UV Absorption Spectroscopy for the Diffusion of Plasma-Generated Reactive Species through a Skin Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
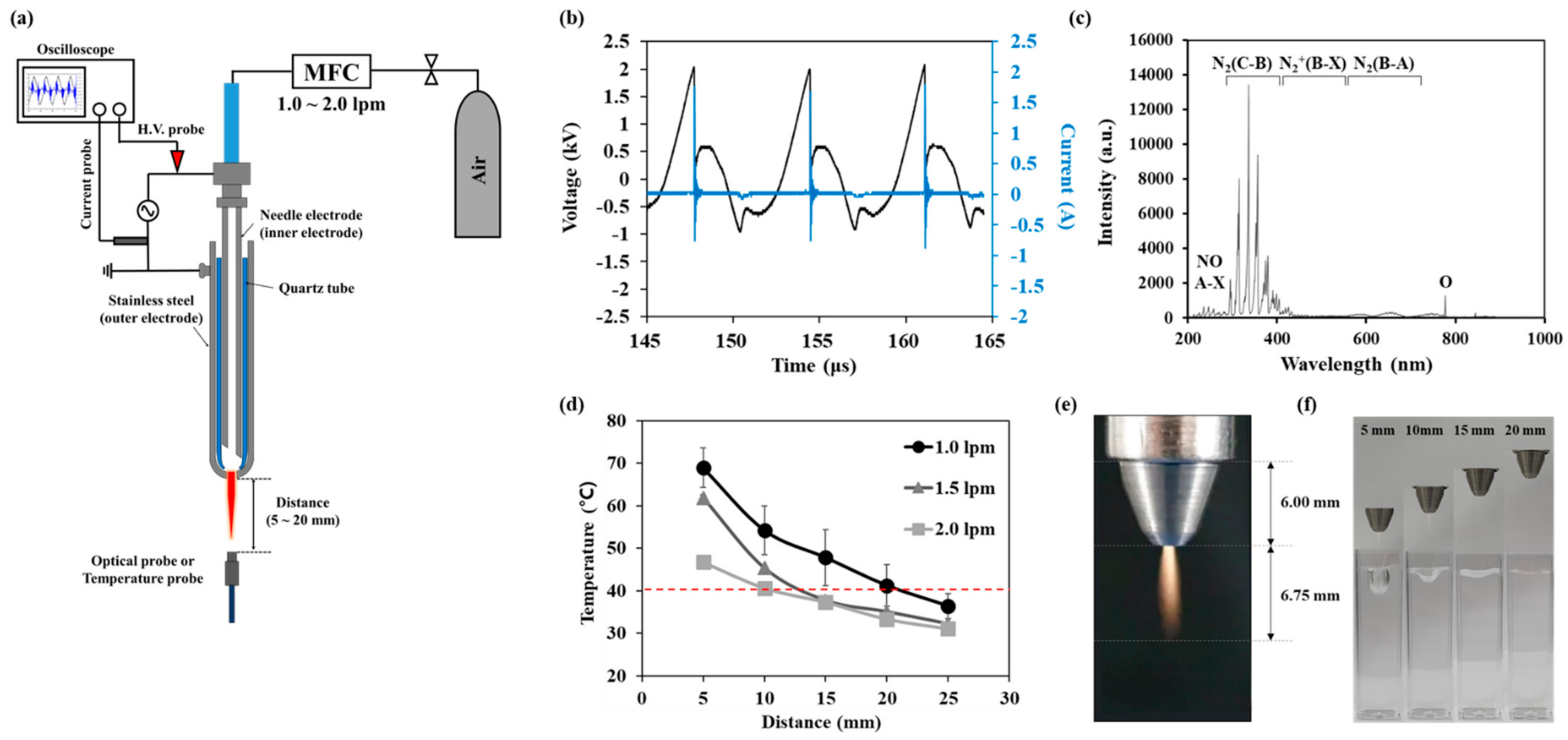
2.1. Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma (NTAPP)
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. UV Absorption Spectroscopy (UVAS)
- At first, fitting the spectrum with H2O2 reference spectrum of a region longer than 245 nm.
- Then, 195 nm to 205 nm region is fitted with the NO3− reference spectrum.
- Finally, the NO2− reference spectrum is used in the range from 205 nm to 215 nm.
