Abstract
Currently, many children undergo precocious puberty, resulting in short stature due to premature closure of the growth plate. Pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) stimulation induces cell proliferation of articular chondrocytes. We developed a method for growth promotion using equipment with PEMF. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the effects of PEMF on the growth rate of growth plates using an animal model. An experimental study was conducted on 16 3-week-old rats to validate the effects of the growth care device on growth and development by PEMF stimulation at 28 Hz and 20 Gauss. The tibia bones of the groups with and without PEMF administration were dissected after 10 days, and then, the length of the growth plate of the knee and levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 hormone in serum were measured. The length of the growth plate on the tibia bone and the levels of circulating IGF-1 were significantly increased by 25.6% and 13.6%, respectively, in the experimental group to which PEMF was applied compared to those of the control group, without any side effects. These results suggest that PEMF can safely stimulate growth of the growth plate in a non-invasive manner to promote bone growth.
1. Introduction
Pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMFs) have been widely employed since the 1970s to treat fractures that do not heal well through the normal bone healing process; PEMF is a safe, non-invasive, and efficacious method for the treatment of diseases associated with fractures and was first approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1979 [1,2]. PEMF has also been suggested as an alternative treatment for osteoarthritis in the clinic [3]. Numerous studies have reported a therapeutic effect on fractures or other diseases in actual clinical use; it is known that PEMF therapy has no significant side effects [4,5].
Bone growth in children depends on growth plates situated near the end of all long bones in the body. The growth plate (physis) is a thin plate-shaped (narrow disc of cartilage) cartilage that is responsible for longitudinal bone growth and is the result of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation [6,7]. These plates consist of cartilage cells and chondrocytes, which form a scaffold that supports the formation of new bone tissue and are generated from stem cells called chondroprogenitors [8]. Various biological signals, including growth hormone, directly or indirectly divide and thicken the chondrocytes in the hypertrophic zone, and the cartilage on the side of the bone body is replaced with new bone, resulting in bone elongation [9]. However, it is still not clear how this process is maintained throughout childhood. Recently, a study conducted by a European collaborative research team, including the Karolinska Institute in Sweden, identified the mechanism of origin and differentiation of stem cells, which are the main factors in growth plate activity, using a fluorescent staining method that can differentiate each cell in mice [10].
The postnatal growth plate chondrocytes are divided into three layers that contribute to the longitudinal growth of long bones [11]. The resting zone is located at the top of the growth plate and maintains the integrity of the growth plate structure. Below these are “proliferating zone chondrocytes”, which are flat and, as the name suggests, divide and proliferate in the longitudinal direction. They resemble a pillar made of bricks. At the bottom are “hypertrophic chondrocytes”, which are enlarged cells. These cells do not divide and eventually die, and bone cells fill the empty spots to lengthen the bone body [11]. The resting chondrocytes serve as progenitor cells or stem-like cells to provide a renewable source to populate the whole growth plate. These chondrocytes within the resting zone divide and form proliferating chondrocytes, and the lower proliferating chondrocytes are converted into hypertrophic chondrocytes by terminal differentiation [12].
Thus, the length of growth of the bone body is determined by the extent to which the stem cells in the growth plate undergo symmetric cell division and how smooth the signal exchange is between the three types of chondrocytes.
If the chondrocytes stimulate and activate signal exchange and differentiation, growth plate growth is promoted. Accordingly, studies on pulsed magnetic field stimulation for the proliferation of various chondrocytes are being conducted.
De Mattei M. et al. [13] analyzed the proliferation pattern of human articular chondrocytes after applying PEMFs of 75 Hz, 2.3 mT to them for a long time, and observed that the proliferation of chondrocytes was induced. In addition, the effect of electromagnetic fields (EMFs) at 75 Hz and 2.3 mT on bovine articular cartilage cultured in vitro for 24 h was investigated; it was reported that EMFs exert a cartilage protection effect on the in vitro cultured articular cartilage due to the anabolic activity of EMFs and promote the synthesis of proteoglycans in the in vitro culture of small joint cartilage. The continuous application of 75 Hz, 2.3 mT of PEMF in human nasal and knee joint cartilage cells for 6–30 h resulted in increased cell proliferation in both knee articular (joint) cartilage and nasal cartilage cells [14].
In another study, human chondrocytes were subjected to a static magnetic field (SMF) of 0.6 T and PEMF (21.2 MHz cycle per 15 ms, continuous signal duration per 2 ms, amplification of 250 W, 3 dBm (0.1 V), and maximum output) for 72 h. When cultured with continuous application, cells treated with SMF showed a significantly higher rate of increased viability compared to control cells, whereas the increase in viability between cells treated with PEMF and non-treated control cells was not significant. This could be due to frequency-dependent effects on human cells [15].
In another study, a human chondrocyte cell culture exposed to PEMF showed a significantly higher rate of mitosis (almost two-fold) compared to chondrocytes in untreated cultures [16]. When PEMF of 10–15 Gauss and 10–30 Hz was applied to human chondrocytes and the cells were cultured for 5 days, in the case of control group cells without PEMF treatment, the rate of increase in cell numbers through mitosis reached 130%. In the case of the cells treated with PEMF, the rate of increase in the number of cells through mitosis was significantly increased to 192%. In addition, after 9 days, the control group showed a 207% increase in cell number, but in the PEMF group, the cell number increased significantly to 393%.
