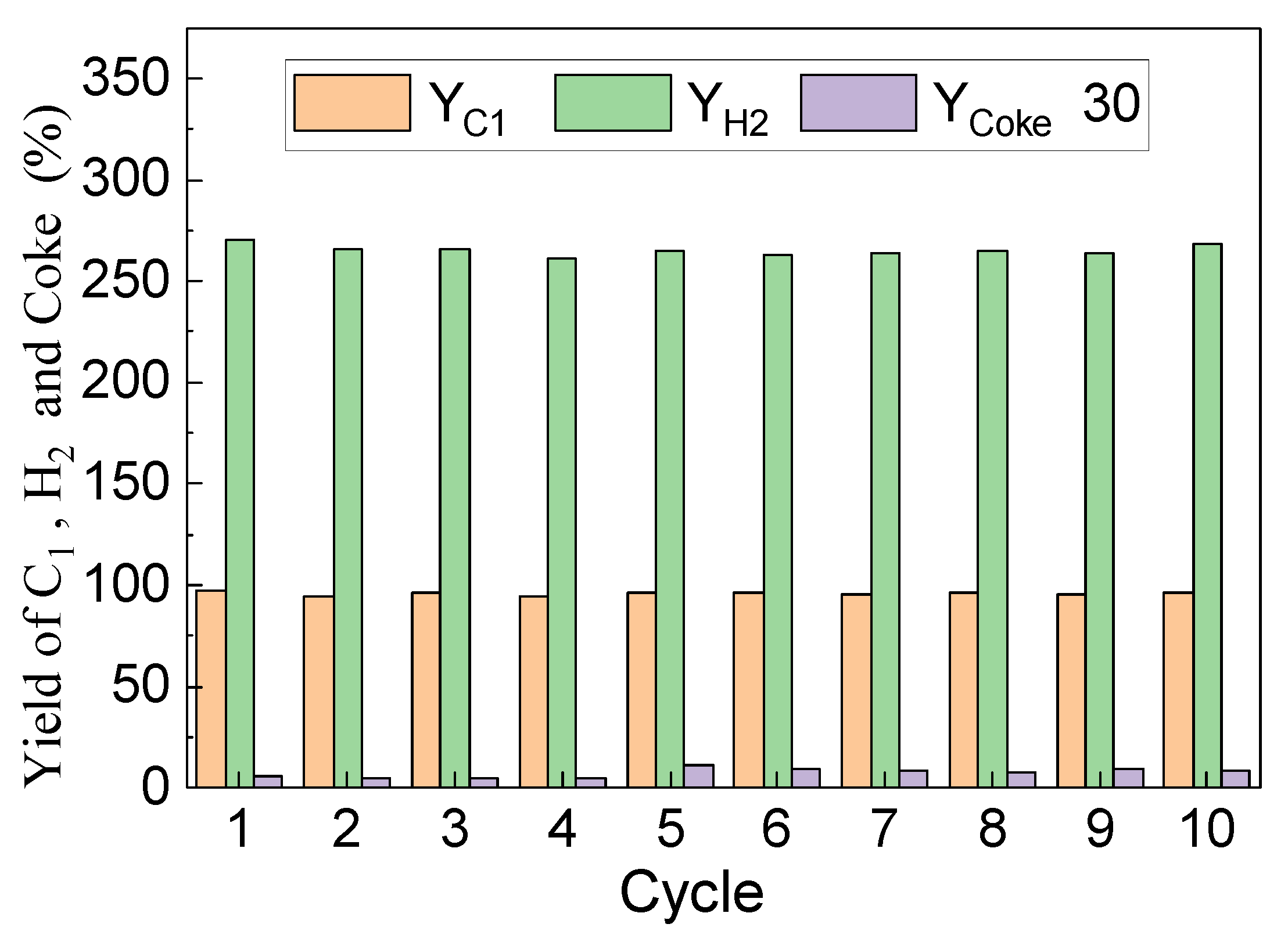Abstract
Chemical looping biomass gasification is a novel technology converting biomass into syngas, and the selection of oxygen carrier is key for efficient tar conversion. The performance of LaFe1-xNix as a robust catalytic oxygen carrier was investigated in the chemical looping conversion of toluene (tar model compound) into syngas in a fixed bed. LaM (M = Fe, Ni, Mn, Co, and Cu) was initially compared to evaluate the effect of transition metal on toluene conversion. LaFe (partial oxidation) and LaNi (catalytic pyrolysis) exhibited better performance in promoting syngas production than other oxygen carriers. Therefore, Ni-substituted ferrite LaFe1-xNix (x = 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1) was further developed. The effects of Ni-substitution, steam/carbon ratio (S/C), and temperature on toluene conversion into C1 and H2 were evaluated. Results showed that the synergistic effect of Fe and Ni promoted toluene conversion, improving H2 yield yet with serious carbon deposition. Steam addition promoted toluene steam reforming and carbon gasification. With S/C increasing from 0.8 to 2.0, the C1 and H2 yield increased from 73.9% to 97.5% and from 197.7% to 269.6%, respectively. The elevated temperature favored toluene conversion and C1 yield. LaFe0.6Ni0.4 exhibited strong reactivity stability during toluene conversion at S/C = 1.6 and 900 °C.
1. Introduction
Carbon dioxide is considered the most important greenhouse gas that can trap heat from the atmosphere. Human activity has caused the increase in atmosphere CO2 concentration by near 50% since the pre-industrial level (from 280 ppm to 417 ppm in October in 2021) [1]. Therefore, the reduction of CO2 emission is one of the primary tasks during the following decades. Countries over the world are trying to cooperate to reduce CO2 emissions. Therefore, effective methods to reduce CO2 emission are a key factor for CO2 reduction.
It is widely accepted that biomass is an important renewable carbon-neutral energy. Efficient development and utilization of biomass energy will play a very important role in solving energy and ecological environment problems, including biomass energy solidification, liquefaction, gasification, and direct combustion. Biomass gasification [2] is a relatively mature technique using gasification agents (like highly pure O2, air, H2O, and CO2) to convert biomass to syngas which can be used as feedstock for power generation or Fischer Tropsch synthesis. In view of the high volatile content in biomass, tar is an inevitable by-product in biomass gasification, including high hydrocarbons such as benzene, toluene naphthalene, etc. [3]. It not only reduces the syngas yield (about 5–15% of the total energy) [4], but also easily causes problems such as pipeline and equipment blockage and corrosion [5]. Tar production is also an obstacle concerning the development of biomass gasification technology. Therefore, efficient tar removal or conversion technology is very important for the biomass gasification process.
There are two main methods for tar removal, i.e., non-catalytic and catalytic methods. The former involves the use of a wet scrubber [6,7] or a secondary tar process outside the gasification reactor [8,9]. The catalytic method mainly includes catalytic cracking and catalytic reforming [10,11,12,13,14,15]. It could remove tar during biomass utilization and adjust the gas compositions of biogas. A highly reactive catalyst is the key point for in-situ tar removal. At present, the mainstream catalysts include natural ore (dolomite and olivine) [15,16], alkali metal [17,18], transition metal (Ni, Fe, Co et al.) [19,20,21,22,23] and carbon-based material [24]. Ordinarily, catalysts with a single active component have usually exhibited some shortcomings. For example, Ni catalyst is prone to cause sintering, carbon deposition, and sulfur poisoning. Natural ore with low price often presents low reactivity. The alkali metal and carbon-based catalyst often face the problems of reactivity decay due to deterioration of surface structure during longtime operation. Multicomponent catalysts can make up for the deficiency of single-component catalysts attracting increasing attention [21,22,23].
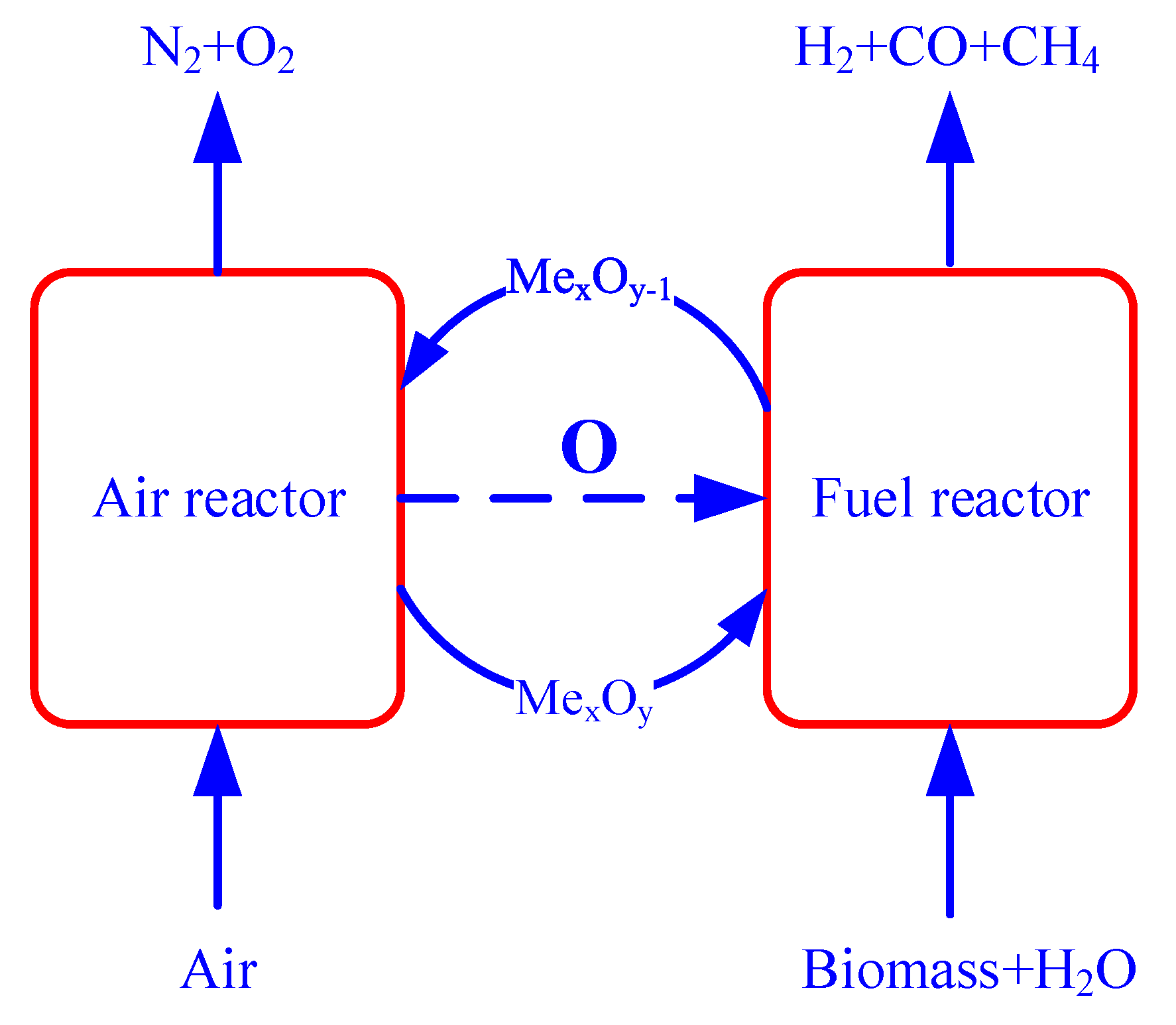
Chemical looping gasification (CLG) is a novel technology that uses lattice oxygen in an oxygen carrier to transfer oxygen from air to fuel to initiate biomass gasification. Figure 1 shows the schematic diagram of CLG performed by redox reaction that could be described by R1–R3. The oxygen carrier is oxidized by air in the air reactor. The oxidized oxygen carrier is used to initiate partial oxidation of biomass to produce syngas in the gasification reactor. The application of oxygen carriers is a key factor for the CLG process, and two main strategies are often used. Method 1 is to use traditional transition metal oxide with a low ratio of oxygen carrier to biomass to prevent excessive oxidation. Most of the research focused on materials of iron ore, Mn, Fe, and et al. [25,26,27,28]. Method 2 is to use an oxygen carrier with low oxidative activity to initiate partial oxidation rather than full oxidation. These kinds of oxygen carriers are often mixed oxides like ferrites or perovskites-based materials [29,30,31]. The mixed oxides oxygen carrier often has the advantages of different materials and even a synergy effect on fuel conversion. The application of these oxygen carriers in the biomass brings new opportunities yet tar removal is still one important issue during chemical looping biomass gasification.
