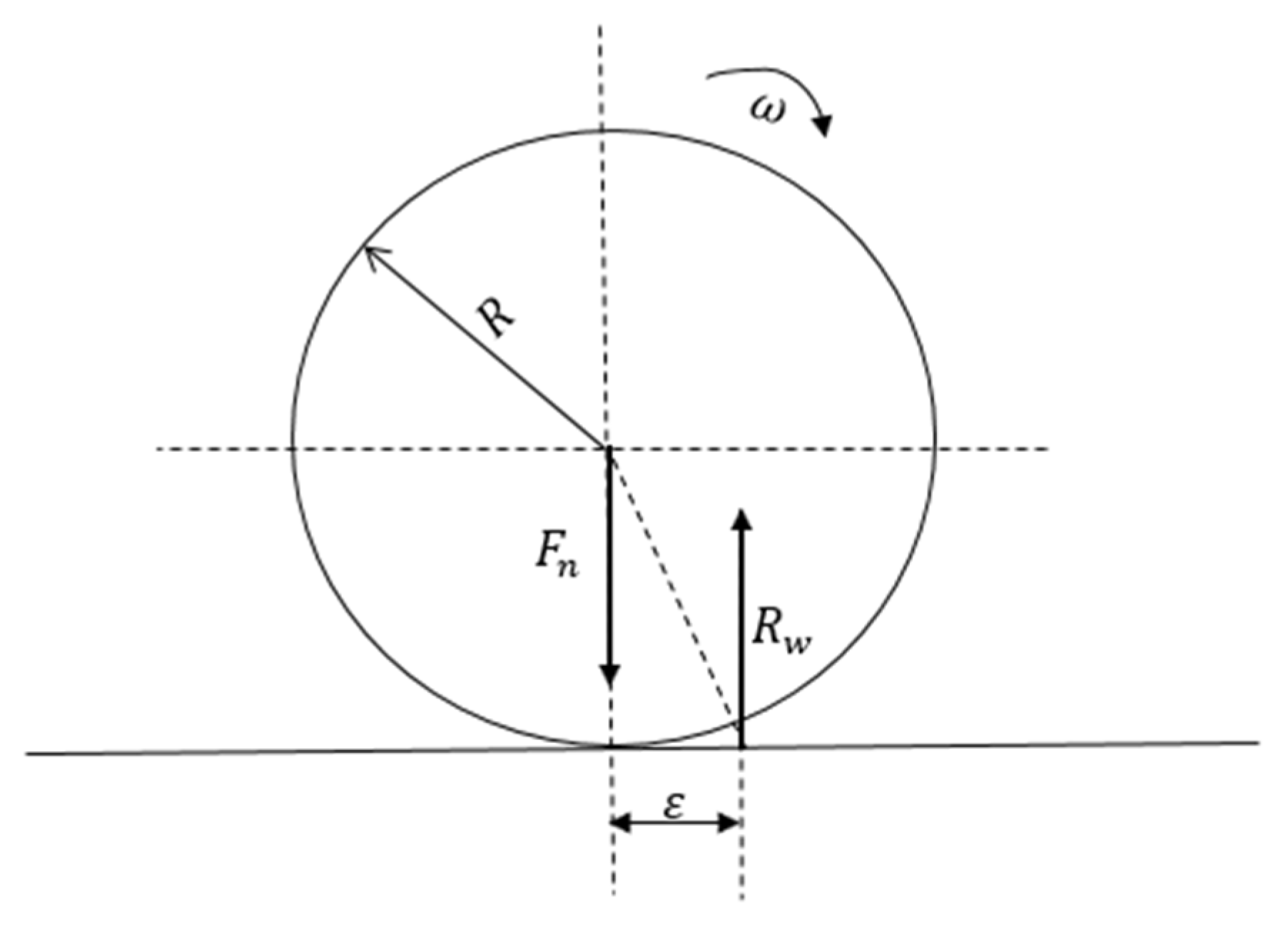
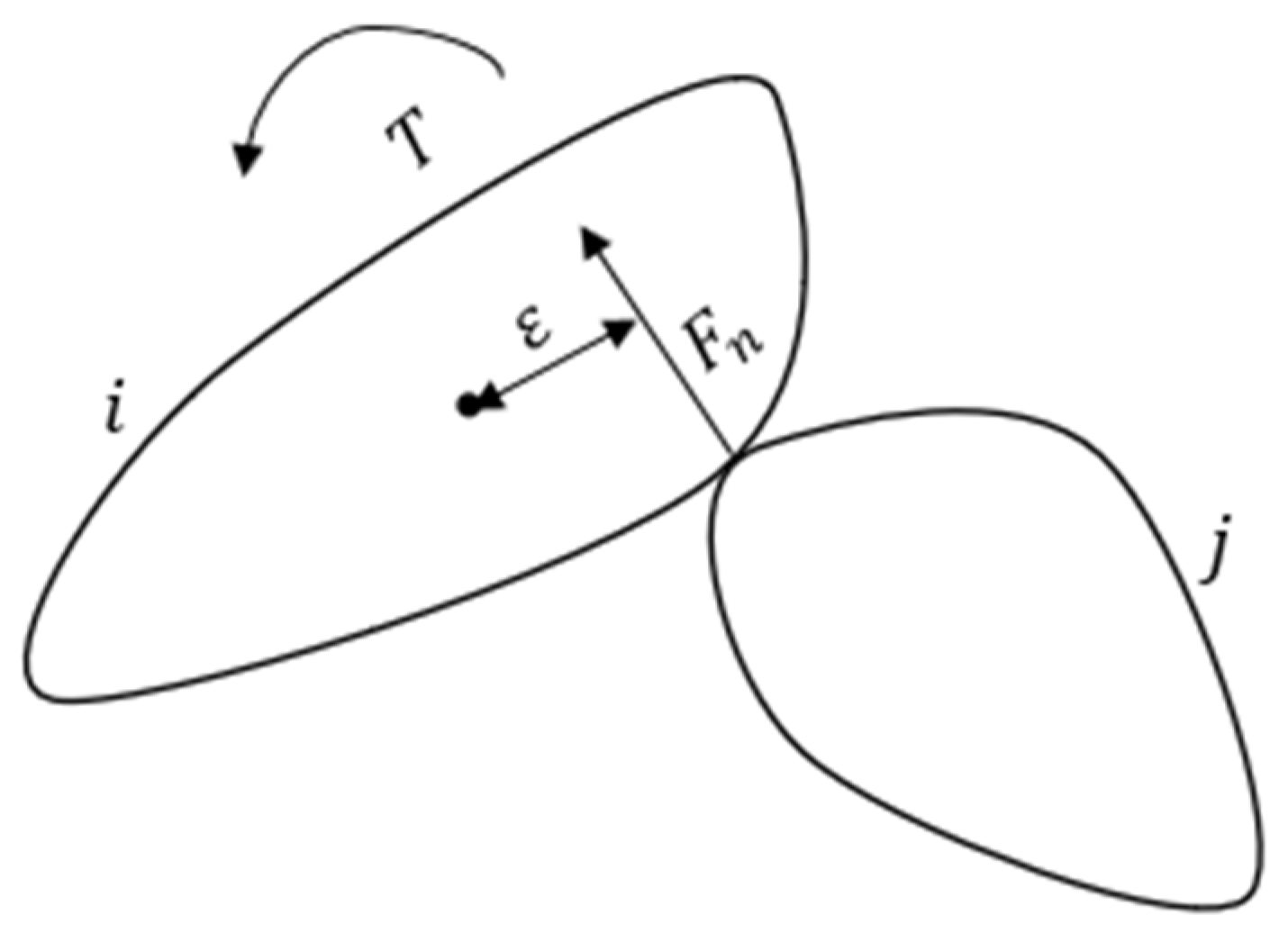
2.3. Rolling Friction
2.4. Numerical Model
3. Results and Discussions
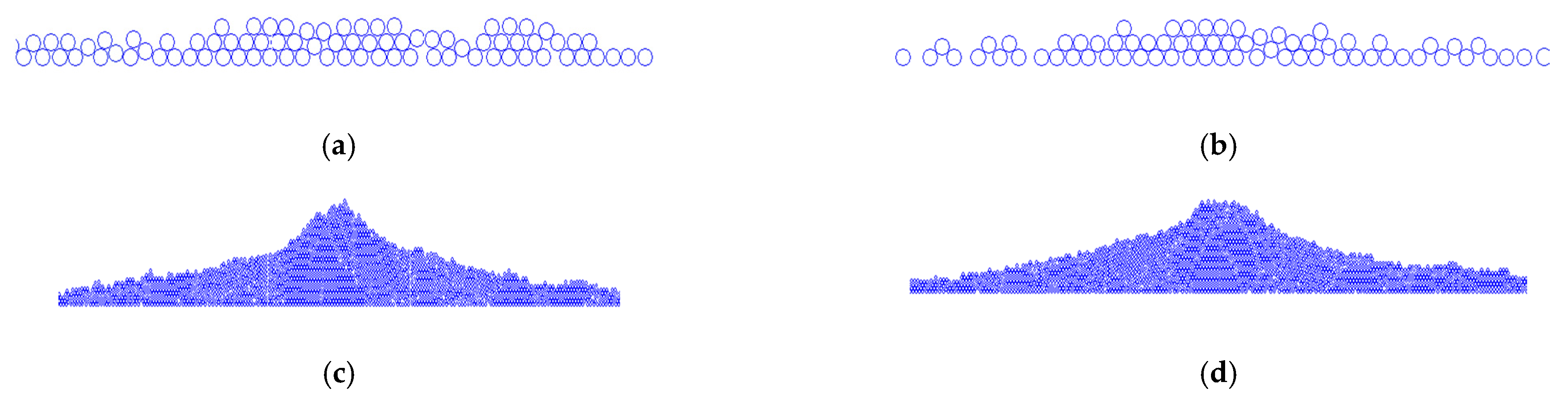
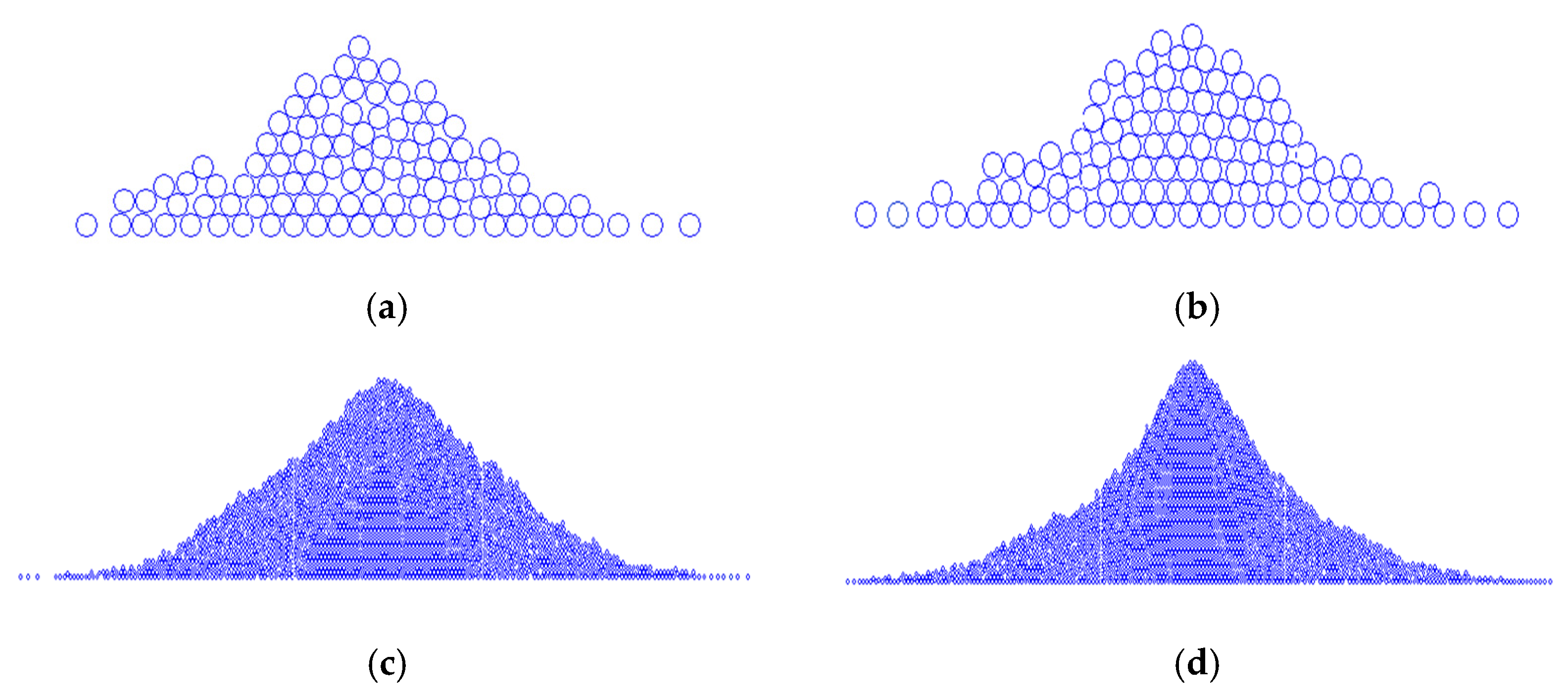
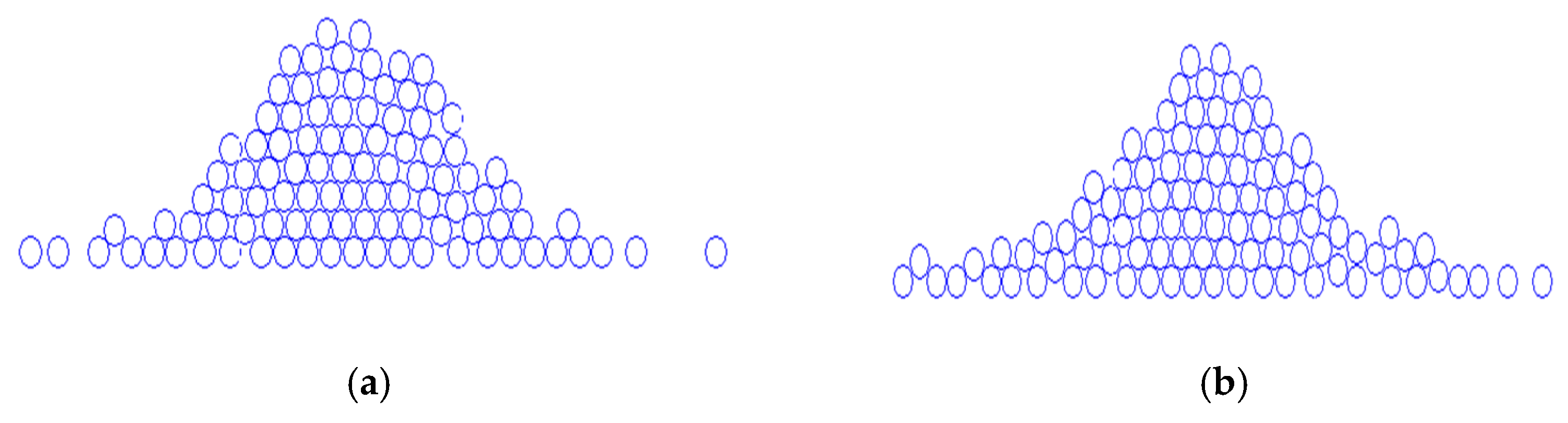
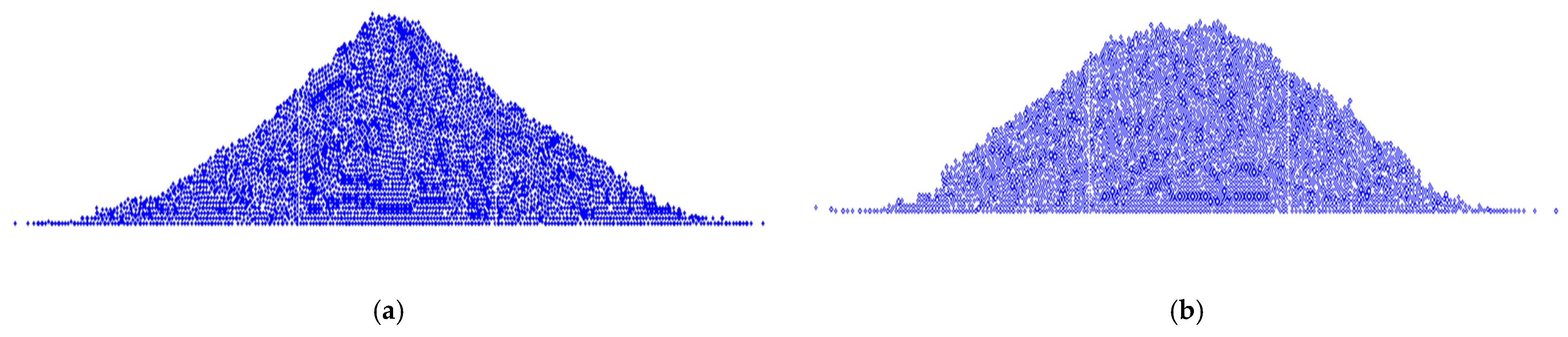
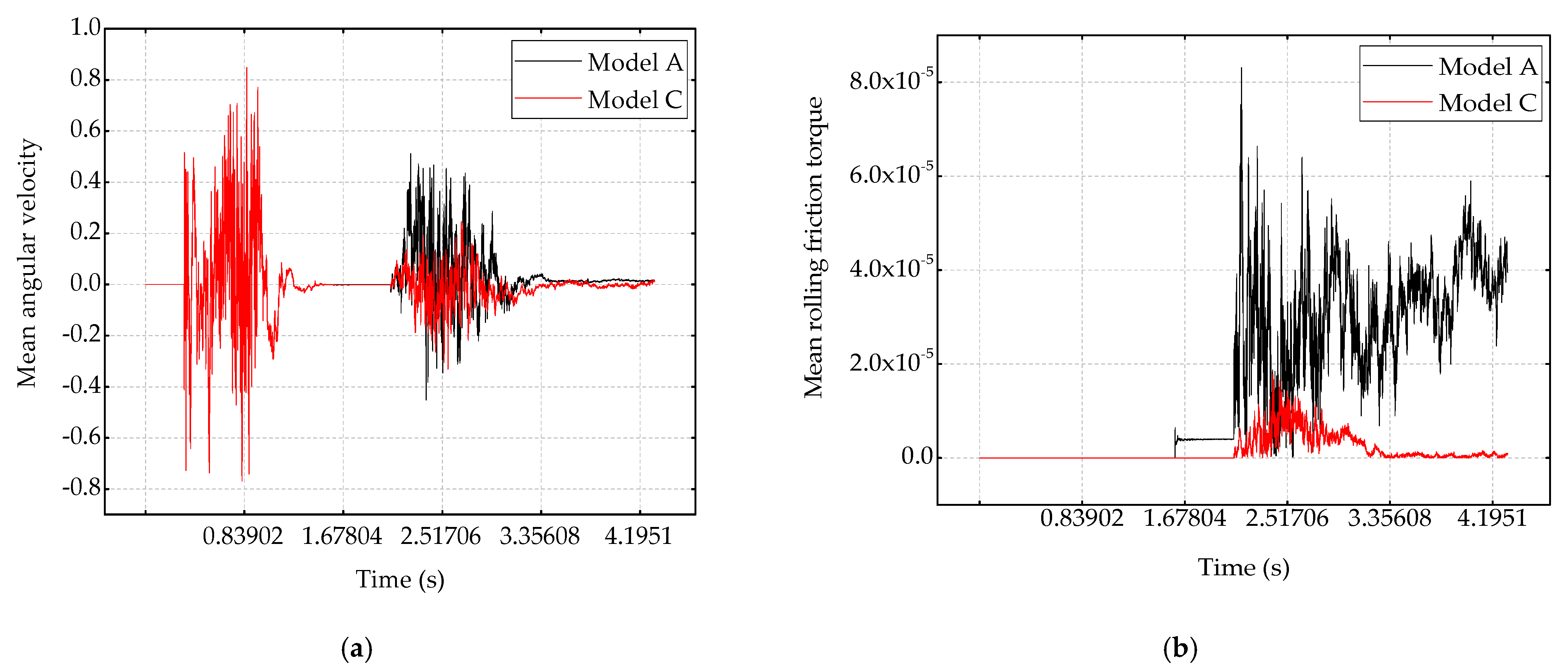
3.1. Rolling Friction Effect on Dry Coarse Soil
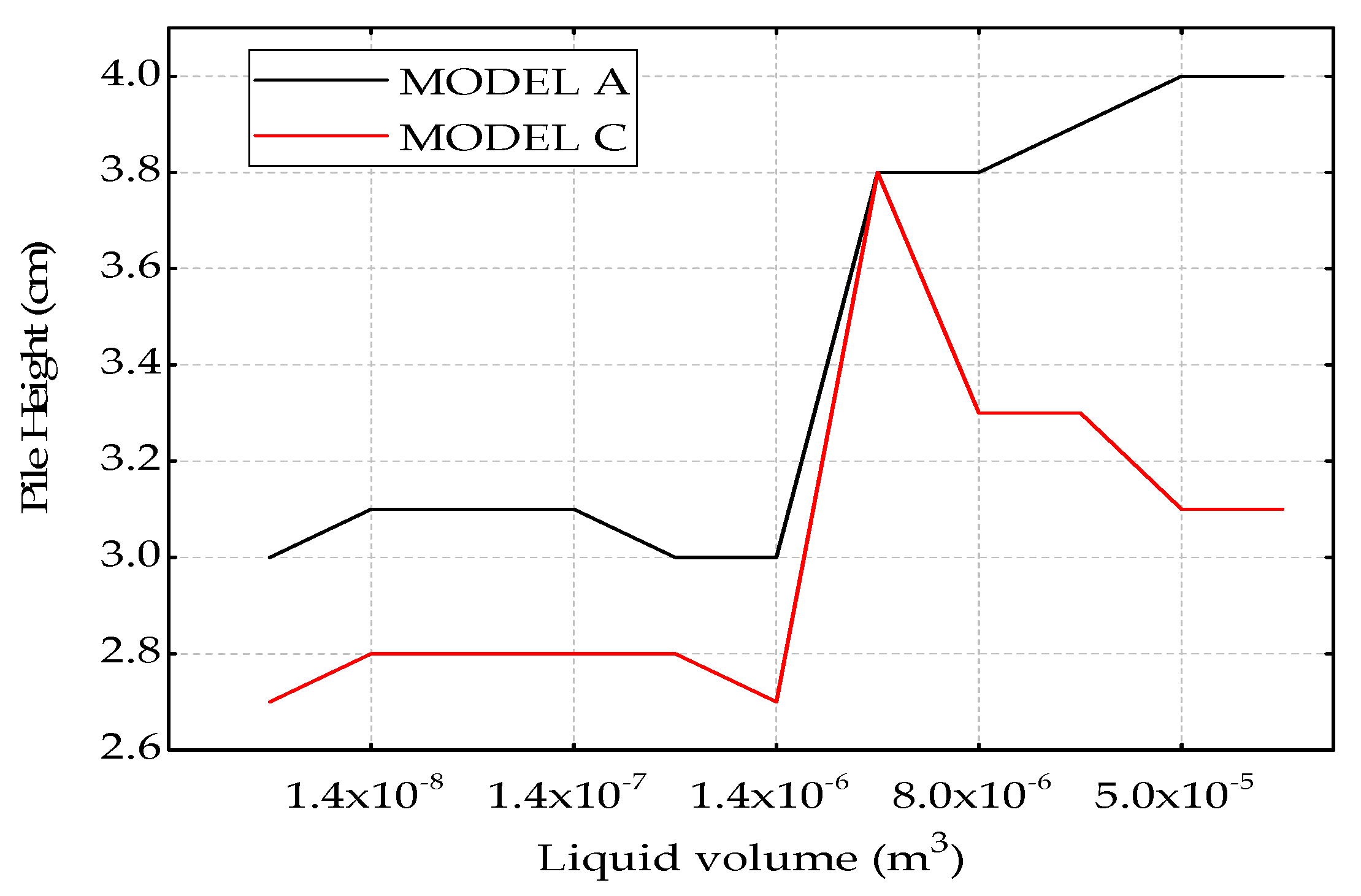
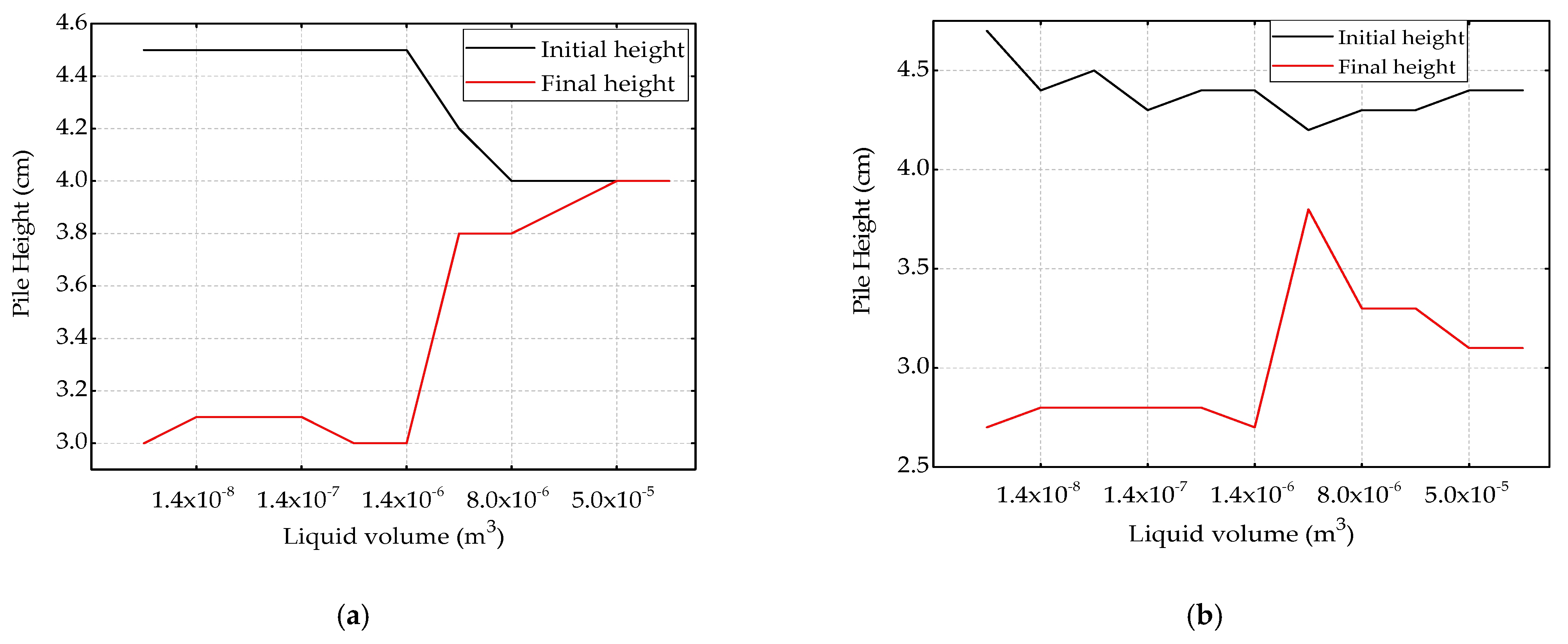
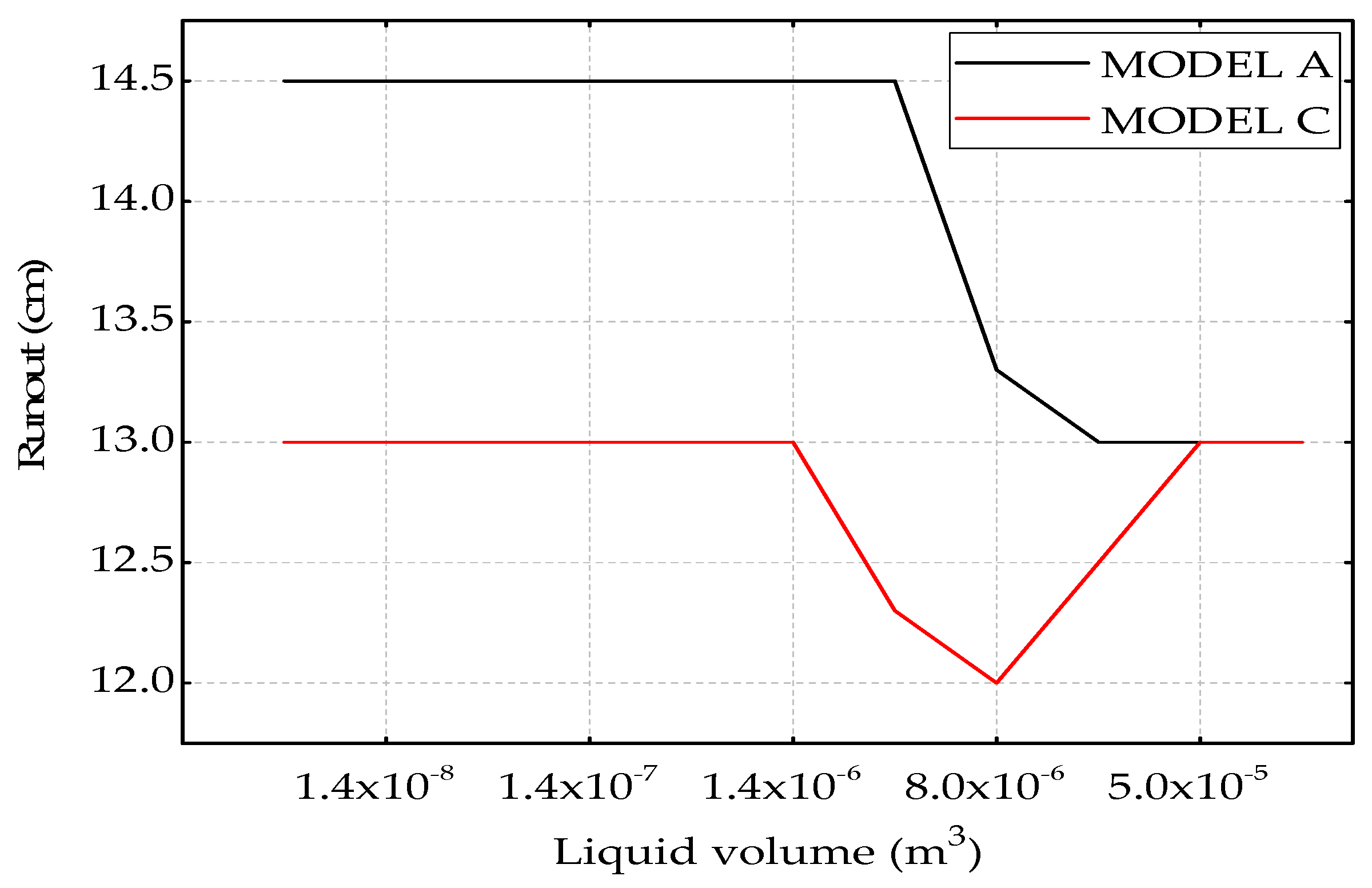
3.2. Rolling Friction Effect on Wet Coarse Soil
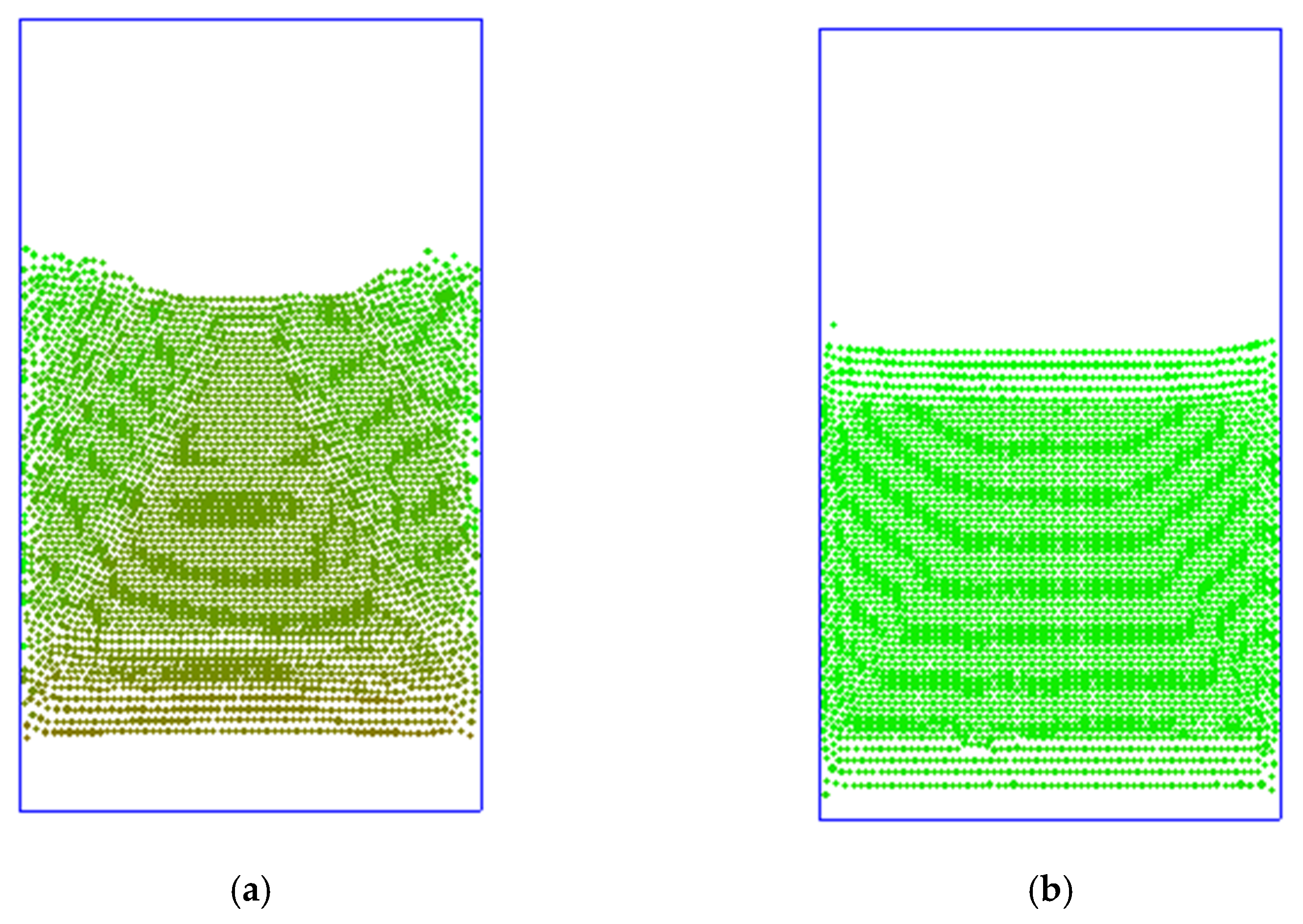
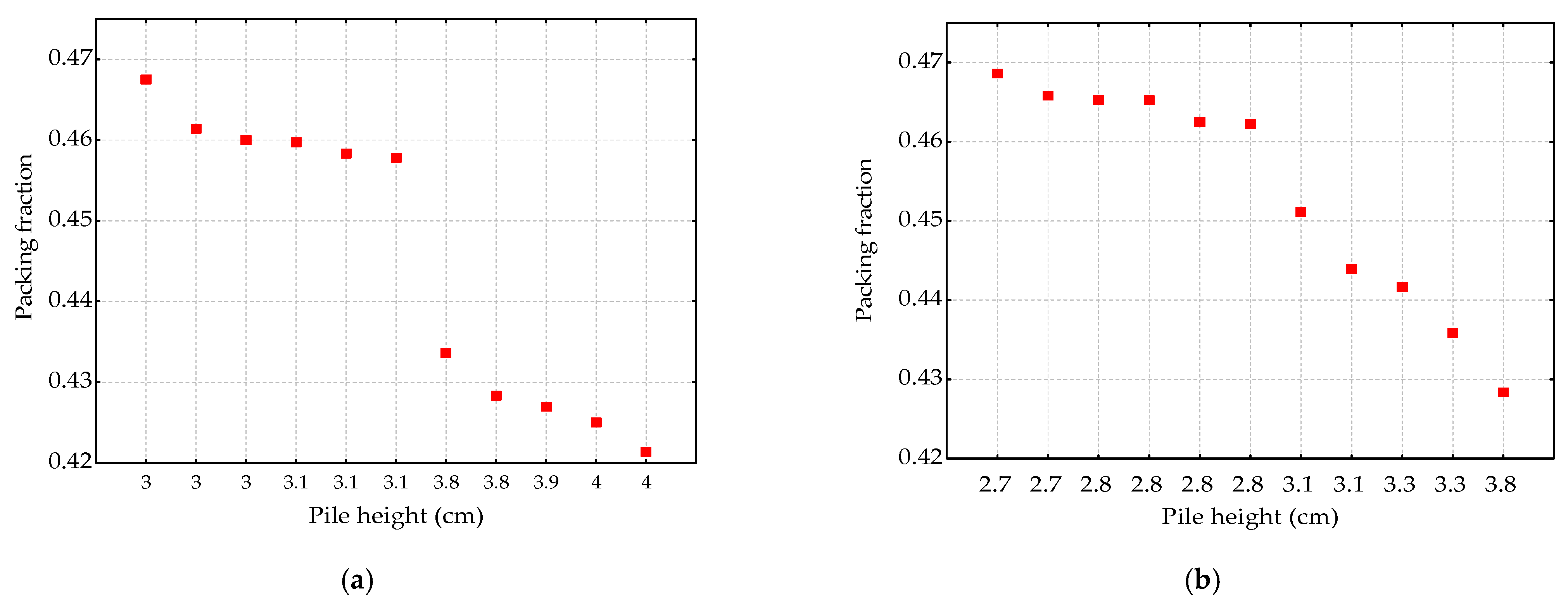
3.3. Initial Particles Packing Effect
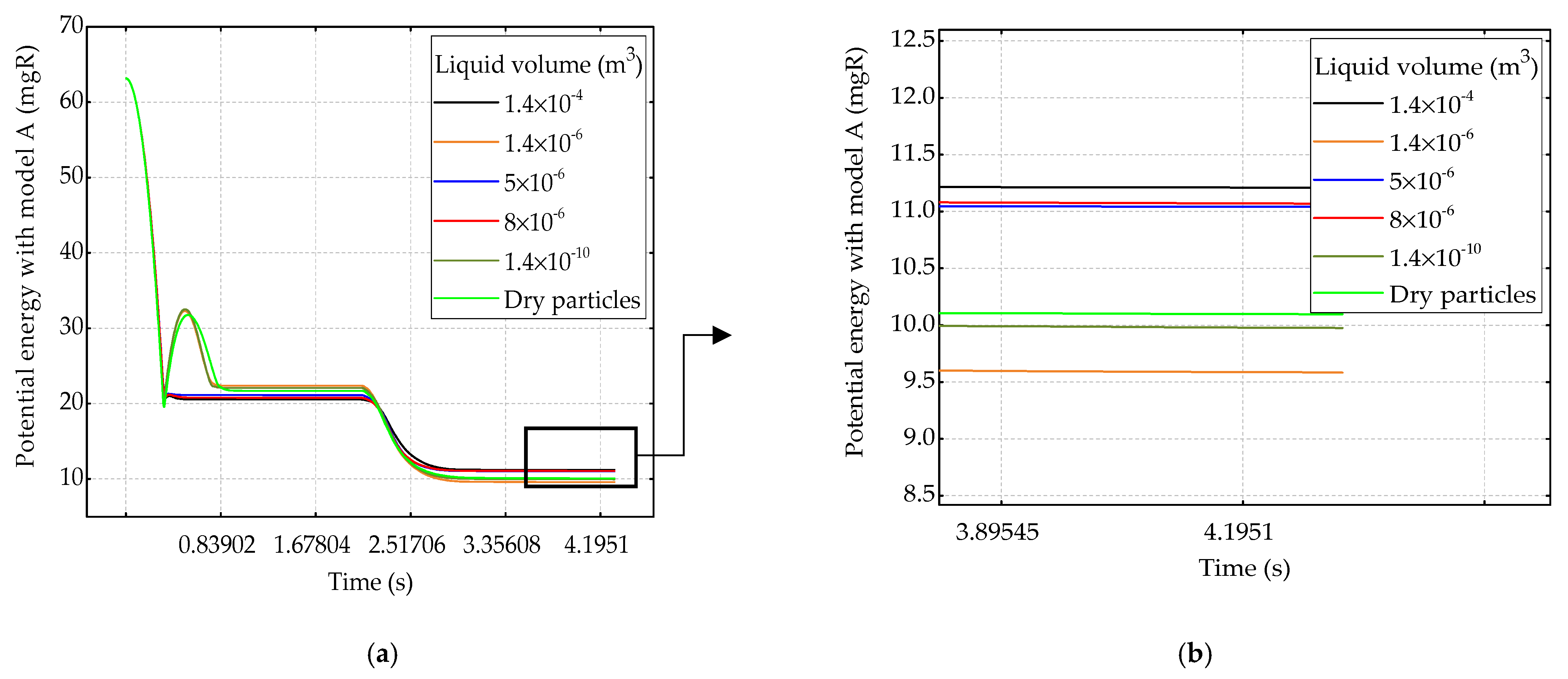
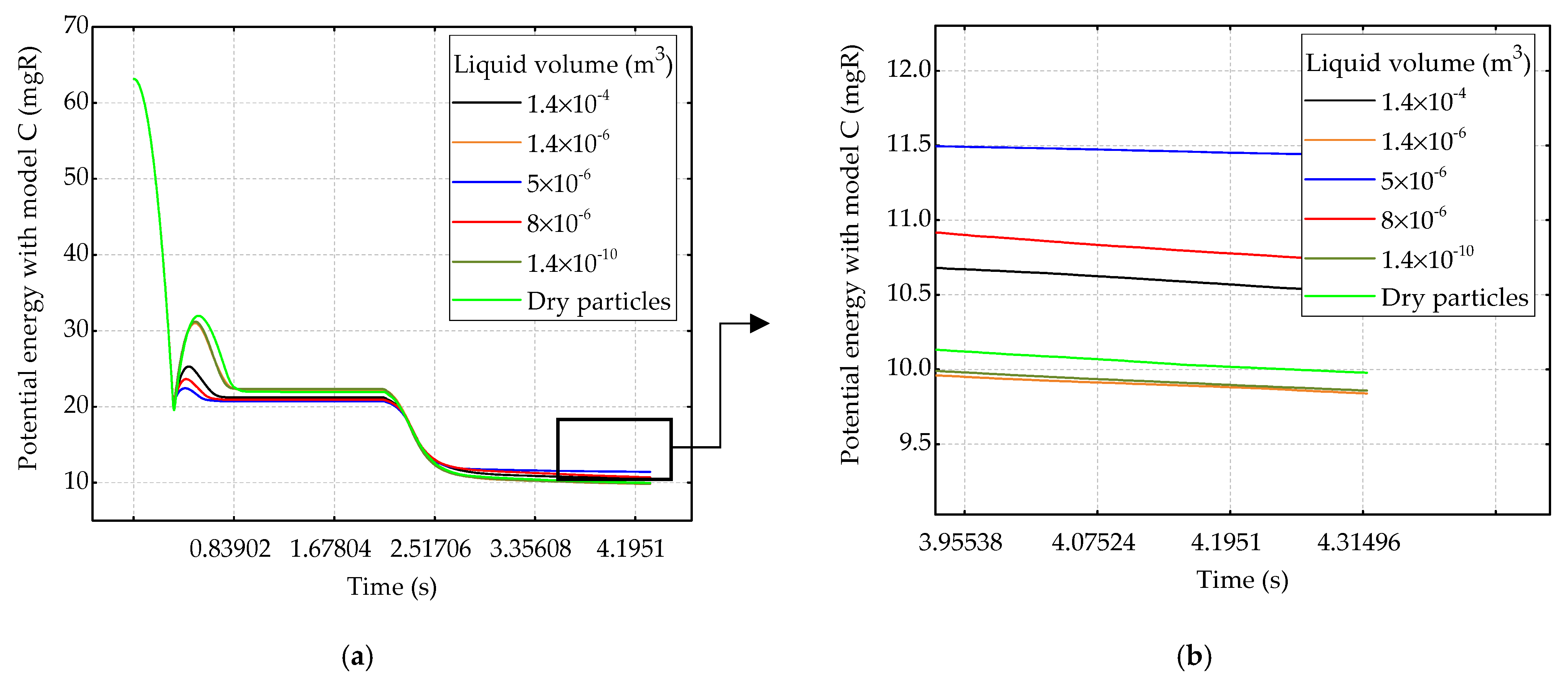
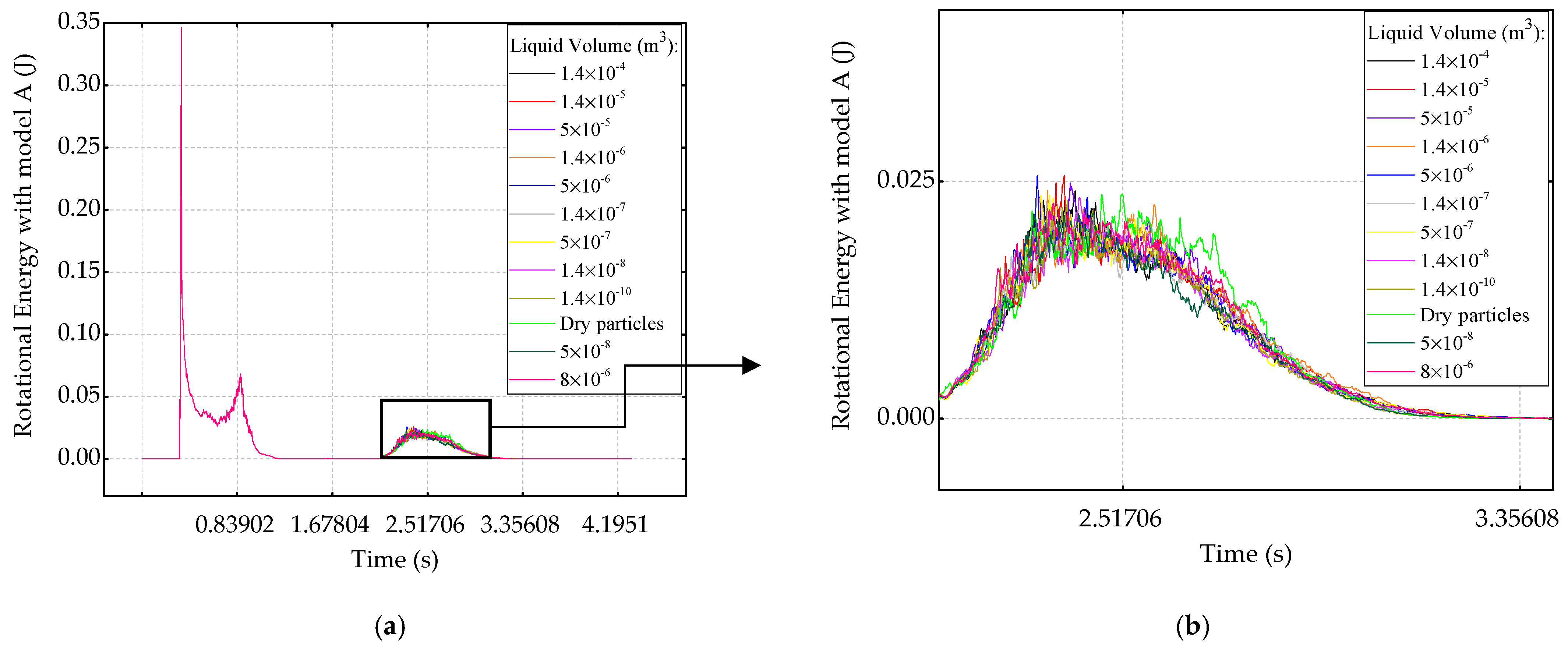
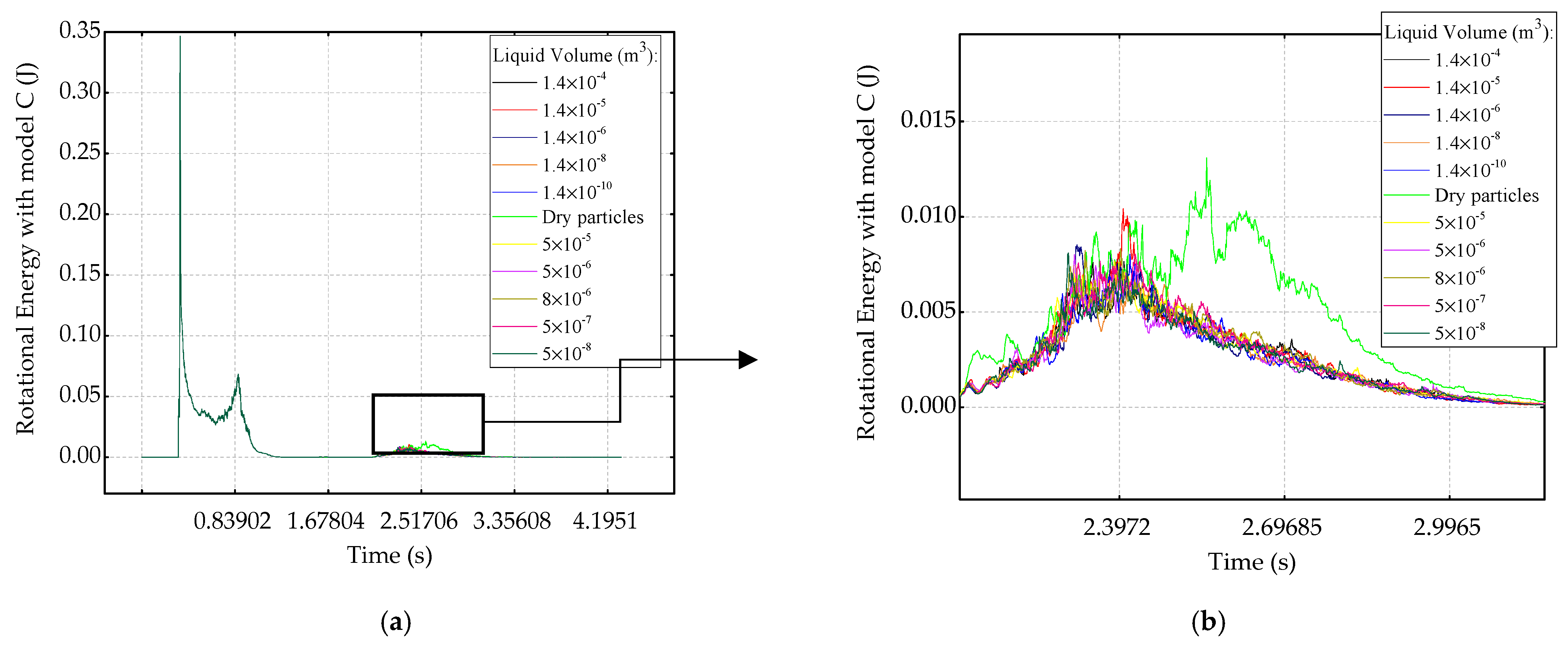
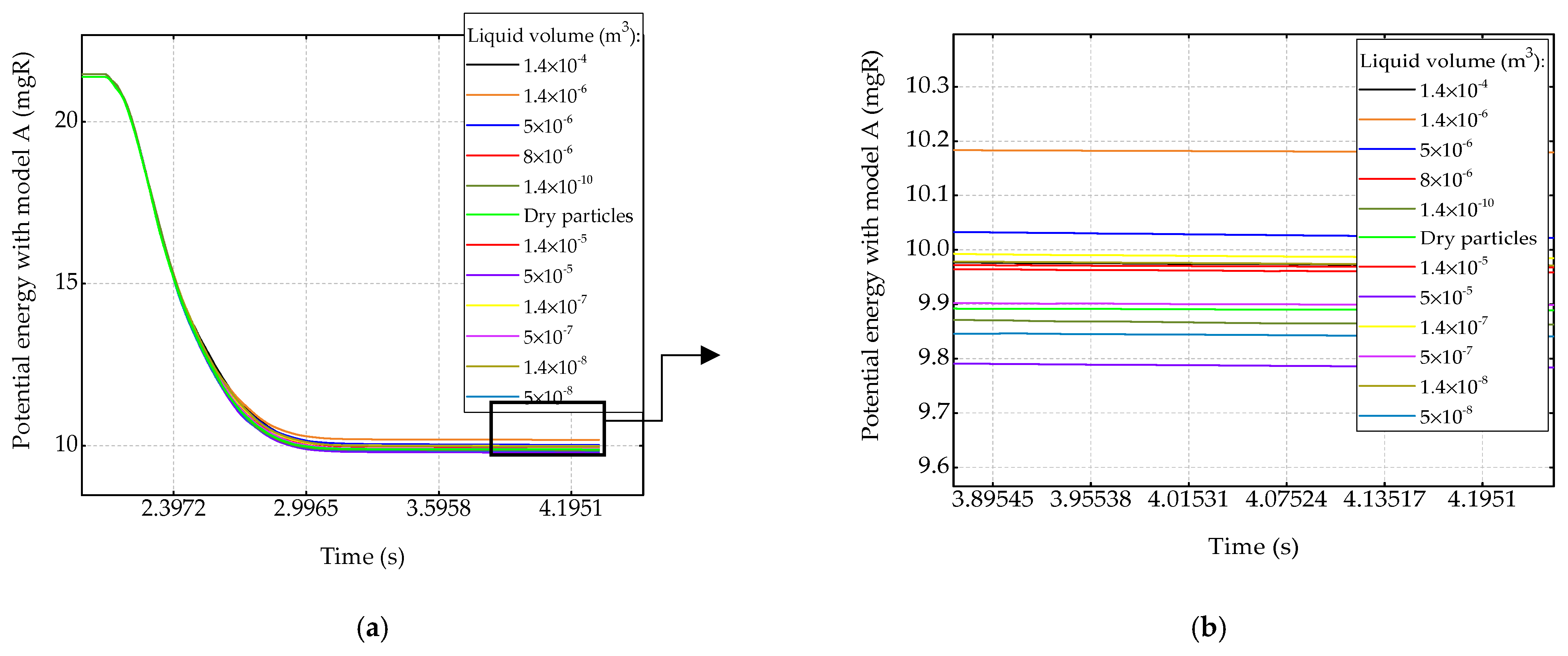
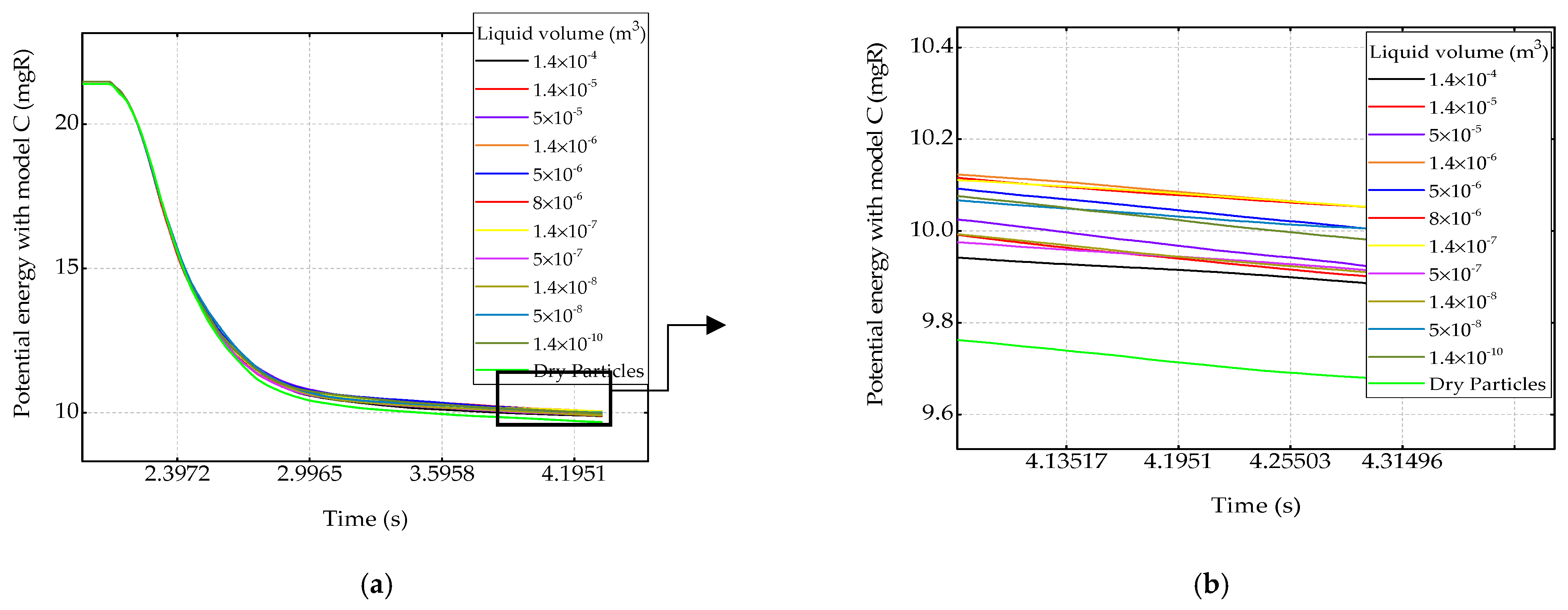
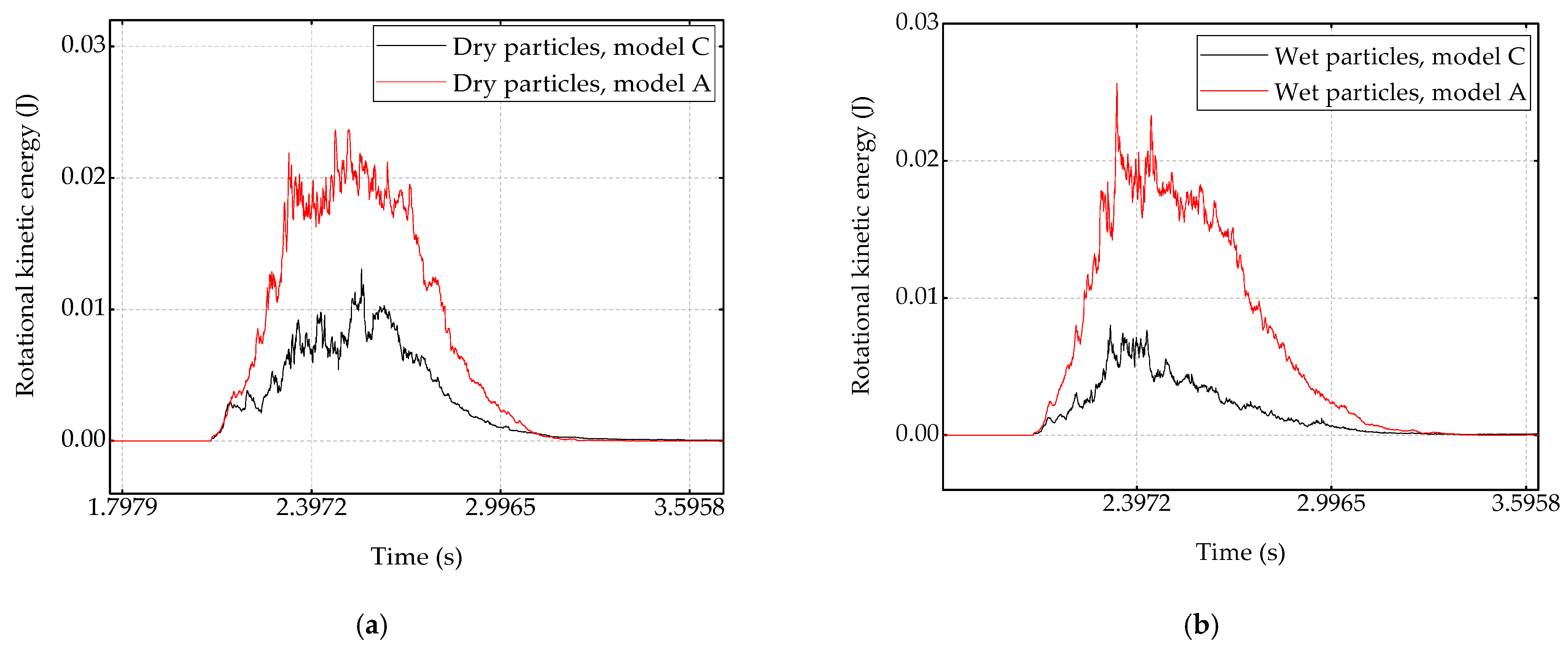
3.4. Energy Monitoring
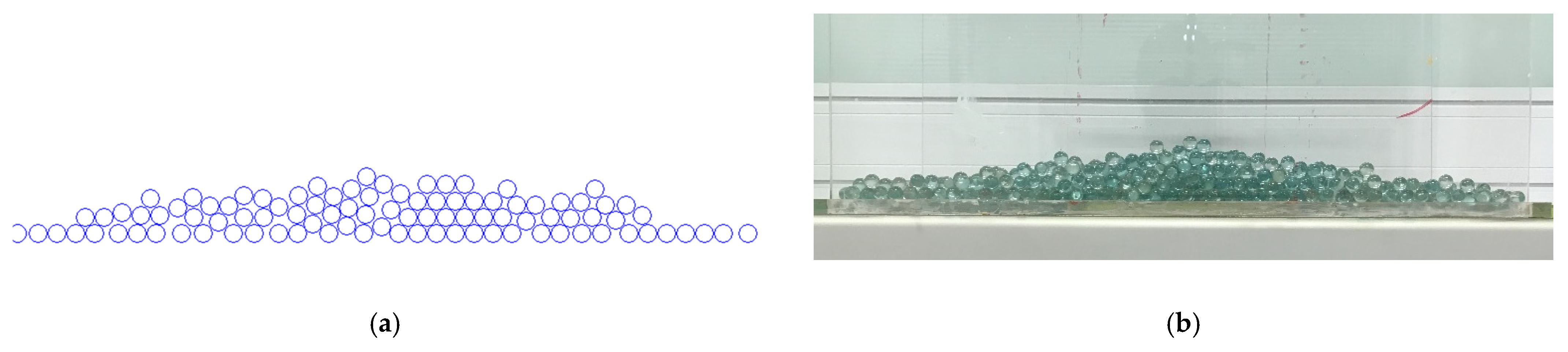
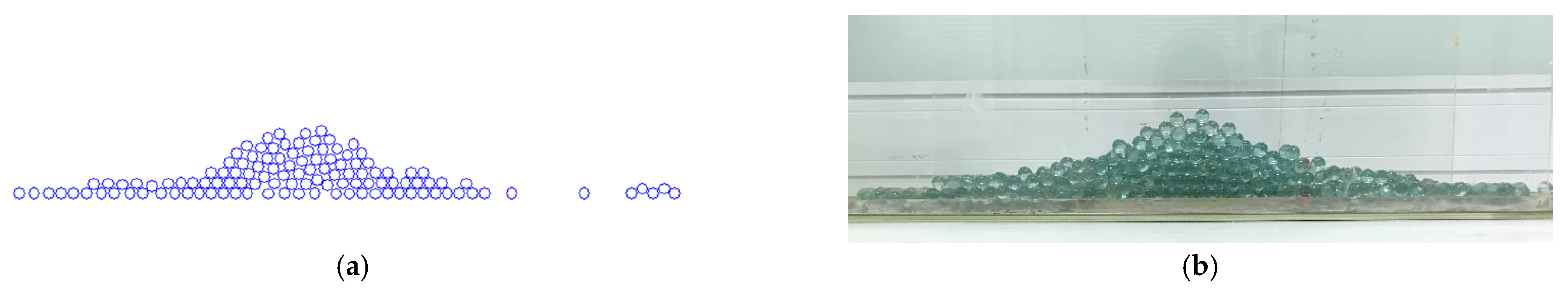
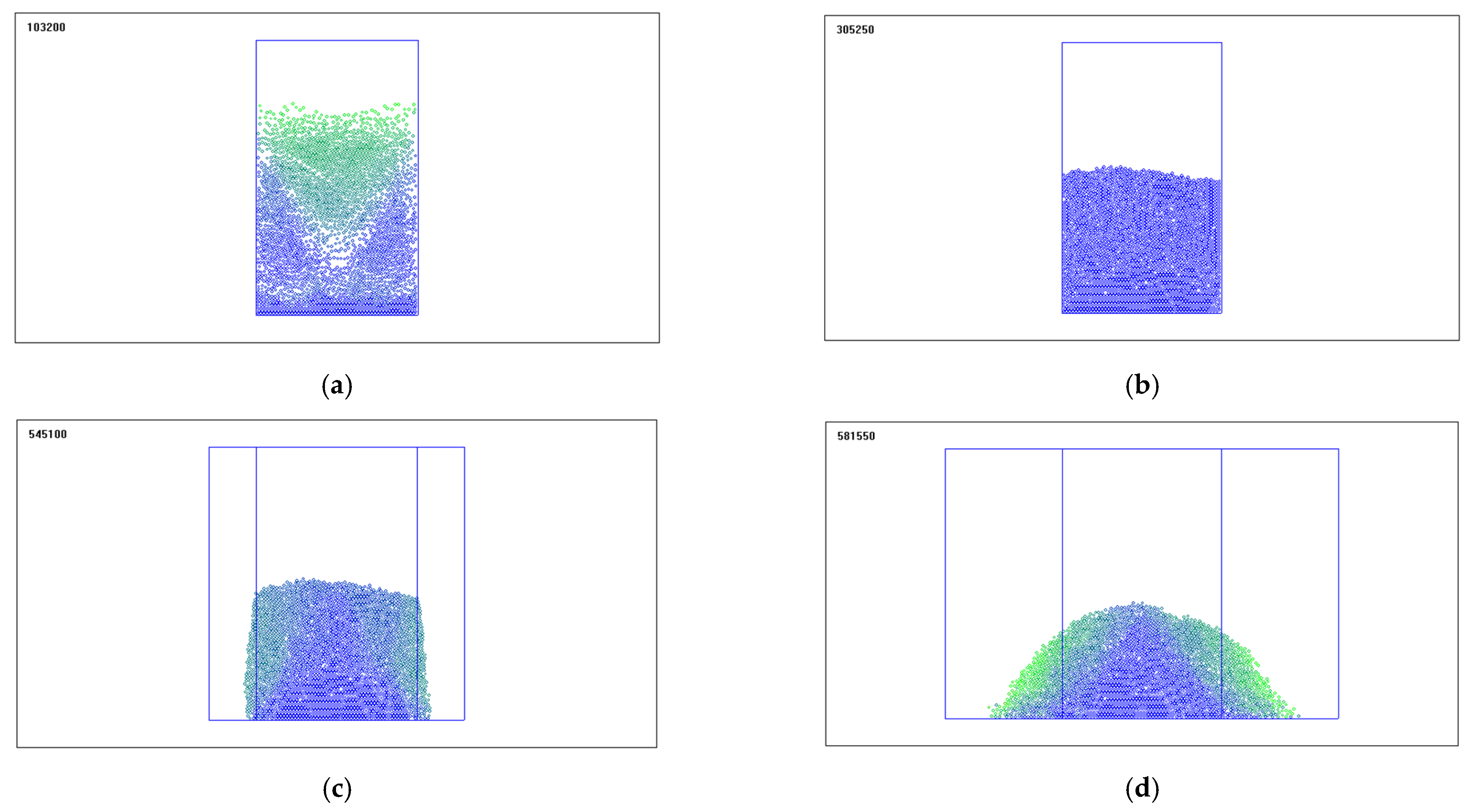
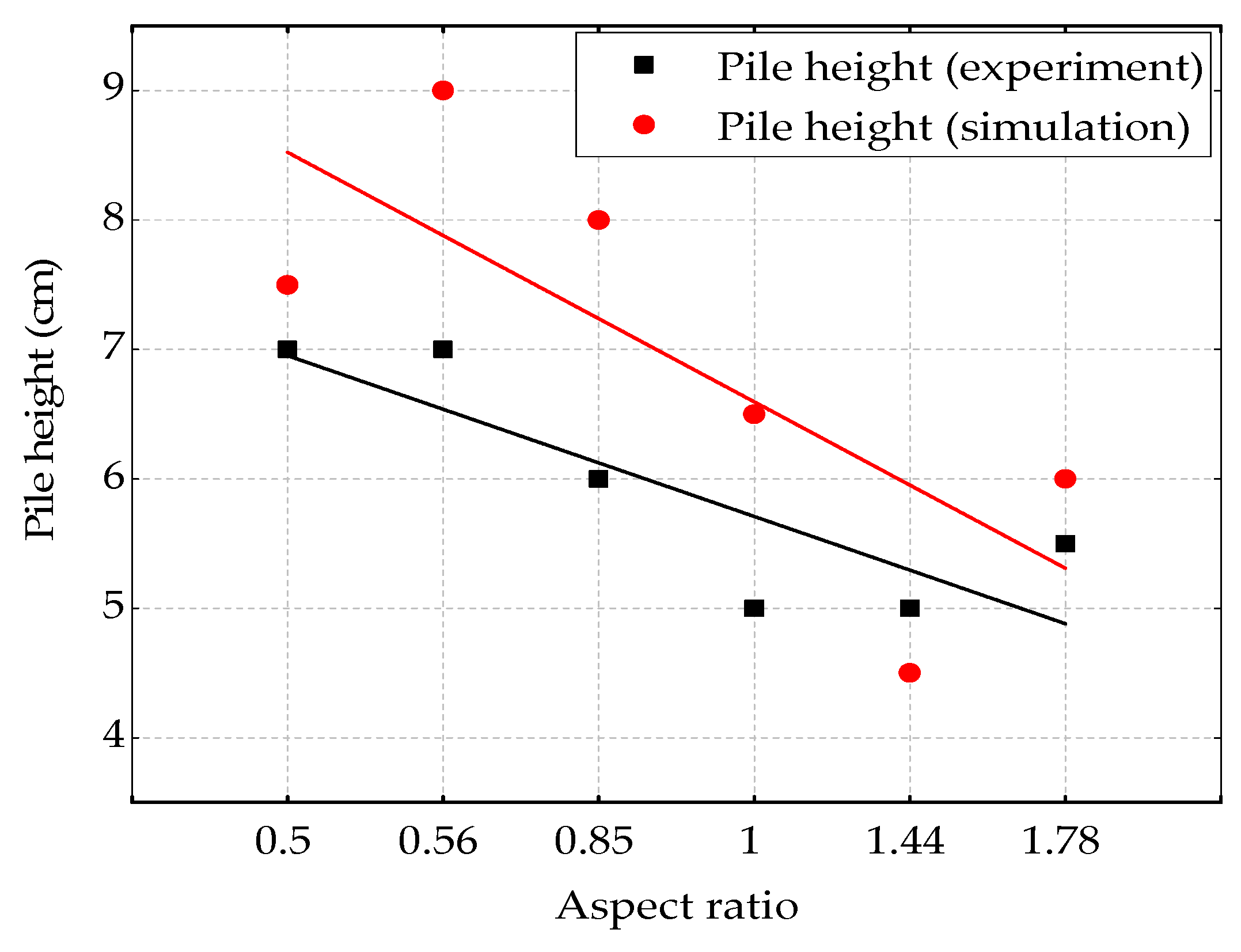
3.5. Model Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, W.-T.; Aubry, N.; Antaki, J.F.; Massoudi, M. Normal stress effects in the gravity driven flow of granular materials. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2017, 92, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Richard, P.; Nicodemi, M.; Delannay, R.; Ribière, P.; Bideau, D. Slow relaxation and compaction of granular systems. