Abstract
Untreated wastewater used for irrigating crops is the major source of toxic heavy metals and other pollutants in soils. These heavy metals affect plant growth and deteriorate the quality of edible parts of growing plants. Phytohormone (IAA) and exopolysaccharides (EPS) producing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria can reduce the toxicity of metals by stabilizing them in soil. The present experiment was conducted to evaluate the IAA and EPS-producing rhizobacterial strains for improving growth, physiology, and antioxidant activity of Brassica juncea (L.) under Cd-stress. Results showed that Cd-stress significantly decreased the growth and physiological parameters of mustard plants. Inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA and EPS-producing rhizobacterial strains, however, significantly retrieved the inhibitory effects of Cd-stress on mustard growth, and physiology by up regulating antioxidant enzyme activities. Higher Cd accumulation and proline content was observed in the roots and shoot tissues upon Cd-stress in mustard plants while reduced proline and Cd accumulation was recorded upon rhizobacterial strains inoculation. Maximum decrease in proline contents (12.4%) and Cd concentration in root (26.9%) and shoot (29%) in comparison to control plants was observed due to inoculation with Bacillus safensis strain FN13. The activity of antioxidant enzymes was increased due to Cd-stress; however, the inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains showed a non-significant impact in the case of the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POX) and catalase (CAT) in Brassica juncea (L.) plants under Cd-stress. Overall, Bacillus safensis strain FN13 was the most effective strain in improving the Brassica juncea (L.) growth and physiology under Cd-stress. It can be concluded, as the strain FN13 is a potential phytostabilizing biofertilizer for heavy metal contaminated soils, that it can be recommended to induce Cd-stress tolerance in crop plants.
1. Introduction
The cultivated area in the world is decreasing due to urbanization and industrialization on fertile agricultural lands [1,2]. In the current scenario, increasing the cultivation area seems difficult so strategies are required to improve the crop productivity per unit area on the existing land base. The use of agrochemicals and intensive cultivation may result in deterioration of land resources and environmental quality [3,4]. To meet the irrigation water requirements, farmers use wastewater to grow crops particularly around metropolitans and industrial cities that cause soil and environmental pollution [5,6]. Untreated wastewater is used by farmers to grow crops that is the major source of toxic heavy metals and other pollutants in soils [7] which limits crop production and hence pose a serious threat to food security in peri-urban areas.
Brassica juncea (L.) is the second most important oilseed crop of Pakistan that is important not only due to its contribution in local oil production but also used as fodder crop [8]. Farmers around the cities grow Brassica juncea (L.) crop as fodder for dairy animals on soils contaminated with heavy metals. These metals accumulated in edible parts of growing crops [9] which enter the food chain due to fodder consumption by animals. Most of the heavy metals are toxic for plants and other organism and cadmium is one of the most toxic ones [10,11].
It is well established that cadmium is a toxic metal for plants that is transported in plants through several root-linked proteins i.e., metal transporters and channels before its accumulation in edible parts [12]. Moreover, its bioavailability, uptake, and translocation in plant tissues and toxicity is affected by edaphic, climatic, and other anthropogenic activities [13,14]. Cadmium compounds are more soluble than other heavy metals which favor its bioavailability, absorption, and accumulation in plant systems. Cadmium can easily be translocated to aerial parts so Cd-induced phytotoxicity has widely been reported in literature [15,16]. Cadmium-induced negative impacts on plants include physiological, morphological, biochemical, and molecular changes in plants. It can also induce oxidative stress that can cause inhibition of seed germination, water, and ionic imbalance, decrease in photosynthesis, cellular organelles and cell membrane disintegration, and a decrease in protein synthesis that lead to a decrease in crop productivity [17,18].
Plants respond to Cd-stress by synthesizing stress-related proteins and signaling molecules. Plant roots release several chelating compounds which reduce the heavy metals uptake by plants [19]. Nutrient management is the other possible response in plants under Cd-stress [20]. Heavy metal contamination of soils is a complex process and several conventional physicochemical methods are being used to remediate the metal-contaminated soils which are costly, less efficient and are not applicable for large systems [21]. Use of phytohormone-producing heavy metal-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) is considered as alternate strategy to decontaminate heavy metal polluted soils that is more efficient, inexpensive, sustainable, and ecofriendly approach [22,23,24]. The PGPR produce phytohormones in addition to several other growth-promoting traits that can reduce the heavy metal toxicity and improve crop growth under heavy metal polluted soil conditions [25,26].
Phytohormone-producing Cd-tolerant PGPR can be effective to induce resistance against heavy metal toxicity in crop plants. The Cd-tolerant PGPR strains help to reduce Cd uptake of crop plants by stabilizing it in the soil through production of exopolysaccharides [27,28]. Scientists have reported several Cd-tolerant PGPR strains belonging to different genera [16,18,29,30]. These strains have multifarious plant growth promoting (PGP) traits in additions to phytohormone producing ability [31,32] thus can be used to develop biofertilizer to grow vegetables and other crops on metal contaminated soils.
Although, inoculation with PGPR may enhance the uptake and translocation of heavy metals in plants as reported by Wu et al. [33], the inoculation with Cd-tolerant PGPR can, however, be used as an effective strategy to reduce the uptake and translocation of Cd to above ground parts [34]. Recently, Zeng et al. [35] reported that Cd-tolerant PGPR in combination with hydroxyapatite helped in the immobilization of Cd in soil thus reducing their uptake. They argued that enhanced sequestration of Cd in soil was due to production of phytohormones, siderophores and polymeric substances. Naveed et al. [32] reported that Enterobacter sp. MN17 inoculation on seed in combination with gravel sand and biochar resulted in a significant improvement in nutritional quality of Pisum sativum by reducing the Cd uptake. They suggested the combined use of Enterobacter sp. MN17, gravel sand, and biochar as an effective approach to grow pea and other vegetables under Cd-contaminated soils.
Siderophore-producing, heavy metal tolerant PGPR can accelerate bioavailability and accumulation of nutrients in plants and thus help to reduce the deleterious effects of heavy metals on plants. Inoculation with phytohormone-producing, metal tolerant bacterial strains Bacillus cereus and Pseudomonas moraviensis decreased the toxic effects of heavy metals on wheat growth under saline sodic soil conditions [36]. Keeping in view the above facts, we hypothesized that IAA and EPS-producing rhizobacterial strains may induce Cd tolerance in Brassica juncea by retrieving the negative impacts caused by Cd-stress. In our previous studies [37], it has been established that the strains FN13, FN14 and FN16 have the ability to phytostabilize Cd in contaminated soil due to accumulation of Cd in their bodies along with production of IAA, EPS, and siderophores. Therefore, the present study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy of these strains on growth, physiological alterations, biochemical constituents, and Cd tolerance in Brassica juncea (L.) under artificially Cd-spiked soil.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Bacterial Strains and Seed Inoculation
The phytohormone producing rhizobacterial strains FN13, FN14 and FN16 previously isolated and characterized by Nazli et al. [37] were collected from the Soil Microbiology and Biotechnology Laboratory, Department of Soil Science, Islamia University of Bahawalpur, (IUB), Pakistan. Brassica juncea (L.) seeds of latest commercial variety (Pioneer 45S42), widely accepted in the farmer community, were collected from Oilseeds Research Station, Khanpur, Pakistan, surface sterilized using 2% solution of sodium hypochlorite. The surface sterilized Brassica juncea (L.) seeds were rinsed with sterile distilled water for decontamination.
The strains were grown in Dworkin and Foster (DF) minimal media modified with Cd (1000 µg mL−1 of Cd) and incubated at 30 ± 1 °C in shaking (100 rpm) incubator (Model SI9R-2, Shellab, Riverside, OH, USA) for 48 h. After incubation, the bacterial cells were harvested by centrifugation at 9000 rpm and 22 °C for 20 min (Model: UNIVERSAL 320R, Hettich, Germany). The pellets were re-suspended in sterilized distilled water and the washing procedure was repeated. The pellets were dissolved in sterilized distilled water to obtain uniform cell density (OD600 = 0.45; cell count 108 colony-forming units (CFU) mL−1). The final cultures with a uniform population were taken in sterile flasks to be used as inoculant.
The surface-disinfected seeds were inoculated with 48-h old culture of respective bacterial strains by dipping in broth culture for 30 min. For uninoculated control, Brassica juncea (L.) seeds were dipped in sterile distilled water for 30 min.
2.2. Soil Sampling, Analysis, and Pot Filling
Soil samples were collected and were analyzed for determination of soil physic-chemical properties, micronutrients profiles, etc. following the standard protocols [38] as presented in (Table 1). The analysis of the soil showed that it was sandy clay loam in texture with deficient in nutrients. Moreover, soil was analyzed for heavy metal contamination, if any, using atomic absorption spectroscopic (AAS) model AAS-240FS, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA, after the aqua-regia digestion treatment according to the method as described by Hseu et al. [39]. Soil was used to fill the pots and for Cd-stressed treatments, Cd was used at 150 mg kg−1 of soil as CdCl2. There was 8 kg of soil in each pot having an actual size of 12″ height and 12″ diameter.

Table 1.
Physico-chemical characteristics of soil used for pot experiment.
2.3. Experimental Design and Treatment Plan
Twenty seeds of inoculated and un-inoculated treatments were planted in respective pots. The experiment was conducted in wire house by carefully managing the natural growth conditions. Every effort was made so that the natural temperature and light should not be disturbed. Completely randomized design (CRD) with two factors was used to arrange the experimental units (pots). Two Cd-stress levels (0 and 150 mg kg−1), and three PGPR strains were evaluated in the presence of unstressed and stressed control. To minimize the error, each treatment was replicated thrice. Ten days after germination, extra plants were removed by thinning and a uniform plant population was maintained. The plant nutrients requirement was fulfilled using sulphate of potash (SOP), diammonium phosphate (DAP), and urea, for K, P and N as per recommended doses for Brassica juncea (L.) crop while micronutrients were applied as liquid fertilizer. For the fertilization and irrigation, standard agronomic practices were followed. For irrigation, tap water with an EC value of 0.13 dS m−1 was used that was according to irrigation quality standards as described by US Department of Agriculture, USA.
