Design and Implementation of Split-Leg Type Elliptical Whole-Body Birdcage RF Coil at 1.5 T MRI
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
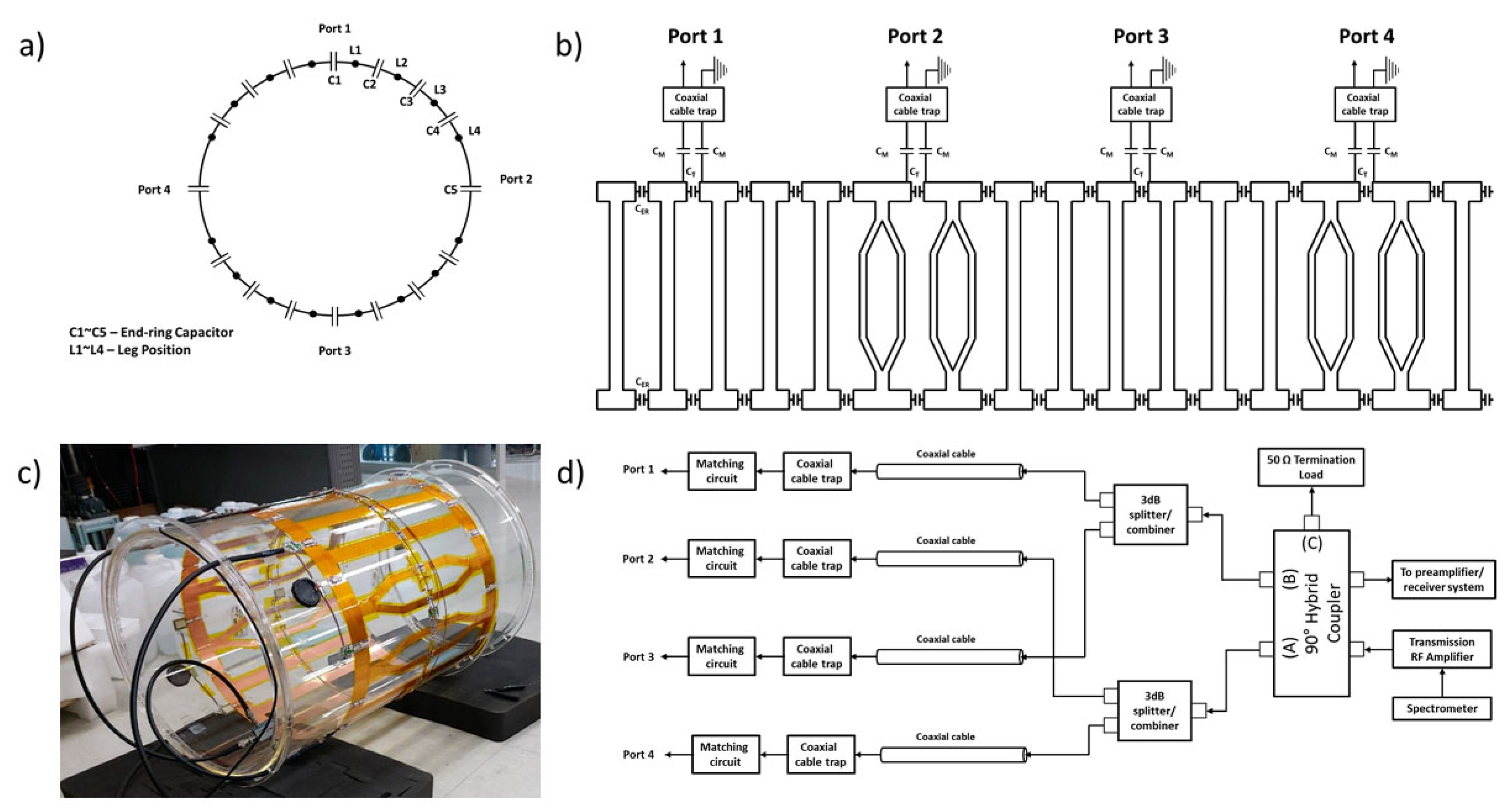
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. EM Simulation and Optimization
2.2. RF Coil Design and Construction
2.3. Magnetic Resonance (MR) Experiment
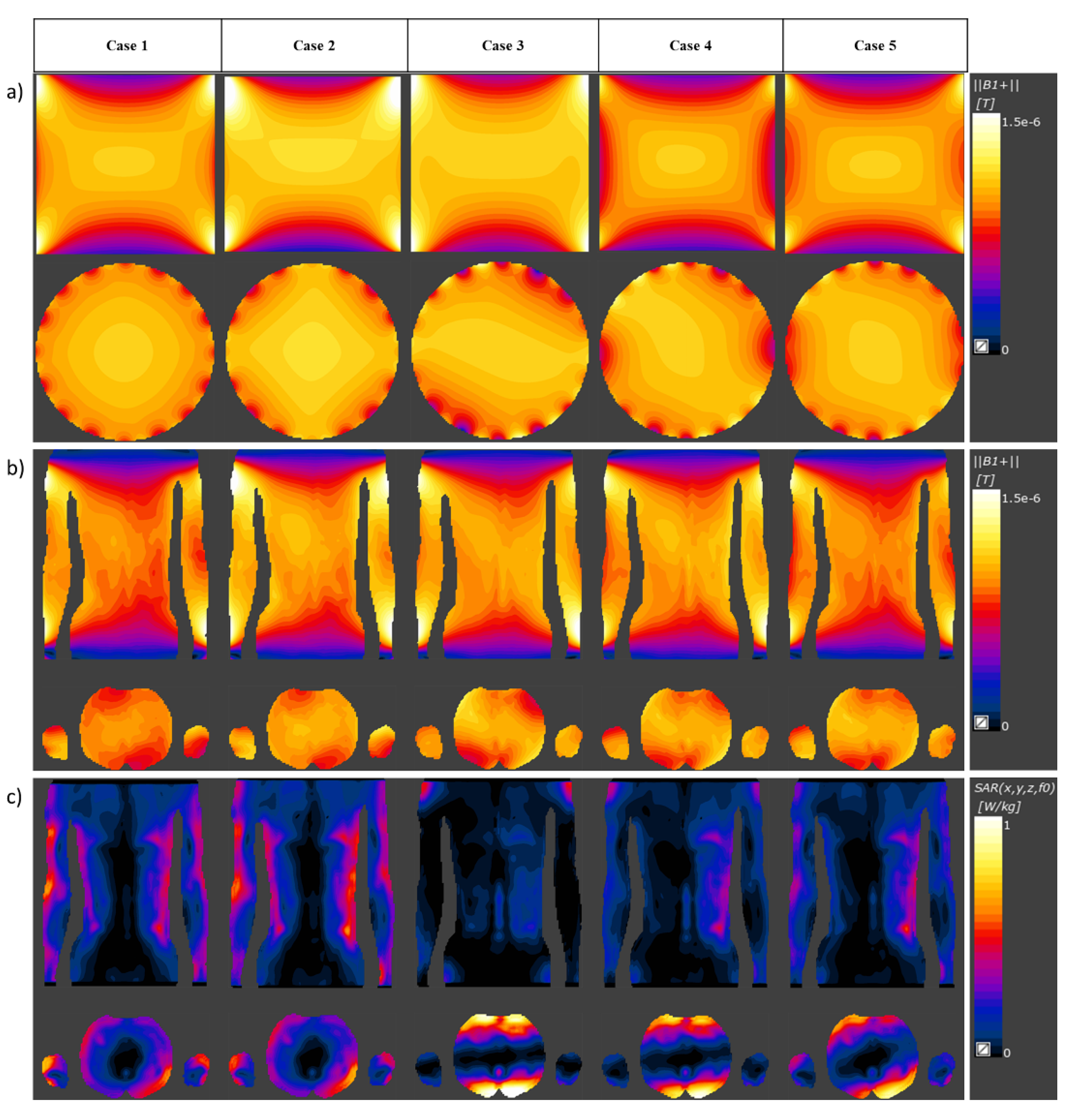
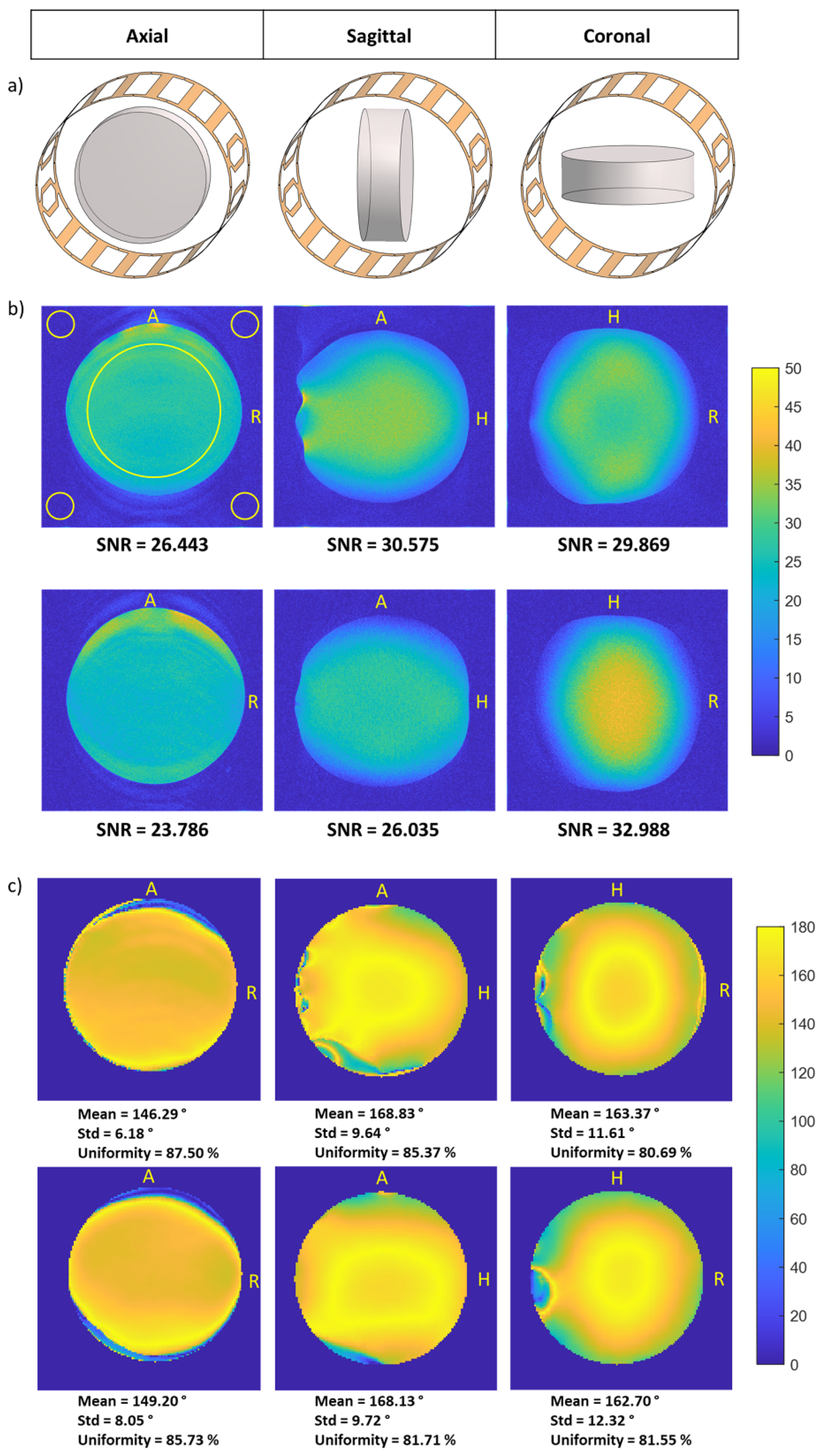
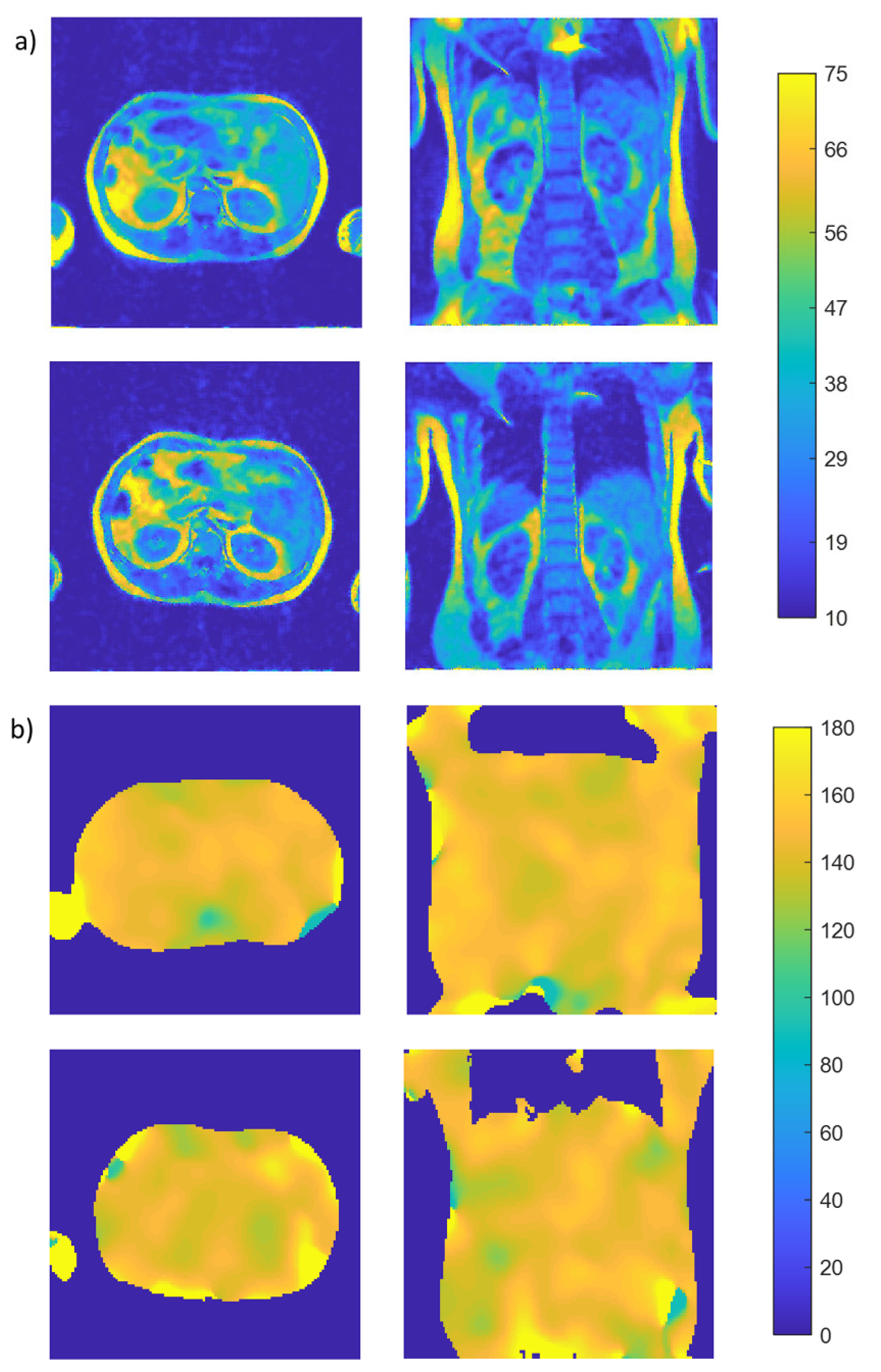
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayes, C.E.; Edelstein, W.A.; Schenck, J.F.; Mueller, O.M.; Eash, M. An efficient, highly homogeneous radiofrequency coil for whole-body NMR imaging at 1.5 T. J. Magn. Reson. 1985, 63, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, G.H.; Hayes, C.E.; Pelc, A.J.; Edelstein, W.A.; Mueller, O.M.; Hart, H.R.; Hardy, C.J.; O’Donnell, M.; Barber, W.D. Comparison of linear and circular polarization for magnetic resonance imaging. J. Magn. Reson. 1985, 64, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.N.; Hoult, D.I.; Sank, V.J. Quadrature detection coils—A further √2 improvement in sensitivity. J. Magn. Reson. 1983, 54, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimson, W.E.; Martin, P.A.; Griffiths, R.D.; Edwards, R.H. An elliptical cross-section birdcage body coil. In Proceedings of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Berlin, Germany, 8 August 1992; p. 272. [Google Scholar]
- Riauka, T.A.; Vermeulen, F.E.; Capjack, C.E.; Allen, P.S. Bird-cage resonators with noncircular cross-sectional geometries. In Proceedings of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, New York, NY, USA, 27 April 1996; p. 397. [Google Scholar]
- De Zanche, N.; Chhina, N.; Teh, K.; Randell, C.; Pruessmann, K.P.; Wild, J.M. Asymmetric quadrature split birdcage coil for hyperpolarized 3He lung MRI at 1.5 T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tropp, J. The theory of the bird-cage resonator. J. Magn. Reson. 