Chlorobenzene Removal Using DBD Coupled with CuO/γ-Al2O3 Catalyst
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Preparation of Catalysts
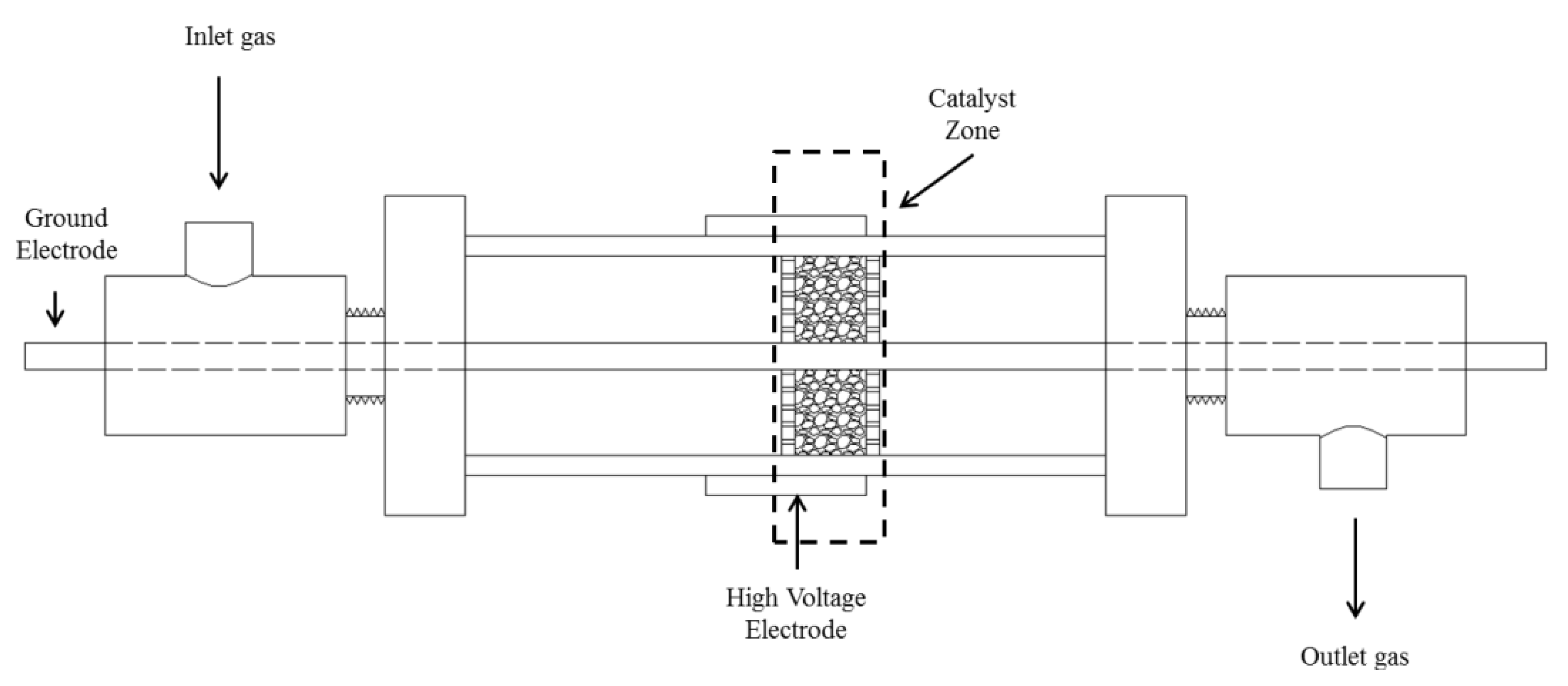
2.2. Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussion
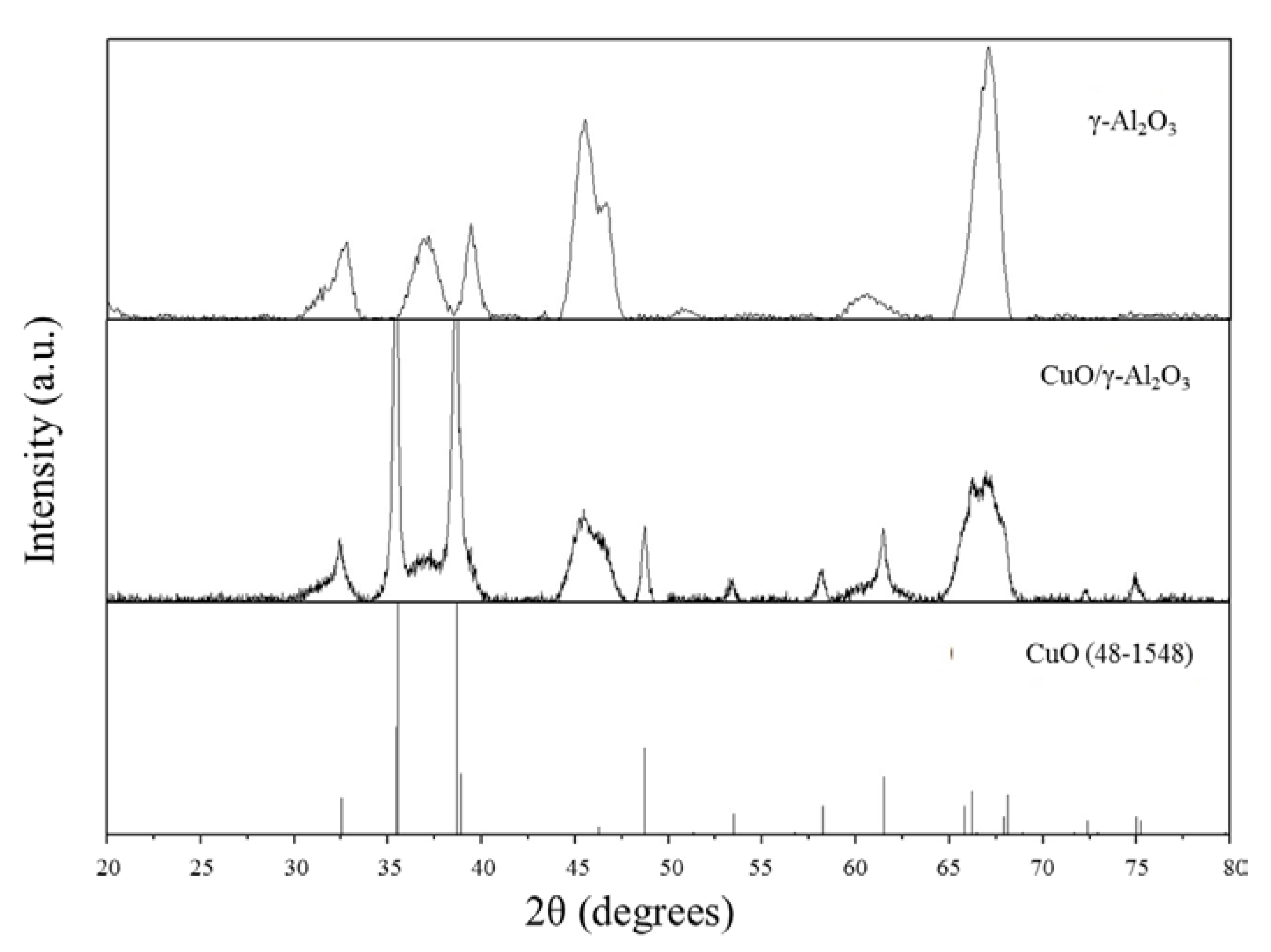
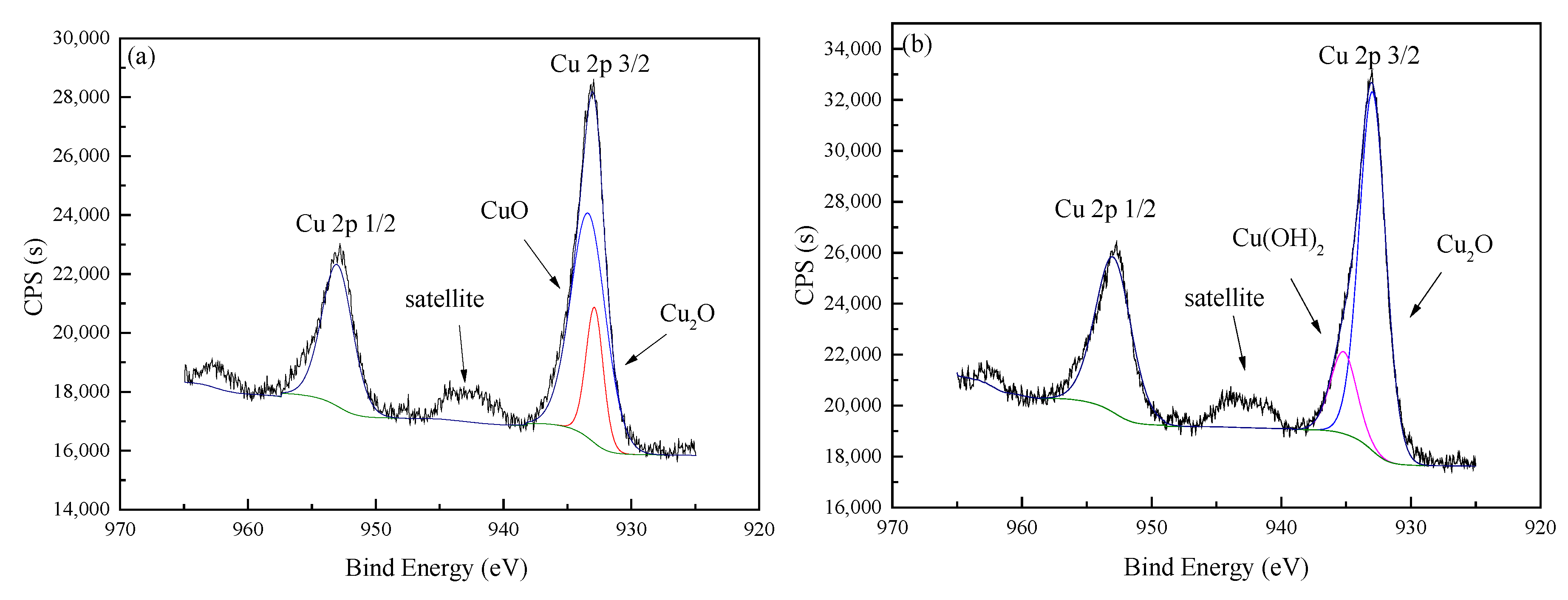
3.1. Preparation of Catalysts
3.2. Effect of SED on the Performance of DBD Reactor
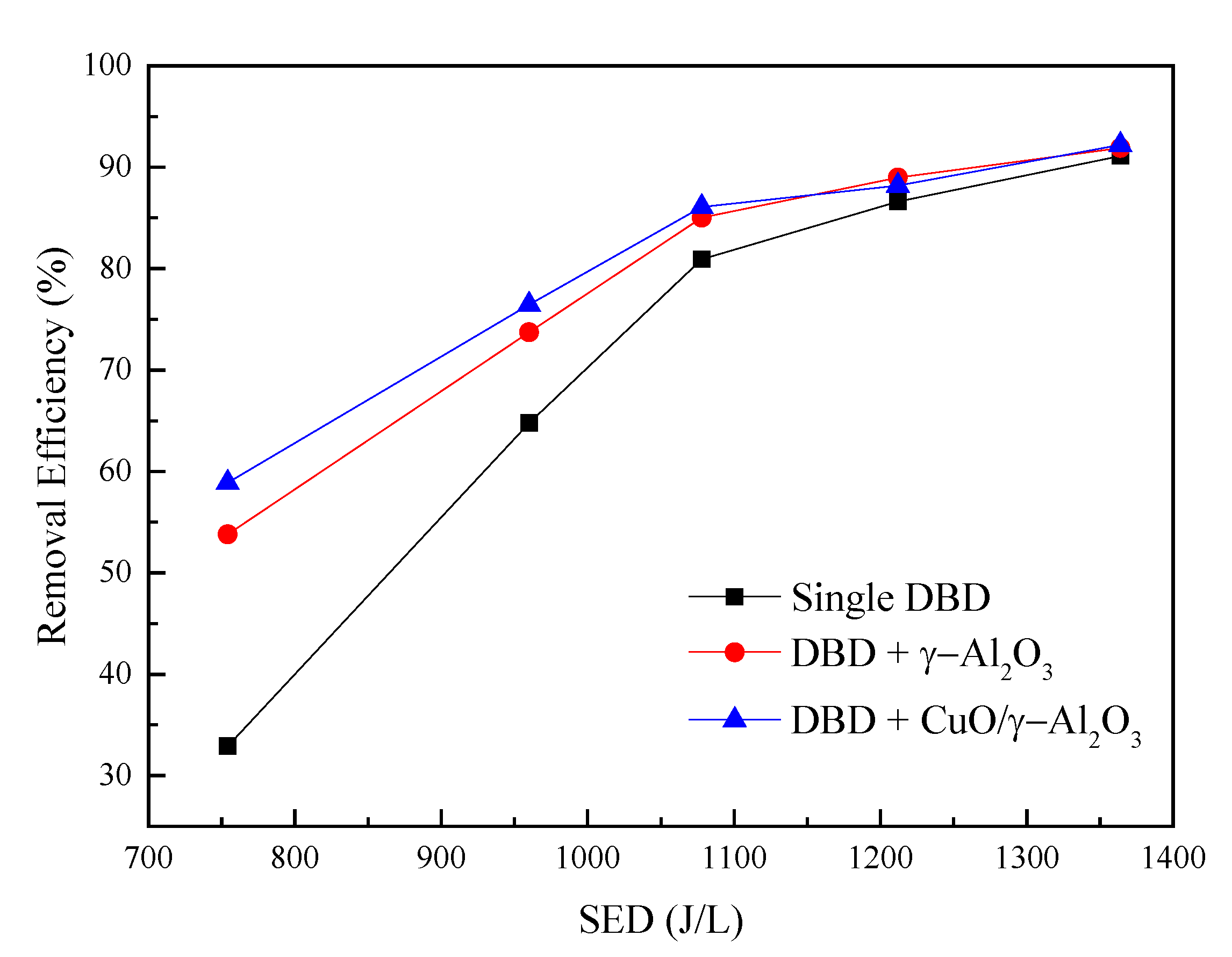
3.2.1. Chlorobenzene Removal Efficiency
3.2.2. COx Selectivity
3.2.3. Ozone Production
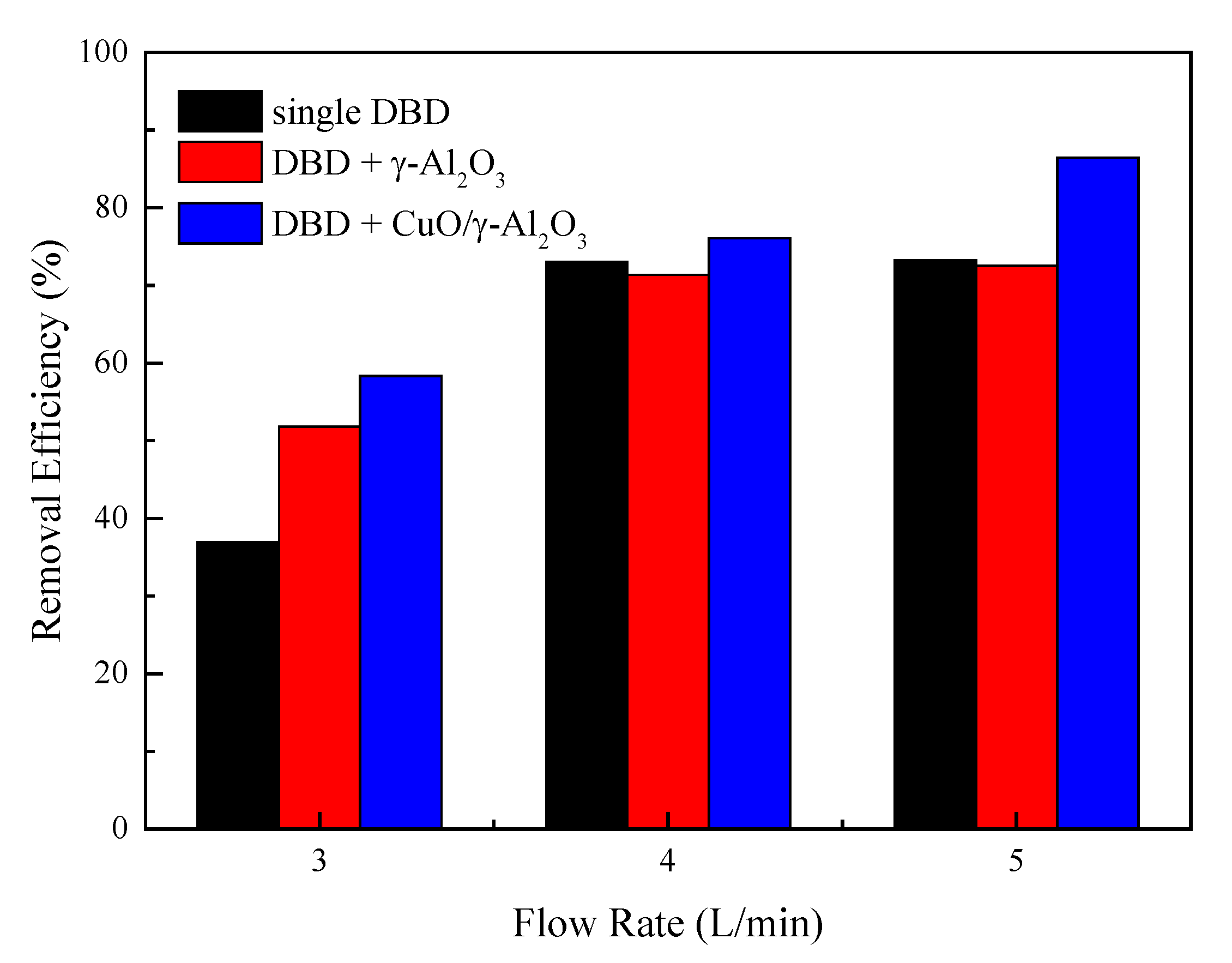
3.3. Effect of Flow Rate on the Performance of DBD Reactor
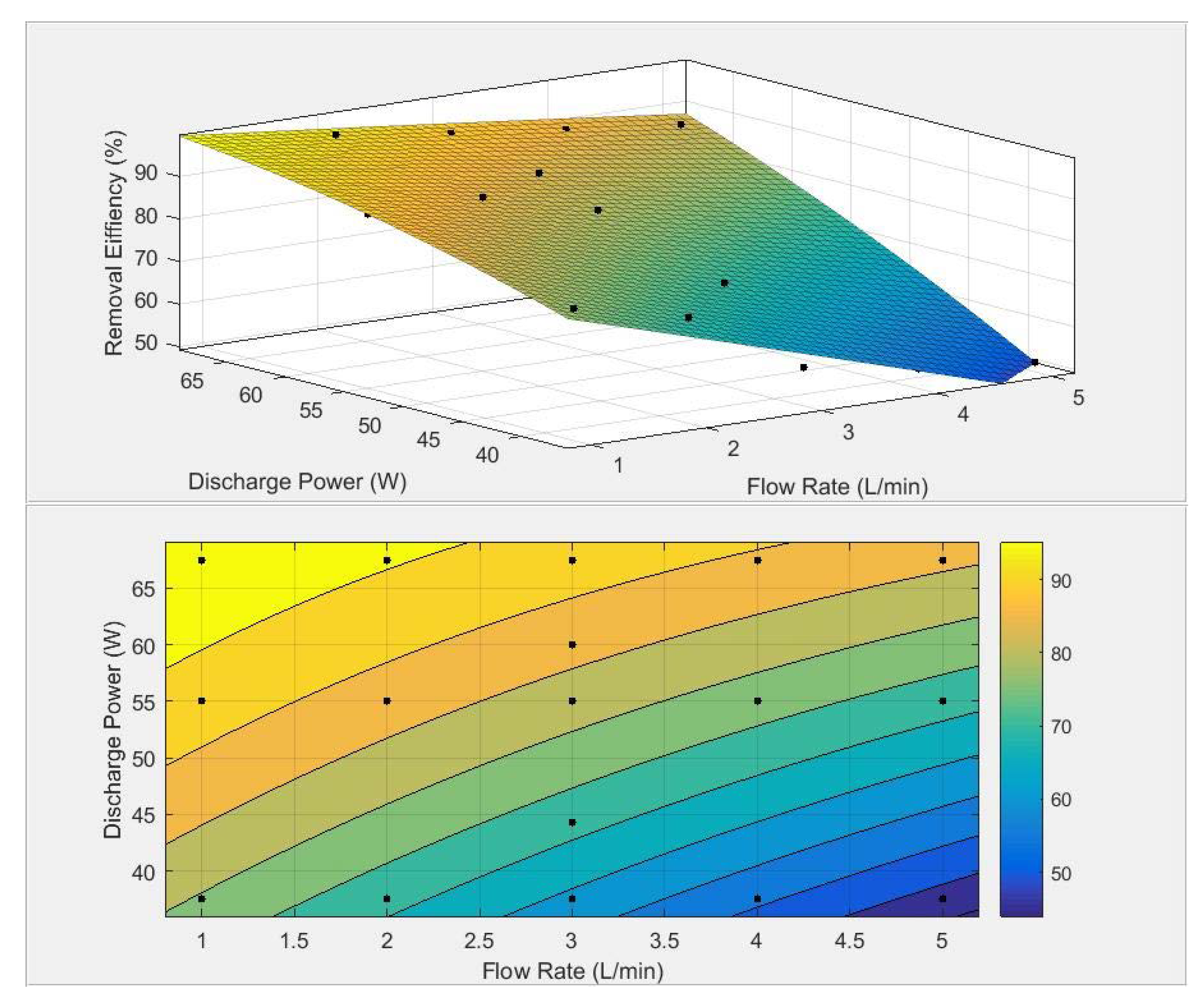
3.4. RSM Analysis
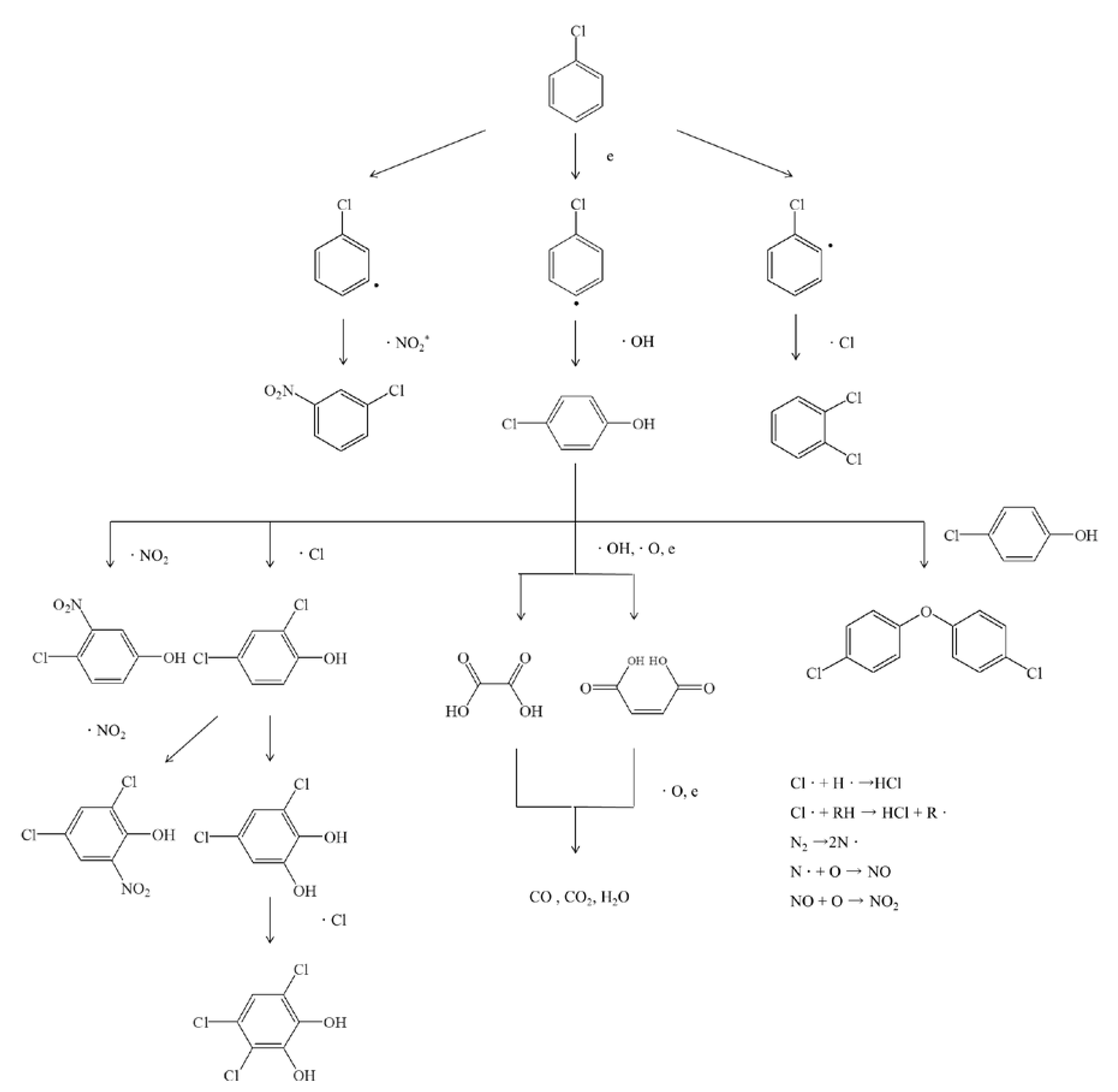
3.5. Byproducts Analysis and Reaction Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.; Pawliszyn, J. Analysis of Organic Compounds in Environmental Samples by Headspace Solid Phase Microextraction. J. High Resolut. Chromatogr. 1993, 16, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terytze, K.; Mende, W. Low volatile chlorinated hydrocarbons in aquatic sediments in Berlin and surrounding areas. Land Degrad. Dev. 1993, 4, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.M.; Dahlen, P.; Johnson, P. Temporal variability of chlorinated volatile organic compound vapor concentrations in a residential sewer and land drain system overlying a dilute groundwater plume. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 702, 134756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.B.; Lei, C.; Wei, C.H.; Zeng, G.M. Chlorinated volatile organic compounds (Cl-VOCs) in environment-sources, potential human health impacts, and current remediation technologies. Environ. Int. 2014, 71, 118–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Chen, X.Y.; Fan, Q.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, M.J. The role of anthropogenic chlorine emission in surface ozone formation during different seasons over eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 137697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K.; Yazdani, A.; Yates, P. Chlorinated Solvents: Will the Alternatives be Safer. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1991, 41, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.Z.; Gao, J.J.; Lu, L.; Zhao, D.; Cheng, K.; Qiu, P.P. Temporal Trends and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Hazardous Air Pollutant Emission Inventory from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10364–10371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Tian, H.Z.; Hua, S.B.; Zhu, C.Y.; Gao, J.J.; Xue, Y.F.; Hao, J.M.; Wang, F.; Zhou, J.R. A