2.4. Recording of Plant Morphological Parameters and Physio-Chemical Analyses
After 50 days of sowing, plant morphological parameters related to growth were recorded according to experimental standards. The seedling vigor index (SVI) was calculated through the formula as described by Bal et al. [40]. For the calculation of effectiveness of rhizobacterial inoculation in Brassica juncea L. plants, the Cd-tolerance index was also calculated using the formula modified from Shetty et al. [41].
The leaf chlorophyll contents were measured in terms of SPAD value using SPAD meter [42]. To determine relative water contents (RWC) of Brassica juncea (L.) leaves, following formula was used [43].
2.5. Analysis of Proline and Antioxidant Enzymes
For the determination of proline contents in Brassica juncea (L.) leaves, leaf sample (0.5 g) was processed by homogenization using sulphosalyclic acid (3%) in flasks as described by Bates et al. [44]. After homogenization, the contents were filtered using Whatman No. 2 followed by adding acid ninhydrin and glacial acetic acid. The mixture was left in shaking water bath for one hour adjusting at 100 °C. After one hour, the flasks were cooled in ice bath to stop the reaction. The contents of the mixture were extracted using toluene followed by measuring the absorbance using spectrophotometer (Model; Carry 60; Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) at 520 nm. The standard curve was prepared for the proline concentration measurements as described by Bates et al. [44]. The proline value was expressed as µmol g−1.
For the analysis of antioxidant enzymes, the samples were extracted according to the procedure as described by Pandey et al. [45] in which, the fresh plant tissues (0.5 g) were homogenized in a pestle mortal placed in an ice bath, by adding 5 mL of cooled 50 mM phosphate extraction buffer solution of pH 7.8 [Na2HPO·12H2O (16.385 g) + NaH2PO4·2H2O (0.663 g) dissolved in distilled water and making the final volume 1000 mL]. Afterwards, the homogenized mixture was centrifuged at 13,000× g for 10 min at 4 °C and the supernatant was used for the determination of antioxidants enzymes activities. The 50% inhibition in photochemical reduction of nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT) was recorded as one enzyme unit. The superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was measured according to the method of Giannopolitis and Ries [46]; the extracted sample (0.025 mL) was mixed with 0.25 mL of H2O2 (300 mM) and 2.725 mL of reaction solution (75 µM NBT + 20 µM riboflavin + 100 µM EDTA-Na2 + 130 mM methionine) along with control contain all the reagents except sample. The samples were incubated for 15 min in light to complete the reaction and the absorbances were measured at 560 nm wavelength on UV-VIS spectrophotometer (Model G6860A, Agilent Technologies Cary 60 UV-Vis, Mulgrave, Victoria, Australia). Afterwards the SOD activity was determined by the formula given in the Equation (1) provided by Fick and Qualset [47]. For the determination of peroxidase (POX), 2.8 mL phosphate extraction buffer solution was mixed with 0.1 mL Guaicol (1.5%), 0.1 mL H2O2 (300 mM) and 0.1 mL of enzyme extract. The absorbance of the sample was taken at 470 nm on an ultraviolet–visible (UV-VIS) spectrophotometer. Whereas the catalase (CAT) activity was determined by the method of Chance and Maehly [48]. The final sample was made by mixing enzyme extract (0.1 mL) with 2.8 mL phosphate extraction buffer solution and 0.1 mL H2O2 (300 mM). The absorbance of the final samples was measured on spectrophotometer at 240 nm wavelength. The POX and CAT activities were determined using Equation (2).
SOD activity = {(Ack − Ae) × V} ÷ {0.5 × Ack × W × Vt}
- Ack is the OD of buffer solution used for extraction
- Ae is the OD of the sample
- W is fresh sample weight
- Vt is the volume of enzyme extract used for final sample preparation
POX and CAT activities = (Activity × A × V/a)/(E × W)
- Activity = Absorbance of sample
- A = total volume of reaction mixture prepared for test
- V = volume of enzyme extract used in reaction mixture
- E = activity constant i.e., 26.6 mM/cm for POX and 39.4 mM/cm for CAT
- W = fresh weight of the sample
- a = volume of the used enzymes extract
2.6. Chemical Analysis of Metal Cd
For the analysis of Cd in root and shoot of Brassica juncea (L.) plants, the samples were prepared by drying in an oven at 70 °C for 4 to 6 h followed by grinding. The samples were digested by using HNO3 and HClO4 3:1 ratio (v/v). After placing the samples overnight with acid mixture, the samples were digested on hot plate at 350 °C until the appearance of white fumes. The flasks were removed from the hot plate, cooled and the contents were filtered. Cadmium concentration was measured on atomic absorption spectrophotometer (AAS) model AAS-240FS, Agilent, USA, as described by Yang et al. [49].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Data of the bioassay and growth trial were statistically analyzed. For this purpose, the CRD design was used in factorial arrangement. Tukey’s test was used to compare means [50] and the Excel (MS office 365) was used to calculate standard error, means and to draw graphs.
3. Results
3.1. Growth Parameters
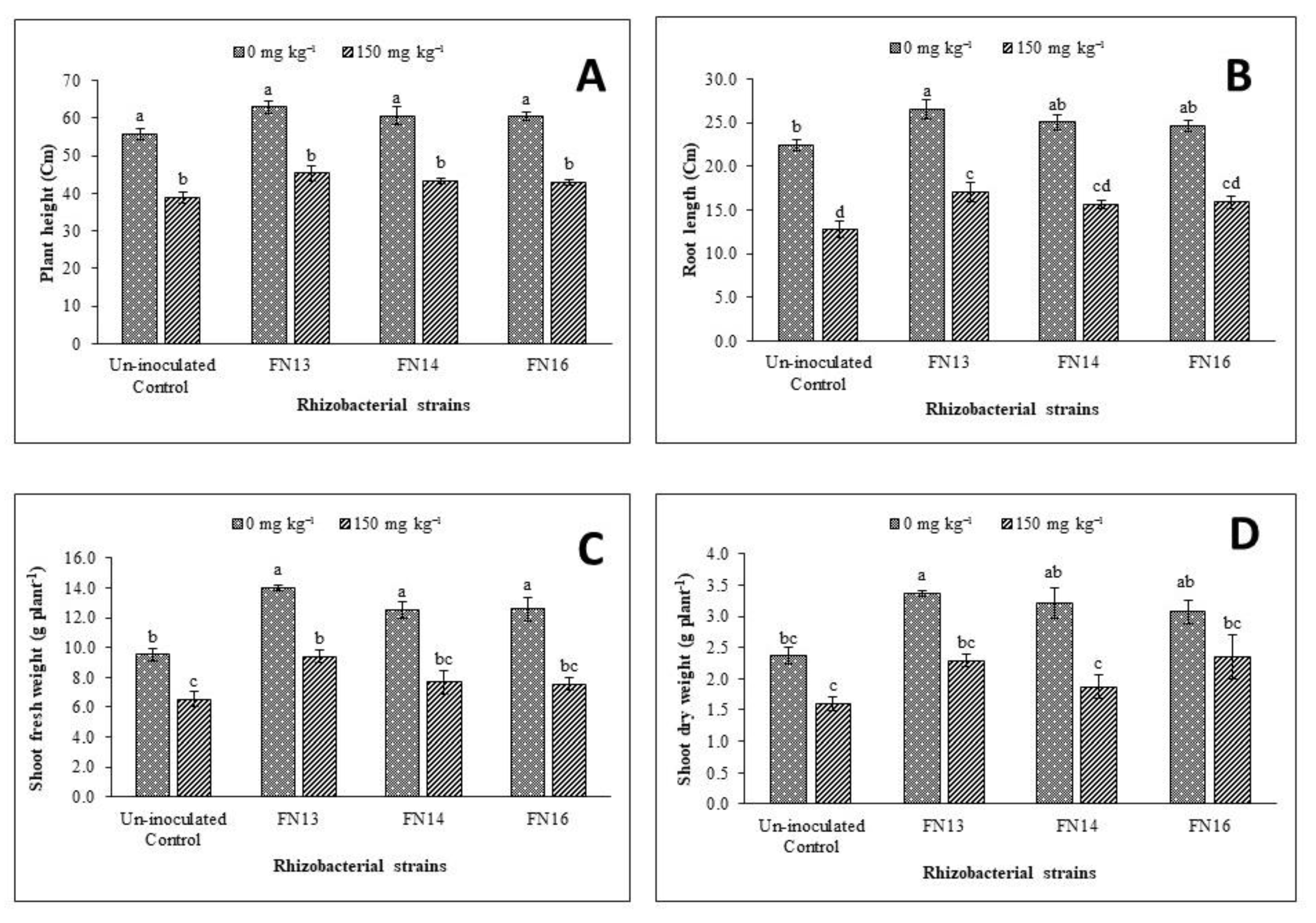
Results of the impact of Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains on plant height of Brassica juncea (L.) under Cd-stressed pot conditions showed that Cd-stress has a significant negative effect on plant height when compared to control (Figure 1A). The negative effects of Cd-stress on plant height were minimized due to inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains. Under normal conditions, the minimum plant height was observed by the uninoculated plants while the maximum plant height was recorded by the plants inoculated with FN13 that was 13% higher than uninoculated unstressed control plants. All the strains were effective in enhancing the plant height of Brassica juncea (L.) ranging from 8% to 13% but this increase was non-significant when compared with uninoculated plants. The Cd-stressed plants showed 30.1% less plant height than uninoculated plants and these results were statistically significant. Inoculation was also effective in enhancing plant height under Cd-stressed conditions where the increase ranged from 10.2 to 16.5% when compared with uninoculated control plants. Under Cd-stress, the maximum plant height was given by strain FN13.