2.4. Agarose Tissue Model
2.5. Preparation of the Stratum Corneum (SC) Layer with Lipid Solution and Pig Skin
2.6. Optical Microscopy and Contact Angle Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Electrical and Optical Characteristics of NTAPP
3.2. RONS UV Absorption Spectra Profiles
3.3. Generation of RONS in DI Water by NTAPP Treatment
3.4. Permeation of NTAPP-Generated RONS through Agarose Gel
3.5. Effect of the Stratum Corneum Made of Lipid Extracted from Hacat Cells on the Permeability of RONS
3.6. Effect of a Pig Skin on the Permeability of RONS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A





References
- Ikehara, S.; Sakakita, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Akimoto, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yamagishi, M.; Kim, J.; Ueda, M.; Ikeda, J.-I.; Nakanishi, H.; et al. Plasma Blood Coagulation Without Involving the Activation of Platelets and Coagulation Factors. Plasma Process. Polym. 2015, 12, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Jin, Q.; Zheng, C.; Deng, G.; Yin, S.; Liu, Z. Pulsed cold plasma-induced blood coagulation and its pilot application in stanching bleeding during rat hepatectomy. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2018, 20, 044005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubinova, S.; Zaviskova, K.; Uherkova, L.; Zablotskii, V.; Churpita, O.; Lunov, O.; Dejneka, A. Non-thermal air plasma promotes the healing of acute skin wounds in rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep45183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirpour, S.; Fathollah, S.; Mansouri, P.; Larijani, B.; Ghoranneviss, M.; Tehrani, M.M.; Amini, M.R. Cold atmospheric plasma as an effective method to treat diabetic foot ulcers: A randomized clinical trial. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, K.W.; Moy, R.L.; Fincher, E.F. Advances in plasma skin regeneration. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2008, 7, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, M.; Adhikari, B.; Kaushik, N.; Lee, S.-J.; Kaushik, N.K.; Choi, E.H. Melanoma Growth Analysis in Blood Serum and Tissue Using Xenograft Model with Response to Cold Atmospheric Plasma Activated Medium. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.B.; Seo, I.H.; Chae, M.-W.; Park, J.W.; Choi, E.H.; Uhm, H.S.; Baik, K.Y. Anticancer Activity of Liquid Treated with Microwave Plasma-Generated Gas through Macrophage Activation. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 2946820-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, V.; Yadav, P. Transdermal drug delivery system: An overview. Asian J. Pharm. 2012, 6, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, P.; Cross, S. Transdermal drug delivery: Basic principles for the veterinarian. Vet. J. 2006, 172, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.G.; Kim, J.H.; Jo, S.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Won, C.H. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Prevents Wrinkle Formation via an Antiaging Process. Plasma Med. 2020, 10, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, J.-K.; Hong, J.-W.; Kim, G.-C. Low-temperature atmospheric plasma increases the expression of anti-aging genes of skin cells without causing cellular damages. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2013, 305, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fubini, B.; Hubbard, A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) generation by silica in in-flammation and fibrosis. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.D.; Ridnour, L.A.; Isenberg, J.S.; Flores-Santana, W.; Switzer, C.H.; Donzelli, S.; Hussain, P.; Vecoli, C.; Paolocci, N.; Ambs, S.; et al. The chemical biology of nitric oxide: Implications in cellular signaling. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uhm, H.S.; Ki, S.H.; Baik, K.Y.; Choi, E.H. Influence of oxygen on generation of reactive chemicals from nitrogen plasma jet. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarani, A.; Nikiforov, A.; Leys, C. Atmospheric pressure plasma jet in Ar and Ar/H2O mixtures: Optical emission spectroscopy and temperature measurements. Phys. Plasmas 2010, 17, 063504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naidis, G.V. Production of active species in cold helium–air plasma jets. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2014, 23, 065014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietz, A.M.; Kushner, M.J. Air plasma treatment of liquid covered tissue: Long timescale chemistry. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 425204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlackt, C.C.W.; Van Boxem, W.; Bogaerts, A. Transport and accumulation of plasma generated species in aqueous solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 6845–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Gan, L.; Nie, L.; Sun, F.; Lu, X.; He, G. On the penetration of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species generated by a plasma jet into and through mice skin with/without stratum corneum. Phys. Plasmas 2019, 26, 043504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Koga, K.; Shiratani, M. Experimental identification of the reactive oxygen species transported into a liquid by plasma irradiation. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 59, 110502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Yang, Y.; Duan, J.; Sun, F.; Lu, X.P.; He, G. Effect of tissue thickness and liquid composition on the penetration of long-lifetime reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) generated by a plasma jet. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 345204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.-S.; Szili, E.J.; Gaur, N.; Hong, S.H.; Furuta, H.; Kurita, H.; Mizuno, A.; Hatta, A.; Short, R.D. How to assess the plasma delivery of RONS into tissue fluid and tissue. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 304005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.-S.; Szili, E.J.; Ogawa, K.; Short, R.; Ito, M.; Furuta, H.; Hatta, A. UV–vis spectroscopy study of plasma-activated water: Dependence of the chemical composition on plasma exposure time and treatment distance. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 57, 0102B9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Liu, D.; He, T.; Guo, L.; Xu, D.; Kong, M. Quantifying the concentration and penetration depth of long-lived RONS in plasma-activated water by UV absorption spectroscopy. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 015014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrynin, D.; Fridman, G.; Friedman, G.; Fridman, A.A. Deep Penetration into Tissues of Reactive Oxygen Species Generated in Floating-Electrode Dielectric Barrier Discharge (FE-DBD): An In Vitro Agarose Gel Model Mimicking an Open Wound. Plasma Med. 2012, 2, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szili, E.J.; Bradley, J.; Short, R. A ‘tissue model’ to study the plasma delivery of reactive oxygen species. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 152002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Liu, D.; Xu, H.; Liu, Z.; Xu, D.; Li, D.; Li, Q.; Rong, M.; Kong, M. A ‘tissue model’ to study the barrier effects of living tissues on the reactive species generated by surface air discharge. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 205204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szili, E.J.; Oh, J.-S.; Hong, S.H.; Hatta, A.; Short, R. Probing the transport of plasma-generated RONS in an agarose target as surrogate for real tissue: Dependency on time, distance and material composition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 202001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakaki, T.; Miyake, T.; Hirakawa, T.; Sakugawa, H. pH Dependent Photoformation of Hydroxyl Radical and Absorbance of Aqueous-Phase N(III) (HNO2and NO2-). Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2561–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riordan, E.; Minogue, N.; Healy, D.; O’Driscoll, P.; Sodeau, J.R. Spectroscopic and Optimization Modeling Study of Nitrous Acid in Aqueous Solution. J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasio, C.; Chu, L. Photochemistry of Nitrous Acid (HONO) and Nitrous Acidium Ion (H2ONO+) in Aqueous Solution and Ice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, J.S.; Marley, N.A.; Cunningham, M.M. Measurement of the absorption constants for nitrate in water between 270 and 335 nm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, R.B.; McLane, C.K.; Oldenberg, O. Ultraviolet Absorption Spectrum of Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adosraku, R.K.; Choi, G.T.; Constantinou-Kokotos, V.; Anderson, M.M.; Gibbons, W.A. NMR lipid profiles of cells, tissues, and body fluids: Proton NMR analysis of human erythrocyte lipids. J. Lipid Res. 1994, 35, 1925–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focus, A.; King, B.Y.M. Focus on Plasma: The application of plasma devices in aesthetic medicine. PMFA J. 2017, 4, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Z. Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasmas (CAPs) for Skin Wound Healing. In Plasma Medicine-Concepts and Clinical Applicaions; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernhardt, T.; Semmler, M.L.; Schäfer, M.; Bekeschus, S.; Emmert, S.; Boeckmann, L. Plasma Medicine: Applications of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma in Dermatology. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xaubet, M.; Giuliani, L.; Grondona, D.; Minotti, F. Experimental and theoretical study of an atmospheric air plasma-jet. Phys. Plasmas 2017, 24, 013502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westblom, U.; Agrup, S.; Aldén, M.; Cederbalk, P. Detection of nitrogen atoms in flames using two-photon laser-induced fluorescence and investigations of photochemical effects. Appl. Opt. 1991, 30, 2990–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, M.S.; Tiede, R.; Gavenis, K.; Daeschlein, G.; Bussiahn, R.