1989, 82, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascone, R.J.; Garcia, B.J.; Fitzgerald, T.M.; Vullo, T.; Zipagan, R.; Cahill, P.T. Generalized electrical analysis of low-pass and high-pass birdcage resonators. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1991, 9, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, T.K.; Hayes, C.E.; Kang, Y.W. An analytical model for the design of RF resonators for MR body imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1991, 21, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vullo, T.; Zipagan, R.T.; Pascone, R.; Whalen, J.P.; Cahill, P.T. Experimental design and fabrication of birdcage resonators for magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1992, 24, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpen, M.D. Equivalent circuit for birdcage resonators. Magn. Reson. Med. 1993, 29, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novikov, A. Advanced theory of driven birdcage resonator with losses for biomedical magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 29, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vullo, T.; Pascone, R.; Mancuso, R.; Zipagan, R.; Cahill, P.T. Transmission line analysis of noncylindrical birdcage resonators. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1994, 12, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, L.K.; Crozier, S.; Doddrell, D.M. An analysis and optimization of elliptical RF probes used in magnetic resonance imaging. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1996, 7, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Collins, C.M.; Dardzinski, B.J.; Chin, C.L.; Smith, M.B. A method to create an optimum current distribution and homogeneous B1 field for elliptical birdcage coils. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997, 37, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifer, M.C. Theory of the quadrature elliptic birdcage coil. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997, 38, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riauka, T.A.; De Zanche, N.F.; Thompson, R.; Vermeulen, F.E.; Capjack, C.E.; Allen, P.S. A numerical approach to non-circular birdcage RF coil optimization: Verification with a fourth-order coil. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 41, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, T.S.; Lee, R.; Baertlein, B.A.; Yu, Y.; Robitaille, P.M. Computational analysis of the high pass birdcage resonator: Finite difference time domain simulations for high-field MRI. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2000, 18, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wright, S.M. Analysis of RF penetration effects in MRI using finite-difference time-domain method. In Proceedings of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, New York, NY, USA, 14 August 1993; p. 1327. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.M.; Chen, J.; Chew, W.C.; Gan, H.; Magin, R.L.; Dimbylow, P.J. Computation of electromagnetic fields for high-frequency magnetic resonance imaging applications. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guclu, C.; Kashmar, G.; Nalcioglu, O.; Hacinliyan, A. An FEM approach for the characterization of the RF field homogeneity at high field. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997, 37, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Jeng, S.K.; Lin, F.H.; Kuan, W.P. Quantitative analysis of magnetic resonance radio-frequency coils based on method of moments. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1999, 35, 2118–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.K.; Liu, F.; Weber, E.; Crozier, S. Hybrid numerical techniques for the modelling of radiofrequency coils in MRI. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 937–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J. Electromagnetic Analysis and Design in Magnetic Resonance Imaging; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Chen, J. On the SAR and field inhomogeneity of birdcage coils loaded with the human head. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997, 38, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Feng, Z.; Jin, J.M. Numerical simulation of SAR and B1-field inhomogeneity of shielded RF coils loaded with the human head. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1998, 45, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, C.M. Numerical field calculations considering the human subject for engineering and safety assurance in MRI. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemdiasov, R.A.; Obi, A.A.; Ludwig, R. A numerical postprocessing procedure for analyzing radio frequency MRI coils. Concepts Magn. Reson. Part A 2011, 38, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, M.; Turner, R. Fast MRI coil analysis based on 3-D electromagnetic and RF circuit co-simulation. J. Magn. Reson. 2009, 200, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beqiri, A.; Hand, J.W.; Hajnal, J.V.; Malik, S.J. Comparison between simulated decoupling regimes for specific absorption rate prediction in parallel transmit MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IEC 60601-2-33:2010. Medical Electrical Equipment—Part 2–33. Particular Requirements for the Basic Safety and Essential Performance of Magnetic Resonance Equipment for Medical Diagnosis, 3rd ed.; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, C.M.; Li, S.; Yang, Q.X.; Smith, M.B. A Method for Accurate Calculation of B1 Fields in Three Dimensions. Effects of Shield Geometry on Field Strength and Homogeneity in the Birdcage Coil. J. Magn. Reson. 1997, 125, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayes, C.E.; Eash, M.G.; General Electric Co. Shield for Decoupling RF and Gradient Coils in an NMR Apparatus. U.S. Patent 4,642,569, 10 February 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, C.M. Electromagnetics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Physical Principles, Related Applications, and Ongoing Developments; Morgan & Claypool Publishers: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistler, J.; Diehl, D.; Renz, W.; Eberler, L. Homogeneity improvement using a 2 port birdcage coil. In Proceedings of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Berlin, Germany, 19 May 2007; p. 1063. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, C.L.; Collins, C.M.; Li, S.; Dardzinski, B.J.; Smith, M.B. BirdcageBuilder: Design of specified-geometry birdcage coils with desired current pattern and resonant frequency. Concepts Magn. Reson. 2002, 15, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christ, A.; Kainz, W.; Hahn, E.G.; Honegger, K.; Zefferer, M.; Neufeld, E.; Rascher, W.; Janka, R.; Bautz, W.; Chen, J. Virtual Family—Development of surface-based anatomical models of two adults and two children for dosimetric simulations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 55, N23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberi, E.A.; Gati, J.S.; Rutt, B.K.; Menon, R.S. A transmit-only/receive-only (TORO) RF system for high-field MRI/MRS applications. Magn. Reson. Med. 2000, 43, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.M.; Beck, B.L.; Duensing, G.R.; Fitzsimmons, J.R. Common mode signal rejection methods for MRI: Reduction of cable shield currents for high static magnetic field systems. Concepts Magn. Reson. Part B Magn. Reason. Eng. 2003, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.H.; Hilal, S.K.; Cho, Z.H.; Mun, I.K. Radio frequency field intensity mapping using a composite spin-echo sequence. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1990, 8, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, E.F.; Bronskill, M.J.; Drost, D.J.; Och, J.; Pooley, R.A.; Sobol, W.T.; Clarke, G. AAPM Report MR TG-1: Acceptance Testing and Quality Assurance Procedures for Magnetic Resonance Imaging Facilities; American Association of Physicists in Medicine: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Henkelman, R.M. Measurement of signal intensities in the presence of noise in MR images. Med. Phys. 1985, 12, 232–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgenfrei, B.L.; Edelstein, W.A. Optimizing MRI signal-to-noise ratio for quadrature unmatched RF coils: Two preamplifiers are better than one. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 36, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mispelter, J.; Lupu, M. Homogeneous resonators for magnetic resonance: A review. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2008, 11, 340–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zanche, N.; Yahya, A.; Vermeulen, F.E.; Allen, P.S. Analytical approach to noncircular section birdcage coil design: Verification with a Cassinian oval coil. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 53, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Uniform Phantom | In Vivo Human | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence | Composite Spin-Echo | T1-Weighted Spin-Echo | Composite Spin-Echo | T1-Weighted Spin-Echo |
| Nominal FA (°) | 180 | 90 | 180 | 90 |
| TE/TR (ms) | 25/1600 | 15/500 | 15.4/600 | 13.2/600 |
| FOV (mm2) | 500 × 500 | 500 × 500 | 420 × 420 | 420 × 420 |
| Acquisition matrix | 256 × 256 | 128 × 128 | 128 × 128 | 256 × 256 |
| Slice thickness (mm) | 5 | 5 | 8 | 8 |
| Average | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Scan time (min) | 10 min 38 s | 4 min 16 s | 4 min 1 s | 2 min 41 s |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical Uniform Phantom | |||||
| Uniformity (%) | 74.29 | 70.21 | 69.68 | 73.28 | 76.25 |
| Total input power (watt) normalized to 1 µT | 24.41 | 33.03 | 36.52 | 37.16 | 29.89 |
| Transmit efficiency | 0.202 | 0.174 | 0.166 | 0.164 | 0.187 |
| at 20 kW (µT) | 28.63 | 24.61 | 23.40 | 23.20 | 26.47 |
| Human “Duke” Model | |||||
| Total input power (watt) normalized to 1 µT | 21.57 | 31.46 | 25.96 | 30.37 | 24.21 |
| Mean 10 g-avg SAR (watt/kg) | 0.093 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.093 |
| Peak 10 g-avg SAR (watt/kg) | 0.78 | 0.89 | 1.44 | 1.16 | 0.97 |
| Transmit efficiency | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.18 | 0.20 |
| at 20 kW (µT) | 30.45 | 25.21 | 27.76 | 25.66 | 28.74 |
| Unloaded | Light Loader Phantom | Heavy Loader Phantom | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reflection Coef. (S11) | −7.73 dB | −18.09 dB | −24.62 dB |
