Pedobarography: A Review on Methods and Practical Use in Foot Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
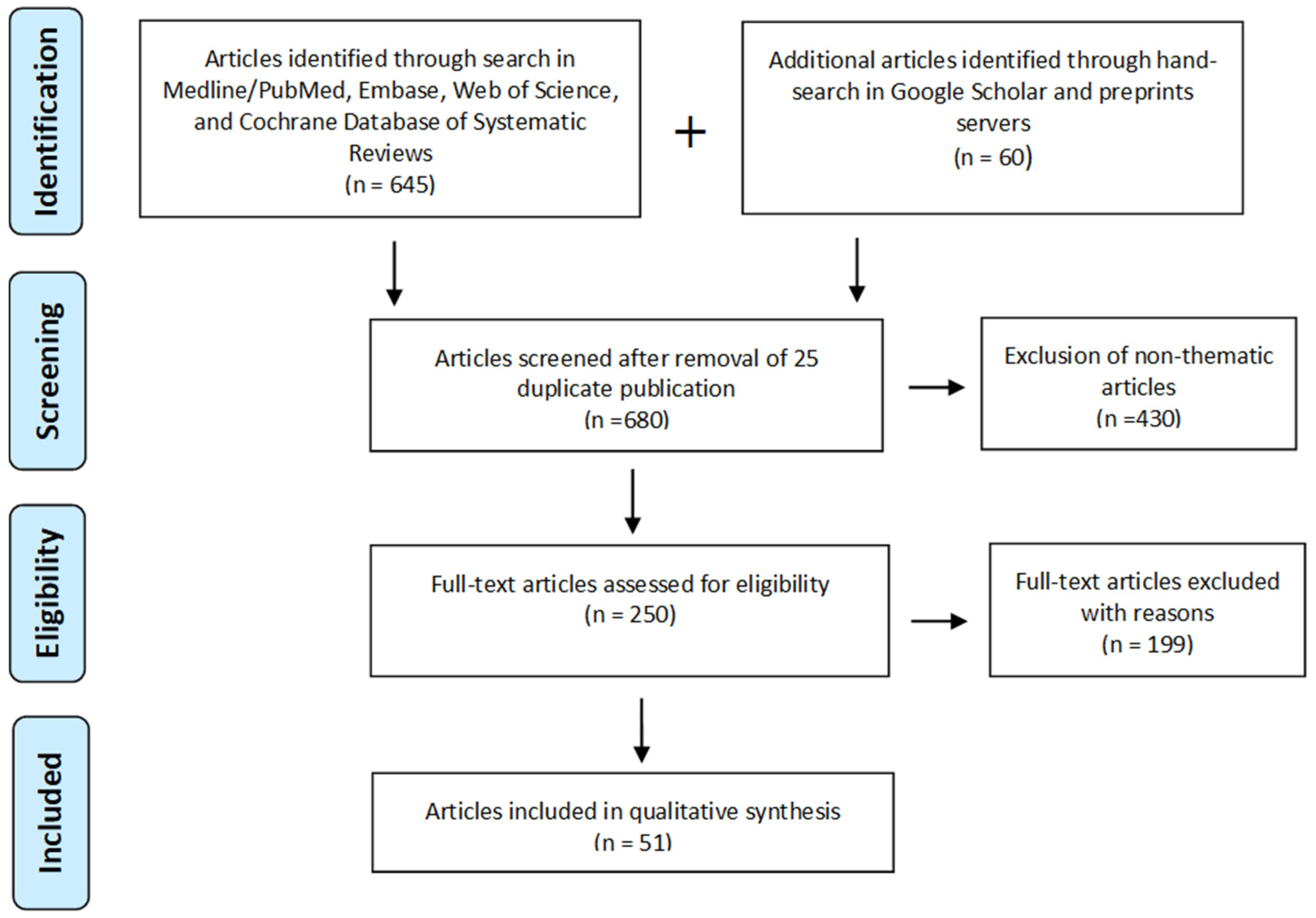
2. Material and Methods
Literature Search
- Methodology AND Pedobarography or Plantar Pressure Distribution or Foot Pressure Distribution or Underfoot Pressure Distribution;
- Examination AND Pedobarography or Plantar Pressure Distribution or Foot Pressure Distribution or Underfoot Pressure Distribution;
- Procedure AND Pedobarography or Plantar Pressure Distribution or Foot Pressure Distribution or Underfoot Pressure Distribution.
- Peer-reviewed journal articles and published conference papers;
- Studies describing the procedure for performing a pedobarographic examination;
- Publications focusing on pedobarographic systems and masking foot regions.