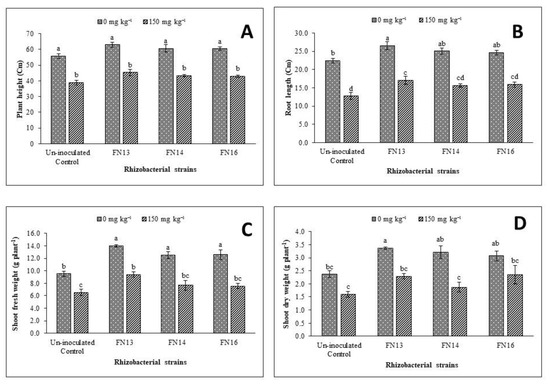
Figure 1.
Effects of Cd-tolerant, phytohormone (IAA)-producing rhizobacterial strains on growth parameters ((A) plant height; (B) root length; (C) shoot fresh weight; (D) shoot dry weight) of Brassica juncea (L.) under Cd-stress in pot trial; (n = 3): Means with same alphabets do not differ statistically from one another (p ≤ 0.05).
From the data regarding root length (Figure 1B), it was observed that Cd-stress significantly decreased the root length of Brassica juncea (L.) plants. Inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains improved the root length of Brassica juncea (L.) under normal conditions and Cd-stress in the pot trial. Under Cd-stress, the maximum improvement (33.8%) in root length as compared to respective un-inoculated control plants was observed due to inoculation with rhizobacterial strain FN13. Inoculation was also effective under unstressed conditions where the increase in root length compared with control plants due to inoculation with different rhizobacterial strains ranged from 9.5% to 18.1%. Maximum improvement (18.1%) in root length under unstressed conditions was observed due to inoculation with FN13 followed by FN14.
Inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains was also effective in enhancing the shoot fresh and dry weight of Brassica juncea (L.) under normal as well as Cd-stressed conditions in pot trial (Figure 1C,D). Under Cd-stress, minimum shoot fresh and dry weight was found in the uninoculated treatment. Maximum improvement in shoot fresh weight (47%) of Brassica juncea (L.) plants was given by the strain FN13 under unstressed conditions while the same strain gave the maximum improvement in shoot dry weight (46.6%) over uninoculated control plants under Cd-stress. Under Cd-stressed conditions, the improvement in shoot dry weight ranged from 16.4% to 46.6%. The effect of inoculation on shoot dry weight was non-significant for all strains under unstressed conditions and Cd-stress except for FN13 under unstressed conditions where significant improvement in shoot dry weight than control was observed.
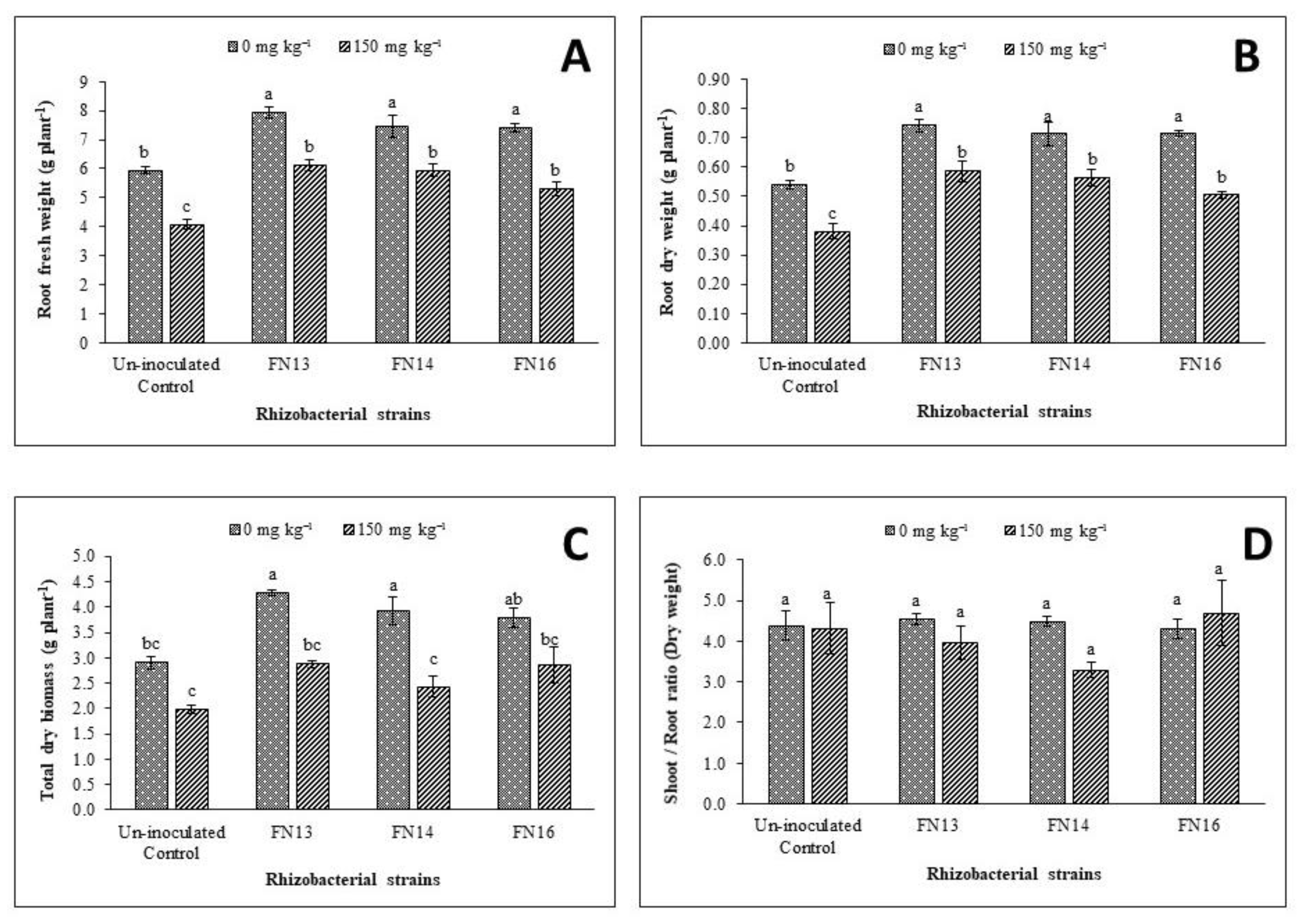
Data regarding the effect of Cd-stress on root fresh weight (Figure 2A), showed a significant decrease than control plants. Under unstressed conditions, 5.95 g plant−1 root fresh weight was noted that decreased to 4.08 g plant−1 under Cd-stress. Thus, a decrease of 31.4% over the unstressed control plants was observed due to Cd-stress. Inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains diluted the effect of Cd-stress on root fresh weight of Brassica juncea (L.) thus resulted a significant improvement over the uninoculated Cd-stressed control plants. Under Cd-stress, the improvement in root fresh weight due to inoculation with rhizobacterial strains ranged from 29.8% to 50% with maximum improvement due to inoculation with FN13. Under unstressed conditions, the maximum improvement (33.2%) in root fresh weight was also observed due to inoculation with FN13 followed by 25.5% and 24.4% improvement in root fresh weight by the strain FN16 and FN14, respectively.
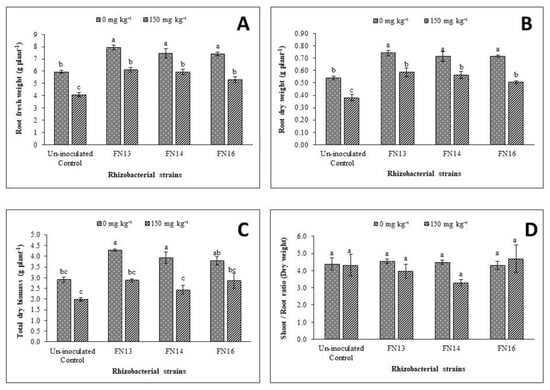
Figure 2.
Effect of Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains on growth parameters ((A) root fresh weight; (B) root dry weight; (C) total dry matter; (D) shoot/root ratio) of Brassica juncea (L.) under Cd-stress in pot trial; (n = 3): Means with same alphabets do not differ statistically from one another (p ≤ 0.05).
Data showed that Cd-stress significantly decreased the root dry weight of Brassica juncea (L.) plants with a reduction of 29.8% over the unstressed control plants (Figure 2B). Inoculation with rhizobacterial strains had a significant effect on root dry weight of Brassica juncea (L.) grown under unstressed conditions and Cd-stress. The impact, however, was more prominent under Cd-stress where an increase of 32.8% to 54.3% was observe than the control. Under unstressed conditions, the inoculation gave up to 32.2–37.6% increase in root dry weight when compared with uninoculated control. Maximum improvement (37.6%) in root dry weight under unstressed conditions was observed due to inoculation with FN13. Under Cd-stress, maximum improvement (54.3%) in root dry weight was noted due to inoculation with FN13 followed by 48.5% in the treatment with inoculation of FN14.
