EM-Driven Multi-Objective Optimization of a Generic Monopole Antenna by Means of a Nested Trust-Region Algorithm
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
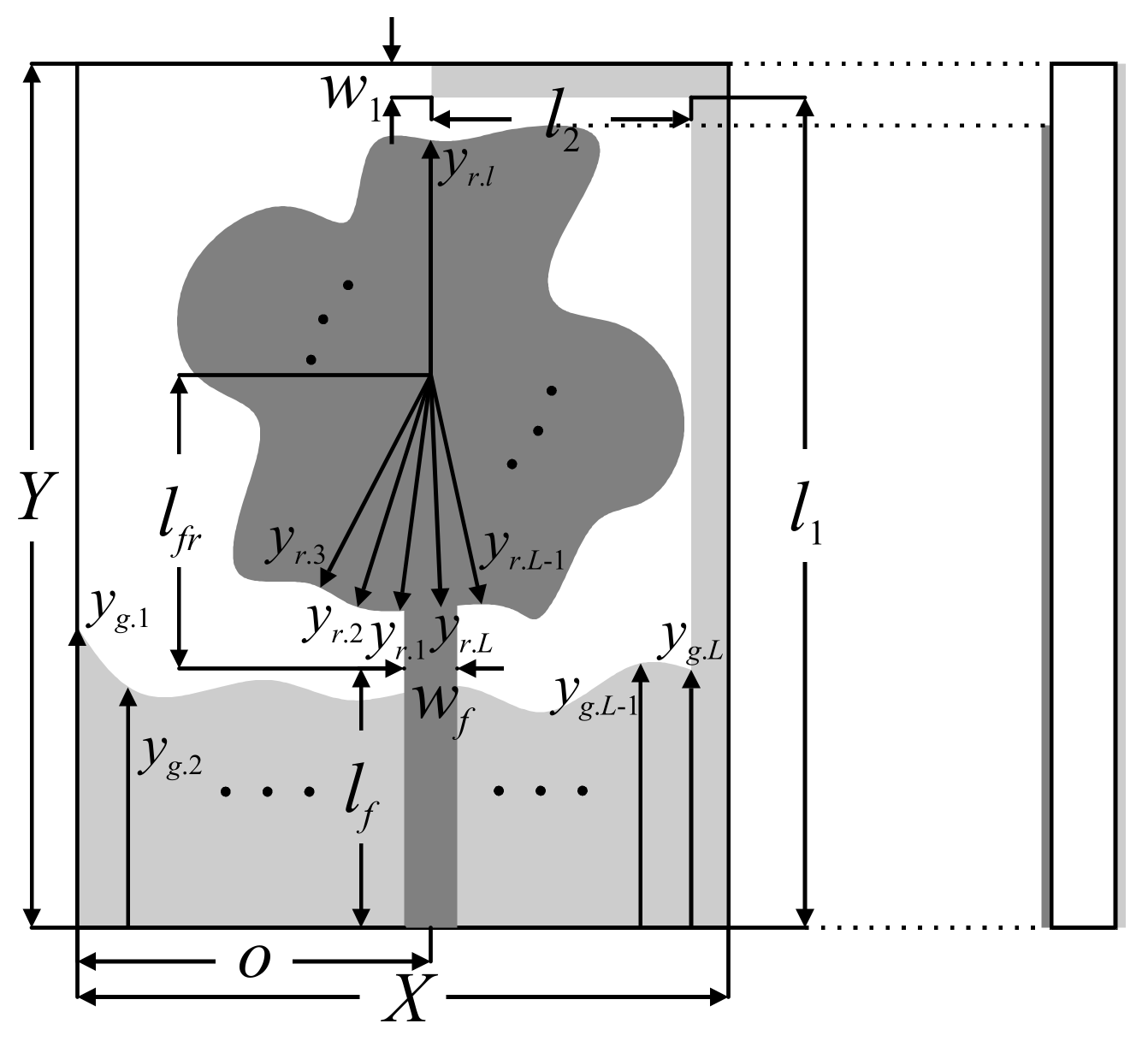
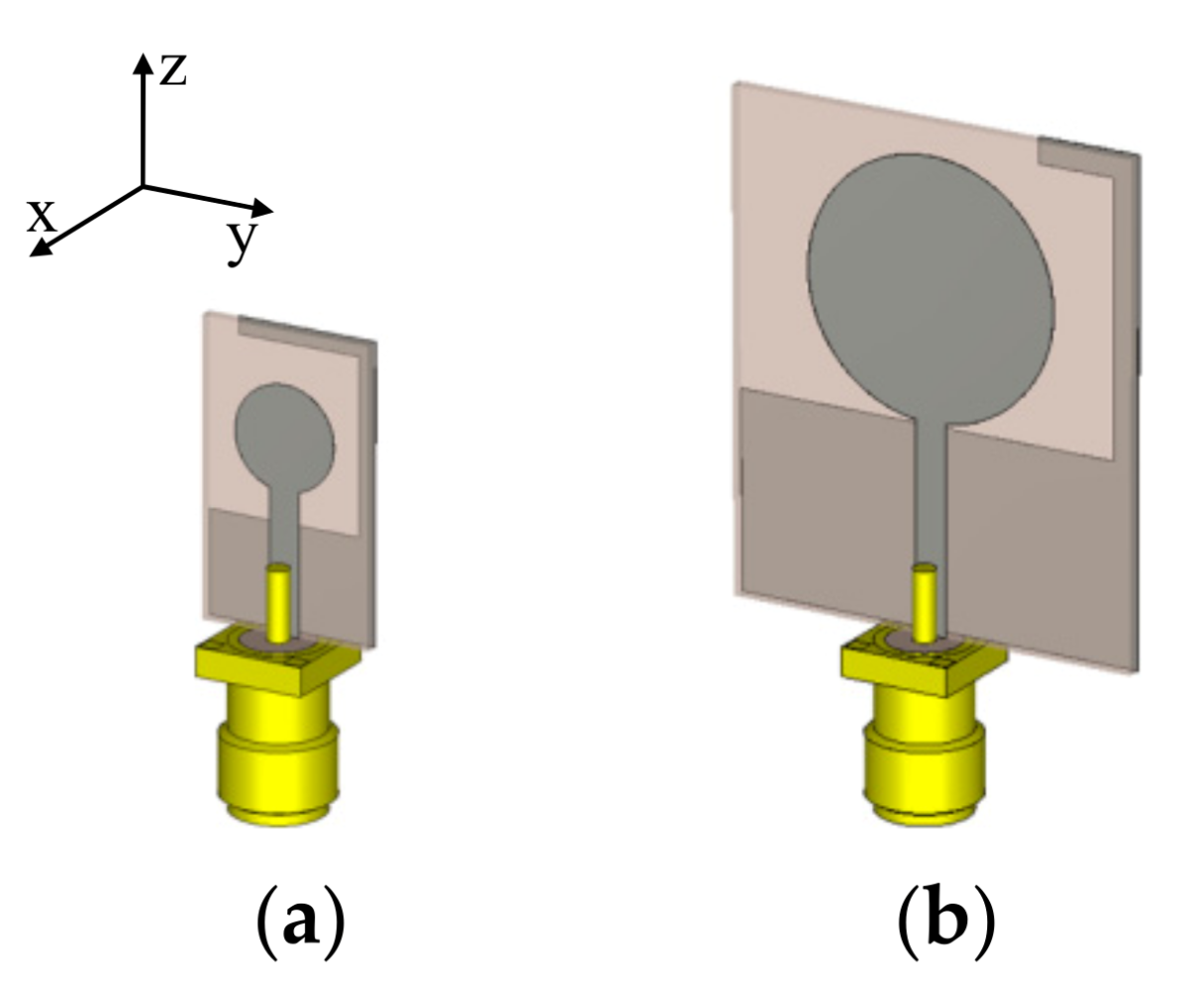
2. Generic UWB Monopole Antenna
3. Design Methodology
