Evaluation of the Anthropogenic Metal Pollution at Osisko Lake: Sediments Characterization for Reclamation Purposes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lake History
2.2. Sampling and Samples Preparation
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Physical and Chemical Characterizations
- If NNP < −20 kg CaCO3/t to acidic drainage generator
- If NNP > 20 kg CaCO3/t to non-acid drainage generator
- Uncertain if NNP between −20 and + 20 kg CaCO3/t
- If NPR < 1 to acid drainage generator
- If NPR > 3 to non-acid drainage generator
- Uncertain if NP/AP between 1 and 3
2.3.2. Mineralogical Characterization
2.3.3. Environmental Leaching Tests
3. Results
3.1. Physical Characteristics
3.2. Chemical Characteristics of Pore Waters, Lake Water and Solid Samples
3.2.1. Pore Water and Lake Water
3.2.2. Chemical Characteristics of Sediments and Vase
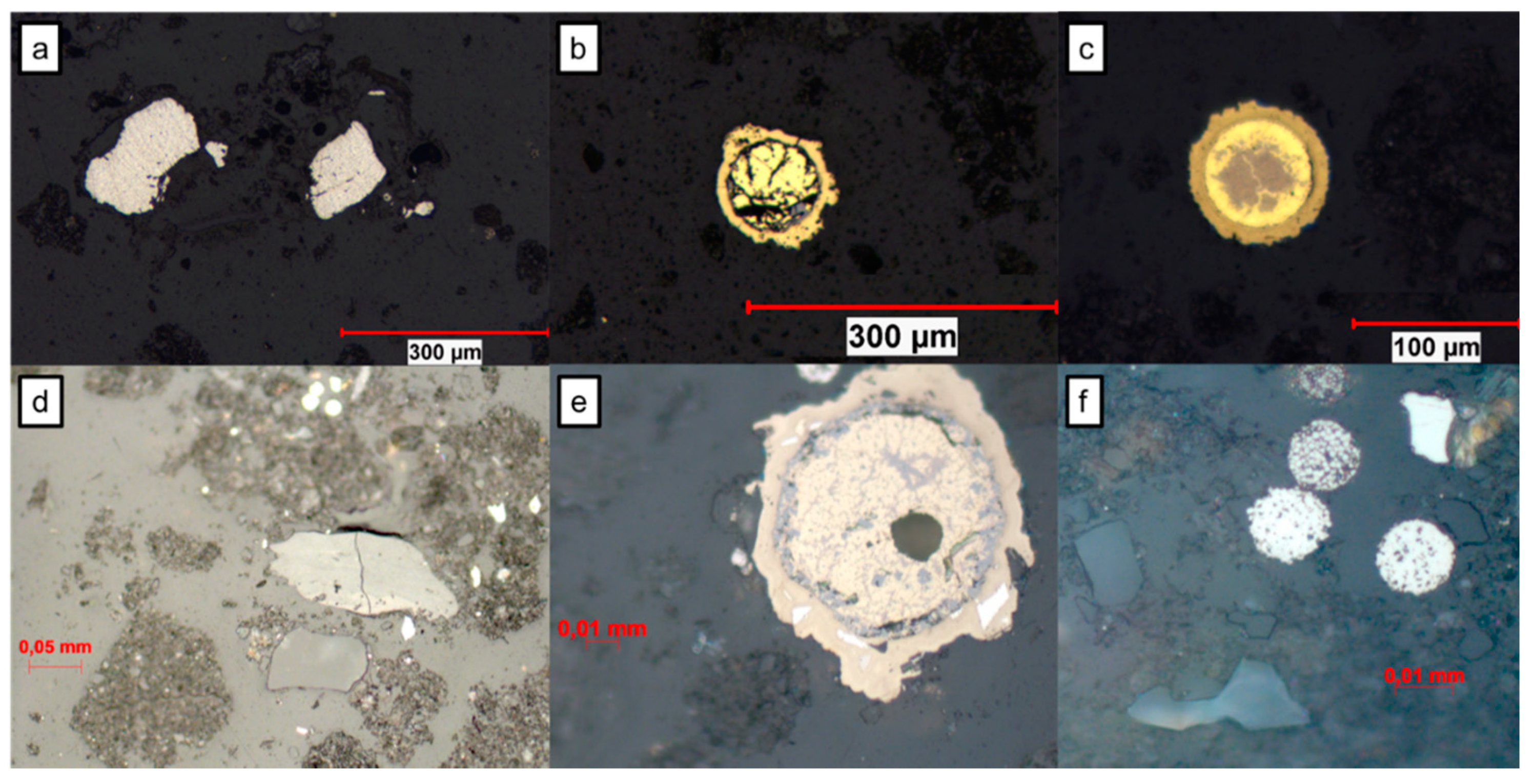
3.3. Mineralogical Characterization
3.4. Environmental Behavior of Sediments, Vase and a Composite Sample
3.4.1. Acidity and Neutralization Potentials
3.4.2. Weathering Cells Results
3.4.3. Dismantling
4. Discussion
4.1. Geochemical Quality of Sediments and Lake Water
4.2. Strategies to Mitigate the Risk Posed by Dredged Sediments
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, W.; Coveney, R.; Chen, J. Environmental quality assessment on a river system polluted by mining activities. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Wang, Q.; Liang, Z.; Zheng, D. Characterization of heavy metal concentrations in the sediments of three freshwater rivers in Huludao City, Northeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 154, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Du, C.; Chen, X. Characteristics and accumulation of heavy metals in sediments originated from an electroplating plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakan, S.M.; Đorđević, D.S.; Manojlović, D.D.; Predrag, P.S. Assessment of heavy metal pollutants accumulation in the Tisza river sediments. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3382–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-Martorell, J.J.; Galindo-Riaño, M.D.; García-Vargas, M.; Granado-Castro, M.D. Bioavailability of heavy metals monitoring water, sediments and fish species from a polluted estuary. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Niu, J.; Tang, Z. Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvin, C.; Allan, L.; McCarry, B.; Bryant, D. Chemico/biological investigation of contaminated sediment from the Hamilton Harbour area of western Lake Ontario. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1993, 22, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemt, W.H.; Kay, M.L.; Wiklund, J.A.; Wolfe, B.B.; Hall, R.I. Assessment of vanadium and nickel enrichment in Lower Athabasca River floodplain lake sediment within the Athabasca Oil Sands Region (Canada). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louriño-Cabana, B.; Lesven, L.; Charriau, A.; Billon, G.; Ouddane, B.; Boughriet, A. Potential risks of metal toxicity in contaminated sediments of Deûle river in Northern France. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 2129–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rath, P.; Panda, U.C.; Bhatta, D.; Sahu, K.C. Use of sequential leaching, mineralogy, morphology and multivariate statistical technique for quantifying metal pollution in highly polluted aquatic sediments—A case study: Brahmani and Nandira Rivers, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikumar, P.; Nasir, U. Ecotoxicological impact assessment of heavy metals in core sediments of a tropical estuary. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1742–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blowes, D.W.; Jambor, J.L.; Alpers, C.N. The Environmental Geochemistry of Sulfide Mine-Wastes; Mineralogical Association of Canada: Québec, QC, Canada, 1994; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Elghali, A.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B.; Genty, T. Spatial mapping of acidity and geochemical properties of oxidized tailings within the former Eagle/Telbel mine site. Minerals 2019, 9, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Shan, B. Historical records of heavy metal accumulation in sediments and the relationship with agricultural intensification in the Yangtze-Huaihe region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 399, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viguri, J.R.; Irabien, M.J.; Yusta, I.; Soto, J.; Gómez, J.; Rodriguez, P.; Martinez-Madrid, M.; Irabien, J.A.; Coz, A. Physico-chemical and toxicological characterization of the historic estuarine sediments: A multidisciplinary approach. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepland, A.; Andersen, T.J.; Lepland, A.; Arp, H.P.H.; Alve, E.; Breedveld, G.D.; Rindby, A. Sedimentation and chronology of heavy metal pollution in Oslo Harbor, Norway. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savard, N. L’Environnement à Rouyn-Noranda: Un Espace en Déséquilibre Suite à L’Activité Minière. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Montréal, Montréal, QC, Canada, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Beaulieu, M. Guide d’Intervention: Protection des Sols et Réhabilitation des Terrains Contaminés; Ministère du Développement Durable, de l’Environnement et de la Lutte contre les Changements Climatiques: Québec, QC, Canada, 2016.
