pH-Responsive Hollow Polymeric Microspheres from Irradiated Cyclic Ether Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Polymeric Microspheres
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Morphology Observation and Average Molecular Weight
2.3.2. Chemical Structure Analysis
2.3.3. Measurement of Performance of Hydrophobic Carriers
3. Results and Discussions
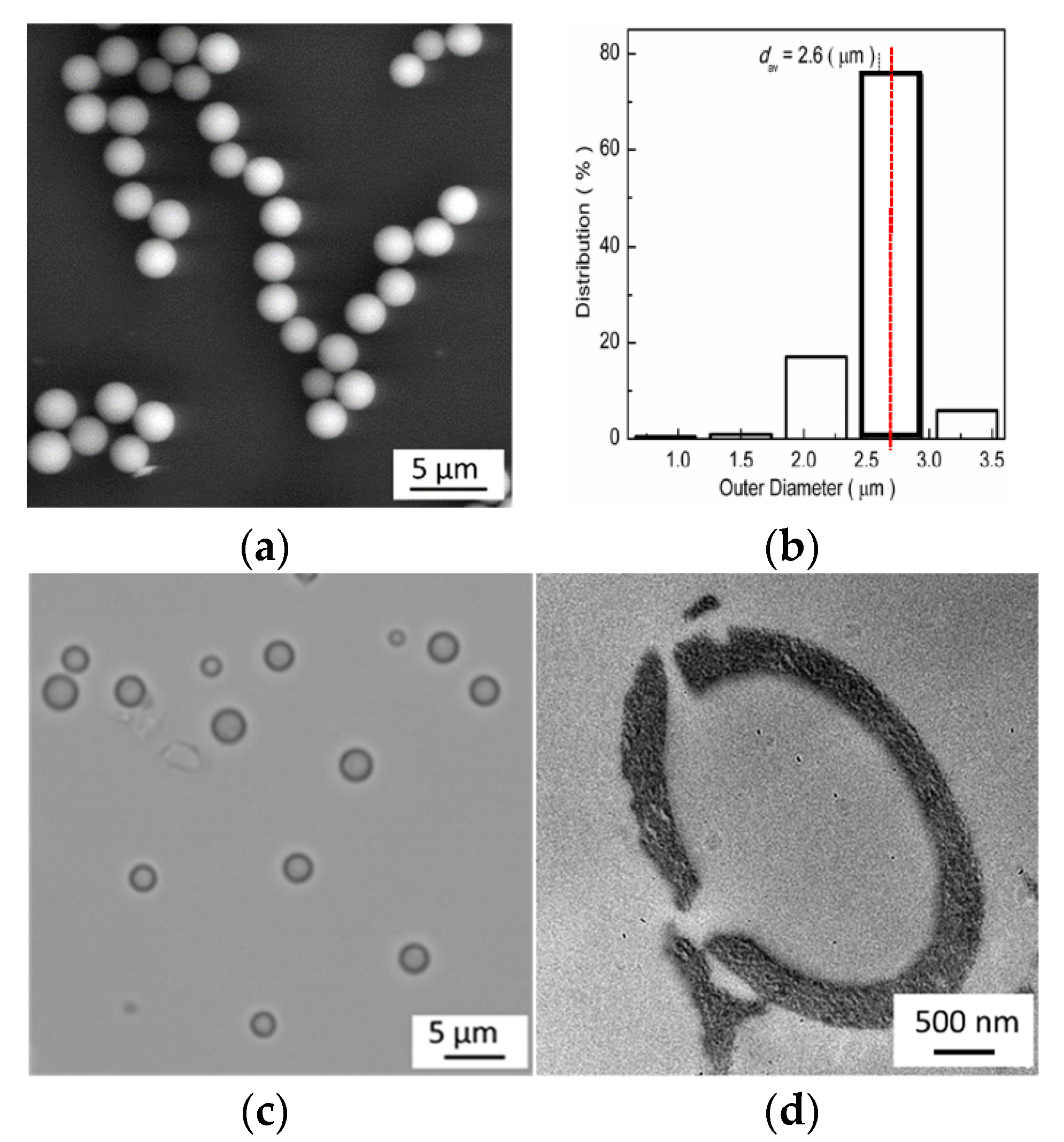
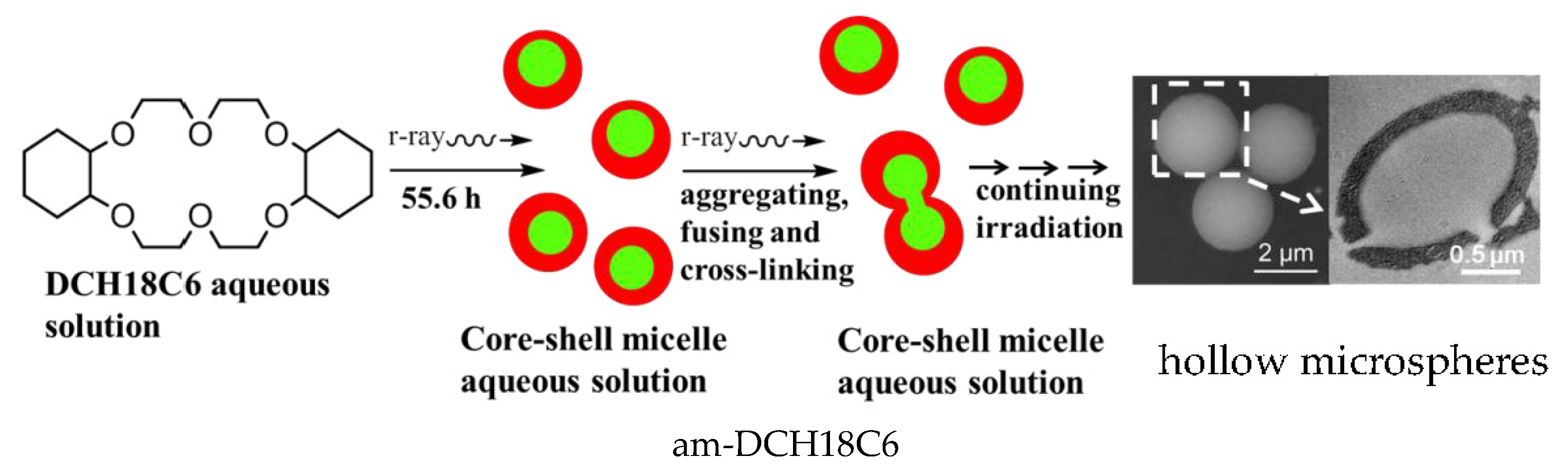
3.1. Characteriziation of Microshpheres and Possible Formation Mechanism
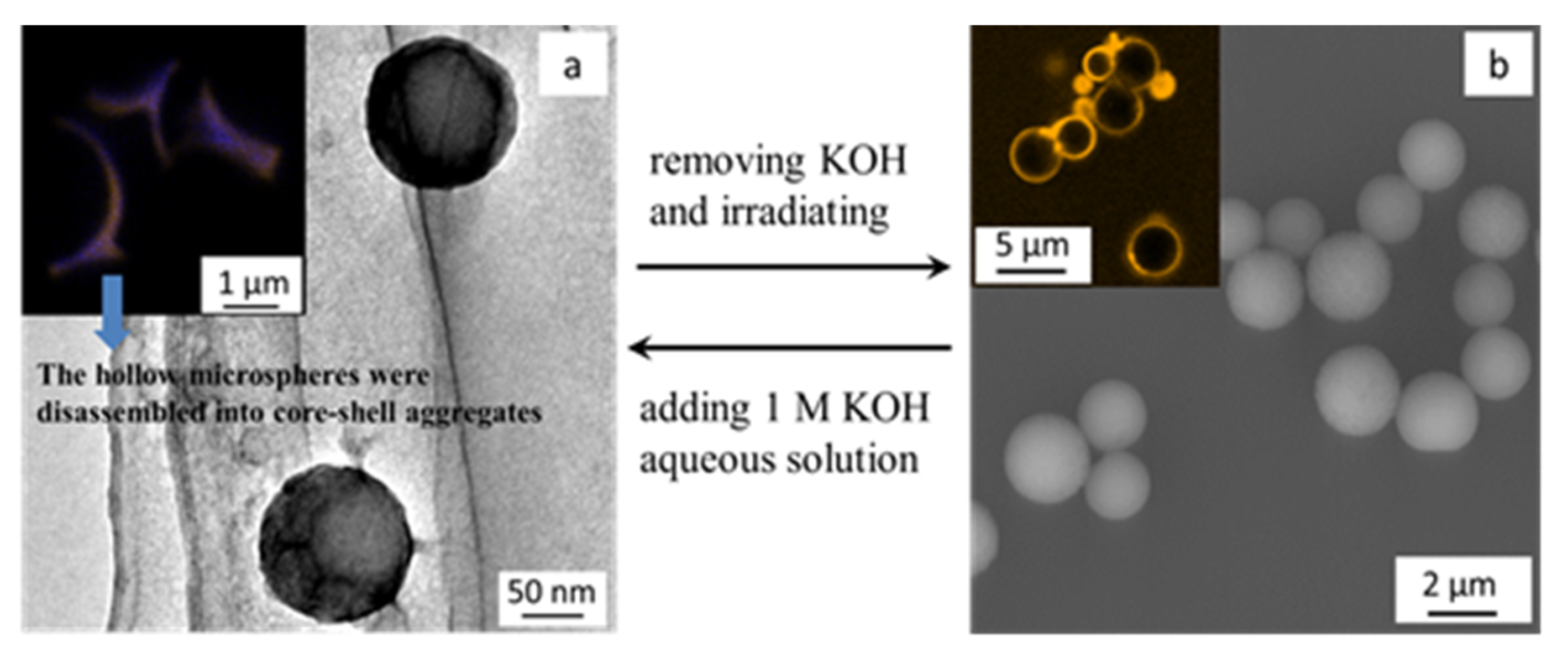
3.2. pH-Trigged Molecular Release
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raza, S.; Yong, X.; Yang, B.; Xu, R.; Deng, J. Biomass trans-Anethole-Based Hollow Polymer Particles: Preparation and Application as Sustainable Absorbent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 10011–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, G.; Tüysüz, H.; Duyckaerts, N.; Knossalla, J.; Wang, G.-H.; Schüth, F. Hollow Nano- and Microstructures as Catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14056–14119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R. Reactive Template Method to Synthesize Gold Nanoparticles with Controllable Size and Morphology Supported on Shells of Polymer Hollow Microspheres and Their Application for Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation in Water. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; West, K.R.; Scherman, O.A. Hollow mesoporous raspberry-like colloids with removable caps as photoresponsive nanocontainers. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7840–7844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, B.; Han, D.; Boissière, O.; Ayotte, P.; Zhao, Y. Manipulation of block copolymer vesicles using CO2: Dissociation or “breathing”. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 2011–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Bao, B.; Tao, J.; Zhao, S.; Han, X.; Liu, H. Deswelling Dynamics of Thermoresponsive Microgel Capsules and Their Ultrasensitive Sensing Applications: A Mesoscopic Simulation Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcea, M.; Möhwald, H.; Skirtach, A.G. Stimuli-responsive LbL capsules and nanoshells for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 730–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Peng, Y.; Seekell, R.P.; Kheir, J.N.; Polizzotti, B.D. Hyperbaric polymer microcapsules for tunable oxygen delivery. J. Control Release 2020, 327, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselova, M.V.; Loh, H.M.; Trushina, D.B.; Ketkar, A.; Abakumova, T.O.; Zatsepin, T.S.; Kakran, M.; Brzozowska, A.M.; Lau, H.H.; Gorin, D.A.; et al. Biodegradable Polymeric Multilayer Capsules for Therapy of Lung Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 5610–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, W.; Fang, J.; Yin, J. Polymer-based porous microcarriers as cell delivery systems for applications in bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Int. Mater. Rev. 2021, 66, 77–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, F.; Caruso, R.A.; Möhwald, H. Nanoengineering of Inorganic and Hybrid Hollow Spheres by Colloidal Templating. Science 1998, 282, 1111–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; You, L. Preparation and characterization of polystyrene/polycarbonate composite hollow microspheres by microencapsulation method. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 3604–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, D.B.; Antipov, A.A.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Möhwald, H. Layer-by-Layer Engineering of Biocompatible, Decomposable Core−Shell Structures. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, R.; Freemont, T.J.; Saunders, B.R. Hollow polymer particles that are pH-responsive and redox sensitive: Two simple steps to triggered particle swelling, gelation and disassembly. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1443–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, G.; Yan, R.