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irazábal, J.; Salazar, F.; Oñate, E. Numerical modelling of granular materials with spherical discrete particles and the bounded rolling friction model. Application to railway ballast. Comput. Geotech. 2017, 85, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundall, P.A.; Strack, O.D.L. A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies. Géotechnique 1979, 29, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić, M.; Shen, H.H.; Shen, H.T. The stress tensor in granular shear flows of uniform, deformable disks at high solids concentrations. J. Fluid Mech. 1990, 219, 81–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babic, M. Discrete Particle Numerical Simulation of Granular Material Behavior; Clarkson University: Postdam, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, J.J.; Ahrné, L. Food powder handling and processing: Industry problems, knowledge barriers and research opportunities. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2005, 44, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M. Foundation Analysis and Design. Eng. Geol. 1984, 20, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hashemi, H.M.B.; Al-Amoudi, O.S.B. A review on the angle of repose of granular materials. Powder Technol. 2018, 330, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rackl, M.; Grötsch, F.E.; Rusch, M.; Fottner, J. Qualitative and quantitative assessment of 3D-scanned bulk solid heap data. Powder Technol. 2017, 321, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zou, S.; Yin, Z. Discrete Element Method Simulations of the Inter-Particle Contact Parameters for the Mono-Sized Iron Ore Particles. Materials 2017, 10, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosn, R.A.; Sibille, L.; Benahmed, N.; Chareyre, B. Discrete numerical modeling of loose soil with spherical particles and interparticle rolling friction. Granul. Matter 2017, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillip Grima, A.; Wilhelm Wypych, P. Discrete element simulations of granular pile formation: Method for calibrating discrete element models. Eng. Comput. 2011, 28, 314–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, T.; Katterfeld, A. Scalability of Angle of Repose Tests for the Calibration of DEM Parameters; Engineers Australia: Barton, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Khanal, M.; Elmouttie, M.; Adhikary, D. Effects of particle shapes to achieve angle of repose and force displacement behaviour on granular assembly. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 1972–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Rasmuson, A.; Thalberg, K.; Niklasson Björn, I. Numerical modelling of breakage and adhesion of loose fine-particle agglomerates. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 116, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunazawa, Y.; Fujihashi, D.; Fukui, S.; Sakai, M.; Tokoro, C. Contact force model including the liquid-bridge force for wet-particle simulation using the discrete element method. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrieli, F.; Artoni, R.; Santomaso, A.; Cola, S. Discrete particle simulations and experiments on the collapse of wet granular columns. Phys. Fluids 2013, 25, 103303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrieli, F.; Lambert, P.; Cola, S.; Calvetti, F. Micromechanical modelling of erosion due to evaporation in a partially wet granular slope. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Géoméch. 2012, 36, 918–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, D.; Imamura, S.; Nakamura, M.; Noguchi, R. Angle of repose of Martian wet sand using discrete element method: Implication for the seasonal cycle of recurring slope lineae(RSL) by relative humidity. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.06144. [Google Scholar]
- Staron, L.; Hinch, E.J. Study of the collapse of granular columns using two-dimensional discrete-grain simulation. J. Fluid Mech. 2005, 545, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Chen, J.-F.; Rotter, J.M.; Ooi, J.Y. Assessment of rolling resistance models in discrete element simulations. Powder Technol. 2011, 206, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.C.; Wright, B.D.; Yang, R.Y.; Xu, B.H.; Yu, A.B. Rolling friction in the dynamic simulation of sandpile formation. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 1999, 269, 536–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertz, H. On the Contact of Rigid elastic SOLIDS and on Hardness, Chapter 6; MacMillan: New York, NY, USA, 1882. [Google Scholar]
- Mindlin, R.D.; Deresiewicz, H. Elastic Spheres in Contact under Varying Oblique Forces. J. Appl. Mech. 1953, 20, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.C.; Xu, B.H.; Yu, A.B.; Zulli, P. Numerical investigation of the angle of repose of monosized spheres. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 021301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N. Intermolecular and Surface Forces; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Muguruma, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Tsuji, Y. Numerical simulation of particulate flow with liquid bridge between particles (simulation of centrifugal tumbling granulator). Powder Technol. 2000, 109, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, W.G. Elements of Mechanics: For the Use of Colleges, Academies, and High Schools; A.S. Barnes & Burr: New York, NY, USA, 1859. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, E. Measurement of the Repose Angle of aTablet Granulation*. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 1955, 44, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.L.; Lakshminarasimhan, J.; Sethuraman, R.; Sivakumar, S.M. Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Dynamics; PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.: Delhi, India, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wensrich, C.; Katterfeld, A. Rolling friction as a technique for modelling particle shape in DEM. Powder Technol. 2012, 217, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yu, A. A theoretical analysis of the force models in discrete element method. Powder Technol. 2006, 161, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markauskas, D.; Kačianauskas, R. Investigation of rice grain flow by multi-sphere particle model with rolling resistance. Granul. Matter 2010, 13, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, B.; Yu, A.; Zulli, P. An experimental and numerical study of the angle of repose of coarse spheres. Powder Technol. 2002, 125, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Yu, H.-S.; Harris, D. A novel discrete model for granular material incorporating rolling resistance. Comput. Geotech. 2005, 32, 340–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, G.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.-J. Discrete element method for the characterization of soil properties in Plate-Sinkage tests. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 2743–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.Y.; Zou, R.P.; Yu, A.B. Numerical study of the packing of wet coarse uniform spheres. AIChE J. 2003, 49, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lube, G.; Huppert, H.E.; Sparks, R.S.J.; Hallworth, M.A. Axisymmetric collapses of granular columns. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 508, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.-H.; Li, X.; Yuan, Q. Validation of discrete element method by simulating a 2D assembly of randomly packed elliptical rods. Acta Geotech. 2017, 12, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, S.; Langston, P.; Webb, C.; York, T. Experimental validation of polyhedral discrete element model. Powder Technol. 2011, 214, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Name of Variables | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Diameter (mm) | 10 | |
| Number of particles | - | 3600 |
| Particle Density (Kg/m3) | 3270 | |
| Damping Coefficient | 0.012 | |
| Sliding friction coefficient | 0.36 | |
| Coefficient of restitution | 0.96 | |
| Coefficient of rolling friction | 0.4 | |
| Rolling viscous damping ratio | 0.5 | |
| Young’s Modulus (MPa) | 70 | |
| Poisson Ratio | 0.3 | |
| Surface tension | 0.073 | |
| Initial liquid volume per particle (m3) | 1.4 × 10−10 to 1.4 × 10−4 | |
| Contact angle (rad) | 0 | |
| Lateral walls opening velocity (m/s) | 1.8 | |
| Initial packing concentration | 0.88 |
| States | Liquid Content |
|---|---|
| Pendular | |
| Funicular | 9.2 < M (%) < 26.7 |
| Capillary | M (%) 26.7 |