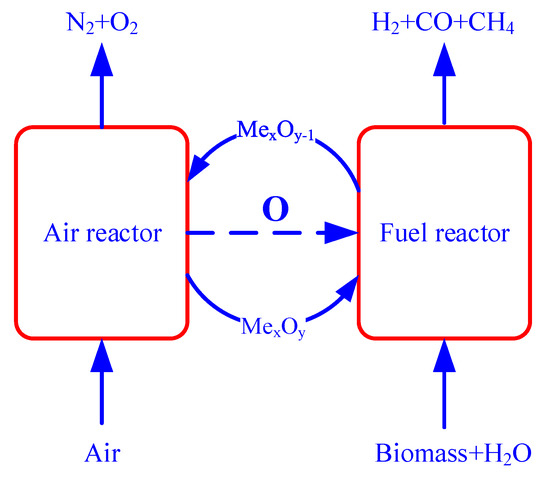
Figure 1.
The schematic diagram of chemical looping gasification.
2MexOy-1 + O2 → MexOy
Biomass → C + gas (H2, CO, CO2, CH4, CaHbOc)
2(a-c)MexOy + 2CaHbOc → 2(a-c)MexOy-1 + bH2 + 2cCO
Accordingly, this paper uses lanthanum and main transition metal of Ni, Fe, Co, Mn, and Cu to synthesize oxygen carrier (also as a catalytic material) for toluene (as a tar model compound) conversion. The effect of metal oxide type, S/C ratio, the temperature on the gas product, toluene conversion, and hydrogen production was evaluated. The oxygen carrier was characterized by XRD, SEM, and EDX.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Material Preparation
A modified sol-gel method [32,33] was used to prepare the oxygen carrier and a representative synthesis procedure is described below. Initially, Ni(NO3)2·6H2O (99.0%,), Fe(NO3)3·9H2O (99%) and La(NO3)3·6H2O (99%) with a designed ratio were dissolved in deionized water at 80 °C. Citric acid and ethylene glycol were successively added at the molar ratio of ethylene glycol:citric acid:cation = 3.5:2.5:1. The mixed solution was kept stirring at 80 °C till to form a viscous gel. The gel was then dried at 180 °C and calcined at 900 °C for 3 h to obtain a stable structure. To be specific, the oxygen carrier was named after the main elements and their content. For example, LaFe0.6Ni0.4 represents the oxygen carrier with the molar ratio of La:Fe:Ni = 1:0.6:0.4. Two series of oxygen carriers were prepared i.e., LaM (M = Fe, Ni, Mn, Co, and Cu) and LaFe1-xNix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8). The perovskite or mixed oxides as catalytic materials towards the toluene conversion and syngas production were evaluated. The former was used to evaluate the effect of typical transition metals on toluene conversion and syngas production. The latter aimed to optimize the performance and improve the catalytic effect on toluene conversion. The oxygen carrier was then crushed and double sieved to the size range of 0.1–0.3 mm for use.
2.2. Experimental Setup and Procedure
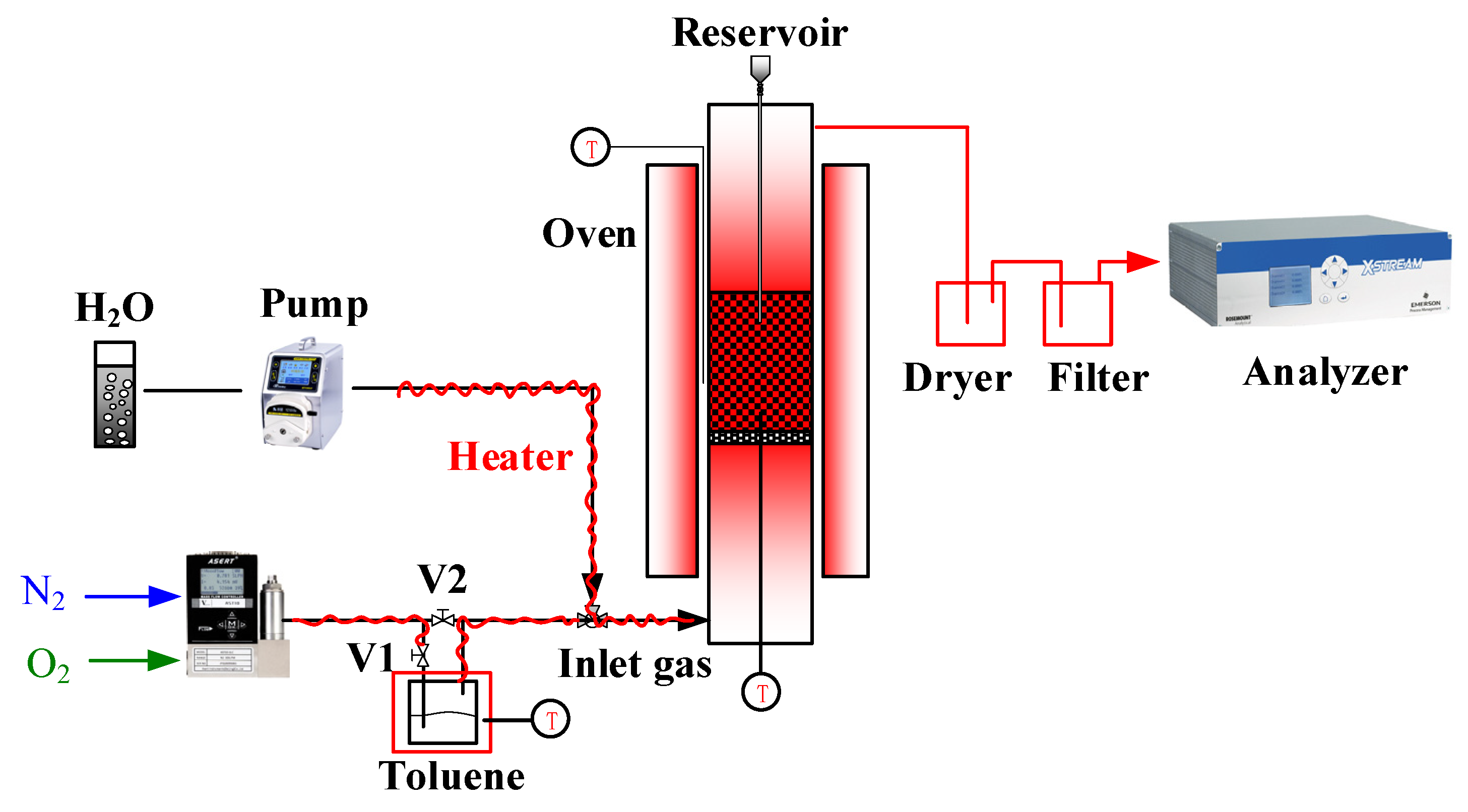
The chemical looping conversion of toluene was carried out in a fixed bed system, as is shown in Figure 2. Simply, the system contains inlet gas, reaction bed, gas purification device, and gas analyzer. The flow of the inlet gas (N2 and O2) and H2O was accurately controlled by mass flow controllers and micro-pump, respectively. By switching the valve V1 and V2, the carrying gas N2 can be controlled to enter the air-tight toluene tank to bring toluene into the reactor. The toluene was placed in a water bath. The vapor-liquid equilibrium partial pressure of toluene was adjusted by adjusting the water bath temperature. Then, the toluene input flow can be quantitatively controlled by fixing the carrying gas flow. The reaction chamber was a quartz tube (i.d = 26 mm, L = 600 mm) with a porous distributor plate at the middle. The reaction chamber was heated with the temperature sensor installed 3 mm below the porous plate to monitor the reactor temperature. The outlet gas was introduced to a purification device for water and fine powder removal. Finally, the outlet gas compositions (CO, CO2, CH4, H2, and O2) were online analyzed with an X-stream analyzer. C1 mentioned in the investigation refers to CO, CO2, and CH4. For each test, the sample successively underwent toluene/N2/steam and air-regeneration. N2 sweeping was performed between each process.
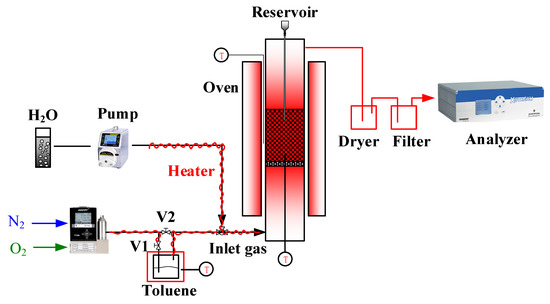
Figure 2.
The diagram of the fixed bed for the chemical looping conversion of toluene.
Several series of the experiment was conducted, and Table 1 shows the main parameters during the toluene step. In test 1, thermal pyrolysis was conducted at typical temperatures without bed materials as the reference condition. In test 2, a batch sample of 10 g catalytic oxygen carrier was employed as bed material to investigate the catalytic partial oxidation of toluene. The duration for the toluene step was set at 10 min except for the case of LaCu in which the tar (due to low toluene conversion) blocked the outlet pipeline and the experiment was interrupted. Then, test 3 was further conducted to optimize the catalyst effect of oxygen carriers to promote H2 production by adding Ni into ferrite. In test 4, steam was introduced to enhance the toluene conversion and syngas production (H2 + CO). Finally, S/C and temperature were further optimized in Test 5 with LaFe0.6Ni0.4.

Table 1.
Main experiment parameters for toluene conversion.
2.3. Material Characterization
The phase patterns were collected to determine the chemical compositions of oxygen carriers by X-ray diffractometer (XRD, D/MAX-2550-18 kW) using Cu Ka radiation (60 kV, 200 mA) at room temperature. The phase pattern was collected with the angle from 20 to 80° with a step of 0.02°. Scanning electron microscopes (SEM, FEI Quanta 200) were used to analyze the morphological features of oxygen carriers. Simultaneously, the EDX was conducted to evaluate the element distribution on the oxygen carrier.
2.4. Data Process
During the toluene conversion, toluene would be converted into H2, coke, C1 (CO, CO2, and CH4), and high hydrocarbon. The content of non-condensable high hydrocarbon content was maintained at a low level, and it was neglected. Therefore, the outlet gas flow could be calculated using the N2 balance method with known inlet N2 flow. H2 yield was defined as the amount of actual hydrogen production with the respect to the theoretical hydrogen from toluene. The C1 yield was also similarly defined. The coke formation during the toluene step would be oxidized to form carbonaceous gas (CO and CO2) during the following step. Therefore, the coke yield was defined as the amount of carbonaceous gas in the air step with respect to the amount of carbon in the toluene.
