Long-Term Trends in Regional Wet Mercury Deposition and Lacustrine Mercury Concentrations in Four Lakes in Voyageurs National Park
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Wet Deposition
2.3. Lake Water
2.4. Lake Levels
2.5. Mercury in Lake Biota
3. Results
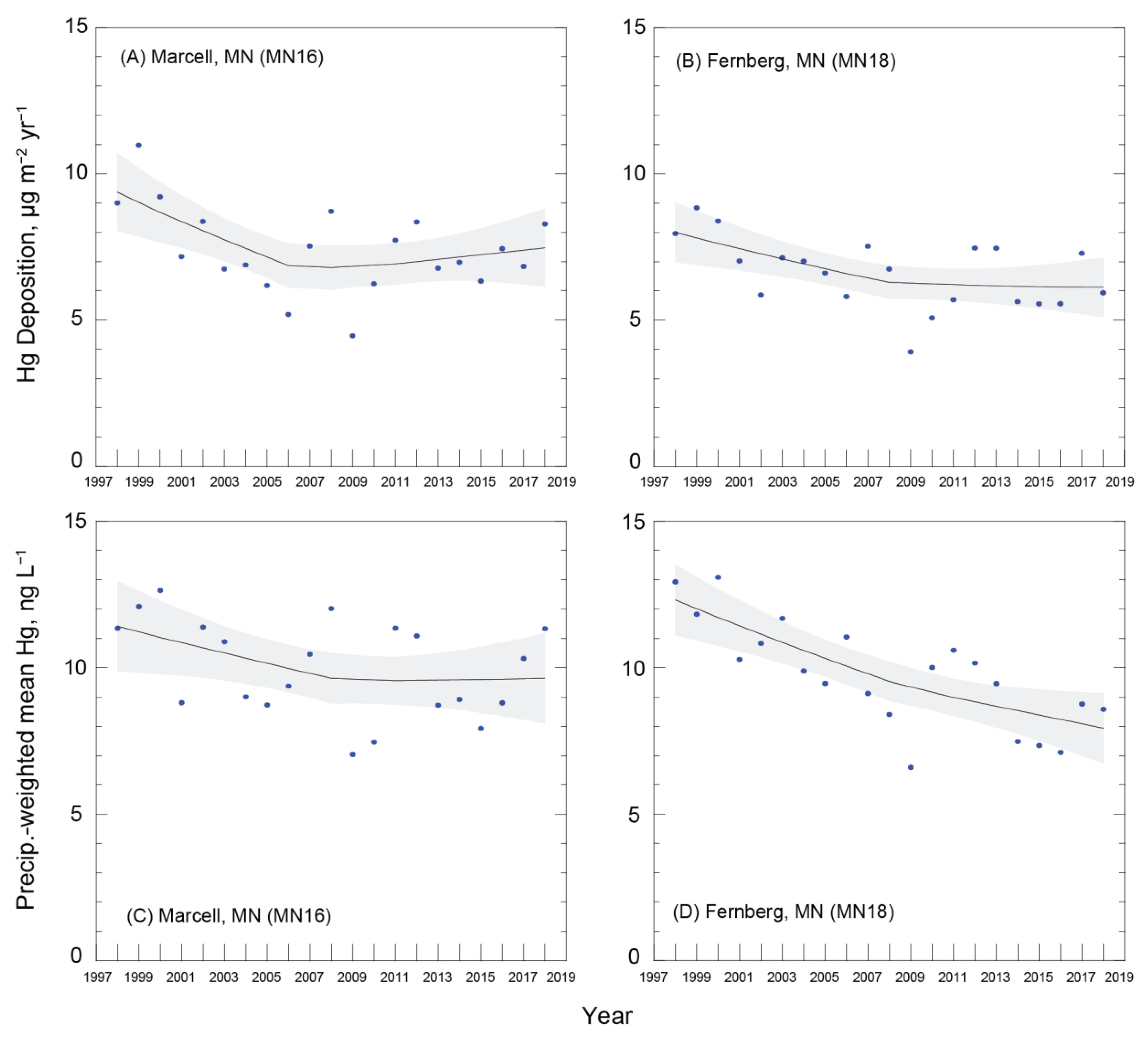
3.1. Wet Deposition Trends
3.2. Trends in Epilimnetic Methylmercury, Total Mercury, and Sulfate Concentrations
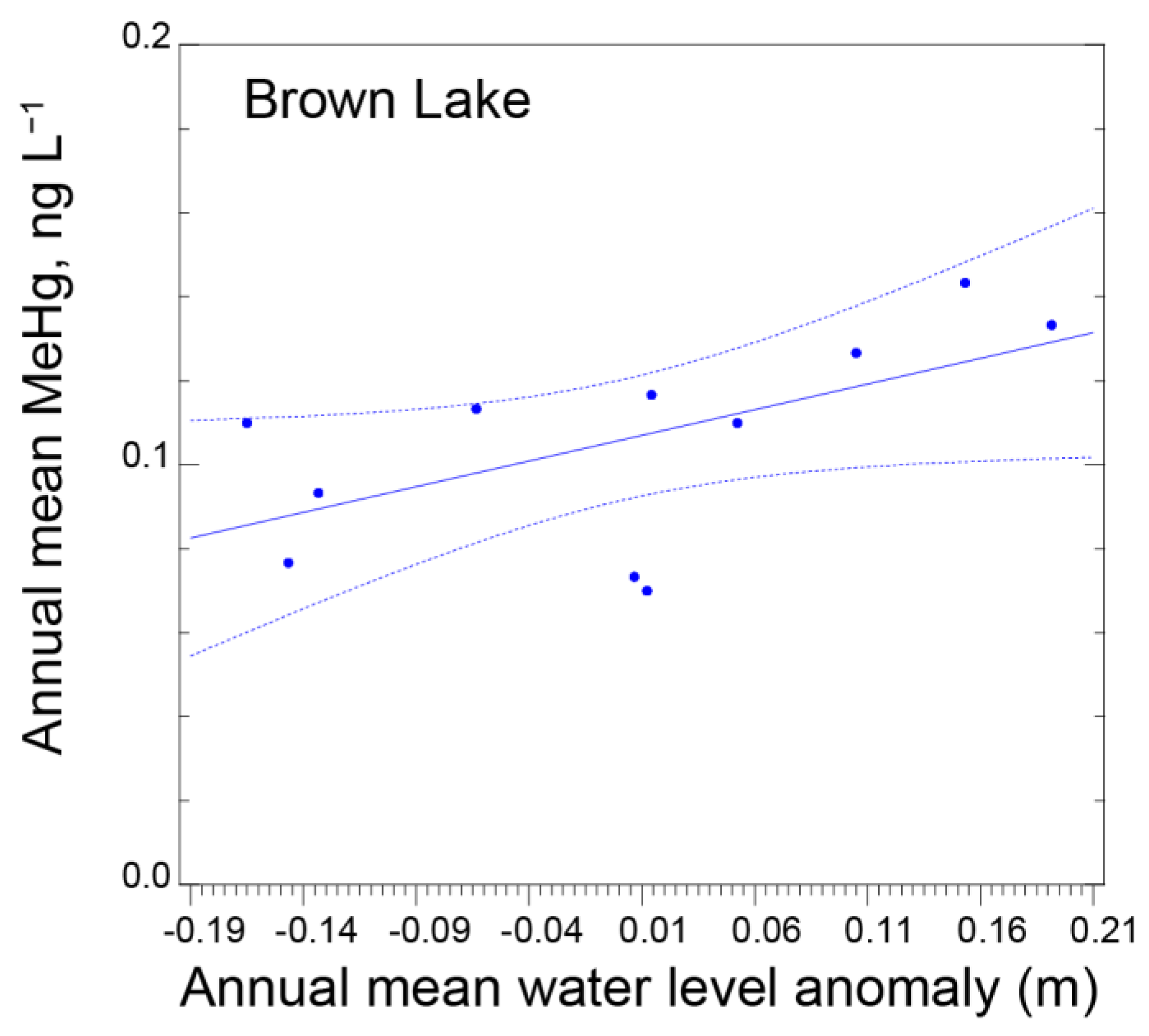
3.3. Lake Level Fluctuations
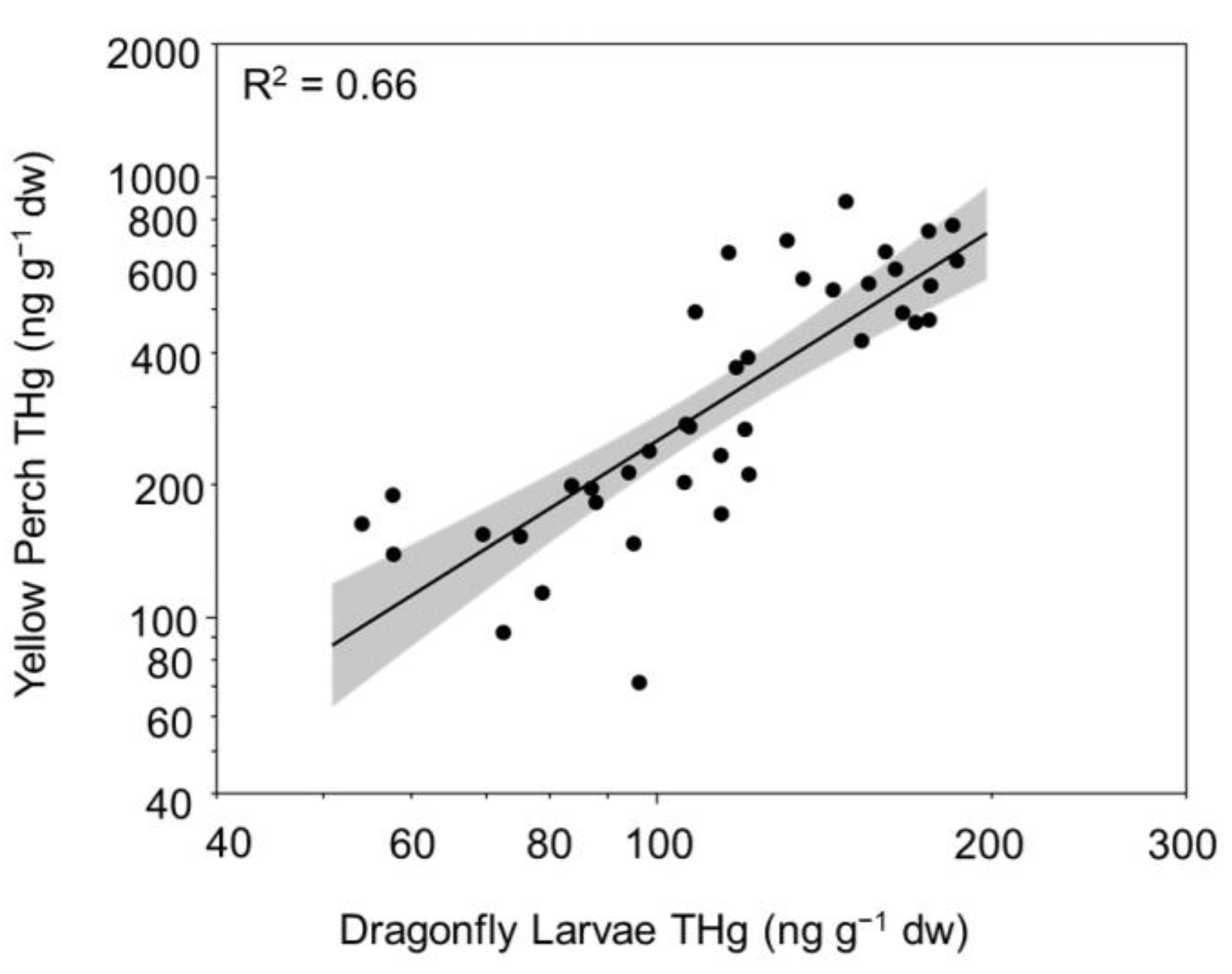
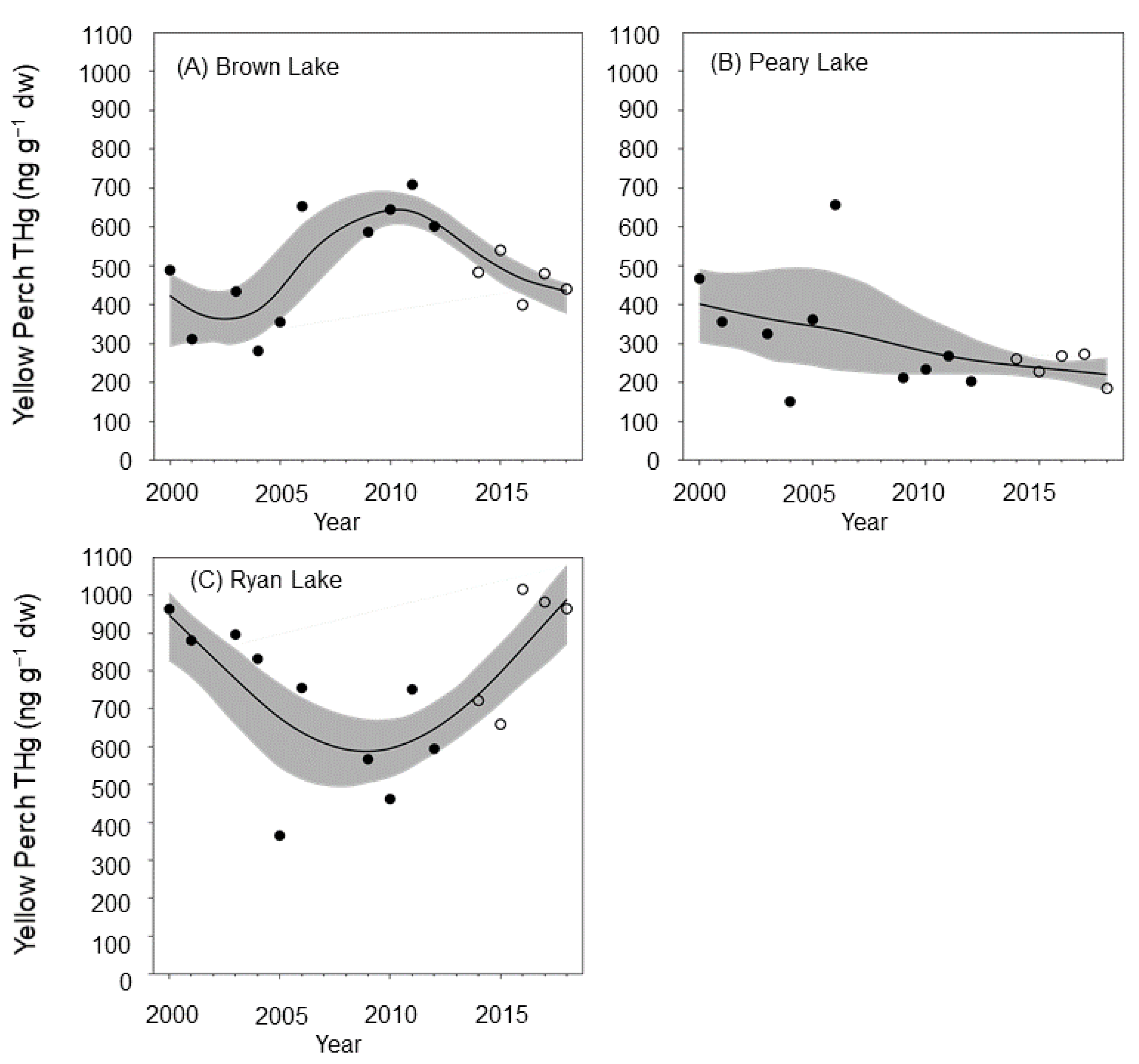
3.4. Mercury Trends in Lake Biota
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swain, E.B.; Engstrom, D.R.; Brigham, M.E.; Henning, T.A.; Brezonik, P.L. Increasing rates of atmospheric mercury deposition in midcontinental North America. Science 1992, 257, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2010 Biennial National Listing of Fish Advisories. 2011. Available online: https://archive.epa.gov/ow/ost/web/html/technical_factsheet_2010.html (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Wiener, J.G.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Heinz, G.H.; Scheuhammer, A.M. Ecotoxicology of mercury, Chapter 16. In Handbook of Ecotoxicology, 2nd ed.; Hoffman, D.J., Rattner, B.A., Burton, G.A., Jr., Cairns, J., Jr., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 409–463. [Google Scholar]
- Orihel, D.M.; Paterson, M.J.; Blanchfield, P.J.; Bodaly, R.A.; Hintelmann, H. Experimental evidence of a linear relationship between inorganic mercury loading and methylmercury accumulation by aquatic biota. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4952–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, C.C.; Henry, E.A.; Mitchell, R. Sulfate stimulation of mercury methylation in freshwater sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compeau, C.G.; Bartha, R. Sulfate-reducing bacteria—principal methylators of mercury in anoxic estuarine sediment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 50, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeremiason, J.D.; Engstrom, D.R.; Swain, E.B.; Nater, E.A.; Johnson, B.M.; Almendinger, J.E.; Monson, B.A.; Kolka, R.K. Sulfate addition increases methylmercury production in an experimental wetland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3800–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engstrom, D.R.; Swain, E.B. Recent declines in atmospheric mercury deposition in the Upper Midwest. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2017 National Emissions Inventory Technical Support Document. 2020; p. 486. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2020-04/documents/nei2017_tsd_full_30apr2020.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Government of Canada. Air Pollutants Emissions Inventory Online Search. 2020. Available online: https://pollution-waste.canada.ca/air-emission-inventory (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Nopmongcol, U.; Beardsley, R.; Kumar, N.; Knipping, E.; Yarwood, G. Changes in United States deposition of nitrogen and sulfur compounds over five decades from 1970 to 2020. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 209, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevnick, P.E.; Canfield, D.E.; Gorski, P.R.; Shinneman, A.L.C.; Engstrom, D.R.; Muir, D.C.G.; Smith, G.R.; Garrison, P.J.; Cleckner, L.B.; Hurley, J.P.; et al. Deposition and cycling of sulfur controls mercury accumulation in Isle Royale fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7266–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jacob, D.J.; Horowitz, H.M.; Chen, L.; Amos, H.M.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Slemr, F.; Louis, V.L.S.; Sunderland, E.M. Observed decrease in atmospheric mercury explained by global decline in anthropogenic emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Streets, D.G.; Horowitz, H.M.; Lu, Z.; Levin, L.; Thackray, C.P.; Sunderland, E.M. Global and regional trends in mercury emissions and concentrations, 2010–2015. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 201, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giang, A.; Song, S.; Muntean, M.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Harvey, A.; Berg, E.; Selin, N.E. Understanding factors influencing the detection of mercury policies in modelled Laurentian Great Lakes wet deposition. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2018, 20, 1373–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Minamata Convention on Mercury. 2020. Available online: https://www.mercuryconvention.org/ (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Hutcheson, M.S.; Smith, C.M.; Rose, J.; Batdorf, C.; Pancorbo, O.; West, C.R.; Strube, J.; Francis, C. Temporal and spatial trends in freshwater fish tissue mercury concentrations associated with mercury emissions reductions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monson, B.; Staples, D.; Bhavsar, S.; Holsen, T.; Schrank, C.; Moses, S.; McGoldrick, D.; Backus, S.; Williams, K. Spatiotemporal trends of mercury in walleye and largemouth bass from the Laurentian Great Lakes Region. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, N.; Tang, R.W.K.; Bhavsar, S.P.; Arhonditsis, G.B. Fish Mercury Levels Appear to Be Increasing Lately: A Report from 40 Years of Monitoring in the Province of Ontario, Canada. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5404–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykstra, C.R.; Route, W.T.; Williams, K.A.; Meyer, M.W.; Key, R.L. Trends and patterns of PCB, DDE, and mercury contamination in bald eagle nestlings in the upper Midwest. J. Great Lakes Res. 2019, 45, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Brigham, M.E.; Stuewe, L.; Menheer, M.A. Mercury Data from Small Lakes in Voyageurs National Park, Northern Minnesota, 2000–02. 2003; U.S. Geological Survey; Open-File Report 03-480; p. 18. Available online: http://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/ofr2003480 (accessed on 1 February 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiener, J.G.; Knights, B.C.; Sandheinrich, M.B.; Jeremiason, J.D.; Brigham, M.E.; Engstrom, D.R.; Woodruff, L.G.; Cannon, W.F.; Balogh, S.J. Mercury in soils, lakes, and fish in Voyageurs National Park (Minnesota)—importance of atmospheric deposition and ecosystem factors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6261–6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, L.G.; Sandheinrich, M.; Brigham, M.E.; Cannon, W.F. Impact of wildfire on levels of mercury in forested watershed systems–Voyageurs National Park, Minnesota. 2009; U.S. Geological Survey; Scientific Investigations Report 2009-5151; p. 19. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/sir/2009/5151/ (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Brigham, M.E.; Sandheinrich, M.B.; Gay, D.A.; Maki, R.P.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Wiener, J.G. Lacustrine responses to decreasing wet mercury deposition rates—results from a case study in northern Minnesota. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6115–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonesten, L. Catchment Area Composition and Water Chemistry Heavily Affects Mercury Levels in Perch (Perca Fluviatilis L.) in Circumneutral Lakes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 144, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallemeyn, L.W.; Holmberg, K.L.; Perry, J.A.; Odde, B.Y. Aquatic Synthesis for Voyageurs National Park; Information and Technology Report 2003-0001; U.S. Geological Survey: International Falls, MN, USA, 2003; p. 96. Available online: http://www.cerc.usgs.gov/pubs/center/pdfdocs/ITR2003-0001.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Prestbo, E.M.; Gay, D.A. Wet deposition of mercury in the U.S. and Canada, 1996-2005: Results and analysis of the NADP mercury deposition network (MDN). Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4223–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Method 1669—Sampling Ambient Water for Trace Metals at EPA Water Quality Criteria Levels; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; p. 35, EPA 821/R-96-011.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Method 1631, Revision E—Mercury in Water by Oxidation, Purge and trap, and Cold Vapor Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; p. 35, EPA-821-R-02-019.