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Sun, P. One-Stage Synthesis of Cagelike Porous Polymeric Microspheres and Application as Catalyst Scaffold of Pd Nanoparticles. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 3730–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, O.; Şen, M.; Karadağ, E.; Saraydın, D. A review on the radiation synthesis of copolymeric hydrogels for adsorption and separation purposes. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1999, 56, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.L.; Cheng, Y.R.; Liu, Y.F.; Liu, F.; Yang, B. A facile route to ZnS-polymer nanocomposite optical materials with high nanophase content via gamma-ray irradiation initiated bulk polymerization. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, A.; Clochard, M.-C.; Coqueret, X.; Dispenza, C.; Driscoll, M.S.; Ulański, P.; Al-Sheikhly, M. Polymerization Reactions and Modifications of Polymers by Ionizing Radiation. Polymers 2020, 12, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Ge, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhang, S. Novel One-Step Route for Synthesizing CdS/Polystyrene Nanocomposite Hollow Spheres. Langmuir 2004, 20, 5192–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.Y.; Wang, M.Z.; Cong, Y.H.; Liu, W.J.; Ge, X.W.; Zhang, Z.C. The mechanism of Co-60 gamma-ray radiation induced interfacial redox reaction in inverse emulsion and its application in the synthesis of polymer microcapsules. Polymer 2007, 48, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, R.T.; Hight, C.; Yildiz, U.; Schaeffer, N.; Valliant, E.M.; Jones, J.R.; Stevens, M.M.; Weaver, J.V.M. Reversible aggregation of responsive polymer-stabilized colloids and the pH-dependent formation of porous scaffolds. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 7560–7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, S.; Cui, Z.; Peng, J.; Li, J.; Zhai, M.; Huang, J. One-step radiation-induced construction of multi-responsive self-assemblies using simple cyclic ethers. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 5959–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliverstov, A.F.; Ershov, B.G. Radiation-Chemical Transformations of Dicyclohexyl-18-Crown-6 in Aqueous-Solutions. High Energy Chem. 1988, 22, 173–176. [Google Scholar]
- Janik, I.; Ulanski, P.; Hildenbrand, K.; Rosiak, J.M.; Von Sonntag, C. Hydroxyl-radical-induced reactions of poly(vinyl methyl ether): A pulse radiolysis, EPR and product study in deoxygenated and oxygenated aqueous solutions. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2000, 2, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, M.; Kudoh, H.; Wu, G.; Wach, R.A.; Muroya, Y.; Katsumura, Y.; Nagasawa, N.; Zhao, A.L.; Yoshii, F. Laser Photolysis of Carboxymethylated Chitin Derivatives in Aqueous Solution. Part 1. Formation of Hydrated Electron and a Long-Lived Radical. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, C.; Peng, J.; Li, J.; Zhai, M. pH-Responsive Hollow Polymeric Microspheres from Irradiated Cyclic Ether Aqueous Solution. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8652. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188652
Yu C, Peng J, Li J, Zhai M. pH-Responsive Hollow Polymeric Microspheres from Irradiated Cyclic Ether Aqueous Solution. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(18):8652. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188652
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Chuhong, Jing Peng, Jiuqiang Li, and Maolin Zhai. 2021. "pH-Responsive Hollow Polymeric Microspheres from Irradiated Cyclic Ether Aqueous Solution" Applied Sciences 11, no. 18: 8652. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188652
APA StyleYu, C., Peng, J., Li, J., & Zhai, M. (2021). pH-Responsive Hollow Polymeric Microspheres from Irradiated Cyclic Ether Aqueous Solution. Applied Sciences, 11(18), 8652. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188652





