Effect of Biomimetic Surface Geometry, Soil Texture, and Soil Moisture Content on the Drag Force of Soil-Touching Parts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
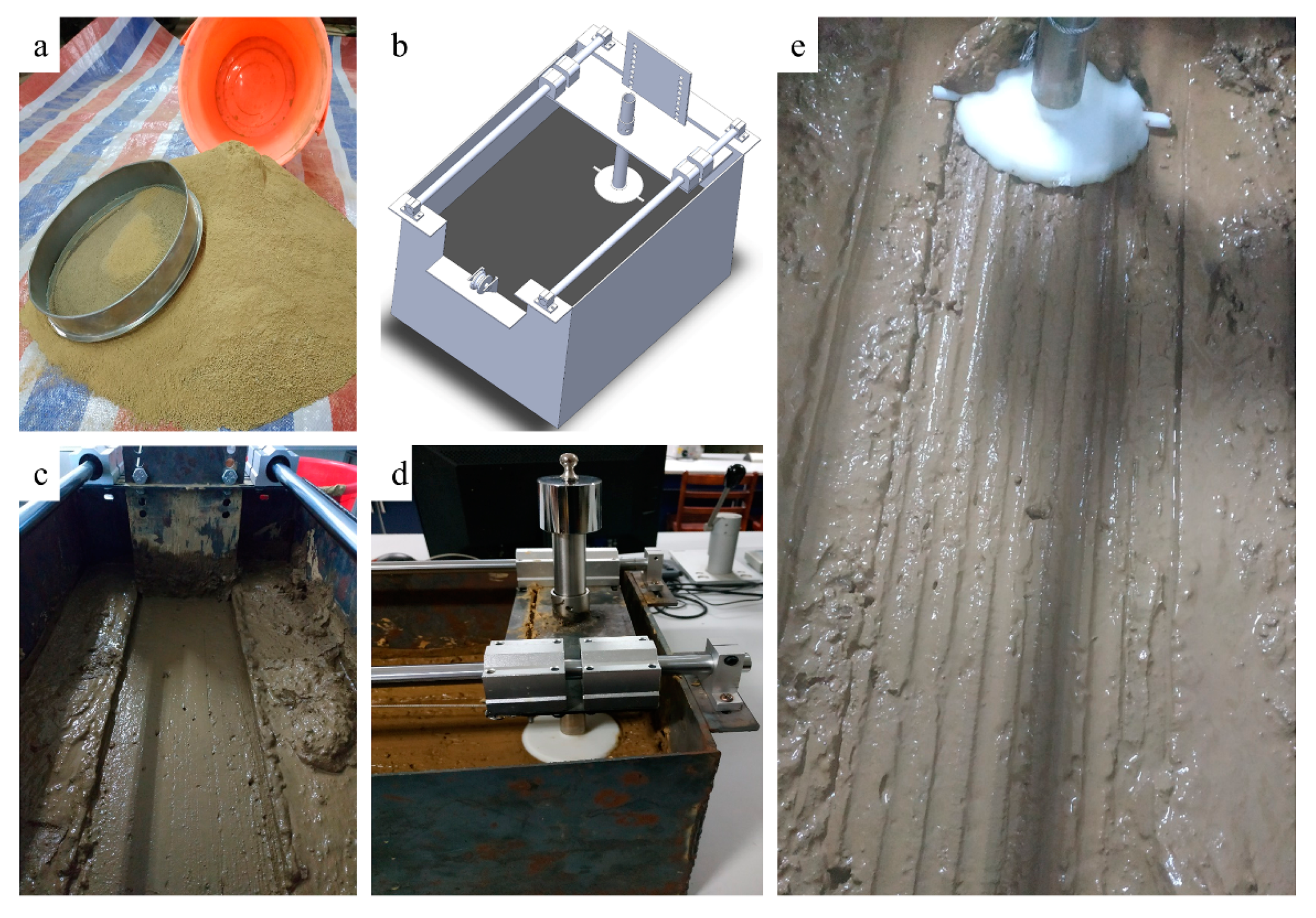
2.1. Soil Preparation
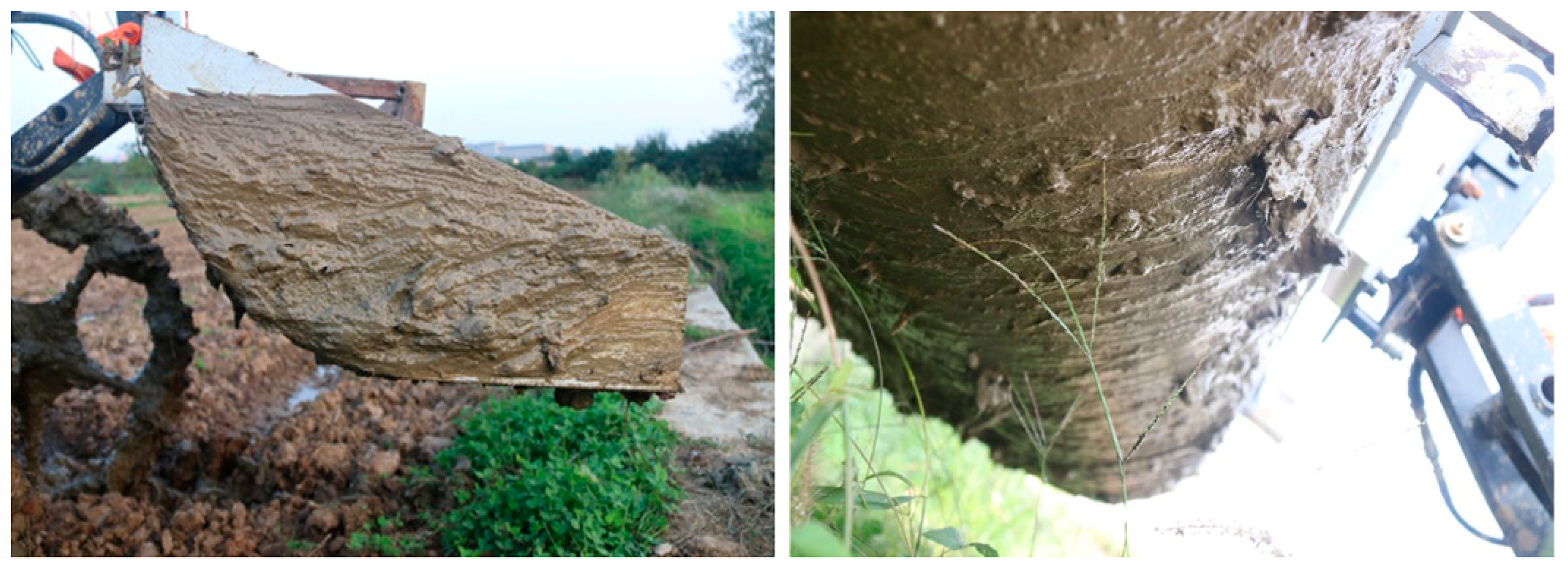
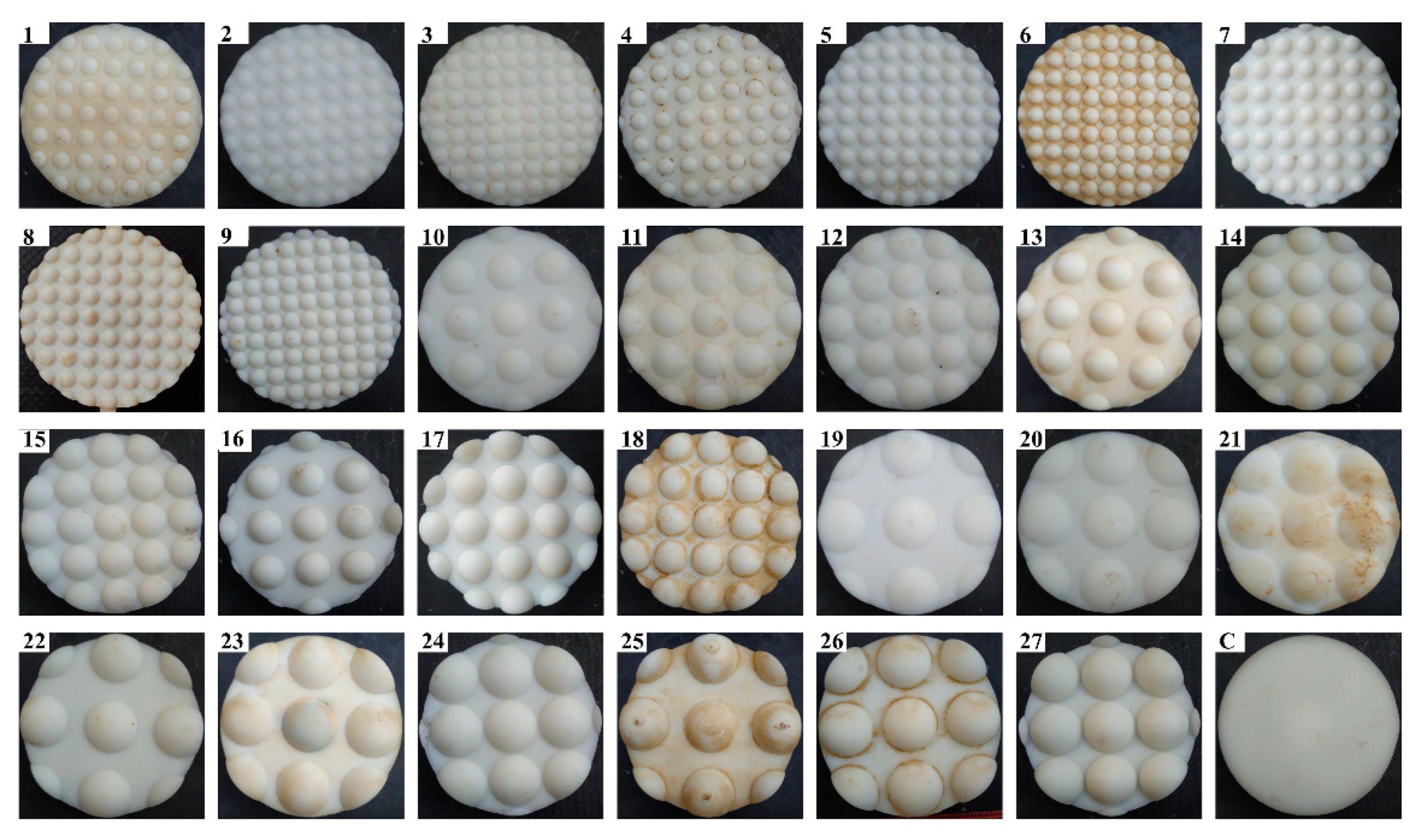
2.2. Preparation of the Test Discs and Soil Bin
2.3. Drag Force Test
2.4. Design of Experiment and Statistics
3. Results
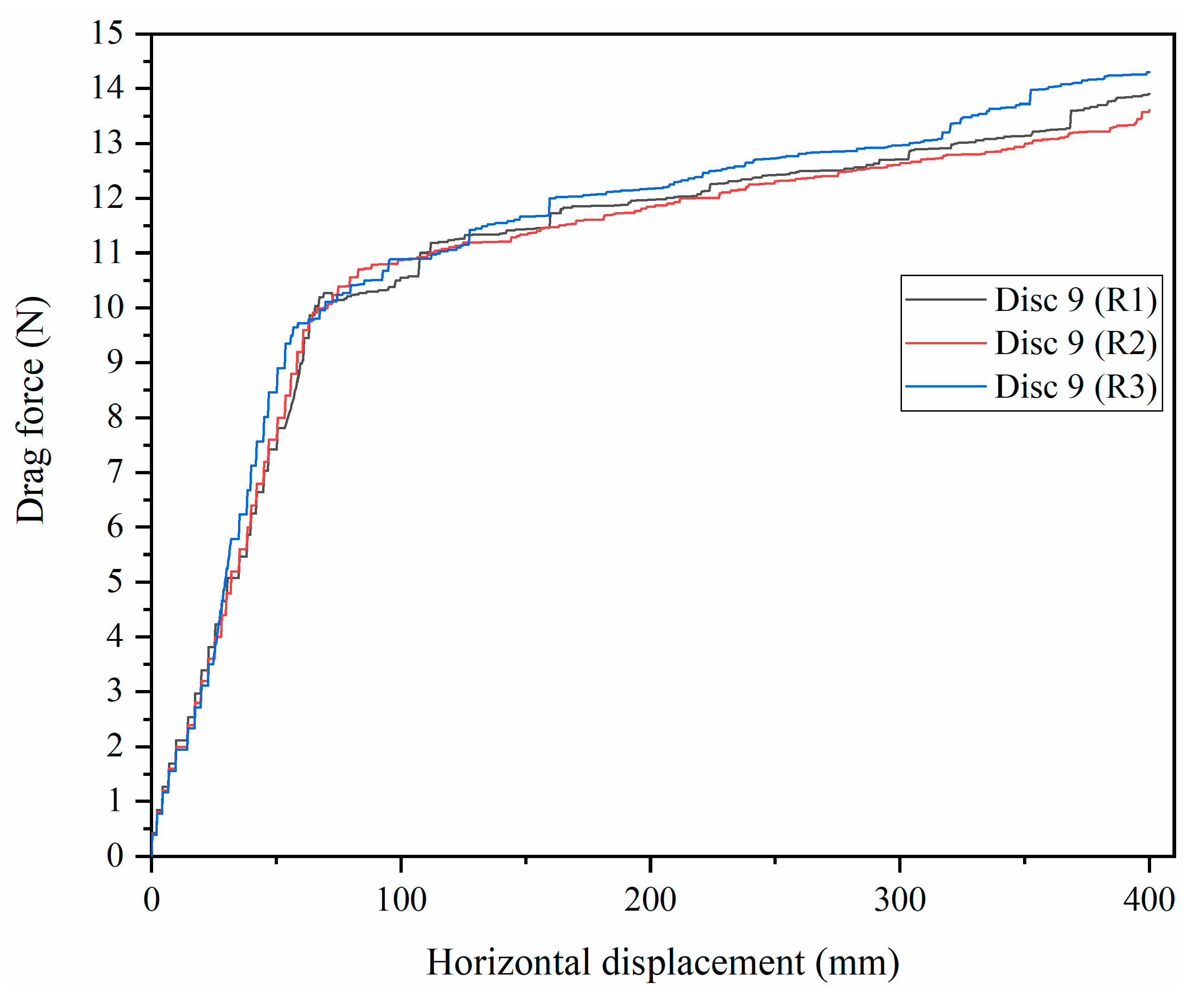
3.1. The Exploratory Experiment Findings
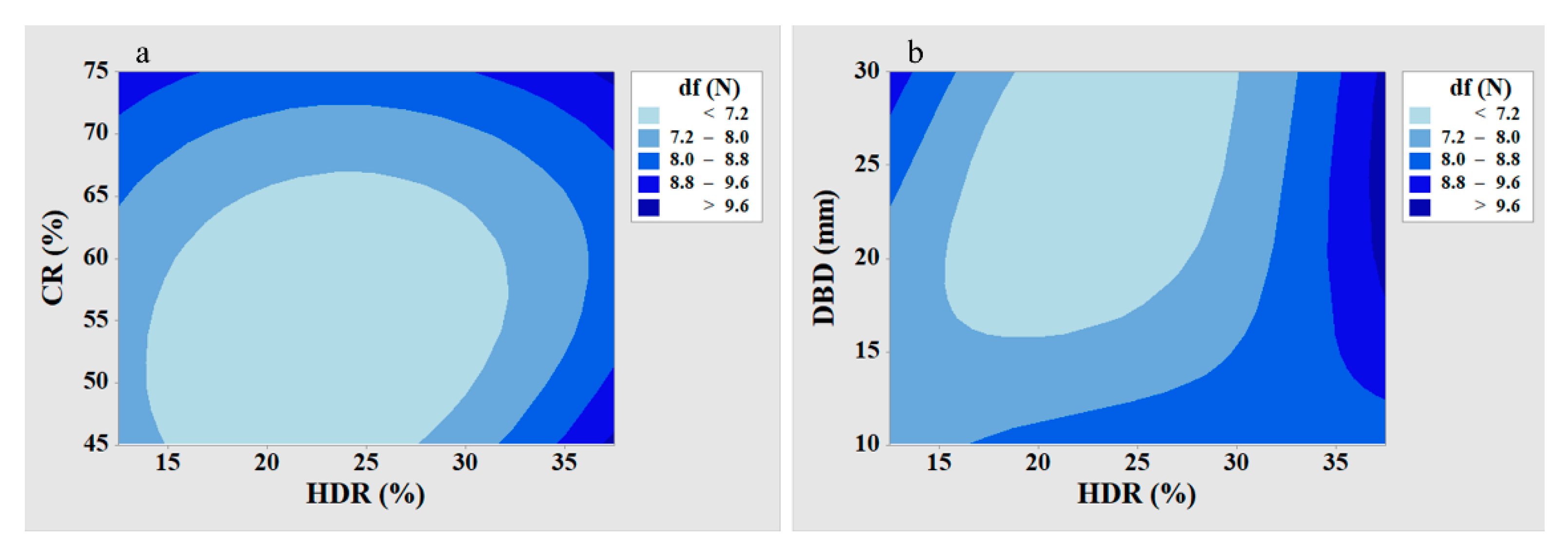
3.2. Full Factorial Experiment Results
3.2.1. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) for Drag Force (df)
3.2.2. Analysis of the S/N Ratio for Drag Force (df)
3.3. Confirmation of Experiment Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lal, R.; Shukla, M.R. Principles of Soil Physics, Part II; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 182–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X. Theoretical analysis of the adhesion force of soil to solid materials. Biosyst. Eng. 2004, 87, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshtasb, A.; Fielke, J.; Desbiolles, J. A review of soil/tool adhesion principles and approaches to reducing limitations of disc seeders. In Agricultural Technologies in a Changing Climate: The 2009 CIGR International Symposium of the Australian Society for Engineering in Agriculture; Engineers Australia: Darwin City, Australia, 2009; pp. 208–215. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.Q.; Tong, J.; Li, J.Q.; Chen, B.C. Soil adhesion and biomimetics of soil-engaging components: A review. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 2001, 79, 239–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desbiolles, J.M. Disc Seeders: An Overview of Benefits and Limitations Experienced in the Paddock. Doctoral Dissertation, SANTFA, Clare, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Luquan, R.; Dexing, C.; Bingcong, C. A Summary of Study on Soil Adhesion. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1990, 6, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Barzegar, M.; Hashemi, S.J.; Nazokdast, H.; Karimi, R. Evaluating the draft force and soil-tool adhesion of a UHMW-PE coated furrower. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 163, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountaine, E.R. Investigations into the mechanism of soil adhesion. J. Soil Sci. 1954, 5, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marani, S.M.; Shahgholi, G.; Moinfar, A. Effect of nano coating materials on reduction of soil adhesion and external friction. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 193, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Goering, C.E.; Rohrbach, R.P.; Buckmaster, D.R. Engineering Principles of Agricultural Machines, 2nd ed.; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2006; Chapter 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, P.; Salokhe, V.M. Theoretical analysis of microscopic forces at soil-tool interfaces: A review. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2006, 3, 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Science Glossary Terms Committee. Glossary of Soil Science Terms; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xue, W.; Ma, Y.; Tong, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, J. DEM and soil bin study on a biomimetic disc furrow opener. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 156, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Ito, N.; Kito, K.; Garcia, P.P. Study on use of vibration to reduce soil adhesion. J. Terramech. 1998, 35, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tong, J.; Zhang, Z. DEM simulation of bionic subsoilers (tillage depth > 40 cm) with drag reduction and lower soil disturbance characteristics. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2018, 119, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salokhe, V.M.; Gee-Clough, D.; Manzoor, S.; Singh, K.K. Improvement of the tractive performance of cage wheel lugs by enamel coating. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1990, 45, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Cong, Q.; Tong, J.; Chen, B. Reducing adhesion of soil against loading shovel using bionic electro-osmosis method. J. Terramech. 2001, 38, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, P.; Salokhe, V.M.; Nakashima, H. Modification of a mouldboard plough surface using arrays of polyethylene protuberances. J. Terramech. 