where Fout,fuel and Fout,air represent the outlet gas flow during the toluene step and air step, respectively. The inlet N2 flow is 1.2 L/min and Wi,fuel and Wi,air are the concentration of composition i (i = CO, CO2, CH4, and H2) in the toluene step and j (i = CO, CO2, and O2) in the air step. The inlet toluene flow Ftoluene is 0.286 g/min, and molar weigh of toluene is 92.14 g/mol. and were defined as the instantaneous yield of C1 and H2, respectively.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Enhanced Fuel Conversion by Catalytic Oxygen Carrier
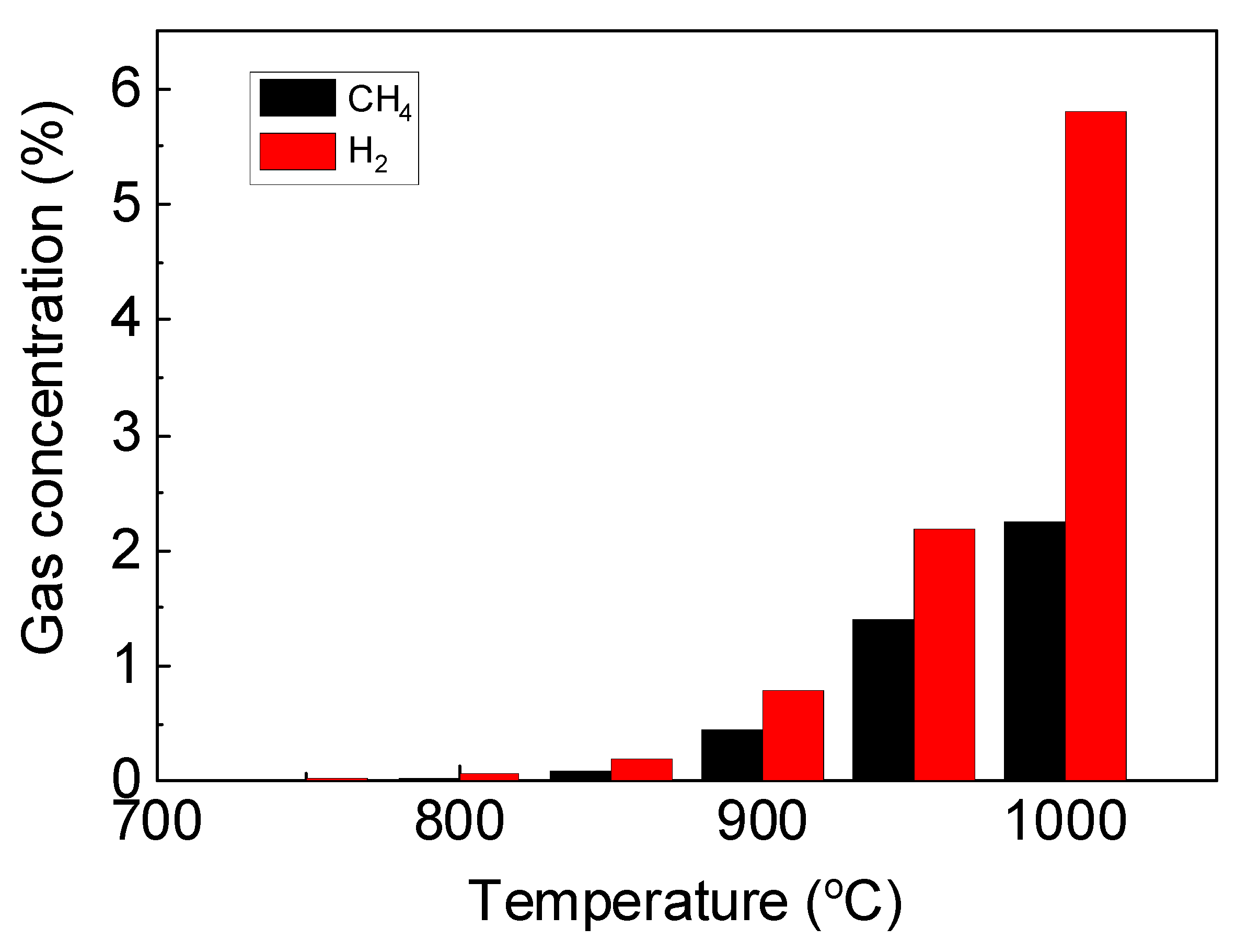
Initially, the toluene was introduced to the reactor without bed material to carry out the thermal pyrolysis as the reference condition. Without an oxygen carrier, the toluene was primarily converted into H2 and CH4 rather than CO or CO2. The elevated temperature favored the thermal pyrolysis of toluene. Although, the concentration of H2 and CH4 was lower than 1% at 900 °C, and was still very low even at 1000 °C. The results were in agreement with open literature that the efficient toluene conversion without catalyst would require extremely high operation temperature which would result in extra operation cost [34].
Different oxidized oxygen carriers of LaM (M = Fe, Mn, Co, Cu, and Ni) were used as bed materials for chemical looping conversion of toluene at 900 °C, and the gas product evolution was shown in Figure 3. The concentration of gas products varied greatly, depending on the material. When LaNi was used, the main reaction could be roughly divided into 3 stages according to the gas concentration. Full oxidation of toluene occurred in stage 1 where CO2 increased during the first 1 min and CO and H2 were maintained at a low level. After that, with the lattice oxygen carrier being used up, CO2 gradually decreased, and some CO was formed. Simultaneously, due to the catalytic effect of Ni on toluene conversion, H2 concentration increased to the maximum of about 12%. After that, H2 concentration gradually decreased to 6% with coke formation covering the activity center of the catalyst. It could be seen that the oxidized LaNi would cause full oxidation of toluene. The reduced oxygen carrier would play a catalytic effect on toluene conversion and H2 yield yet the coke would cause reactivity deterioration.
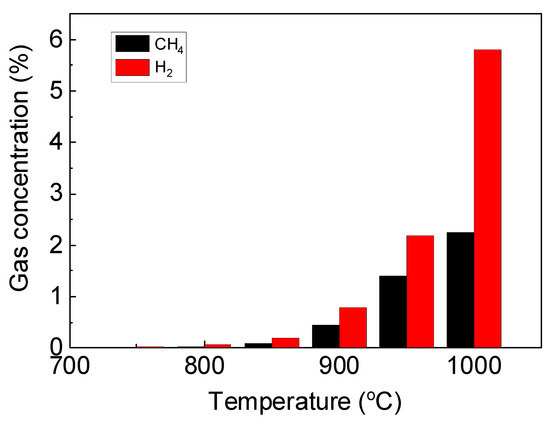
Figure 3.
Gas concentration during thermal toluene pyrolysis at typical temperature without bed material.
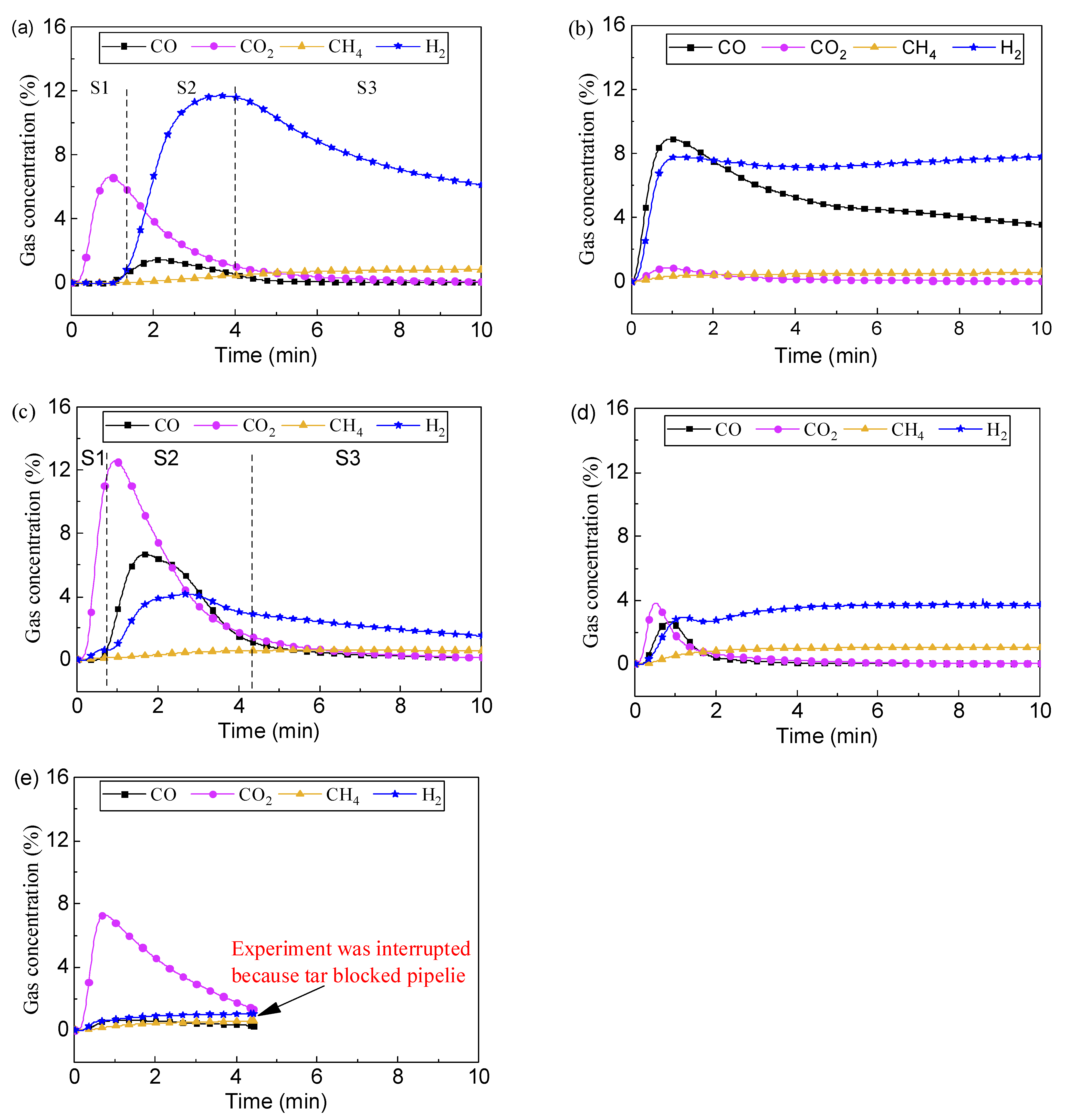
Figure 4 shows the gas composition when different oxygen carriers were used. When LaFe was used, the gas composition changed a lot. A high CO concentration (peaking at about 9%) was observed, and gradually decreased with the oxygen carrier was consumed. During the whole reaction stage, both CH4 and CO2 maintained at a low level. H2 concentration maintained at about 8% during the whole reaction stage without an obvious decrease like the case of LaNi. Meanwhile, although with some decrease, CO concentration maintained till the end of the reaction. It means that the oxygen carrier can continuously provide lattice oxygen for partial oxidation, and mitigate serious coke formation. Overall, compared with LaNi, LaFe was easier to motivate partial oxidation rather than full oxidation, favoring syngas yield.
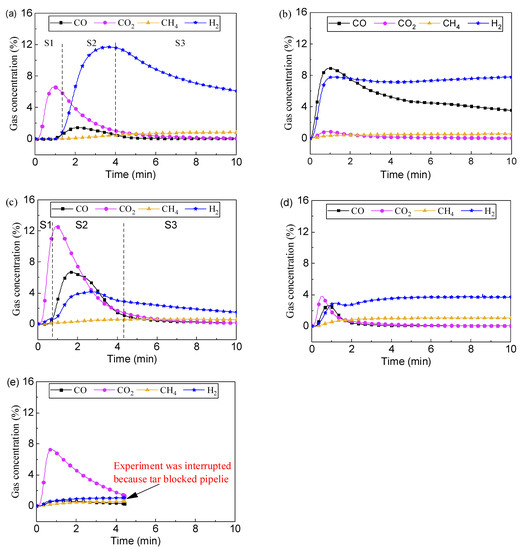
Figure 4.
Gas concentration versus reaction time at 900 °C with typical oxygen carrier: (a) LaNi, (b) LaFe, (c) LaCo, (d) LaMn and (e) LaCu.
When LaCo was used, a much higher CO2 concentration (peaking over 12%) than both LaNi and LaFe was observed, and H2 and CO maintained at a low level during this stage. This indicates that a full oxidation reaction mainly occurred in this stage. Afterward, CO2 decreased, and CO and H2 appeared, indicating the occurrence of partial oxidation of toluene. The higher CO concentration than H2 concentration indicates full oxidation of H2 into H2O. After 4 min, the CO concentration decreased to a low level revealing the exhaust of available lattice oxygen in the oxygen carrier. However, the H2 concentration was much lower than the case of LaNi and LaFe over the whole reaction stage, and it indicates a lower catalytic effect of LaCo on toluene conversion.
Compared with LaCo, the LaMn exhibited similar performance in toluene conversion but with lower complete oxidation ability and higher catalytic performance. Initially, full oxidation of toluene occurred with CO2 concentration peaking below 4%. After the exhaustion of lattice oxygen, the catalytic pyrolysis occurred, and the H2 concentration was stable at about 4%.
For the oxygen carrier of LaCu, the CO2 concentration was observed during the early reaction indicating full oxidation. After that, H2 concentration still maintained at a low level similar to the reference condition of thermal pyrolysis without catalyst. The toluene conversion was very low, with the tar blocking the pipeline and the experiment was interrupted. It indicates that the reduced LaCu has no catalytic effect on toluene conversion.