Data showed that total dry biomass was decreased due to Cd-stress however this decrease was non-significant when compared with unstressed control plants (Figure 2C). Inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains lessen the negative effect of Cd-stress thus resulted in improvement of total dry biomass. Inoculation with these strains was, however, more effective in enhancing the total dry biomass under unstressed conditions than Cd-stressed conditions. Under Cd-stress, the maximum response was given by the strain FN13 that was non-significantly related to other strains and control plants. Under unstressed conditions, the maximum improvement (41.8%) in total dry biomass was observed due to inoculation with rhizobacterial strain FN13 that showed significantly better results than the respective control. The strain FN14 also showed significantly better results in improving the total dry biomass of Brassica juncea (L.) seedlings than control under same conditions but the effect of FN16 on total dry biomass was not significantly different from control plants.
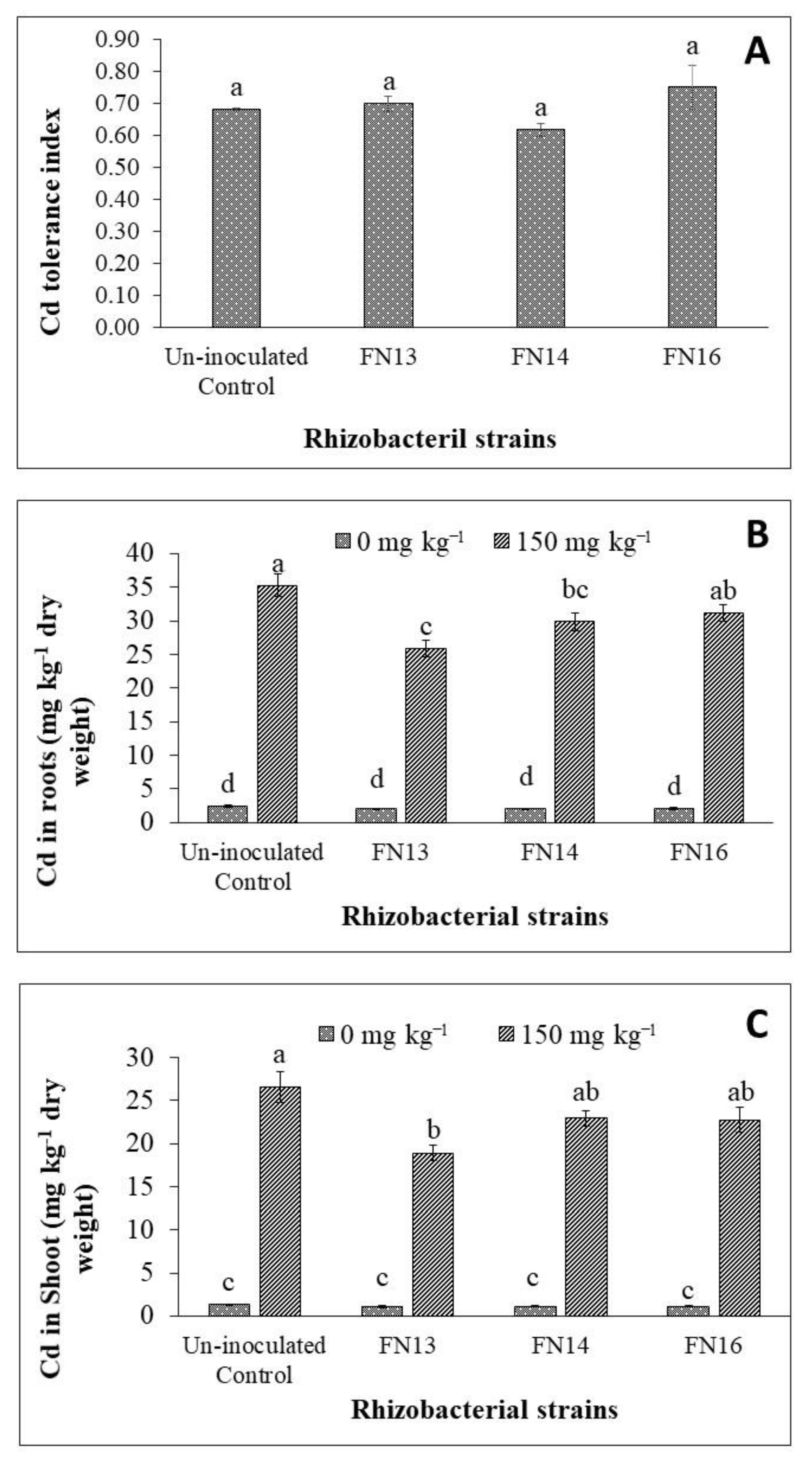
Shoot to root ratio was calculated for Brassica juncea (L.) plants under unstressed conditions and Cd-stress. The Cd-stress showed a non-significant effect on shoot to root ratio of Brassica juncea (L.) plants (Figure 2D). Inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains showed non-significant effect on shoot to root ratio of Brassica juncea (L.). Under unstressed conditions, FN16 decreased shoot to root ratio while the results of other two strains were not significant than control. Under Cd-stress, the strains, however, showed different results than under unstressed conditions. The strains FN13 and FN14 decreased the shoot to root ratio while the strain FN16 resulted a non-significant increase over the uninoculated Cd-stressed plants. The decrease in shoot to root ratio of plants inoculated with FN13 and FN14 might be due to a greater effect of these strains on root growth than on shoot growth that resulted in a decrease in shoot to root ratio on Brassica juncea (L.) plants grown under Cd-stress. Data showed that inoculation with rhizobacterial strains showed variable effect on Cd tolerance index of Brassica juncea (L.) plants (Figure 3A). The strains FN13 and FN14 caused a non-significant decrease while the strain FN16 resulted a non-significant increase in Cd tolerance index of Brassica juncea (L.) plants.
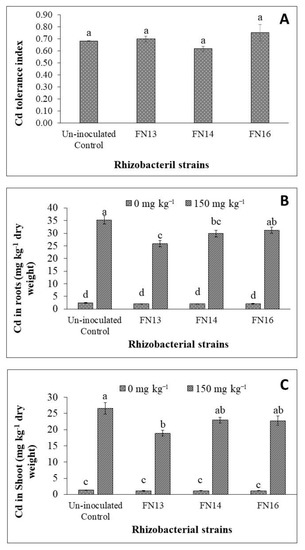
Figure 3.
Effects of Cd-tolerant, IAA and EPS-producing rhizobacterial strains on Cd concentration in Brassica juncea (L.) plant tissues under Cd-stress in pot trial; (n = 3); Means with same alphabets do not differ statistically from one another (p ≤ 0.05) (A) Cd tolerance index; (B) Cd in roots; (C) Cd in shoot.
3.2. Physiological Parameters
Data regarding SPAD value showed that Cd-stress significantly decreased the SPAD value of Brassica juncea (L.) plants (Table 2). Minimum SPAD value (38.94) was observed in the Cd-stressed control plants that was 27.2% less than the plants grown under unstressed conditions. Inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains effectively reduced the effect of Cd-stress on SPAD value of Brassica juncea (L.) thus resulting in a significant improvement over the uninoculated Cd-stressed control plants. Under Cd-stress, the improvement in SPAD value due to inoculation with rhizobacterial strains ranged from 10.4% to 17.7% with the maximum improvement caused by the strain FN13. The strains FN14 and FN16 gave non-significant improvement in SPAD value when compared with the uninoculated Cd-stressed control plants. Under unstressed conditions, the maximum improvement (13%) in SPAD value of Brassica juncea (L.) plants was observed due to inoculation with FN13 followed by FN14 and FN16, respectively.

Table 2.
Effects of Cd-tolerant, IAA and exopolysaccharides (EPS)-producing rhizobacterial strains on physiological parameters of Brassica juncea (L.) plants under Cd-stress in pot trial; (n = 3).
Results regarding the effect of Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains on relative water contents of Brassica juncea (L.) under Cd-stressed conditions (Table 2) showed that Cd-stress has a significantly negative impact on RWC when compared with unstressed control plants. The negative effect of Cd-stress on RWC was diluted due to inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains. Under unstressed conditions, the minimum RWC was observed in the leaves of uninoculated plants while the maximum RWC was given by the plants inoculated with FN13 that was 5.6% higher than uninoculated unstressed control plants. All the strains were effective in enhancing the RWC of Brassica juncea (L.) ranging from 3.0% to 5.6% but the improvement was not significantly different from control plants. The Cd-stressed plants showed 23.4% less RWC than uninoculated control plants and these results were statistically significant. Inoculation was effective but non-significant in improving RWC under Cd-stressed conditions where the increase in RWC ranged from 2.0% to 11.3% when compared with uninoculated control plants. Under Cd-stress, the maximum RWC were given by the inoculation with strain FN13 followed by FN16.
3.3. Stress-Related Metabolites and Antioxidants
Proline contents were significantly increased due to Cd-stress where up to 86.3% increase in proline contents was observed as compared to control (Table 2). Inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains was significantly effective in diluting the effect of Cd-stress on proline contents of Brassica juncea (L.) thus resulting in a significant decrease in proline contents over the uninoculated Cd-stressed control plants. Under Cd-stress, the decrease in proline contents due to inoculation with rhizobacterial strains ranged from 10.2% to 12.4% with the maximum decrease by the strain FN13. The strain FN16 gave non-significant decrease in proline contents when compared with uninoculated Cd-stressed control plants. Under unstressed conditions, the inoculation with all strains gave non-significant decrease in proline contents of Brassica juncea (L.) plants.