Thus, this study aimed to evaluate the effects of PEMF treatment on the growth rate of growth plates in an animal model. Using a device with a frequency of 28 Hz and a magnetic field strength of 20 Gauss, a PEMF was applied to the knee tibia of rats to evaluate changes in the size of the growth plate and the level of growth hormone. In addition, to determine the side effects of exposure to pulsed magnetic field, changes in weight and dietary efficiency, kidney and liver function levels, and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels were evaluated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PEMF Product
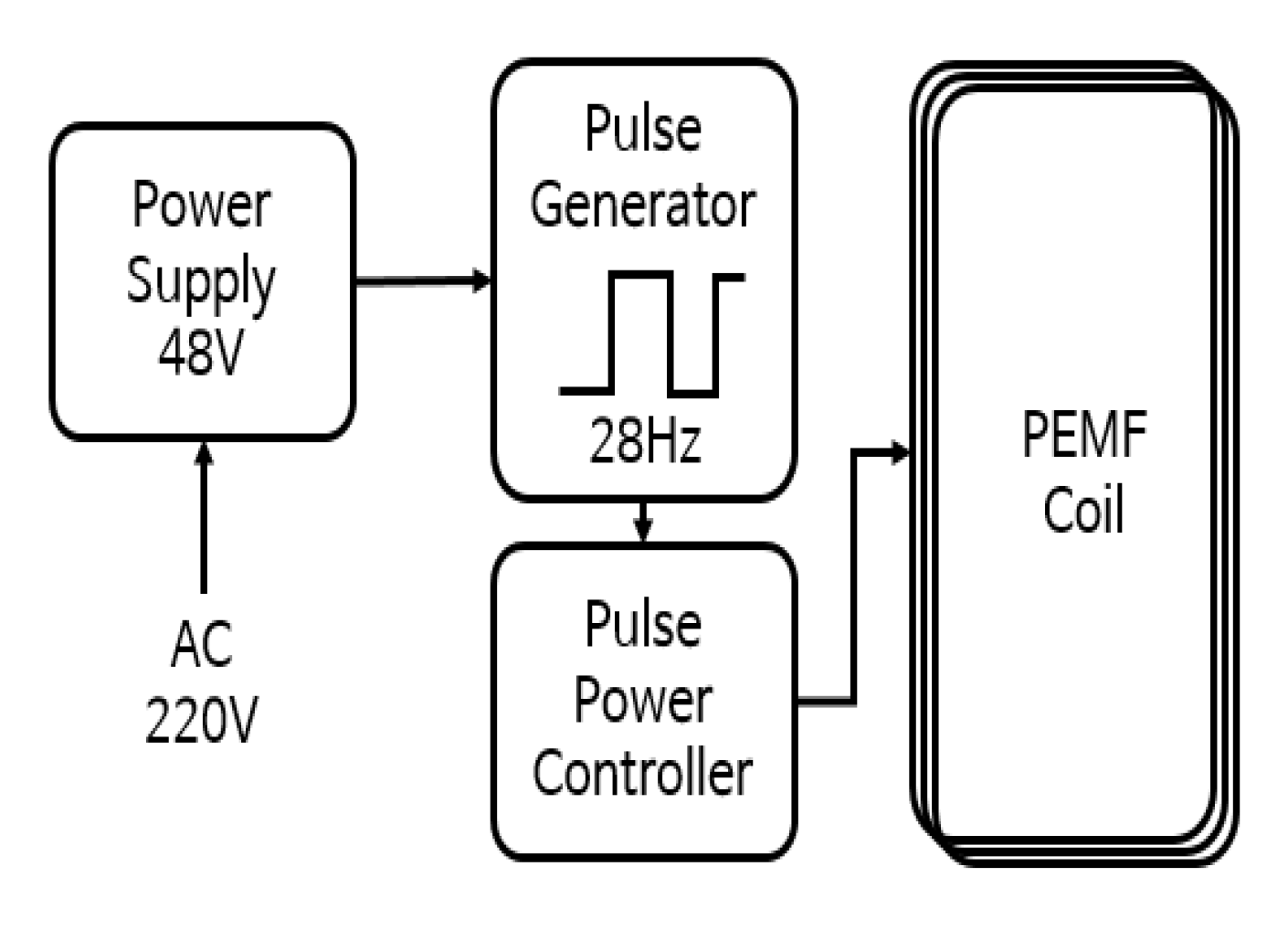
The electric circuit device that generates the PEMF was manufactured in a cage shape so that the magnetic field was focused on the leg joints of the rats. When 220 V AC power was applied, AC was converted into 48 V DC power through a switching mode power supply (SMPS), and energy in the form of pulses was transferred to the PEMF-generating coil (Figure 1). The pulse was output at 28 Hz (28 times per second), and a driving pulse in the form of a square wave was generated using a microprocessor (ATtiny2313A, Microchip, Chandler, AZ, USA) with a duty ratio of 50%, which is the on-time to off-time ratio. A 3 V driving pulse was generated, and current amplification was required owing to insufficient current energy for driving the coil. Thus, a solid-state relay (SSR) for the direct current was used. The SSR plays a key role in transferring energy to the magnetic field coil by amplifying the 3 V pulse signal generated by the microprocessor to 48 V.
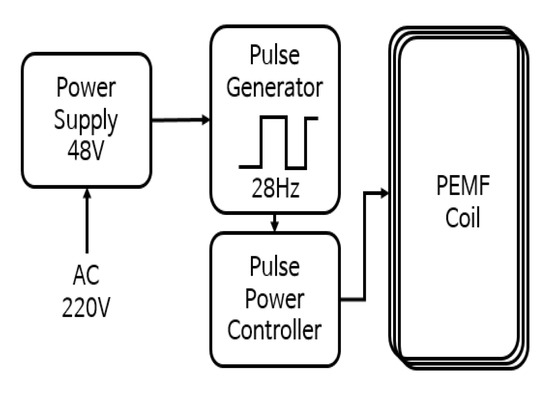
Figure 1.
Diagram of the PEMF device.
The pulsed magnetic field coil uses an enameled copper wire (with a diameter of 0.3 mm) with an insulating coating, and has a cube shape of 350 (width) mm × 300 (length) mm × 30 (height) mm. The total number of turns is 100. Finally, the driving current is adjusted so that the intensity of the output magnetic field becomes approximately 20 G at the center of the coil. The pulse field measuring device is a Hall element-type Gauss meter (Model 3251, Yokogawa, Tokyo, Japan), and an oscilloscope (XDS3062A, Tektronix, San Jose, CA, USA) is used to set the pulse frequency.
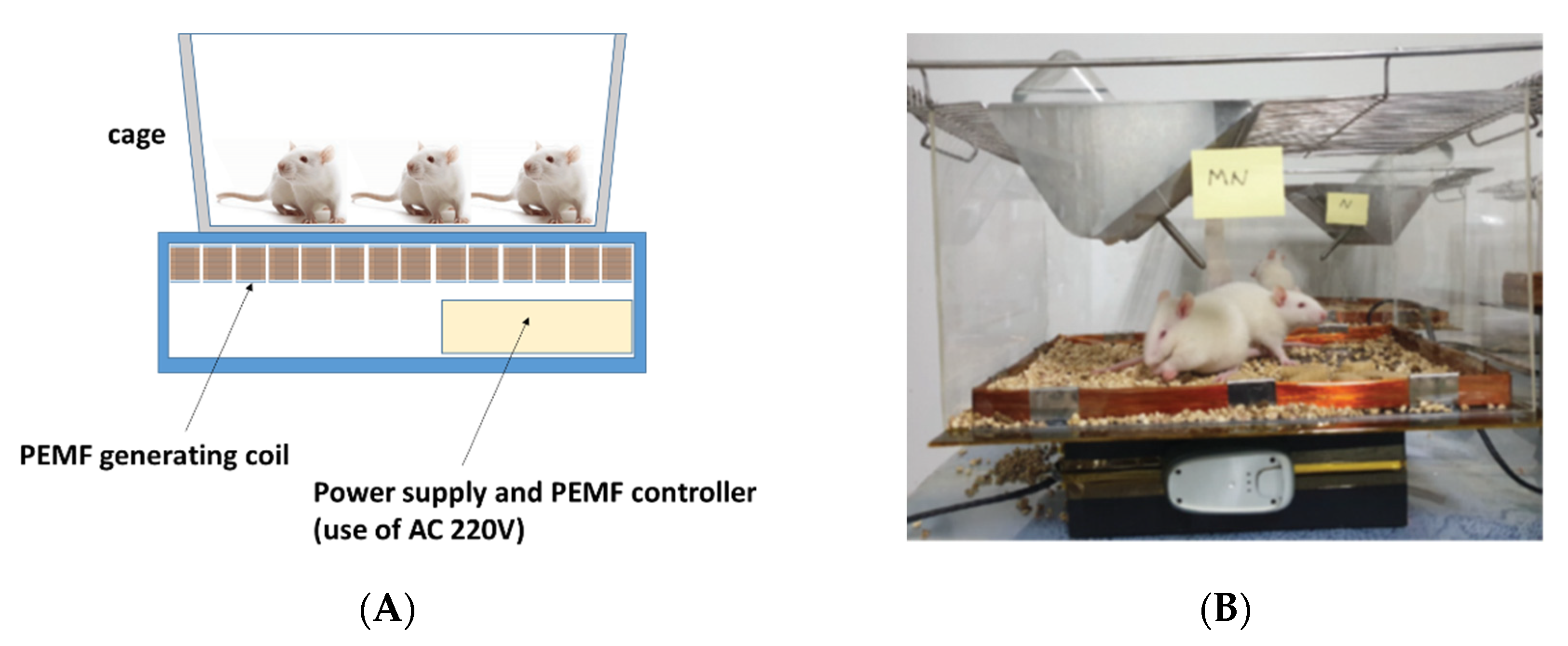
The fabricated PEMF device was finished in a cage shape to conduct the experiment in the general breeding environment of the rats (Figure 2A). At the lower end of the cage, a box case with a built-in pulse magnetic field controller was placed, and the cage body made of transparent acrylic was located at the upper end of the pulse magnetic field controller. Sawdust was laid inside the pulsed magnetic field coil so that the rats could conduct normal activities, and a feeding or water container was mounted on the upper part of the cage. The conditions were the same as the general breeding environment of the rats.