- Vermette, S.; Bloom, N.; Tokos, J.; Welker, M.; Verry, S.; Lindberg, S. The Mercury Deposition Network (NADP/MDN): Transition Phase, February 1995 to February 1996; National Atmospheric Deposition Program, Illinois State Water Survey: Champaign, IL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss-Penzias, P.S.; Gay, D.A.; Brigham, M.E.; Parsons, M.T.; Gustin, M.S.; Schure, A.T. Trends in mercury wet deposition and mercury air concentrations across the U.S. and Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helsel, D.R.; Hirsch, R.M.; Ryberg, K.R.; Archfield, S.A.; Gilroy, E.J. Statistical Methods in Water Resources: U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods, Book 4, Chapter A3; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; p. 458. [CrossRef]
- VanderMeulen, D.D.; Lafrancois, B.M.; Edlund, M.B.; Hobbs, J.M.R.; Damstra, R. Pairing modern and paleolimnological approaches to evaluate the nutrient status of lakes in Upper Midwest National Parks. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2016, 52, 1401–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWild, F.J.; Olson, M.L.; Olund, S.D. Determination of Methyl Mercury by Aqueous Phase Ethylation, Followed by Gas Chromatographic Separation with Cold Vapor Atomic Fluorescence Detection; Open-File Report 01-445; U.S. Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 2002; p. 14. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2001/ofr-01-445/ (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Method 1630—Methyl Mercury in Water by Distillation, Aqueous Ethylation, Purge and Trap, and Cold Vapor Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; p. 55, EPA-821-R-01-020.
- Elias, J.E.; Axler, R.; Ruzycki, E.; VanderMeulen, D. Water Quality Monitoring Protocol for Inland Lakes: Great Lakes Inventory and Monitoring Network, Version 1.1; National Park Service: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2015; p. 384. Available online: https://irma.nps.gov/DataStore/Reference/Profile/2224131 (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Eagles-Smith, C.A.; Nelson, S.J.; Flanagan-Pritz, C.M.; Willacker, J.J., Jr.; Klemmer, A. Total Mercury Concentrations in Dragonfly Larvae from U.S. National Parks (ver. 4.0, 20 October 2020). U.S. Geological Survey: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagles-Smith, C.A.; Willacker, J.J.; Nelson, S.J.; Pritz, C.M.F.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Chen, C.Y.; Ackerman, J.T.; Grant, E.H.C.; Pilliod, D.S. A National-Scale Assessment of Mercury Bioaccumulation in United States National Parks Using Dragonfly Larvae As Biosentinels through a Citizen-Science Framework. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8779–8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haro, R.J.; Bailey, S.W.; Northwick, R.M.; Rolfhus, K.R.; Sandheinrich, M.B.; Wiener, J.G. Burrowing Dragonfly Larvae as Biosentinels of Methylmercury in Freshwater Food Webs. Environmental Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8148–8156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, J.G.; Haro, R.J.; Rolfhus, K.R.; Sandheinrich, M.B.; Bailey, S.W.; Northwick, R.M.; Gostomski, T.J. Bioaccumulation of Persistent Contaminants in Fish and Larval Dragonflies in Six National Park Units of the Western Great Lakes Region, 2008–2009; National Park Service: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2013; p. 55, Natural Resource Data Series NPS/GLKN/NRDS—2013/427. Available online: https://irma.nps.gov/DataStore/Reference/Profile/2192699 (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Schmeltz, D.; Evers, D.; Driscoll, C.; Artz, R.; Cohen, M.; Gay, D.; Haeuber, R.; Krabbenhoft, D.; Mason, R.; Morris, K.; et al. MercNet—A national monitoring network to assess responses to changing mercury emissions in the United States. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, G.A. Water Quality of Lakes and Streams in Voyageurs National Park, Northern Minnesota, 1977-84; Water-Resources Investigations Report 88-4016; U.S. Geological Survey: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1991; p. 95. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/wri/1988/4016/report.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Driscoll, C.T.; Driscoll, K.M.; Fakhraie, H.; Civerolo, K. Long-term temporal trends and spatial patterns in the acid-base chemistry of lakes in the Adirondack region of New York in response to decreases in acidic deposition. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 146, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watras, C.J.; Grande, D.; Latzka, A.W.; Tate, L.S. Mercury trends and cycling in northern Wisconsin related to atmospheric and hydrologic processes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 76, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watras, C.J.; Teng, H.-Y.; Latzka, A.W.; Meyer, M.W.; Zhang, Z. Near-Decadal Oscillation of Water Levels and Mercury Bioaccumulation in the Laurentian Great Lakes Region. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandheinrich, M.B.; Wiener, J.G. Methylmercury in freshwater fish—recent advances in assessing toxicity of environmentally relevant exposures. In Environmental Contaminants in Biota—Interpreting Tissue Concentrations, 2nd ed.; Beyer, W.N., Meador, J.P., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 169–190. [Google Scholar]
- Wiener, J.G.; Haro, R.J.; Rolfhus, K.R.; Sandheinrich, M.B.; Bailey, S.W.; Northwick, R.M.; Gostomski, T.J. Bioaccumulative Contaminants in Aquatic Food Webs in Six National Park units of the Western Great Lakes Region—2008–2012; Natural Resource Report NPS/GLKN/NRR—2016/1302; National Park Service: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2016; p. 136. Available online: https://irma.nps.gov/DataStore/Reference/Profile/2233537 (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Lehmann, C.M.B.; Gay, D.A. Monitoring long-term trends of acidic wet deposition in US precipitation—results from the National Atmospheric Deposition Program. Power Plant Chem. 2011, 13, 378–385. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman Wasik, J.K.; Mitchell, C.P.J.; Engstrom, D.R.; Swain, E.B.; Monson, B.A.; Balogh, S.J.; Jeremiason, J.D.; Branfireun, B.A.; Eggert, S.L.; Kolka, R.K.; et al. Methylmercury declines in a boreal peatland when experimental sulfate deposition decreases. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6663–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.C.; Rudd, J.W.M.; Amyot, M.; Babiarz, C.L.; Beaty, K.G.; Blanchfield, P.J.; Bodaly, R.A.; Branfireun, B.A.; Gilmour, C.C.; Graydon, J.A.; et al. Whole-ecosystem study shows rapid fish-mercury response to changes in mercury deposition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16586–16591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, R.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Mason, R.; Murray, M.W.; Reash, R.; Saltman, T. (Eds.) Ecosystem Responses to Mercury Contamination—Indicators of Change; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; p. 216. [Google Scholar]




| Year | 1990 | 2000 | 2005 | 2008 | 2011 | 2014 | 2017 | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air emissions of mercury, total for all sectors, Mg yr−1 | ||||||||
