On the Possibility to Use the Charge Imbalance in Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy: A New Online, In Vivo, Noninvasive Dose Monitoring System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Low-Noise Acquisition Electronic
- A current–voltage converter (I–V), based on an OPA128 (Texas Instruments) operational amplifier, coupled with a high-resistance feedback resistor (1 G) and a 100-pF capacitor, in parallel to the resistance. This configuration limits the maximum cutting frequency to 1.6 Hz; moreover, it allows the control of the autoinduced oscillations in the converter and avoids overshoot phenomena. The I–V converter response is linear in the output range of −10 V ≤ V ≤ +10 V. The conversion range will hence be -10 nA ≤ I ≤ +10 nA.
- A low-pass filter made of a Resistive-Capacitance (RC) network, with a cut frequency of 0.9 Hz and an attenuation of −68 dB at 50 Hz. The filter has two main roles: it protects the OPA128 operational amplifier from possible electrostatic discharges (ESD) induced both by patient and/or medical personnel during the pretreatment phases; it also weakens the 50-Hz noise currents, induced in the patient by the environment’s electromagnetic fields, by a factor 2.500.
- A couple of Junction gate Field-Effect Transistors (JFET), which protect the OPA128 whenever the I–V converter reaches saturation. If the I–V converter works inside its operational range, the two JFETs are not operative and the leakage currents they introduce are negligible (order of 100 fA).
- An active, inverting, second-order, low-pass filter. Its main aim is to cut (with a slope of 40 dB per decade) the residual noise at the output of the I–V converter. The inverting characteristic of this filter was designed to compensate the negative voltage sign at the output of the I–V converter. With this solution, the final output voltage will be positive, i.e., of the same sign as the input current.
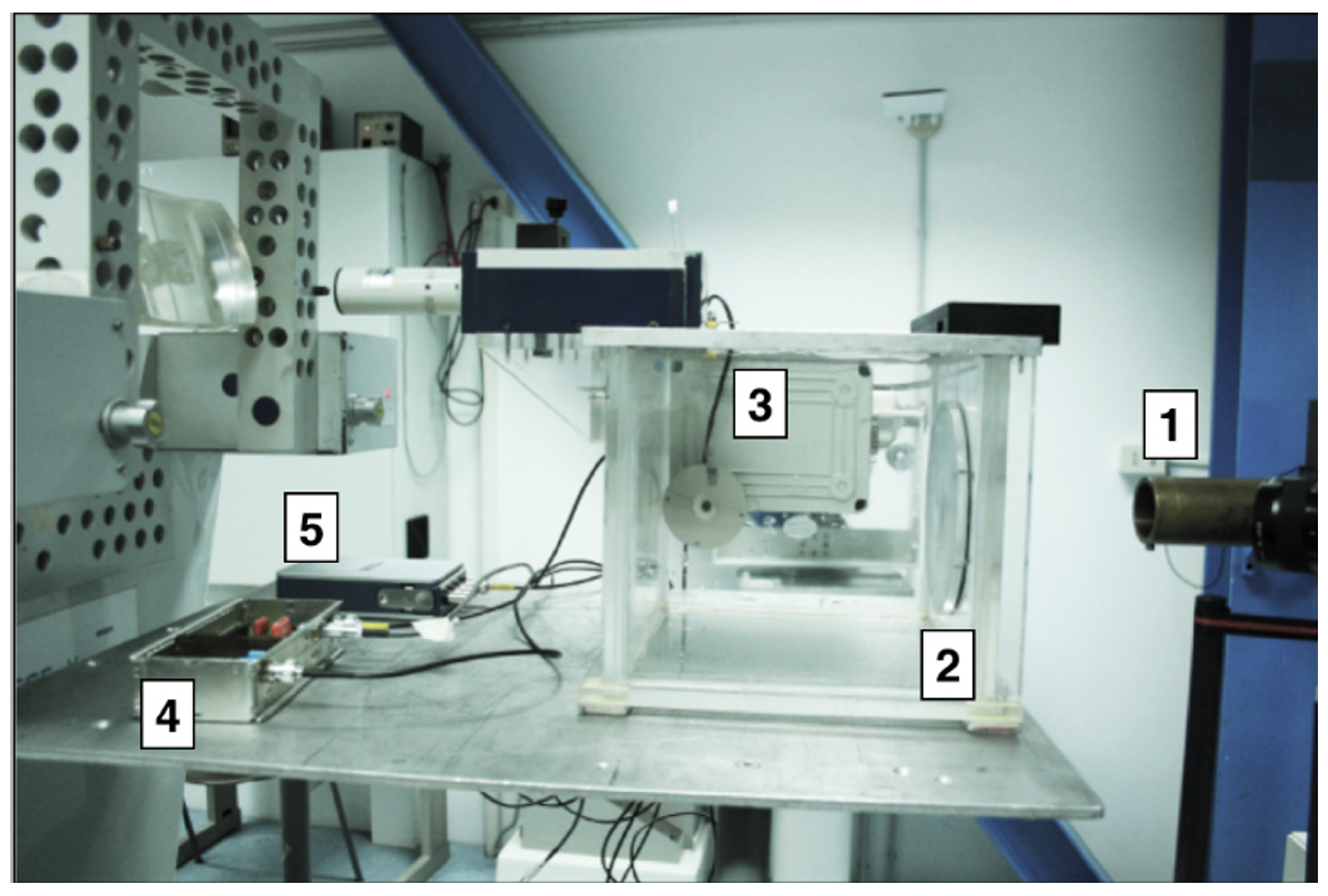
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
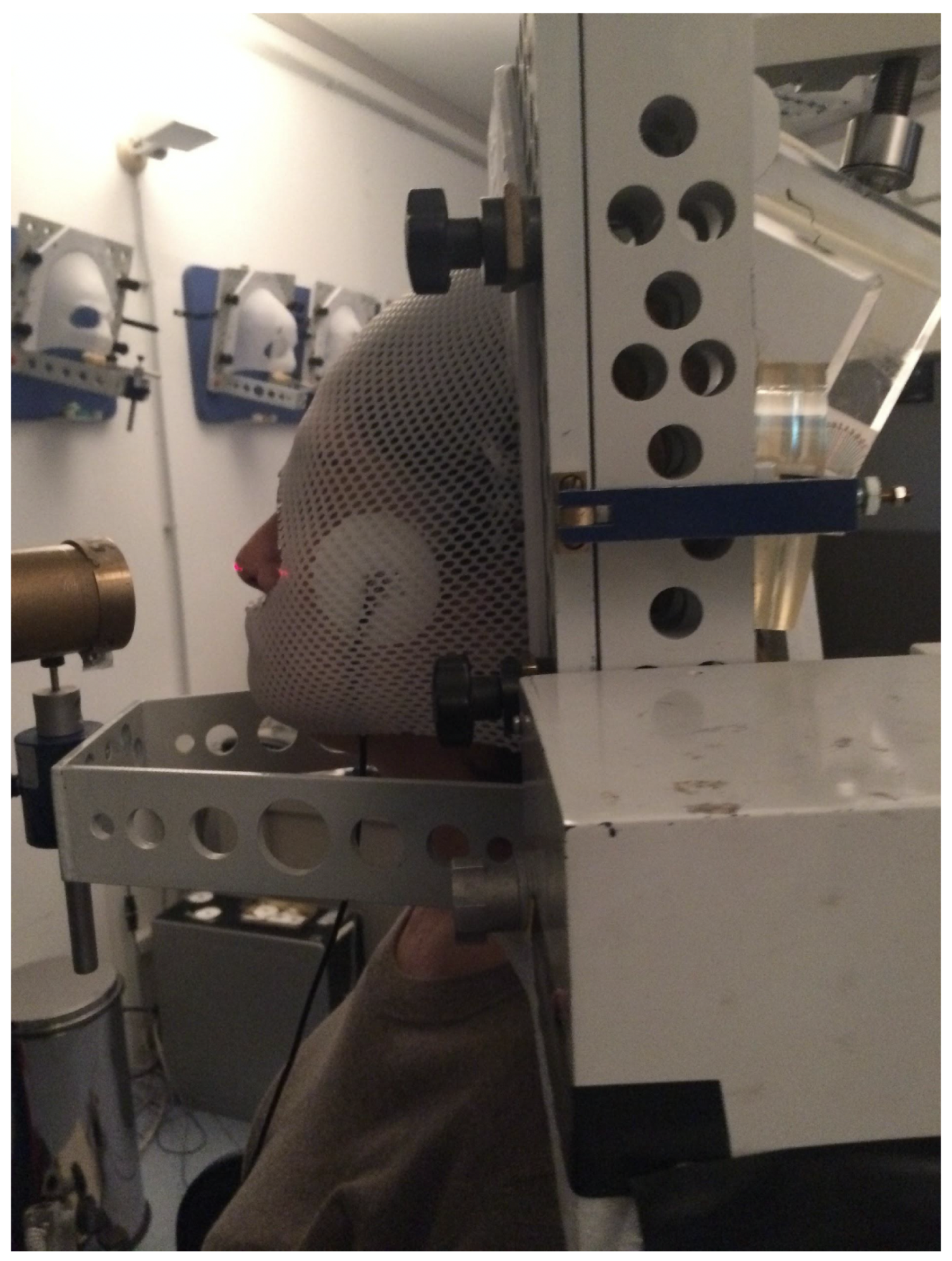
2.3. Set-Up for In Vivo Irradiation
3. Results and Discussion
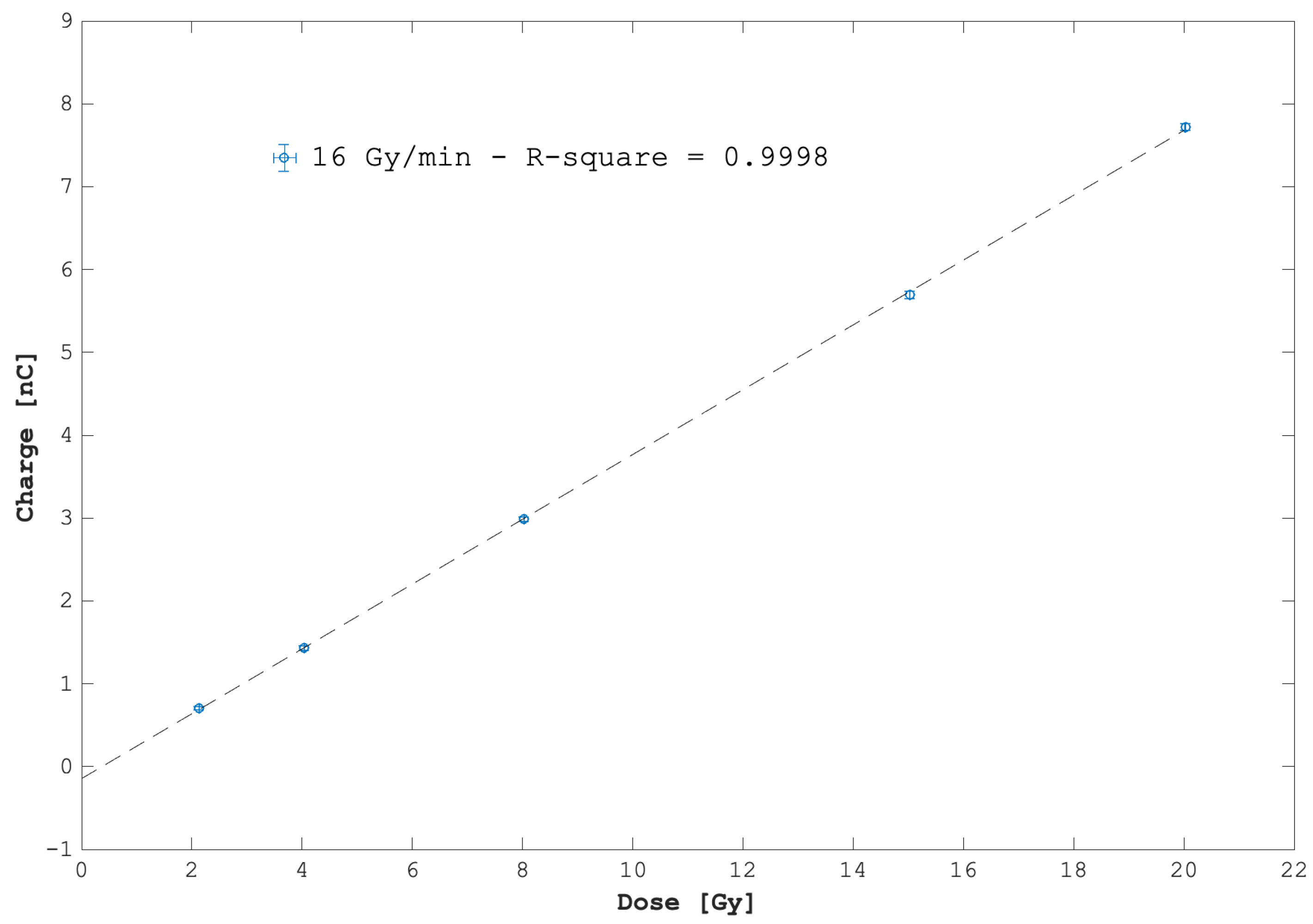
3.1. Dose and Dose-Rate Dependence