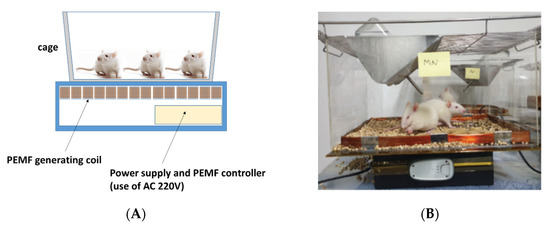
Figure 2.
Installation of experimental cage. (A) Diagram of the experimental cage and pulsed electromagnetic field device and (B) installation of the experimental cage.
Eight cages with a built-in pulse magnetic field device were manufactured, and four cages each were employed for the normal and experimental groups.
2.2. Animals
Female Sprague-Dawley rats (25 days old) were purchased from Central Lab Animal Inc. (Seoul, Korea). The study was performed according to the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Daejeon University (Approval No. DJUARB2020-038). All animals were housed in an air-conditioned animal room at a temperature of 21 ± 2 °C and humidity of 50 ± 5% under a 12:12 h light/dark cycle and had ad libitum access to food and water for 1 week.
2.3. Experiment
After 10-day acclimatization, eight animals in the normal group and the experimental group (2 rats/cage) were selected randomly. The pulsed magnetic field was inactive for the normal group, whereas the experimental group was exposed to the pulsed magnetic field for 10 h a day from 9:00 a.m. to 7:00 p.m. The animals were kept under the same conditions, except for the presence or absence of the pulsed magnetic field operation (Figure 2B).
During the 10-day experiment, weight and dietary food intake were measured every day, and after 10 days, the following procedure was performed to measure the growth rate of the tibial growth plate.
2.4. Measurement of Growth Rate of the Tibia Growth Plate
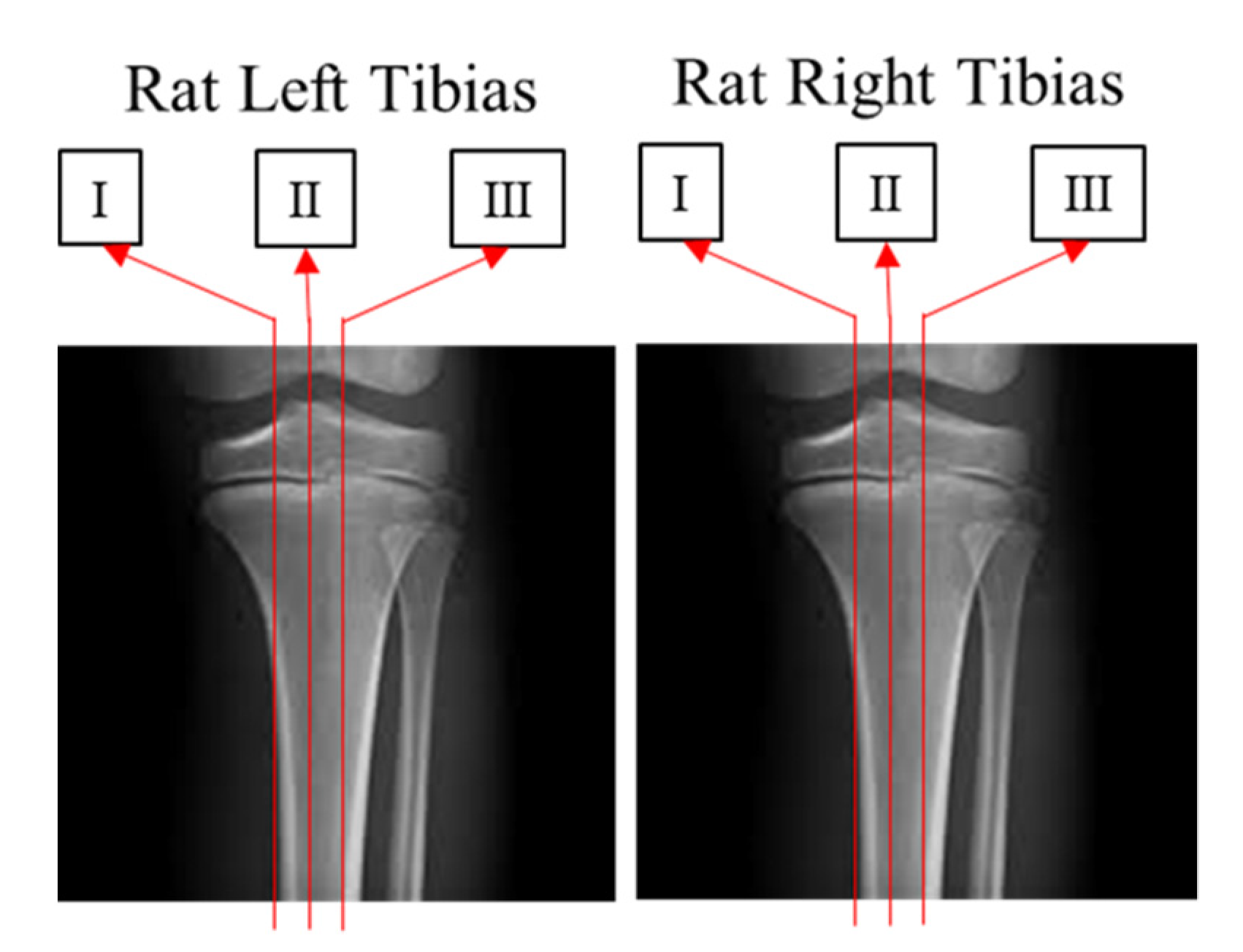
Tetracycline hydrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) (20 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally before sacrifice, as previously described [17]. The tibia was removed and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, decalcified in 50 mM EDTA solution (Sigma-Aldrich), and dehydrated in 30% sucrose solution overnight. The dehydrated tibia was cut along the sagittal plane to a thickness of 40 µm using a cryostat (CM3050S, Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany). After installation of a cryostat, the distance between the cartilage and bone junction in the growth plate and the proximal endpoint of the tetracycline label was measured, and the distance was divided into three parts to evaluate the growth rate of the longitudinal bone growth plate (Figure 3). The tetracycline label was examined using a fluorescence microscope (BX50, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan), and the distance was measured in a blinded manner by three other researchers using Image J software (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA).
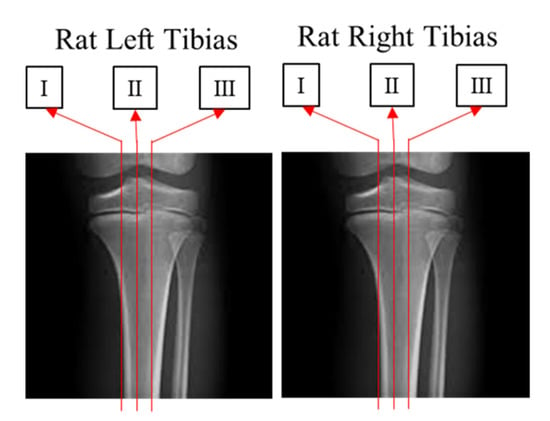
Figure 3.
