Association between Anthropometric Variables, Sex, and Visual Biofeedback in Dynamic Postural Control Assessed on a Computerized Wobble Board
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Procedures
2.2. Wobble Board Test
2.3. Statistical Analysis
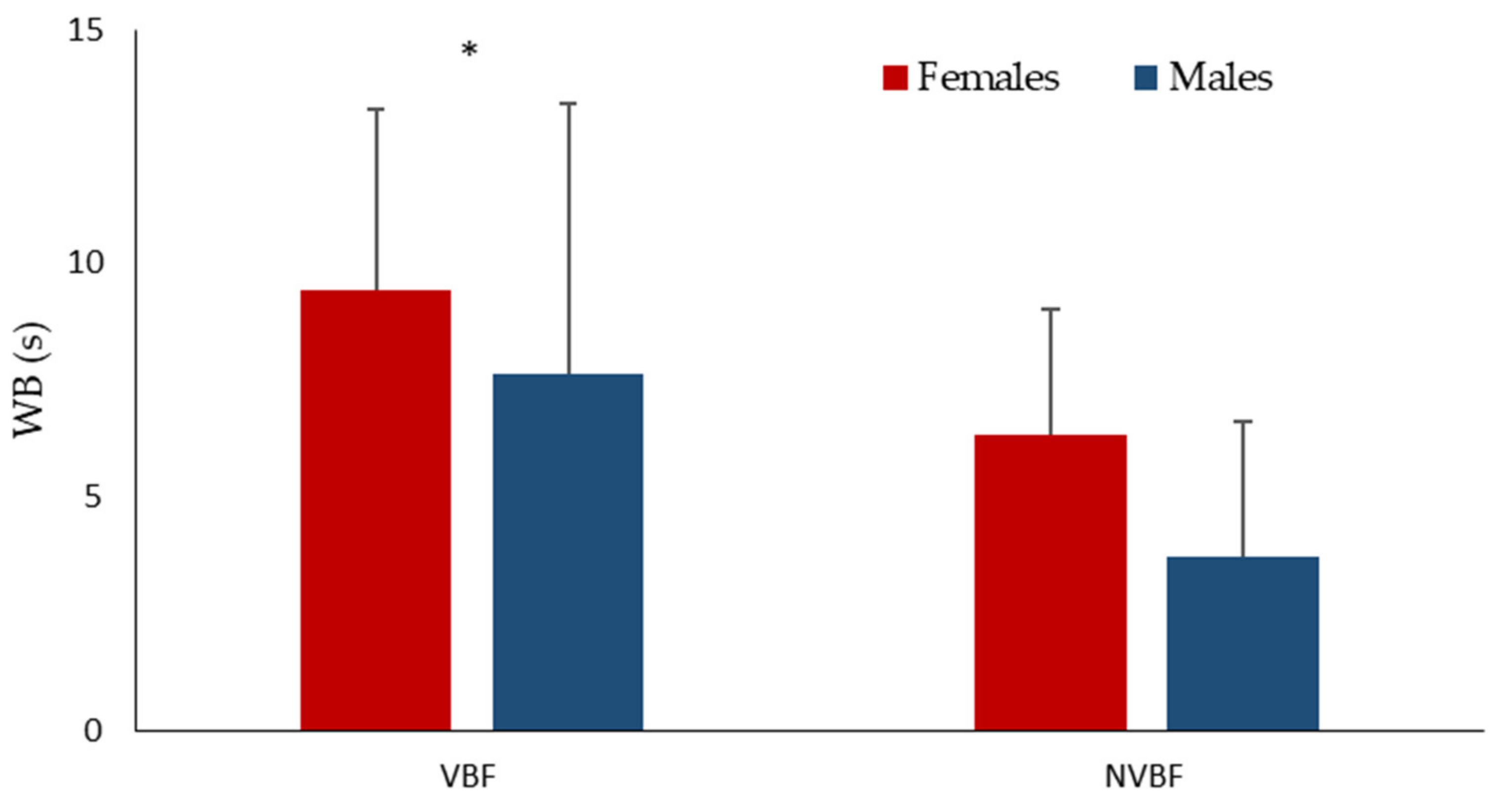
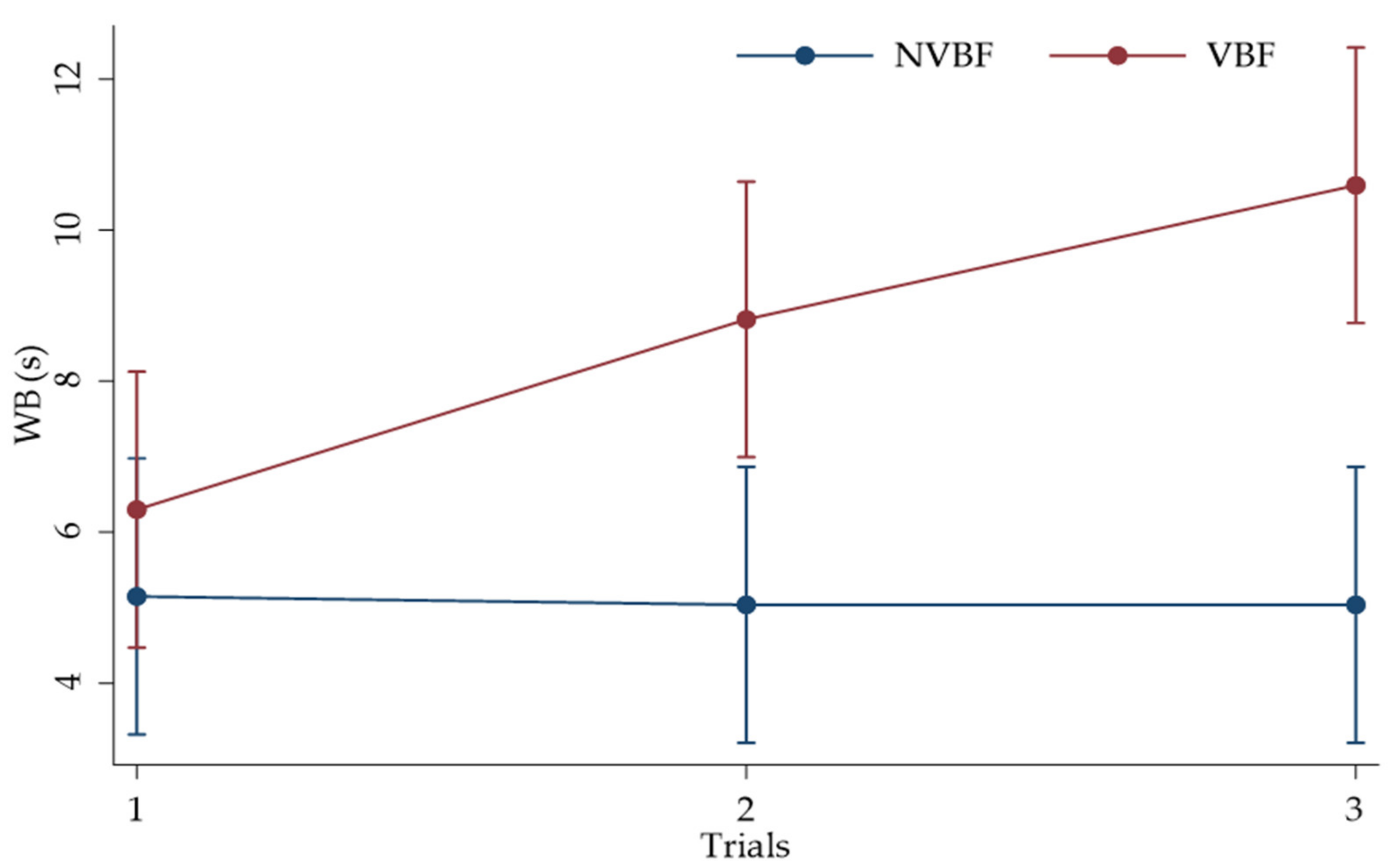
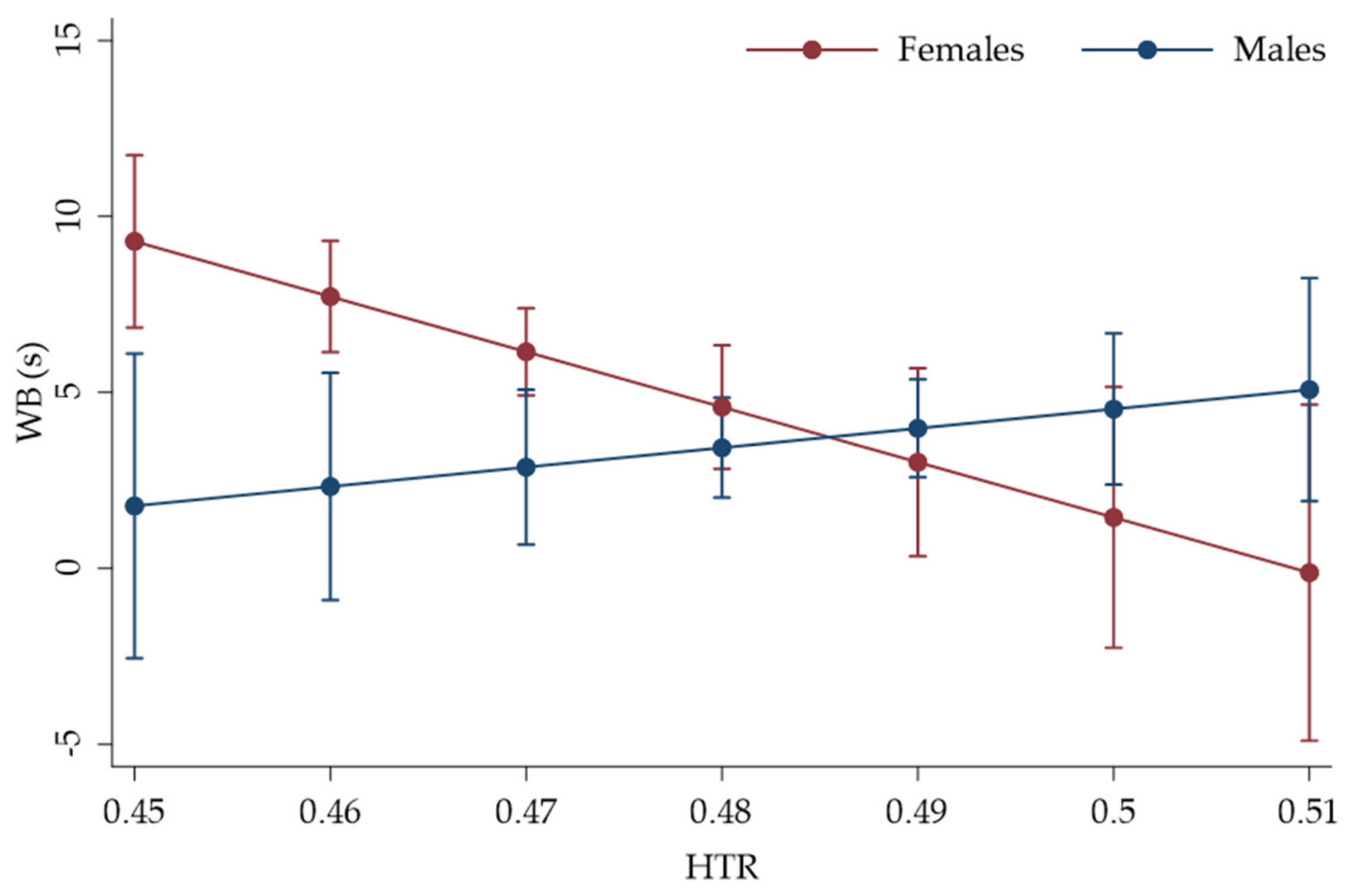
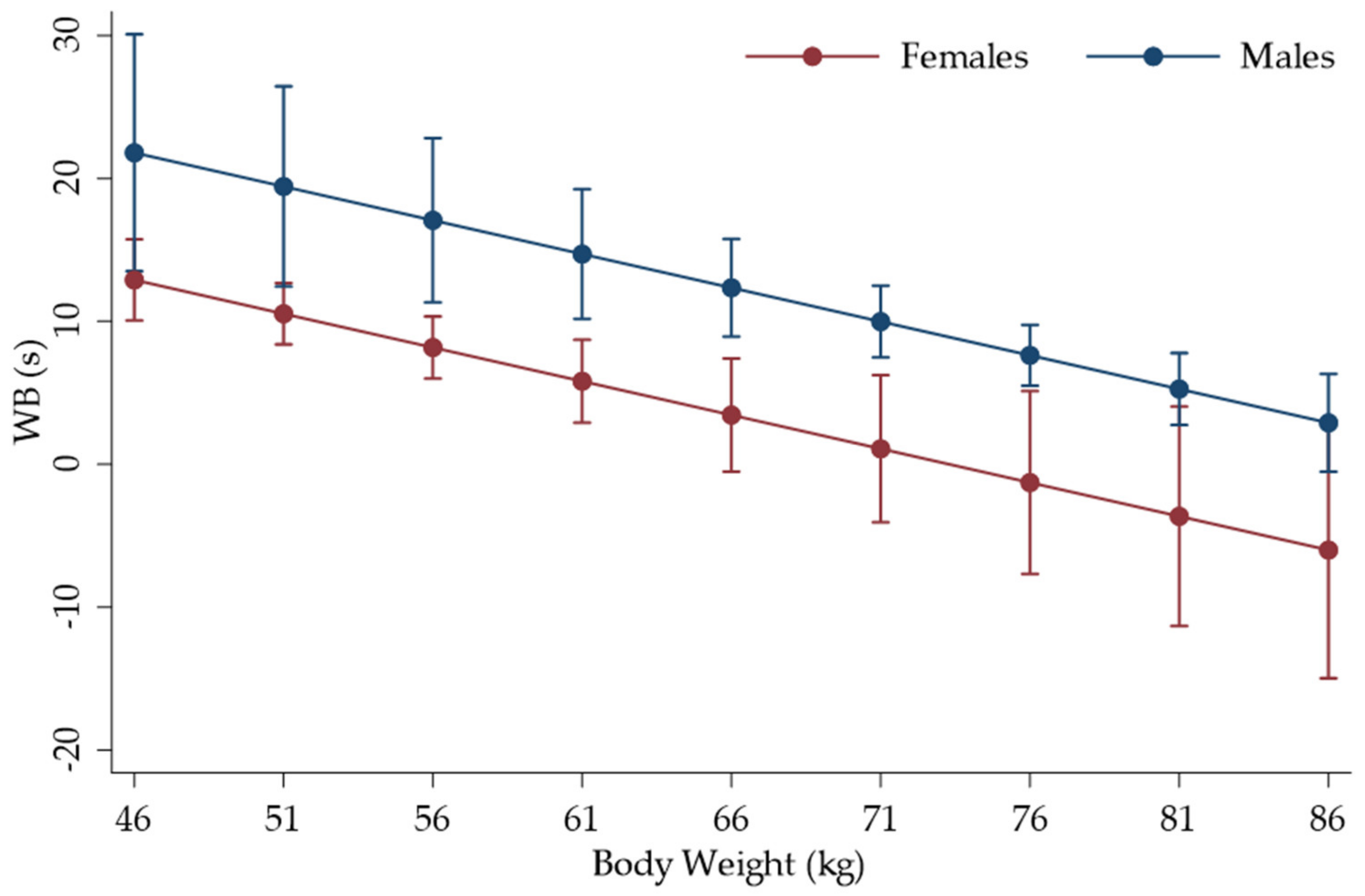
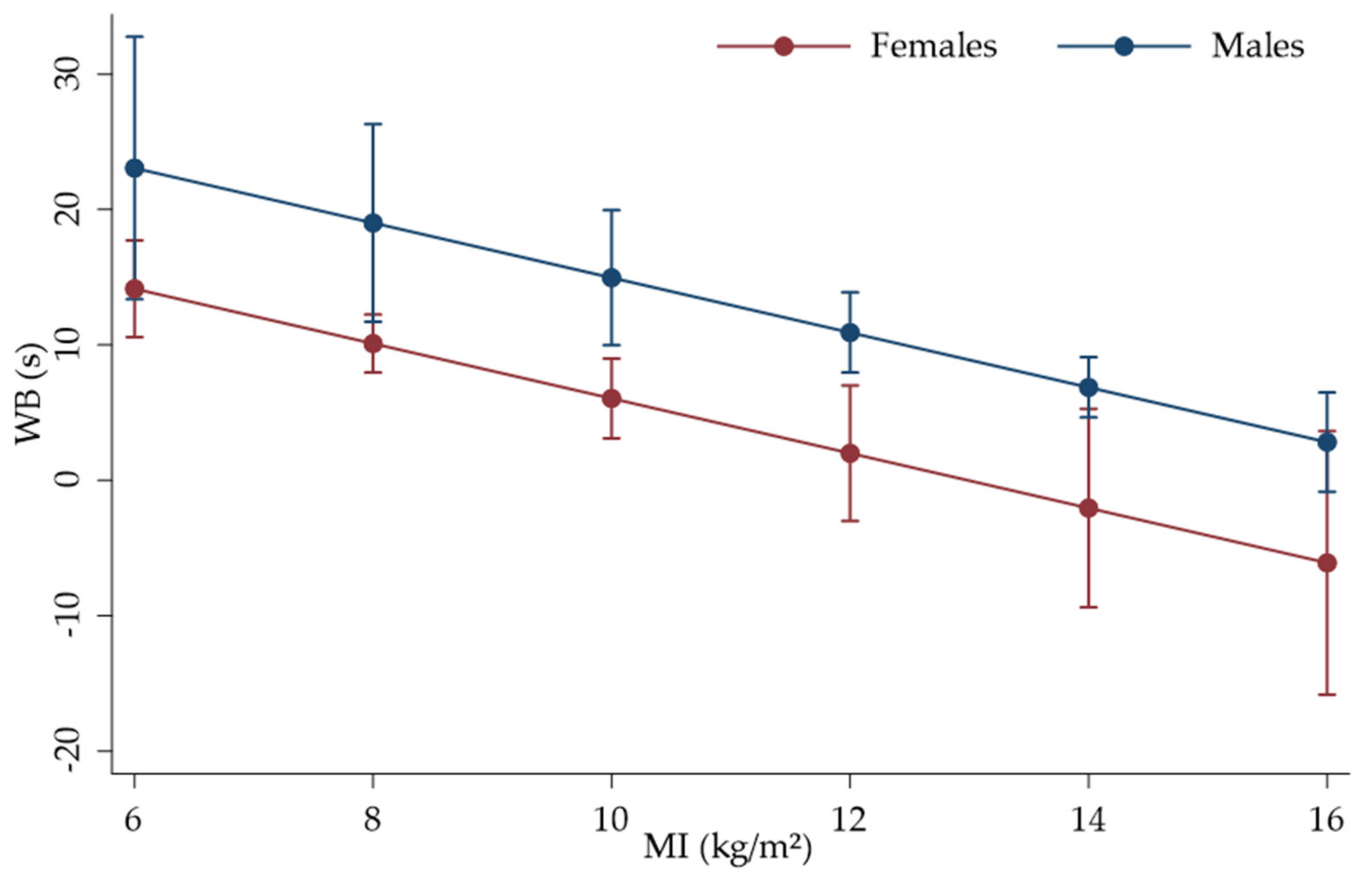
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pollock, A.S.; Durward, B.R.; Rowe, P.J.; Paul, J.P. What is balance? Clin. Rehabil. 2000, 14, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horak, F.B. Postural orientation and equilibrium: What do we need to know about neural control of balance to prevent falls? Age Ageing 2006, 35, ii7–ii11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yim-Chiplis, P.K.; Talbot, L.A. Defining and Measuring Balance in Adults. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2000, 1, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGraw, B.; McClenaghan, B.A.; Williams, H.G.; Dickerson, J.; Ward, D.S. Gait and postural stability in obese and nonobese prepubertal boys. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2000, 81, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.; da Silva, R.A.; de Oliveira, M.R.; Souza, R.D.N.; Borges, R.J.; Vieira, E.R. Effect of body mass index and fat mass on balance force platform measurements during a one-legged stance in older adults. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 30, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiari, L.; Cappello, A.; Lenzi, D.; Della Croce, U. An improved technique for the extraction of stochastic parameters from stabilograms. Gait Posture 2000, 12, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, A.; Giancotti, G.F.; Fuchs, P.X.; Wagner, H.; da Silva, R.A.; Cortis, C. Y balance test: Are we doing it right? J. Sci. Med. Sport 2020, 23, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Park, W.; Levy, M.S.; Jung, E.S. The effects