3.1. Multi-Objective Design Problem
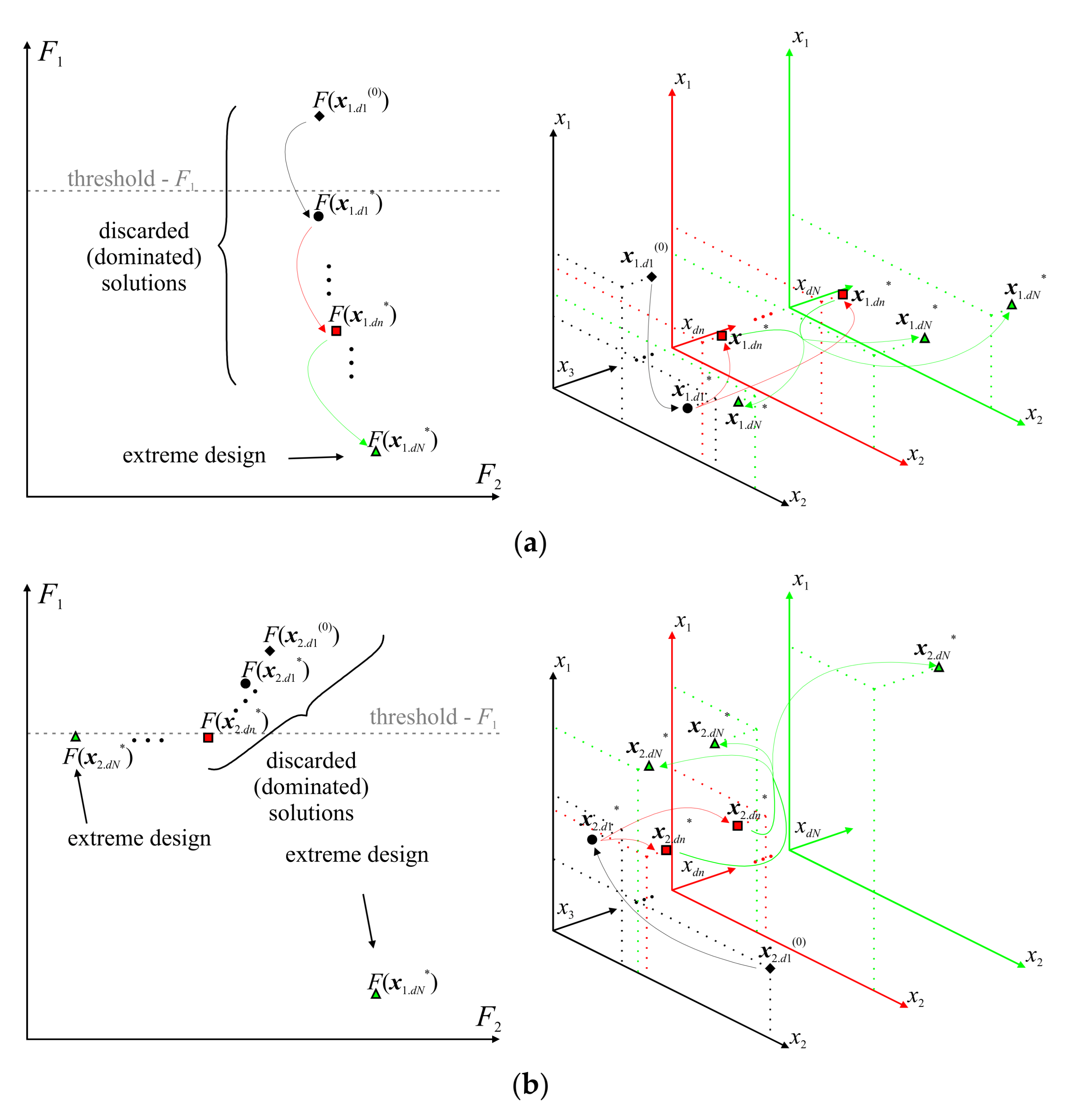
3.2. Nested Optimization with a Variable Number of Design Parameters
- 1.
- 2.
- Find design xdn+1* using xdn+1(0) as a starting point for optimization;
- 3.
- If n = N, END; otherwise, set n = n + 1 and go to 1.
