Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, Degradation Behavior, and Implant Testing of Hot-Rolled Biodegradable ZKX500 Magnesium Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
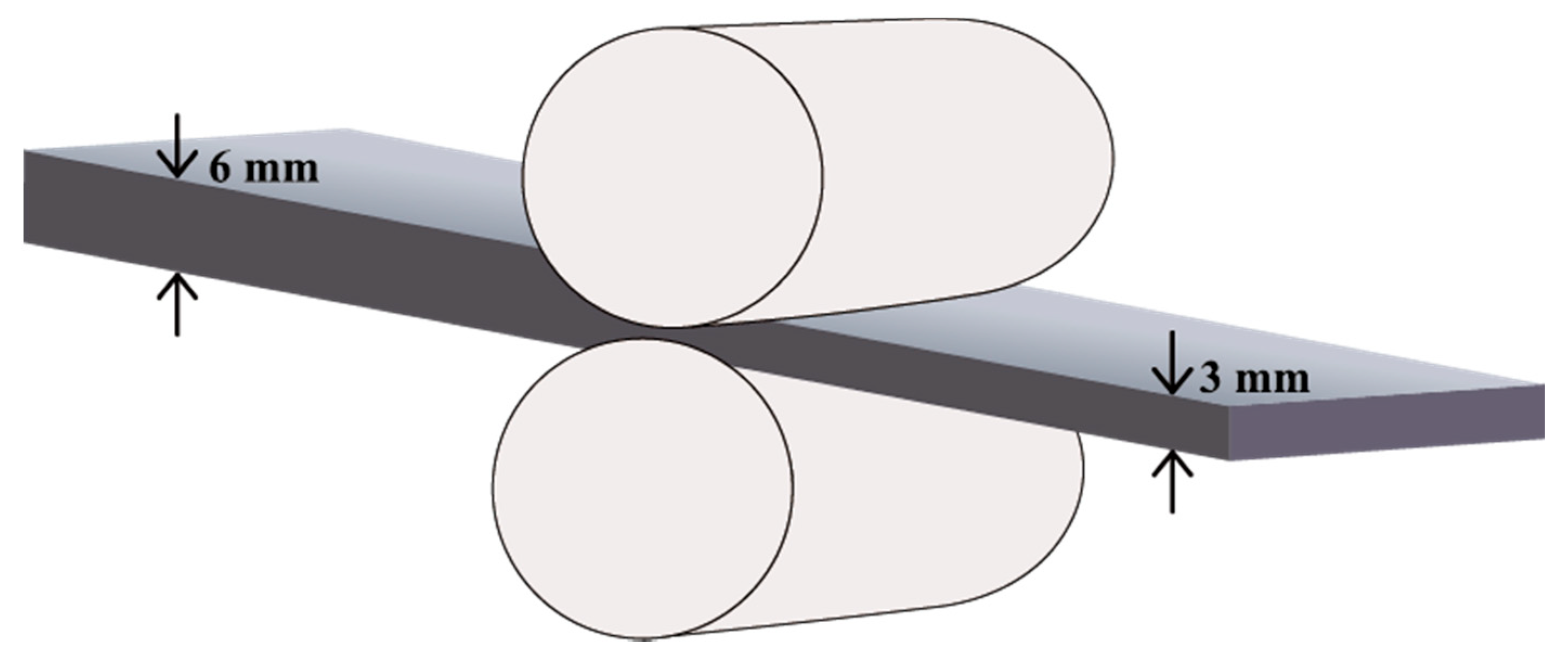
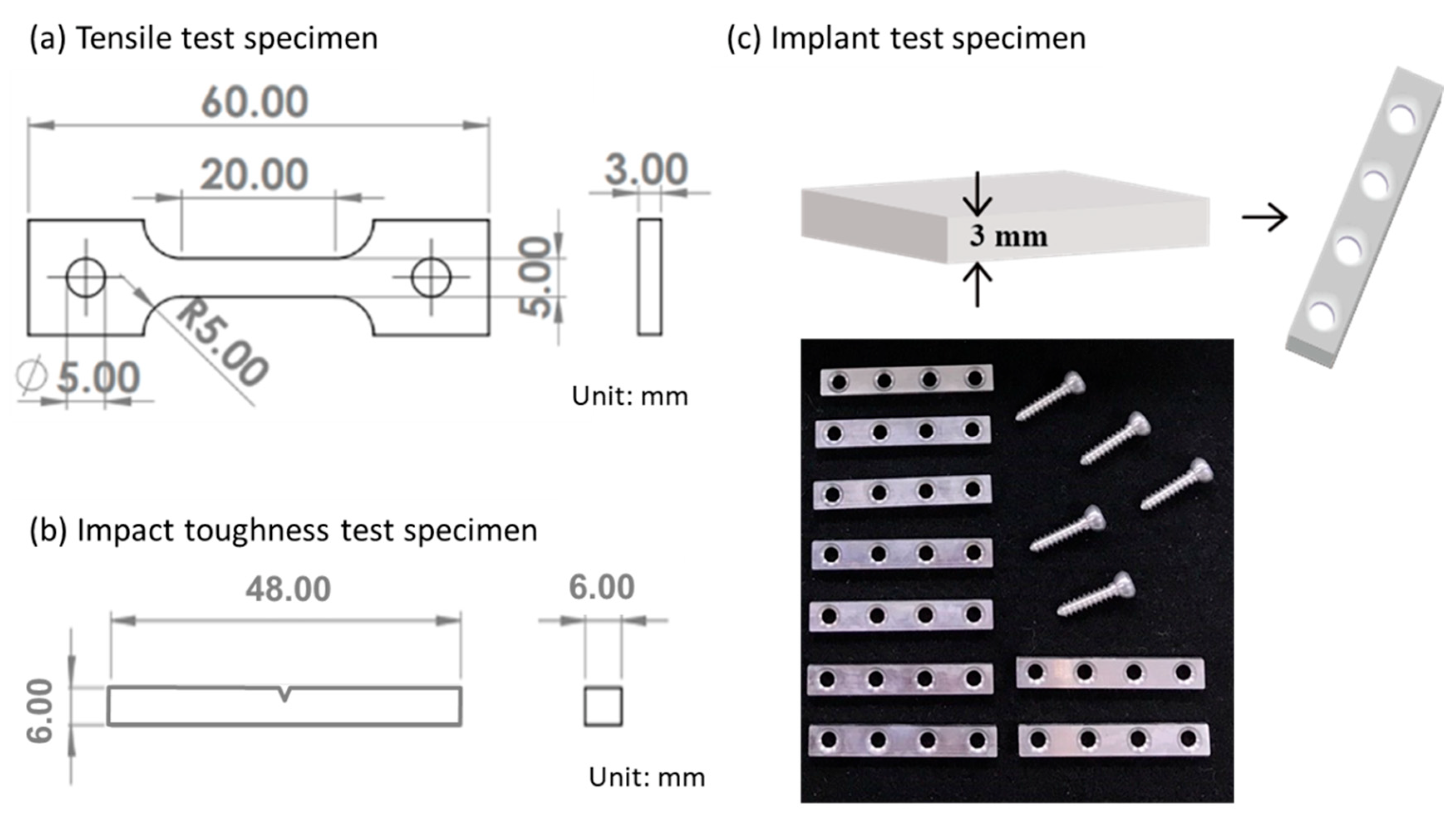
2.2. Microstructure Characterization and Mechanical Properties
2.3. In Vitro Degradation Test
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assessments
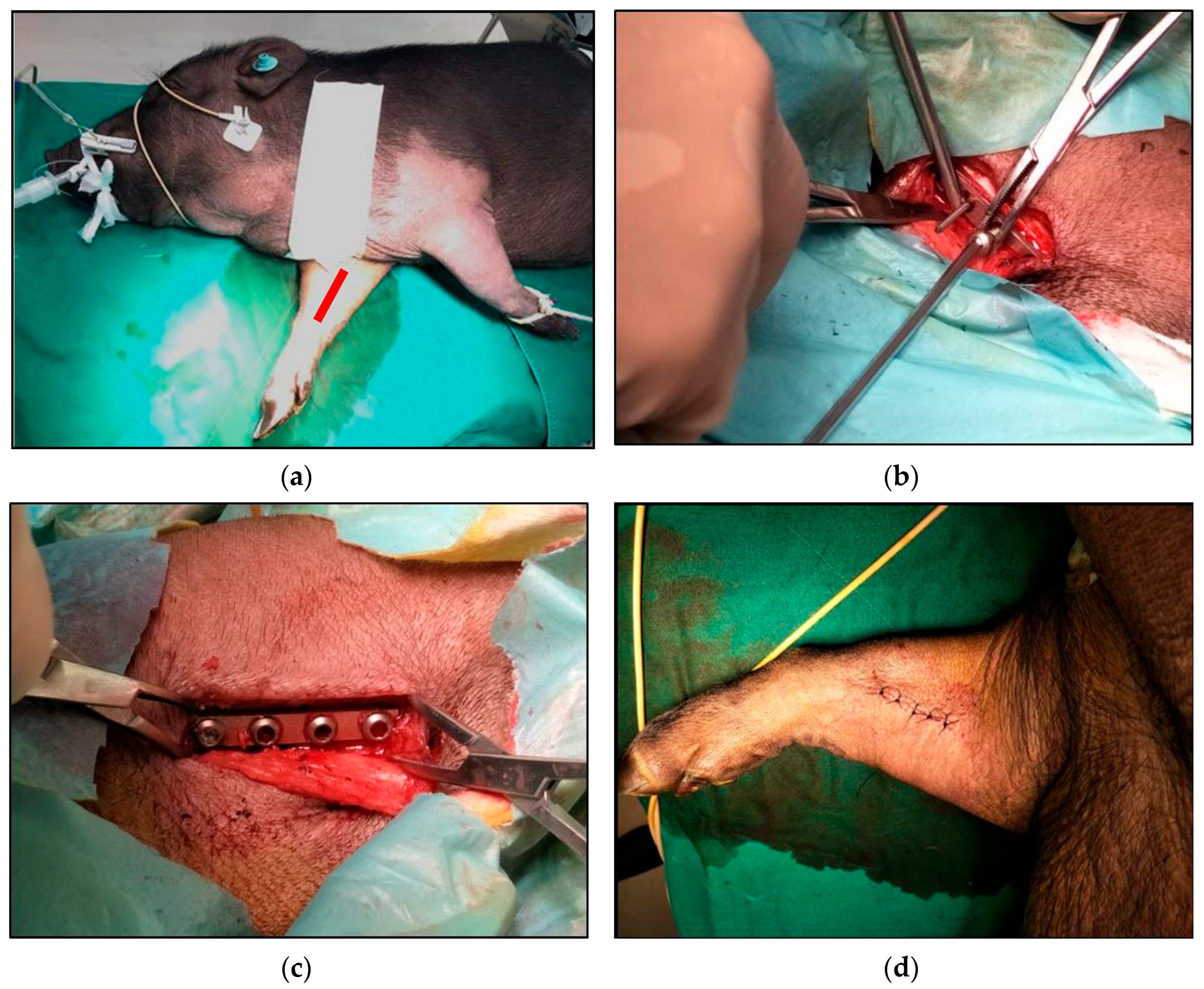
2.5. In Vivo Implantation Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
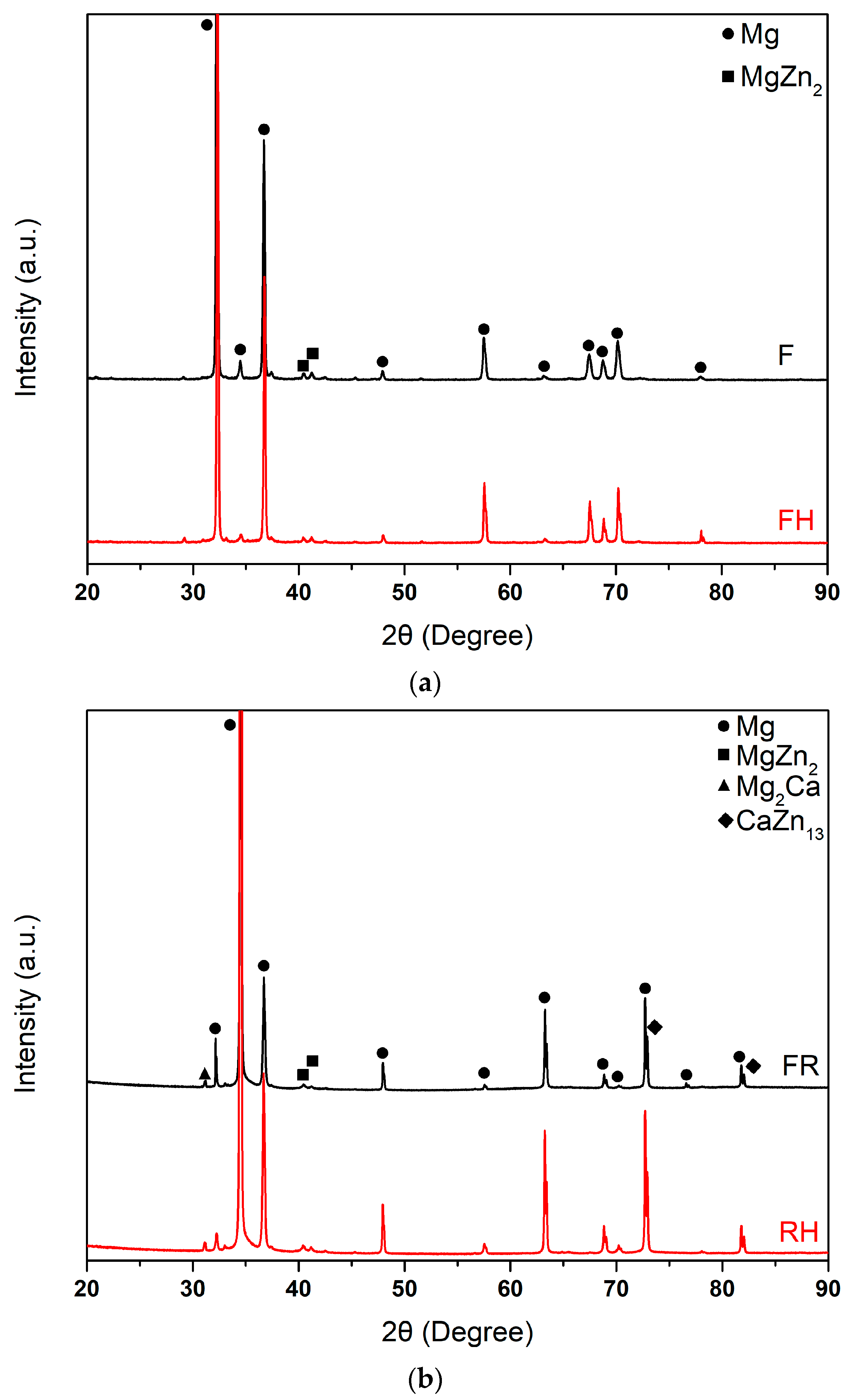
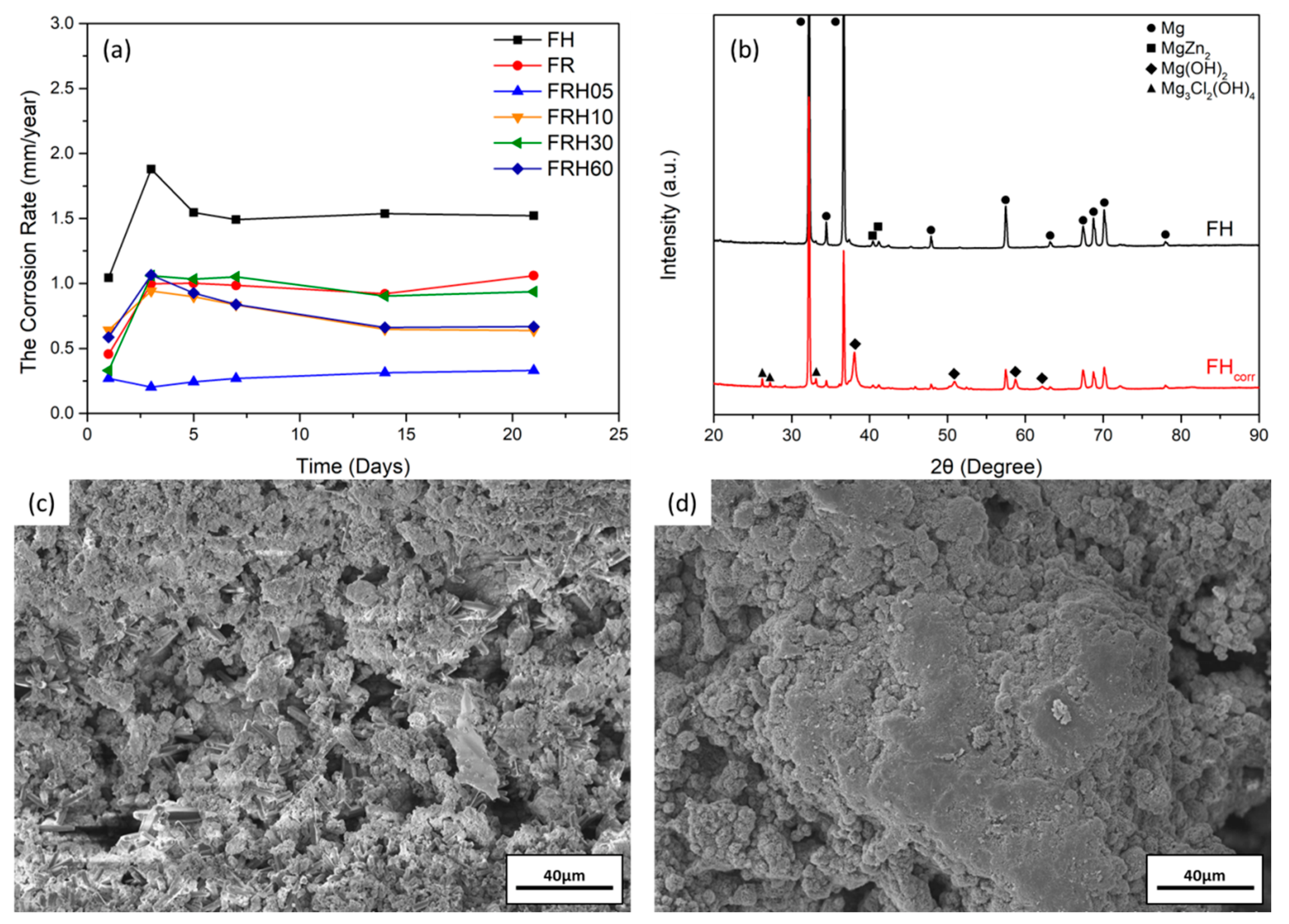
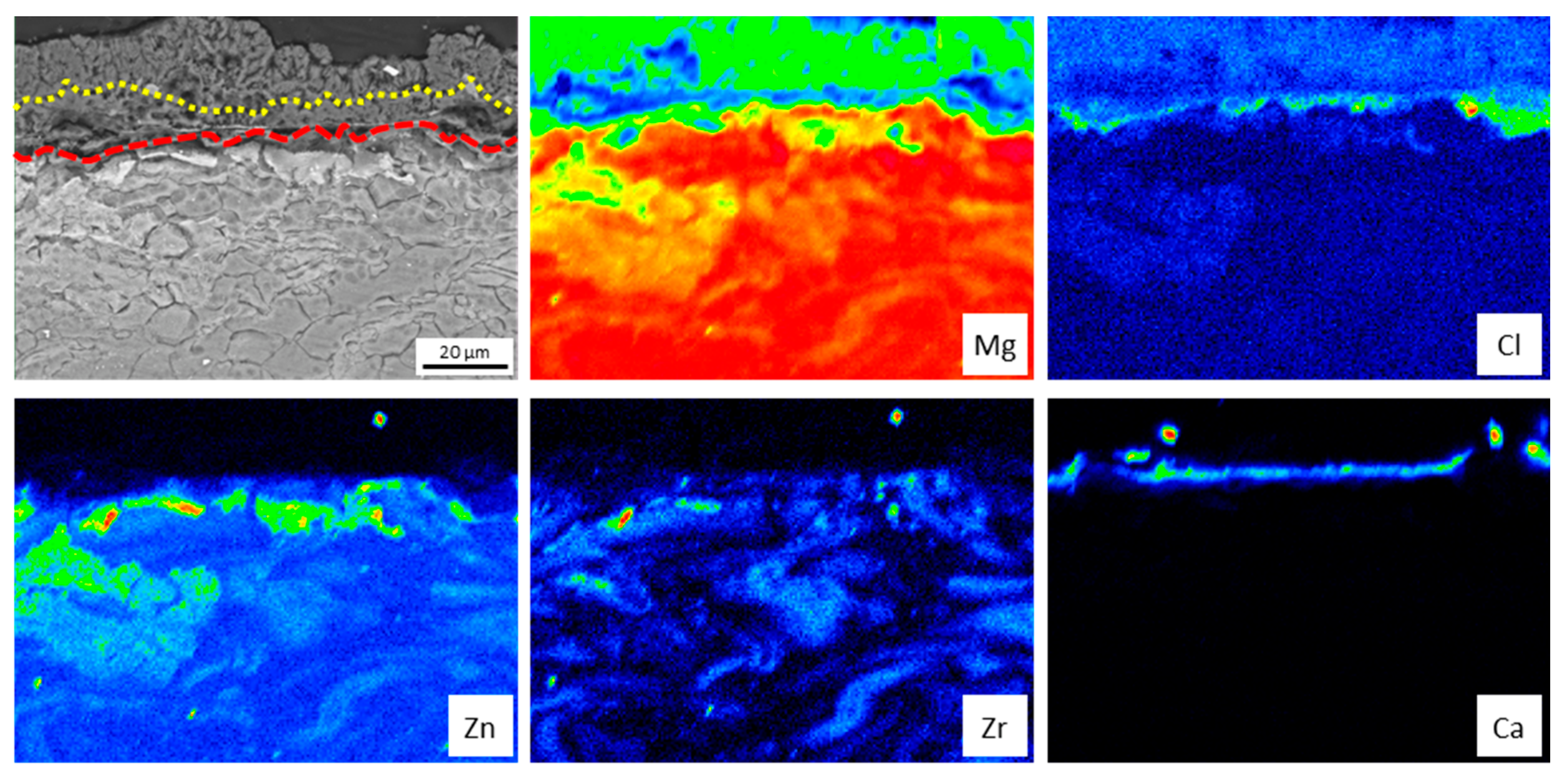
3.1. Microstructure and Phase Analysis
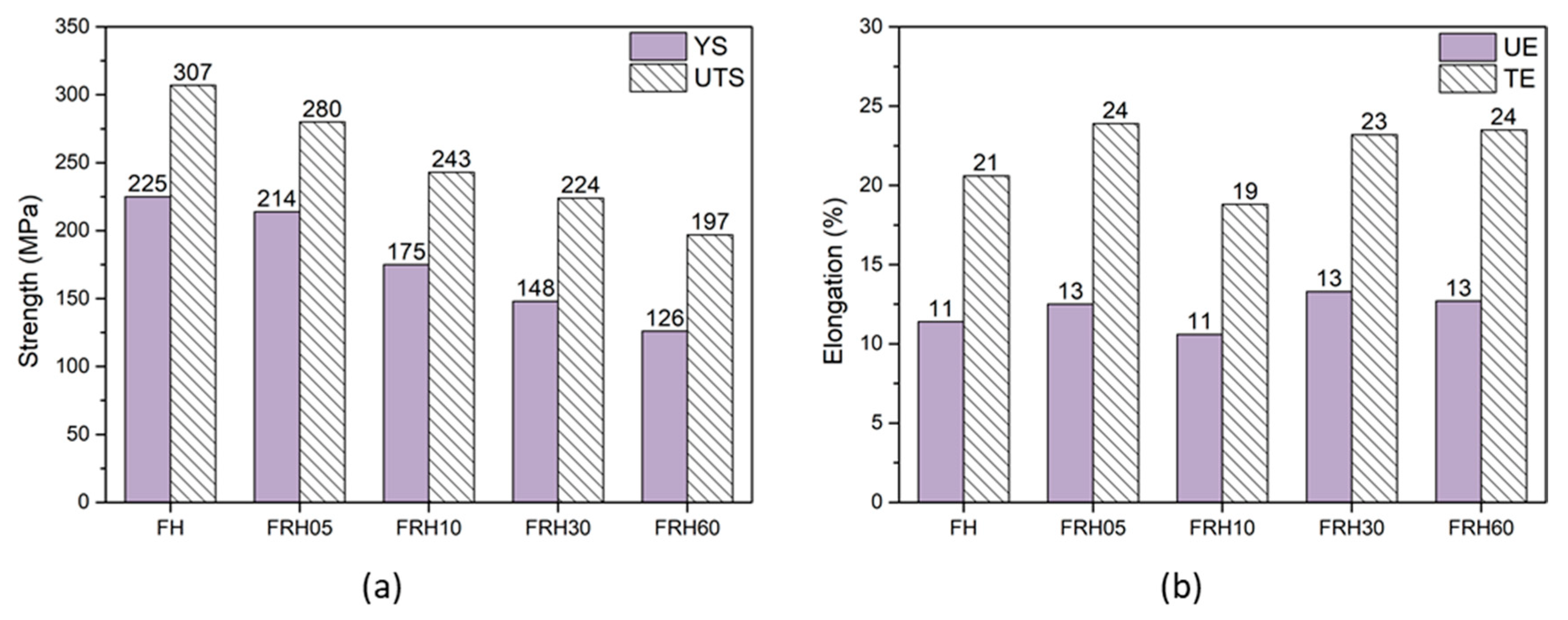
3.2. Hardness and Tensile Mechanical Properties
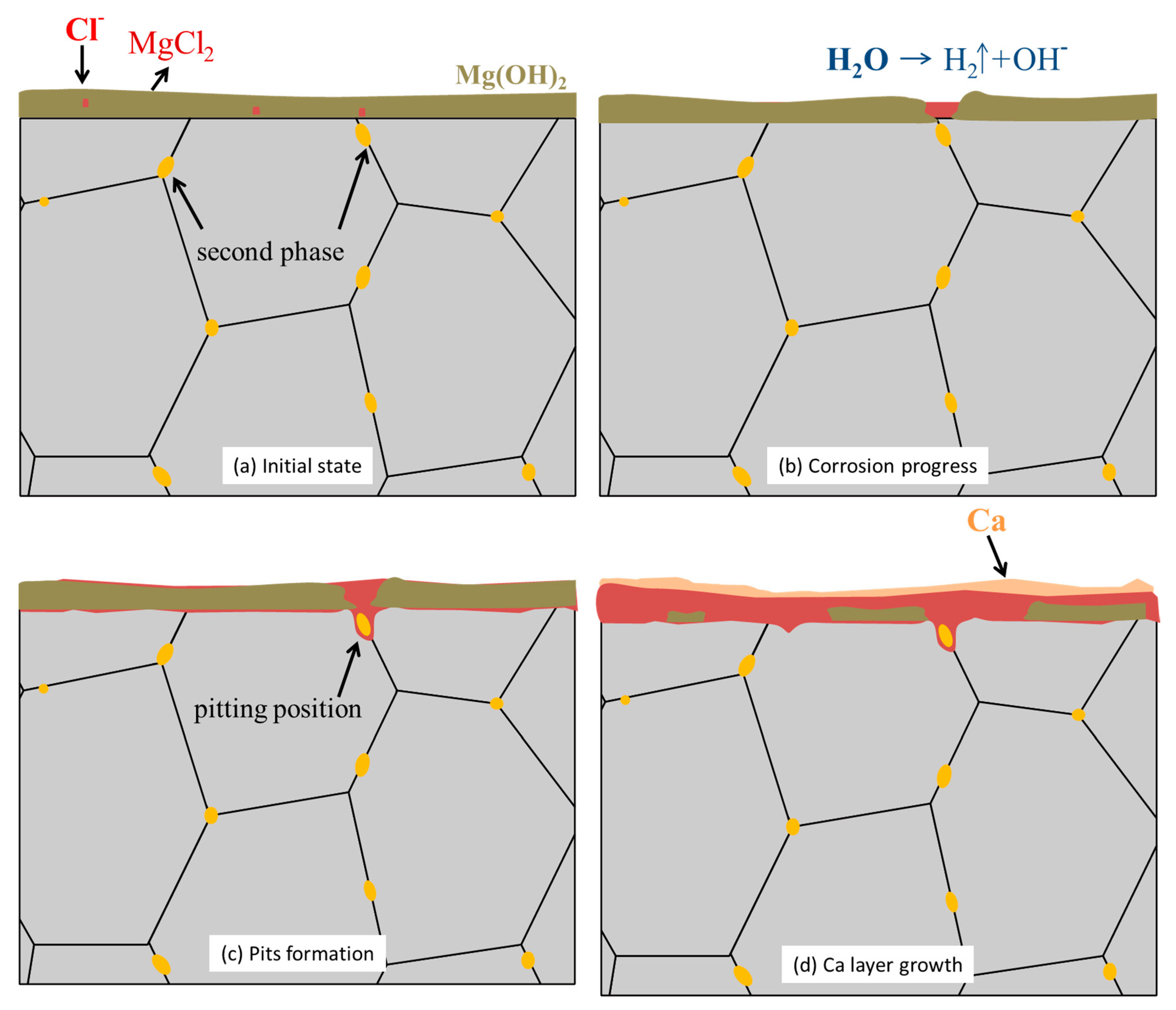
3.3. In Vitro Immersion Test
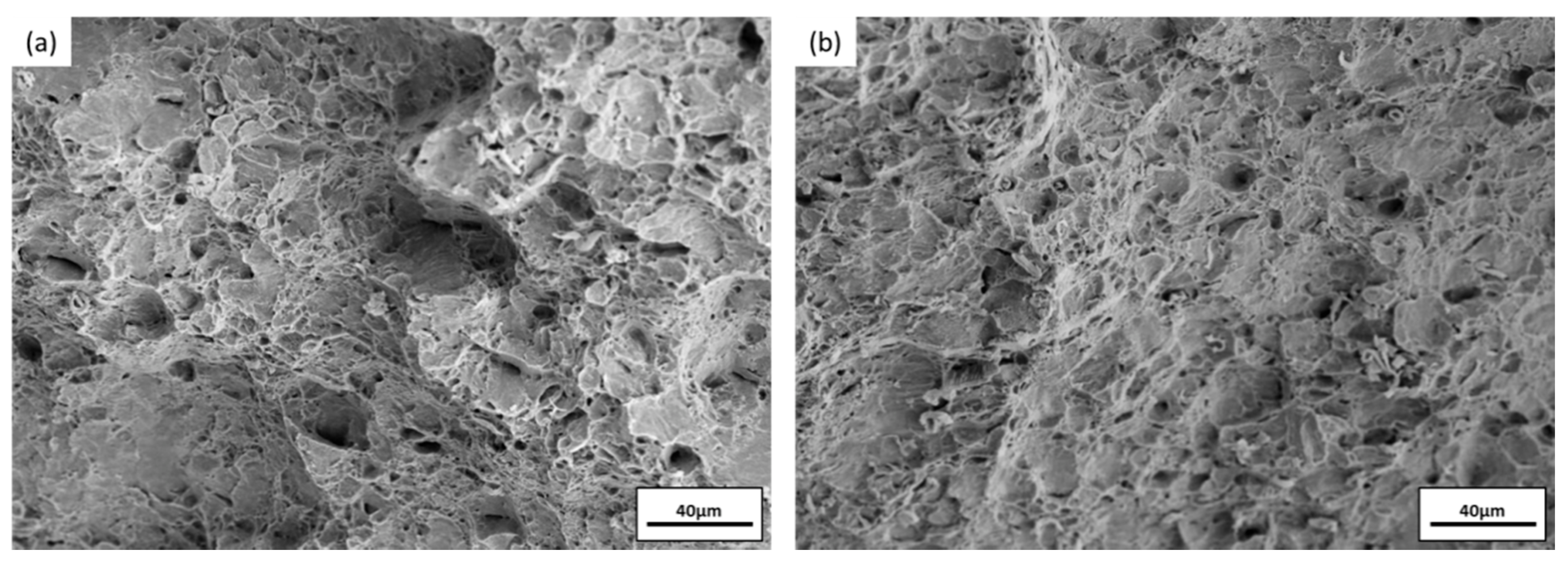
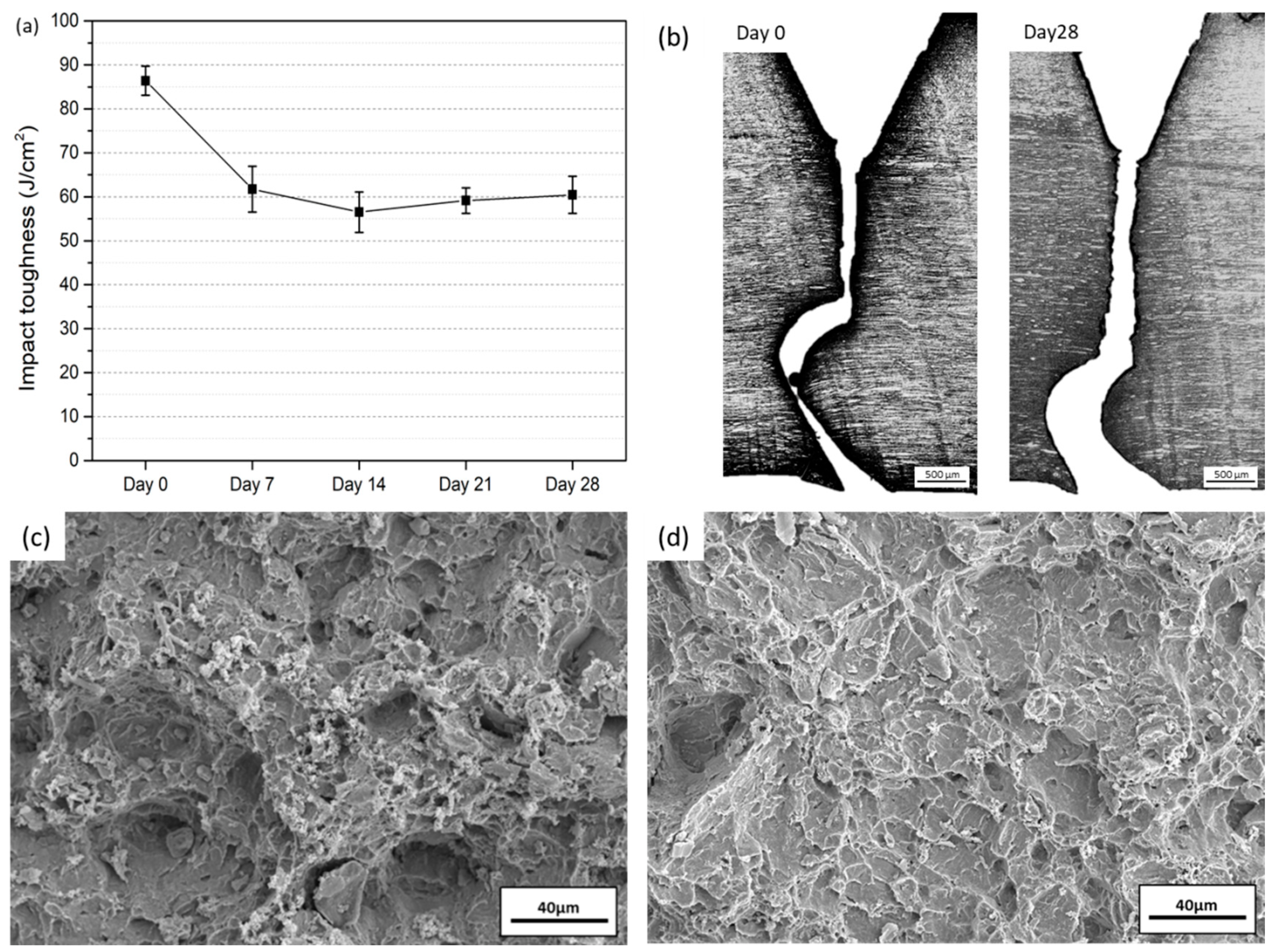
3.4. Impact Toughness after Immersion