2007, 44, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Moayad, B.Z.; Ma, Y.H.; Sun, J.Y.; Chen, D.H.; Jia, H.L.; Ren, L.Q. Effects of biomimetic surface designs on furrow opener performance. J. Bionic Eng. 2009, 6, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Reddy, M.M.; Yi, Q.S. Influence of cutting fluid conditions and cutting parameters on surface roughness and tool wear in turning process using Taguchi method. Measurement 2016, 78, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kıvak, T. Optimization of surface roughness and flank wear using the Taguchi method in milling of Hadfield steel with PVD and CVD coated inserts. Measurement 2014, 50, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirende, B.; Li, J.; Wen, L.; Simalenga, T.E. Effects of bionic non-smooth surface on reducing soil resistance to disc ploughing. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 2960–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, P.; Salokhe, V.M. Influence of dimensions of UHMW-PE protuberances on sliding resistance and normal adhesion of Bangkok clay soil to biomimetic plates. J. Bionic Eng. 2006, 3, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagar, A.A.; Ji, C.; Ding, Q.; Adamowski, J.; Chandio, F.A.; Mari, I.A. Soil failure patterns and draft as influenced by consistency limits: An evaluation of the remolded soil cutting test. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 137, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Kheir, A.; Al-Dhumri, S.; Alghamdi, A.G.; Omar, E.S.H.; Aboelsoud, H.M.; Abou El Hassan, W.H. Exploring optimal tillage improved soil characteristics and productivity of wheat irrigated with different water qualities. Agronomy 2019, 9, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manivel, D.; Gandhinathan, R. Optimization