A Laser-Based Method for the Detection of Honey Adulteration
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. LIBS Setup
2.3. Data Analysis
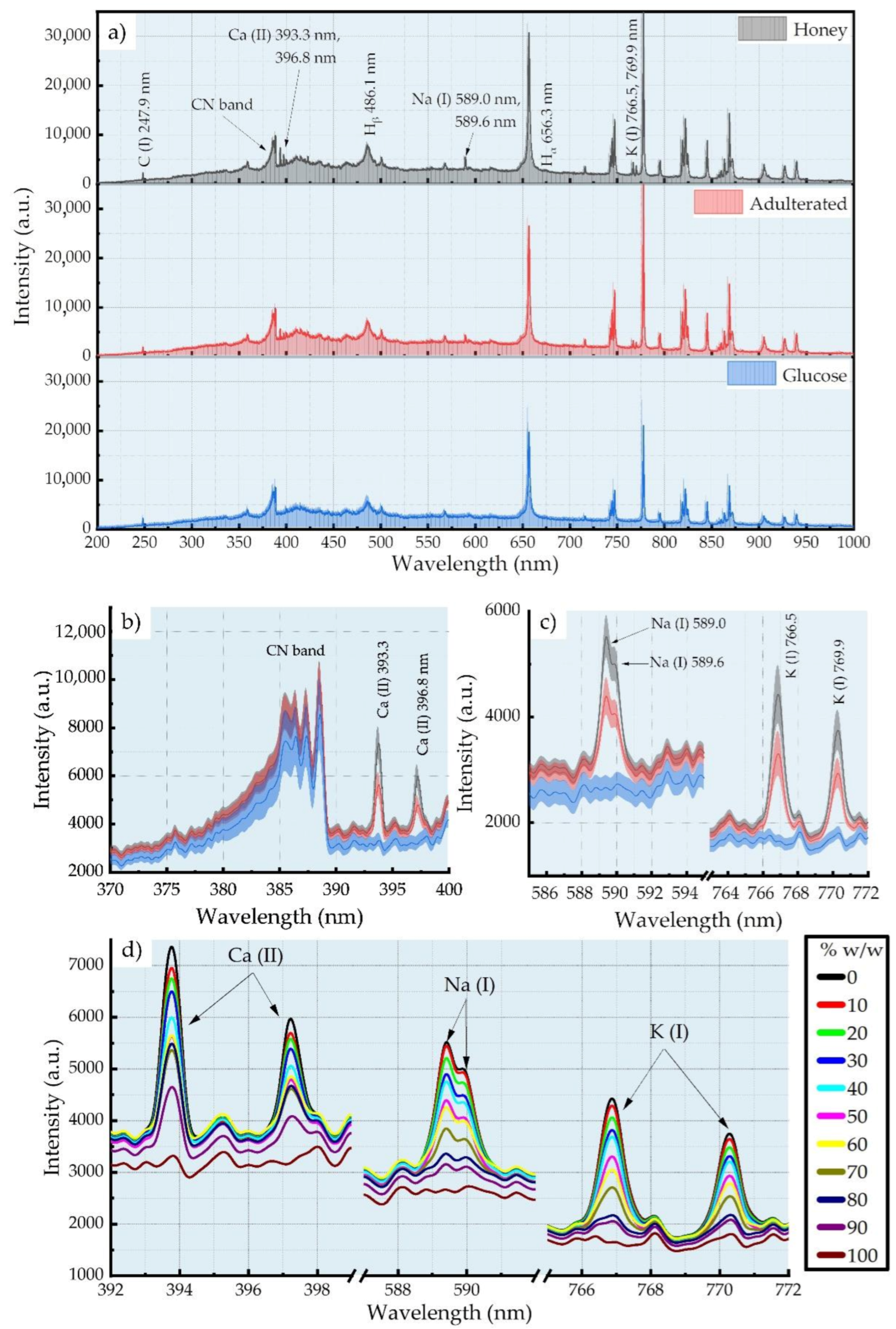
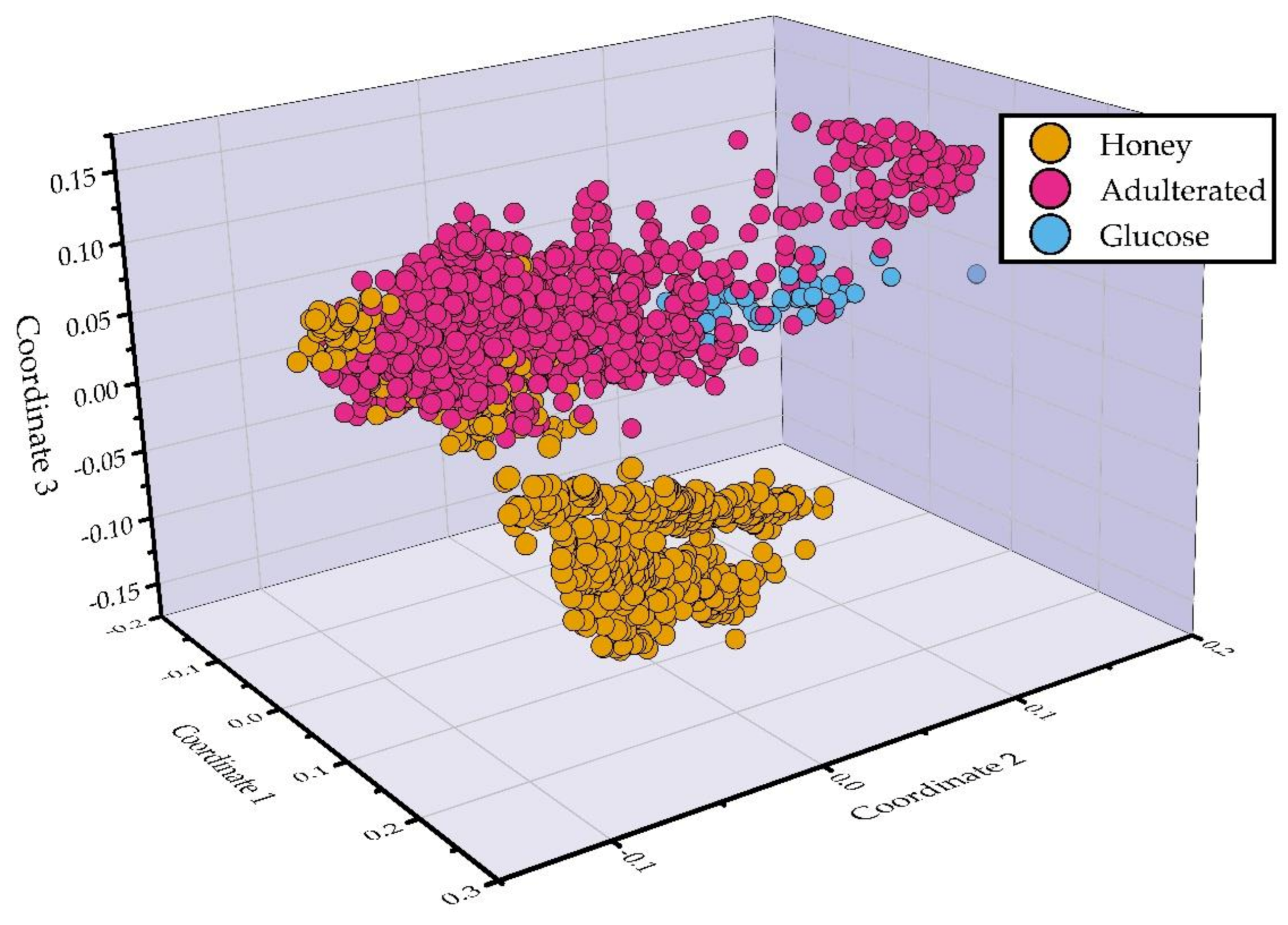
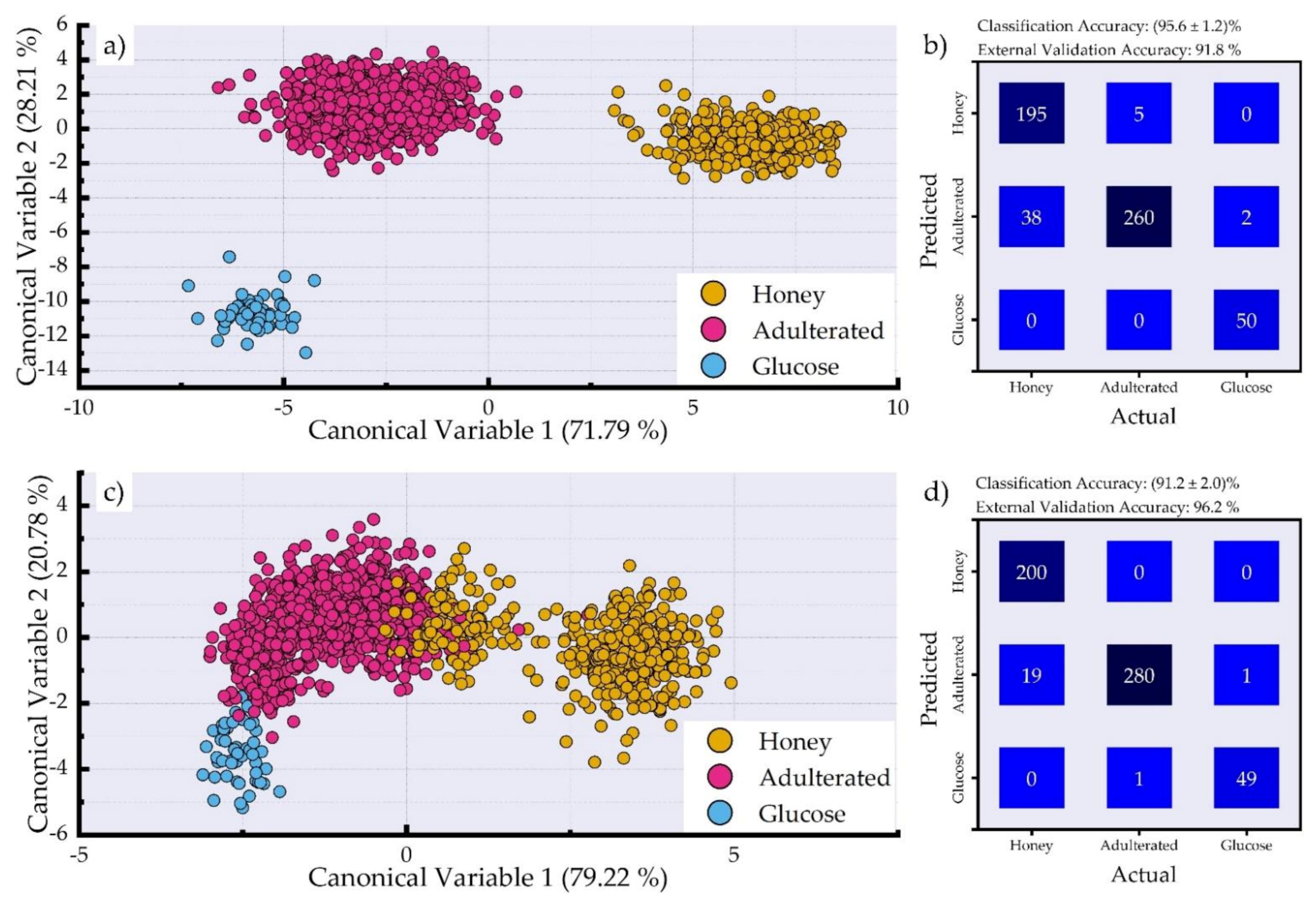
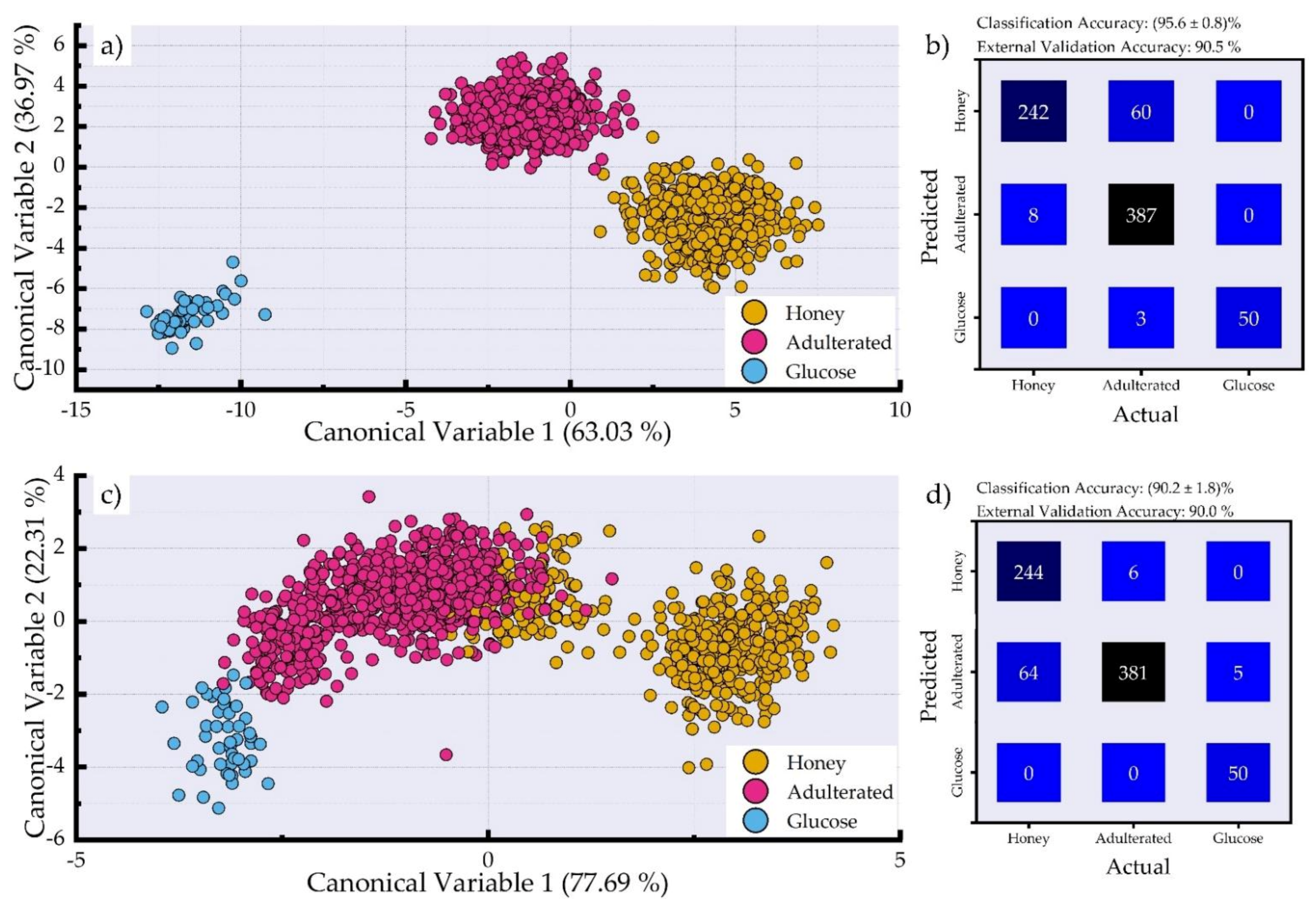
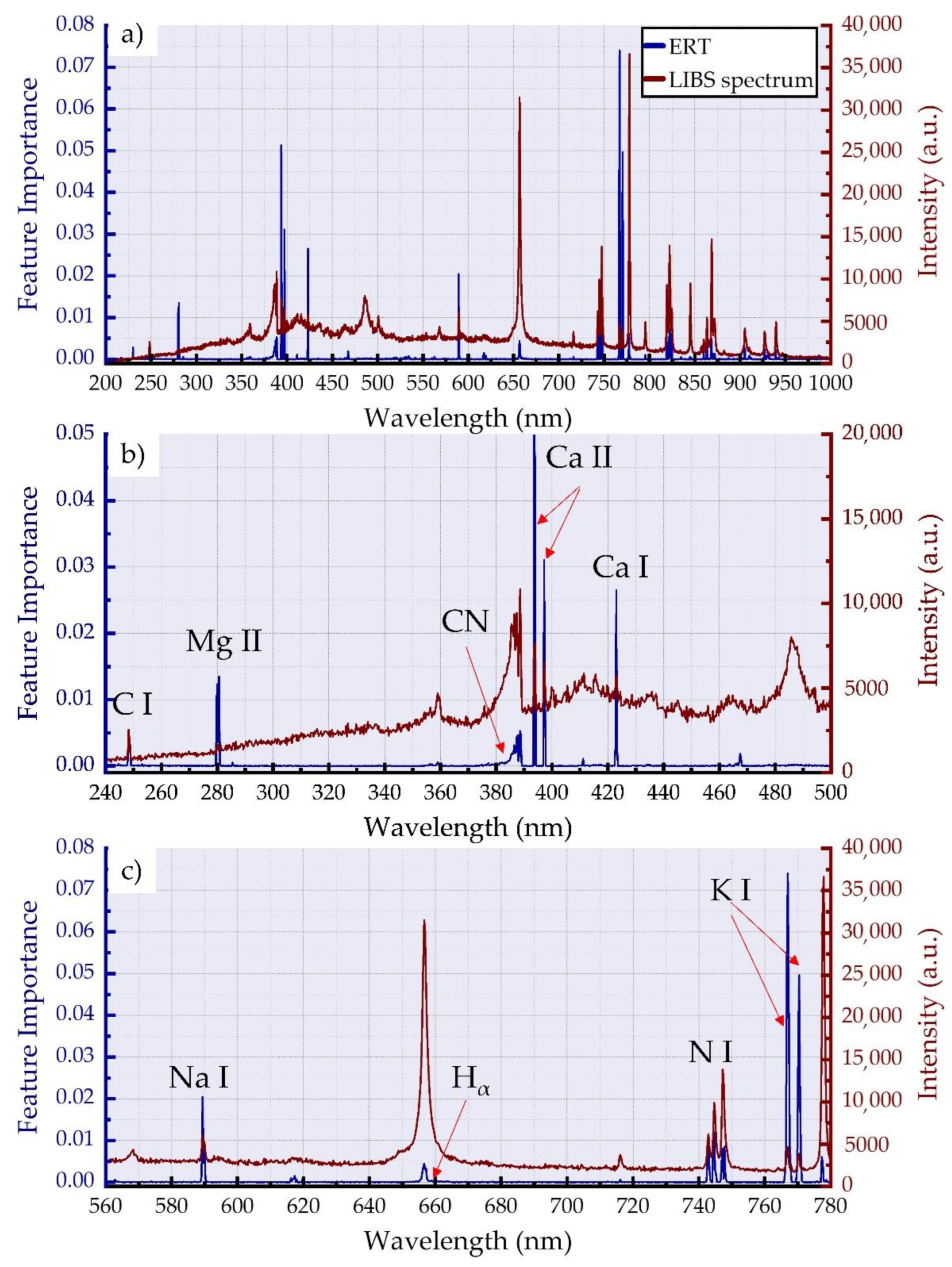
3. Results
3.1. LIBS Spectra of Honey and Adulterated Honey Samples
3.2. Dimensionality Reduction and Classification of LIBS Spectra for Adulteration Detection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M. Bee Products-Chemical and Biological Properties; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 9783319596891. [Google Scholar]
- Escuredo, O.; Seijo, M.C. Honey: Chemical composition, stability and authenticity. Foods 2019, 8, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doner, L.W. The sugars of honey—A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1977, 28, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baglio, E. Chemistry and Technology of Honey Production; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Anklam, E. A review of the analytical methods to determine the geographical and botanical origin of honey. Food Chem. 1998, 63, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.C.; Spink, J.; Lipp, M. Development and application of a database of food ingredient fraud and economically motivated adulteration from 1980 to 2010. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, G.F.; Nichols, J.P.; Capps, O. Observations on Economic Adulteration of High-Value Food Products: The Honey Case. J. Food Distrib. Res. 2003, 34, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Padovan, G.J. Detection of adulteration of commercial honey samples by the 13C/12C isotopic ratio. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, M. Detection of adulteration in mulberry pekmez samples added various sugar syrups with 13C/12C isotope ratio analysis method. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabañero, A.I.; Recio, A.J.L.; Rez, M.R. Ä Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry: A New Perspective on Honey Adulteration Detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9719–9727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, Q.; Wang, L.; Linlin, W.; Shi, H.; Cao, H.; Cao, B. Detection of honey adulteration with starch syrup by high performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Shan, Y.; Su, D.; Ma, Q.; Wen, R.; Li, J. Qualitative and quantitative detection of honey adulterated with high-fructose corn syrup and maltose syrup by using near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremers, D.A.; Radziemski, L.J. Handbook of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; John Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2013; ISBN 9781119971122. [Google Scholar]
- Noll, R. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; ISBN 9783642206689. [Google Scholar]
- Hermann, J.; Lorusso, A.; Perrone, A.; Strafella, F.; Dutouquet, C.; Torralba, B. Simulation of emission spectra from nonuniform reactive laser-induced plasmas. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 053103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulos, P.; Palagas, C.; Angelopoulos, G.; Papamantellos, D.; Couris, S. Calibration Measurements in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy using nanosecond and picosecond lasers. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2004, 59, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattmann, R.; Sturm, V.; Noll, R. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of steel samples using multiple Q-switch Nd: YAG laser pulses. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1995, 28, 2181–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzagianni, M.; Couris, S. Femtosecond laser induced breakdown spectroscopy of air–methane mixtures. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2013, 561-562, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giacomo, A.; Dell’Aglio, M.; De Pascale, O.; Gaudiuso, R.; Santagata, A.; Teghil, R. Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy methodology for the analysis of copper-based-alloys used in ancient artworks. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2008, 63, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senesi, G.S.; Manzari, P.; Consiglio, A.; De Pascale, O. Identification and classification of meteorites using a handheld LIBS instrument coupled with a fuzzy logic-based method. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 1664–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapin, W.; Meslin, P.-Y.; Maurice, S.; Wiens, R.; Laporte, D.; Chauviré, B.; Gasnault, O.; Schröder, S.; Beck, P.; Bender, S.; et al. Quantification of water content by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy on Mars. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2017, 130, 82–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jolivet, L.; Leprince, M.; Moncayo, S.; Sorbier, L.; Lienemann, C.-P.; Motto-Ros, V. Review of the recent advances and applications of LIBS-based imaging. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2019, 151, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živković, S.; Botto, A.; Campanella, B.; Lezzerini, M.; Momčilović, M.; Pagnotta, S.; Palleschi, V.; Poggialini, F.; Legnaioli, S. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy elemental mapping of the construction material from the Smederevo Fortress (Republic of Serbia). Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2021, 181, 106219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, A.P.; Leme, F.D.O.; Nomura, C.S.; Naozuka, J. Elemental imaging by Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy to evaluate selenium enrichment effects in edible mushrooms. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ke, C.; Xu, T.; He, Y. A brief review of new data analysis methods of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: Machine learning. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2020, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnotta, S.; Lezzerini, M.; Campanella, B.; Legnaioli, S.; Poggialini, F.; Palleschi, V. A new approach to non-linear multivariate calibration in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy analysis of silicate rocks. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2020, 166, 105804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrábel, J.; Kepes, E.; Duponchel, L.; Motto-Ros, V.; Fabre, C.; Connemann, S.; Schreckenberg, F.; Prasse, P.; Riebe, D.; Junjuri, R.; et al. Classification of challenging Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy soil sample data-EMSLIBS contest. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2020, 169, 105872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, F.; Zhou, F.; Song, K.; Zhang, C.; Ye, L.; He, Y. Challenging applications for multi-element analysis by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in agriculture: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senesi, G.S.; Cabral, J.S.; Menegatti, C.R.; Marangoni, B.; Nicolodelli, G. Recent advances and future trends in LIBS applications to agricultural materials and their food derivatives: An overview of developments in the last decade (2010–2019). Part II. Crop plants and their food derivatives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongbonga, Y.G.M.; Ghalila, H.; Onana, M.B.; Ben Lakhdar, Z. Classification of vegetable oils based on their concentration of saturated fatty acids using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). Food Chem. 2014, 147, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyftokostas, N.; Stefas, D.; Kokkinos, V.; Bouras, C.; Couris, S. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy coupled with ma-chine learning as a tool for olive oil authenticity and geographic discrimination. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyftokostas, N.; Nanou, E.; Stefas, D.; Kokkinos, V.; Bouras, C.; Couris, S. Classification of Greek Olive Oils from Different Regions by Machine Learning-Aided Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and Absorption Spectroscopy. Molecules 2021, 26, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilge, G.; Sezer, B.; Eseller, K.E.; Berberoglu, H.; Topcu, A.; Boyaci, I.H. Determination of whey adulteration in milk powder by using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncayo, S.; Manzoor, S.; Rosales, J.; Anzano, J.; Caceres, J. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of milk for the detection of adulteration by Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS). Food Chem. 2017, 232, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Se, K.W.; Ghoshal, S.K.; Wahab, R.A. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy unified partial least squares regression: An easy and speedy strategy for predicting Ca, Mg and Na content in honey. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2019, 136, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastra-Mejías, M.; Izquierdo, M.; González-Flores, E.; Cancilla, J.C.; Izquierdo, J.G.; Torrecilla, J.S. Honey exposed to laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for chaos-based botanical classification and fraud assessment. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 199, 103939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nespeca, M.G.; Vieira, A.L.; Júnior, D.S.; Neto, J.A.; Ferreira, E.C. Detection and quantification of adulterants in honey by LIBS. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 125886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Xie, W.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, F.; Liu, F. Fast Quantification of Honey Adulteration with Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and Chemometric Methods. Foods 2020, 9, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Zhou, F.; Peng, J.; Sun, M. Fast Classification of Geographical Origins of Honey Based on Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and Multivariate Analysis. Sensors 2020, 20, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefas, D.; Gyftokostas, N.; Couris, S. Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy for elemental analysis and discrimination of honey samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part. B At. Spectrosc. 2020, 172, 105969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Du-bourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Borg, I.; Groenen, P.J.F.; Mair, P. Applied Multidimensional Scaling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; ISBN 9783642318481. [Google Scholar]
- Tharwat, A.; Gaber, T.; Ibrahim, A.; Hassanien, A.E. Linear discriminant analysis: A detailed tutorial. AI Commun. 2017, 30, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geurts, P.; Ernst, D.; Wehenkel, L. Extremely randomized trees. Mach. Learn. 2006, 63, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| 15 Honey Samples |
|---|
| 4 fir honey samples 5 thyme honey samples 4 multifloral honey samples 2 pine honey samples |
| 27 adulterated honey samples |
| 9 fir honey adulterated samples (10–90% (w/w)) 9 thyme honey adulterated samples (10–90% (w/w)) 9 multifloral honey adulterated samples (10–90% (w/w)) |
| 3 glucose syrup samples |
| In total: 45 samples |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stefas, D.; Gyftokostas, N.; Kourelias, P.; Nanou, E.; Kokkinos, V.; Bouras, C.; Couris, S. A Laser-Based Method for the Detection of Honey Adulteration. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6435. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146435
Stefas D, Gyftokostas N, Kourelias P, Nanou E, Kokkinos V, Bouras C, Couris S. A Laser-Based Method for the Detection of Honey Adulteration. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(14):6435. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146435
Chicago/Turabian StyleStefas, Dimitrios, Nikolaos Gyftokostas, Panagiotis Kourelias, Eleni Nanou, Vasileios Kokkinos, Christos Bouras, and Stelios Couris. 2021. "A Laser-Based Method for the Detection of Honey Adulteration" Applied Sciences 11, no. 14: 6435. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146435
APA StyleStefas, D., Gyftokostas, N., Kourelias, P., Nanou, E., Kokkinos, V., Bouras, C., & Couris, S. (2021). A Laser-Based Method for the Detection of Honey Adulteration. Applied Sciences, 11(14), 6435. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146435