Three parts (I, II, III) of the left and right tibias.
2.5. Measurement of Levels of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 and Nitric Oxide
After the end of the experiment, blood from the animals was collected by cardiac puncture, and serum was separated by centrifugation. Serum IGF-1 and cortisol levels were measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit according to the manufacturer’s protocol (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA). Nitric oxide (NO) levels were measured using an NO assay kit (Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA).
2.6. Blood Biochemical Analysis
To investigate kidney and liver function, serum creatinine, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels in the serum were measured using an automated chemistry analyzer. Serum LDH levels were also measured as a marker of common tissue injuries.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Effect on Longitudinal Bone Growth Rate
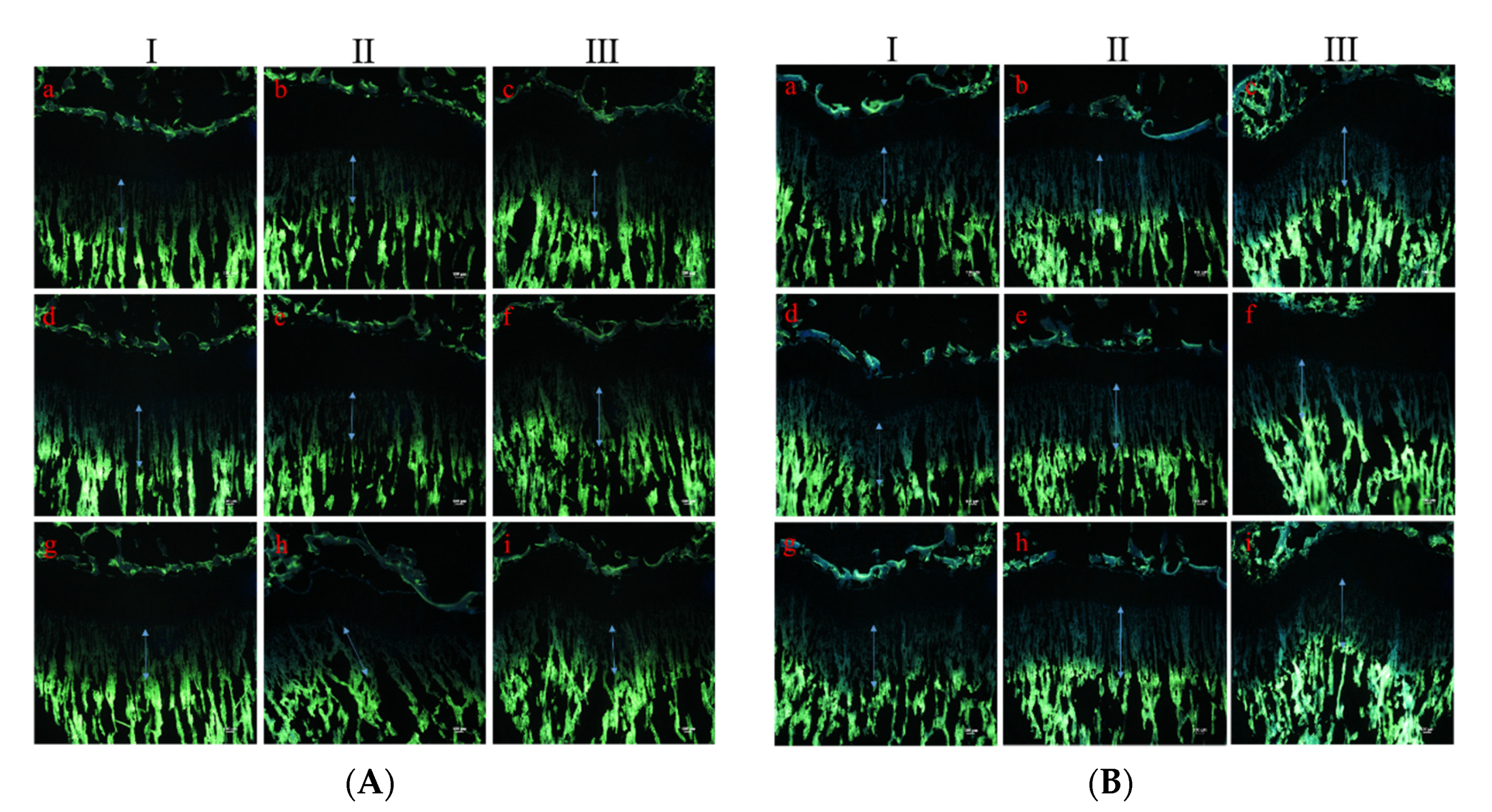
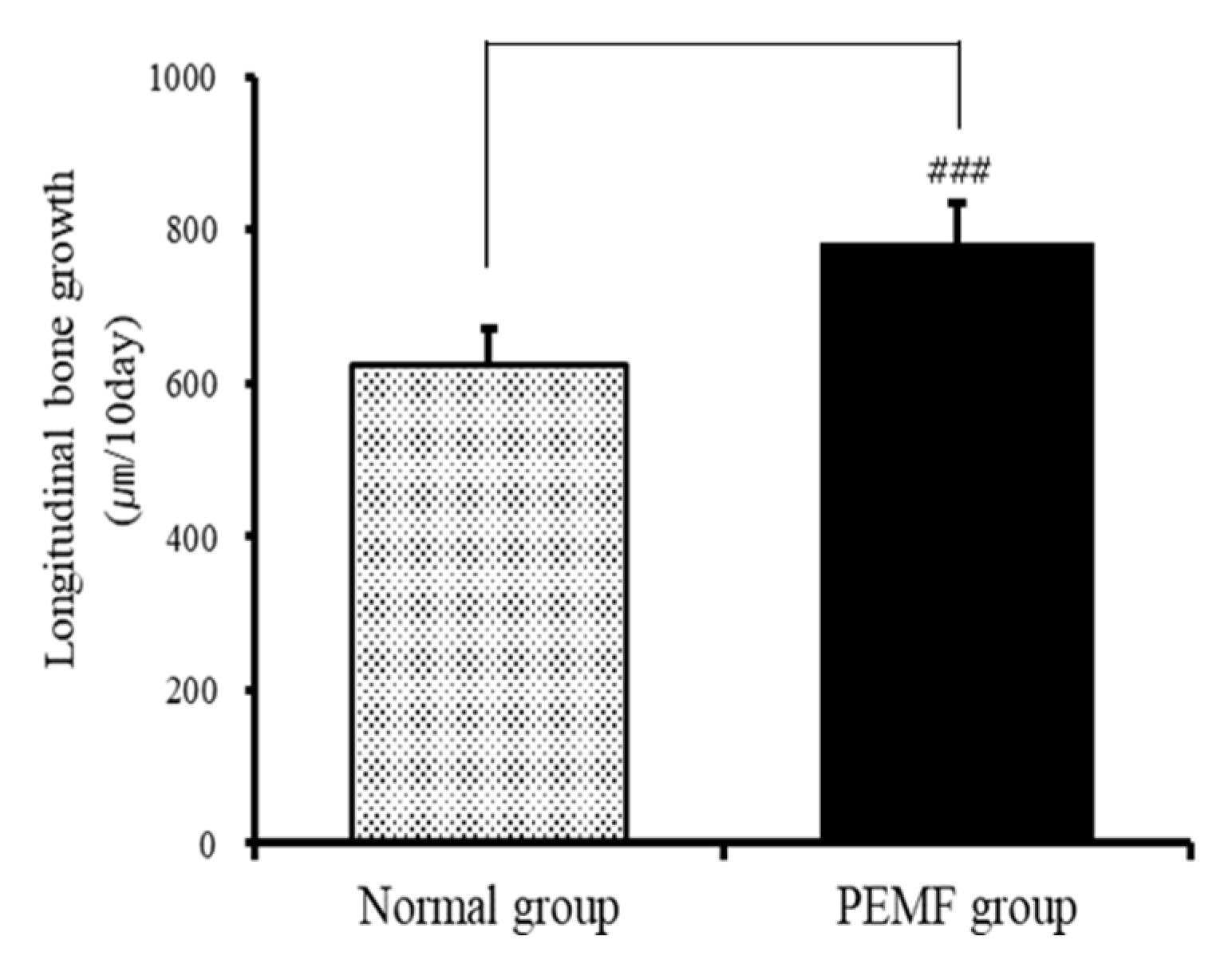
To evaluate the effect of PEMFs on the longitudinal bone growth rate, tetracycline was used as a fluorescent marker to label the newly formed bone under the growth plate of the proximal tibia. The distance between the cartilage and bone junction in the growth plate and the proximal endpoint of the tetracycline label showed that the bone growth rate in the normal group was 624.63 ± 45.97 μm, while that in the experimental group was 784.56 ± 50.38 μm. Thus, the bone growth rate of the PEMF-treated experimental group was 25.6%, which was significantly higher on average than that of the normal group (p < 0.001; Figure 4 and Figure 5).