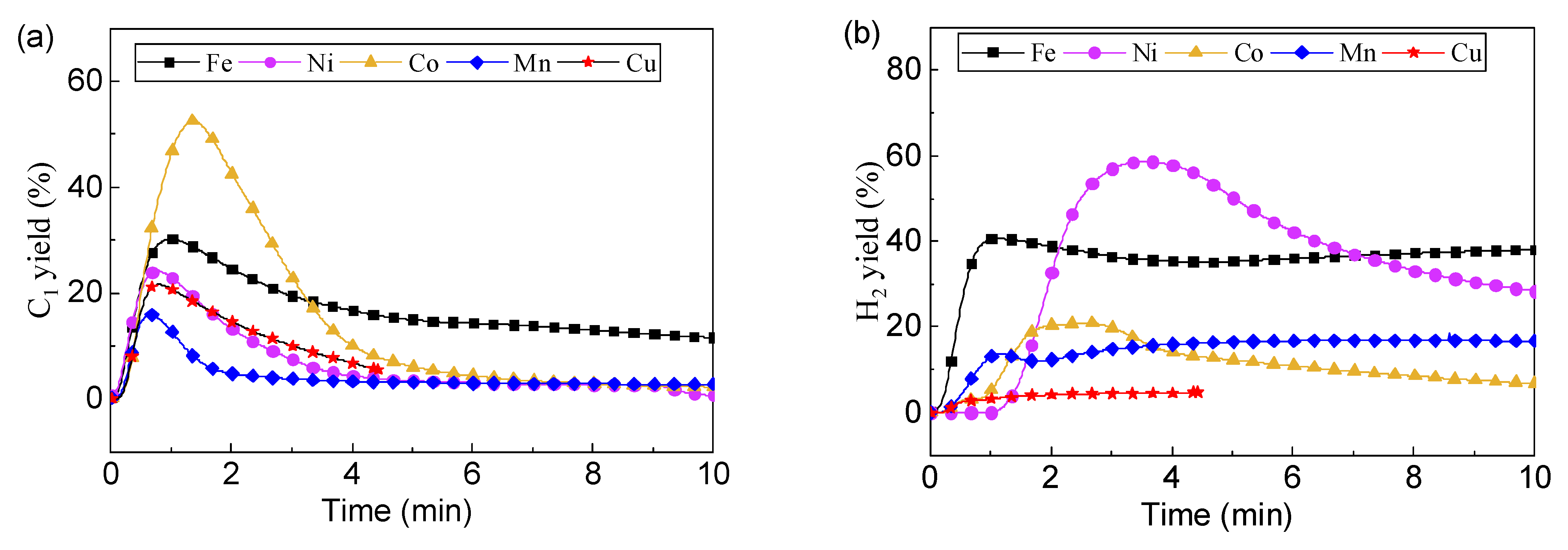
Figure 5 shows the C1 yield as a function of time using different oxygen carriers. C1 yield exhibited a first increasing and then decreasing trend with time. According to C1 yield peak, the reactivity decreased in the order of LaCo > LaFe > LaNi > LaCu > LaMn. However, Ni exhibited the best catalytic effect on hydrocarbons conversion, resulting in the highest H2 yield. Instead, after the consumption of lattice oxygen, the LaMn and LaCo exhibited lower catalysis reactivity for toluene conversion with H2 yield lower than 20%. The LaFe oxygen carrier exhibited a strong oxygen capacity, supporting partial oxidation. The reduced LaFe would also have a catalytic effect on toluene conversion, and H2 yield maintained at about 40%. The H2 yield decreased in the order of LaNi> LaFe > LaCo ≈ LaMn > LaCu.
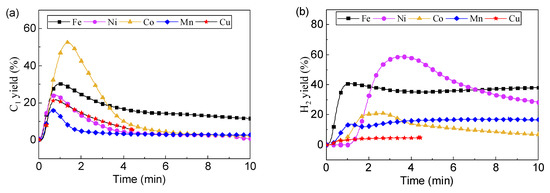
Figure 5.
Chemical looping toluene conversion at 900 °C: (a) C1 yield and (b) H2 yield.
Overall, under a different mechanism, LaFe and LaNi caused the most yield of H2. However, H2 yield was still far below 100%, and serious carbon deposition occurred, affecting the catalytic effect. Therefore, improving the activity of oxygen carriers is very important for the conversion of toluene into C1 and H2.
3.2. LaFe1-xNix Oxygen Carrier
Section 3.1 indicates that LaFe was prone to initiate partial oxidation rather than full oxidation and LaNi exhibited a better catalytic effect on pyrolysis, and both can promote the H2 yield. Therefore, the both Ni and Fe tuned oxygen carriers were prepared with typical ratio, i.e., LaFe1-xNix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8).
3.2.1. Characterization of Oxygen Carrier
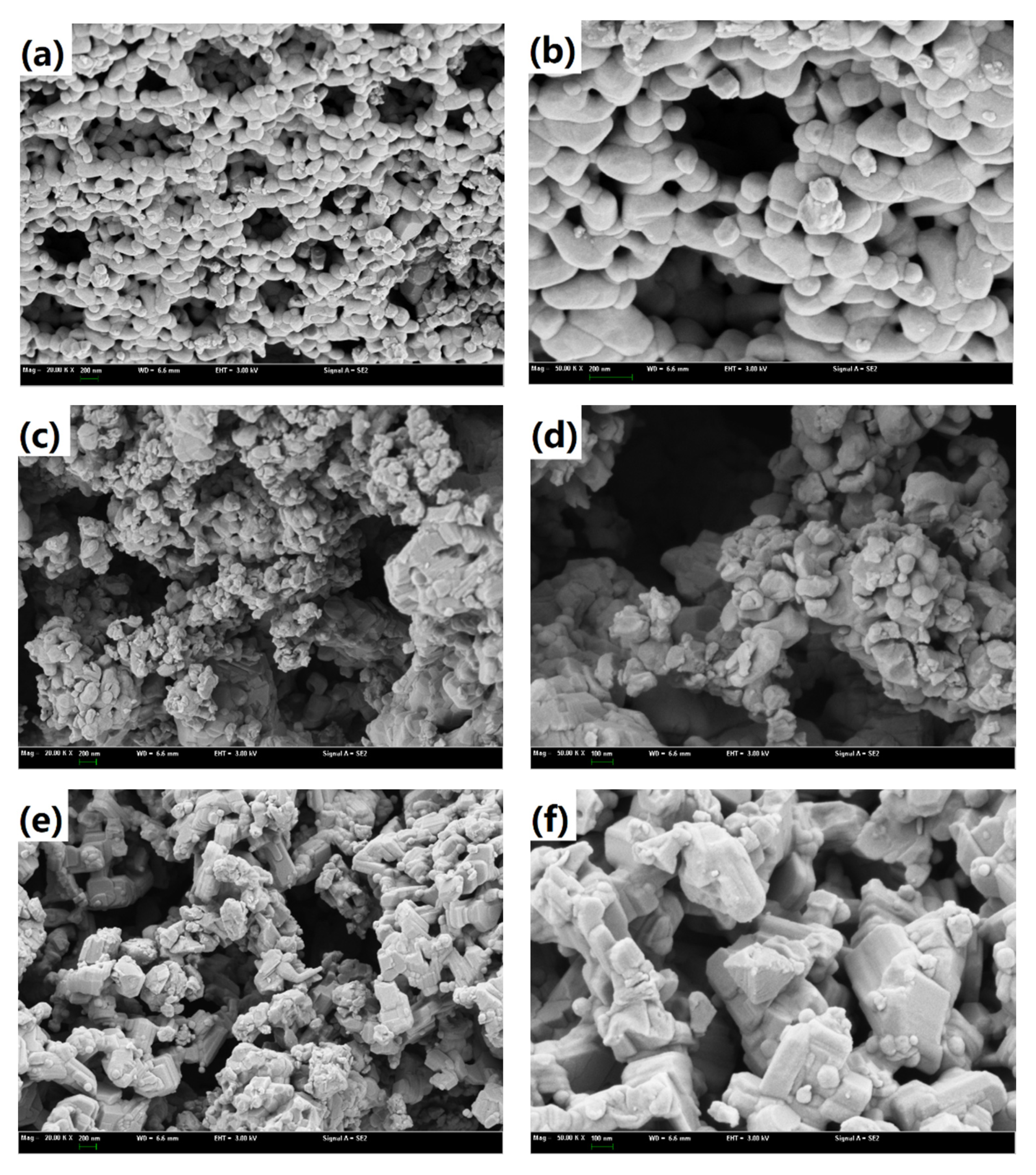
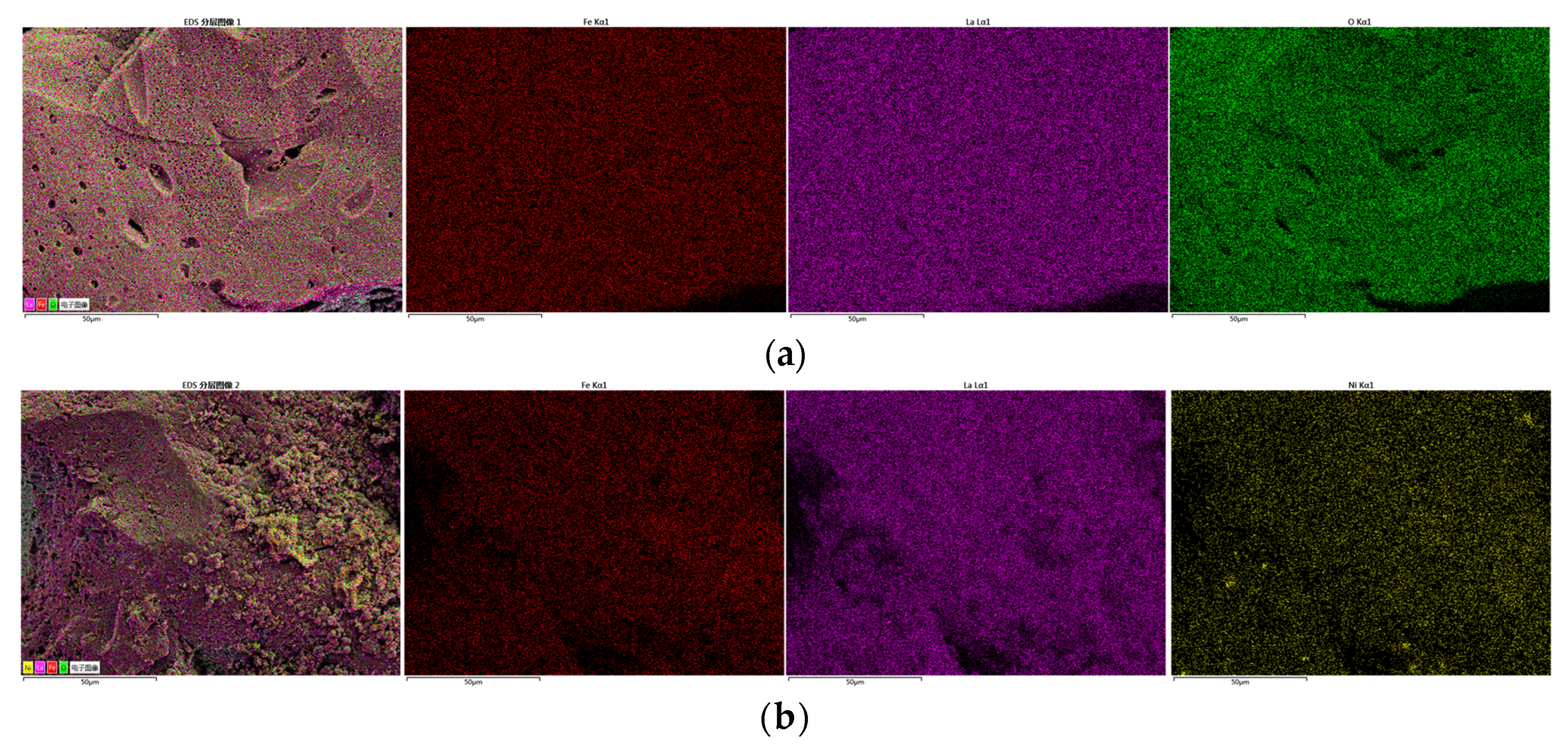
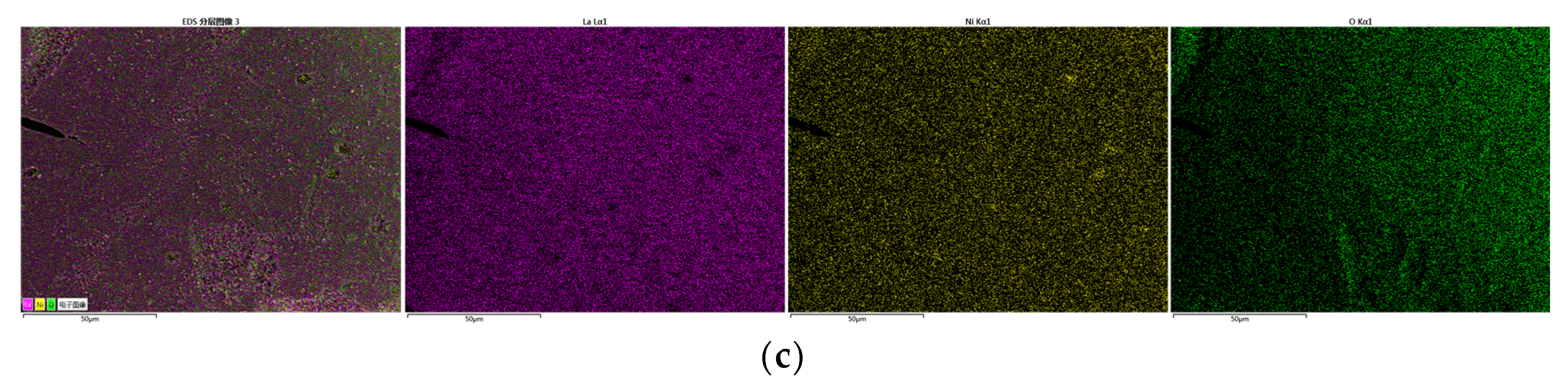
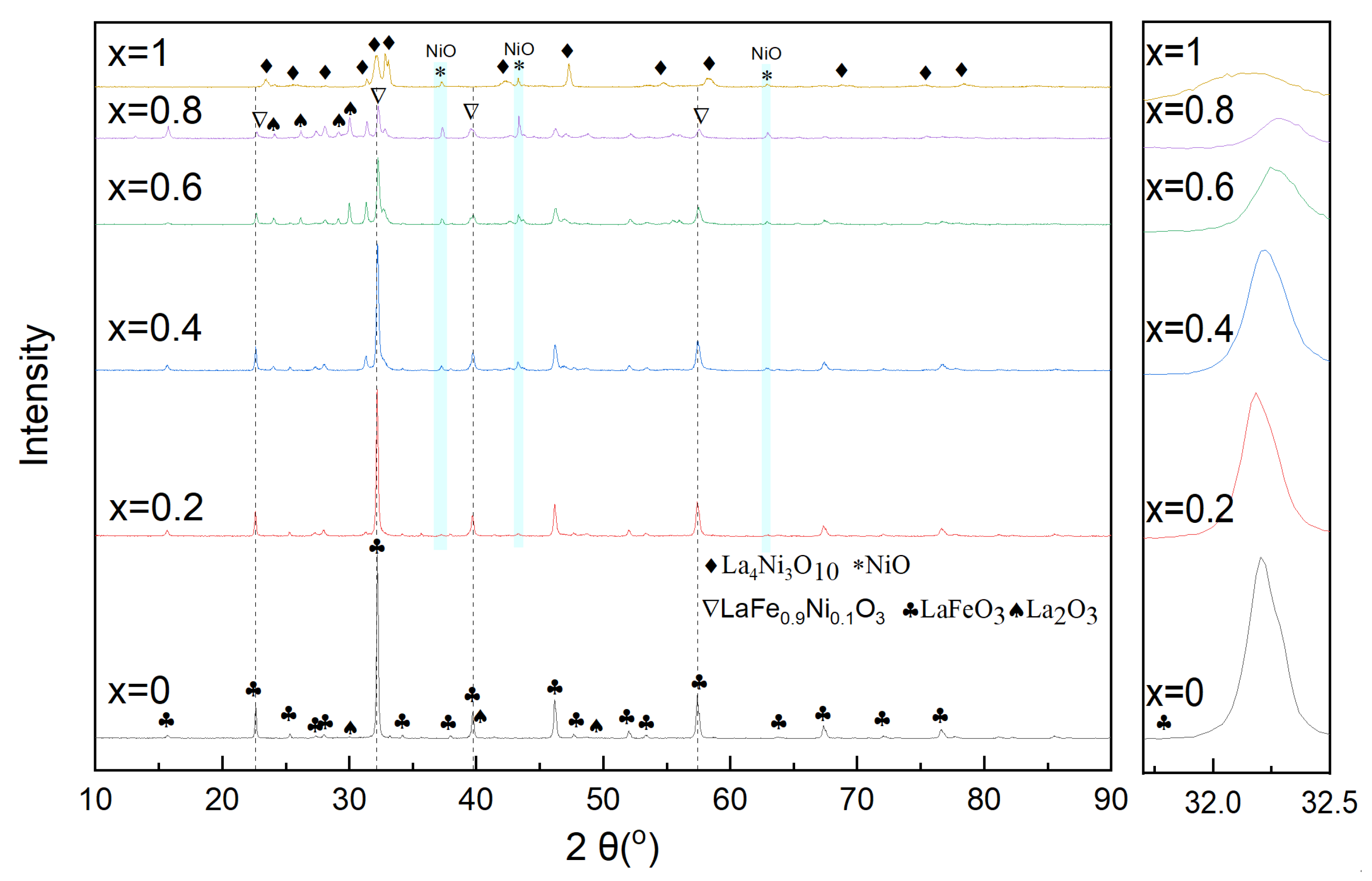
LaFe, LaFe0.6Ni0.4 (represents the LaFe1-xNix), and LaNi were selected to analyze the micro surface morphology and phase composition. Figure 6 shows the typical micro-morphology of LaFe, LaFe1-xNix, and LaNi. The surface of LaFe was regularly covered with small grains of 50–100 nm. Its porous surface was almost closed because of the oxidation of the oxygen carrier. With the addition of Ni (LaFe1-xNix), the surface became more porous, and the grains turned smaller. It favored the gas diffusion into the active center of the oxygen carrier. The LaNi also exhibited a more porous surface covered with disordered nano-crystallines. Overall, these oxygen carriers prepared by the sol-gel method were nano-materials, and the addition of Ni into LaFe helped to improve a porous surface without observable sintering. Figure 7 also shows the EDS analysis of LaFe, LaFe1-xNix, and LaNi. It is clear that all these elements mapping are almost the same for each oxygen carrier sample, indicating uniform dispersion of the main elements. It also means that these oxygen carriers were well prepared without element agglomeration.