of obesity and standing time on postural sway during prolonged quiet standing. Ergonomics 2009, 52, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.C.; Mochizuki, L.; Silva Luna, N.M.; Ayama, S.; Canonica, A.C.; Greve, J.M.D.A. Relation between the Sensory and Anthropometric Variables in the Quiet Standing Postural Control: Is the Inverted Pendulum Important for the Static Balance Control? Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 985312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nolan, L.; Grigorenko, A.; Thorstensson, A. Balance control: Sex and age differences in 9- to 16-year-olds. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2005, 47, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hue, O.; Simoneau, M.; Marcotte, J.; Berrigan, F.; Doré, J.; Marceau, P.; Marceau, S.; Tremblay, A.; Teasdale, N. Body weight is a strong predictor of postural stability. Gait Posture 2007, 26, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainenti, M.R.M.; Rodrigues, É.D.; de Oliveira, J.F.; Ferreira, A.D.; Dias, C.M.; Silva, A.L.D.S. Adiposity and postural balance control: Correlations between bioelectrical impedance and stabilometric signals in elderly Brazilian women. Clinics 2011, 66, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Iwakura, H.; Inoue, F. Motion analysis in the movements of standing up from and sitting down on a chair. A comparison of normal and hemiparetic subjects and the differences of sex and age among the normals. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1982, 15, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Masui, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Matsuyama, Y.; Sakano, S.; Kawasaki, M.; Suzuki, S. Gender differences in platform measures of balance in rural community-dwelling elders. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2005, 41, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, E.C.; Trew, M.E.; Bruce, A.M.; Kuisma, R.M.E.; Smith, A.W. Gender differences in balance performance at the time of retirement. Clin. Biomech. 