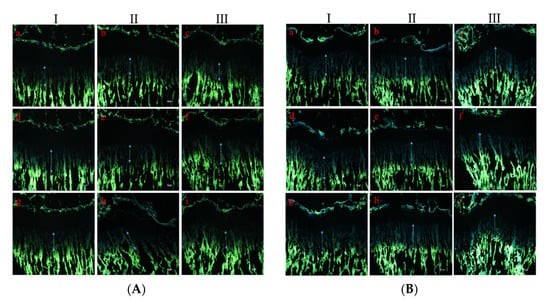
Figure 4.
Typical fluorescent photography of the proximal growth plate of tibia. (A) Typical fluorescent images of the proximal growth plate of the tibia in the normal group. (B) Typical fluorescent images of the proximal growth plate of the tibia in the PEMF-treated group.
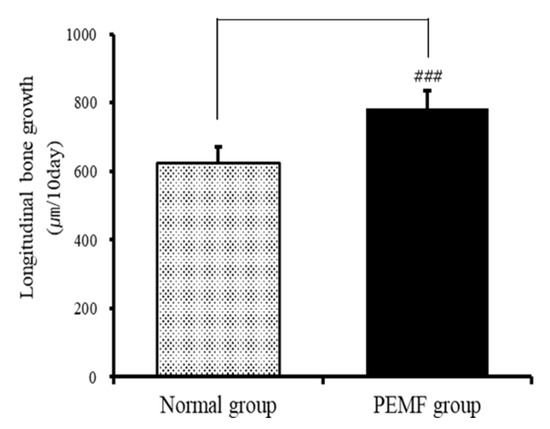
Figure 5.
Effects of PEMF treatment on bone growth rate in the proximal growth plate of the tibia. Results are expressed as means ± SEM (n = 8). ### p < 0.001 compared with the normal group.
3.2. Changes in Weight and Food Efficiency
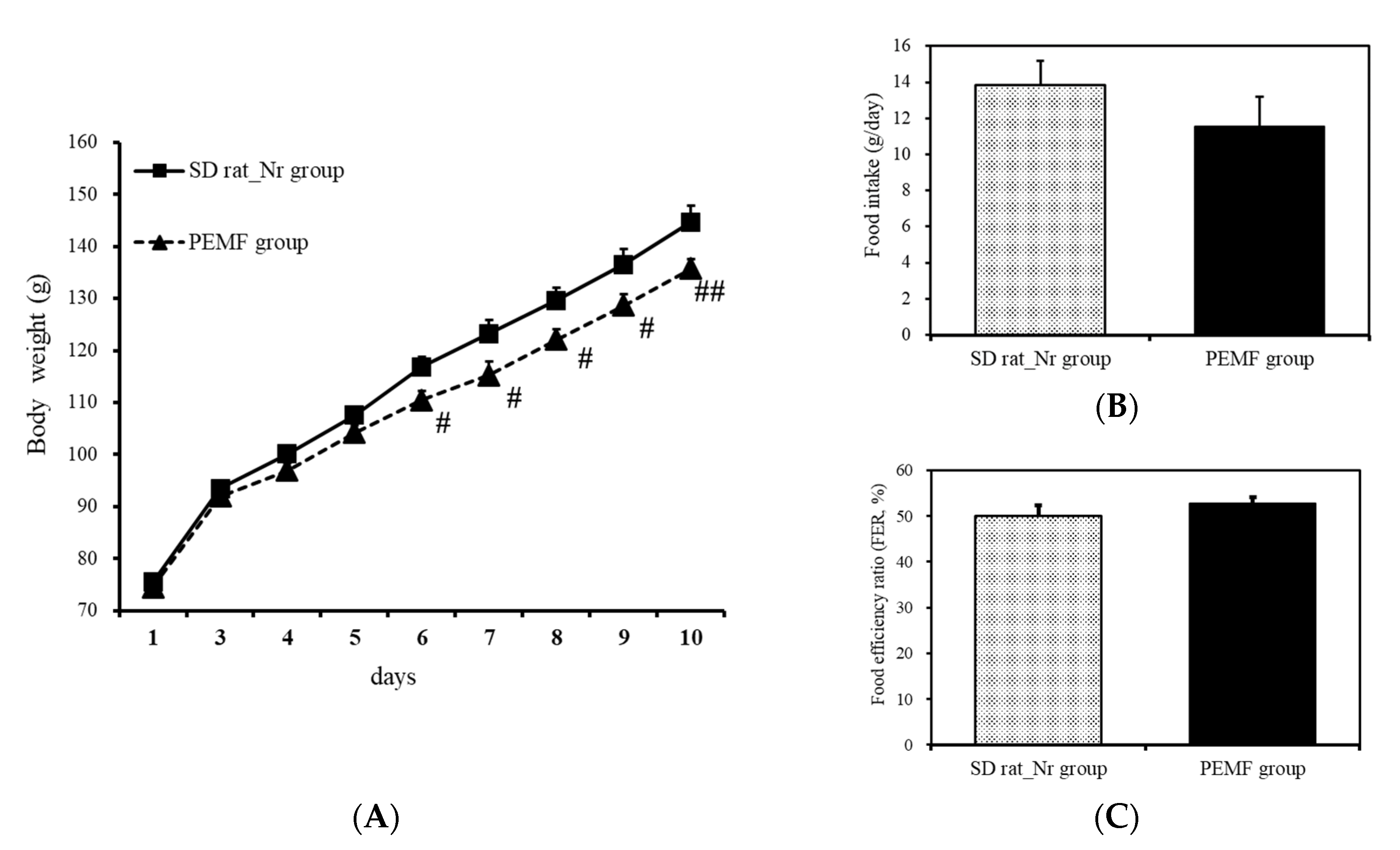
Body weight and food efficiency were measured to determine whether treatment with PEMF influenced food intake. After following up for 10 days, the weight of the normal group increased by 69.25 g from 75.48 ± 1.12 g to 144.73 ± 3.09 g on average, while that of the experimental group increased by 61.18 g from 74.55 ± 0.95 g to 135.73 ± 1.79 g on average, indicating that the PEMF-treated groups exhibited a lower body weight gain than the normal group (Figure 6A).