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Pedobarographic Measurements
4.2. Difficulties and Ambiguities concerning Pedobarography
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López-López, D.; Pérez-Ríos, M.; Ruano-Ravina, A.; Losa-Iglesias, M.E.; Becerro-de-Bengoa-Vallejo, R.; Romero-Morales, C.; Calvo-Lobo, C.; Navarro-Flores, E. Impact of quality of life related to foot problems: A case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, D.; Becerro-de-Bengoa-Vallejo, R.; Losa-Iglesias, M.E.; Palomo-López, P.; Rodríguez-Sanz, D.; Brandariz-Pereira, J.M.; Calvo-Lobo, C. Evaluation of foot health related quality of life in individuals with foot problems by gender: A cross-sectional comparative analysis study. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e023980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.H.; Yang, W.T.; Wu, C.P.; Chang, L.W. Would foot arch development in children characterize a body maturation process? A prospective longitudinal study. Biomed. J. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hösl, M.; Böhm, H.; Oestreich, C.; Dussa, C.U.; Schäfer, C.; Döderlein, L.; Nader, S.; Fenner, V. Self-perceived foot function and pain in children and adolescents with flexible flatfeet—Relationship between dynamic pedobarography and the foot function index. Gait Posture 2020, 77, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereiro-Buceta, H.; Becerro-de-Bengoa-Vallejo, R.; Losa-Iglesias, M.E.; López-López, D.; Navarro-Flores, E.; Martínez-Jiménez, E.M.; Martiniano, J.; Calvo-Lobo, C. The Effect of Simulated Leg-Length Discrepancy on the Dynamic Parameters of the Feet during Gait-Cross-Sectional Research. Healthcare 2021, 9, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galbusera, F.; Cina, A.; Panico, M.; Albano, D.; Messina, C. Image-based biomechanical models of the musculoskeletal system. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2020, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorkowski, J.; Grzegorowska, O.; Pokorski, M. Artificial intelligence in the healthcare system: An overview. In Best Practice in Health Care; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1335, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ozkan, H.; Ege, T.; Koca, K.; Can, N.; Yurttas, Y.; Tunay, S. Pedobarographic measurements after repair of Achilles tendon by minimal invasive surgery. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2016, 82, 271–274. [Google Scholar]
- Skopljak, A.; Muftic, M.; Sukalo, A.; Masic, I.; Zunic, L. Pedobarography in diagnosis and clinical application. Acta Inform. Med. 2014, 22, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abboud, R.J. Relevant foot biomechanics. Curr. Orthop. 2002, 16, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lefebvre, T.; Malthête, J. Lettres d’Etienne-Jules Marey à Georges Demenÿ, 1880–1894; AFRHC: Paris, France, 2002; ISBN 10: 2913758002. [Google Scholar]
- Beely, F. Zur Mechanik des Stehens. Arch. Klin. Chir. 1882, 27, 457–468. [Google Scholar]
- Seitz, L. Die vordeven stutzpunkte des fusses under normalen and pathologische verhaltnissen. Z. Orthop. Chir. 1901, 8, 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Elftman, H. A cinematic study of the distribution of pressure in the human foot. Anat. Rec. 1934, 59, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Muneta, T.; Asahina, S.; Furuya, K. Forefoot pressures during walking in feet afflicted with hallux valgus. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1996, 323, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, R.P.; Heat, A.L. The definition of human locomotion on the basis of measurement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1947, 1, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh, P.R.; Ae, M. A technique for the display of pressure distributions beneath the foot. J. Biomech. 1980, 13, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, E.M.; Cavanagh, P.R.; Albert, H.T.; Macmillan, N.H. A piezoelectric method of measuring the vertical contact stress beneath the human foot. J. Biomed. Eng. 1982, 4, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péruchon, E.; Jullian, J.M.; Rabischong, P. Wearable unrestraining footprint analysis system. Applications to human gait study. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1989, 27, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, D.R.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Leggett, S.R.; Mathien, C.A.; Main, J.A.; Hunter, D.C.; Duncan, G.E. Accuracy of five electronic pedometers for measuring distance walked. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1996, 28, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, Y. Use of the pedometer for promoting daily walking exercise. J. Int. Comm. Health Phys. Educ. Recreat. 1993, 29, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanathan, A.K.; Kiran, P.; Arnold, G.P.; Wang, W.; Abboud, R.J. Repeatability of the Pedar-X in-shoe pressure measuring system. Foot Ankle Surg. 2010, 16, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurney, J.K.; Marshall, P.W.; Rosenbaum, D.; Kersting, U.G. Test-retest reliability of dynamic plantar loading and foot geometry measures in diabetics with peripheral neuropathy. Gait Posture 2013, 37, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, L.; Pape, J.P.; Kostakev, M.; Peterlein, C.D. Pedobarographic changes during first month after subtalar extra-articular screw arthroereisis (SESA) operation of juvenile flexible flatfoot. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2020, 140, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, M.; Kocadal, O.; Akman, B.; Poyanlı, O.S.; Kemah, B.; Atay, E.F. Proximal femoral nail shows better concordance of gait analysis between operated and uninjured limbs compared to hemiarthroplasty in intertrochanteric femoral fractures. Injury 2016, 47, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorkowski, J.; Grzegorowska, O.; Kotela, I. The use of pedobarographic examination to biomechanical evaluation of foot and ankle joint in adult—Own experience. Ortop. Traumatol. Rehabil. 2015, 17, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurney, J.K.; Kersting, U.G.; Rosenbaum, D.; Dissanayake, A.; York, S.; Grech, R.; Ng, A.; Milne, B.; Stanley, J.; Sarfati, D. Pedobarography as a clinical tool in the management of diabetic feet in New Zealand: A feasibility study. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2017, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lorkowski, J.; Grzegorowska, O.; Kotela, I. The use of pedobarographic examination in children—Own experience and review of literature. Fizjoterapia Pol. 2015, 14, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Stolz, B.; Grim, C.; Lutter, C.; Gelse, K.; Schell, M.; Swoboda, B.; Carl, H.D.; Hotfiel, T. Assessing foot loads in continuous passive motion (CPM) and active knee joint motion devices. Sportverletz Sportschaden 2021, 35, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Mei, Q.; Fernandez, J.; Gu, Y. A biomechanical evaluation of the acute hallux abduction manipulation intervention. Gait Posture 2020, 76, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellstrom, P.A.R.; Folke, M. Carried weight affects walking speed monitoring with the IngVaL system. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2019, 261, 317–320. [Google Scholar]
- Vilarinho, D.; Theodosiou, A.; Leitão, C.; Leal-Junior, A.G.; Domingues, M.F.; Kalli, K.; André, P.; Antunes, P.; Marques, C. POFBG-embedded cork insole for plantar pressure monitoring. Sensors 2017, 17, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fishco, W.D.; Ellis, M.B.; Cornwall, M.W. Influence of a metatarsus adductus foot type on plantar pressures during walking in adults using a pedobarograph. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2015, 54, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.T.; Lee, J.S. Normal pressures and reliability of the Gaitview system in healthy adults. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2012, 36, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, S.; Ng, A.; Clough, T. The long-term outcome of silastic implant arthroplasty of the first metatarsophalangeal joint: A retrospective analysis of one hundred and eight feet. Int. Orthop. 2012, 36, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reed, L.; Bennett, P.J. Changes in foot function with the use of Root and Blake orthoses. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2001, 91, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorkowski, J.; Mazur, T. Application of the pedobarography in hallux valgus diagnosis. Scr. Period 2000, 3, 409–413. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.S.; Kim, H.W.; Park, C.I.; Rha, D.; Park, C.W. Dynamic foot pressure measurements for assessing foot deformity in persons with spastic cerebral palsy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 87, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellstrom, P.A.R.; Åkerberg, A.; Ekström, M.; Folke, M. Evaluation of the IngVaL pedobarography system for monitoring of walking speed. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2018, 24, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kernozek, T.; Roehrs, T.; McGarvey, S. Analysis of plantar loading parameters pre and post-surgical intervention for hallux valgus. Clin. Biomech. 1997, 12, S18–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomgren, M.; Turan, I.; Agadir, M. Gait analysis in hallux valgus. J. Foot Surg. 1991, 30, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Konings-Pijnappels, A.P.M.; Tenten-Diepenmaat, M.; Dahmen, R.; Verberne, S.K.; Dekker, J.; Twisk, J.W.R.; Roorda, L.D.; van der Leeden, M. Forefoot pathology in relation to plantar pressure distribution in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional study in the Amsterdam foot cohort. Gait Posture 2019, 68, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, A.; Singer, K.; Tinley, P. Comparison of the reliability of plantar pressure measurements using the two-step and midgait methods of data collection. Foot Ankle Int. 1999, 20, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stess, R.M.; Jensen, S.R.; Mirmiran, R. The role of dynamic plantar pressures in diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaff, P.S.; Cavanagh, P.R. Shoes for the insensitive foot: The effect of a “rocker bottom” shoe modification on plantar pressure distribution. Foot Ankle 1990, 11, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, T.R.; Miller, F.; Castagno, P.; Richards, J.; Lipton, G. A method of dynamic foot-pressure measurement for the evaluation of pediatric orthopaedic foot deformities. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1998, 18, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanagh, P.R.; Rodgers, M.M.; Iiboshi, A. Pressure distribution under symptom-free feet during barefoot standing. Foot Ankle 1987, 7, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rome, K.; Survepalli, D.G.; Lobo, M.; Dalbeth, N.; McQueen, F.; McNair, P.J. Evaluating intratester reliability of manual masking of plantar pressure measurements associated with chronic gout. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2011, 101, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S.J.; Stoecklein, H.; Yu, J.C.; Syrkin, G.; Hillstrom, H.; Deland, J.T. The accuracy of an automasking algorithm in plantar pressure measurements. HSS J. 2011, 7, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorkowski, J.; Lorkowska, B.; Skawina, A. Underfoot pressure distribution of patients with spinal problems. Acta Kinesiol. Univ. Tart. 2001, 6, 152–155. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.N.; Liang, W.D.; Zhou, F.H.; Li, H.T.; Zhang, L.X.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Li, J.J. Comparison of walking quality variables between incomplete spinal cord injury patients and healthy subjects by using a footscan plantar pressure system. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 354–360. [Google Scholar]