2005, 20, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortis, C.; Pesce, C.; Capranica, L. Inter-limb coordination dynamics: Effects of visual constraints and age. Kinesiology 2018, 50, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Dozza, M.; Chiari, L.; Horak, F.B. Audio-Biofeedback Improves Balance in Patients With Bilateral Vestibular Loss. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1401–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornwell, T.; Woodward, J.; Wu, M.; Jackson, B.; Souza, P.; Siegel, J.; Dhar, S.; Gordon, K.E. Walking With Ears: Altered Auditory Feedback Impacts Gait Step Length in Older Adults. Front. Sport. Act. Living 2020, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halická, Z.; Lobotková, J.; Bučková, K.; Hlavačka, F. Effectiveness of different visual biofeedback signals for human balance improvement. Gait Posture 2014, 39, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.-T.; Wang, C.-M.; Chung, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-L. Effects of visual feedback rhythmic weight-shift training on hemiplegic stroke patients. Clin. Rehabil. 2004, 18, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dault, M.C.; de Haart, M.; Geurts, A.C.; Arts, I.M.; Nienhuis, B. Effects of visual center of pressure feedback on postural control in young and elderly healthy adults and in stroke patients. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2003, 22, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rougier, P.; Boudrahem, S. Effects of visual feedback of center-of-pressure displacements on undisturbed upright postural control of hemiparetic stroke patients. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2010, 28, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackley, C.M.; Lincoln, N.B. Single blind randomized controlled trial of visual feedback after stroke: Effects on stance symmetry and function. Disabil. Rehabil. 