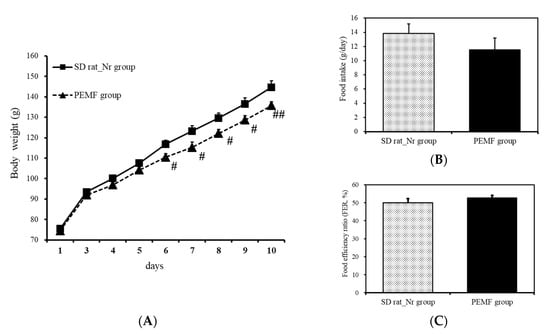
Figure 6.
Body weight and food intakes. (A) Body weight change, (B) food intake, and (C) food efficiency ratio. Results are expressed as means ± SEM (n = 8). # p < 0.05 and ## p < 0.01 compared with the normal group.
Food efficiency was defined as the ratio of the average weight gain to the actual weight of food consumed between the 1st and 10th days. In the normal group, the average daily food intake was 13.83 g and the food efficiency ratio was 50.1%. The daily food intake of the experimental group was 11.57 g, which was 2.26 g less daily than the normal group, but the food efficiency ratio was 52.8%. Despite the low food intake of the experimental group, the food efficiency ratio was 2.7% higher; however, the difference was not statistically significant (Figure 6B,C).
3.3. Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Levels in the Serum
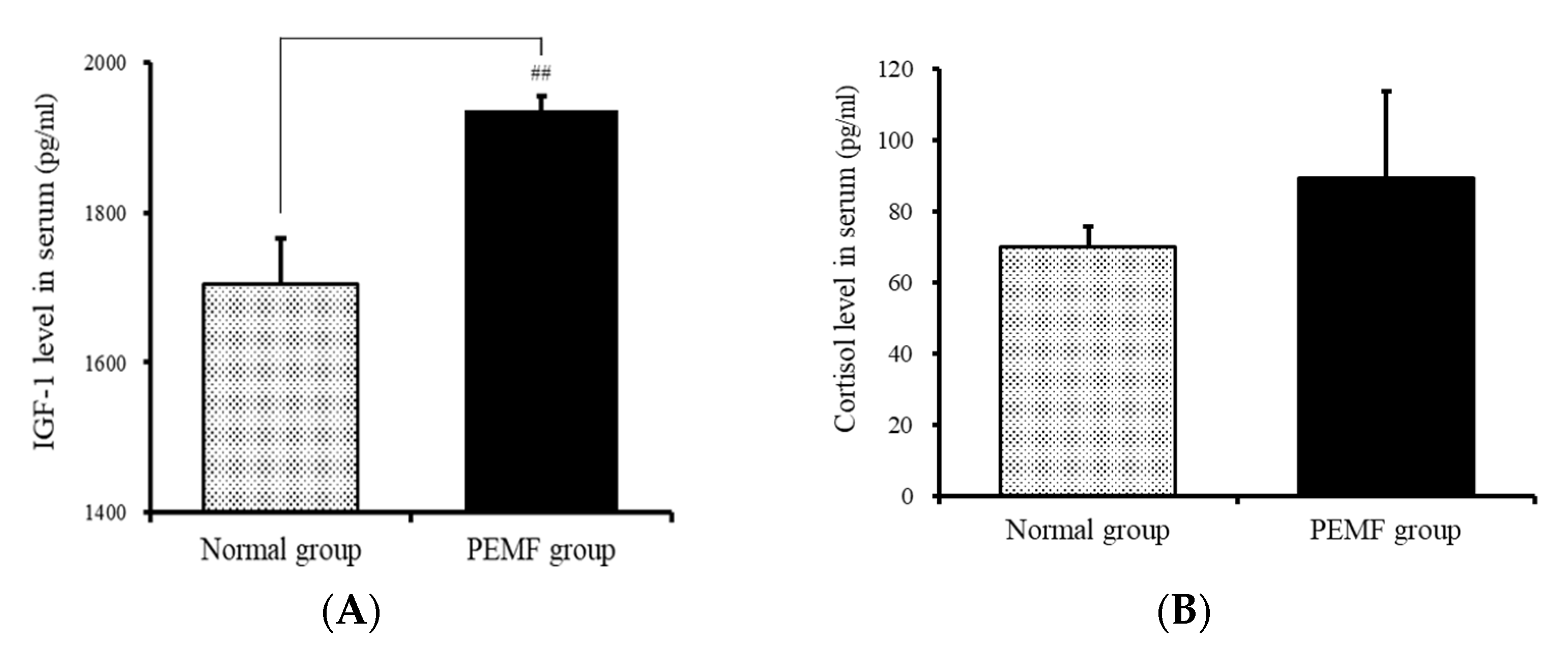
Changes in IGF-1 levels were analyzed. The levels of IGF-1 were 1704.92 ± 60.49 and 1936.9 ± 18.99 pg/mL, respectively, in the normal and experimental groups. Thus, the levels were 13.6% higher in the experimental group than in the normal group (Figure 7A). The levels of cortisol in the normal and experimental groups were 70.08 ± 5.55 and 89.31 ± 24.33 pg/mL, respectively, and the p value was 0.45, indicating no significant difference (Figure 7B).
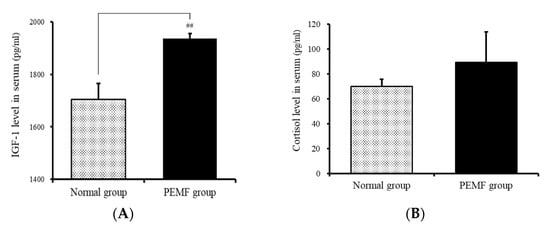
Figure 7.
Effect of PEMF treatment on circulating (A) IGF-1 and (B) cortisol levels in the serum. Results are expressed as means ± SEM (n = 8). ## p < 0.01 compared with the normal group.