- Chae, Y.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Yi, T.I. Clinical and biomechanical effects of low-dye taping and figure-8 modification of low-dye taping in patients with heel pad atrophy. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 42, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Yan, Y.B.; Zhao, X.; Wen, X.X.; Shang, L.; Huang, L.Y.; Lei, W. Pedobarographic analysis following Pemberton’s pericapsular osteotomy for unilateral developmental dysplasia of the hip: An observational study. Medicine 2015, 94, e932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.J.; Chang, W.H.; Choi, B.O.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Ryu, G.H.; Kim, Y.H. Gait performance and foot pressure distribution during wearable robot-assisted gait in elderly adults. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2017, 14, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolopoulos, C.S.; Anderson, E.G.; Solomonidis, S.E.; Giannoudis, P.V. Evaluation of the gait analysis FSCAN pressure system: Clinical tool or toy? Foot 2000, 10, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodburn, J.; Helliwell, P. Observations on the F-Scan in-shoe pressure measuring system. Clin. Biomech. 1997, 12, S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, C.; Turner, D.; Miller, K. Determinants of plantar pressures in the diabetic foot. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2002, 16, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, T.; Davids, J.R.; Bagley, A. A biomechanical analysis of gait during pregnancy. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2000, 82, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soames, R.W.; Stott, J.R.; Goodbody, A.; Blake, C.D.; Brewerton, D.A. Measurement of pressure under the foot during function. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1982, 20, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Nigg, B.M.; Hulliger, M.; de Koning, J. Influence of sensory input on plantar pressure distribution. Clin. Biomech. 1995, 10, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacarin, T.A.; Sacco, I.C.; Hennig, E.M. Plantar pressure distribution patterns during gait in diabetic neuropathy patients with a history of foot ulcers. Clinics 2009, 64, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lorkowski, J. Methodology of pedobarographic examination—Own experiences and review of literature. Przegl. Lek. 2006, 63 (Suppl. 5), 23–27. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Burnfield, J.M.; Few, C.D.; Mohamed, O.S.; Perry, J. The influence of walking speed and footwear on plantar pressures in older adults. Clin. Biomech. 2004, 19, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellis, E. Plantar pressure distribution during barefoot standing, walking and landing in preschool boys. Gait Posture 2001, 14, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, H.; Allard, P.; Prince, F.; Labelle, H. Symmetry and limb dominance in able-bodied gait: A review. Gait Posture 2000, 12, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaney, B.; Meyer, K.; Cornwall, M.W.; McPoil, T.G. A comparison of the dynamic pedobarograph and EMED systems for measuring dynamic foot pressures. Foot Ankle Int. 1995, 16, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J. The clinical use of pedobarography. Acta Orthop. Belg. 1993, 59, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, E.; Devreux, I.; Embaby, H.; Alsayed, A.; Alshehri, M. Changes in foot plantar pressure in pregnant women. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2017, 30, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Articles (n) | |
|---|---|
| Pedobarographic systems | 10 |
| Pedobarographic measurements | 6 |
| Masking foot regions | 9 |
| Conducting the examination | 13 |
| Types of pedobarographic assessments | 3 |
| Basic information/definitions | 4 |
| Limitations in pedobarographic examination | 24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorkowski, J.; Gawronska, K.; Pokorski, M. Pedobarography: A Review on Methods and Practical Use in Foot Disorders. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112211020
Lorkowski J, Gawronska K, Pokorski M. Pedobarography: A Review on Methods and Practical Use in Foot Disorders. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(22):11020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112211020
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorkowski, Jacek, Karolina Gawronska, and Mieczyslaw Pokorski. 2021. "Pedobarography: A Review on Methods and Practical Use in Foot Disorders" Applied Sciences 11, no. 22: 11020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112211020
APA StyleLorkowski, J., Gawronska, K., & Pokorski, M. (2021). Pedobarography: A Review on Methods and Practical Use in Foot Disorders. Applied Sciences, 11(22), 11020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112211020






