Performance Estimation of Intensity Accumulation Display by Computer-Generated Holograms
Abstract
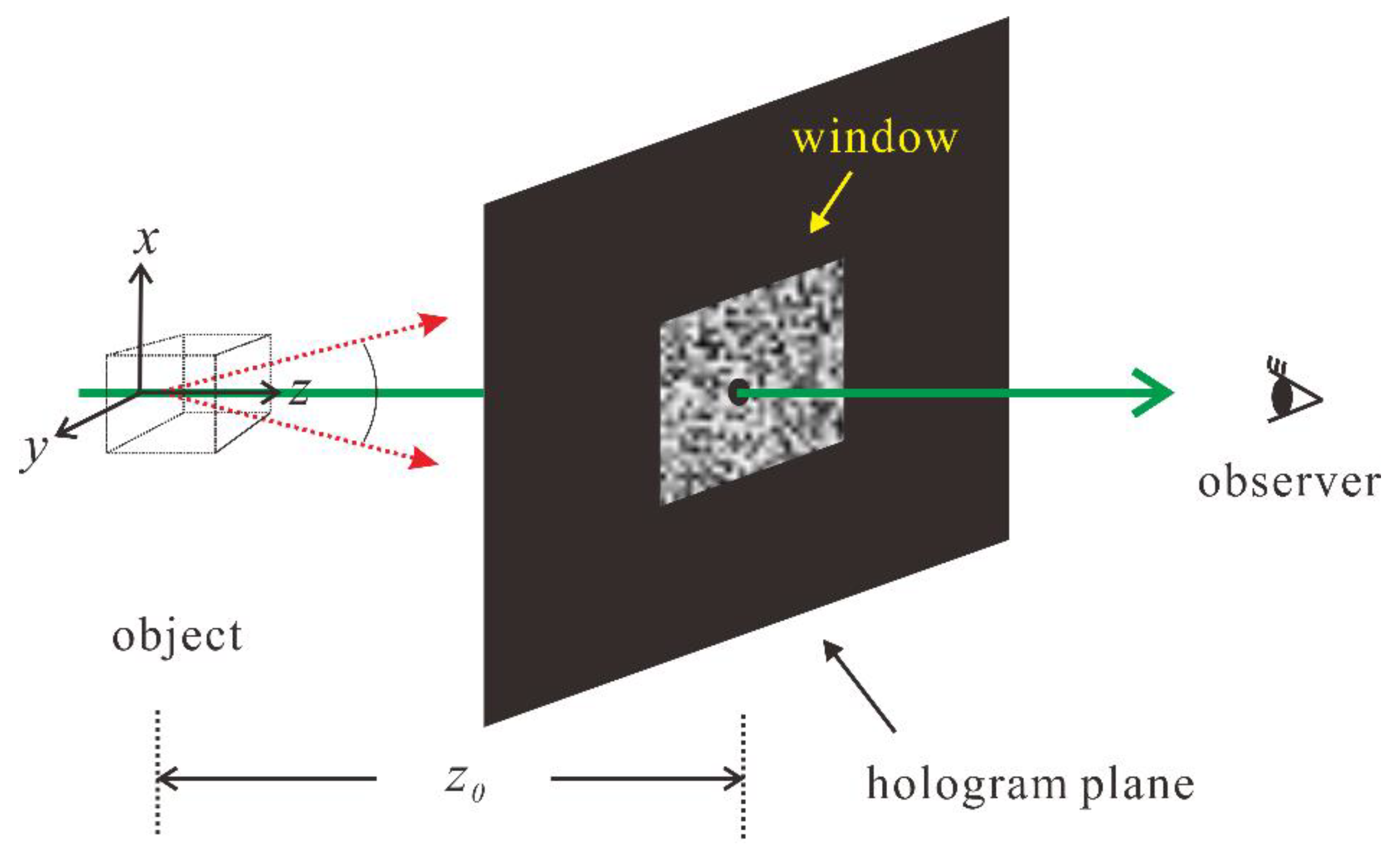
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Binary Computer-Generated Holograms
2.2. Processing of the Object Function
2.3. Noise Model of Intensity Accumulation
3. Simulation
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poon, T.-C. (Ed.) Digital Holography and Three-Dimensional Display; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Takaki, Y.; Yokouchi, M.; Okada, N. Improvement of grayscale representation of the horizontally scanning holographic display. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 24926–24936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaki, Y.; Yokouchi, M. Speckle-free and grayscale hologram reconstruction using time-multiplexing technique. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 7567–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sando, Y.; Barada, D.; Yatagai, T. Full-color holographic 3D display with horizontal full viewing zone by spatiotemporal-division multiplexing. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 7622–7626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, M.; Takada, N.; Araki, H.; Ikawa, S.; Maeda, Y.; Niwase, H.; Oikawa, M.; Kakue, T.; Shimobaba, T.; Ito, T. Color representation method using RGB color binary-weighted computer-generated holograms. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2018, 16, 080901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Shimobaba, T.; Kakue, T.; Ito, T. Time-division color holographic projection in large size using a digital micromirror device. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-P.; Yu, C.-Q.; Tsang, P.W.M. Enhanced direct binary search algorithm for binary computer-generated Fresnel holograms. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 3735–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennison, B.K.; Allebach, J.P.; Sweeney, D.W. Efficient design of direct-binary-search computer-generated holograms. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1991, 8, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seldowitz, M.A.; Allebach, J.P.; Sweeney, D.W. Synthesis of digital holograms by direct binary search. Appl. Opt. 1987, 26, 2788–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, N.; Yatagai, T. Phase optimization of a kinoform by simulated annealing. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Jiao, S.; Liu, J.-P.; Lei, T.; Yuan, X. Error diffusion method with optimized weighting coefficients for binary hologram generation. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 5547–5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheremkhin, P.A.; Kurbatova, E.A.; Evtikhiev, N.N.; Krasnov, V.V.; Rodin, V.G.; Starikov, R.S. Comparative analysis of off-axis digital hologram binarization by error diffusion. J. Opt. 2021, 23, 075703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.; Park, J.-H. Quality enhancement of binary-encoded amplitude holograms by using error diffusion. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 38140–38154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, C.; Gao, Y.; Lei, T.; Yuan, X. Complex-amplitude holographic projection with a digital micromirror device (DMD) and error diffusion algorithm. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 2020, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlipala, M.; Kozacki, T. Color LED DMD holographic display with high resolution across large depth. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 4255–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goorden, S.A.; Bertolotti, J.; Mosk, A.P. Superpixel-based spatial amplitude and phase modulation using a digital micromirror device. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 17999–18009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, K.; Saita, Y.; Toritani, R.; Xia, P.; Nitta, K.; Matoba, O. Improvement of image quality of 3D display by using optimized binary phase modulation and intensity accumulation. J. Display Technol. 2016, 12, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-P.; Wu, M.