Effect of Plasma Surface Modification on Print Quality of Biodegradable PLA Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Plasma Treatment
2.3. Testing of Selected Film Properties before and after Plasma Treatment
2.4. Flexographic Printing Process
2.5. Evaluation of Prints
3. Results and Discussion
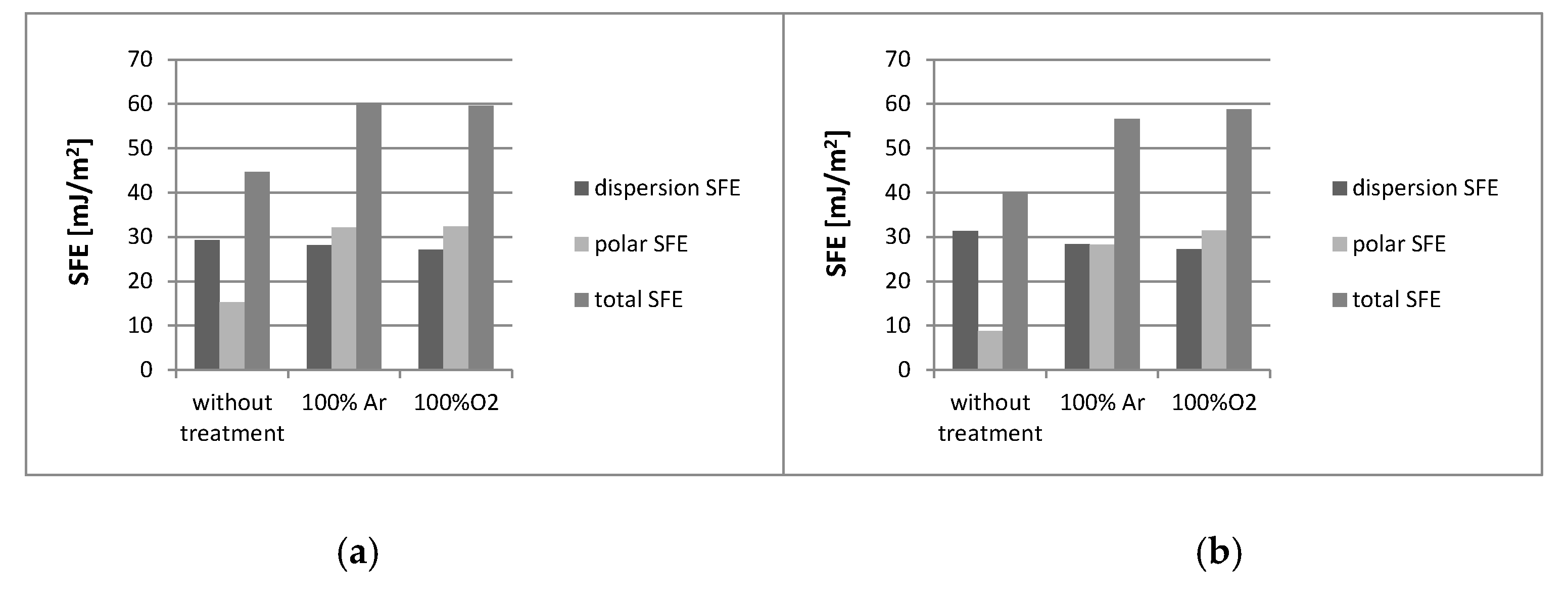
3.1. Effect of Plasma Activation on Film Properties That Can Affect Printability
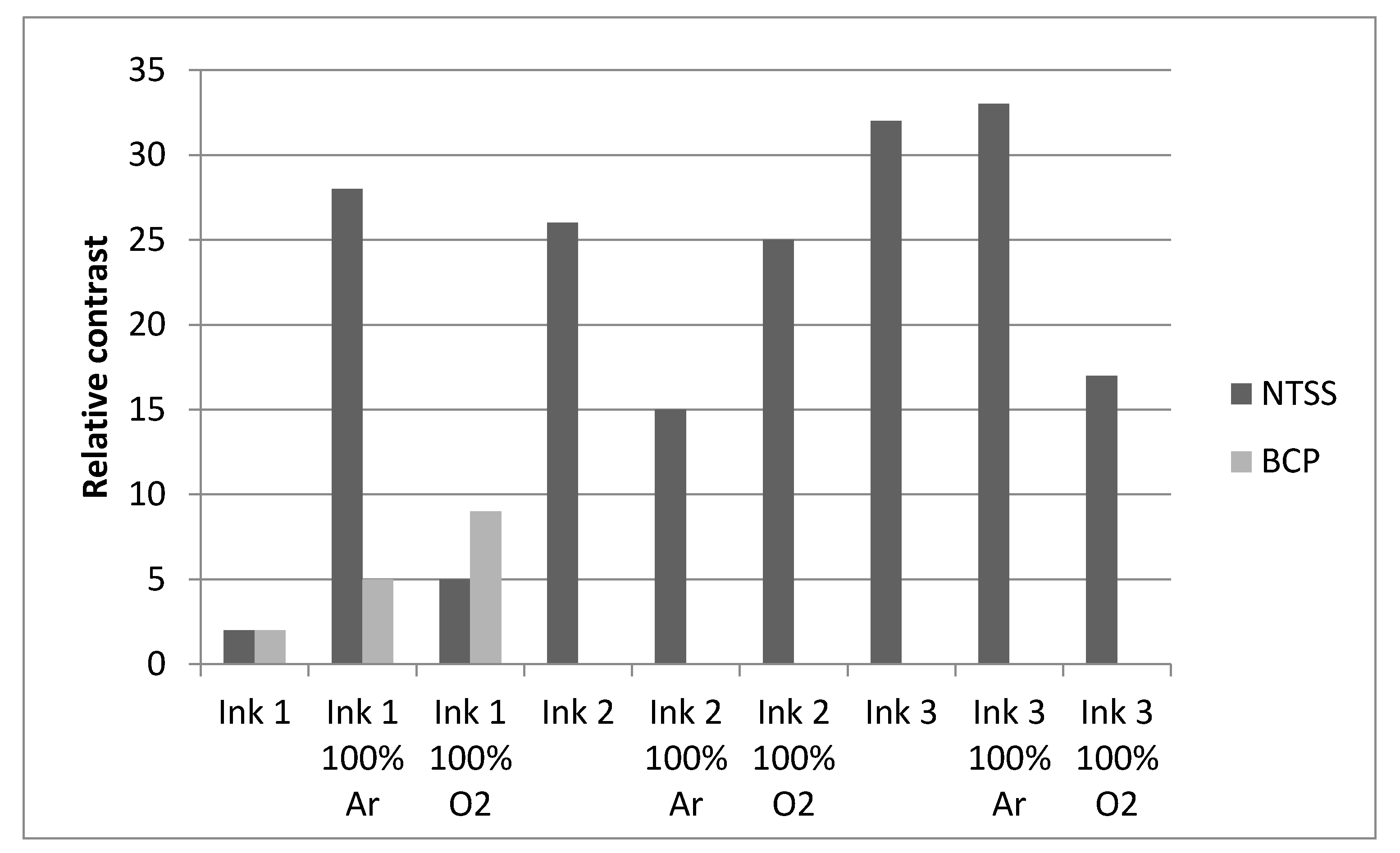
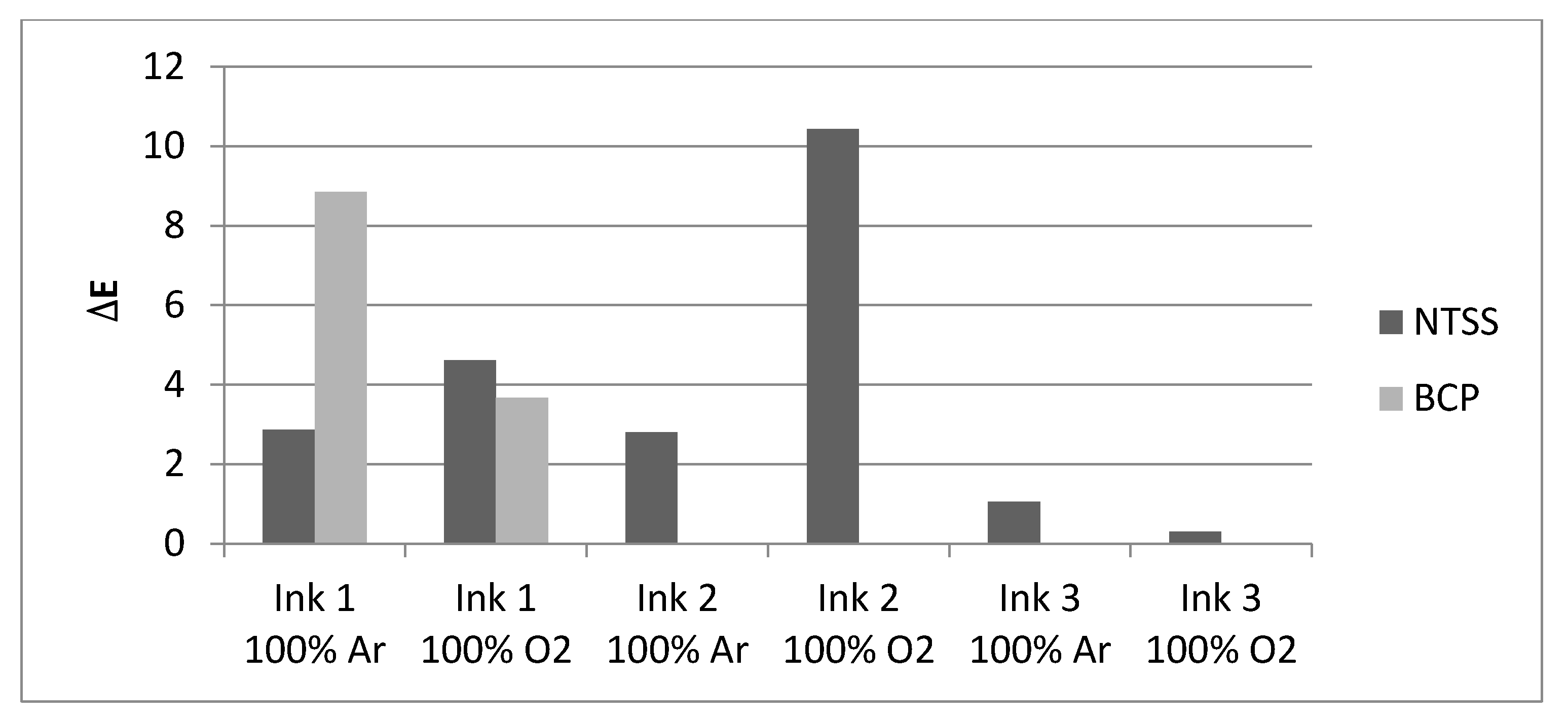
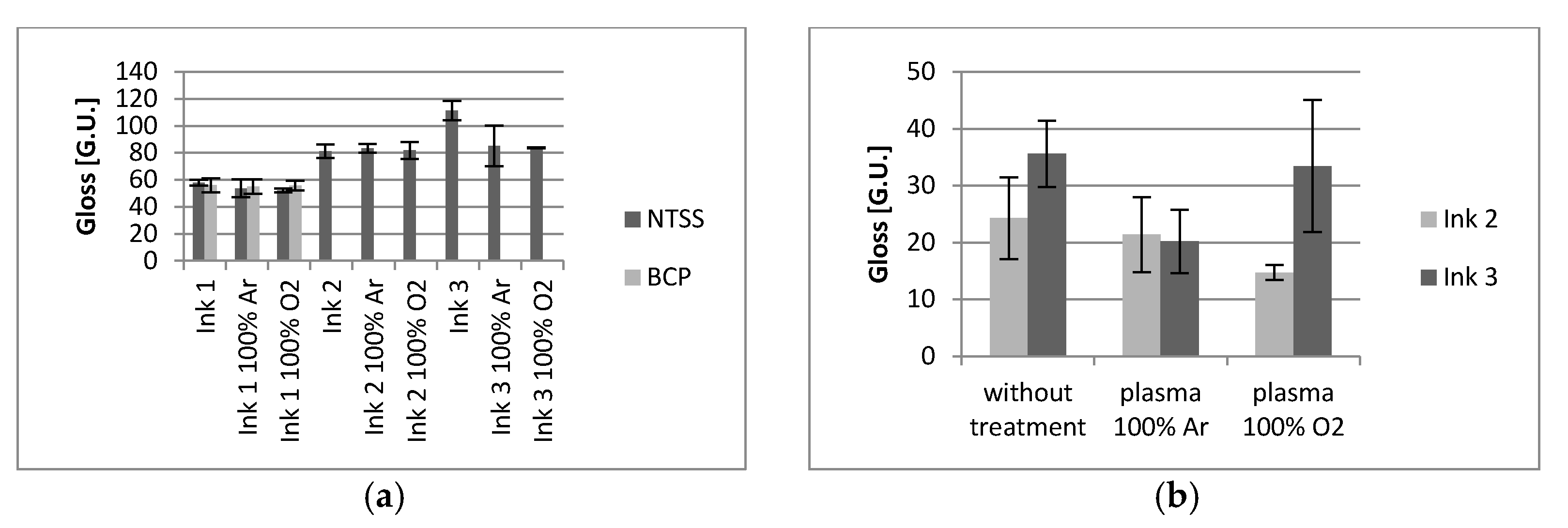
3.2. Effect of Plasma Activation on Print Quality
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rujnić-Sokele, M.; Pilipović, A. Challenges and opportunities of biodegradable plastics: A mini review. Waste Manag. Res. J. A Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2017, 35, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narancic, T.; O’Connor, K.E. Plastic waste as a global challenge: Are biodegradable plastics the answer to the plastic waste problem? Microbiology 2019, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiciotto, L.; Rothenberg, G. Biodegradable Plastics: Standards, Policies, and Impacts. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nofar, M. PLA binary bioblends with other biopolymers. In Multiphase Polylactide Blends, 1st ed.; Nofar, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 157–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, G.; Auras, R.; Singh, S.P. Comparison of the degradability of poly(lactide) packages in composting and ambient exposure conditions. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2007, 20, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamiński, M.Ł.; Novák, I.; Mičušík, M.; Małolepszy, A.; Toczyłowska-Mamińska, R. Discharge Plasma Treatment as an Efficient Tool for Improved Poly(lactide) Adhesive–Wood Interactions. Materials 2021, 14, 3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipphan, H. (Ed.) Handbook of Print Media. Technologies and Production Methods, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebska, J. Chapter 11—Flexographic Printing. In Printing on Polymers, 1st ed.; Izdebska, J., Thomas, S., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.-W. Processes for environmentally friendly and/or cost-effective manufacturing. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2021, 36, 987–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattner, M.; Bohn, D. Chapter 20 - Characterization of Print Quality in Terms of Colorimetric Aspects. In Printing on Polymers, 1st ed.; Izdebska, J., Thomas, S., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J. Aspects of Flexographic Print Quality and Relationship to some Printing Parameters. Ph.D. Thesis, Karlstad University, Karlstad, Sweden, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, I.; Zjakic, I.; Budimir, I. Assessment of the print quality parameters’ impact on the high-quality flexographic print visual experience. Imaging Sci. J. 2015, 63, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentzhog, M.; Fogden, A. Print quality and resistance for water-based flexography on polymer-coated boards: Dependence on ink formulation and substrate pretreatment. Prog. Org. Coat. 2006, 57, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żołek-Tryznowska, Z.; Rombel, M.; Petriaszwili, G.; Dedijer, S.; Kašiković, N. Influence of Some Flexographic Printing Process Conditions on the Optical Density and Tonal Value Increase of Overprinted Plastic Films. Coatings 2020, 10, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebska, J. Evaluation of Quality of Flexographic Print on Selected Biodegradable Films. Ph.D. Thesis, Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Izdebska-Podsiadły, J. Chapter 6—Application of Plasma in Printed Surfaces and Print Quality. In Non-Thermal Plasma Technology for Polymeric Materials; Thomas, S., Mozetič, M., Cvelbar, U., Špatenka, P., Praveen, K.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 159–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Hou, W. Correlations of surface free energy and solubility parameters for solid substances. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 544, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, J. Chapter 10—Wettability Analysis and Water Absorption Studies of Plasma Activated Polymeric Materials. In Non-Thermal Plasma Technology for Polymeric Materials; Thomas, S., Mozetič, M., Cvelbar, U., Špatenka, P., Praveen, K.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2019; pp. 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Geyter, N.; Morent, R. Chapter 7—Cold plasma surface modification of biodegradable polymer biomaterials. In Biomaterials for Bone Regeneration; Dubruel, P., Van Vlierberghe, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 202–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraczewski, K.; Rytlewski, P.; Malinowski, R.; Żenkiewicz, M. Comparison of some effects of modification of a polylactide surface layer by chemical, plasma, and laser methods. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 346, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebska-Podsiadły, J. The influence of the operating parameters of the plasma activator on improvement of PLA film wettability. Opakowanie 2017, 10, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Izdebska-Podsiadły, J. Impact of low-temperature plasma treatment parameters on wettability and printability of PLA film. Int. Circ. Graph. Educ. Res. 2020, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mozetič, M. Surface Modification to Improve Properties of Materials. Materials 2019, 12, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vesel, A.; Mozetič, M. Chapter 7—Low-Pressure Plasma-Assisted Polymer Surface Modifications. In Printing on Polymers, 1st ed.; Izdebska, J., Thomas, S., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, W.T.; Bousfield, D.W.; Kettle, J.; Aspler, J. Influence of ink chemistry and surface energy on flexographic print quality. In TAPPI 11th Advanced Coating Fundamentals Symposium, Proceedings of the The Latest Advances in Coating Research and Development, Munich, Germany, 11–13 October 2010; TAPPI Press: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2010; pp. 309–332. [Google Scholar]
- Mesic, B.; Lestelius, M.; Engström, G. Influence of corona treatment decay on print quality in water-borne flexographic printing of low-density polyethylene-coated paperboard. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2006, 19, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domińczuk, J.; Krawczuk, A. Comparison of Surface Free Energy Calculation Methods. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 791, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, F.A.; Elsayad, S.Y.; Bakry, A.; Eid, M.A. Surface properties and printability of polypropylene film treated by an air dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Surf. Coat. Int. Part B Coat. Transactions. 2006, 89, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebska-Podsiadły, J.; Dörsam, E. Effects of argon low temperature plasma on PLA film surface and aging behaviors. Vacuum 2017, 145, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebska-Podsiadły, J.; Dörsam, E. Storage stability of the oxygen plasma-modified PLA film. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2021, 44, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque-Agudo, V.; Hierro-Oliva, M.; Gallardo-Moreno, A.M.; González-Martín, M.L. Effect of plasma treatment on the surface properties of polylactic acid films. Polym. Test. 2021, 96, 107097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankaj, S.K.; Bueno-Ferrer, C.; Misra, N.N.; O’Neill, L.; Jiménez, A.; Bourke, P.; Cullen, P.J. Characterization of polylactic acid films for food packaging as affected by dielectric barrier discharge atmospheric plasma. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 21, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Żenkiewicz, M.; Rytlewski, P.; Malinowski, R. Compositional, physical and chemical modification of polylactide. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2010, 43, 192–199. [Google Scholar]