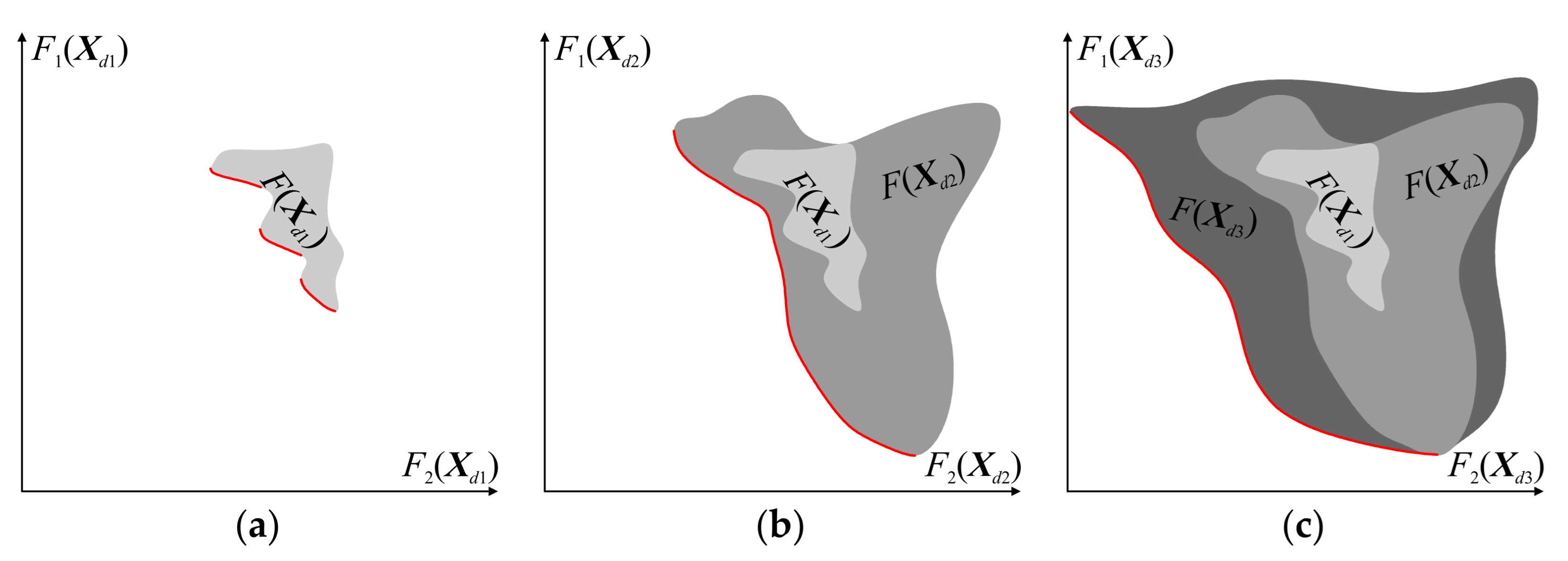
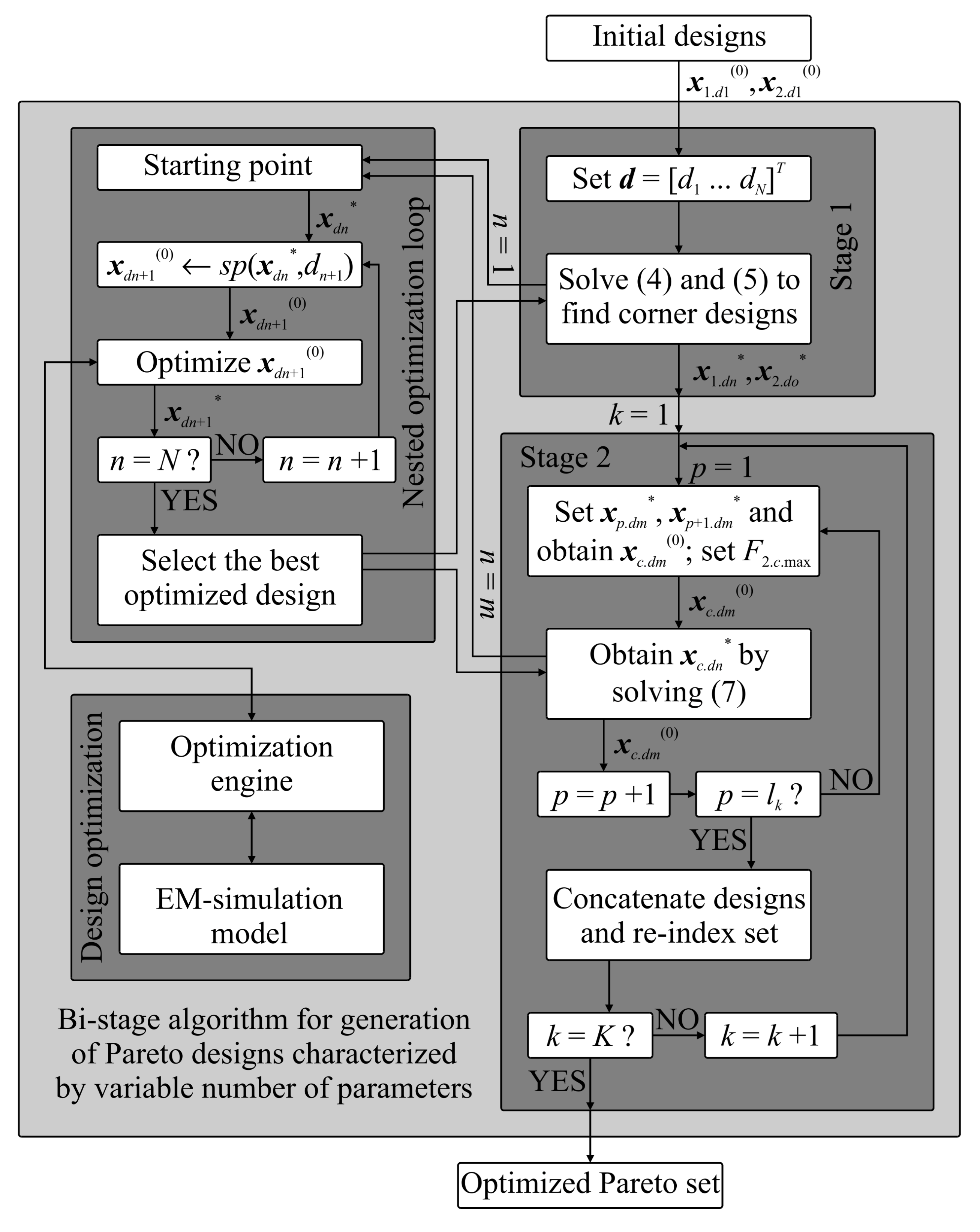
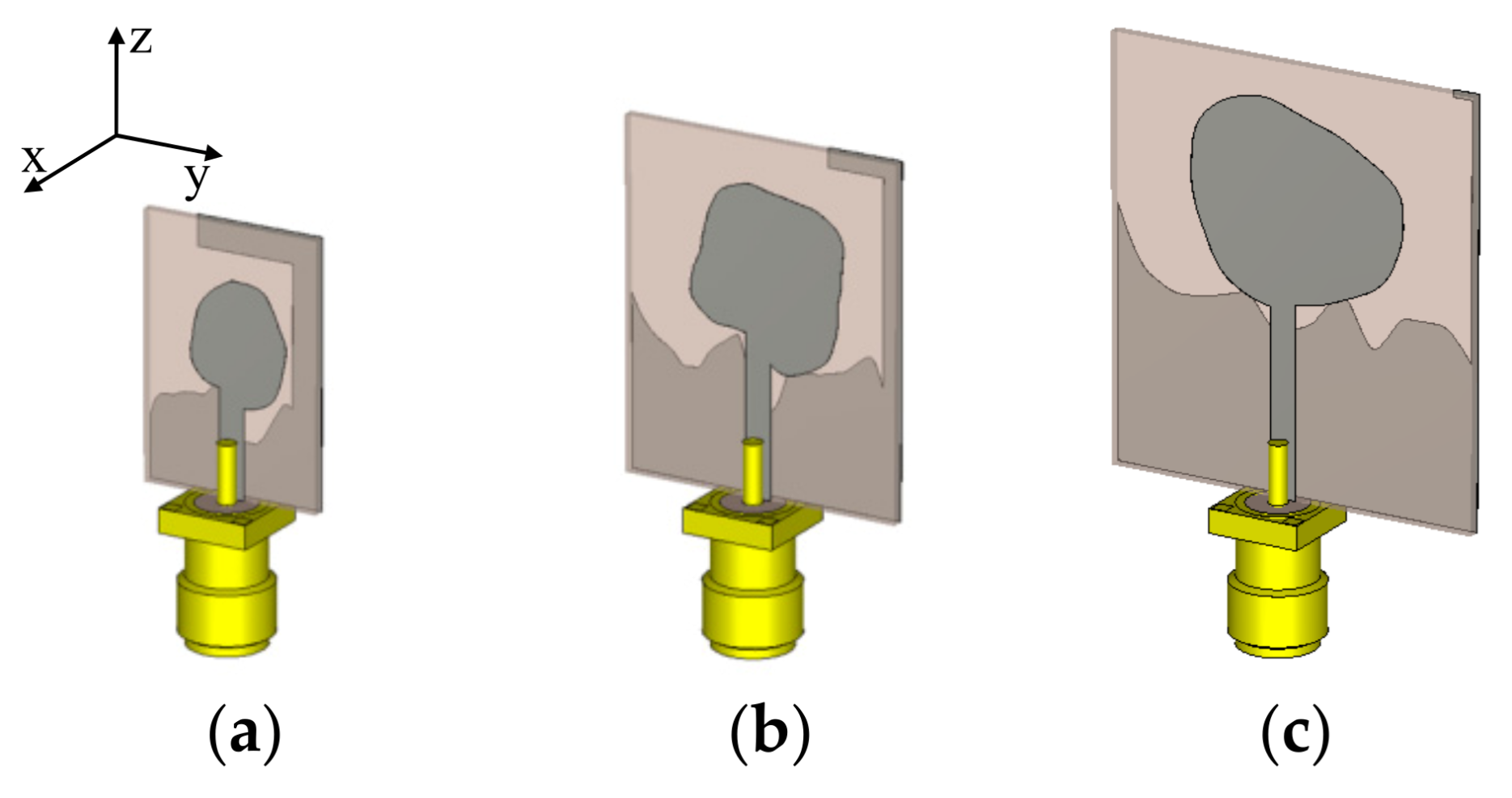
3.3. Generation of Trade-Off Designs
- 1.
- Set the initial designs x1.d1(0) and x2.d1(0); set d = [d1 d2 … dm … dn … dN]T;
- 2.
- Obtain x1.dn* and x2.do* (n ≤ N, o ≤ N) by solving Equations (4) and (5) in a nested loop (see Section 3.2);
- 3.
- Set k = 1;
- 4.
- Set p = 1;
- 5.
- Set xp.dm* ← sp(xp.dn*, dm), xp+1.dm* ← sp(xp+1.do*, dm) (see Section 2), and then calculate xc.dm(0) and set F2.c.max;
- 6.
- Generate xc.dn* by solving Equation (7) in a nested optimization loop;
- 7.
- If p = lk, go to 7; otherwise set p = p + 1 and go to 5;
- 8.
- Concatenate the designs as {x1.d*, xb+1.dn*, x2.dn*, xb+2.dn*, …, xlk−1.dn*, x2lk−1.dn*, xlk.dn*}, and then reindex the resulting set;
- 9.
- If k = K, END; otherwise, set k = k + 1 and go to 4.
3.4. Optimization Engine
- 1.
- 2.
- Generate the Jacobian J(x(i)) and construct the local approximation model G(i);
- 3.
- Find x(i+1) by solving Equation (8);
- 4.
- Evaluate R(x(i+1)) and calculate ρ;
- 5.
- If ρ > 0.75, set r(i+1) = 2r(i). If ρ < 0.25, set r(i+1) = r(i)/3;
- 6.
- If ρ < 0, go to 3; otherwise, go to 7;
- 7.
- If the termination condition is met, END; otherwise, set i = i + 1 and go to 2.