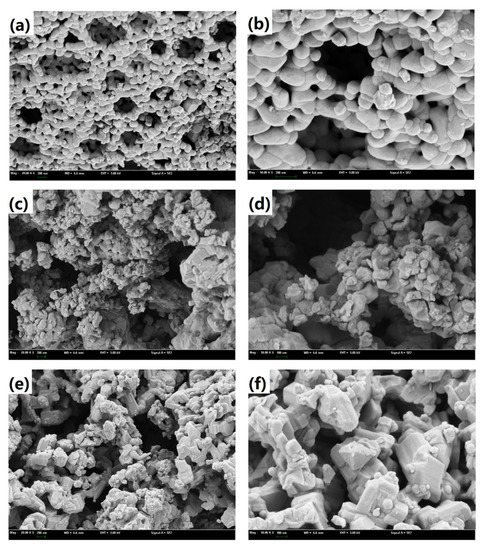
Figure 6.
SEM images of oxygen carriers: (a,b) for LaFe; (c,d) for LaFe1-xNix; (e,f) for LaNi.
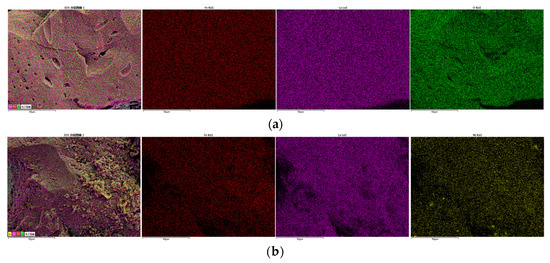
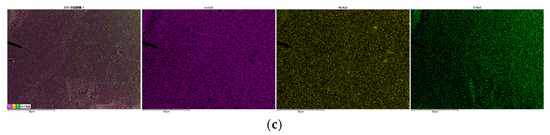
Figure 7.
EDS mapping of main elements of oxygen carriers: (a) LaFe, (b) LaFe1-xNix and (c) LaNi.
The Ni addition in LaFe (LaFe1-xNix) would change the phase patterns of oxygen carriers and the results were shown in Figure 8. For the LaFe oxygen carrier (x = 0), the perovskite phase of LaFeO3 was the only observable compound, and it would exhibit a lower full oxidation reactivity during toluene conversion. Therefore, negligible CO2 was formed when LaFe was used, as is shown in Figure 4. With x increased from 0.2 to 0.8, some LaFe0.9Ni0.1, La2O3, and NiO gradually appeared in addition to LaFeO3, and La4Ni3O10 was formed when x > 0.6. It indicates that excessive Ni addition would initiate complex competitive reactions, depending on Ni amount. Excessive Ni addition cannot be embedded into the perovskite structure of LaFeO3 but resulted in NiO. For the LaNi (x = 1) oxygen carrier, the mixed oxides of NiO and La4Ni3O10 rather than single perovskite were formed, and they would initiate the full oxidation of toluene and lower H2 yield.
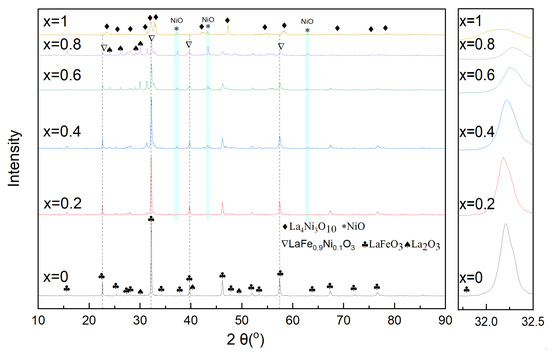
Figure 8.
Phase patterns of LaFe1-xNix oxygen carriers.
3.2.2. Effect of Ni Substitution on Toluene Conversion
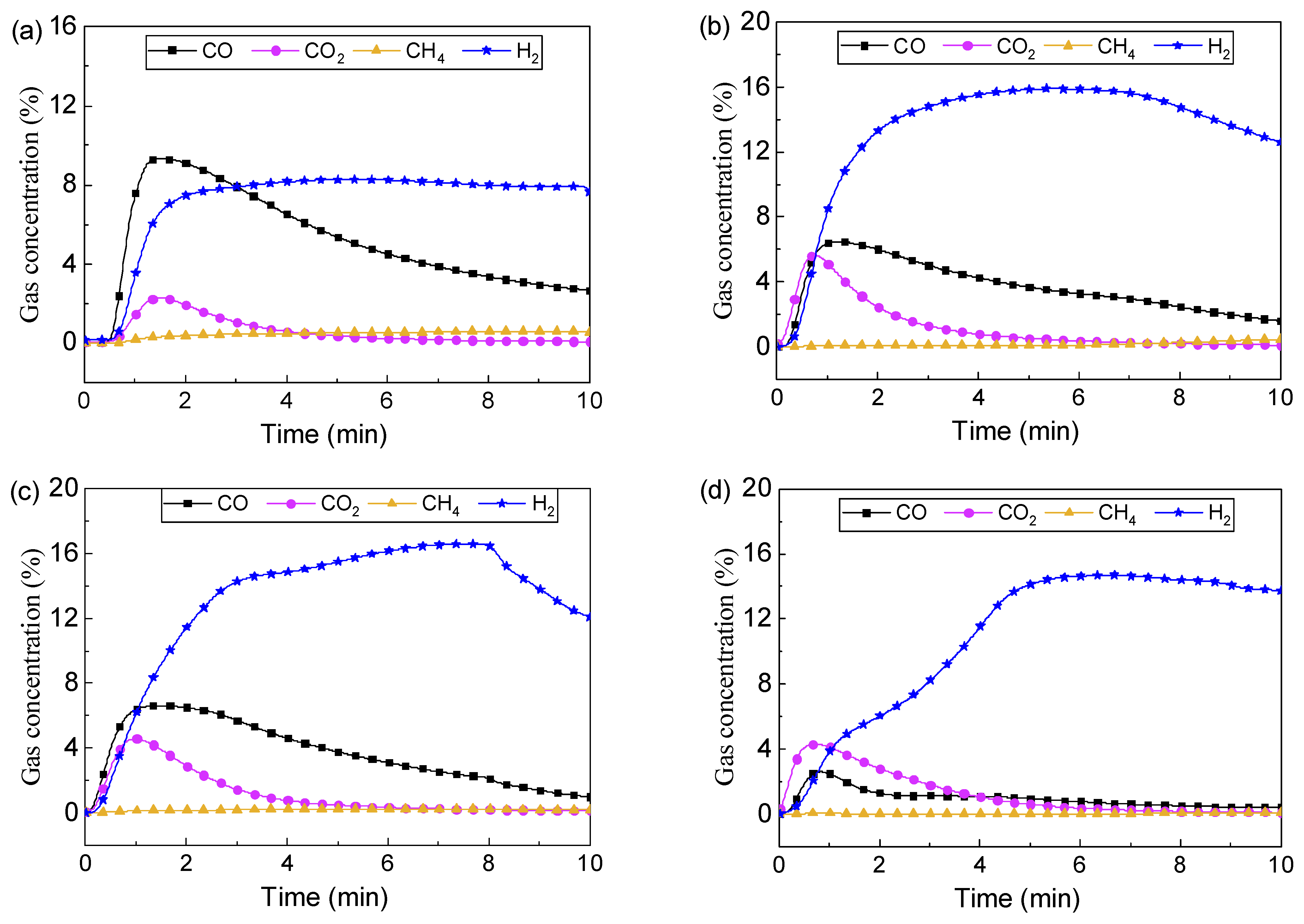
In this part, the performance of four LaFe1-xNix oxygen carriers was compared with LaFe and LaNi at 900 °C and the results are shown in Figure 9. When x = 0.2 (LaFe0.8Ni0.2), the gas products distribution was similar to that for LaFe. With x increasing to 0.4, 0.6, and 0.8, the partial oxidation was somewhat weakened due to less LaFeO3, while the initial oxidation of H2 into H2O was enhanced. However, the overall H2 yield was promoted, and the maximum H2 concentration (reached about 16%) was higher than that in the cases using LaFe and LaNi oxygen carriers. It should be ascribed to the synergistic effect of Fe and Ni in the oxygen carrier. Although not observed in the present investigation, Fe-Ni alloy could be formed in the oxygen carrier with the phase change of oxygen carrier during reactions. It is reported that the Fe-Ni alloy has a strong catalytic effect on CH4 conversion [35] and toluene conversion [36]. Furthermore, our previous paper also reported that the Ni-Fe both tuned oxygen carrier LaFe1-xNix exhibited better performance on CH4 conversion than LaFe or LaNi [37]. A decrease in H2 concentration was observed in the late reaction for these oxygen carriers. It could be ascribed to the serious carbon deposition which covered the catalytic center. Overall, the Fe and Ni tuned oxygen carrier LaFe1-xNix exhibited a strong catalytic effect on promoting toluene conversion.