| Reflection Coef. (S22) | −5.05 dB | −16.03 dB | −20.35 dB |
| Isolation Coef. (S12) | −17.96 dB | −22.69 dB | −22.17 dB |
| Impedance (Z11) | 35.07–j34.33 Ω | 39.69–j4.33 Ω | 44.45–j0.05 Ω |
| Impedance (Z22) | 20.54–j31.6 Ω | 38.61–j8.23 Ω | 47.17–j8.93 Ω |
| Quality factor (Q) | 173.91 | 79.07 | 67.43 |
| Loading | Coil | Axial | Sagittal | Coronal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical Phantom | 2-port commercial circular birdcage | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| 4-port proposed split-type elliptical birdcage | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.15 | |
| In Vivo Human | 2-port commercial circular birdcage | 0.14 | ||
| 4-port proposed split-type elliptical birdcage | 0.16 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, S.; Chung, H.-J.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Lee, H.-K.; Oh, C.-H. Design and Implementation of Split-Leg Type Elliptical Whole-Body Birdcage RF Coil at 1.5 T MRI. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7448. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11167448
Kumar S, Chung H-J, Jeong Y-J, Lee H-K, Oh C-H. Design and Implementation of Split-Leg Type Elliptical Whole-Body Birdcage RF Coil at 1.5 T MRI. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(16):7448. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11167448
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Suchit, Han-Jae Chung, You-Jin Jeong, Heung-Kyu Lee, and Chang-Hyun Oh. 2021. "Design and Implementation of Split-Leg Type Elliptical Whole-Body Birdcage RF Coil at 1.5 T MRI" Applied Sciences 11, no. 16: 7448. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11167448
APA StyleKumar, S., Chung, H.-J., Jeong, Y.-J., Lee, H.-K., & Oh, C.-H. (2021). Design and Implementation of Split-Leg Type Elliptical Whole-Body Birdcage RF Coil at 1.5 T MRI. Applied Sciences, 11(16), 7448. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11167448






