Modification of a Solar Thermal Collector to Promote Heat Transfer inside an Evacuated Tube Solar Thermal Absorber
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. System Configuration
2.2. Calculation
2.2.1. Energy Transfer in the Evacuated-Tube Solar Collector System
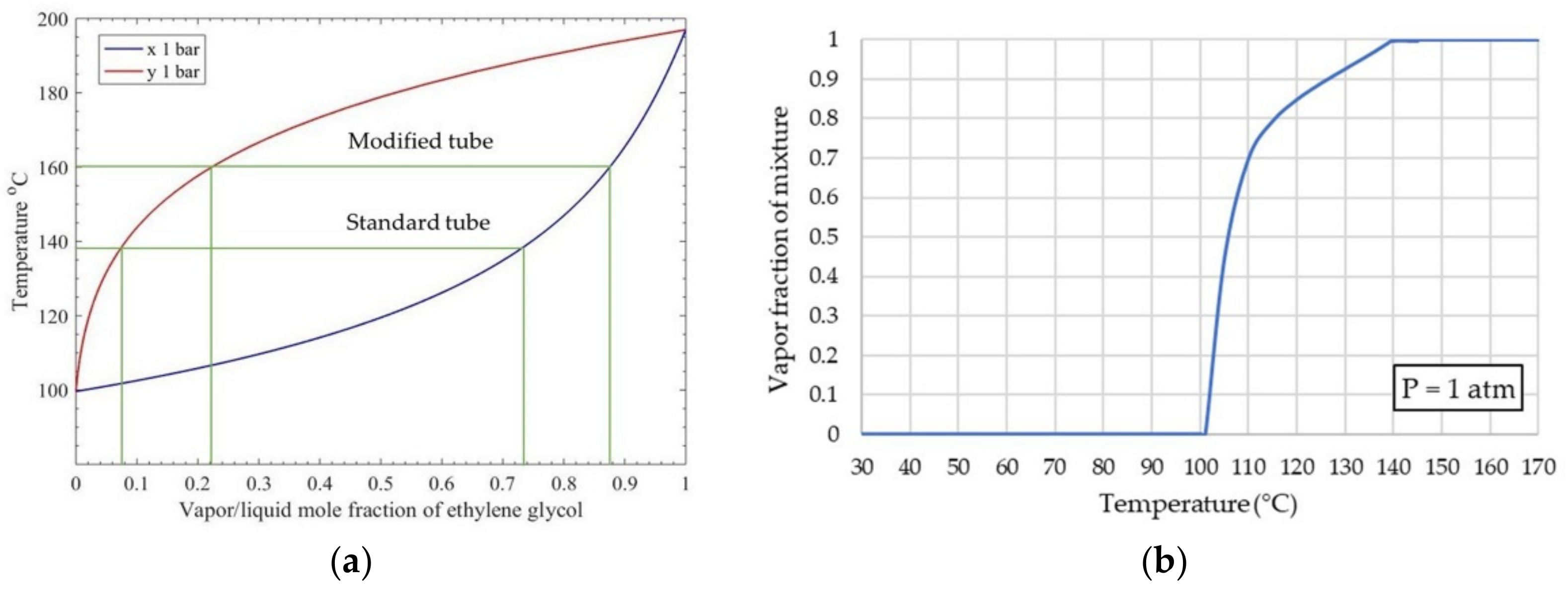
2.2.2. Vapor/Liquid Equilibrium (VLE)
3. Experimental Setup
4. Results and Discussion
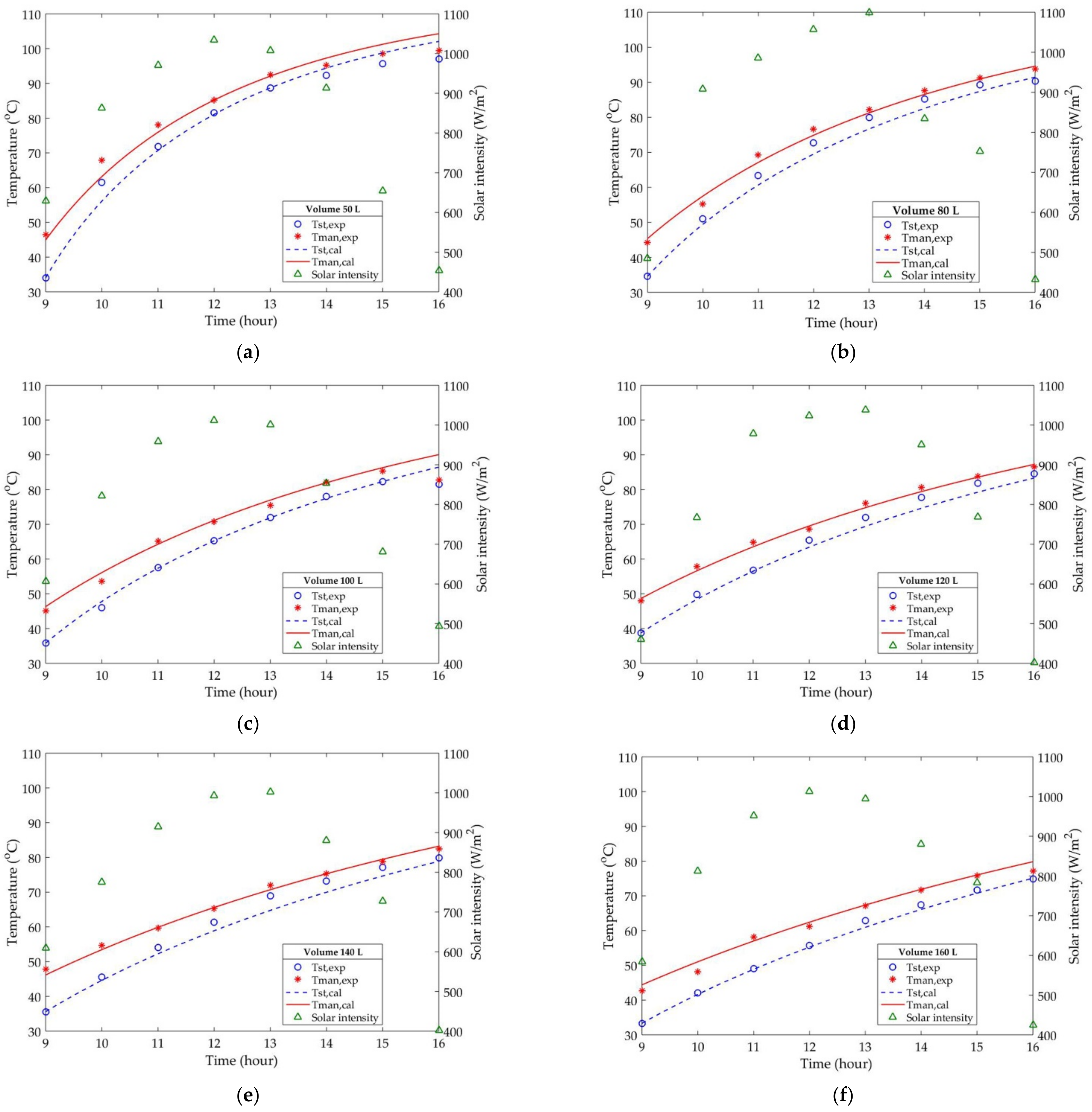
4.1. Experimental Results