comprehensive emission inventory of multiple air pollutants from iron and steel industry in China: Temporal trends and spatial variation characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Li, Q.; Wu, D.; Huo, Y.Q.; Liang, Y.G.; Wang, H.L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, T.; Ye, X.N. Gaseous and Particulate Chlorine Emissions From Typical Iron and Steel Industry in China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, 032729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausse, B.; Garrot, B.; Cornier, C.; Paulin, C.; Simonot-Grange, M.H.; Boutros, F. Adsorption of Chlorinated Volatile Organic Compounds on Hydrophobic Faujasite: Correlation between the Thermodynamic and Kinetic Properties and the Prediction of Air Cleaning. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 1998, 25, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.J.; Chou, S.Y. Contaminated site remedial investigation and feasibility removal of chlorinated volatile organic compounds from groundwater by activated carbon fiber adsorption. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaya, A.; Thompson, R.W.; Denkewicz, R. Liquid and vapor phase adsorption of chlorinated volatile organic compounds on hydrophobic molecular sieves. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 2000, 40, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Cho, S.Y.; Kim, T.Y. Adsorption of chlorinated volatile organic compounds in a fixed bed of activated carbon. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2002, 19, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Lee, J.W.; Shim, W.G.; Suh, S.H.; Moon, H. Adsorption of chlorinated volatile organic compounds on MCM-48. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2003, 48, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisdanurak, N.; Chiarakorn, S.; Wittayakun, J. Utilization of mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized from natural source rice husk silica to chlorinated volatile organic compounds (CVOCs) adsorption. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2003, 20, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.J.; Li, X.Y.; Zhao, Q.D.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.B.; Tade, M. Insight into the mechanism of photocatalytic degradation of gaseous o-dichlorobenzene over flower-type V2O5 hollow spheres. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 15163–15170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.J.; Dong, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.D.; Cui, Y.B.; Ou, X.X.; Qi, X.H. The highly enhanced visible light photocatalytic degradation of gaseous o-dichlorobenzene through fabricating like-flowers BiPO4/BiOBr p-n heterojunction composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 391, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.W.; Li, W.; Liu, F.; Li, M.; Qi, X.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Han, F.L. Construction of CeO2/TiO2 heterojunctions immobilized on activated carbon fiber and its synergetic effect between adsorption and photodegradation for toluene removal. J. Nanopart. Res. 2020, 22, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinchamps, F.; Attianese, A.; Mestdagh, M.M. Catalysts for chlorinated VOCs abatement: Multiple effects of water on the activity of VOx based catalysts for the combustion of chlorobenzene. Catal. Today 2006, 112, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, C.N.; He, F.; Liu, S.T. Effect of ceria morphology on the activity of MnOx/CeO2 catalysts for the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 45665–45672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, H.; Li, C.L. A review and perspective of recent research in biological treatment applied in removal of chlorinated volatile organic compounds from waste air. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den, W.; Pirbazari, M. Modeling and design of vapor-phase biofiltration for chlorinated volatile organic compounds. AICHE J. 2002, 48, 2084–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawi, S.; Te, M. MCM-48 supported chromium catalyst for trichloroethylene oxidation. Catal. Today 1998, 44, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windawi, H.; Zhang, Z.C. Catalytic destruction of halogenated air toxins and the effect of admixture with VOCs. Catal. Today 1996, 30, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everaert, K.; Baeyens, J. Catalytic combustion of volatile organic compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 109, 113–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Yang, S.S.; Shi, Z.N.; Meng, Z.H.; Zhou, R.X. Deep oxidation of chlorinated VOCs over CeO2-based transition metal mixed oxide catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 162, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Li, J.R.; Zuo, S.F. Promoting oxidative activity and stability of CeO2 addition on the MnOx modified kaolin-based catalysts for catalytic combustion of benzene. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 162, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GallastegiVilla, M.; Aranzabal, A.; Gonzalez-Marcos, J.A.; Gonzalez-Velasco, J.R. Metal- loaded ZSM5 zeolites for catalytic purification of dioxin/furans and NOx containing exhaust gases from MWI plants: Effect of different metal cations. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 184, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Cheng, J.; Xing, X.; Sun, Y.G.; Hao, Z.P. Distribution and formation mechanisms of polychlorinated organic by-products upon the catalytic oxidation of 1,2-dichlorobenzene with palladium-loaded catalysts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urashima, K.; Chang, J.S. Removal of Volatile Organic Compounds from Air Streams and Industrial Flue Gases by Non-Thermal Plasma Technology. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2000, 7, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, R.; Tu, X.; Van Gaens, W.; Whitehead, J.C.; Bogaerts, A. Gas Purification by Nonthermal Plasma: A Case Study of Ethylene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6478–6485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.Q.; Song, H.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Zhu, T.L. Simultaneous removal of toluene and styrene by non-thermal plasma-catalysis: Effect of VOCs interaction and system configuration. Chemosphere 2020, 263, 127893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiper, A.S.; Simiand, N.B.; Jorand, F.; Pasquiers, S.; Popa, G.; Posetl, C. Influence of water vapour on acetaldehyde removal efficiency by DBD. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2006, 8, 208–211. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Kan, L.; Sun, T.; Jia, J.P.; Yang, X.L.; Shen, Y.F.; Wang, J.; Lou, Z.Y. The removal of styrene using a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) reactor and the analysis of the by-products and intermediates. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2012, 39, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppiah, J.; Reddy, E.L.; Reddy, P.M.K.; Ramaraju, B.; Karvembu, R.; Subrahmanyam, C. Abatement of mixture of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in a catalytic non-thermal plasma reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 237, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmanyam, C. Catalytic non-thermal plasma reactor for total oxidation of volatile organic compounds. Indian J. Chem. Sect A Inorg. Bio-Inorg. Phys. Theor. Anal. Chem. 2009, 48, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Shahna, F.G.; Ebrahimi, H.; Jaleh, B.; Bahrami, A. Decomposition of gas-phase chloroform using nanophotocatalyst downstream the novel non-thermal plasma reactor: By-products elimination. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 3489–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Njiki, A.; Kamgang-Youbi, G.; Nola, M.; Laminsi, S. Biodegradation kinetic studies and optimization for the elimination of azoic and triphenylmethane dyes using an integrated process combining biological treatment and gliding arc plasma. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerapandian, S.K.P.; Giraudon, J.M.; Geyter, N.D.; De Geyter, N.; Onyshchenko, Y.; Krishnaraj, C.; Sonar, S.; Lofberg, A.; Leus, K.; Van der, P.; et al. Regeneration of Hopcalite used for the adsorption plasma catalytic removal of toluene by non-thermal plasma. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentek, J.; Krawczyk, K.; Michal, M.; Kalczewska, M.; Kroker, T.; Kolb, T.; Schenk, A.; Gericke, K.H.; Schmidt-Szalowski, K. Plasma-catalytic methane conversion with carbon dioxide in dielectric barrier discharges. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 94, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P.; Xu, Y.J.; Wang, X.P.; Guo, Y.B.; Mu, Q.L. Catalytic degradation of 4-chlorophenol with La/TiO2 in dielectric barrier discharge system. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 28994–29002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.B.; Gao, X.; Yu, X.N.; Zheng, C.H.; Tu, X. Catalyst screening for acetone removal in a single-stage plasma-catalysis system. Catal. Today 2015, 256, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Cao, L.; Liu, X.; Fu, W.; Zhao, J. Catalytic behavior and synergistic effect of nonthermal plasma and CuO/AC catalyst for benzene destruction. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 3531–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Zheng, X.L. Plasma-Enhanced Catalytic CuO Nanowires for CO Oxidation. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4762–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Fu, W.; He, C.; Cao, L.F.; Liu, X.H.; Zhao, J.L.; Pan, H. Benzene Removal Using Non-thermal Plasma with CuO/AC Catalyst: Reaction Condition Optimization and Decomposition Mechanism. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2014, 34, 1387–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Jiang, X.Y.; Huang, W.M.; Zheng, X.M. Nonthermal-Plasma-Assisted Selective Catalytic Reaction of NO by CH4 over CuO/TiO2/gamma-Al2O3. Catalyst Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 2967–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.F.; Yu, D.Q.; Duan, L.J.; Yu, W.H.; Huang, L. In-situ fabricated CuO nanowires/Cu foam as a monolithic catalyst for plasma-catalytic oxidation of toluene. Catal. Commun. 2017, 100, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.X.; Lu, J.; Ye, G.G.; Yao, J.Y.; Zou, X.H.; Zhu, X.Z. Decomposition of gaseous chlorobenzene using a DBD combined CuO/alpha-Fe2O3 catalysis system. Environ. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khataeea, A.R.; Kasirib, M.B.; Alidokht, L. Application of response surface methodology in the optimization of photocatalytic removal of environmental pollutants using nanocatalysts. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 1669–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butron-Garcia, M.I.; Jofre-Reche, J.A.; Martin-Martinez, J.M. Use of statistical design of experiments in the optimization of Ar-O2 low-pressure plasma treatment conditions of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) for increasing polarity and adhesion, and inhibiting hydrophobic recovery. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 332, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Salari, D.; Niaei, A.; Panahi, P.N.; Shafiei, S. A modelling study and optimization of catalytic reduction of NO over CeO2-MnOx (0.25)-Ba mixed oxide catalyst using design of experiments. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Z.Y.; Jiang, L.S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Huang, R.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Q.L.; Ning, P. Non-thermal plasma-enhanced low-temperature catalytic desulfurization of electrolytic aluminum flue gas by CuO-ZrSnO4: Experimental and numerical analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 39474–39489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinokuma, S.; Yamashita, N.; Katsuhara, Y.; Kogami, H.; Machida, M. CO oxidation activity of thermally stable Fe–Cu/CeO2 catalysts prepared by dual-mode arc-plasma process. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 3945–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, X.W.; Huang, L.A.; Lei, L.C. Application of in-plasma catalysis and post-plasma catalysis for methane partial oxidation to methanol over a Fe2O3-CuO/γ-Al2O3 catalyst. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2010, 19, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harling, A.M.; Glover, D.J.; Whitehead, J.; Zhang, K. The role of ozone in the plasma-catalytic destruction of environmental pollutants. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 90, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Lee, H.M.; Chen, S.H.; Chang, M.B. Review of Packed-Bed Plasma Reactor for Ozone Generation and Air Pollution Control. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Zhang, H.B.; Ying, D.W.; Wang, Y.L.; Sun, T.H.; Jia, J.P. In Plasma Catalytic Oxidation of Toluene Using Monolith CuO Foam as a Catalyst in a Wedged High Voltage Electrode Dielectric Barrier Discharge Reactor: Influence of Reaction Parameters and Byproduct Control. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, T.; Zhang, X.; Ma, M.F.; Wang, L.F.; Xue, Z.Y.; Hou, Y.M.; Ye, Z.F.; Liu, T.S. 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene decomposition using non-thermal plasma technology. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 034011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahna, F.G.; Bahrami, A.; Alimohammadi, I.; Yarahmadi, R.; Jaleh, B.; Gandomi, M.; Ebrahimi, H.; Abedi, K.A.D. Chlorobenzene degeradation by non-thermal plasma combined with EG-TiO2/ZnO as a photocatalyst: Effect of photocatalyst on CO2 selectivity and byproducts reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.B. Removal of Air Pollutants by Photocatalysis with Ozone in a Continuous-Flow Reactor. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2010, 27, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.H.C.; Lian, L.P.; Zhao, W.X.; Zhang, R.X.; Huo, H.Q. DBD coupled with MnOx/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for the degradation of chlorobenzene. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 034016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Rate (L/min) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| x1 | −1.46 | −0.73 | 0 | 0.73 | 1.46 |
| Discharge Power (W) | 37.5 | 44.3 | 55 | 60 | 67.5 |
| x2 | −1.28 | −0.73 | 0.15 | 0.56 | 1.17 |
| Sample | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| γ-Al2O3 | 168.6 | 0.95 | 22.7 |
| CuO/γ-Al2O3 | 141.3 | 0.72 | 20.5 |
| Response | Model Terms | Sum of Square | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Removal efficiency | Model | 3184.30 | 5 | 636.86 | 91.27 | <0.0001 |
| x1 | 864.36 | 1 | 864.36 | 123.88 | <0.0001 | |
| x2 | 2112.32 | 1 | 2112.32 | 302.74 | <0.0001 | |
| x12 | 0.062 | 1 | 0.062 | 0.01 | 0.9266 | |
| x1x2 | 114.44 | 1 | 114.44 | 16.40 | 0.0019 | |
| x22 | 14.90 | 1 | 14.9 | 2.14 | 0.1719 | |
| Residual | 76.75 | 11 | 6.98 | |||
| Total | 3261.05 | 16 | ||||