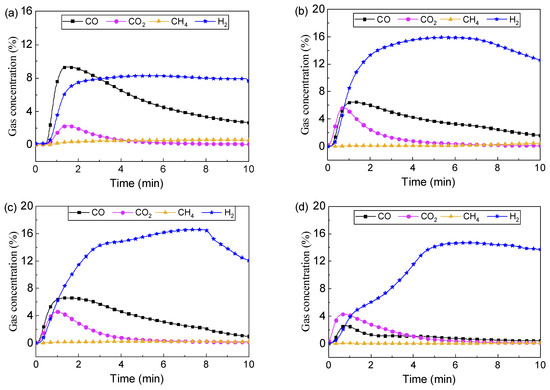
Figure 9.
Gas evolution during chemical looping toluene conversion using LaFe1-xNix at 900 °C: (a) LaFe0.8Ni0.2; (b) LaFe0.6Ni0.4, (c) LaFe0.4Ni0.6, (d) LaFe0.2Ni0.8.
3.2.3. Steam Enhanced Syngas Production
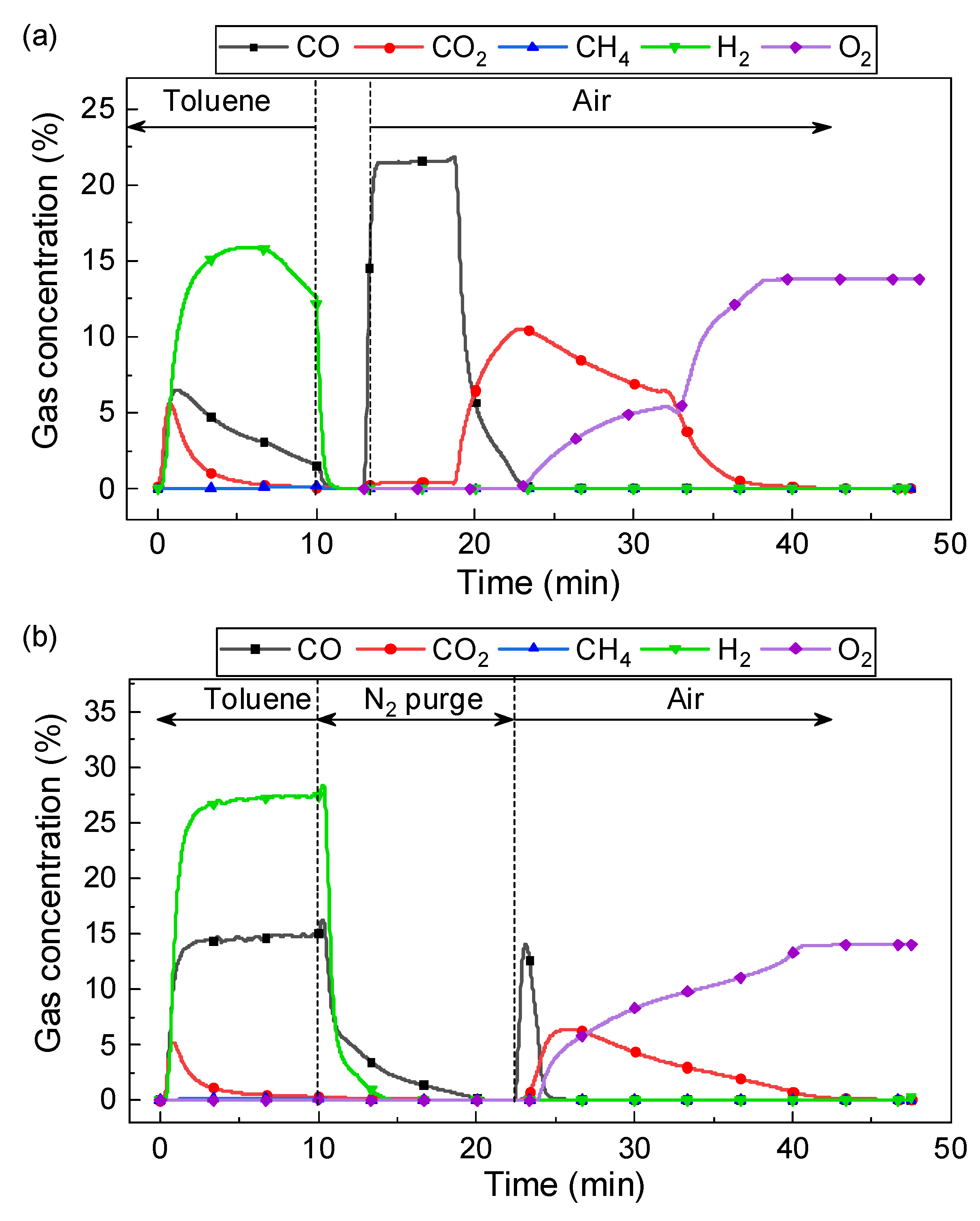
Though LaFeNi exhibited a good performance on toluene pyrolysis, the yield of H2 and C1 is still very low during the toluene step at 900 °C. The C1 yield was much lower than the H2 yield, which can be attributed to carbon deposition. Therefore, steam was added during the toluene step to enhance syngas yield. Figure 10 shows the gas production during 1 typical cycle of chemical looping conversion of toluene using LaFe0.6Ni0.4 at 900 °C with and without steam. Toluene conversion using LaFe0.6Ni0.4 at 900 °C without steam could be referred to Section 3.2.1. Since the Fe and Ni exhibited a catalytic effect on promoting toluene conversion, it would inevitably cause serious carbon deposition on the oxygen carrier. The carbon deposition inevitably covered the catalytic center and reduced toluene conversion during longtime operation. In the chemical looping process, the coke was oxidized by air to form CO and CO2 during the air step (Figure 10a). Due to a large amount of carbon deposition during the toluene step, only CO was formed in the initial 10 min of the oxidation. Afterward, CO2 and O2 appeared successively.
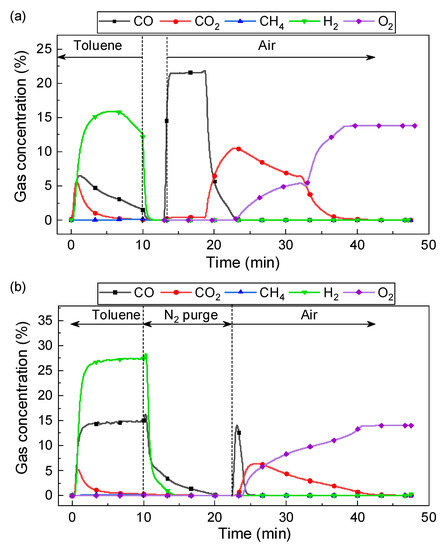
Figure 10.
Gas production during chemical looping conversion of toluene using LaFe0.4Ni0.6O3 at 900 °C: (a) In the absence of H2O, (b) In the presence of H2O.
Steam addition would obviously change the reaction, and the gas evolution is shown in Figure 10b. Two important reactions occurred at the presence of steam, i.e., carbon gasification (C + H2O = CO + H2) and water gas shift reaction (CO + H2O = CO2 + H2). Simultaneously, the presence of steam also caused the reforming of toluene or the intermediate CnH2m + nH2O = nCO + (m+n)H2. They would efficiently prevent coke formation, promoting CO and H2 yield. Correspondingly, the concentration of CO and H2 maintained over 15% and 27%, respectively. Additionally, the reduced oxygen carrier LaFeO3-x would also be oxidized by water splitting (LaFeO3-x + xH2O=LaFeO3 + xH2) [38]. The reduction of oxygen carrier and water splitting would set up an inner circulation of LaFeO3 in the fuel reactor, and it greatly depended on the amount of steam. The inner loop of the oxygen carrier made it as a catalyst enhancing the yield of C1 and H2. A sharp CO2 peak was observed in the initial toluene step, and it was ascribed to the full oxidation effect of oxygen carriers, probably due to the presence of NiO.
It is worth noting that considerable CO was observed during the N2 purging stage after the toluene step, and the duration was about 15 min. A similar phenomenon was not observed in the experiment without steam. Therefore, it should not be attributed to the residual gas product from the toluene step. The presence of steam would cause the recovery of lattice oxygen in the oxygen carrier to form LaFeO3. The lattice oxygen in the oxygen carrier will migrate to the surface where coke is deposited. Similar oxygen migration characteristics were also reported before [39]. As a result, it caused the solid-solid reaction between coke and oxygen carrier forming CO. Correspondingly, the concentration of CO and CO2 in the oxidation step was smaller than that in Figure 10a.
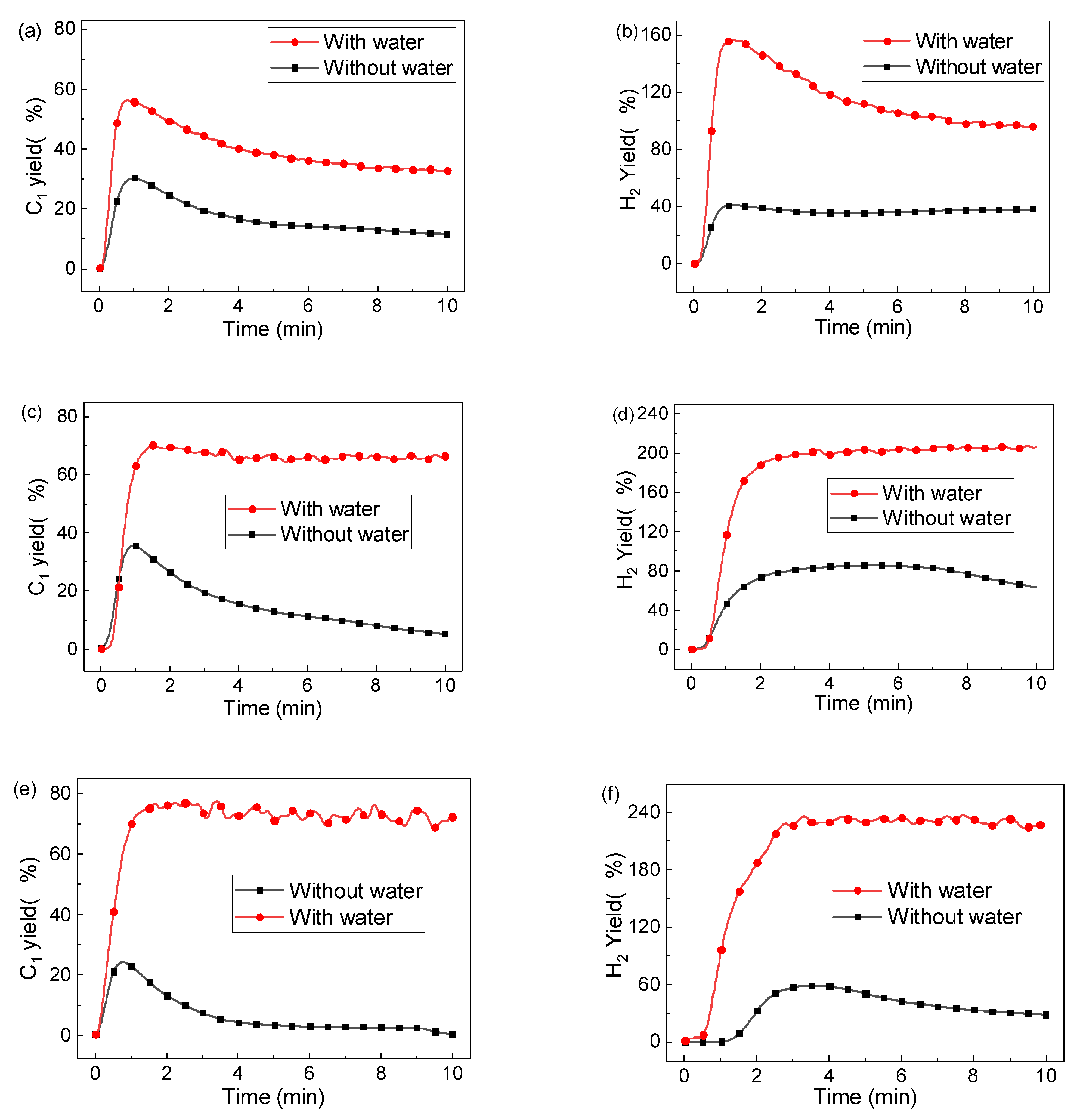
The effect of steam on toluene conversion was also carried out using other oxygen carriers, and Figure 11 compares the gas concentration using typical LaFe1-xNix at 900 °C with and without steam (S/C = 0.8). It can be seen that the steam addition promoted C1 yield to about 80%, and the H2 yield reached about 220%, depending on the Ni ratio in the oxygen carrier. A reactivity deterioration (decrease in C1 and H2 yield) with time was also observed for the LaFe rather than other oxygen carriers. For the Ni tuned oxygen carrier, the C1 and H2 yield tended to be stable during the whole reaction stage. It means that the Ni addition could promoted the 2CxHy + 2xH2O = 2xCO + yH2.