3.2. Short-, Mid-, and Long-Term Reproducibility
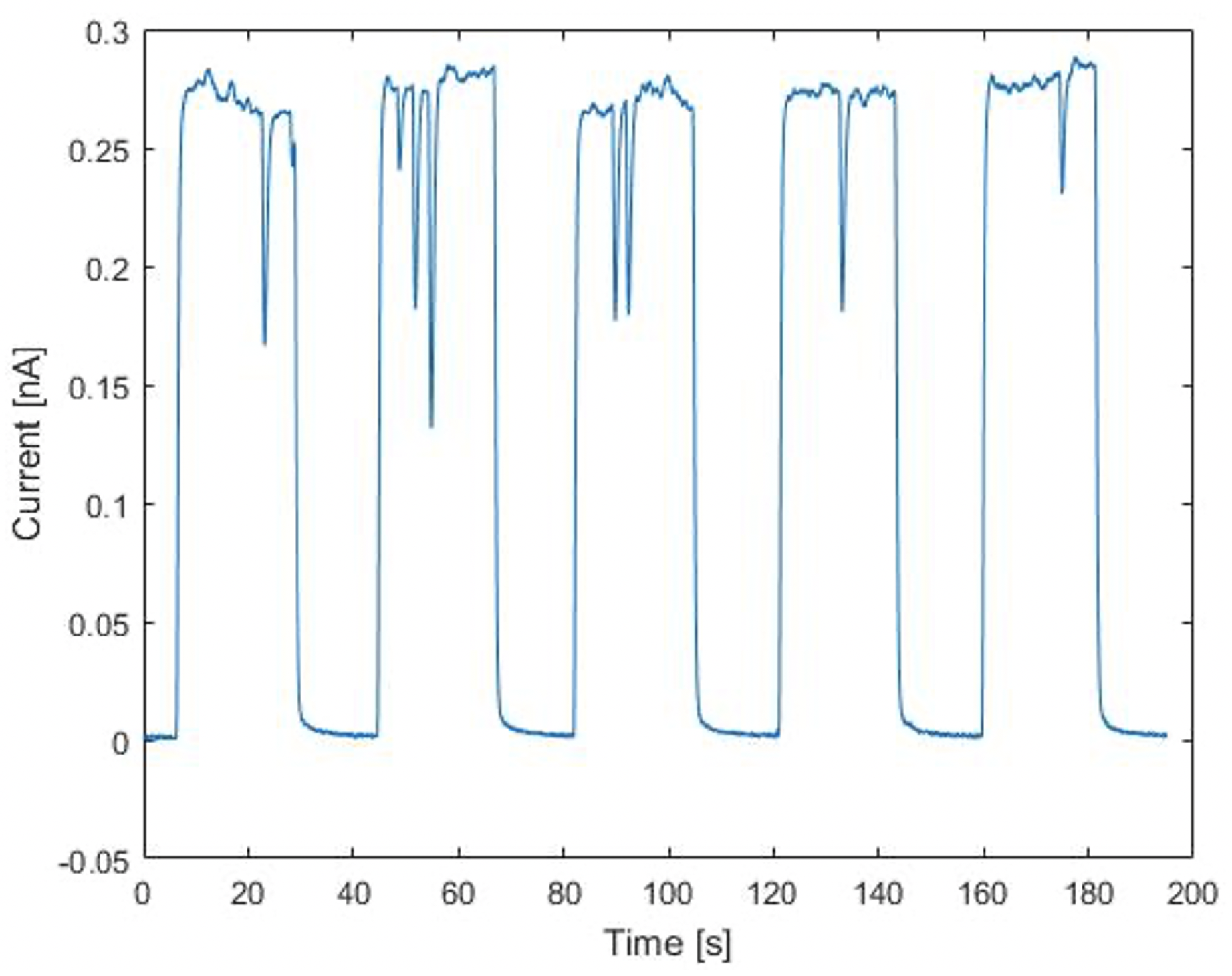
3.3. Current Monitoring Capabilities
3.4. Field-Size Dependence
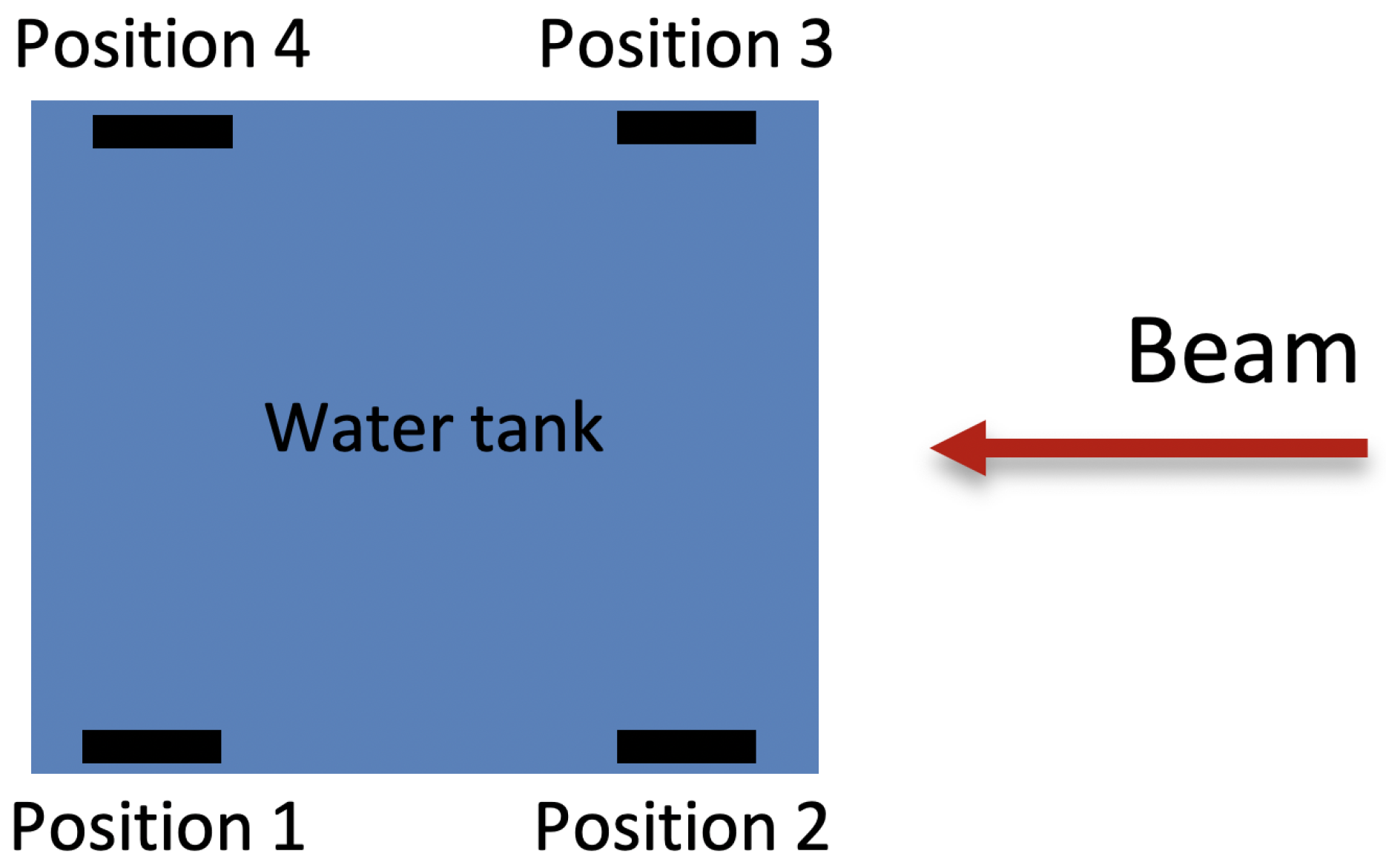
3.5. Position and Temperature Dependence
4. Preliminary In Vivo Tests
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olaciregui-Ruiz, I.; Beddar, S.; Greer, P.; Jornet, N.; McCurdy, B.; Paiva-Fonseca, G.; Mijnheer, B.; Verhaegen, F. In vivo dosimetry in external beam photon radiotherapy: Requirements and future directions for research, development, and clinical practice. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijnheer, B.; Beddar, B.; Izewska, J.; Reft, C. In vivo dosimetry in external beam radiotherapy. Med. Phys. 2013, 40, 070903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourhis, J.; Jeanneret Sozzi, W.; Gonçalves Jorge, P.; Gaide, O.; Bailat, C.; Duclos, F.; Patin, D.; Ozsahin, M.; Bochud, F.; Germond, J.; et al. Treatment of a first patient with FLASH-radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves Jorge, P.; Jaccard, M.; Petersson, K.; Gondré, M.; Durán, M.T.; Desorgher, L.; Germond, J.F.; Liger, P.; Vozenin, M.C.; Bourhis, J.; et