3.4. Aspartate Aminotransferase Levels in the Serum
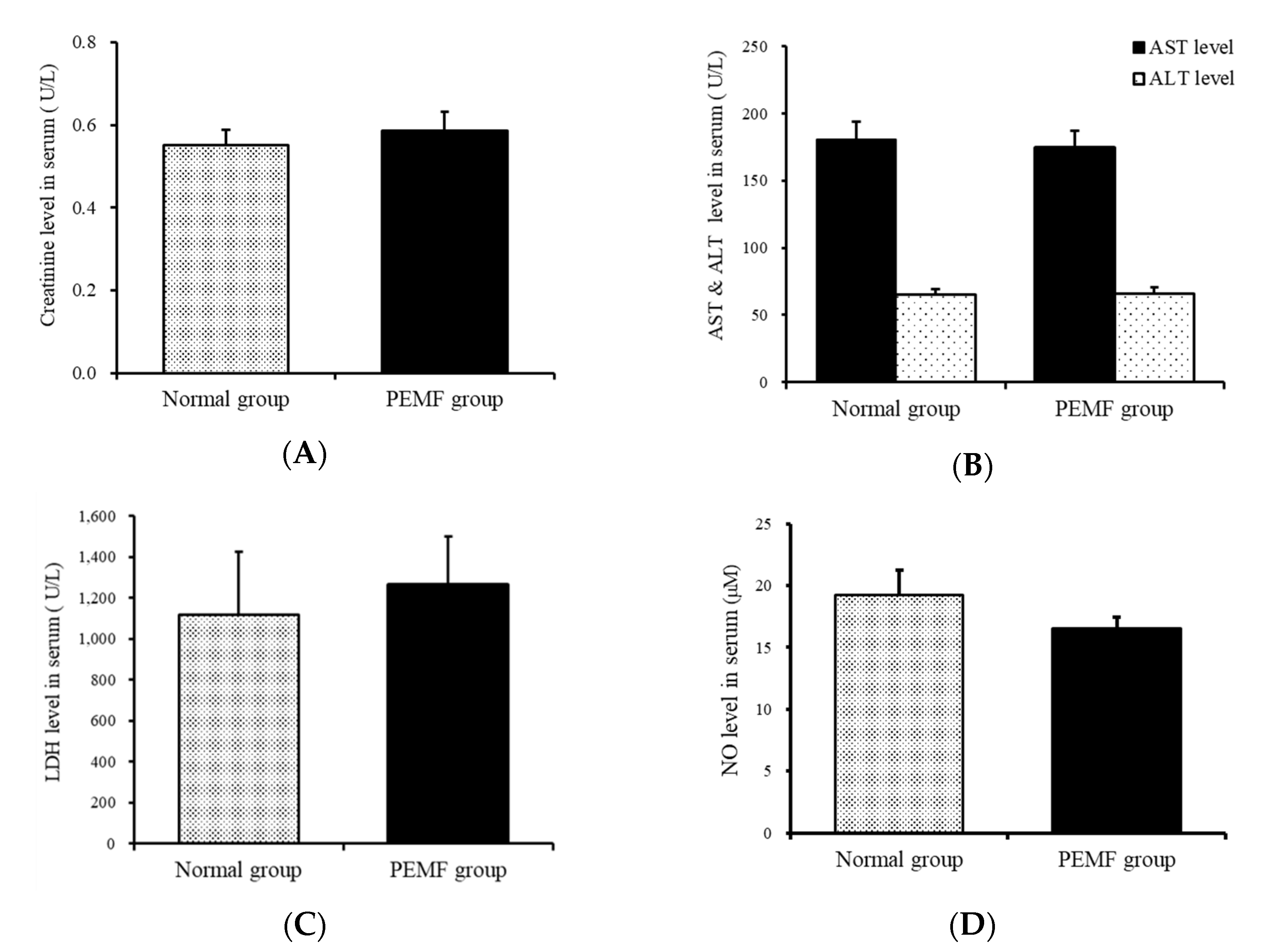
The levels of creatinine, as a renal function marker in the serum, were 0.55 ± 0.44 and 0.59 ± 0.05 U/L in the normal group and the experimental group, respectively, and no significant difference was observed in the levels between the two groups. The AST value, which indicates liver function, was 180.88 ± 4.17 and 174 ± 4.88 U/L in the normal and experimental groups, respectively, with a p value of 0.6, showing no significant difference (Figure 8A,B).
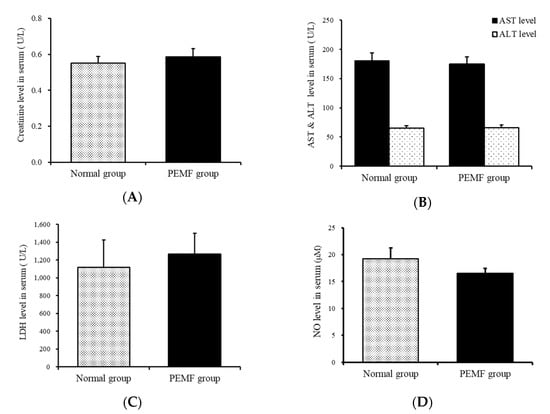
Figure 8.
Effect of PEMF treatment on creatinine, AST, ALT, LDH, and NO levels in the serum. (A) Creatinine, (B) AST and ALT, (C) LDH, and (D) NO levels. Effects of PEMF treatment on kidney and liver function, circulating cell damage, and inhibiting inflammation were evaluated by ELISA and biochemical analysis.
3.5. LDH Levels in the Serum
The levels of LDH in the serum were assessed as a marker of tissue damage. The LDH levels in the normal and experimental groups were 1115.63 ± 308.83 and 1264.71 ± 234.67 U/L, respectively, and the p value was 0.38, indicating no significant difference (Figure 8C).
3.6. NO Levels in the Serum
The NO levels in the serum were 19.23 ± 2.00 pg/mL and 16.50 ± 0.96 U/L in the normal and experimental groups, respectively, and the p value was 0.38, indicating no significant difference (Figure 8D).
4. Discussion
We investigated the effect of PEMF treatment on growth of the tibial growth plate through anatomical observations and blood tests after raising eight rats in the experimental group exposed to a pulsed magnetic field of 28 Hz and 20 Gauss for 10 h for 10 days, in comparison to the normal group.
As for the size of the growth plate, the experimental group exposed to the pulsed magnetic field showed a higher growth rate with a highly significant difference, and the circulating IGF-1 hormone levels also showed a higher serum concentration in the experimental group exposed to a pulsed magnetic field.
Bone elongation is a complex process driven by multiple intrinsic (hormones, growth factors) and extrinsic (nutrition, environment) variables [18]. Because the growth of biological tissues, including bones and growth plates, is closely associated with nutrient supply, it is necessary to determine whether the growth of the growth plate is due to the pulsed magnetic field or the amount of food consumed, if the experimental group is given more food than the normal group. However, as a result of daily tracking of dietary amount and weight, the experimental group had a lower dietary intake than the normal group. Thus, the difference in the growth rate of the growth plate can be inferred as an effect of the pulsed magnetic field. Dietary efficiency was 2% higher in the experimental group, which showed a lower food intake and body weight than the normal group. Considering that the difference between the growth plates between the two groups was 25.6%, it is difficult to say that dietary efficiency also contributed to the difference in the growth rate of the growth plate.
Because growth during childhood is closely regulated by various systemic factors, such as insulin, growth hormone, and IGF-1 [19], the correlation between growth plate growth rate and IGF-1 is also an important basis for judgment. IGF-1, a 70-amino acid peptide biosynthesized mainly in the liver as an endocrine hormone, is both the main mediator of growth hormone action and a growth hormone-independent growth factor that stimulates cell proliferation and differentiation and protects cells from apoptosis [19]. IGF-1 is also expressed in growth plates, where it works in a paracrine/autocrine manner to contribute to longitudinal bone growth [20,21]. Thus, in this study, we evaluated whether PEMFs stimulate circulatory IGF-1, which plays a major role in stimulating bone growth. From the growth plate size comparison result, the serum IGF-1 levels in the PEMF-stimulated experimental group were higher than those in the normal group; thus, it can be inferred that PEMF contributed to growth plate size by promoting the secretion of IGF-1, and a correlation was confirmed. IGF-1 levels increased after stimulation with PEMF despite no dietary changes, enabling growth of the growth plate.
Even if the growth plate, by PEMF stimulation, shows a significant difference and the growth rate is higher, if the pulsed magnetic field damages the living tissue of the rat or causes side effects that cause toxicity, it cannot be concluded that there is a direct effect. Blood analysis revealed that there were no toxic side effects due to PEMF, with creatinine, AST, and ALT values within the normal range. In addition, no side effects from inflammatory reactions, such as cell damage and destruction, by pulsed magnetic fields were observed.