1997, 19, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.; Brouwer, B.J.; Culham, E. Use of visual feedback in retraining balance following acute stroke. Phys. Ther. 2000, 80, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winstein, C.; Gardner, E.; McNeal, D.; Barto, P.; Nicholson, D. Standing balance training: Effect on balance and locomotion in hemiparetic adults. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1989, 70, 755–762. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, M.W.; Crowell, C.R.; Striegel, A.D.; Villano, M.; Schmiedeler, J.P. Relative efficacy of various strategies for visual feedback in standing balance activities. Exp. Brain Res. 2013, 230, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.M.; Burden, A.M. Validity of weight distribution and sway measurements of the Balance Performance Monitor. Physiother. Res. Int. 2000, 5, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmsted, L.C.; Carcia, C.R.; Hertel, J.; Shultz, S. Efficacy of the star excursion balance tests in detecting reach deficits in subjects with chronic ankle instability. J. Athl. Train. 2002, 37, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hertel, J.; Braham, R.A.; Hale, S.A.; Olmsted-Kramer, L.C. Simplifying the Star Excursion Balance Test: Analyses of Subjects With and Without Chronic Ankle Instability. J. Orthop. Sport. Phys. Ther. 2006, 36, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laessoe, U.; Svendsen, A.W.; Christensen, M.N.; Rasmussen, J.R.; Gaml, A.S. Evaluation of functional ankle instability assessed by an instrumented wobble board. Phys. Ther. Sport 2019, 35, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, A.; Giancotti, G.F.; Fuchs, P.X.; Wagner, H.; Varalda, C.; Capranica, L.; Cortis, C. Dynamic Balance Evaluation: Reliability and Validity of a Computerized Wobble Board. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 1709–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.; Bentman, S. An investigation into the reliability and variability of wobble board performance in a healthy population using the SMARTwobble instrumented wobble board. Phys. Ther. Sport 2014, 15, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, A.; Fuchs, P.X.; De Maio, M.; Wagner, H.; Cortis, C. A novel approach to measuring wobble board performance in individuals with chronic ankle instability. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, A.; Giancotti, G.F.; Fuchs, P.X.; Wagner, H.; Varalda, C.; Cortis, C. Wobble board balance assessment in subjects with chronic ankle instability. Gait Posture 2019, 68, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, A.; Ozawa, H.; Goda, K.; Fukunaga, T. Moment of inertia of whole body using an oscillating table in adolescent boys. J. Biomech. 1995, 28, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kręcisz, K.; Kuczyński, M. Attentional demands associated with augmented visual feedback during quiet standing. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inojosa, H.; Schriefer, D.; Trentzsch, K.; Klöditz, A.; Ziemssen, T. Visual Feedback and Postural Control in Multiple Sclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami Meibodi, M.K.; Naghizad, J.; Shamsoddini, A. The effect of balance rehabilitation interventions with and without visual feedback on balance and proprioception of knee in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injury: A randomized clinical trial. Sport Sci. Health 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignolo, L.; Basta, G.; Carozzo, S.; Bilotta, M.; Todaro, M.R.; Serra, S.; Ciancarelli, I.; Tonin, P.; Cerasa, A. A body-weight-supported visual feedback system for gait recovering in stroke patients: A randomized controlled study. Gait Posture 2020, 82, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Davies, J.L.; Button, K.; Al-Amri, M. Effect of visual feedback on the performance of the star excursion balance test. J. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. Eng. 2019, 6, 205566831986213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kons, R.L.; Sakugawa, R.L.; Rossato, M.; Diefenthaeler, F.; Detanico, D. Neuromuscular and postural control in visually and nonvisually impaired judo athletes: Case study. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2019, 15, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vando, S.; Longo, S.; Cavaggioni, L.; Maurino, L.; Larion, A.; Invernizzi, P.L.; Padulo, J. The Effects of Short-Term Visual Feedback Training on the Stability of the Roundhouse Kicking Technique in Young Karatekas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Anna, C.; Schmid, M.; Bibbo, D.; Bertollo, M.; Comani, S.; Conforto, S. The Effect of Continuous and Discretized Presentations of Concurrent Augmented Visual Biofeedback on Postural Control in Quiet Stance. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bechly, K.E.; Carender, W.J.; Myles, J.D.; Sienko, K.H. Determining the preferred modality for real-time biofeedback during balance training. Gait Posture 2013, 37, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhasan, H.; Hood, V.; Mainwaring, F. The effect of visual biofeedback on balance in elderly population: A systematic review. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cawsey, R.P.; Chua, R.; Carpenter, M.G.; Sanderson, D.J. To what extent can increasing the magnification of visual feedback of the centre of pressure position change the control of quiet standing balance? Gait Posture 2009, 29, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiari, L.; Rocchi, L.; Cappello, A. Stabilometric parameters are affected by anthropometry and foot placement. Clin. Biomech. 2002, 17, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, D.A.; Patla, A.E.; Ishac, M.; Gage, W.H. Motor mechanisms of balance during quiet standing. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2003, 13, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.C.; Challis, J.H.; Bartok, C.; Costigan, F.A.; Newell, K.M. Obesity, mechanical and strength relationships to postural control in adolescence. Gait Posture 2012, 35, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.; Luna, N.; Mochizuki, L.; Barbieri, F.; Santos, S.; D’Andreia Greve, J. The influence of anthropometric factors on postural balance: The relationship between body composition and posturographic measurements in young adults. Clinics 2012, 67, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kejonen, P.; Kauranen, K.; Vanharanta, H. The relationship between anthropometric factors and body-balancing movements in postural balance. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2003, 84, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikstrom, E.A. Validity and Reliability of Nintendo Wii Fit Balance Scores. J. Athl. Train. 2012, 47, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrisley, D.M.; Stephens, M.J.; Mosley, S.; Wojnowski, A.; Duffy, J.; Burkard, R. Learning Effects of Repetitive Administrations of the Sensory Organization Test in Healthy Young Adults. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransson, P.-A.; Tjernström, F.; Hafström, A.; Magnusson, M.; Johansson, R. Analysis of short- and long-term effects of adaptation in human postural control. Biol. Cybern. 2002, 86, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransson, P.A.; Johansson, R.; Tjernstrom, F.; Magnusson, M. Adaptation to vibratory perturbations in postural control. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2003, 22, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Characteristics | Female (n = 14) | Male (n = 13) | Total (n = 27) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 24.0 ± 1.9 | 26.5 ± 3.3 | 25.3 ± 1.0 |
| Lower limb length (cm) | 74.5 ± 3.6 | 85.7 ± 3.8 | 80.1 ± 0.1 |
| Body mass (kg) | 53.3 ± 4.4 | 76.0 ± 6.9 | 64.7 ± 1.7 |
| Height (cm) | 158.9 ± 5.6 | 176.5 ± 5.3 | 167.7 ± 0.2 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.2 ± 1.7 | 24.4 ± 1.9 | 22.8 ± 0.1 |
| WB | Coef. | Std. Err. | Z | p > |z| | 95% Conf. | Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (F = 0; M = 1) | −102.8941 | 39.55309 | −2.60 | 0.009 | −180.4167 | −25.37143 |
| HTR | −156.8785 | 57.26048 | −2.74 | 0.006 | −269.1069 | −44.65001 |
| Sex x HTR | 211.9493 | 82.81277 | 2.56 | 0.010 | 49.63925 | 374.2593 |
| Cons | 79.88784 | 26.85465 | 2.97 | 0.003 | 27.2537 | 132.522 |
