Short-Facelift Approach in Temporal Artery Biopsy: Is It Safe?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
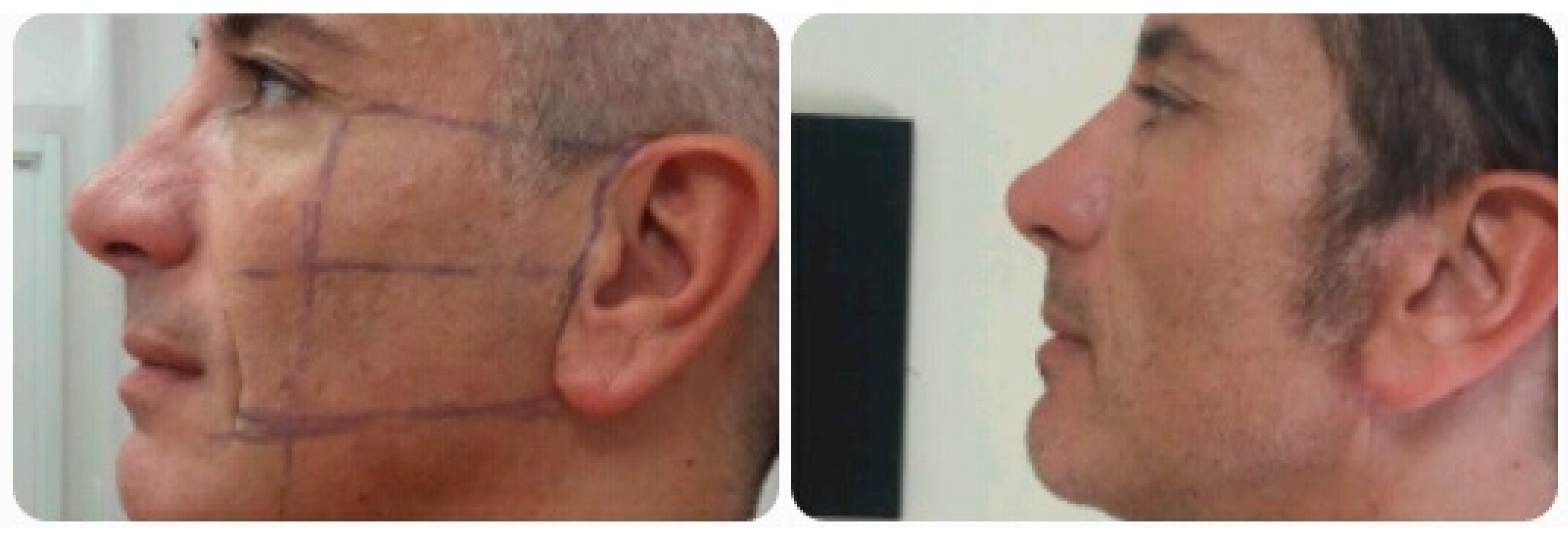
3. Methods
4. Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borchers, A.T.; Gershwin, M.E. Giant cell arteritis: A review of classification, pathophysiology, geoepidemiology and treatment. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, A544–A554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvarani, C.; Cantini, F.; Hunder, G.G. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant-cell arteritis. Lancet 2008, 372, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, N. Temporal arteritis: An approach to suspected vasculitides. Prim. Care 2010, 37, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epperly, T.D.; Moore, K.E.; Harrover, J.D. Polymyalgia rheumatica and temporal arthritis. Am. Fam. Phys. 2000, 62, 789–796. [Google Scholar]
- Meskimen, S.; Cook, T.D.; Blake, R.L., Jr. Management of giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatic. Am. Fam. Phys. 2000, 61, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar]
- Schallhorn, J.; Haug, S.J.; Yoon, M.K.; Porco, T.; Seiff, S.R.; McCulley, T.J. A national survey of practice patterns: Temporal artery biopsy. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 1930–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawardene, A.R.; Chant, H. Facial nerve injury during temporal artery biopsy. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2014, 96, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hunder, G.G.; Bloch, D.A.; Michel, B.A.; Stevens, M.B.; Arend, W.P.; Calabrese, L.H.; Edworthy, S.M.; Fauci, A.S.; Leavitt, R.Y.; Lie, J.T.; et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1990, 33, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, D.M.; Ruchman, M.C.; Keltner, J.L. Skip areas in temporal arteritis. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1976, 94, 2072–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacy, R.C.; Rizzo, J.F.; Cestari, D.M. Subtleties in the histopathology of giant cell arteritis. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2011, 26, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.K.; Horton, J.C.; McCulley, T.J. Facial nerve injury: A complication of superficial temporal artery biopsy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 152, 251–255.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murchison, A.P.; Bilyk, J.R. Brow ptosis after temporal artery biopsy: Incidence and associations. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 2637–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colella, G.; Rauso, R.; Tartaro, G.; Biondi, P. Skin injury and great auricular nerve sacrifice after parotidectomy. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2009, 20, 1078–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markose, G.; Graham, R.M. Gillies temporal incision: An alternate approach to superficial temporal artery biopsy. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 55, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde-Ferreirós, A.; Fraile-Alonso, M.D.C.; Román-Curto, C. “Book Flap” Approach for Temporal Artery Biopsy. Dermatol. Surg. 2020, 46, 1361–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlesworth, P. Regarding temporal artery biopsy technique. Dermatol. Surg. 2001, 27, 608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Czyz, C.N.; Allen, J.B.; Cahill, K.V.; Nabavi, C.B.; Foster, J.A. Effects of incision location on specimen quality and complications for temporal artery biopsy. Vascular 2019, 27, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, N.; D’Souza, A. Facelift approach for parotidectomy: An evolving aesthetic technique. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 148, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melvin, T.A.; Eliades, S.J.; Ha, P.K.; Fakhry, C.; Saunders, J.M.; Califano, J.A.; Blanco, R.G. Neck dissection through a facelift incision. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 2700–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tae, K.; Ji, Y.B.; Song, C.M.; Sung, E.S.; Chung, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, H.J. Feasibility of robot-assisted modified radical neck dissection by post-auricular facelift approach. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameters | Results (Mean) |
|---|---|
| Length of specimen (cm) | 2.60 cm |
| Pathology Report (%) | 73.91 % positive for GCA |
| Scar quality (VAS) | 4.04 |
| Postoperative Complications | Results (Mean) |
|---|---|
| Hematoma | 2 (8.69%) |
| Infection | 1 (4.34%) |
| Partial Wound Dehiscence | 2 (8.69%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faenza, M.; Piccolo, G.; Funaro, M.; Grella, R.; Pantano, I.; Ciccia, F. Short-Facelift Approach in Temporal Artery Biopsy: Is It Safe? Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10739. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210739
Faenza M, Piccolo G, Funaro M, Grella R, Pantano I, Ciccia F. Short-Facelift Approach in Temporal Artery Biopsy: Is It Safe? Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(22):10739. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210739
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaenza, Mario, Giuseppina Piccolo, Mariano Funaro, Roberto Grella, Ilenia Pantano, and Francesco Ciccia. 2021. "Short-Facelift Approach in Temporal Artery Biopsy: Is It Safe?" Applied Sciences 11, no. 22: 10739. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210739
APA StyleFaenza, M., Piccolo, G., Funaro, M., Grella, R., Pantano, I., & Ciccia, F. (2021). Short-Facelift Approach in Temporal Artery Biopsy: Is It Safe? Applied Sciences, 11(22), 10739. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210739