- Bhagowati, B.; Ahamad, K.U. A review on lake eutrophication dynamics and recent developments in lake modeling. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2019, 19, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvidat, J. Gestion d’un Sédiment de Dragage Marin Contaminé: Caractérisation de la Réactivité Biogéochimique, Valorisation en Mortier et Evaluation Environnementale. Ph.D. Thesis, INSA de Lyon, Lyon, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Amar, H.; Benzaazoua, M.; Edahbi, M.; Villeneuve, M.; Joly, M.-A.; Elghali, A. Reprocessing feasibility of polymetallic waste rock for cleaner and sustainable mining. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 220, 106683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, H.; Benzaazoua, M.; Elghali, A.; Bussière, B.; Duclos, M. Upstream environmental desulphurisation and valorisation of waste rocks as a sustainable AMD management approach. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 215, 106555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordstrom, D.K.; Southam, G. Chapter 11. Geomicrobiology of sulfide mineral oxidation. Geomicrobiology 1997, 35, 361–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Wang, L.; Xiao, M. Changes in speciation and leaching behaviors of heavy metals in dredged sediment solidified/stabilized with various materials. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8294–8301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Temminghoff, E.J.; Lofts, S.; Tipping, E.; Van Riemsdijk, W.H. Complexation with dissolved organic matter and solubility control of heavy metals in a sandy soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4804–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grybos, M.; Davranche, M.; Gruau, G.; Petitjean, P. Is trace metal release in wetland soils controlled by organic matter mobility or Fe-oxyhydroxides reduction? J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 314, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouyn-Noranda, V.D. Etude sur L’état du lac Osisko; Rouyn-Noranda: Québec, QC, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, E.E.; Hopkins, B.G. Estimation of soil organic matter by weight loss-on-ignition. SSSA Spec. Pub. 2015, 46, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Elghali, A.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bouzahzah, H.; Bussière, B.; Villarraga-Gómez, H. Determination of the available acid-generating potential of waste rock, part I: Mineralogical approach. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 99, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.W.; Scheske, M. A method to calculate the neutralization potential of mining wastes. Environ. Earth Sci. 1997, 32, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H.M. A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1969, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R.; Luna-Sánchez, R.; Lapidus, G.; González, I.; Monroy, M. An experimental strategy to determine galvanic interactions affecting the reactivity of sulfide mineral concentrates. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 78, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testing, A.S.F. Classification of soils for engineering purposes. Ann. B. ASTM Stand. 1985, 395–408. [Google Scholar]
- Environnement Canada et ministère du Développement durable, Canada. Critères Pour L’évaluation de la Qualité des Sédiments au Quebec et Cadres D’application: Prévention, Dragage et Restauration; Environment Canada: Fredericton, NB, Canada, 2007; p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkin, R.; Barnes, H. Formation processes of framboidal pyrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, V.P.; Zhang, Y.L. A review: Pyrite oxidation mechanisms and acid mine drainage prevention. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 25, 141–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migniot, C. Action des courants, de la houle et du vent sur les sédiments. La Houille Blanche 1977, 1977, 9–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elghali, A.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B.; Genty, T. In situ effectiveness of alkaline and cementitious amendments to stabilize oxidized acid-generating tailings. Minerals 2019, 9, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cravotta, C.A. Dissolved metals and associated constituents in abandoned coal-mine discharges, Pennsylvania, USA. Part 2: Geochemical controls on constituent concentrations. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froelich, P.; Klinkhammer, G.; Bender, M.; Luedtke, N.; Heath, G.; Cullen, D.; Dauphin, P.; Hammond, D.; Hartman, B.; Maynard, V. Early oxidation of organic matter in pelagic sediments of the eastern equatorial Atlantic: Suboxic diagenesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1979, 43, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Dagenais, A.-M.; Archambault, M. Kinetic tests comparison and interpretation for prediction of the Joutel tailings acid generation potential. Environ. Earth Sci. 2004, 46, 1086–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcil, A.; Erust, C.; Ozdemiroglu, S.; Fonti, V.; Beolchini, F. A review of approaches and techniques used in aquatic contaminated sediments: Metal removal and stabilization by chemical and biotechnological processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 86, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjoveanu, G.; De Gisi, S.; Casale, R.; Todaro, F.; Notarnicola, M.; Teodosiu, C. A life cycle assessment study on the stabilization/solidification treatment processes for contaminated marine sediments. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-L.; Zhao, L.-Y.; McCabe, B.A.; Chen, Y.-H.; Morrison, L. Dredged marine sediments stabilized/solidified with cement and GGBS: Factors affecting mechanical behaviour and leachability. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 733, 138551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, F.; De Gisi, S.; Notarnicola, M. Contaminated marine sediment stabilization/solidification treatment with cement/lime: Leaching behaviour investigation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21407–21415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Chen, K.; Chen, D. Effect of organics on heavy metal-contaminated river sediment treated with electro-osmosis and solidification/stabilization methods. Materials 2020, 13, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- United Stated Einvironmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Treatment Technologies for Site Cleanup: Annual Status Report, 12th ed.; EPA-542-R-03; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Gang, Y.; Won, E.-J.; Ra, K.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, K.-W.; Kim, K. Environmental assessment of contaminated marine sediments treated with solidification agents: Directions for improving environmental assessment guidelines. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 139, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvidat, J.; Benzaazoua, M.; Chatain, V.; Bouzahzah, H. Environmental evaluation of dredged sediment submitted to a solidification stabilization process using hydraulic binders. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17142–17157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paria, S.; Yuet, P.K. Solidification-stabilization of organic and inorganic contaminants using portland cement: A literature review. Environ. Rev. 2006, 14, 217–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elghali, A.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B.; Bouzahzah, H. Determination of the available acid-generating potential of waste rock, part II: Waste management involvement. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 100, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Belem, T.; Bussière, B. Chemical factors that influence the performance of mine sulphidic paste backfill. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghali, A.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B.; Kennedy, C.; Parwani, R.; Graham, S. The role of hardpan formation on the reactivity of sulfidic mine tailings: A case study at Joutel mine (Québec). Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 654, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