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Emmert, S.; Von Woedtke, T.; Ahmed, R. Introduction to DIN-specification 91315 based on the characterization of the plasma jet kINPen® MED. Clin. Plasma Med. 2016, 4, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirc, E.; Balosetti, B.; Miklavčič, D.; Reberšek, M. Electronic Emulator of Biological Tissue as an Electrical Load during Electroporation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, B.; Szili, E.J.; Lamichhane, P.; Short, R.D.; Lim, J.S.; Attri, P.; Masur, K.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Hong, S.-H.; Choi, E.H. The role of UV photolysis and molecular transport in the generation of reactive species in a tissue model with a cold atmospheric pressure plasma jet. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 093701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kruszelnicki, J.A.; Lietz, A.M.; Kushner, M.J. Atmospheric pressure plasma activation of water droplets. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 355207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasper, J.M.; Iii, C.A.C.; Cooper, C.D. Control of Nitrogen Oxide Emissions by Hydrogen Peroxide-Enhanced Gas-Phase Oxidation of Nitric Oxide. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1996, 46, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garaix, G.; Horne, G.P.; Venault, L.; Moisy, P.; Pimblott, S.M.; Marignier, J.; Mostafavi, M. Decay Mechanism of NO3• Radical in Highly Concentrated Nitrate and Nitric Acidic Solutions in the Absence and Presence of Hydrazine. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 5008–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, J.; Ma, M.; Yusupov, M.; Cordeiro, R.M.; Lu, X.; Bogaerts, A. The penetration of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species across the stratum corneum. Plasma Process. Polym. 2020, 17, 202000005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeDuc, M.; Guay, D.; Leask, R.; Coulombe, S. Cell permeabilization using a non-thermal plasma. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 115021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasopoulos, D.; Svarnas, P.; Gerakis, A. Cold plasma bullet influence on the water contact angle of human skin surface. J. Electrost. 2019, 102, 103378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbrecht, M. Detection of contamination in DNA and protein samples by photometric measurements. Appl. Note 2013, 279, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, M.C.; Yusupov, M.; Cordeiro, R.M.; Bogaerts, A. Unraveling the permeation of reactive species across nitrated membranes by computer simulations. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakel, Z.; Nunes, C.; Lima, S.; Reis, S. Development of a novel human stratum corneum model, as a tool in the optimization of drug formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, T.; Neubert, R.H. State of the Art in Stratum Corneum Research. Part II: Hypothetical Stratum Corneum Lipid Matrix Models. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 33, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Equation Number | Reaction |
|---|---|
| (1) | OH + OH + M → H2O2 + M |
| (2) | HO2 + HO2 → H2O2 +O2 |
| (3) | H2O2 + O → HO2 + OH |
| (4) | HO2 + H2O2 → OH + H2O + O2 |
| (5) | H2O2 + H → OH + H2O |
| (6) | NO + OH → HNO2 |
| (7) | HNO2 + OH → H2O + NO2 |
| (8) | NO + HO2 → OH + NO2 |
| (9) | NO2 + H → OH + NO |
| (10) | HNO3 + NH2 → NH3 + NO3 |
| (11) | NH3 + NO3 → HNO3 + NH2 |
| (12) | NO2 + OH → HNO3 |
| (13) | HNO3 + OH → H2O + NO3 |
| (14) | NO2− + O3 → NO3− + O2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ki, S.H.; Masur, K.; Baik, K.Y.; Choi, E.H. UV Absorption Spectroscopy for the Diffusion of Plasma-Generated Reactive Species through a Skin Model. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11177958
Ki SH, Masur K, Baik KY, Choi EH. UV Absorption Spectroscopy for the Diffusion of Plasma-Generated Reactive Species through a Skin Model. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(17):7958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11177958
Chicago/Turabian StyleKi, Se Hoon, Kai Masur, Ku Youn Baik, and Eun Ha Choi. 2021. "UV Absorption Spectroscopy for the Diffusion of Plasma-Generated Reactive Species through a Skin Model" Applied Sciences 11, no. 17: 7958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11177958
APA StyleKi, S. H., Masur, K., Baik, K. Y., & Choi, E. H. (2021). UV Absorption Spectroscopy for the Diffusion of Plasma-Generated Reactive Species through a Skin Model. Applied Sciences, 11(17), 7958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11177958