- Moraczewski, K.; Stepczyńska, M.; Malinowski, R.; Rytlewski, P.; Jagodziński, B.; Żenkiewicz, M. Stability studies of plasma modification effects of polylactide and polycaprolactone surface layers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 377, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordá-Vilaplana, A.; Fombuena, V.; García-García, D.; Samper, M.D.; Sánchez-Nácher, L. Surface modification of polylactic acid (PLA) by air atmospheric plasma treatment. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 58, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.C.; Masuoka, T. Degradation properties of PLA and PHBV films treated with CO2-plasma. React. Funct. Polym. 2009, 69, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, N.; Narushima, K.; Tsutsui, Y.; Ohyama, Y. Surface modification and degradation of poly(lactic acid) films by Ar-plasma. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2002, 16, 1041–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, N.; Narushima, K.; Lim, S.K. Effects of aromatic groups in polymer chains on plasma surface modification. Inc. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.Y.; Oh, Y.A.; Roh, S.H.; Kim, J.K.; Min, S.C. Cold Oxygen Plasma Treatments for the Improvement of the Physicochemical and Biodegradable Properties of Polylactic Acid Films for Food Packaging. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, E86–E96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwong, C.; Rachtanapun, P.; Wongchaiya, P.; Auras, R.; Boonyawan, D. Effect of plasma treatment on hydrophobicity and barrier property of polylactic acid. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 2933–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetto, E.; Jury, C.; Igos, E.; Carton, J.; Hild, P.; Vergne, C.; Di Martino, J. Using atmospheric plasma to design multilayer film from polylactic acid and thermoplastic starch: A screening Life Cycle Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laput, O.; Vasenina, I.; Salvadori, M.C.; Savkin, K.; Zuza, D.; Kurzina, I. Low-temperature plasma treatment of polylactic acid and PLA/HA composite material. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 11726–11738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Geyter, N.; Morent, R.; Desmet, T.; Trentesaux, M.; Gengembre, L.; Dubruel, P.; Leys, C.; Payen, E. Plasma modification of polylactic acid in a medium pressure DBD. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 3272–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demina, T.S.; Piskarev, M.S.; Shpichka, A.I.; Gilman, A.B.; Timashev, P.S. Wettability and aging of polylactide films as a function of AC-discharge plasma treatment conditions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1492, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, I.; Popelka, A.; Luyt, A.S.; Chehimi, M.M.; Špírková, M.; Janigová, I.; Kleinová, A.; Stopka, P.; Šlouf, M.; Vanko, V.; et al. Adhesive properties of polyester treated by cold plasma in oxygen and nitrogen atmospheres. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 235, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Qu, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wan, L.; Yang, J.; Bei, J.; Wang, S. Characterization of surface property of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) after oxygen plasma treatment. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4777–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahouli, A.; Sylvestre, A.; Laithier, J.-F.; Pairis, S.; Garden, J.-L.; André, E.; Jomni, F.; Yangui, B. Effect of O2, Ar/H2 and CF4 plasma treatments on the structural and dielectric properties of parylene-C thin films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 215306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Fina, A.; Venturello, A.; Geobaldo, F. Effects of gas atmospheres on poly(lactic acid) film in acrylic acid plasma treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 283, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiącek, A.E.; Terpiłowski, K.; Jurak, M.; Worzakowska, M. Effect of low-temperature plasma on chitosan-coated PEEK polymer characteristics. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 78, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Herrmann, A.; Dohse, A.; Borris, J.; Weidlich, E.-R. Printing of µm structures with nano inks using a novel combination of high-resolution plasma printing and subsequent rotogravure printing. Plasma Process. Polym. 2019, 16, 1900080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, R.R.; Bhat, N.V. The mechanism of adhesion and printability of plasma processed PET films. Mater. Res. Innovat. 2003, 7, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, U.; Ahmed, H.; Al-Halwagy, A.; Garamoon, A. Surface characteristics and printing properties of PET fabric treated by atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 45, 11001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.W. The use of plasma pre-treatment for enhancing the performance of textile ink-jet printing. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2007, 21, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuntapichedkul, B.; Tantayanon, S.; Laohhasurayotin, K. Practical approach in surface modification of biaxially oriented polypropylene films for gravure printability. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 314, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, J.; Keif, M.; Rong, X.; Singh, J.; Vorst, K. Flexography Printing Performance of PLA Film. J. Appl. Packag. Res. 2009, 3, 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, X.; Keif, M. A Study of PLA Printability with Flexography. TAGA Proc. 2007, 605–613. [Google Scholar]
- Ataeefard, M. Study of PLA Printability with Flexography Ink: Comparison with Common Packaging Polymer. Prog. Color. Colorants Coat. 2019, 12, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Hansuebsai, A.; Nawakitwong, S. Printability Analysis of Compostable Films by Flexographic Water Based Ink. Key Eng. Mater. 2020, 843, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebska, J. Chapter 1—Printing on Polymers: Theory and Practice. In Printing on Polymers, 1st ed.; Izdebska, J., Thomas, S., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Żołek-Tryznowska, Z. Chapter 6—Rheology of printing inks, In Printing on Polymers, 1st ed.; Izdebska, J., Thomas, S., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Kuvaldina, E.V.; Rybkin, V.V.; Titov, V.A.; Shikova, T.G.; Shutov, D.A. Oxidation and Degradation of Polypropylene in an Oxygen Plasma. High. Energy Chem. 2004, 38, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busscher, H.J.; van Pelt, A.W.J.; de Boer, P.; de Jong, H.P.; Arends, J. The effect of surface roughening of polymers on measured contact angles of liquids. Colloids Surf. 1984, 9, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.K.; Rani, R. Analysis of the Relationship between Solid Ink Density, Dot Gain and Print Contrast in Digital Printing. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Comput. Technol. 2016, 6, 130–131. [Google Scholar]
- Valdec, D.; Miljkovic, P.; Auguštin, B. The influence of printing substrate properties on colour characterization in flexography according to the ISO specifications. Teh. Glas. 2017, 11, 73–77. [Google Scholar]

| Nativia BOPLA NTSS | EarthFirst PLA BCP | |
|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation used | NTSS | BCP |
| Surface free energy (mJ/m2) | 37 | 38 |
| Gloss (GU) | 80 (45°) | 125 (60°) |