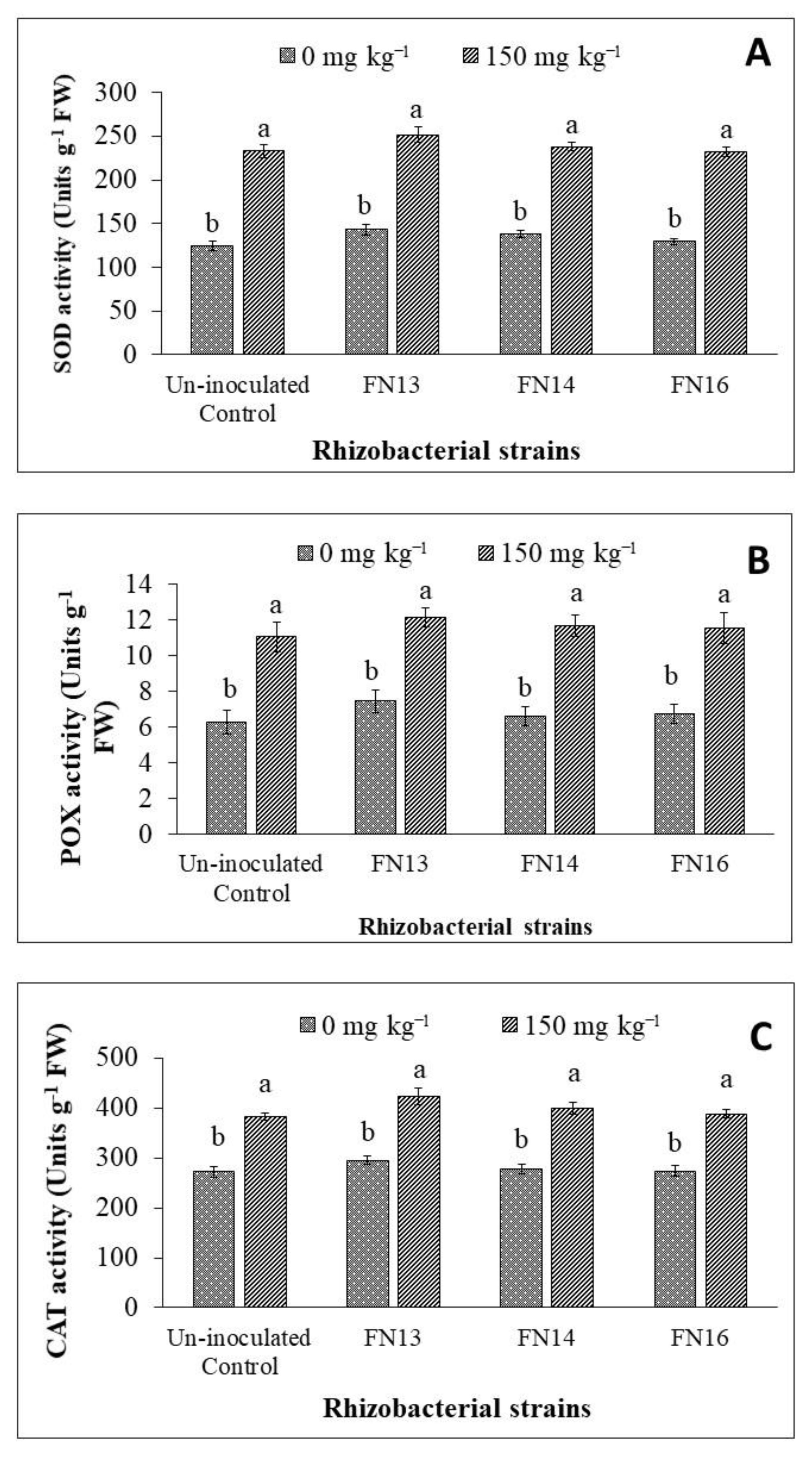
Data regarding SOD activity of Brassica juncea (L.) plants showed that the activity of SOD enzyme was increased due to Cd-stress (Figure 4A). The inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains further enhanced the SOD activity in Brassica juncea (L.) plants under Cd-stress. The increase, however, was non-significant when compared with the respective uninoculated control plants. Under Cd-stress, the maximum SOD activity (251.74 units g−1 fresh weight) was observed in the plants inoculated with strain FN13 followed by FN14 and FN16. The strains also showed non-significant increase in SOD activity of Brassica juncea (L.) plants under unstressed conditions.
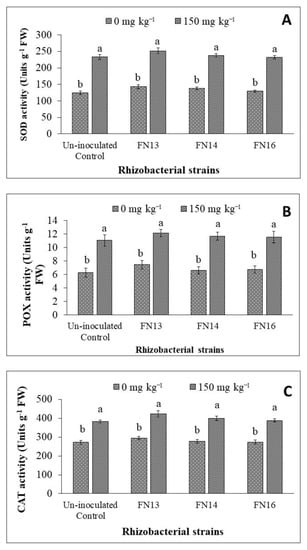
Figure 4.
Effects of Cd-tolerant, IAA and EPS-producing rhizobacterial strains on antioxidant enzymes ((A) SOD activity; (B) POX activity; (C) CAT activity) of Brassica juncea (L.) plants under Cd-stress in pot trial; (n = 3); Means with same alphabets do not differ statistically from one another (p ≤ 0.05).
As observed in the case of SOD activity, the POX activity of Brassica juncea (L.) plants was also significantly increased due to Cd-stress (Figure 4B). The inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains further enhanced the POX activity in Brassica plants under Cd-stress. The increase, however, was non-significant when compared with respective uninoculated control plants. Under Cd-stress, the maximum POX activity was observed in the plants inoculated with strain FN13 followed by FN14 and FN16. All strains showed non-significant increase in POX activity of Brassica juncea (L.) plants under unstressed conditions and Cd-stress.
The results of CAT activity were also in line with those of SOD and POX activities. The CAT activity of Brassica juncea (L.) plants was also significantly increased due to Cd-stress (Figure 4C). The inoculation with rhizobacterial strains further enhanced the CAT activity in Brassica plants under Cd-stress. The increase, however, was non-significant when compared with respective uninoculated control plants. Under Cd-stress, the maximum CAT activity was observed in the plants inoculated with strain FN13 followed by FN14 and FN16. All strains showed non-significant increase in CAT activity of Brassica juncea (L.) plants under unstressed conditions and Cd-stress.
3.4. Cadmium Concentration in Root and Shoot
It was observed that Cd-stress significantly enhanced the Cd concentration in root of Brassica juncea (L.) plants (Figure 3B). Inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains reduced the Cd concentration in root of Brassica juncea (L.) seedlings under Cd2+ stress. Maximum Cd concentration (35.3 µg g−1) was observed in the roots of plants in the uninoculated control. Minimum Cd concentration was observed in the roots of plants inoculated with rhizobacterial strain FN13 where significantly less Cd was observed than in control. The strains FN14 and FN16 also decreased the Cd concentration in roots of Brassica juncea (L.) plants but this decrease was non-significant in the case of FN16 when compared with the respective uninoculated control. Overall, rhizobacterial strains gave up to 11.7 to 26.9% decrease in Cd concentration in roots when compared with respective Cd-stressed control plants. Unstressed plants showed negligible concentration of Cd as compared to Cd-stressed plants.
As observed in the case of Cd concentration in roots, Cd-stress also significantly increased the Cd concentration in shoots of Brassica juncea (L.) plants (Figure 3C). The Cd concentration in shoot was decreased due to inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains. It was observed that Cd-concentration in shoots was less as compared to Cd in roots of Brassica juncea (L.) plants. Under Cd-stress, the maximum Cd concentration (26.6 mg kg−1) was observed in the shoot of plants under uninoculated control treatment. The strain FN13 was the most effective treatment in reducing the Cd concentration in shoot of Brassica juncea (L.) plants which reduced the Cd concentration up to 29% less than control. The results of FN13 were non-significant with those of FN14 and FN16 but significantly better than the control. The strains FN14 and FN16 also decreased the Cd concentration in the shoot of Brassica juncea (L.) plants but this decrease was not significantly different than the control. Under unstressed conditions, the Cd concentration was up to 1.33 mg kg−1 in the shoot of Brassica juncea (L.) plants under uninoculated treatment. The inoculation showed Cd concentration of shoots ranging from 1.08 to 1.14 mg kg−1.
4. Discussion
In the present study, the impact of Cd-tolerant, IAA and EPS-producing PGPR strains on growth, physiology, and antioxidant enzyme system of Brassica juncea (L.) plants under Cd-stress was investigated. The scarcity of irrigation water compels farmers to use untreated wastewater and industrial effluents for crop production particularly in developing countries [7,51]. While it is known that wastewater increases crop production due to dissolved nutrients and beneficial impacts on soil properties, it is also a source of heavy metals in soils and growing crops [9,52]. Heavy metals are potentially toxic for plants, animals, and human beings due to their non-biodegradable nature [53,54,55]. In response to metal stress, plants produce antioxidants and free radicals in addition to activation stress responsive genes [56]. They produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) in plants that are regulated by production of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants [55,57]. These antioxidative enzymes include CAT, peroxidase, SOD, polyphenol oxidase (PPO) and guaiacol peroxidase (GPOX), etc. [58] while proline is the major non-enzymatic osmoprotectant produced in plants.
In our study, Cd-stress decreased plant growth that might be due to reduction of water and nutrient uptake by Brassica juncea (L.) plants exposed to Cd-stress as a result of decreased root growth [18]. Results of our studies are supported with the work of Dutta et al. [59] who reported that Cd-stress negatively affected the growth of B. juncea. Cadmium stress also decreases the root volume thus changes the size of the root system [60] that affects the exposure of roots to soil, water and nutrients that decrease in crop performance. Plants produce osmolytes as a defensive strategy to cope with stress conditions.
Stress tolerance in plants can be induced exogenously by application of osmoprotectants, amendments or inoculation with PGPR having the ability to produce different plant growth regulators or exopolysaccharides [61,62,63]. These microbes use different mechanisms such as production of exopolysaccharides, ACC-deaminase activity, catalase activity, phytohormone production and chitinase activity to induce stress tolerance in crop plants [26,64]. Bacillus strains are reported to be involved in inducing physiological alterations in plants as an adaptive strategy under stress [65]. The use of Cd immobilizing bacterial strains in combination with different immobilizing amendments have also shown their worth under stress [32].