| United States | 223 | -- | 95 | 55 | 51 | 47 | 30 | −86.6% |
| Canada | 34.3 | 9.5 | 7.9 | 6.6 | 3.8 | 3.5 | 3.0 | −91.2% |
| Total US and Canada | 257 | -- | 103 | 62 | 55 | 51 | 33 | −87.2% |
| Lake Name | Lake Area (ha) | W.A. (ha) | % Wetlands | Lake Volume (106 m3) | Maximum Depth (m) | Mean Depth (m) | pH | Renewal Time (yr) | ANC (µeq L−1) | TOC (mg L−1) | Secchi Transparency Depth (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown | 30.8 | 158.9 | 9.9 | 1.3 | 8.2 | 4.2 | 7.0 | 0.8 | 129 | 9.4 | 2.7 |
| Peary | 45.3 | 734.6 | 19.8 | 1.2 | 4.6 | 2.6 | 7.2 | 0.6 | 195 | 10.1 | 2.4 |
| Ryan | 14.2 | 86.9 | 6.4 | 0.3 | 3.7 | 2.1 | 6.9 | 1.2 | 130 | 12.7 | 2.8 |
| Shoepack | 123.8 | 1735 | 25.8 | 3.6 | 7.3 | 2.9 | 6.5 | 0.7 | 114 | 15.5 | 1.3 |
| Hg Deposition, µg m2 | Precip.-Weighted [Hg], ng L−1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDN/NTN Site | EV1998 | EV2018 | % Change | EV1998 | EV2018 | % Change |
| Marcell (MN16) | 9.37 | 7.47 | −20% | 11.41 | 9.63 | −16% |
| [8.05, 10.70] | [6.14, 8.80] | [9.88, 12.95] | [8.10, 11.17] | |||
| Fernberg (MN18) | 8.00 | 6.12 | −24% | 12.31 | 7.93 | −36% |
| [6.99, 9.01] | [5.11, 7.12] | [11.12, 13.50] | [6.74, 9.13] | |||
| Mean percent change: | −22% | −26% | ||||
| MeHgaq | THgaq | Sulfate | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EV2001 | EV2018 | % Change | EV2001 | EV2018 | % Change | EV2001 | EV2018 | % Change | |
| Brown | 0.0854 | 0.0582 | −32% | 1.94 | 1.53 | −21% | 1.31 | 0.88 | −33% |
| [0.037, 0.134] | [0.011, 0.106] | [1.57, 2.32] | [1.16, 1.90] | [0.95, 1.66] | [0.58, 1.17] | ||||
| Peary | 0.1706 | 0.0468 | −73% | 1.58 | 1.11 | −29% | 1.24 | 0.71 | −43% |
| [0.140, 0.201] | [0.018, 0.076] | [1.26, 1.89] | [0.81. 1.41] | [0.33, 2.15] | [−0.05, 1.46] | ||||
| Ryan | 0.2380 | 0.1243 | −48% | 3.35 | 1.78 | −47% | 2.79 | 1.66 | −41% |
| [0.194, 0.281] | [0.086, 0.162] | [2.53, 4.17] | [1.08, 2.50] | [2.31, 3.26] | [1.26, 2.05] | ||||
| Shoepack | 0.2592 | 0.1941 | −25% | 2.73 | 2.44 | −11% | 1.63 | 0.61 | −62% |
| [0.182, 0.337] | [0.108, 0.281] | [2.28, 3.18] | [1.85, 3.02] | [0.66, 2.59] | [−0.17, 1.39] | ||||
| mean = −44% | mean = −27% | mean = −45% | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brigham, M.E.; VanderMeulen, D.D.; Eagles-Smith, C.A.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Maki, R.P.; DeWild, J.F. Long-Term Trends in Regional Wet Mercury Deposition and Lacustrine Mercury Concentrations in Four Lakes in Voyageurs National Park. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041879
Brigham ME, VanderMeulen DD, Eagles-Smith CA, Krabbenhoft DP, Maki RP, DeWild JF. Long-Term Trends in Regional Wet Mercury Deposition and Lacustrine Mercury Concentrations in Four Lakes in Voyageurs National Park. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(4):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041879
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrigham, Mark E., David D. VanderMeulen, Collin A. Eagles-Smith, David P. Krabbenhoft, Ryan P. Maki, and John F. DeWild. 2021. "Long-Term Trends in Regional Wet Mercury Deposition and Lacustrine Mercury Concentrations in Four Lakes in Voyageurs National Park" Applied Sciences 11, no. 4: 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041879
APA StyleBrigham, M. E., VanderMeulen, D. D., Eagles-Smith, C. A., Krabbenhoft, D. P., Maki, R. P., & DeWild, J. F. (2021). Long-Term Trends in Regional Wet Mercury Deposition and Lacustrine Mercury Concentrations in Four Lakes in Voyageurs National Park. Applied Sciences, 11(4), 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041879