of surface roughness and tool wear in hard turning of austempered ductile iron (grade 3) using Taguchi method. Measurement 2016, 93, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, M.H.; Ozcelik, B.; Kuram, E.; Demirbas, E. Evaluation of vegetable based cutting fluids with extreme pressure and cutting parameters in turning of AISI 304L by Taguchi method. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.Q.; Han, Z.W.; Li, J.Q.; Tong, J. Experimental investigation of bionic rough curved soil cutting blade surface to reduce soil adhesion and friction. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 85, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, P.; Salokhe, V.M. Bio-Inspired Macro-Morphologic Surface Modifications to Reduce Soil–Tool Adhesion. In Bio-Inspired Surfaces and Applications; World Scientific Publishing: London, UK, 2016; Chapter 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Wu, B.; Song, Z.; Gao, Z.; Sun, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhuang, J. Research on the drag reduction mechanism of antlion (Myrmeleon sagax) larvae nonsmooth structural surface. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2020, 83, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Symbol | Level Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Disc coverage ratio (CR) (%) | A | 45 | 60 | 75 |
| Dome height-to-diameter ratio (HDR) (%) | B | 12.5 | 25 | 37.5 |
| Dome base diameter (DBD) (mm) | C | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| Property | Paddy Field | Sunflower Field |
|---|---|---|