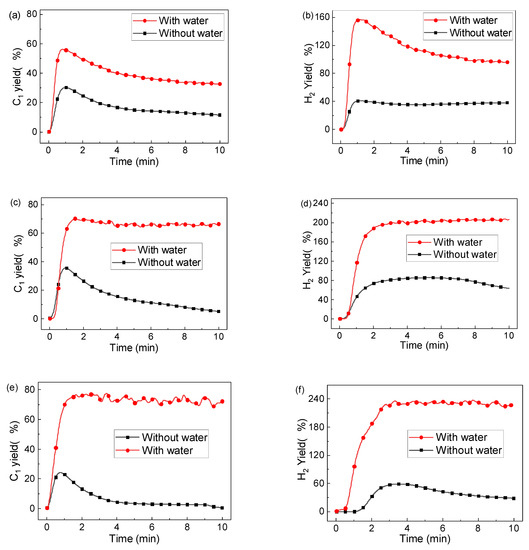
Figure 11.
C1 yield and H2 yield during chemical looping toluene conversion using different LaFeNi with and without steam at 900 °C: (a) C1 yield and (b) H2 yield for LaFe, (c) C1 yield and (d) H2 yield for LaFe0.6Ni0.4, (e) C1 yield and (f) H2 yield for LaNi.
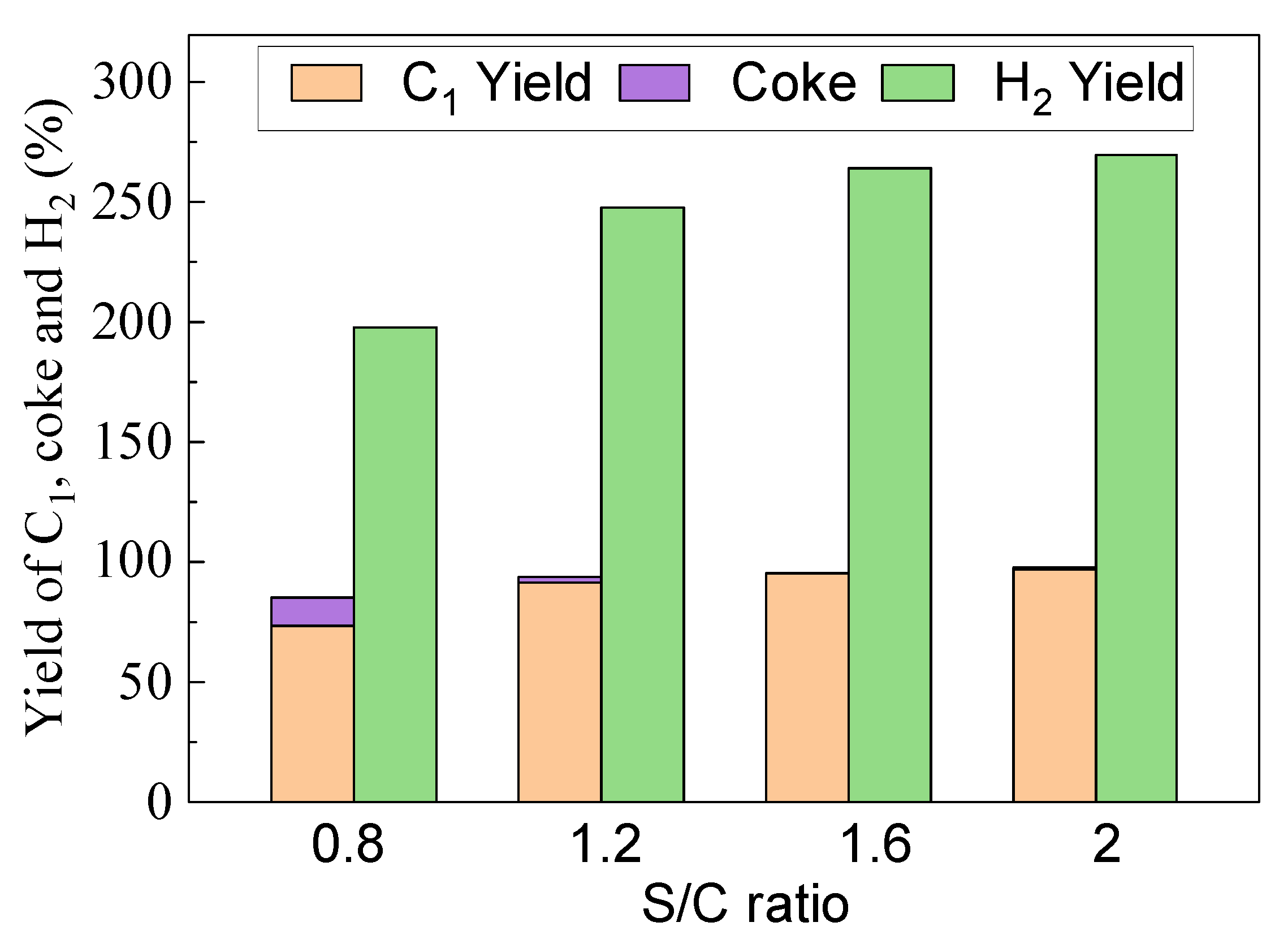
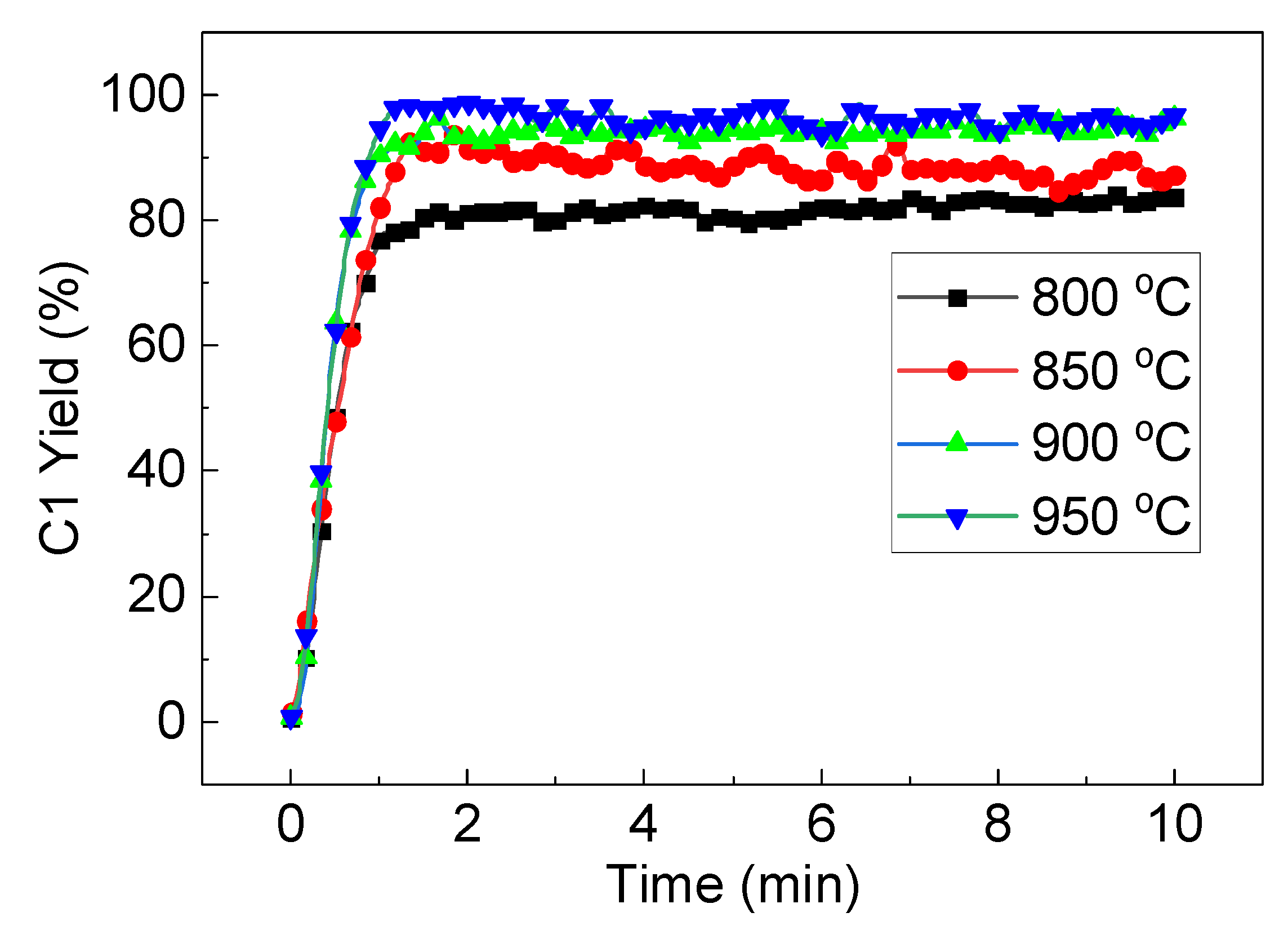
LaFe0.6Ni0.4 was selected to evaluate the effect of S/C, and Figure 12 compares the effect of the S/C ratio on carbon conversion and H2 production at 900 °C. With the S/C increasing from 0.8 to 2, both the C1 yield and H2 yield exhibited an increasing trend, while coke formation decreased. The C1 yield, coke formation and H2 yield were 73.9%, 11.4% and 197.9% at S/C=0.8, and they became 99%, 0.1% and 275.6% at S/C = 2. Although the oxygen carrier would catalyze toluene conversion and steam would further promote toluene conversion, the presence of steam would recovery the lattice oxygen in the oxygen carrier, which means that the lattice oxygen in the oxygen carrier was not consumed as a whole. Therefore, S/C < 1 was not enough for toluene conversion in theory. It would also result in serious coke formation, and coke yield was 11.4% at S/C = 0.8. With the progress of the reaction, more and more coke covered the active center of the oxygen carrier and reduced its catalytic activity. When S/C was greater than 1.2, the carbon deposition was almost eliminated by steam-reforming, resulting in a significant increase in the total conversion of toluene and H2 yield. When the S/C exceeded 1.6, the C1 yield and H2 yield even reached 96% and 265%, respectively. The further increase in S/C also decreased the residence time of toluene and its conversion. Therefore, S/C=1.6 was further selected to investigate the effect of temperature (800–950 °C) on C1 yield, and the results are shown in Figure 13. Since the steam reforming and carbon gasification are both intensively endothermic, and the elevated temperature can stably promote the toluene conversion into C1. C1 yield tended to stabilize at about 81% at 800 °C, and 96% at 900 °C. Further increase in temperature did not help too much for toluene conversion.