3.5. Cytotoxicity Test
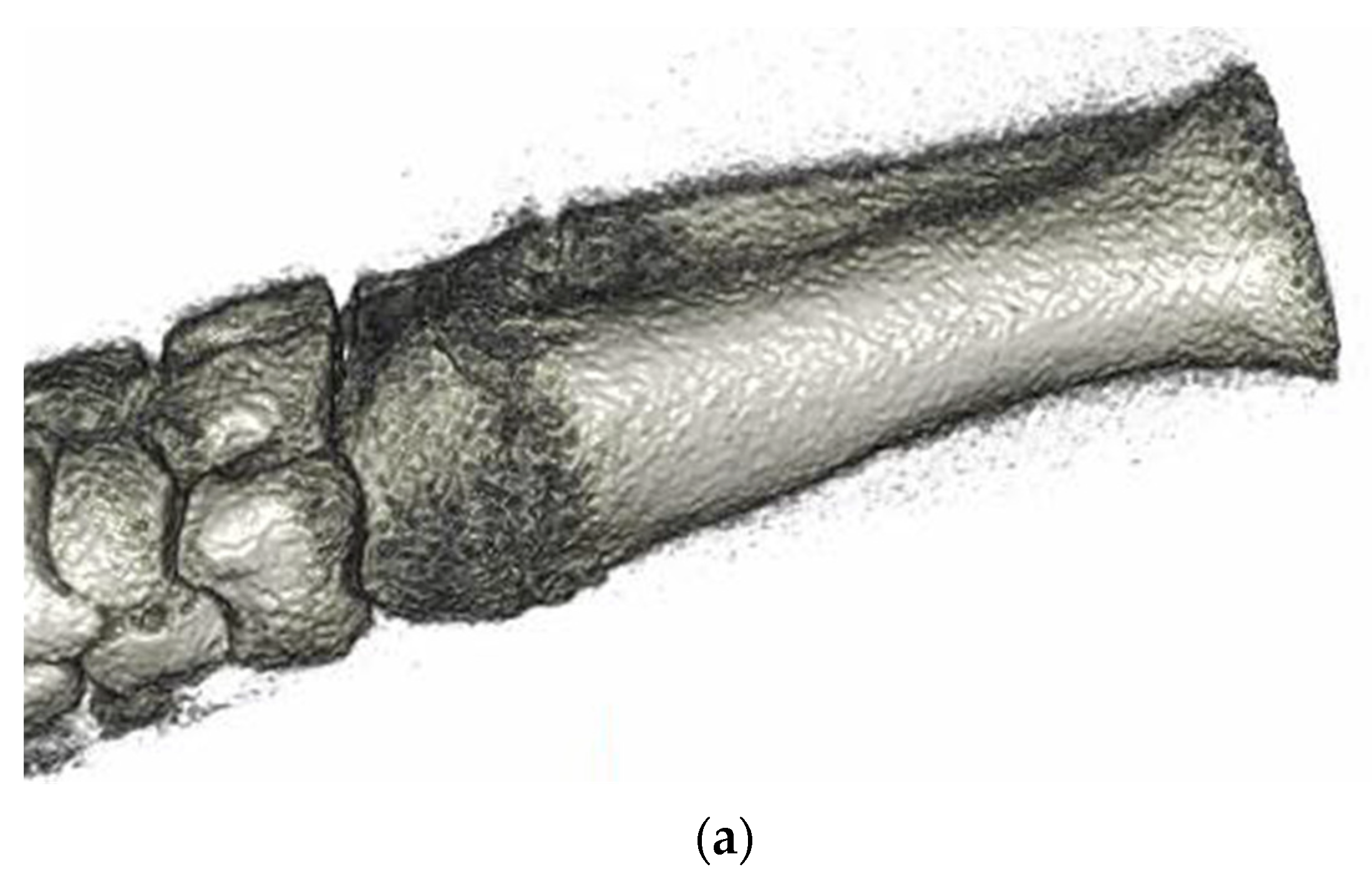
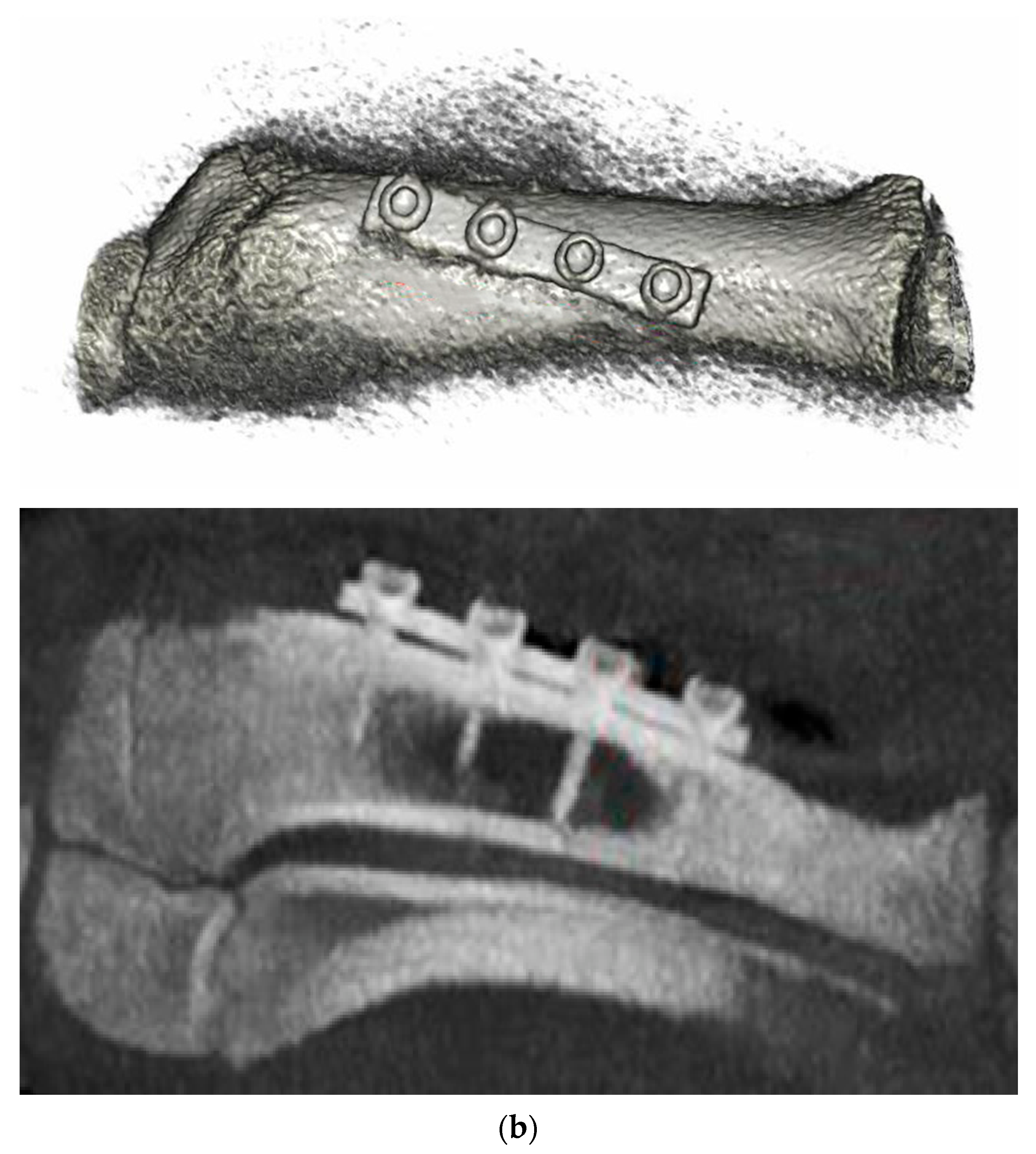
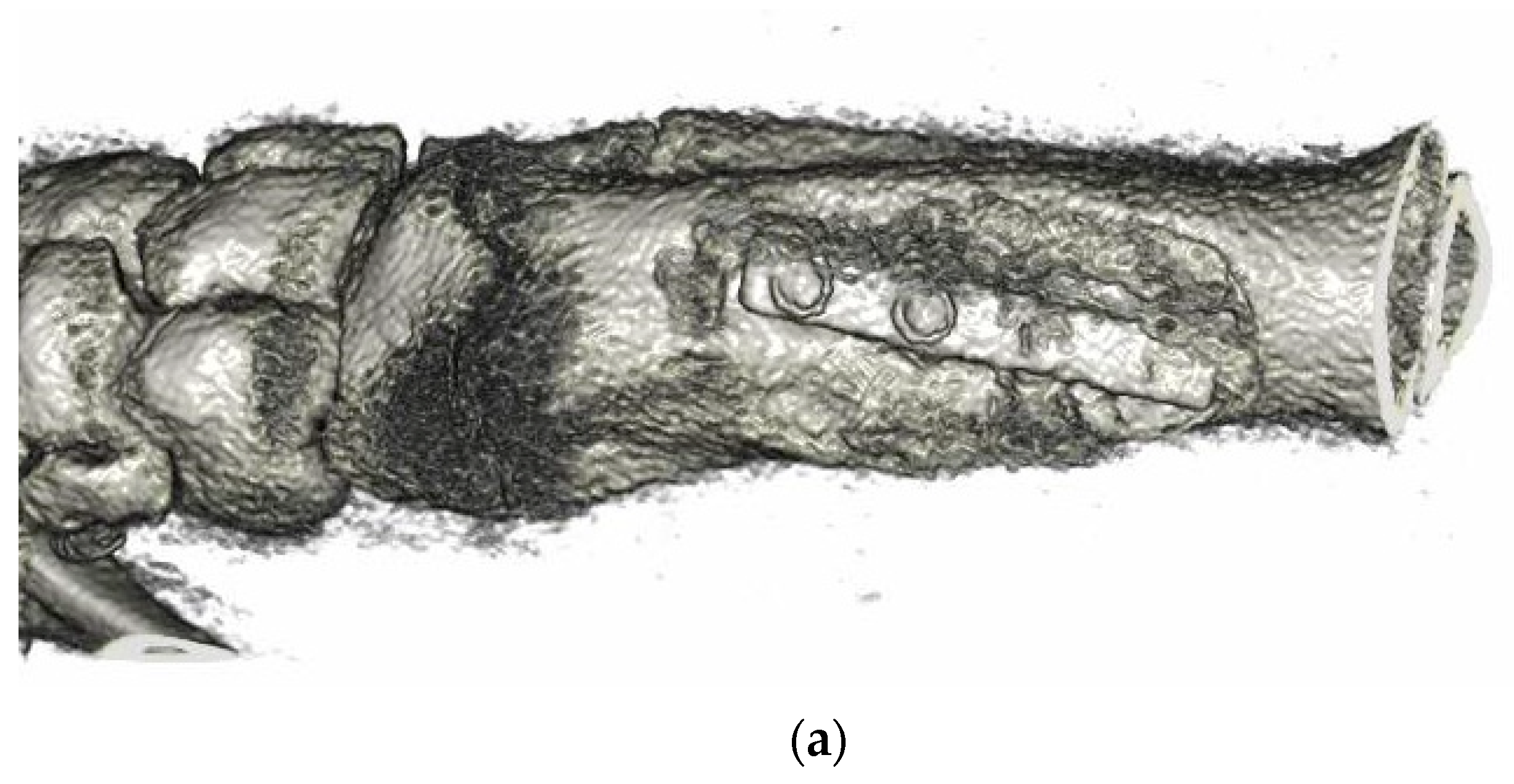
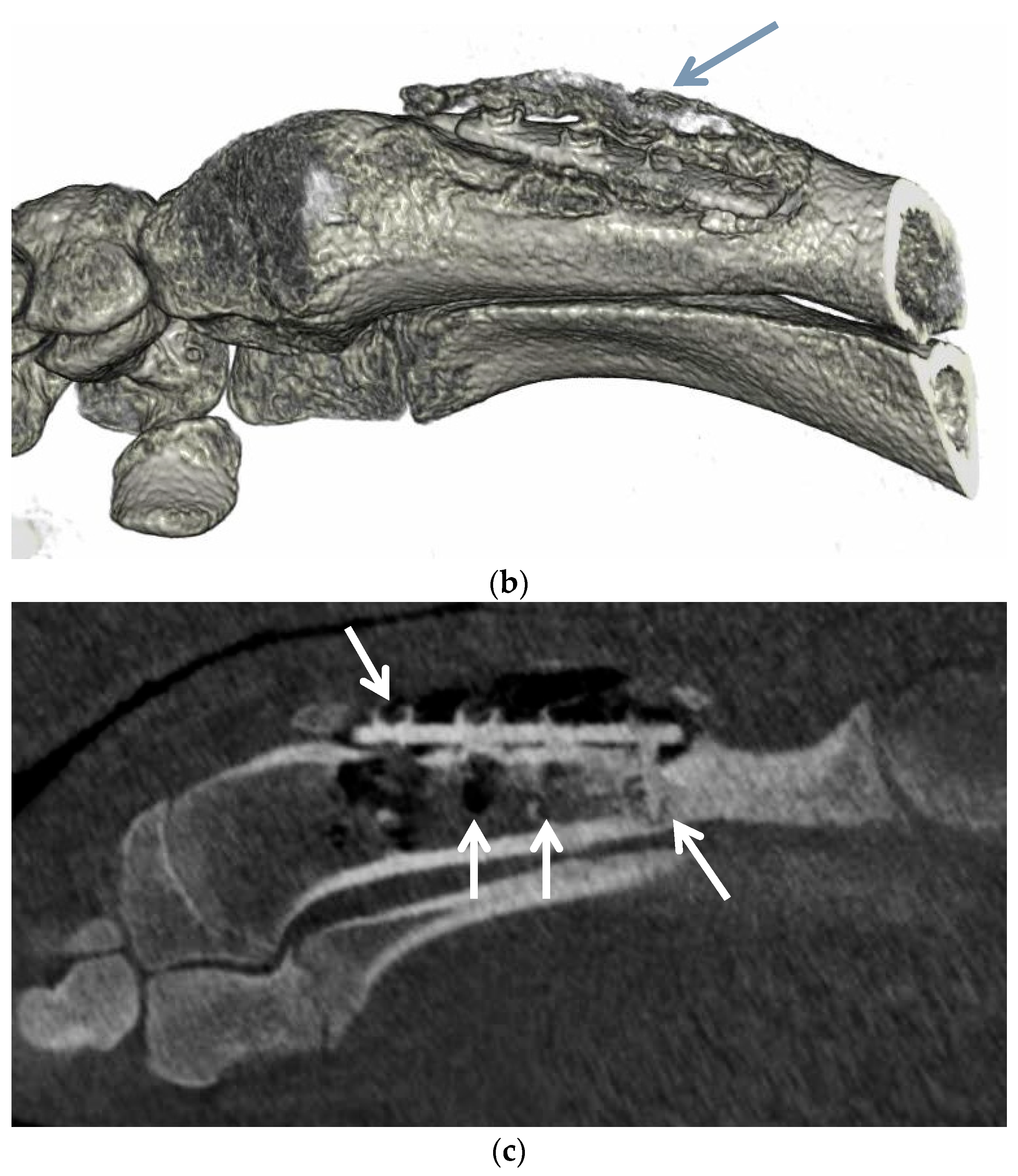
3.6. Animal Implantation Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, G.-L. Corrosion electrochemistry of magnesium (Mg) and its alloys. Corros. Magnes. Alloy. 2011, 2011, 3–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Lian, Y.; He, G. A review on ignition mechanisms and characteristics of magnesium alloys. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2020, 8, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Smith, C.; Sankar, J. Recent advances on the development of magnesium alloys for biodegradable implants. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4561–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohlen, J.; Wendt, J.; Nienaber, M.; Kainer, K.U.; Stutz, L.; Letzig, D. Calcium and zirconium as texture modifiers during rolling and annealing of magnesium–zinc alloys. Mater. Charact. 