4.2. Model Validation
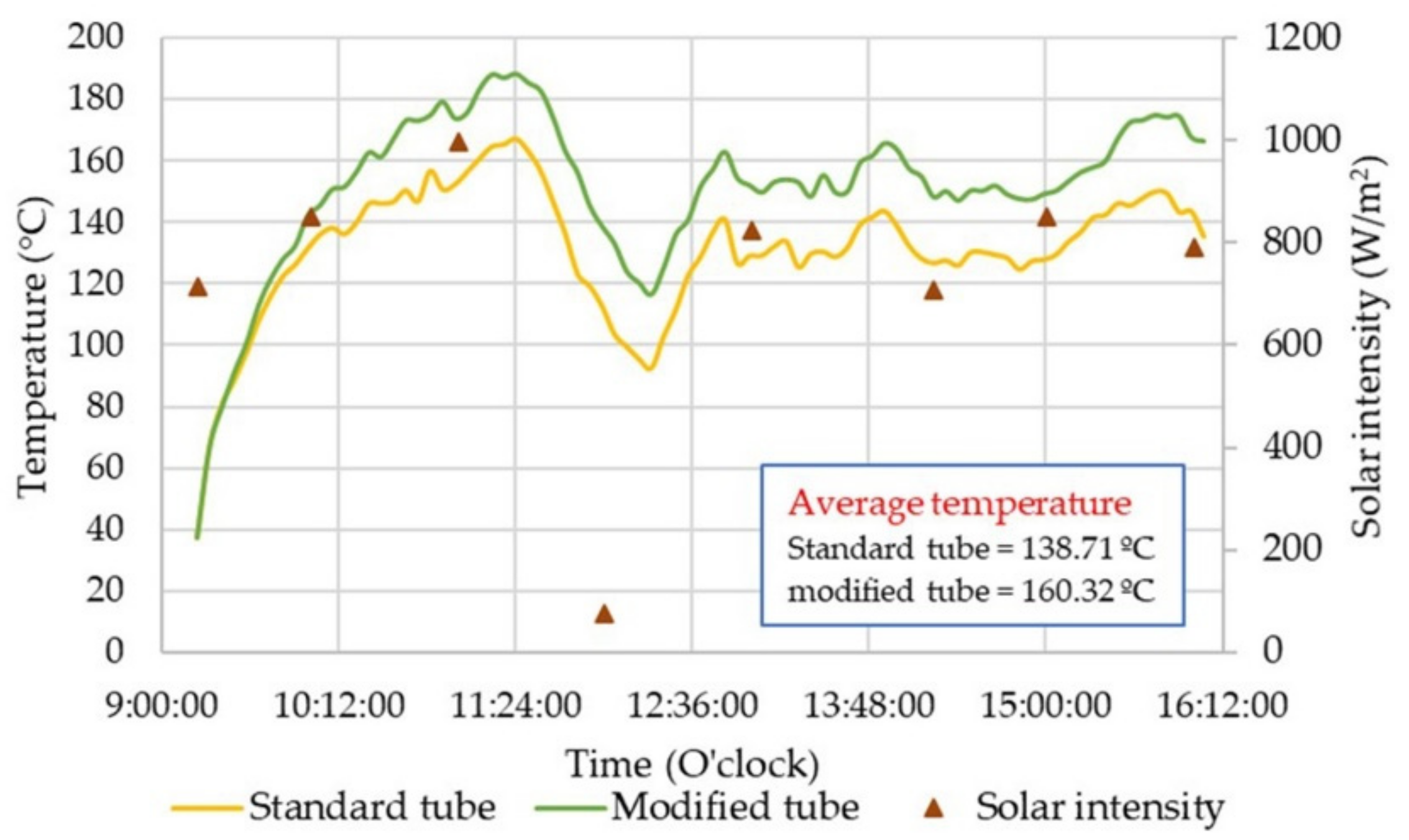
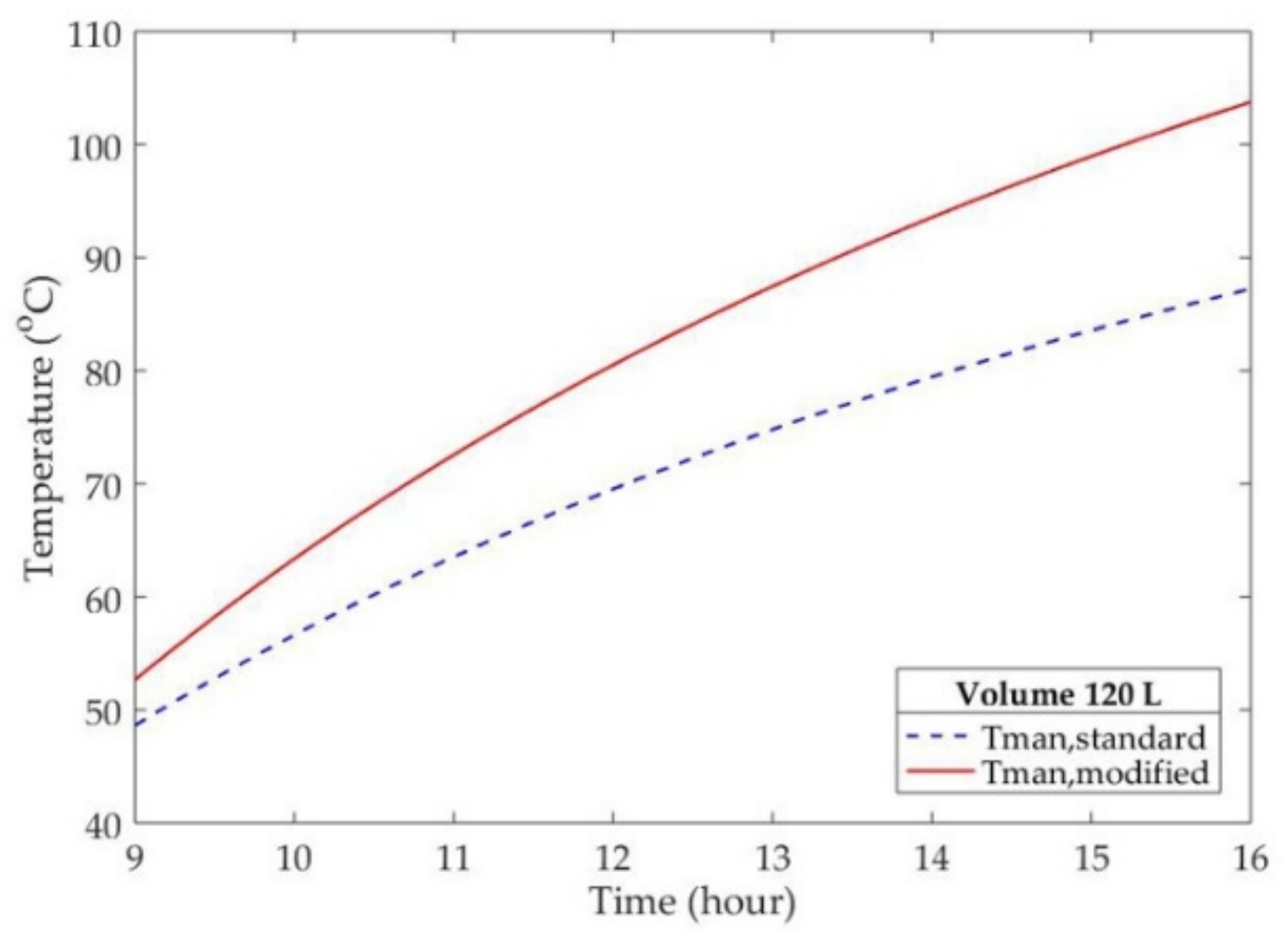
4.3. Evacuated Tube Modification
4.4. Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | Area (m2) | Symbols | |
| cp | Specific heat capacity (J/kg·K) | π | Pi |
| D | Diameter of tip (m) | ρ | Density (kg/m3) |
| h | Heat transfer coefficient (W/m2·K) | μ | Viscosity (Pa·s) |
| I | Solar intensity (W/m2) | η | Efficiency |
| k | Thermal conductivity (W/m·K) | ∆ | Difference |
| L | Length of tube (m) | Φ | Ratio of fugacity coefficient |
| Mass flow rate (kg/s) | ϕ | Fugacity coefficients | |
| N | Number of tubes | γ | Activity coefficients |
| Nu | Nusselt number | Subscripts | |
| P | Pressure (atm) | a | Ambient |
| Pr | Prandtl number | ETC | Evacuated tuber solar collector |
| Heat transfer rate (W) | loss | Heat loss | |
| R | Gas constant (J/mol⋅K) | man | Outlet from manifold |
| Re | Reynolds number | rad | Radiation |
| T | Temperature (°C or K) | s | Surface |
| Tlm | Log mean temperature (°C or K) | St | Storage |
| U | Overall heat transfer coefficient (W/m2·K) | tip | Tip |
| v | Velocity (m/s) | i | Composition |
| V | Volume of heating medium (m3) | Superscripts | |
| x,y | Mole fraction | l | Liquid |
| sat | Saturated | ||
| v | Vapor | ||
References
- Areas with Solar Power Potential. Available online: http://weben.dede.go.th/webmax/content/areas-solar-power-potential (accessed on 30 August 2019).