| Name of Variables | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Diameter (mm) | 10 | |
| Number of particles | - | From 80 to 160 |
| Particle Density (Kg/m3) | 2500 | |
| Sliding friction coefficient | 0.26 | |
| Coefficient of restitution | 0.73 | |
| Coefficient of rolling friction | 0.03 | |
| Young’s Modulus (MPa) | 11 | |
| Poisson Ratio | 0.29 | |
| Initial packing concentration | 0.88 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ndiaye, B.C.; Gao, Z.; Fall, M.; Zhang, Y. Effect of the Rolling Friction on the Heap Formation of Dry and Wet Coarse Discs. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6043. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136043
Ndiaye BC, Gao Z, Fall M, Zhang Y. Effect of the Rolling Friction on the Heap Formation of Dry and Wet Coarse Discs. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(13):6043. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136043
Chicago/Turabian StyleNdiaye, Becaye Cissokho, Zhengguo Gao, Massamba Fall, and Yajun Zhang. 2021. "Effect of the Rolling Friction on the Heap Formation of Dry and Wet Coarse Discs" Applied Sciences 11, no. 13: 6043. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136043
APA StyleNdiaye, B. C., Gao, Z., Fall, M., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Effect of the Rolling Friction on the Heap Formation of Dry and Wet Coarse Discs. Applied Sciences, 11(13), 6043. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11136043








