Featured Application
Since this research achieved high efficiency of Ti:sapphire lasers in which all components including Ti:sapphire crystals are easily commercially available, these results should help increase the utility of Ti:sapphire lasers and expand their practical range of applications.
Abstract
Despite the importance of improving the efficiency of lasers in order to expand their utility range, the improvement of the efficiency of Ti:sapphire lasers has not progressed due to their high crystal losses. Therefore, we improved the efficiency of CW Ti:sapphire lasers by high-intensity pumping, which is one of the most effective methods of suppressing the efficiency reduction due to losses. Using a easily commercially available 0.25 wt.%, figure of merit (FOM) 200 Ti:sapphire crystal, optics and a pump source, we achieved an optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 32.4% with a slope efficiency of 42.5% at an incident pump power of 5.0 W which corresponds the maximum pumping intensity of . Furthermore, we ensured the reliability of our theoretical analysis by reproducing the experimental results. From this reliable theory, double-pass pumping and increasing the pump power to 25 W resulted in the highest optical-to-optical conversion and slope efficiencies for the incident pump power of 55.9% and 59.6%, respectively, at a high intrinsic residual loss of 4.0%. Even if losses doubled or deviated from the optimum condition for the highest efficiency, the efficiency reduction due to these factors was only a few percent. These results show that with high-intensity pumping, lasers with efficiencies well exceeding half of the quantum limit can be achieved even if all components, including Ti:sapphire crystals, are easily commercially available.
1. Introduction
Ti:sapphire crystals have become the most widely used gain materials for tunable and ultrashort pulse lasers, owing to their broad gain bandwidth [,]. Ti:sapphire lasers have many applications; however, most of these applications are limited to basic research [,,]. Achieving high efficiency without the use of special elements that are expensive or not commercially available and difficult to purchase is one criterion for extending the range of applications to practical use. Lowering the required pump power by increasing the efficiency will not only reduce the size and cost but also improve its reliability.
Table 1 compares the properties of Ti:sapphire lasers [,,,,,,,,,,]. Although the pulse widths approach the bandwidth limit of the gain medium, their optical-to-optical conversion efficiencies for the incident pump power remain extremely low, only a few percent [,,]. To increase the efficiency of ultrashort pulse lasers, it is first necessary to increase the efficiency of the underlying continuous-wave (CW) lasers. Therefore, it is important to increase the efficiency of CW lasers close to their quantum efficiency of approximately 70%, which is the efficiency limit. However, the disadvantages of Ti:sapphire crystals in improving laser efficiencies are higher losses and smaller products of the emission cross-section and fluorescence lifetime . The efficiency reduction due to losses is particularly high in gain media with small products, such as Ti:sapphire crystals. Therefore, usage of low-loss Ti:sapphire crystals with a high figure of merit (FOM) as laser gain media easily enables high efficiency. However, the loss increases with a higher doping concentration of Ti3+-ions, and the maximum FOM becomes lower as the doping concentration increases. The loss also does not reach a negligibly low level even when the doping concentration is reduced within the range where the pump absorption is sufficient for lasing [,,,,,,,,,]. According to our investigation, the maximum FOM of normally commercial crystals is approximately 200 at a -ion doping concentration of 0.25 wt.%. To purchase low-loss crystals with FOM exceeding 250 (from CRYTUR [], OPTOGAMA [], CASTECH [], NEWLIGHT Photonics []) or 300 (from Altechna [], Roditi [], EKSMA OPTICS [], Opt City [], CRYiNK []), special orders must be placed with crystal growth companies. This makes them extremely expensive, if available at all.

Table 1.
Comparison of Ti:sapphire lasers. These efficiencies are for the incident pump power to the gain medium.
Regarding high-efficiency CW Ti:sapphire lasers, first, in 1991, Harisson et al. achieved a high optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 28.0% and a high slope efficiency of 32.0% by Ar-ion laser-pumping with unknown FOM []. The highest optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 35% and slope efficiency of 40% of Ar-ion-laser-pumped CW Ti:sapphire lasers were achieved by Pinto et al. in 1994 []. However, they used extremely low-loss commercially unavailable crystals with a high FOM of 1000, which were obtained through collaboration with Union Carbide. Since Union Carbide’s products do not currently contain Ti:sapphire crystals, such extremely low-loss crystals would not be available, even if specially ordered []. They used crystals with a -ion doping concentration of 0.1 wt.%, but the FOM available at this concentration is generally less than approximately 400 [,,,,,,,,,] and, of course, low-loss crystals with such FOM must be specially ordered []. The highest efficiencies among fiber-laser-based SHG laser-pumped CW Ti:sapphire lasers were achieved by Samanta et al. in 2012 []. Using Ti:sapphire crystals with a FOM of 270 or higher, which may be easily commercially available, they achieved an optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of approximately 24% and a slope efficiency of 32.9%.