| R2 = 0.9766, Adj R2 = 0.966, RMSE = 2.632, cv = 2.66% | ||||||
| CO2 selectivity | Model | 198.39 | 5 | 39.68 | 30.16 | 0.0027 |
| x1 | 76.18 | 1 | 19.04 | 14.47 | 0.0126 | |
| x2 | 109.83 | 1 | 109.83 | 83.49 | 0.0003 | |
| x12 | 1.58 | 1 | 1.58 | 1.20 | 0.3231 | |
| x1x2 | 2.72 | 1 | 2.72 | 2.07 | 0.2100 | |
| x22 | 2.58 | 1 | 2.58 | 1.96 | 0.2203 | |
| Residual | 14.47 | 11 | 1.32 | |||
| Total | 212.86 | 16 | ||||
| R2 = 0.9466, Adj R2 = 0.922, RMSE = 1.016, cv = 3.03% | ||||||
| Name | Structure | DBD Reactor | DBD-Catalysis Reactor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxalic acid | 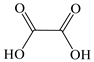 | √ * | √ |
| Maleic acid |  | √ | √ |
| Benzene, 1,2 (or 1,3 or 1,4)-dichloro- | 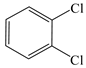 | √ | √ |
| Acetic Acid, Dichloro- | 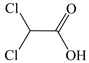 | √ | √ |
| 2,5-Cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione, 2-chloro- |  | √ | |
| Benzene, 1-chloro-3 (or 2 or 4)-nitro- |  | √ | √ |
| 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol |  | √ | √ |
| Phenol, 2,4-dichloro-6-nitro- | 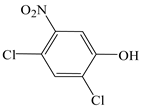 | √ | |
| Phenol,2,4-dichloro- |  | √ | √ |
| Pyrocatechol, 3,4,6-trichloro- | 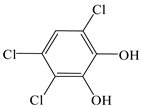 | √ | |
| Benzene, 1,1′-oxybis [4-chloro- | 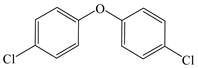 | √ | √ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, X.; Wang, G.; Lian, L.; Gao, F.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, W.; Hou, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, R. Chlorobenzene Removal Using DBD Coupled with CuO/γ-Al2O3 Catalyst. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146433
Jin X, Wang G, Lian L, Gao F, Zhang R, Zhao W, Hou J, Chen S, Zhang R. Chlorobenzene Removal Using DBD Coupled with CuO/γ-Al2O3 Catalyst. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(14):6433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146433
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Xingpeng, Guicheng Wang, Liping Lian, Fan Gao, Renxi Zhang, Weixuan Zhao, Jianyuan Hou, Shanping Chen, and Ruina Zhang. 2021. "Chlorobenzene Removal Using DBD Coupled with CuO/γ-Al2O3 Catalyst" Applied Sciences 11, no. 14: 6433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146433
APA StyleJin, X., Wang, G., Lian, L., Gao, F., Zhang, R., Zhao, W., Hou, J., Chen, S., & Zhang, R. (2021). Chlorobenzene Removal Using DBD Coupled with CuO/γ-Al2O3 Catalyst. Applied Sciences, 11(14), 6433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146433