In the current study, rhizobacteria having the potential to produce EPS and IAA under Cd-stress along with other plant growth promoting (PGP) traits showed their potential to improve growth of Brassica juncea (L.) plants under Cd-stressed conditions. These strains enhanced the root and shoot growth thus improving the total dry matter of Brassica juncea (L.) plants. This increase in plant biomass might be attributed to improvement in root growth due to production of IAA by these strains that led to enhanced shoot growth. It has been well documented in literature that auxins, especially IAA, are involved in root tissue differentiation, cell division and elongation, and root initiation [62,66]. The potential of Bacillus aryabhattai SRB02 to induce oxidative stress tolerance in soybean has been reported by Park et al. [67] which they attributed to a change in phytohormones level of plants by the inoculated strains.
This increase in plant growth might also be due to the production of exopolysaccharides by inoculated strains. The EPS produced by bacterial strains help in binding the soil particles, improves soil structure, increase moisture retention capacity of soil and help in biofilm formation by the bacterial strains [68]. The PGPR increase crop tolerance to Cd-stress due to production of exopolysaccharides, siderophores, and plant hormones along with other PGP traits [69,70]. The PGPR strains used in our study also have potential to solubilize inorganic phosphate along with IAA and EPS production ability that might have helped them to proliferate more in the root zone that enhanced their colonization. The solubilization of phosphate in turn enhanced their survival efficacy under stress [71] subsequently helping in plant growth promotion. Belimov et al. [72] reported that the rhizobacterial strain Ralstonia mannitolilytica KUCd7 effectively removed Cd from Cd-amended media, solubilized inorganic phosphate, and produced siderophores in addition to 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC)-deaminase activity. They also observed that the inoculation of Brassica juncea L. with this bacterium improved plant growth through reduction in Cd-uptake.
In our study, inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains reduced the negative effects of Cd-stress on physiological parameters thus improved the SPAD value and RWC of Brassica juncea (L.) plants under Cd-stress over control. The improvement in plant physiology under Cd-stress might be due to EPS and IAA production ability of these strains. Similarly, Ahmad et al. [71] reported the improvement in SPAD value and relative water content due to inoculation with PGPR strains having the ability to produce IAA along with ACC-deaminase activity [73]. Several other PGP traits of bacterial strains are also involved in improving the growth and physiology of inoculated plants [74,75]. Improvement in RWC of plants is a good indicator of reliving stressed conditions. Inoculated plants showed more RWC because these strains increased the size of the root system by initiating secondary roots. Solubilization of phosphate by these strains might also have helped generate more root proliferation [70] thus enabling plants to explore more soil for water and nutrients.
The SPAD value represents the chlorophyll value that is a way of non-destructive leaf chlorophyll contents measurements that correlated the crop nitrogen status to chlorophyll contents. In previous studies, increase in chlorophyll contents after inoculation with PGPR under Cd-stress has been reported [76]. Increased chlorophyll content due to inoculation might happen as a result of enhanced Mg2+ that accelerated the production of photosynthates [76]. The increase in chlorophyll content is also correlated to improvement in nutrient uptake by crop plants due to phosphate solubilization, siderophores production and IAA production by inoculated strains [77,78].
Plants use several adjustments under stressed environments to cope with negative effects of these stresses. Production of proline under stress is one of those adjustments [71]. Accumulation of proline and other organic metabolites occurs in plants for osmotic adjustment under stress [79]. Production of higher levels of proline by crop plants under Cd-stress has been reported [29,80]. The higher concentration of proline under acts to adjust intercellular osmotic potential in crop plants [81] that requires additional metabolic energy. This additional energy is met by shifting the normal metabolic processes and thus plants experience stressed conditions [82]. In our study, inoculation with Cd-tolerant, IAA-producing rhizobacterial strains having the potential of EPS production decrease the production of proline that might be due to reduction in negative effects of Cd-stress due to IAA, EPS and siderophores production by these strains. These results are supported by the previous work conducted by several scientists under stressed conditions [29,31,71,83,84].
In our studies, Cd concentration in Brassica juncea (L.) root was significantly increased under Cd-stress that was reduced due to inoculation with Cd-tolerant PGPR strains. This might be due to EPS and IAA-producing ability of these PGPR strains. It has been well documented that cadmium-tolerant PGPR strains help to reduce Cd uptake by crop plants by stabilizing it in the soil through production of exopolysaccharides [27]. For example, Siripornadulsil and Siripornadulsil [69] reported the reduced uptake and accumulation of Cd in rice grains.
The reduction in Cd uptake due to phytostabilization of heavy metals by using EPS, and IAA-producing bacterial strains has also been reported by Marchal et al. [85]. Recently, Zeng et al. [35] reported that Cd-tolerant PGPR helped in the immobilization of Cd in soil thus reducing their uptake due to enhanced sequestration of Cd in soil by producing phytohormones, siderophores and polymeric substances. Although, inoculation with PGPR may enhance the uptake of heavy metals in plants [33], the phytostabilization of heavy metals is also an effective strategy to reduce Cd uptake by growing plants [34]. In another study, Ahmad et al. [29] reported that rhizobacterial strains belonging to the genera Serratia, Bacillus, Stenotrophomonas, and Klebsiella improved growth of crop plants due to decrease in Cd-uptake. They attributed these positive effects to IAA production ability of Cd-tolerant PGPR strains. The increased biomass production due to the decrease in Cd uptake in maize after inoculation with PGPR strains under stress has also been reported by Naveed et al. [86].
In our studies, Brassica juncea (L.) plants exposed to Cd-stress showed higher the production of antioxidants (SOD, POX and CAT) that is a defense mechanism used by crop plants exposed to osmotic stress [87]. Enhanced activities of antioxidant enzymes have also been reported in previous studies [80]. The SOD scavenges and catalyzes the ROS specie superoxide and converts it in to H2O2 and molecular oxygen under stressed soil environments [88]. The H2O2 is also an intermediate ROS which is toxic to plants. This H2O2 is converted into water and oxygen by other antioxidant enzymes i.e., CAT and POX [89]. Previous studies also report the enhanced activities of POX and CAT in plants under Cd-stress [18,90] while SOD activity showed variable behavior under different studies. The increased activity of SOD has been reported in Brassica juncea [80] while other studies report the decrease in SOD activities in plants under Cd-stress [91].
The heavy metal tolerant PGPR with metal immobilizing ability have been well documented to enhance plant growth, physiology, and antioxidant status by reducing the metal bioavailability and accumulation in plant tissues [91,92]. Several PGPR strains have been documented to reduce the negative effects of ROS produced under stress [16,32,79] through enzymatic antioxidants. Enhanced CAT activity in crop plants due to inoculation with Cd-tolerant PGPR under Cd-stress has also been reported in previous studies [15,93]. A positive impact of inoculation with Klebsiella pneumoniae strain K5 on activities of SOD, and CAT has also been reported by Pramanik et al. [25]. Wang et al. [94,95] reported the effectiveness of Sphingomonas SaMR12 to alleviate Cd-stress in rapeseed by regulating the Reduced glutathione (GSH)-AsA cycle through activities of antioxidant enzyme systems. In our study, the strain FN13 showed significantly better results than other two strains in improving the growth, physiology, and antioxidants status of Brassica juncea (L.) plants that might be due to better survival efficacy of the strain FN13 under Cd-stress. This might also be due to better PGP traits such as siderophore production, IAA production and EPS production of the strain FN13 as reported by Nazli [14]. The strain FN13 was identified as Bacillus safensis strain FN13 and has been submitted to the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) website under the accession number MT229105 [37].
5. Conclusions
Cadmium pollution is the major issue for vegetables, fodders and oilseed crops growing around the vicinity of big cities as it directly enters the food web. In the current study, exopolysaccharides and IAA-producing bacterial strains improved the growth, and physiology of Brassica juncea (L.) plants under Cd-stress. However, a non-significant difference was observed in the activity of antioxidant enzymes between inoculated and uninoculated Brassica juncea (L.) plants under Cd-stress. Overall, Bacillus safensis strain FN13 was the most effective strain in improving the Brassica juncea (L.) growth and physiology under Cd-stress. In addition, it also helped to immobilize Cd in soil. It can be concluded that the strain FN13 is a potential phytostabilizing biofertilizer for heavy metal-contaminated soils that can be recommended to effectively utilize Cd contaminated soils for growing crop plants.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.N., X.W. and M.A.; Methodology, F.N. and M.A. Software, A.M., B., M.N. and A.D.; Validation, M.N., A.H., M.J. Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M.A. and F.N.; Writing—Review and Editing, A.M., N.P. and X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We confirm that no external funding is received for this research project during experimentation.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the research facilities provided by the Soil Microbiology and Biotechnology Laboratory, Department of Soil Science, the Islamia University of Bahawalpur. The first author also acknowledges the Department of Agriculture (Research), Government of the Punjab, for grant of study leave to complete the Ph.D. degree from the Islamia University of Bahawalpur.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest whether financial or relational during the preparation and submission of this work.