- Ma, L.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liang, R. Thermal Performance Analysis of the Glass Evacuated Tube Solar Collector with U-Tube. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhady, M.S.; Nasreldin, M.; Elsheikh, M.N. Improving the Performance of Evacuated Tube Heat Pipe Collectors Using Oil and Foamed Metals. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 2683–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyhat, M.M.; Valizade, M.; Abdolahzade, S.; Maerefat, M. Thermal Efficiency Enhancement of Direct Absorption Parabolic Trough Solar Collector (DAPTSC) by Using Nanofluid and Metal Foam. Energy 2020, 192, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafraz, M.M.; Tlili, I.; Baseer, M.A.; Safaei, M.R. Potential of Solar Collectors for Clean Thermal Energy Production in Smart Cities Using Nanofluids: Experimental Assessment and Efficiency Improvement. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olia, H.; Torabi, M.; Bahiraei, M.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Goodarzi, M.; Safaei, M.R. Application of Nanofluids in Thermal Performance Enhancement of Parabolic Trough Solar Collector: State-of-the-Art. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarafraz, M.M.; Tlili, I.; Tian, Z.; Bakouri, M.; Safaei, M.R.; Goodarzi, M. Thermal Evaluation of Graphene Nanoplatelets Nanofluid in a Fast-Responding HP with the Potential Use in Solar Systems in Smart Cities. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghaderian, J.; Sidik, N.A.C.; Kasaeian, A.; Ghaderian, S.; Okhovat, A.; Pakzadeh, A.; Samion, S.; Yahya, W.J. Performance of Copper Oxide/Distilled Water Nanofluid in Evacuated Tube Solar Collector (ETSC) Water Heater with Internal Coil under Thermosyphon System Circulations. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 121, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujawar, N.H.; Shaikh, S.M. Thermal Performance Investigation of Evacuated Tube Heat Pipe Solar Collector with Nanofluid. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Res. Technol. 2016, 5, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizade, M.; Heyhat, M.M.; Maerefat, M. Experimental Comparison of Optical Properties of Nanofluid and Metal Foam for Using in Direct Absorption Solar Collectors. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 195, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitratos, A.; Sobhansarbandi, S.; Pozdin, V.; Zakhidov, A.; Hassanipour, F. Evacuated Tube Solar Collectors Integrated with Phase Change Materials. Sol. Energy 2016, 129, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvakumar, P.; Somasundaram, P.; Thangavel, P. Performance Study on Evacuated Tube Solar Collector Using Therminol D-12 as Heat Transfer Fluid Coupled with Parabolic Trough. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 85, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Seo, T. Thermal Performances Comparisons of the Glass Evacuated Tube Solar Collectors with Shapes of Absorber Tube. Renew. Energy 2007, 32, 772–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, L.J.; Furbo, S. Vertical Evacuated Tubular-Collectors Utilizing Solar Radiation from All Directions. Appl. Energy 2004, 78, 371–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, M.T.; Milani, D.; Nomvar, M.; Abbas, A. Computer-Aided Design for High Efficiency Latent Heat Storage—A Case Study of a Novel Domestic Solar Hot Water Process. Comput. Aided Chem. Eng. 2017, 40, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Falahi, A.; Alobaid, F.; Epple, B. A New Design of an Integrated Solar Absorption Cooling System Driven by an Evacuated Tube Collector: A Case Study for Baghdad, Iraq. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, A.A. Optimization of Evacuated Tube Collector Parameters for Solar Industrial Process Heat. Int. J. Energy Environ. Res. 2017, 5, 55–73. [Google Scholar]
- Isafiade, A.J.; Kravanja, Z.; Bogataj, M. Design of Integrated Solar Thermal Energy System for Multi-Period Process Heat Demand. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 52, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picón-Núñez, M.; Martínez-Rodríguez, G.; Fuentes-Silva, A.L. Targeting and Design of Evacuated-Tube Solar Collector Networks. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 52, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, A.; Elsheniti, M.B.; Elsamni, O.A. Optimum Number and Arrangement of Evacuated-Tube Solar Collectors under Various Operating Conditions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 199, 112032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengel, Y.A.; Ghajar, A.J. Heat and Mass Transfer Fundamental and Application, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 283, pp. 424–454. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.M. Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, 8th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 1950; Volume 27, pp. 450–508. [Google Scholar]
- Solar Cell. Available online: http://www2.dede.go.th/solarcell/Datafiles/InstallByPanya.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2020).