4. Numerical Results
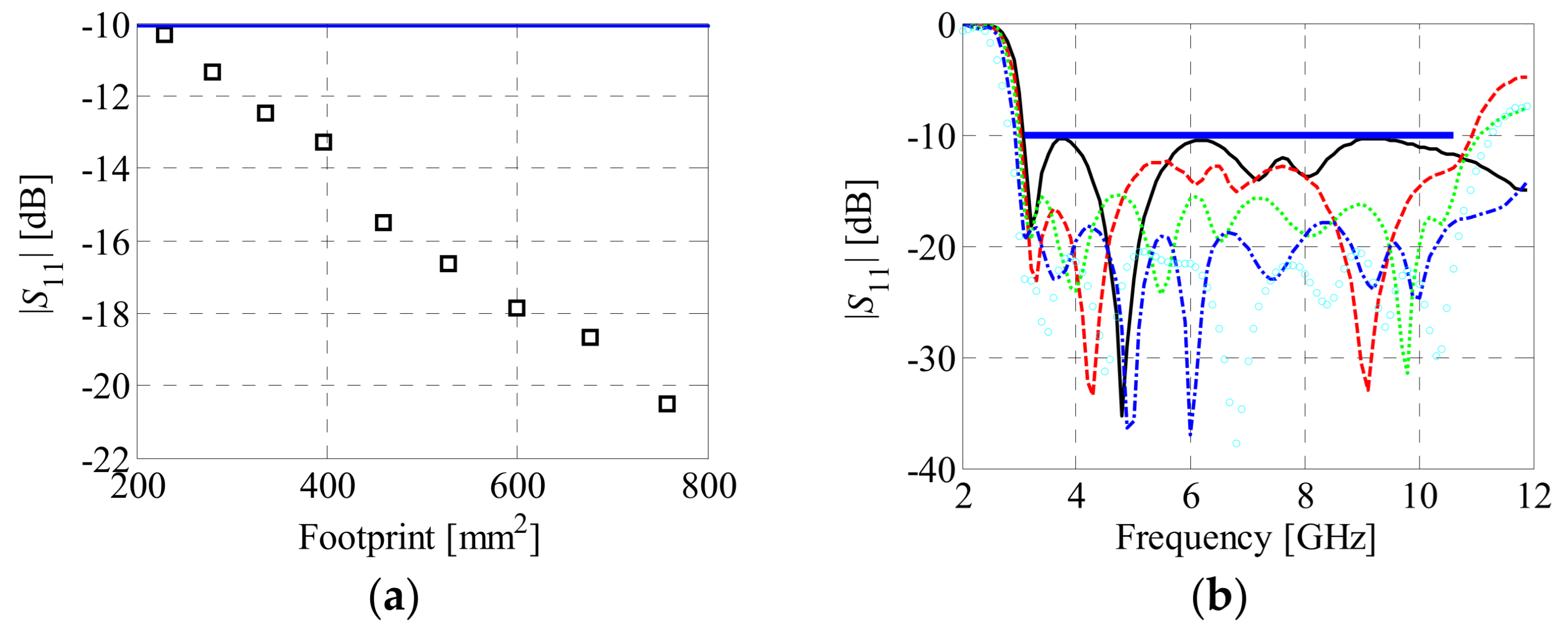
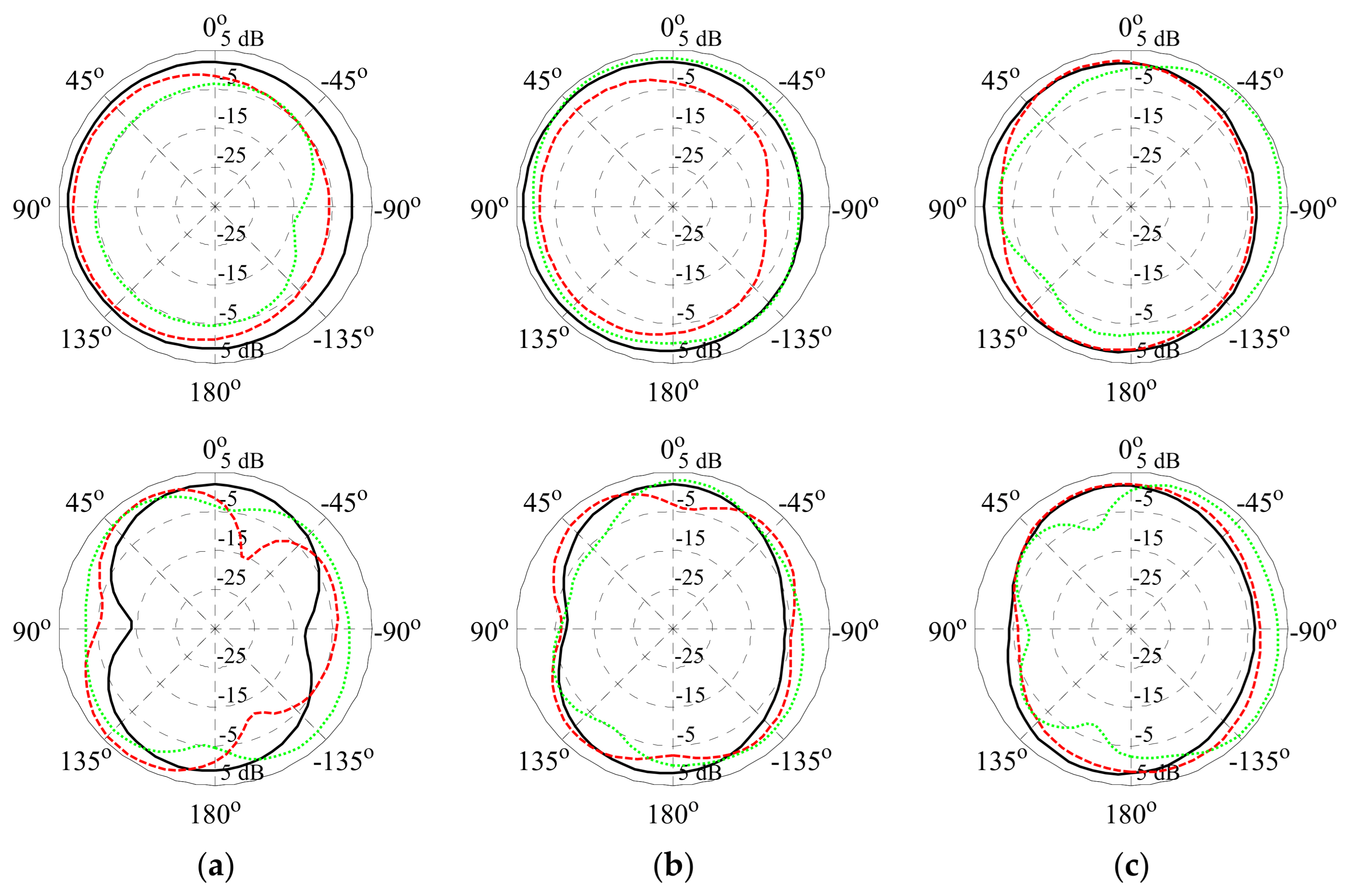
4.1. Bi-Objective Antenna Optimization
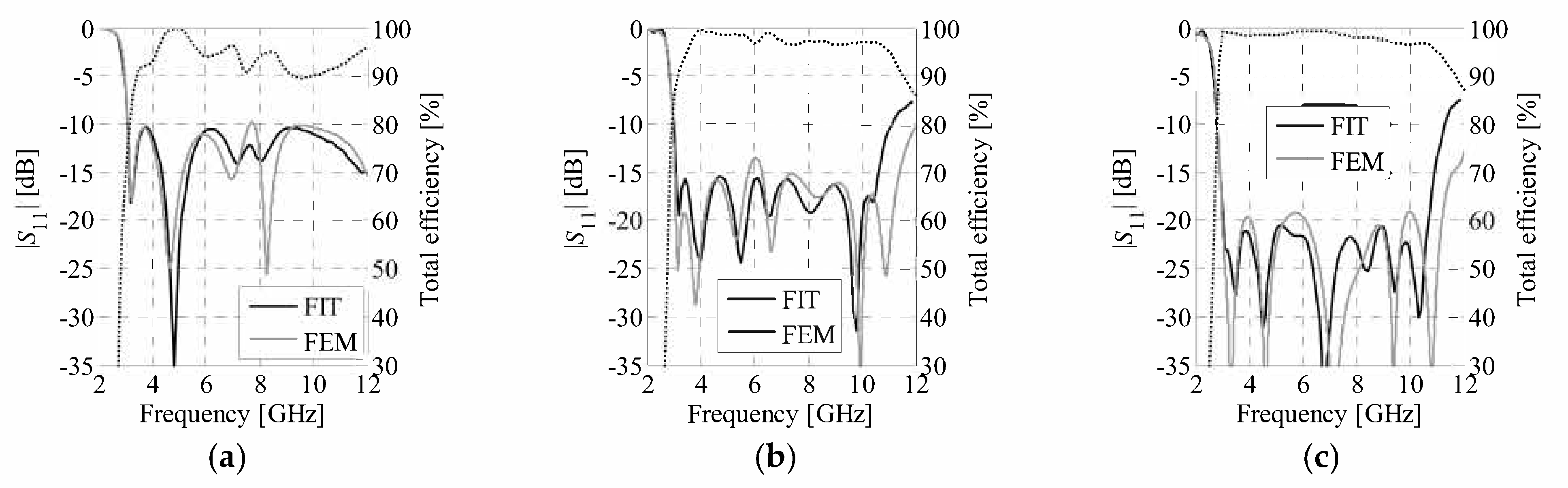
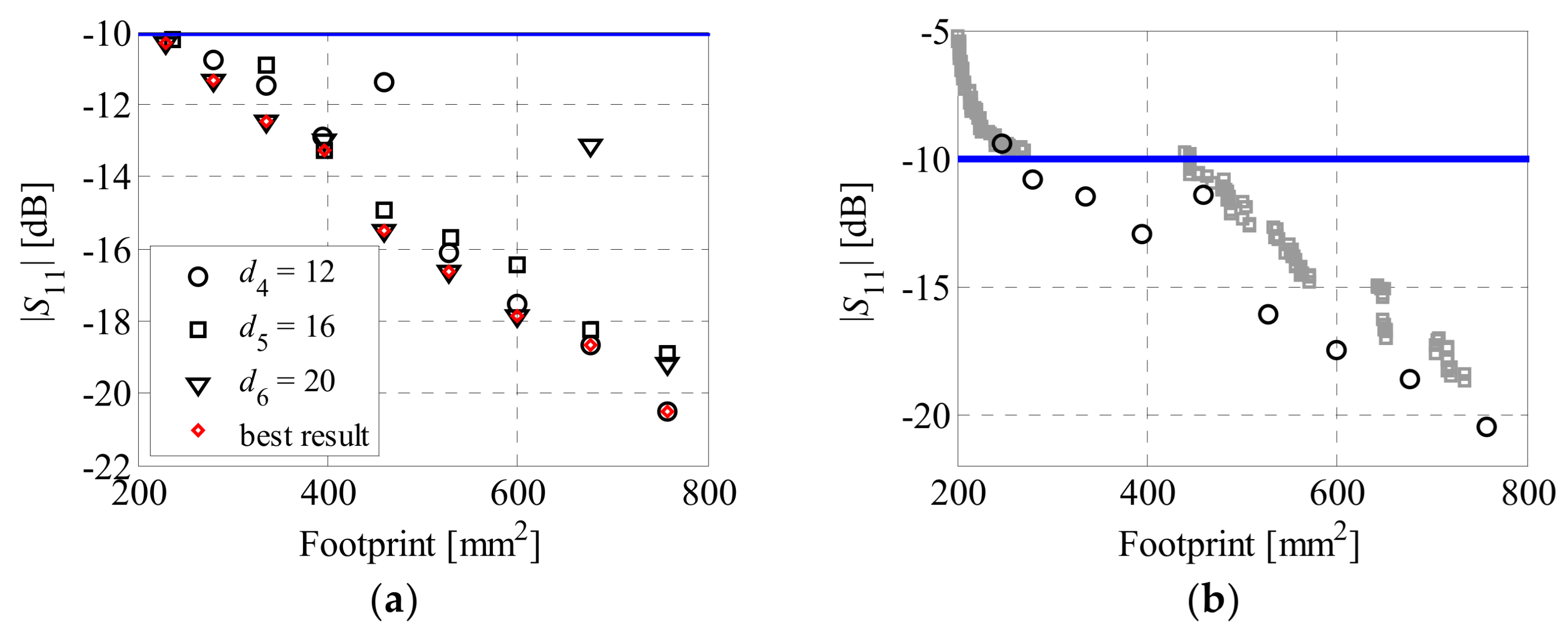
4.2. Comparisons and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costanzo, A.; Dardari, D.; Aleksandravicius, J.; Decarli, N.; Del Prete, M.; Fabbri, D.; Fantuzzi, M.; Guerra, A.; Masotti, D.; Pizzotti, M.; et al. Energy autonomous UWB localization. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2017, 1, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, C.C.; Costa, J.R.; Fernandes, C.A. Hybrid UHF/UWB antenna for passive indoor identification and localization systems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Prop. 2013, 61, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.G.; Zhu, H.; You, S.Z.; Tang, C.Q. UWB-based localization system aided with inertial sensor for underground coal mine applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 6652–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decarli, N.; Guidi, F.; Dardari, D. Passive UWB RFID for tag localization: Architectures and design. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuchat, P.N.; Hesse, H.; Domahidi, A.; Lygeros, J. Enabling optimization-based localization for IoT devices. IEEE IoT J. 2019, 6, 5639–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shmaliy, Y.S.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. UWB-based indoor human localization with time-delayed data using EFIR filtering. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 16676–16683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; Pack, S. OB-DETA: Observation-based directional energy transmission algorithm in energy harvesting networks. J. Comm. Netw. 2019, 21, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.I.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, J.W.; Jang, J.E.; Choi, J.P. Exploiting the mutual coupling effect on dipole antennas for RF energy harvesting. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Prop. Lett. 2016, 15, 1301–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Chiu, S.; Murch, R.D. A dual-port triple-band L-probe microstrip patch rectenna for ambient RF energy harvesting. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Prop. Lett. 2017, 16, 3071–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, D.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; Xiang, Y. Broadband Dual Circularly Polarized Dielectric Resonator Antenna for Ambient Electromagnetic Energy Harvesting. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 4961–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.N.; Singh, P.; Kanaujia, B.K. A modified microstrip line fed compact UWB antenna for WiMAX/ISM/WLAN and wireless communications. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2019, 104, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-L.; Su, T.; Liu, Z.-X. High-Gain Grating Antenna With Surface Wave Launcher Array. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotte, D.; Siragusa, R.; Duroc, Y.; Tedjini, S. A concept of pressure sensor based on slotted waveguide antenna array for passive MMID sensor networks. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 5583–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Chen, X.; Jiang, S.; Hu, Z.; Liu, T.; Calatayud, D.G.; Mao, B.; He, D. A graphene-assembled film based MIMO antenna array with high isolation for 5G wireless communication. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.H.; Park, W.B.; Yun, J.; Lim, H.J.; Hwang, K.C. A low-profile HF meandered dipole antenna with a ferrite-loaded artificial magnetic conductor. App. Sci. 2021, 11, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Capobianco, A.D.; Asif, S.M.; Anagnostou, D.E.; Shubair, R.M.; Braaten, B.D. A compact CSRR-enabled UWB diversity antenna. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsath, M.G.N.; Kanagasabai, M. Compact UWB Monopole Antenna for Automotive Communications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. Lett. 2015, 63, 4204–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Qin, H. Compact ACS-fed UWB monopole antenna with extra Bluetooth band. Electron. Lett. 2014, 50, 1263–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumoulin, A.; John, M.; Ammann, M.J.; McEvoy, P. Optimized monopole and dipole antennas for UWB asset tag location systems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. Lett. 2012, 60, 2896–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.M.; Shameena, V.A.; Dinesh, R.; Mohanan, P. Compact semicircular directive dipole antenna for UWB applications. Electron. Lett. 2011, 47, 1260–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, W.S.; Rowe, W.S.T. An UWB Conical Monopole Antenna for Multiservice Wireless Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kishk, A. A novel low-profile compact directional ultra-wideband antenna: The self-grounded bow-tie antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. Lett. 2012, 60, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.X.; Mao, C.X.; Zhu, H. A compact notched band UWB slot antenna with sharp selectivity and controllable bandwidth. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. Lett. 2013, 61, 3961–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cheung, S.W.; Yuk, T.I. Compact MIMO Antenna for Portable Devices in UWB Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. Lett. 2013, 61, 4257–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshna, T.K.; Deepak, U.; Sajitha, V.R.; Vasudevan, K.; Mohanan, P. A compact UWB MIMO antenna with reflector to enhance isolation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. Lett. 2015, 63, 1873–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimipour, M.; Aryanian, I. Demonstration of Broadband Reflectarray Using Unit Cells With Spline-Shaped Geometry. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. Lett. 2019, 67, 3831–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Yang, J.; Dahlström, J.; Flygare, J.; Pantaleev, M.; Billade, B. Optimization and realization of quadruple-ridge flared horn with new spline-defined profiles as a high-efficiency feed from 4.6 GHz to 24 GHz. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. Lett. 2019, 67, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, M.; Bakr, M.; Sangary, N. Antenna design exploiting adjoint sensitivity-based geometry evolution. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2013, 7, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizzi, L.; Viani, F.; Azaro, R.; Massa, A. Optimization of a spline-shaped UWB antenna by PSO. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2007, 6, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivanen, J.I.; Mäkinen, R.A.; Rahola, J.; Järvenpää, S.; Ylä-Oijala, P. Gradient-based shape optimisation of ultra-wideband antennas parameterised using splines. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2010, 4, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Jin, R.; Geng, J.; Wu, Q.; Yang, G. Auto-design of band-notched UWB antennas using mixed model of 2D GA and FDTD. Electron. Lett. 2008, 44, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhadi, S.; Komjani, N.; Soleimani, M. Ultra wideband antenna design using discrete Green’s functions in conjunction with binary particle swarm optimization. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2016, 10, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.P.T.S.; Senthilkumar, L.; Meenakshi, M. Material distributive topology design of UWB antenna using parallel computation of improved BPSO with FDTD. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2018, 11, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalbakhsh, A.; Afzal, M.U.; Esselle, K.P.; Smith, S. Design of an artificial magnetic conductor surface using an evolutionary algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications (ICEAA), Verona, Italy, 11–15 September 2017; pp. 885–887. [Google Scholar]