| WB | Coef. | Std. Err. | Z | p > |z| | 95% Conf. | Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (F = 0; M = 1) | 8.899321 | 3.434602 | 2.59 | 0.010 | 2.167625 | 15.63102 |
| Body mass (kg) | −0.472319 | 0.136382 | −3.46 | 0.001 | −0.7396228 | −0.2050153 |
| Cons | 34.62342 | 7.349873 | 4.71 | 0.000 | 20.21793 | 49.02891 |
| WB | Coef. | Std. Err. | Z | p > |z| | 95% Conf. | Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (F = 0; M = 1) | 8.915472 | 3.681939 | 2.42 | 0.015 | 1.699004 | 16.13194 |
| MI (kg/m2) | −2.024108 | 0.6322252 | −3.20 | 0.001 | −3.263246 | −0.7849689 |
| Cons | 26.29451 | 5.375726 | 4.89 | 0.000 | 15.75828 | 36.83074 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Maio, M.; Cortis, C.; Iannaccone, A.; da Silva, R.A.; Fusco, A. Association between Anthropometric Variables, Sex, and Visual Biofeedback in Dynamic Postural Control Assessed on a Computerized Wobble Board. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8370. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188370
De Maio M, Cortis C, Iannaccone A, da Silva RA, Fusco A. Association between Anthropometric Variables, Sex, and Visual Biofeedback in Dynamic Postural Control Assessed on a Computerized Wobble Board. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(18):8370. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188370
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Maio, Marianna, Cristina Cortis, Alice Iannaccone, Rubens A. da Silva, and Andrea Fusco. 2021. "Association between Anthropometric Variables, Sex, and Visual Biofeedback in Dynamic Postural Control Assessed on a Computerized Wobble Board" Applied Sciences 11, no. 18: 8370. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188370
APA StyleDe Maio, M., Cortis, C., Iannaccone, A., da Silva, R. A., & Fusco, A. (2021). Association between Anthropometric Variables, Sex, and Visual Biofeedback in Dynamic Postural Control Assessed on a Computerized Wobble Board. Applied Sciences, 11(18), 8370. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188370