References
- Kanianska, R. Agriculture and its impact on land-use, environment, and ecosystem services. In Landscape Ecology—The Influences of Land Use and Anthropogenic Impacts of Landscape Creation; Almusaed, A., Ed.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2016; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M.; Dubey, N.K.; Chauhan, D.K. Silicon nanoparticles more effectively alleviated UV-B stress than silicon in wheat (Triticum aestivum) seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 110, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopittke, P.M.; Menzies, N.W.; Wang, P.; McKenna, B.A.; Lombi, E. Soil and the intensification of agriculture for global food security. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, A.; Naveed, M.; Saeed, Q.; Ashraf, M.N.; Hussain, A.; Abbas, T.; Kamran, M.; Minggang, X. Application potentials of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and fungi as an alternative to conventional weed control methods. In Sustainable Crop Production; IntechOpen, Limited: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhu, D.; Morris, N. The effect of the urban wastewater treatment ratio on agricultural water productivity: Based on provincial data of China in 2004–2010. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.A.; Naveed, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Gao, B.; Mustafa, A.; Núñez-Delgado, A. Combined application of biochar and sulfur regulated growth, physiological, antioxidant responses and Cr removal capacity of maize (Zea mays L.) in tannery polluted soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 259, 110051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Natasha, B.I.; Sarwar, T.; Shah, A.H.; Niazi, N.K. A Review of environmental contamination and health risk assessment of wastewater use for crop irrigation with a focus on low and high-income countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, L.A.; Saeed, M.A.; Amjad, N. Present status and future prospects of mechanized production of oilseed crops in Pakistan-a review. Pak. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 23, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Chaoua, S.; Boussaa, S.; Gharmali, A.E.; Boumezzough, A. Impact of irrigation with wastewater on accumulation of heavy metals in soil and crops in the region of Marrakech in Morocco. J. Saudi. Soc. Agric. Sci. 2019, 18, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, G.; Sarwar, N.; Saifullah, A.A.; Ghafoor, A. Heavy metals (Cd, Ni and Pb) contamination of soils, plants and waters in Madina town of Faisalabad metropolitan and preparation of GIS based maps. Adv. Crop Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Malik, Z.; Parveen, A.; Zong, Y.; Abbasi, G.H.; Rafiq, M.T.; Shaaban, M.; Mustafa, A.; Bashir, S.; Rafay, M.; et al. Biochar alleviates Cd phytotoxicity by minimizing bioavailability and oxidative stress in pak choi (Brassica chinensis L.) cultivated in Cd-polluted soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, M.A.; Elyamine, A.M.; Moussa, M.G.; Cai, M.; Zhao, X.; Hu, C. Cadmium in plants: Uptake, toxicity, and its interactions with selenium fertilizers. Metallomics 2019, 11, 238–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, A.S.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Kumar, V. Root exudates ameliorate cadmium tolerance in plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazli, F. Inducing Heavy Metal Stress Tolerance in Brassica juncea (L.) through Phytohormone Producing Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Soil Science, The Islamia University of Bahawalpur, Bahawalpur, Pakistan, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Luo, S.; Chen, J.; Xiao, X.; Chen, L.; Zeng, G.; Liu, C.; He, Y. Effect of endophyte-infection on growth parameters and cd-induced phytotoxicity of Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveed, M.; Mustafa, A.; Azhar, S.Q.; Kamran, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Núñez-Delgado, A. Burkholderia phytofirmans PsJN and tree twigs derived biochar together retrieved Pb-induced growth, physiological and biochemical disturbances by minimizing its uptake and translocation in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.). J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 257, 109974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.A.; Popova, L.P. Functions and toxicity of cadmium in plants: Recent advances and future prospects. Turkish J. Bot. 2013, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, Z.; Naveed, M.; Imran, M.; Bashir, M.A.; Sattar, A.; Mustafa, A.; Hussain, A.; Xu, M. Combined use of Enterobacter sp. MN17 and zeolite reverts the adverse effects of cadmium on growth, physiology and antioxidant activity of Brassica napus. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DalCorso, G.; Farinati, S.; Furini, A. Regulatory networks of cadmium stress in plants. Plant Signal Behav. 2010, 5, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Cadmium stress tolerance in crop plants: Probing the role of sulfur. Plant Signal Behav. 2011, 6, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartacci, M.F.; Argilla, A.; Baker, A.J.M.; Navari-Izzo, F. Phytoextraction of metals from a multiply contaminated soil by Indian mustard. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Lata, C. Heavy metal stress, signaling, and tolerance due to plant-associated microbes: An overview. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N. Plant-microbial Interactions and their Role in Sustainable Agriculture and Sustainability of Agriculture Soils. Recent Pat. Food Nutr. Agric. 2020, 11, 94–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Bano, A.M.; Babar, A. Impacts of plant growth promoters and plant growth regulators on rainfed agriculture. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramanik, K.; Mitra, S.; Sarkar, A.; Soren, T.; Maiti, T.K. Characterization of cadmium-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae MCC 3091 promoted rice seedling growth by alleviating phytotoxicity of cadmium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24419–24437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.A.; Naveed, M.; Mustafa, A.; Abbas, A. The good, the bad, and the ugly of rhizosphere microbiome. In Probiotics and Plant Health; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 253–290. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, K.; Jamwal, V.L.; Gandhi, S.G.; Ohri, P.; Bhardwaj, R. Metal resistant PGPR lowered Cd uptake and expression of metal transporter genes with improved growth and photosynthetic pigments in Lycopersicon esculentum under metal toxicity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Bano, A.; Ali, S.; Babar, M.A. Crosstalk amongst phytohormones from planta and PGPR under biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 90, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Akhtar, M.J.; Zahir, Z.A.; Naveed, M.; Mitter, B.; Sessitsch, A. Cadmium-tolerant bacteria induce metal stress tolerance in cereals. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2014, 21, 11054–11065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Pathak, B.; Fulekar, M.H. Characterization of PGP traits by heavy metals tolerant Pseudomonas putida and Bacillus safensis strain isolated from rhizospheric zone of weed (Phyllanthus urinaria) and its efficiency in Cd and Pb removal. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 954–975. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N.; Bano, A. Exopolysaccharide producing rhizobacteria and their impact on growth and drought tolerance of wheat grown under rainfed conditions. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Mustafa, A.; Majeed, S.; Naseem, Z.; Saeed, Q.; Khan, A.; Nawaz, A.; Baig, K.S.; Chen, J. Enhancing cadmium tolerance and pea plant health through Enterobacter sp. MN17 inoculation together with biochar and gravel sand. Plants 2020, 9, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; He, T.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, S.; Wang, T.; Xu, F.; Xu, H. Insight into the mechanisms of plant growth promoting strain SNB6 on enhancing the phytoextraction in cadmium contaminated soil. J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 385, 121587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolie, C.U.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, D.; Zhang, L.; Su, M.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, H. Cadmium immobilization in aqueous solution by Aspergillus niger and geological fluorapatite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7647–7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, H.; Jijie, L.; Chen, Q.; Li, W.; Wu, L.; Tang, J.; Ma, L. The immobilization of soil cadmium by the combined amendment of bacteria and hydroxyapatite. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, T.U.; Bano, A.; Naz, I. Alleviation of heavy metals toxicity by the application of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and effects on wheat grown in saline sodic field. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2017, 19, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazli, F.; Jamil, M.; Hussain, A.; Hussain, T. Exopolysaccharides and indole-3-acetic acid producing Bacillus safensis strain FN13 potential candidate for phytostabilization of heavy metals. Environ. Monitor. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, J.; Estefan, G.; Rashid, A. Soil and Plant Analysis Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; International Center for Agriculture in Dry Areas (ICARDA): Aleppo, Syria, 2001; p. 172. [Google Scholar]
- Hseu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tsai, C.; Tsui, C.; Cheng, S.; Liu, C.; Lin, H. Digestion methods for total heavy metals in sediments and soils. Water Air Soil Poll 2002, 141, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, H.; Nayak, L.; Das, S.; Adhya, T.K. Isolation of ACC deaminase producing PGPR from rice rhizosphere and evaluating their plant growth promoting activity under salt stress. Plant Soil 2013, 366, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, G.; Hetrick, D.; Schwat, P. Effects of mycorrhizal fertilizers amendments on zinc tolerance of plants. Environ. Pollut. 1995, 88, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Bronson, K.F.; Singh, Y.; Singh, B.; Peng, S. Use of chlorophyll meter sufficiency indices for nitrogen management of irrigated rice in Asia. Agron. J. 2000, 92, 875–879. [Google Scholar]
- Mayak, S.; Tirosh, T.; Glick, B.R. Plant growth-promoting bacteria confer resistance in tomato plants to salt stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 42, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, L.S.; Waldern, R.P.; Teare, I.D. Rapid determination of free proline for water status studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Ghosh, P.K.; Ghosh, S.; De, T.K.; Maiti, T.K. Role of heavy metal resistant Ochrobactrum sp. and Bacillus spp. strains in bioremediation of a rice cultivar and their PGPR like activities. J. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannopolitis, C.N.; Ries, S.K. Superoxide dismutases. Plant Physiol. 1977, 59, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, G.N.; Qualset, C.O. Genetic control of endosperm amylase activity and gibberellic acid Reoponses in standard-height and short-statured wheats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 892–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chance, B.; Maehly, A.C. Assay of catalase and peroxidase. Meth. Enzymol. 1955, 2, 764–775. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, H.; Jiang, R. Accumulation of cadmium in the edible parts of six vegetable species grown in Cd-contaminated soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, R.G.D.; Torrie, J.H.; Dicky, D.A. Principles and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach, 3rd ed.; McGraw Hill Book International Co.: Singapore, 1997; pp. 204–227. [Google Scholar]