| Dry bulk density (kg m−3) | 1557 | 1412 |
| Liquid limit (%) | 42 | 36 |
| Plastic limit (%) | 20 | 17 |
| Texture 1 | Silty loam | Sandy clay loam |
| Sand | 22 ± 1.5% | 54 ± 2.5% |
| Silt | 63 ± 1.8% | 25 ± 1.5% |
| Clay | 15 ± 1% | 21 ± 1.1% |
| Disc No. | Parameter Combinations | h (mm) | n | L (mm) | Drag Force (N) | Δ (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | |||||||||
| Control | - | - | - | - | 9.2 | 9.3 | 8.9 | 9.1 | - |
| 1 | 1.25 | 45 | 13.0 | 7.8 | 7.6 | 7.4 | 7.6 | 16.5 | |
| 2 | 1.25 | 60 | 11.5 | 7.2 | 7.4 | 7.1 | 7.2 | 20.9 | |
| 3 | 1.25 | 75 | 10.2 | 9.8 | 9.4 | 10 | 9.7 | −6.6 | |
| 4 | 2.5 | 45 | 13.0 | 7 | 6.8 | 6.9 | 6.9 | 24.2 | |
| 5 | 2.5 | 60 | 11.5 | 7.1 | 7.3 | 6.8 | 7 | 23.1 | |
| 6 | 2.5 | 75 | 10.2 | 8.7 | 8.5 | 8.4 | 8.5 | 6.6 | |
| 7 | 3.75 | 45 | 13.0 | 9.8 | 9.4 | 9.2 | 9.5 | −4.4 | |
| 8 | 3.75 | 60 | 11.5 | 8.3 | 8.2 | 8.3 | 8.3 | 8.8 | |
| 9 | 3.75 | 75 | 10.2 | 10.8 | 10.5 | 11.3 | 10.9 | −19.8 | |
| 10 | 2.5 | 11 | 26.0 | 7.5 | 7.3 | 7.2 | 7.3 | 19.8 | |
| 11 | 2.5 | 15 | 23.0 | 7.4 | 7.8 | 8 | 7.7 | 15.4 | |
| 12 | 2.5 | 19 | 20.4 | 9.7 | 9.2 | 9.1 | 9.3 | −2.2 | |
| 13 | 5.0 | 11 | 26.0 | 6.9 | 6.8 | 7.1 | 6.9 | 25.3 | |
| 14 | 5.0 | 15 | 23.0 | 6.6 | 7 | 6.5 | 6.8 | 24.2 | |
| 15 | 5.0 | 19 | 20.4 | 6.8 | 7.3 | 6.9 | 7 | 23.1 | |
| 16 | 7.5 | 11 | 26.0 | 9.5 | 9.3 | 9.2 | 9.3 | −2.2 | |
| 17 | 7.5 | 15 | 23.0 | 7.9 | 8.1 | 8.5 | 8.2 | 9.9 | |
| 18 | 7.5 | 19 | 20.4 | 9.9 | 9.6 | 10 | 9.8 | −7.7 | |
| 19 | 3.75 | 5 | 39.0 | 7.7 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.6 | 16.5 | |
| 20 | 3.75 | 7 | 34.5 | 7.7 | 7.2 | 7.4 | 7.4 | 18.7 | |