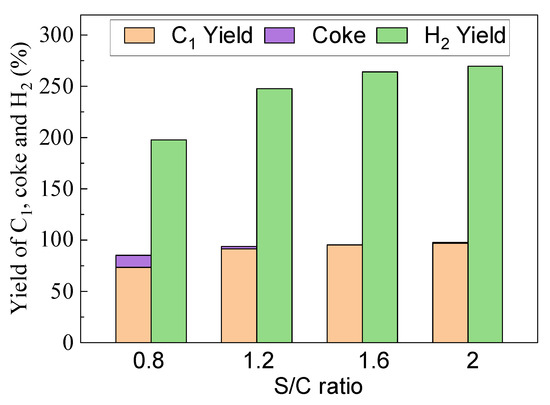
Figure 12.
Effect of S/C ratio on the yield of C1, Coke and H2 at 900 °C using LaFe0.6Ni0.4.
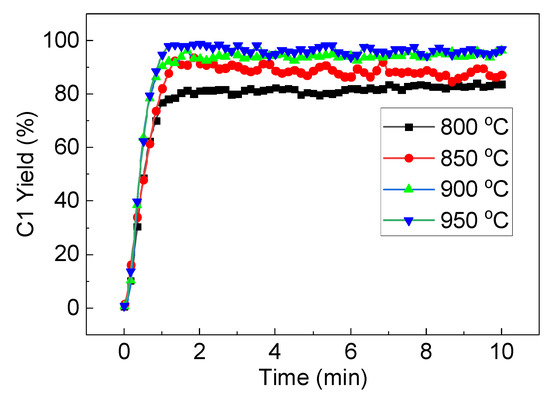
Figure 13.
C1 yield as a function of time versus time at typical temperature and S/C = 1.6.
3.3. Reactivity Stability of LaFe0.6Ni0.4
Reactivity stability is a key factor influencing the selection of oxygen carriers. 10 redox cycles of chemical looping toluene conversion were carried out to evaluate the cycle performance of LaFe0.6Ni0.4 at 900 °C and S/C = 1.6. Figure 14 shows the C1 yield, coke formation, and H2 yield during each cycle. With the cycle increasing, C1 yield and H2 yield firstly slightly decreased and then stabilized at about 95% and 264%. The coke yield maintained at a low value (<0.4%) during the whole cycle. A long time toluene duration (50 min) was also conducted, and C1 and H2 yield was also stable during the whole reaction stage. It indicates that that steam addition could restrain the carbon deposition and maintain an efficient toluene conversion into C1 and H2. Overall, the catalytic oxygen carrier exhibited a stable performance on toluene conversion with steam.
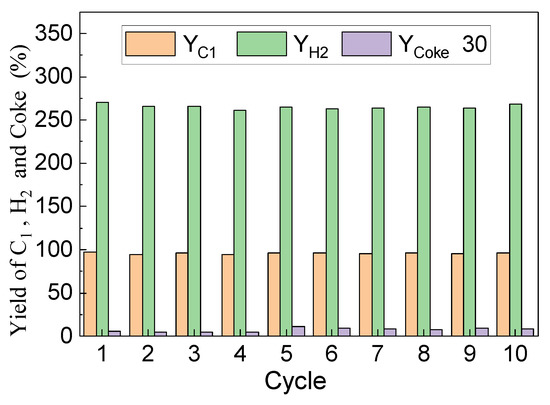
Figure 14.
Yield of C1, H2, and coke (×30) during chemical looping toluene conversion using LaFe0.6Ni0.4 with S/C = 1.6 at 900 °C.
4. Conclusions
The performance of the oxygen carrier is the key to the tar conversion during the chemical looping gasification of biomass. The in-situ conversion of toluene as a biomass tar compound using catalytic oxygen carrier of Ni-decorated LaFeO3 were investigated. The performance of LaM (M = Fe, Ni, Mn, Co, and Cu) with different transition metals was initially evaluated. LaFe (partial oxidation) and LaNi (catalytic pyrolysis) exhibited better reactivity on promoting syngas production than other oxygen carriers. Therefore, Ni-substituted ferrite LaFe1-xNix (x = 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1) was further developed to enhance the toluene conversion. The substitution of Ni (x > 0.4) significantly strengthened the H2 formation, too much Ni substitution would cause either over-oxidation or serious coke formation. Steam addition promoted the toluene steam reforming and carbon gasification, enhancing C1 and H2 yield, and Ni addition can further enhance the reactivity stability of oxygen carrier. With S/C increasing from 0.8 to 2.0, the C1 and H2 yield increasing from 74% to 97% and from 198 to 270%, respectively. The elevated temperature (800–900 °C) also exhibited a positive effect on C1 yield would further increasing C1 yield. A 10-cycle stable operation of chemical looping toluene conversion indicates that the LaFe0.6Ni0.4 has strong reactivity stability for toluene conversion at S/C=1.6 at 900 °C.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.G. and J.Y.; investigation, X.C., G.S., M.N. and S.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, H.G.; writing—review and editing, J.Y., X.C., G.S., M.N. and S.Z.; supervision, H.G. and J.Y.; project administration, H.G. and J.Y.; funding acquisition, H.G. and M.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, 51906100; Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, BK20191015; Science Foundation of Nanjing Institute of Technology, YKJ201608.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Carbon Dioxide. Available online: https://climate.nasa.gov/vital-signs/carbon-dioxide/ (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Ahmad, A.A.; Zawawi, N.A.; Kasim, F.H. Assessing the gasification performance of biomass: A review on biomass gasification process conditions, optimization and economic evaluation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 1333–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordgreen, T.; Liliedahl, T.; Sjostrom, K. Metallic iron as a tar breakdown catalyst related to atmospheric, fluidised bed gasification of biomass. Fuel 2006, 85, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Suzuki, K. Tar property, analysis, reforming mechanism and model for biomass gasification-An overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Andries, J.; Luo, Z.; Spliethoff, H. Biomass pyrolysis/gasification for product gas production: The overall investigation of parametric effects. Energy Convers. Manag. 2003, 44, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmuganandam, K.; Thanikaikarasan, S.; Anichai, J. Refining of producer gas using sand filters: An experimental study. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 4000–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, D.; He, X.; He, J.; Hong, L. Scrubbing of Syngas from MSW Pyrolysis–Volatile Re-forming Process with the Co-produced Oil to Remove Tar and Particulates. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 14312–14320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Rueda, Y.; Zaini, I.N.; Yang, W.; Helsen, L. Thermal tar cracking enhanced by cold plasma—A study of naphthalene as tar surrogate. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 208, 112540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, X.U.; Jia-Qing, L.I.; Xie, J.J.; Huang, Y.-Q.; Yin, X.-L.; Wu, C.-Z. Performance study on simultaneous tar removal and bio-syngas methanation by combining catalysis with nonthermal plasma. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2021, 49, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wei, X.; Li, J.; Che, D.; Liu, H.; Sun, B.; Wang, Q. Experimental Study on Product Gas and Tar Removal in Air–Steam Gasification of Corn Straw in a Bench-Scale Internally Circulating Fluidized Bed. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 1908–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.S.; Kim, J.W.; Seo, M.W.; Mun, T.-Y.; Kim, J.-S. Characteristics of two-stage air gasification of polystyrene with active carbon as a tar removal agent. Energy 2020, 219, 119681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsodikov, M.V.; Chistyakov, A.V.; Konstantinov, G.I.; Borisov, R.S.; Bondarenko, G.N.; Arapova, O.V. Microwave-Assisted Plasma Catalytic Conversion of Tar to Hydrocarbon Products. Pet. Chem. 2021, 61, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhani, B.; Kivevele, T.; Kihedu, J.H.; Jande, Y.A.C. Catalytic tar conversion and the prospective use of iron-based catalyst in the future development of biomass gasification: A review. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2020, 6, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, E.; Kopa, J. Efficient removal of tar from gas fraction resulting from thermo-chemical conversion of biomass using coal fly ash–based catalysts. Renew. Energy 2021, 171, 1290–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.W. A review of dolomite catalyst for biomass gasification tar removal. Fuel 2020, 267, 117095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, X.; Gu, J.; Shi, J. Co-gasification of coal and biomass blends using dolomite and olivine as catalysts. Renew. Energy 2019, 132, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wei, J.; Bai, Y.-H.; Song, X.-D.; Su, W.-G.; Yu, G.-S. Effect of alkali metal occurrence on the pyrolysis behavior of rice straw. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2021, 49, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Memon, M.; Ji, G.; Yang, X.; Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Song, Y.; Raheem, A.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H. Alkali metal bifunctional catalyst-sorbents enabled biomass pyrolysis for enhanced hydrogen production. Renew. Energy 2020, 148, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, D.K.B.; Veksha, A.; Lim, T.; Lisak, G. Highly active and poison-tolerant nickel catalysts for tar reforming synthesized through controlled hydrothermal synthesis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 607, 117779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Salisu, J.; Quan, C.; Williams, P. Modified nickel-based catalysts for improved steam reforming of biomass tar: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 145, 111023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shan, R.; Gu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y. Pyrolysis municipal sludge char supported Fe/Ni catalysts for catalytic reforming of tar model compound. Fuel 2020, 279, 118494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Su, Y.; Zhu, S. Construction of Fe embedded graphene nanoshell/carbon nanofibers catalyst for catalytic cracking of biomass tar: Effect of CO2 etching. Fuel 2021, 305, 121552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Guo, T.; Liu, C. Effects of Cu and Fe Additives on Low-Temperature Catalytic Steam Reforming of Toluene Over Ni/AC Catalysts. Catal. Surv. Asia 2019, 23, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Ueki, Y.; Yoshiie, R.; Naruse, I.; Wang, F.; Han, Z.; Xu, G. Recent progress in tar removal by char and the applications: A comprehensive analysis. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2020, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; He, F.; Zheng, A. Synthesis gas production from biomass gasification using steam coupling with natural hematite as oxygen carrier. Energy 2013, 53, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samprón, I.; Diego, L.; García-Labiano, F.; Izquierdo, M.T.; Abad, A.; Adánez, J. Biomass chemical looping gasification of pine wood using a synthetic Fe2O3/Al2O3 oxygen carrier in a continuous unit. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condori, O.; de Diego, L.F.; Garcia-Labiano, F.; Izquierdo, M.T.; Abad, A.; Adánez, J. Syngas production in a 1.5 kWth biomass chemical looping gasification unit using Fe and Mn ores as the oxygen carrier. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 17182–17196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Li, C.; Guo, Q.; Dang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Lee, D.-J.; Yang, Y. Syngas production by chemical-looping gasification of wheat straw with Fe-based oxygen carrier. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Yan, J.; Shen, L.; Bai, H. Performance and mechanism study of LaFeO3 for biomass chemical looping gasification. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 11151–11166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Liu, W.; Sun, R.; Jiang, S.; Wang, S.; Shen, L. Chemical looping catalytic gasification of biomass over active LaNixFe1-xO3 perovskites as functional oxygen carriers. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 36, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; An, X.; Zhao, S.; Dang, J.; Wang, W. Application of calcium oxide/ferric oxide composite oxygen carrier for corn straw chemical looping gasification. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 125011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zeng, L.; Tian, H.; Li, X.; Gong, J. Enhanced lattice oxygen reactivity over Ni modified WO3-based redox catalysts for chemical looping partial oxidation of methane. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 3548–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Neal, L.M.; Li, F. Li-promoted LaxSr2–xFeO4-d core-shell redox catalysts for oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane under a cyclic redox scheme. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 7293–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehlschlaeger, M.A.; Davidson, D.F.; Hanson, R.K. Thermal decomposition of toluene: Overall rate and branching ratio. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2007, 31, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Haribal, V.P.; Qi, H.; Liu, X.; Hong, H.; Jin, H.; Li, F. Mixed conductive composites for ‘low-temperature’ thermo-chemical CO2 splitting and syngas generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 13173–13182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zheng, A.; Deng, Z.; Wei, G.; Zhao, K.; Chen, D.; He, F.; Zhao, Z.; Li, H.; Li, F. In-situ removal of toluene as a biomass tar model compound using NiFe2O4 for application in chemical looping gasification oxygen carrier. Energy 2020, 190, 116360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, S.; Jiang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Gu, H.; Neal, L.; Li, F. LaNixFe1-xO3-δas a Robust Redox Catalyst for CO2 Splitting and Methane Partial Oxidation. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 13921–13929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, H.; Zhu, X.; Wei, Y.; Zheng, M.; Luo, Y. Designed oxygen carriers from macroporous LaFeO3 supported CeO2 for chemical-looping reforming of methane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 202, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Kang, F.; Qiu, Y.; Cui, D.; Li, M.; Ma, L.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, R. Iron oxides with gadolinium-doped cerium oxides as active supports for chemical looping hydrogen production. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).