- Kamran, M.; Malik, Z.; Parveen, A.; Huang, L.; Riaz, M.; Bashir, S.; Mustafa, A.; Abbasi, G.H.; Xue, B.; Ali, U. Ameliorative effects of biochar on rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) growth and heavy metal immobilization in soil irrigated with untreated wastewater. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, F.; Mustafa, A.; Farooqi, Z.U.R.; Wang, X.; Younas, S.; Mohy-Ud-Din, W.; Ashir Hameed, M.; Mohsin Abrar, M.; Maitlo, A.A.; Noreen, S. Current and Emerging Adsorbent Technologies for Wastewater Treatment: Trends, Limitations, and Environmental Implications. Water 2021, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaleel, C.A.; Jayakumar, K.; Xing, Z.C.; Azooz, M.M. Antioxidant potentials protect Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek plants from soil cobalt stress and improve growth and pigment composition. Plant Omics 2009, 2, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Sabir, A.; Naveed, M.; Bashir, M.A.; Hussain, A.; Mustafa, A.; Zahir, Z.A.; Kamran, M.; Ditta, A.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Saeed, Q.; et al. Cadmium mediated phytotoxic impacts in Brassica napus: Managing growth, physiological and oxidative disturbances through combined use of biochar and Enterobacter sp. MN17. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 265, 110522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Kamran, M.; Zhou, Y.; Parveen, A.; Rehman, M.; Ahmar, S.; Malik, Z.; Mustafa, A.; Anjum, R.M.A.; Wang, B.; et al. Appraising growth, oxidative stress and copper phytoextraction potential of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) grown in soil differentially spiked with copper. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 257, 109994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, H.; Sasaki, T.; Yamammoto, Y.; Wasaki, J. AtALMT3 is involved in malate efflux induced by phosphorus deficiency in Arabidopsis thaliana root hairs. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, Z.M. Mercury toxicity, molecular response and tolerance in higher plants. BioMetals 2012, 25, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, J.K.; Robinson, D.S. Superoxide dismutase. In Oxidative Enzymes in Foods; Robinson, D.S., Eskin, N.A.M., Eds.; Elsevier Applied Science: London, UK, 1991; pp. 49–91. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, P.; Karmakar, A.; Majumdar, S.; Roy, S. Klebsiella pneumoniae (HR1) assisted alleviation of Cd (II) toxicity in Vigna mungo: A case study of biosorption of heavy metal by an endophytic bacterium coupled with plant growth promotion. Euro-Med. J. Environ. Integ. 2018, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Ditta, A.; Ahmad, M.; Mustafa, A.; Ahmad, Z.; Conde-Cid, M.; Tahir, S.; Shah, S.A.A.; Abrar, M.M.; Fahad, S. Processed animal manure improves morpho-physiological and biochemical characteristics of Brassica napus L. under nickel and salinity stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Zhu, L.; Ma, Z.; Wang, J. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SAY09 increases cadmium resistance in plants by activation of auxin-mediated signaling pathways. Genes 2017, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, R.; Zheng, J.; Shen, Z.; Xu, X. Exogenous foliar application of fulvic acid alleviates cadmium toxicity in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 167, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafique, M.; Naveed, M.; Mustafa, A.; Akhtar, S.; Munawar, M.; Kaukab, S.; Ali, H.M.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Salem, M.Z. The Combined Effects of Gibberellic Acid and Rhizobium on Growth, Yield and Nutritional Status in Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoknes, K.; Scholwin, F.; Jasinska, A.; Wojciechowska, E.; Mleczek, M.; Hanc, A.; Niedzielski, P. Cadmium mobility in a circular food-to-waste-to-food system and the use of a cultivated mushroom (Agaricus subrufescens) as a remediation agent. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 245, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, R.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F. Bacillus: A biological tool for crop improvement through bio-molecular changes in adverse environments. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaepen, S.; Vanderleyden, J.; Remans, R. Indole-3-acetic acid in microbial and microorganism-plant signaling. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 31, 425–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.G.; Mun, B.G.; Kang, S.M.; Hussain, A.; Shahzad, R.; Seo, C.W.; Kim, A.Y.; Lee, S.U.; Oh, K.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; et al. Bacillus aryabhattai SRB02 tolerates oxidative and nitrosative stress and promotes the growth of soybean by modulating the production of phytohormones. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alami, Y.; Achouk, W.; Marol, C.; Heulin, T. Rhizosphere soil aggregation and plant growth promotion of sunflowers by an exopolysaccharide-producing Rhizobium sp. strain isolated from sunflower roots. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3393–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siripornadulsil, S.; Siripornadulsil, W. Cadmium-tolerant bacteria reduce the uptake of cadmium in rice: Potential for microbial bioremediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 94, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveed, M.; Bukhari, S.S.; Mustafa, A.; Ditta, A.; Alamri, S.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Rafique, M.; Ashraf, S.; Siddiqui, M.H. Mitigation of nickel toxicity and growth promotion in sesame through the application of a bacterial endophyte and zeolite in nickel contaminated soil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Asghar, H.N.; Asghar, M. Inducing salt tolerance in mung bean through co-inoculation with Rhizobium and PGPR containing ACC-deaminase. Can. J. Microbiol. 2011, 57, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belimov, A.A.; Hontzeas, N.; Safronova, V.I.; Demchinskaya, S.V.; Piluzza, G.; Bullitta, S.; Glick, B.R. Cadmium-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with the roots of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern.). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 7, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, M.; Zhao, B.; Wang, X.; Bashir, S.; Haider, F.U.; Aslam, Z.; Khan, M.I.; Shabaan, M.; Naveed, M.; Mustafa, A. Isolation and Characterization of Oil-Degrading Enterobacter sp. from Naturally Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Soils and Their Potential Use against the Bioremediation of Crude Oil. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Hamid, Y.; Gurajala, H.K.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Effects of CO2 application and endophytic bacterial inoculation on morphological properties, photosynthetic characteristics and cadmium uptake of two ecotypes of Sedum alfredii Hance. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Wang, X.; Hilger, T.H.; Luqman, M.; Nazli, F.; Hussain, A.; Zahir, Z.A.; Latif, M.; Saeed, Q.; Malik, H.A.; et al. Evaluating Biochar-Microbe Synergies for Improved Growth, Yield of Maize, and Post-Harvest Soil Characteristics in a Semi-Arid Climate. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneef, I.; Faizan, S.; Perveen, R.; Kausar, S. Impact of bio-fertilizers and different levels of cadmium on the growth, biochemical contents and lipid peroxidation of Plantago ovata Forsk. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 21, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asari, S.; Tarkowsk, D.; Rolčík., J.; Novák, O.; Palmero, D.V.; Bejaiand, S.; Meijer, F. Analysis of plant growth-promoting properties of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens UCMB5113 using Arabidopsis thaliana as hostplant. Planta 2017, 245, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Naseer, I.; Hussain, A.; Zahid Mumtaz, M.; Mustafa, A.; Hilger, T.H.; Zahir, Z.A.; Minggang, X. Appraising endophyte–plant symbiosis for improved growth, nodulation, nitrogen fixation and abiotic stress tolerance: An experimental investigation with chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Agronomy 2019, 9, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.M.; Naveed, M.; Ahmad, M.; Zahir, Z.A. Rhizosphere bacteria for crop production and improvement of stress tolerance: Mechanisms of action, applications, and future prospects. In Plant Microbes Symbiosis: Applied Facets; Arora, N.K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Ahmad, A.; Hayat, S. Effect of cadmium on the growth and antioxidant enzymes in two varieties of Brassica juncea. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 21, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, J.A.; Viegas Rde, A.; da Rocha, I.M.; Moreira, A.C.; Moreira Rde, A.; Oliveira, J.T. Proline accumulation and glutamine synthase activity are increased by salt induced proteolysis in cashew leaves. J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 160, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, S.P.; Luthra, R.; Kumar, S. Salt-tolerant mutants in glycophytic salinity response (GRS) genes in Catharanthus roseus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Naveed, M.; Arshad, M. Rhizobacteria containing ACC deaminase confer salt tolerance in maize grown on salt affected soils. Can. J. Microbiol. 2009, 55, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Bano, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Guo, J.; Kang, Z.; Babar, M.A. Comparative physiological and metabolic analysis reveals a complex mechanism involved in drought tolerance in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) induced by PGPR and PGRs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchal, M.; Briandet, R.; Halter, D.; Koechler, S.; DuBow, M.S.; Lett, M.C.; Bertin, P.N. Subinhibitory arsenite concentrations lead to population dispersal in Thiomonas sp. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Mitter, B.; Reichenauer, T.G.; Wieczorek, K.; Sessitsch, A. Increased drought stress resilience of maize through endophytic colonization by Burkholderia phytofirmans PsJN and Enterobacter sp. FD17. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 97, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, S.; Hayat, Q.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wani, A.S.; Pichtel, J.; Ahmad, A. Role of proline under changing environments: A review. Plant Signal Behav. 2012, 7, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.D. Dissection of oxidative stress tolerance using transgenic plants. Plant Physiol. 1995, 107, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wei, G.; Li, J.; Qian, Q.; Yu, J. Silicon alleviates salt stress and increases antioxidant enzymes activity in leaves of salt-stressed cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Plant Sci. 2004, 167, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abozeid, A.; Ying, Z.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Z. Ethylene improves root system development under cadmium stress by modulating superoxide anion concentration in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Filardo, F.; Hu, X.; Zhao, X.; Fu, D.H. Cadmium stress alters the redox reaction and hormone balance in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) leaves. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 23, 3758–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.M.; Yi, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yao, J. Application of phosphate solubilizing bacteria in immobilization of Pb and Cd in soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21877–21884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.J.; He, L.Y.; Sheng, X.F. Increased biomass and quality and reduced heavy metal accumulation of edible tissues of vegetables in the presence of Cd-tolerant and immobilizing Bacillus megaterium H3. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ge, C.; Wu, Y.; Sahito, Z.A.; Ma, L.; Pan, F.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, L.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X. The endophytic bacterium Sphingomonas SaMR12 alleviates Cd-stress in oilseed rape through regulation of the GSH-AsA cycle and antioxidative enzymes. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Guo, T.; Xing, Y.; Mo, F.; Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Zhang, F. Effects of plastic mulch and nitrogen fertilizer on the soil microbial community, enzymatic activity and yield performance in a dryland maize cropping system. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 400–412. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).