- Coello, C.A.C.; Van Veldhuizen, D.A.; Lamont, G.B. Evolutionary Algorithms for Solving Multi-Objective Problems, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nocedal, J.; Wright, S. Numerical Optimization, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gould, N.I.; Leyffer, S.; Toint, P.L. Trust-Region Methods; MPS-SIAM Series on Optimization; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.S.; Chiu, Y.H. Application of multiobjective topology optimization to miniature ultrawideband antennas with enhanced pulse preservation. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K. Multi-Objective Optimization Using Evolutionary Algorithms; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, L.V.; Manh, L.H.; Ngoc, C.D.; Beccaria, M.; Pirinoli, P. Automated design of microstrip patch antenna using ant colony optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications, Granada, Spain, 9–13 September 2019; pp. 0587–0590. [Google Scholar]
- Lalbakhsh, A.; Afzal, M.U.; Zeb, B.A.; Esselle, K.P. Design of a dielectric phase-correcting structure for an EBG resonator antenna using particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, 9–12 November 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Lalbakhsh, A.; Esselle, K.P.; Smith, S.L. Design of a single-slab low-profile frequency selective surface. In Proceedings of the Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium, Singapore, 22–25 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Koziel, S.; Bekasiewicz, A. Multi-Objective Design of Antennas Using Surrogate Models; World Scientific: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, N.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Advances in particle swarm optimization for antenna designs: Real-number, binary, single-objective and multiobjective implementations. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. Lett. 2007, 55, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroczka, J. The cognitive process in metrology. Measurement 2013, 46, 2896–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, T.W.; Poplinski, J.D.; Koch, P.N.; Allen, J.K. Metamodels for computer-based engineering design: Survey and recommendations. Eng. Comput. 2001, 17, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziel, S.; Bekasiewicz, A. Pareto ranking bisection algorithm for expedited multi-objective optimization of antenna structures. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 1488–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderas, D.; Sancho, J.I.; Puente, D.; Ling, C.; Chen, X. Ultrawideband Antennas: Design and Applications; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Chiau, C.C.; Chen, X.; Parini, C.G. Study of a printed circular disc monopole antenna for UWB systems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. Lett. 2005, 53, 3500–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolda, T.G.; Lewis, R.M.; Torczon, V. Optimization by direct search: New perspectives on some classical and modern methods. SIAM Rev. 2003, 45, 385–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekasiewicz, A. Low-cost automated design of compact branch-line couplers. Sensors 2020, 20, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CST Microwave Studio; version 2015; Dassault Systems: Vélizy-Villacoublay, France, 2015.