-H.; Tsang, P.W.M. 3D display by binary computer-generated holograms with localized random down-sampling and adaptive intensity accumulation. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 24526–24537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.-J.; Wang, D.; Li, S.-J.; Wang, Q.-H. Speckle noise suppression method in holographic display using time multiplexing. Opt. Eng. 2017, 56, 063107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Yoo, D.; Jeong, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.; Lee, B. Wide-angle speckleless DMD holographic display using structured illumination with temporal multiplexing. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 2148–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-P. Controlling the aliasing by zero-padding in the digital calculation of the scalar diffraction. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2012, 29, 1956–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, P.; Poon, T.-C.; Cheung, W.K.; Liu, J.-P. Computer generation of binary fresnel holography. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, B88–B95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wyrowski, F.; BryngdahI, O. Iterative fourier-transform algorithm applied to computer holography. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1988, 5, 1058–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Chen, C.-L.; Fiddy, M.A. Iterative procedure for improved computer-generated-hologram reconstruction. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 5135–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, J.W. Speckle Phenomena in Optics: Theory and Applications; Viva Books: New Delhi, India, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.-K.-T.; Chen, X.; Svensen, Ø.; Akram, M.N. Speckle reduction in laser projection using a dynamic deformable mirror. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 11152–11166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, N.; Hennelly, B. Quantization noise and its reduction in lensless fourier digital holography. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, B58–B70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-P.; Lu, S.-L. Fast calculation of high-definition depth-added computer-generated holographic stereogram by spectrum-domain look-up table [Invited]. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, A104–A110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Method | PSNR (dB) at Propagations | PSNR (dB) at Accumulations | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RP | 2.04 | 17.36 | 14.04 | 17.86 | 14.04 | 17.86 | 18.59 |
| MIFA (5 iterations) | 3.11 | 11.4 | 9.13 1 | 16.93 2 | 16.93 | 19.91 | 20.42 |
| MIFA (10 iterations) | 3.27 | 9.55 | NA | 15.21 3 | 16.98 | 19.68 | 20.09 |
| LRDS () | 2.08 | 16.79 | 14.2 | 17.9 | 14.2 | 17.9 | 18.61 |
| LRDS+AIA () | 2.24 4 | 42.4 4 | 12.47 | 20.54 | 16.04 | 21.39 | 23.28 4 |
| 10 | 154 | 92 | 63 | 43 | |
| 15 | 224 | 132 | 92 | 62 | |
| 20 | 294 | 173 | 120 | 81 | |
| 25 | 364 | 213 | 149 | 101 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.-P.; Lin, Y.-C.; Jiao, S.; Poon, T.-C. Performance Estimation of Intensity Accumulation Display by Computer-Generated Holograms. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7729. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11167729
Liu J-P, Lin Y-C, Jiao S, Poon T-C. Performance Estimation of Intensity Accumulation Display by Computer-Generated Holograms. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(16):7729. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11167729
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jung-Ping, Yu-Chih Lin, Shuming Jiao, and Ting-Chung Poon. 2021. "Performance Estimation of Intensity Accumulation Display by Computer-Generated Holograms" Applied Sciences 11, no. 16: 7729. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11167729
APA StyleLiu, J.-P., Lin, Y.-C., Jiao, S., & Poon, T.-C. (2021). Performance Estimation of Intensity Accumulation Display by Computer-Generated Holograms. Applied Sciences, 11(16), 7729. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11167729