NO is a free radical involved in the regulation of many physiological processes, such as vascular relaxation, platelet aggregation, immune response, and bone cell function [22]. NO has been shown to be a potent stimulator of chondrocyte apoptosis and contributes to cartilage damage in inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis [23]. High levels of NO inhibit bone resorption and formation and may act to suppress bone turnover in severe inflammation. In chondrocytes of articular and growth plate cartilage, NO inhibits collagen and proteoglycan synthesis, increases susceptibility to cell damage by reactive oxygen species, and induces the apoptotic cascade [24]. Another study reported that the effects of PEMF on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation were mediated by an increase in NO synthesis [25]. Thus, we measured NO levels in the serum and did not show a significant difference between the normal and PEMF groups.
In addition, cortisol levels in the serum were measured, and these levels did not change after stimulation with PEMF. Because cortisol is a major rhythm marker of the circadian system, it can be useful to examine the effects of PEMF on cortisol [26]. Exposure to weak high-frequency PEMF (900 MHz and 217 Hz) in healthy humans induced a slight elevation in cortisol production, but this increase was not significant [27].
5. Conclusions
The significant increase in both growth rate and IGF-1 levels in the experimental group of this study was due to the effect of PEMF. In addition, there were no toxic or inflammatory side effects. Thus, although PEMF does not directly contact the skin or act invasively within the tissue, it can safely stimulate the growth plate in a non-invasive manner to promote growth of the growth plate. However, because this study is based on animal experiments, large-scale clinical studies will be required in the future to be applied to the human body. Because the height growth of children and adolescents works in combination with various factors, techniques for analyzing the direct effects of pulsed magnetic fields and precise clinical trial design are required.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.-S.M., J.-W.S., J.-I.K. and E.-M.N.; Methodology, J.-W.S. and S.-H.K.; Validation, S.-H.K.; Investigation, W.-K.Y. and M.-J.K.; Data Curation, W.-K.Y. and M.-J.K.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, Y.-Y.S.; Writing—Review and Editing, Y.-Y.S., M.-Y.Y. and S.-H.K.; Visualization, Y.-Y.S. and S.-H.K.; Supervision, S.-H.K.; Project Administration, J.-W.S.; Funding Acquisition, J.-W.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Gyeonggi-do, Korea, under the “R&D project supporting this invention (R&D, Z2020005)” supervised by the Gyeonggido Business & Science Accelerator (GBSA).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institute of Health, and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Deajeon University (protocol code DJUARB2020-038).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Peltier, L.F. A brief historical note on the use of electricity in the treatment of fracture. Clin. Orthop. 1981, 161, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garratt, A.C. Electrophysiology and Electrotherapeutics; Ticker and Fields: Boston, MA, USA, 1861; p. 657. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Xie, W.; Ye, W.; He, C. Effects of electromagnetic fields on osteoarthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshiwi, A.M.; Hamada, H.A.; Mosaad, D.; Ragab, I.M.A.; Koura, G.M.; Alrawaili, S.M. Effect of pulsed electromagnetic field on nonspecific low back pain patients: A randomized controlled trial. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2019, 23, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadalà, M.; Morales-Medina, J.C.; Vallelunga, A.; Palmieri, B.; Laurino, C.; Iannitti, T. Mechanisms and therapeutic effectiveness of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy in oncology. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3128–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Eerden, B.C.; Karperien, M.; Wit, J.M. Systemic and local regulation of the growth plate. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 782–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Roan, E.; Williams, J.L. Regional variations in growth plate chondrocyte deformation as predicted by three-dimensional multi-scale simulations. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagin, A.S.; Newton, P.T. Postnatal skeletal growth is driven by the epiphyseal stem cell niche: Potential implications to pediatrics. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 87, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Späth, S.S.; Andrade, A.C.; Chau, M.; Nilsson, O. Local regulation of growth plate cartilage. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 21, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, P.T.; Li, L.; Zhou, B.; Schweingruber, C.; Hovorakova, M.; Xie, M.; Sun, X.; Sandhow, L.; Artemov, A.V.; Ivashkin, E.; et al. A radical switch in clonality reveals a stem cell niche in the epiphyseal growth plate. Nature 2019, 567, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallett, S.A.; Ono, W.; Ono, N. Growth Plate Chondrocytes: Skeletal Development, Growth and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lui, J.C. Home for a rest: Stem cell niche of the postnatal growth plate. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 246, R1–R11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mattei, M.; Caruso, A.; Pezzetti, F.; Pellati, A.; Stabellini, V.; Sollazzo, V.; Traina, G.C. Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on human articular chondrocyte proliferation. Connect. Tissue Res. 2001, 42, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzetti, F.; De Mattei, M.; Caruso, A.; Cadossi, R.; Zucchini, P.; Carinci, F.; Traina, G.C.; Sollazzo, V. Effects of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields on Human Chondrocytes: An in vitro Study. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1999, 65, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolfa, S.; Skorvánek, M.; Stolfa, P.; Rosocha, J.; Vasko, G.; Sabo, J. Effects of static magnetic field and pulsed electromagnetic field on viability of human chondrocytes in vitro. Physiol. Res. 2007, 56, S45–S49. [Google Scholar]
- Gierse, H.; Breul, R.; Faensen, M.; Markoll, R. Pulsed signal therapy (PST) stimulates mitosis of human chondrocytes in culture. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Biomedical Engineering; Singapore Humanitas Press: Singapore, 2000; pp. 473–474. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Kim, Y.S.; Song, J.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, H.J.; Guo, H.; Kim, H. Effects of phlomis umbrosa root on longitudinal bone growth rate in adolescent female rats. Molecules 2016, 21, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- L Racine, H.; A Serrat, M. The actions of IGF-1 in the growth plate and its role in postnatal bone elongation. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2020, 18, 210–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat-Yablonski, G.; Phillip, M. Nutritionally-induced catch-up growth. Nutrients 2015, 7, 517–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Song, J.; Kim, H. Astragalus Extract Mixture HT042 Increases Longitudinal Bone Growth Rate by Upregulating Circulatory IGF-1 in Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 6935802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yakar, S.; Rosen, C.J.; Beamer, W.G.; Ackert-Bicknell, C.L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.L.; Ooi, G.T.; Setser, J.; Frystyk, J.; Boisclair, Y.R.; et al. Circulating levels of IGF-1 directly regulate bone growth and density. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, F.J.; Ochs, R.L.; Schwarz, H.; Lotz, M. Chondrocyte apoptosis induced by nitric oxide. Am. J. Pathol. 1995, 146, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van’t Hof, R.J.; Ralston, S.H. Nitric oxide and bone. Immunology 2001, 103, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teixeira, C.C.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Leboy, P.S.; Adams, S.L.; Shapiro, I.M. Nitric oxide-nitric oxide synthase regulates key maturational events during chondrocyte terminal differentiation. Bone 2005, 37, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, P.; Soejima, K.; Ito, G. Nitric oxide mediates the effects of pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation on the osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. Nitric Oxide 2002, 7, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touitou, Y.; Selmaoui, B. The effects of extremely low-frequency magnetic fields on melatonin and cortisol, two marker rhythms of the circadian system. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 14, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mann, K.; Wagner, P.; Brunn, G.; Hassan, F.; Hiemke, C.; Röschke, J. Effects of pulsed high-frequency electromagnetic fields on the neuroendocrine system. Neuroendocrinology 1998, 67, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).