- Fonseca, C.M. Multiobjective Genetic Algorithms with Application to Control Engineering Problems. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Automatic Control and Systems Engineering, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chahat, N.; Zhadobov, M.; Sauleau, R.; Ito, K. A compact UWB antenna for on-body applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. Lett. 2011, 59, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Mathur, V. Wheel shaped modified fractal antenna realization for wireless communications. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2017, 79, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopikrishna, M.; Krishna, D.D.; Aanandan, C.K.; Mohanan, P.; Vasudevan, K. Design of a microstip fed step slot antenna for UWB communication. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2009, 51, 1126–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.T.; Lee, C.H. Compact Slot Antenna for UWB Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2010, 9, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Roshna, T.K.; Deepak, U.; Sajitha, V.R.; Mohanan, P. Coplanar stripline-fed compact UWB antenna. Electron. Lett. 2014, 50, 1181–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Design | Number of Model Evaluations [R] | Total [R] | Total [h] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 1 | n = 2 | n = 3 | n = 4 | n = 5 | n = 6 | |||
| x1.dn* | 64 | 92 | 94 | 156 | 326 | 284 | 1016 | 36.97 |
| x2.dn* | N/A | N/A | N/A | 187 | 2 | 192 | 381 | 13.86 |
| x3.dn* | N/A | N/A | N/A | 158 | 41 | 145 | 344 | 12.52 |
| x4.dn* | N/A | N/A | N/A | 193 | 119 | 98 | 410 | 14.92 |
| x5.dn* | N/A | N/A | N/A | 128 | 198 | 146 | 472 | 17.18 |
| x6.dn* | N/A | N/A | N/A | 127 | 119 | 284 | 530 | 19.28 |
| x7.dn* | N/A | N/A | N/A | 158 | 41 | 238 | 437 | 15.90 |
| x8.dn* | N/A | N/A | N/A | 156 | 81 | 96 | 333 | 12.12 |
| x9.dn* | 56 | 46 | 118 | 156 | 40 | 50 | 466 | 16.96 |
| Total | 120 | 138 | 212 | 1419 | 967 | 1533 | 4389 | 159.71 |
| Antenna | fL [GHz] | Bandwidth [GHz] | Dimensions [mm × mm] | Size [mm2] | Dimensions [λg × λg] | Footprint # [λg2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [55] | 2.9 | 6.6 | 32.0 × 36.0 | 1152 | 0.56 × 0.64 | 0.359 |
| [56] | 3.0 | 8.0 | 28.0 × 38.0 | 1064 | 0.51 × 0.69 | 0.352 |
| [57] | 3.1 | 8.4 | 14.5 × 28.0 | 406 | 0.27 × 0.52 | 0.140 |
| [11] | 2.9 | 19.3 | 25.0 × 17.0 | 425 | 0.44 × 0.30 | 0.132 |
| [18] | 3.0 | 7.8 | 10.0 × 32.5 | 325 | 0.18 × 0.59 | 0.106 |
| [54] | 3.0 | 7.6 | 10.0 × 25.0 | 250 | 0.17 × 0.43 | 0.073 |
| [58] | 3.1 | 8.3 | 7.00 × 25.0 | 175 | 0.13 × 0.47 | 0.061 |
| This work | 3.1 | 8.9 | 12.5 × 18.4 | 230 | 0.32 × 0.22 | 0.069 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bekasiewicz, A.; Koziel, S.; Plotka, P.; Zwolski, K. EM-Driven Multi-Objective Optimization of a Generic Monopole Antenna by Means of a Nested Trust-Region Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093958
Bekasiewicz A, Koziel S, Plotka P, Zwolski K. EM-Driven Multi-Objective Optimization of a Generic Monopole Antenna by Means of a Nested Trust-Region Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(9):3958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093958
Chicago/Turabian StyleBekasiewicz, Adrian, Slawomir Koziel, Piotr Plotka, and Krzysztof Zwolski. 2021. "EM-Driven Multi-Objective Optimization of a Generic Monopole Antenna by Means of a Nested Trust-Region Algorithm" Applied Sciences 11, no. 9: 3958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093958
APA StyleBekasiewicz, A., Koziel, S., Plotka, P., & Zwolski, K. (2021). EM-Driven Multi-Objective Optimization of a Generic Monopole Antenna by Means of a Nested Trust-Region Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 11(9), 3958. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11093958