| 21 | 3.75 | 9 | 30.6 | 9.3 | 9.3 | 9.2 | 9.3 | −2.2 | |
| 22 | 7.5 | 5 | 39.0 | 6.9 | 7.3 | 6.9 | 7 | 23.1 | |
| 23 | 7.5 | 7 | 34.5 | 6.4 | 6.6 | 6.7 | 6.6 | 27.5 | |
| 24 | 7.5 | 9 | 30.6 | 7.8 | 7.8 | 7.4 | 7.7 | 15.4 | |
| 25 | 11.25 | 5 | 39.0 | 9.8 | 10 | 9.5 | 9.8 | −7.7 | |
| 26 | 11.25 | 7 | 34.5 | 9 | 9.1 | 9 | 9 | 1.1 | |
| 27 | 11.25 | 9 | 30.6 | 10.2 | 9.7 | 10.5 | 10.1 | −11 | |
| Variance Source | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | Contribution/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR | 2 | 11.80 | 5.90 | 77.49 | 0.000 | 29.4 |
| HDR | 2 | 23.53 | 11.76 | 154.55 | 0.000 | 58.5 |
| DBD | 2 | 0.63 | 0.31 | 4.12 | 0.043 | 1.6 |
| CR HDR | 4 | 2.18 | 0.55 | 7.17 | 0.003 | 5.4 |
| CR DBD | 4 | 1.14 | 0.28 | 3.74 | 0.034 | 2.8 |
| 0.08 | 2.3 | |||||
| Total | 26 | 40.18 | 100 |
| Level | Control Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CR (%) | HDR (%) | DBD (mm) | |
| 1 | −17.95 | −18.14 | −18.38 |
| 2 | −17.56 | −17.07 | −18.02 |
| 3 | −19.15 | −19.46 | −18.27 |
| Delta | 1.59 | 2.39 | 0.36 |
| Order | HDR > CR > DBD | ||
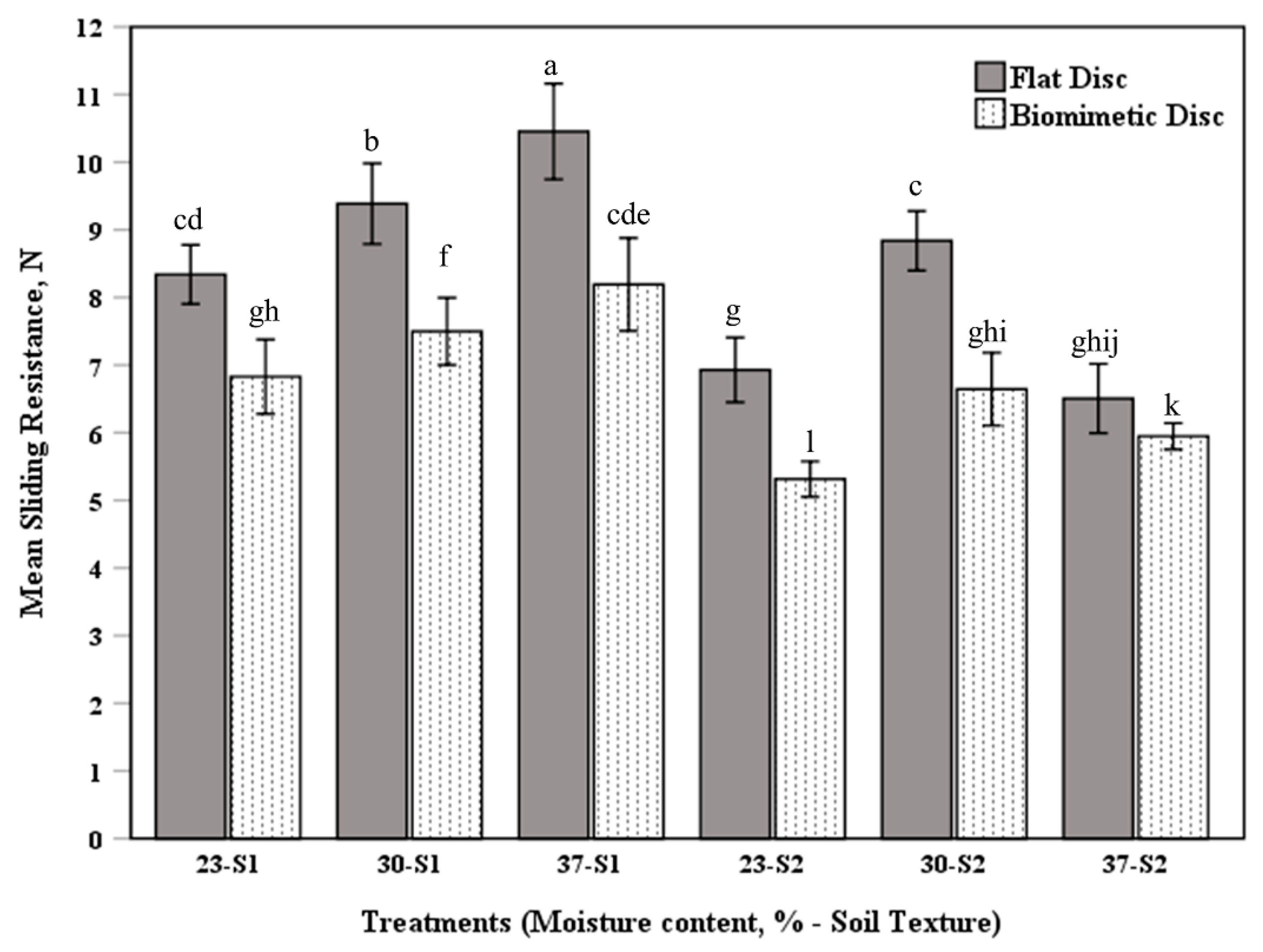
| Test Condition | Disc Type | Mean τ (N) | Std. Dev | t Value | p Value | Δ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23% MC, S1 | Flat | 8.3 | 0.37 | 9.67 | 0.001 | 18.1 |
| Biomimetic | 6.8 | 0.43 | ||||
| 30% MC, S1 | Flat | 9.4 | 0.50 | 5.67 | 0.005 | 24.5 |
| Biomimetic | 7.1 | 0.37 | ||||
| 37% MC, S1 | Flat | 10.5 | 0.57 | 16.65 | <0.001 | 21.9 |
| Biomimetic | 8.2 | 0.53 | ||||
| 23% MC, S2 | Flat | 6.9 | 0.40 | 8.45 | 0.001 | 23.2 |