2015, 101, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawar, S.; Slater, T.; Burnett, T.; Zhou, X.; Scamans, G.; Fan, Z.; Thompson, G.; Withers, P. Crystallographic effects on the corrosion of twin roll cast AZ31 Mg alloy sheet. Acta Mater. 2017, 133, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yan, H.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Tian, J. Effect of twinning and dynamic recrystallization on the high strain rate rolling process. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Hu, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, E. Grain growth kinetics of a fine-grained AZ31 magnesium alloy produced by hot rolling. J. Alloy. Compd. 2010, 493, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Bi, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Yan, J.; Song, J.; Sheng, H.; Guo, H.; Li, Y. Biodegradation behavior of magnesium and ZK60 alloy in artificial urine and rat models. Bioact. Mater. 2017, 2, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Hung, F.-Y.; Lin, Y.-L.; Lin, C.-Y. Biodegradation ZK50 magnesium alloy compression screws: Mechanical properties, biodegradable characteristics and implant test. J. Orthop. Sci. 2020, 25, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradnezhad, S.; Razaghian, A.; Taghiabadi, R.; Abedi, H.R.; Salandari-Rabori, A.; Emamy, M. Effect of Ca additions on evolved microstructures and subsequent mechanical properties of a cast and hot-extruded Mg–Zn–Zr magnesium alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 104, 4265–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. Standard Practice for Laboratory Immersion Corrosion Testing of Metals; ASTM-G31–72; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Gebresellasie, K.; Collins, B.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.; Sankar, J.; Lee, Y.-C.; Yun, Y. Degradation Rates of Pure Zinc, Mag-nesium, and Magnesium Alloys Measured by Volume Loss, Mass Loss, and Hydrogen Evolution. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, J.; Shadanbaz, S.; Kirkland, N.T.; Stace, E.; Woodfield, T.; Staiger, M.P.; Dias, G.J. Magnesium alloys: Predicting in vivo corrosion with in vitro immersion testing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100B, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO E. 10993–5: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices- Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. Available online: https://webstore.ansi.org/preview-pages/BSI/preview_30356171.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Klein-Júnior, C.A.; Zimmer, R.; Hentschke, G.S.; Machado, D.C.; Dos Santos, R.B.; Reston, E.G. Effect of heat treatment on cyto-toxicity of self-adhesive resin cements: Cell viability analysis. Eur. J. Dent. 2018, 12, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Imwinkelried, T.; Beck, S.; Schaller, B. Pre-clinical testing of human size magnesium implants in miniature pigs: Implant degradation and bone fracture healing at multiple implantation sites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 108, 110389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostaed, E.; Hashempour, M.; Fabrizi, A.; Dellasega, D.; Bestetti, M.; Bonollo, F.; Vedani, M. Microstructure, texture evolution, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of ECAP processed ZK60 magnesium alloy for biodegradable applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 37, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Estrin, Y.; Zúberová, Z. Bio-corrosion of a magnesium alloy with different processing histories. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 2476–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Lei, T.; Li, N.; Feng, F. Effects of Zn on microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of Mg–Zn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2570–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Hamzah, E.; Medraj, M.; Idris, M.H.; Lotfabadi, A.F.; Daroonparvar, M.; Yajid, M.A.M. Effect of heat treat-ment on the microstructure and corrosion behaviour of Mg–Zn alloys. Mater. Corros. 