al. Dosimetric and preparation procedures for irradiating biological models with pulsed electron beam at ultra-high dose-rate. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 34–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüler, E.; Trovati, S.; King, G.; Lartey, F.; Rafat, M.; Villegas, M.; Maxim, P.G. Experimental platform for ultra-high dose rate FLASH irradiation of small animals using a clinical linear accelerator. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 97, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortov, V. Materials for thermoluminescent dosimetry: Current status and future trends. Radiat. Meas. 2007, 42, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroomand-Rad, A.; Blackwell, C.R.; Coursey, B.M.; Gall, K.P. Radiochromic film dosimetry: Recommendations of AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group 55. Med. Phys. 1998, 25, 2093–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, F.F.; Amaral, L.L.; Costa, A.M.; Netto, T.G. In vivo dosimetry with silicon diodes in total body irradiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2014, 95, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.L.; Ekstrand, K.E. Silicon diode dosimetry. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1982, 33, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diode In-Vivo Dosimetry for Patient Receiving External Beam Radiation Therapy; Report of Task Group 62 of the Radiation Therapy Committee Published for the American Association of Physicists in Medicine by Medical Physics Publishing; AAPM Report No. 87; American Association of Physicists in Medicine: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2005.
- Ravichandran, R.; Binukumar, J.P.; Al Amri, I. Diamond detector in absorbed dose measurements in high-energy linear accelerator photon and electron beams. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2016, 2, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cirrone, G.A.P.; Cuttone, G.; Rafaele, L.; Sabini, M.G.; De Angelis, C.; Onori, S.; Pacilio, M.; Bucciolini, M.; Bruzzi, M. Natural and CVD type diamond detectors as dosimeters in hadrontherapy applications. Nucl. Phys. B Proc. Supp. 2003, 125, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucciolini, M.; Banci Buonamici, F.; Mazzocchi, S.; De Angelis, C.; Onori, S.; Cirrone, G.A.P. Diamond detector versus silicon diode and ion chamber in photon beams of different energy and field size. Med. Phys. 2003, 30, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manigandan, D.; Bharanidharan, G.; Aruna, P.; Devan, K.; Elangovan, D.; Patil, V.; Tamilarasan, R.; Vasanthan, S.; Ganesan, S. Dosimetric characteristics of a MOSFET dosimeter for clinical electron beams. Phys. Medica 2009, 25, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirrone, G.A.P.; Cuttone, G.; Lojacono, P.A.; Lo Nigro, S.; Patti, V.I.; Pittera, S.; Raffaele, L.; Sabini, M.G.; Salamone, V.; Valastro, L.M. Preliminary investigation on the use of the MOSFET dosimeter in proton beams. Physica Medica 2006, 22, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Development of Procedures for In Vivo Dosimetry in Radiotherapy; Technical Report Series No. 8; International Atomic Energy Agency: Wien, Austria, 2013.