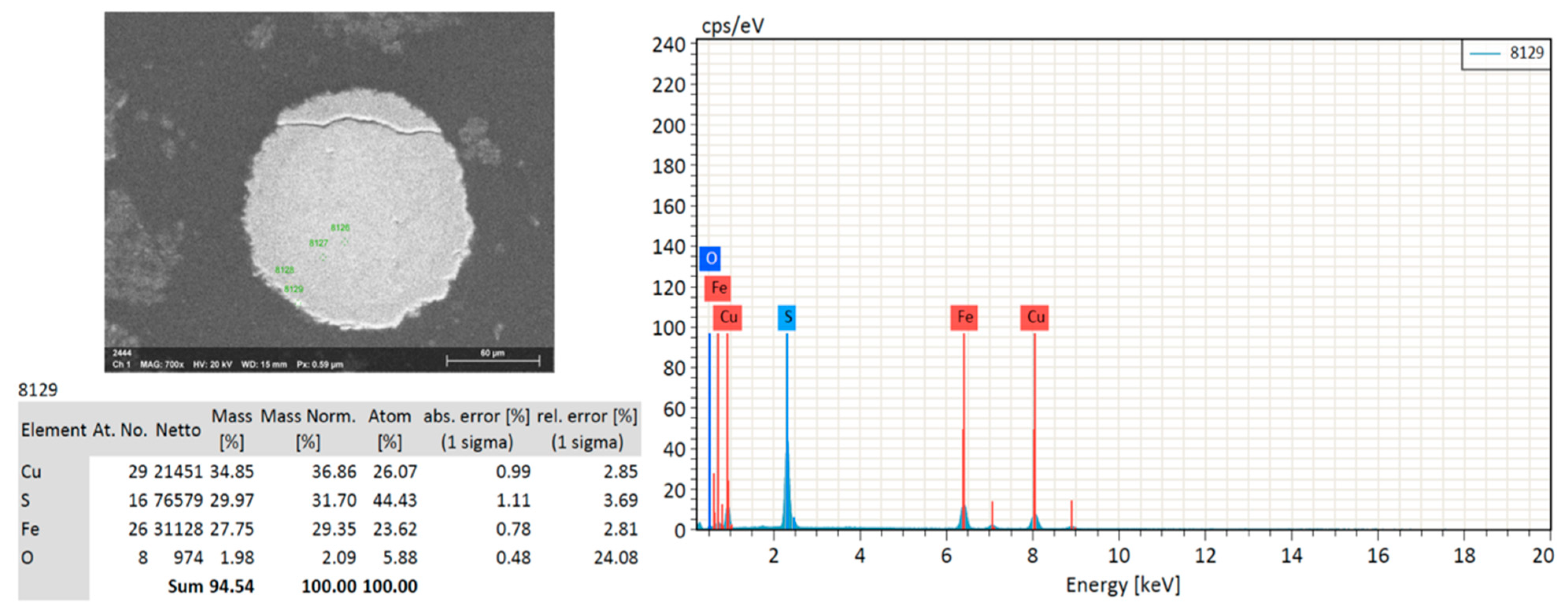





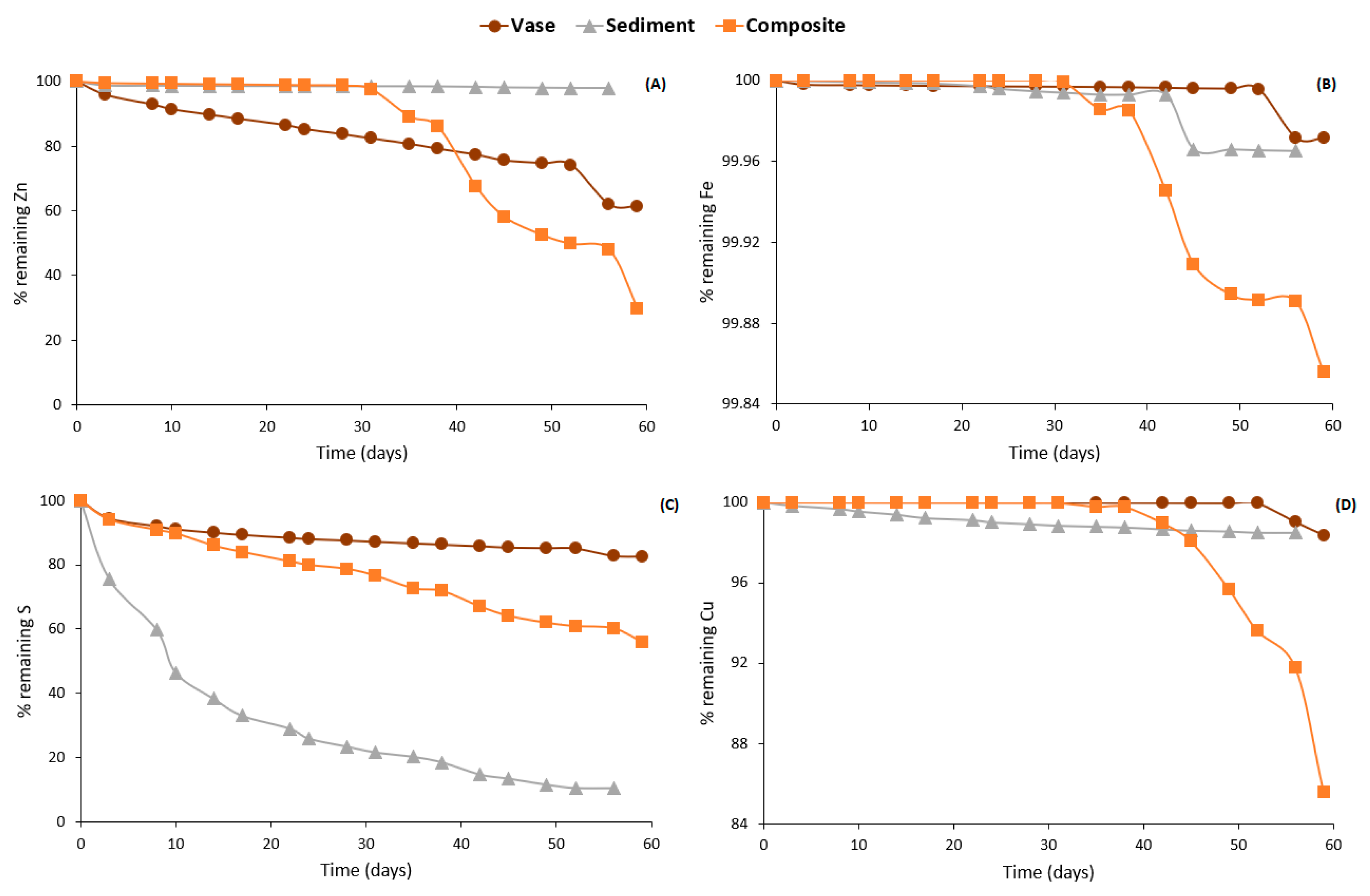
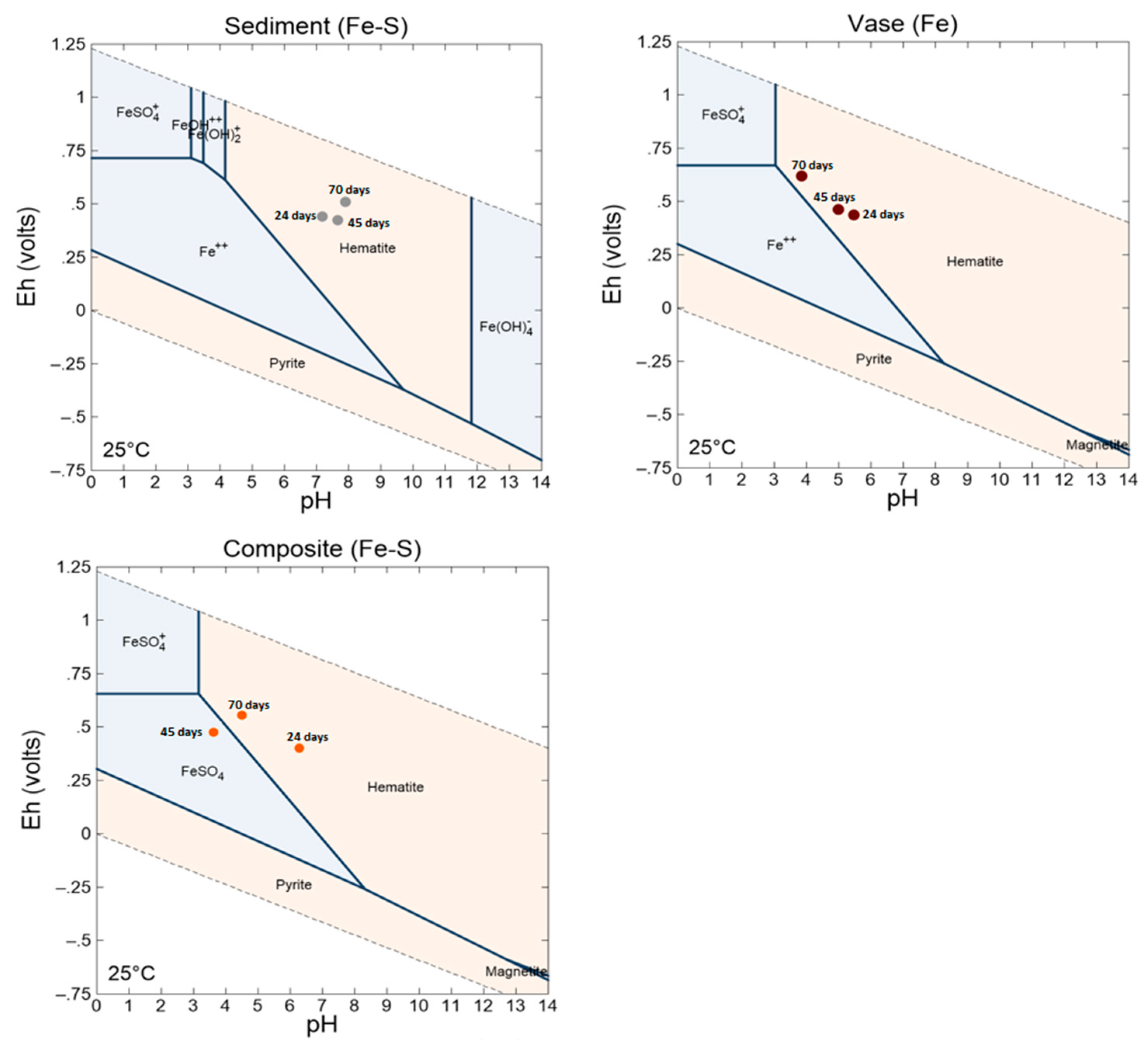
| Parameters | Units | Values | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sediment | Vase | |||||||
| 81,844 | 81,848 | 81,838 | 81,854 | 81,872 | 81,874 | 81,850 | ||
| SSA | m2/g | 17.90 | 17.06 | 14.86 | 17.17 | 26.41 | 20.54 | 35.72 |
| Gs | g/cc | 2.55 | 2.49 | 2.52 | 2.54 | 2.64 | 2.33 | 2.51 |
| D10 | (µm) | 1.50 | 1.68 | 1.44 | 1.40 | 1.15 | NA | NA |
| D50 | (µm) | 6.85 | 7.99 | 6.73 | 6.67 | 3.77 | NA | NA |
| D90 | (µm) | 26.20 | 25.65 | 26.53 | 28.04 | 12.83 | NA | NA |
| Lake Water | Sediment Pore Water | Vase Pore Water | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | 81,830 | 81,833 | 81,835 | 81,837 | 81,841 | 81,843 | 81,847 | 81,853 | 81,871 | 81,873 | 81,875 | 81,839 | 81,845 | 81,849 | 81,851 | |
| Conductivity | µS/cm | 265 | 318 | 254 | 190.4 | 261 | 164.4 | 188.6 | 337 | 175 | 250 | 190.9 | 193.6 | 380 | 306 | 178 |
| pH | - | 7.79 | 8.01 | 7.84 | 7.36 | 7.4 | 7.56 | 7.32 | 7.71 | 7.72 | 7.59 | 7.53 | 7.55 | 6.86 | 7.61 | 7.61 |
| Eh | mV | 526 | 603 | 476 | 513 | 538 | 513 | 517 | 487 | 494 | 498 | 647 | 518 | 580 | 469 | 512 |
| Alkalinity | mgCaCO3/eq | 54.24 | 66.32 | 74.48 | 55.92 | 61.44 | 68.88 | 42.88 | 130.64 | 54.64 | 76.16 | 34.56 | 38.56 | 4.48 | 74.72 | 35.84 |
| Acidity | mgCaCO3/eq | 0.64 | 5.04 | 2.52 | 5.24 | 7.8 | 3.96 | 7.04 | 5.2 | 1.36 | 8.36 | 1.44 | 0.84 | 10.04 | 9.24 | 0.92 |
| Element | DL—mg/L | Chemical composition—mg/L | ||||||||||||||
| Al | 0.01 | 0.214 | 0.225 | 0.242 | 0.237 | 0.539 | 0.343 | 1.03 | 0.255 | 0.151 | 0.198 | 0.182 | 0.079 | 0.228 | 0.218 | 0.208 |
| Si | 0.04 | 0.137 | 6.61 | 7.11 | 10.9 | 15.4 | 15.2 | 18 | 7.15 | 2.78 | 4.35 | 1.37 | 2.84 | 4.89 | 2.19 | 0.582 |
| K | n/d | 1.29 | 4.76 | 2.77 | 1.9 | 2.18 | 1.91 | 1.95 | 3.06 | 2.29 | 2.09 | 1.43 | 1.81 | 1.79 | 1.94 | 1.33 |
| Na | n/d | 24.3 | 28.1 | 28 | 19.6 | 28.2 | 19.9 | 24.5 | 25 | 22.9 | 23.1 | 26.7 | 22.7 | 26.6 | 33 | 23.4 |
| Ca | 0.03 | 22.8 | 49.8 | 18.9 | 17.8 | 14.5 | 15.4 | 10.8 | 36.3 | 20.6 | 22.5 | 19.5 | 18.1 | 35 | 24.3 | 18.1 |
| Mg | 0.001 | 4.31 | 7.8 | 3.82 | 4.21 | 2.92 | 3.38 | 2.11 | 7.15 | 5.01 | 4.18 | 3.73 | 3.45 | 5.73 | 4.55 | 4.01 |
| Mn | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.89 | 0.374 | 1.03 | 0.521 | 0.77 | 0.276 | 1.58 | 0.539 | 0.774 | 0.118 | 0.773 | 0.728 | 0.804 | 0.063 |
| Fe | 0.006 | <0.006 | <0.006 | 0.05 | 0.281 | 0.204 | 0.113 | 0.564 | 0.015 | <0.006 | 0.38 | <0.006 | 0.14 | <0.006 | <0.006 | <0.006 |
| S | 0.09 | 7.67 | 41.6 | 13.9 | 5.65 | 12.6 | 1.98 | 11.7 | 6.15 | 9.39 | 2.67 | 8.99 | 9.62 | 42.1 | 3.95 | 8.22 |