2014, 65, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, T.; Xi, T.; Zheng, Y. Hemolysis and cytotoxicity mechanisms of biodegradable magnesium and its alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 46, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Hardness | F | FH | FR | FRH05 | FRH10 | FRH30 | FRH60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRF | 80 | 77 | 84 | 78 | 75 | 76 | 74 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.-T.; Hung, F.-Y.; Kuan, F.-C.; Hsu, K.-L.; Su, W.-R.; Lin, C.-Y. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, Degradation Behavior, and Implant Testing of Hot-Rolled Biodegradable ZKX500 Magnesium Alloy. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10677. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210677
Huang Y-T, Hung F-Y, Kuan F-C, Hsu K-L, Su W-R, Lin C-Y. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, Degradation Behavior, and Implant Testing of Hot-Rolled Biodegradable ZKX500 Magnesium Alloy. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(22):10677. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210677
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Ying-Ting, Fei-Yi Hung, Fa-Chuan Kuan, Kai-Lan Hsu, Wei-Ren Su, and Chia-Yen Lin. 2021. "Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, Degradation Behavior, and Implant Testing of Hot-Rolled Biodegradable ZKX500 Magnesium Alloy" Applied Sciences 11, no. 22: 10677. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210677
APA StyleHuang, Y.-T., Hung, F.-Y., Kuan, F.-C., Hsu, K.-L., Su, W.-R., & Lin, C.-Y. (2021). Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, Degradation Behavior, and Implant Testing of Hot-Rolled Biodegradable ZKX500 Magnesium Alloy. Applied Sciences, 11(22), 10677. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210677