- Di Venanzio, C.; Marinelli, M.; Milani, E. Characterization of synthetic single crystal diamond Schottky diode for radiotherapy electron beam dosimetry. Med. Phys. 2013, 40, 021712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alnawaf, H.; Butson, M.; Yu, P.K.N. Measurement and effects of MOSKIN detectors on skin dose during high energy radiotherapy treatment. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2012, 35, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirrone, G.A.P.; Cuttone, G.; Lojacono, P.A.; Nigro, S.L.; Mongelli, V.; Patti, I.V.; Privitera, G.; Raffaele, L.; Rifuggiato, D.; Sabini, M.G.; et al. A 62-MeV proton beam for the treatment of ocular melanoma at Laboratori Nazionali del Sud-INFN. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2004, 51, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuttone, G.; Cirrone, G.A.P.; Di Franco, G.; La Monaca, V.; Lo Nigro, S.; Ott, J.; Pittera, S.; Privitera, G.; Raffaele, L.; Reibaldi, A.; et al. CATANA protontherapy facility: The state of art of clinical and dosimetric experience. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2011, 126, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirrone, G.A.P.; Cuttone, G.; Raffele, L.; Salamone, V.; Avitabile, T.; Privitera, G.; Corrado, S.; Amico, A.; La Rosa, G.; Leanza, R.; et al. Clinical and Research Activities at the CATANA Facility of INFN-LNS: From the Conventional Hadrontherapy to the Laser-Driven Approach. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Short-term reproducibility | ≤2% |
| Mid-term reproducibility | ≤2.3% |
| Long-term reproducibility | ≤4.3% |
| Rise Time (s) | Fall Time (s) | FWHM (s) | Charge Integral (nC) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEM | 0.43 ± 0.02 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | 52.03 ± 0.02 | 49.32 ± 0.01 |
| ELECTRODE | 0.80 ± 0.02 | 0.65 ± 0.02 | 52.03 ± 0.02 | 49.50 ± 0.01 |
| Difference [%] | 46 | 43 | 0.02 | 0.36 |
| Session | Time (s) | Charge (nC) | Nominal Dose (cGy) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | 3.32 ± 0.06 | 1366 |
| 2 | 42 | 3.14 ± 0.06 | 1366 |
| 3 | 35 | 3.19 ± 0.06 | 1366 |
| 4 | 44 | 3.35 ± 0.06 | 1366 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cirrone, G.A.P.; Amato, N.; Catalano, R.; Di Domenico, A.; Cuttone, G.; Lojacono, P.; Mazzaglia, A.; Pace, F.; Pittà, G.; Raffaele, L.; et al. On the Possibility to Use the Charge Imbalance in Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy: A New Online, In Vivo, Noninvasive Dose Monitoring System. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11157005
Cirrone GAP, Amato N, Catalano R, Di Domenico A, Cuttone G, Lojacono P, Mazzaglia A, Pace F, Pittà G, Raffaele L, et al. On the Possibility to Use the Charge Imbalance in Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy: A New Online, In Vivo, Noninvasive Dose Monitoring System. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(15):7005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11157005
Chicago/Turabian StyleCirrone, G A Pablo, Nino Amato, Roberto Catalano, Alessandro Di Domenico, Giacomo Cuttone, Pietro Lojacono, Alfio Mazzaglia, Fabrizio Pace, Giuseppe Pittà, Luigi Raffaele, and et al. 2021. "On the Possibility to Use the Charge Imbalance in Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy: A New Online, In Vivo, Noninvasive Dose Monitoring System" Applied Sciences 11, no. 15: 7005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11157005
APA StyleCirrone, G. A. P., Amato, N., Catalano, R., Di Domenico, A., Cuttone, G., Lojacono, P., Mazzaglia, A., Pace, F., Pittà, G., Raffaele, L., Salamone, V., Spatola, C., & Petringa, G. (2021). On the Possibility to Use the Charge Imbalance in Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy: A New Online, In Vivo, Noninvasive Dose Monitoring System. Applied Sciences, 11(15), 7005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11157005