| Ba | 0.001 | 0.027 | 0.047 | 0.017 | 0.03 | 0.025 | 0.026 | 0.028 | 0.05 | 0.037 | 0.038 | 0.036 | 0.055 | 0.205 | 0.04 | 0.026 |
| Cu | 0.003 | 0.031 | 0.01 | 0.008 | <0.003 | 0.021 | 0.003 | 0.015 | <0.003 | <0.003 | <0.003 | <0.003 | <0.003 | 0.048 | <0.003 | <0.003 |
| Ni | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.004 | <0.004 | 0.005 | <0.004 | <0.004 | 0.006 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | <0.004 | 0.052 | <0.004 | <0.004 |
| Sr | n/d | 0.072 | 0.464 | 0.128 | 0.071 | 0.074 | 0.072 | 0.04 | 0.155 | 0.093 | 0.081 | 0.061 | 0.059 | 0.122 | 0.083 | 0.057 |
| Zn | 0.005 | 0.064 | 0.03 | 0.009 | 0.019 | 0.03 | 0.024 | 0.03 | 0.047 | 0.005 | 0.024 | 0.068 | 0.034 | 7.5 | 0.016 | 0.036 |
| Methods | Elements | Unit | DL | Sediments | Vases | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 81,838 | 81,844 | 81,848 | 81,854 | 81,872 | 81,874 | 81,850 | ||||
| ICP-AES | Al | mg/kg | 60.0 | 76,080 | 76,430 | 76,540 | 76,320 | 80,800 | 46,630 | 38,880 |
| As | mg/kg | 5.00 | 106 | 114 | 118 | 151 | 106 | 326 | 334 | |
| Ba | mg/kg | 5.00 | 540 | 551 | 558 | 566 | 639 | 384 | 270 | |
| Ca | mg/kg | 60.0 | 17,100 | 17,430 | 14,730 | 28,060 | 21,450 | 12,120 | 9122 | |
| Cd | mg/kg | 5.00 | <5 | <5 | <5 | <5 | <5 | 77.4 | 107 | |
| Co | mg/kg | 5.00 | 11.7 | 8.02 | 8.79 | 5.18 | 7.32 | 73.3 | 71.3 | |
| Cr | mg/kg | 5.00 | 159 | 126 | 120 | 124 | 129 | 92.2 | 66.8 | |
| Cu | mg/kg | 10.00 | 764 | 111 | 260 | 192 | 214 | 12,130 | 9764 | |
| Fe | mg/kg | 10.00 | 42,300 | 40,190 | 40,100 | 40,440 | 41,600 | 146,200 | 222,300 | |
| K | mg/kg | n/d | 18,460 | 18,830 | 19,320 | 19,650 | 22,280 | 10,140 | 8124 | |
| Mg | mg/kg | 15.0 | 15,960 | 16,060 | 15,310 | 16,830 | 19,840 | 8972 | 7414 | |
| Mn | mg/kg | 5.00 | 739 | 737 | 599 | 758 | 867 | 795 | 609 | |
| Mo | mg/kg | 5.00 | 6.40 | 5.59 | 5.21 | 6.36 | 6.02 | 13.6 | 12.6 | |
| Na | mg/kg | n/d | 18,100 | 18,230 | 17,610 | 18,870 | 22,640 | 11,420 | 8821 | |
| Ni | mg/kg | 5.00 | 73.0 | 55.4 | 54.0 | 55.9 | 57.9 | 105 | 98.0 | |
| Pb | mg/kg | 5.00 | 51.9 | 14.3 | 15.5 | 15.1 | 21.0 | 1392 | 1445 | |
| S | mg/kg | 200 | 2379 | 794 | 2046 | 2229 | 1351 | 53,340 | 48,430 | |
| Si | mg/kg | n/d | 245,100 | 240,900 | 245,300 | 234,900 | 242,500 | 155,300 | 119,500 | |
| Ti | mg/kg | 25.0 | 3358 | 3488 | 3035 | 3256 | 3085 | 1791 | 1404 | |
| Zn | mg/kg | 55.0 | 301 | 114 | 171 | 119 | 169 | 9096 | 11,400 | |
| Ctotal | Wt.% | 0.05 | 1.95 | 1.94 | 2.43 | 2.42 | 0.53 | 8.08 | 6.77 | |
| Corg | Wt.% | cal | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.29 | NA | 6.61 | |
| Cinorg | Wt.% | 0.05 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.233 | NA | 0.160 | |
| Ssulfide | Wt.% | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.04 | NA | 3.73 | ||
| Ssulfate | Wt.% | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.04 | NA | 1.16 | ||