| Biomimetic | 5.3 | 0.20 | ||||
| 30% MC, S2 | Flat | 8.8 | 0.37 | 26.70 | <0.001 | 25.0 |
| Biomimetic | 6.6 | 0.43 | ||||
| 37% MC, S2 | Flat | 6.5 | 0.40 | 3.36 | 0.028 | 9.2 |
| Biomimetic | 5.9 | 0.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salem, A.E.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Zha, X.; Abdeen, M.A.; Zhang, G. Effect of Biomimetic Surface Geometry, Soil Texture, and Soil Moisture Content on the Drag Force of Soil-Touching Parts. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8927. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11198927
Salem AE, Wang H, Gao Y, Zha X, Abdeen MA, Zhang G. Effect of Biomimetic Surface Geometry, Soil Texture, and Soil Moisture Content on the Drag Force of Soil-Touching Parts. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(19):8927. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11198927
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalem, Abouelnadar El., Hongchang Wang, Yuan Gao, Xiantao Zha, Mohamed Anwer Abdeen, and Guozhong Zhang. 2021. "Effect of Biomimetic Surface Geometry, Soil Texture, and Soil Moisture Content on the Drag Force of Soil-Touching Parts" Applied Sciences 11, no. 19: 8927. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11198927
APA StyleSalem, A. E., Wang, H., Gao, Y., Zha, X., Abdeen, M. A., & Zhang, G. (2021). Effect of Biomimetic Surface Geometry, Soil Texture, and Soil Moisture Content on the Drag Force of Soil-Touching Parts. Applied Sciences, 11(19), 8927. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11198927