- Grewal, S.; Grewal, S. Product and Process Design Principles, 3rd ed.; Welter, J., Ed.; Donald Fowley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 534–597. [Google Scholar]
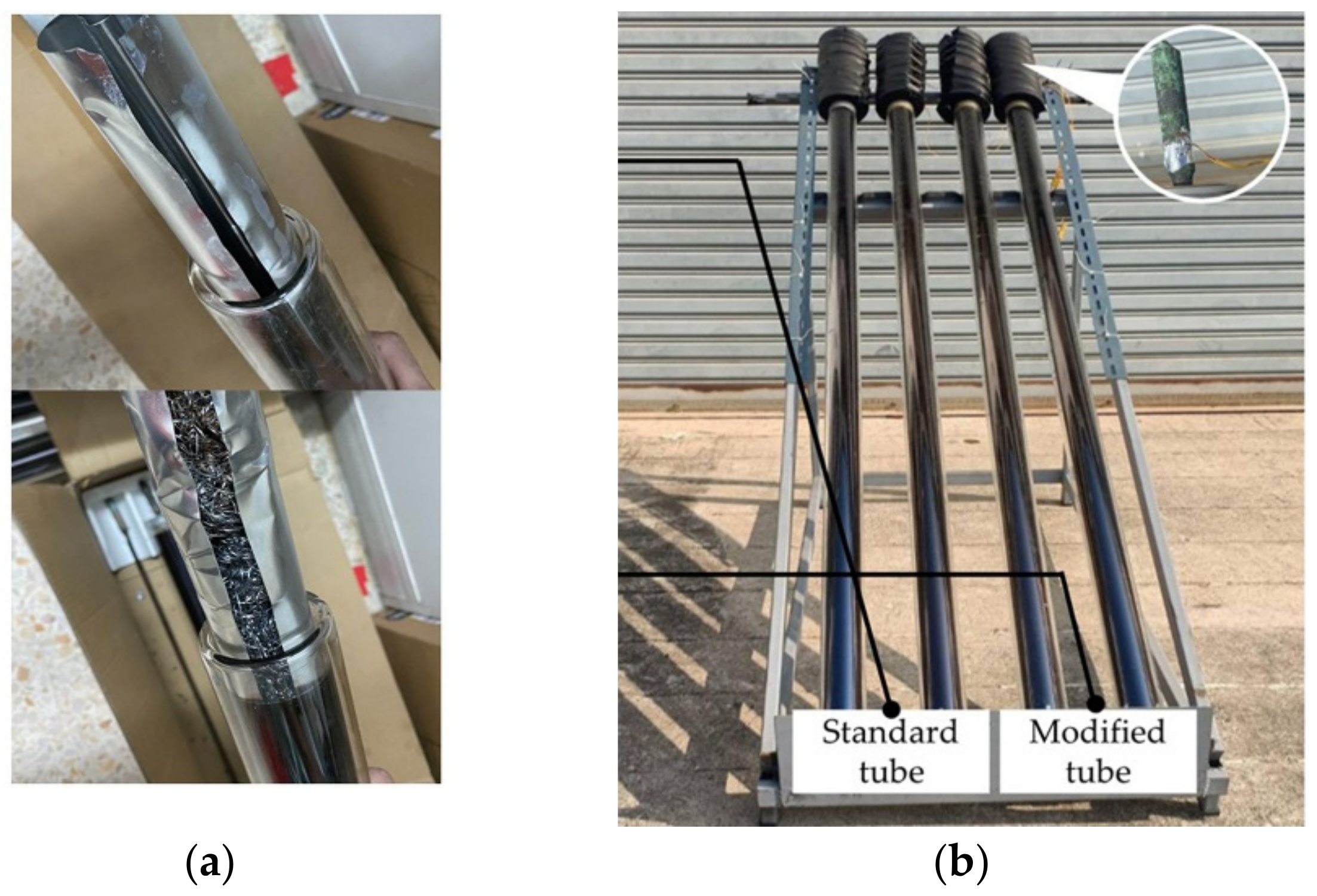
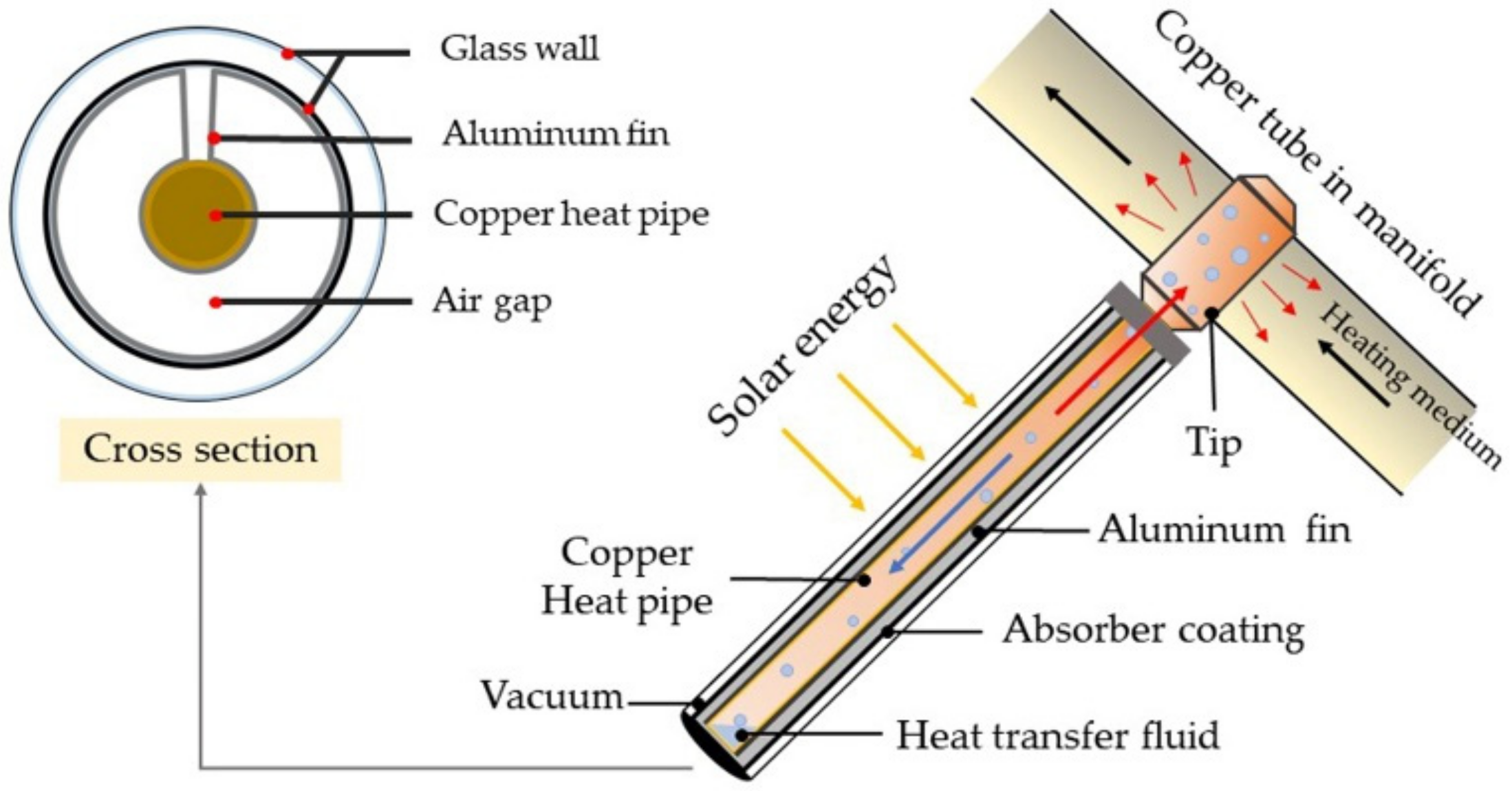




| Evacuated Tube | Heat Transfer Fluid | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inner diameter | 0.047 | m | Component | 10 mol% of ethylene-glycol (EG) in water | |
| Outer diameter | 0.058 | m | |||
| Length | 1.80 | m | Volume | 5 | mL |
| Surface area | 0.15 | m2 | MW of EG | 62.07 | g/mol |
| Number of tubes | 20 | tubes | Density of EG | 1.11 | kg/m³ |
| Copper heat pipe | Air layer | ||||
| Thermal conductivity | 401 | W/m·K | Thermal conductivity | 0.03 | W/m·K |
| Inner diameter | 0.012 | m | Heat transfer coefficient | 10 | W/m2·K |
| Outer diameter | 0.014 | m | Thickness | 0.016 | m |
| Aluminum fin | Stainless-steel scrubber | ||||
| Thermal conductivity | 237 | W/m·K | Thermal conductivity | 15.1 | W/m·K |
| Thickness | 0.5 | mm | Void fraction | 0.02 | |
| Heating medium storage tank | Copper heating medium tube | ||||
| Heating medium | Palm oil | Inner diameter | 0.019 | m | |