| Stotal | Wt.% | 0.009 | 0.163 | 0.054 | 0.181 | 0.214 | 0.098 | 4.913 | 4.380 | |
| XRF Whole rock | LOI | % | −10 | 8.19 | 8.07 | 9.96 | 9.27 | 5.24 | 24.1 | 24 |
| SiO2 | % | 0.01 | 58.2 | 58 | 57.3 | 55.2 | 57.7 | 34.4 | 26.5 | |
| Al2O3 | % | 0.01 | 14.8 | 15.1 | 15 | 14.8 | 15.9 | 9.06 | 7.66 | |
| Fe2O3 | % | 0.01 | 6.56 | 6.39 | 6.27 | 6.39 | 6.53 | 20.6 | 31.7 | |
| MgO | % | 0.01 | 2.84 | 2.87 | 2.67 | 2.95 | 3.5 | 1.52 | 1.3 | |
| CaO | % | 0.01 | 2.56 | 2.65 | 2.19 | 4.17 | 3.22 | 1.77 | 1.34 | |
| K2O | % | 0.01 | 2.43 | 2.54 | 2.52 | 2.55 | 2.92 | 1.29 | 1.04 | |
| Criteria for Assessing the Quality of Freshwater Sediments | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentrations (mg/kg) | ||||||
| Groups | Substances | REC | TSE | COE | CPE | CFE |
| Metals and metalloids | Arsenic | 4.1 | 5.9 | 7.6 | 17 | 23 |
| Cadmium | 0.33 | 0.6 | 1.7 | 3.5 | 12 | |
| Chromium | 25 | 37 | 57 | 90 | 120 | |
| Copper | 22 | 36 | 63 | 200 | 700 | |
| Mercury | 0.094 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.49 | 0.87 | |
| Nickel | ND | ND | 47 | ND | ND | |
| Lead | 25 | 35 | 52 | 91 | 150 | |
| Zinc | 80 | 120 | 170 | 310 | 770 | |
| Element | AP %Ssulfide | NP %Cinorganic | NP Lawrence–Scheske | NNP (Ssulfide, Lawrence) | NPR (Ssulfide, Lawrence) | NNP (Ssulfide, Cinorganic) | NPR (Ssulfide, Cinorganic) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | kg CaCO3/t | kg CaCO3/t | |||||
| Vase (81,850) | 116.56 | 13.29 | 53.64 | −62.92 | 0.46 | −103.27 | 0.11 |
| Sediment (81,872) | 1.25 | 19.44 | 203.88 | 202.63 | 163.10 | 18.19 | 15.55 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Darricau, L.; Elghali, A.; Martel, P.; Benzaazoua, M. Evaluation of the Anthropogenic Metal Pollution at Osisko Lake: Sediments Characterization for Reclamation Purposes. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052298
Darricau L, Elghali A, Martel P, Benzaazoua M. Evaluation of the Anthropogenic Metal Pollution at Osisko Lake: Sediments Characterization for Reclamation Purposes. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(5):2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052298
Chicago/Turabian StyleDarricau, Louise, Abdellatif Elghali, Patrick Martel, and Mostafa Benzaazoua. 2021. "Evaluation of the Anthropogenic Metal Pollution at Osisko Lake: Sediments Characterization for Reclamation Purposes" Applied Sciences 11, no. 5: 2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052298
APA StyleDarricau, L., Elghali, A., Martel, P., & Benzaazoua, M. (2021). Evaluation of the Anthropogenic Metal Pollution at Osisko Lake: Sediments Characterization for Reclamation Purposes. Applied Sciences, 11(5), 2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11052298