| Haze (%) | 1.5 | 7.0 |
| Moisture vapor transmission rate MVTR (g/m2/d) | 440 | 155 |
| Oxygen transmission rate O2TR (cm3/m2/d) | 1100 | 450 |
| Tensile strength MD/TD (N/mm2) | 105/205 | 55.16/55.16 |
| Ink 1 | Ink 2 | Ink 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trade name | FlexiWet (Chespa) | Urania (Chespa) | Wiflex (Chespa) |
| Kind of resin | Acrylic | PA | NC/PU |
| Kind of ink | water-based | solvent-based | solvent-based |
| Measured Parameter. | BCP | NTSS |
|---|---|---|
| Surface roughness (without plasma) (nm) | 130.22 ± 37.09 | 107.32 ± 13.07 |
| Surface roughness (100% Ar plasma) (nm) | 150.02 ± 16.23 | 244.64 ± 14.01 |
| Surface roughness (100% O2 plasma) (nm) | 130.07 ± 48.19 | 89.62 ± 47.61 |
| Weight difference (100% Ar plasma) (mg) | 0.280 ± 0.071 | 0.405 ± 0.064 |
| Weight difference (100% O2 plasma) (mg) | 0.355 ± 0.007 | 0.425 ± 0.064 |
| Measured Parameter | BCP | NTSS |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength (without plasma) (MPa) | 27.54 ±6.35 | 59.84 ± 5.72 |
| Tensile strength (100% Ar plasma) (MPa) | 44.64 ± 23.09 | 102.10 ± 11.44 |
| Tensile strength (100% O2 plasma) (MPa) | 41.24 ± 16.60 | 38.51 ± 5.72 |
| Elongation at break (without plasma) (%) | 6.68 ± 2.80 | 16.70 ± 17.09 |
| Elongation at break (100% Ar plasma) (%) | 3.62 ± 0.79 | 146.00 ± 15.17 |
| Elongation at break (100% O2 plasma) (%) | 3.66 ± 0.52 | 3.24 ± 0.82 |
| Measured Parameter | BCP | NTSS |
|---|---|---|
| ∆E (100% Ar plasma) | 0.61 | 0.48 |
| ∆E (100% O2 plasma) | 0.71 | 0.50 |
| Gloss difference (100% Ar plasma) (GU) | −27.68 | 23.82 |
| Gloss difference (100% O2 plasma) (GU) | −31.81 | 33.47 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Izdebska-Podsiadły, J. Effect of Plasma Surface Modification on Print Quality of Biodegradable PLA Films. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8245. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11178245
Izdebska-Podsiadły J. Effect of Plasma Surface Modification on Print Quality of Biodegradable PLA Films. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(17):8245. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11178245
Chicago/Turabian StyleIzdebska-Podsiadły, Joanna. 2021. "Effect of Plasma Surface Modification on Print Quality of Biodegradable PLA Films" Applied Sciences 11, no. 17: 8245. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11178245
APA StyleIzdebska-Podsiadły, J. (2021). Effect of Plasma Surface Modification on Print Quality of Biodegradable PLA Films. Applied Sciences, 11(17), 8245. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11178245