| Tank diameter | 0.58 | m | Outer diameter | 0.022 | m |
| Tank height | 0.76 | m | |||
| Overall heat transfer coefficient, U | 0.72 | W/m2·K | |||
| Standard Tube | Modified Tube | |
|---|---|---|
| Heating time 1 | 60 min | 60 min |
| Steady temperature of tip | 138.71 °C | 160.32 °C |
| Vapor fraction at tip | 0.986 | 1 |
| Overall heat transfer coefficient per unit area, UA | 30.30 W/K | 306.74 W/K |
| Target | ||
|---|---|---|
| Consumption | 2482 L/day | |
| Operating temperature | 60 °C | |
| Design | Standard ETSC | Modified ETSC |
| Heating medium | Palm oil | Palm oil |
| Mass flow rate | 0.18 kg/s | 0.18 kg/s |
| Inlet temperature | 70 °C | 70 °C |
| Outlet temperature | 80 °C | 80 °C |
| Production rate | 27 MWh /year | 27 MWh /year |
| Number of tubes | 300 tubes (Area = 45 m2) | 240 tubes (Area = 36 m2) |
| Arrangement | 3 parallel sets of 100-tube | 3 parallel sets of 80-tube |
| Capital investment | $16,000 | $13,000 |
| Breakeven | 5.06 years | 4.09 years |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Supankanok, R.; Sriwong, S.; Ponpo, P.; Wu, W.; Chandra-ambhorn, W.; Anantpinijwatna, A. Modification of a Solar Thermal Collector to Promote Heat Transfer inside an Evacuated Tube Solar Thermal Absorber. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4100. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094100
Supankanok R, Sriwong S, Ponpo P, Wu W, Chandra-ambhorn W, Anantpinijwatna A. Modification of a Solar Thermal Collector to Promote Heat Transfer inside an Evacuated Tube Solar Thermal Absorber. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(9):4100. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094100
Chicago/Turabian StyleSupankanok, Rasa, Sukanpirom Sriwong, Phisan Ponpo, Wei Wu, Walairat Chandra-ambhorn, and Amata Anantpinijwatna. 2021. "Modification of a Solar Thermal Collector to Promote Heat Transfer inside an Evacuated Tube Solar Thermal Absorber" Applied Sciences 11, no. 9: 4100. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094100
APA StyleSupankanok, R., Sriwong, S., Ponpo, P., Wu, W., Chandra-ambhorn, W., & Anantpinijwatna, A. (2021). Modification of a Solar Thermal Collector to Promote Heat Transfer inside an Evacuated Tube Solar Thermal Absorber. Applied Sciences, 11(9), 4100. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094100