In 2018, we obtained an optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 31.7% and slope efficiency of 41.2% at a low pump power of 3.5 W [,]. These efficiencies were obtained by high-intensity pumping using commercially available crystals. To our knowledge, the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 31.7% is the highest in experiments using commercially available crystals up to that time. For the first time since either 28.1% in 1991 or approximately 24% in 2012, the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of CW Ti:sapphire lasers using commercially available crystals has been updated. In addition, for the first time since 1994, the new, highest slope efficiency has been updated despite the use of commercially available crystals. In 2021, the efficiencies of Ti:sapphire lasers with injection seeding and high pump power were updated by Takano et al. []. Using high pump powers of more than 20 W, high optical-to-optical conversion efficiencies of approximately 40% or higher (seeding power included) were obtained. The slope efficiency was also as high as 51% in the high pump power range of over 11 W. As of 2022, the highest optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of commercially available CW Ti:sapphire lasers is around 22% or less [].
Thus, here, we propose a method to increase the efficiencies of Ti:sapphire lasers, in which all components are commercially available, by high-intensity pumping. First, we report an experiment on a high-efficiency CW Ti:sapphire laser using commercially available crystals with high-intensity pumping. In this experiment, the obtained optical-to-optical conversion efficiency is 32.4% and the slope efficiency is 42.5%. Furthermore, we have succeeded in confirming the reliability of our theoretical analysis by theoretically reproducing the experimental results. From our reliable theory, by double-pass pumping through the gain medium and increasing the pump power to 25 W, we confirmed that the highest optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 55.9% and slope efficiency of 59.6% can be achieved using high-loss crystals. The analysis also shows that even if the experimental conditions deviate from the optimum, the efficiency reduction is limited to a few percent. These efficiencies are not only the highest among Ti:sapphire lasers, they are so high that they well exceed over half of the quantum limit of the Ti:sapphire lasers of approximately 70%.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment
Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of the Ti:sapphire laser. We employed a simple x-fold laser cavity, which is commonly used for ultrashort pulse laser oscillators. The laser cavity comprises two concave mirrors M1 and M2 (radius of curvature (R) = 100 mm) with dichroic coating, a high reflectance plane end mirror M3 and a plane output coupler M4. These mirrors were purchased from Layertec and are shown in the catalog. We used a 5-mm-long, Brewster-cut Ti:sapphire crystal (GT ADVANCED TECHNOLOGIES []) with a -ion doping concentration of 0.25 wt.% and a FOM of 200 (measured by the manufacturer). The Ti:sapphire crystal was mounted on a copper heat sink and cooled at a room temperature of approximately 20 degrees Celsius.
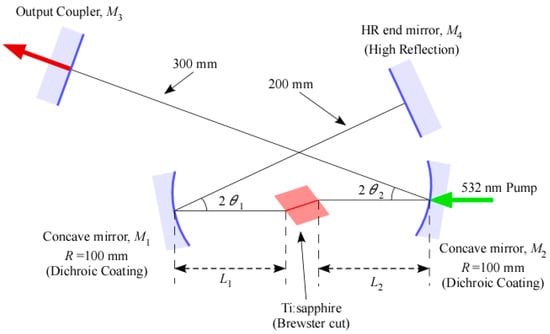
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the CW Ti:sapphire laser. The arm angles of concave mirrors M1 and M2 are and , respectively. The distances from the end faces of the Ti:sapphire crystal and the concave mirrors M1 and M2 are L1 and L2, respectively.
An intracavity-frequency-doubled Nd:YVO4 laser (Spectra-Physics Millennia Pro) was used as the SHG laser pump source for high-intensity pumping. Since the two curvature mirrors are dichroic coated, it is considered that the pump beam passes through the gain medium almost only once. The pump absorption efficiency of the Ti:sapphire crystal at the pump wavelength of 532 nm was measured to be 90.5% for single-pass pumping. If the pump beam is passed twice through the gain medium, the pump absorption efficiency can be increased up to 99.1%. The double-pass pumping can be achieved by reflecting and focusing the pump beam transmitted from the concave mirror M1 back into the gain medium or by using a highly reflective concave mirror M1 and end mirror M4 for the laser and pump beams. This increase in the pump absorption efficiency is effective for further increasing the laser efficiencies.
The pump beam was focused at the center of the crystal. The beam qualities of the pump beam were measured to be 1.0 for the vertical and horizontal axes. The spot radii were measured to be 10.1 μm and 18.3 μm for the vertical and horizontal axes, respectively. The maximum pump power in the experiment was 5.0 W, and the corresponding maximum pump intensity was approximately 860 kW/cm2.
The reasons for this high pump intensity are as follows: First, increasing the laser efficiencies by high-intensity pumping is particularly useful for lasers with gain media such as Ti:sapphire crystals, which have high losses and a small product of emission cross-section and fluorescence lifetime. With high-intensity pumping, we have already achieved the highest optical-to-optical conversion and slope efficiencies in continuous-wave lasers [,] and pulsed lasers in the nanosecond range [,,] using Yb:YAG crystals at room temperature. These efficiencies obtained by high-intensity pumping are close to the quantum limit of the gain medium and are higher than the efficiencies of lasers using other methods that are considered advantageous for higher efficiency, lasers with the gain medium cooled to cryogenic temperatures, thin-disk lasers and fiber lasers.
The maximum pump intensity of those Yb:YAG laser experiments was above . For Ti:sapphire crystals, the product of emission cross-section and fluorescence lifetime is one order of magnitude smaller than that for Yb:YAG crystals. Therefore, in order to obtain a gain of the same order of magnitude as that of the Yb:YAG crystal in the Ti:sapphire crystal, the pump intensity was set to a value one order of magnitude higher than that of the Yb:YAG crystals. In order to lower the pump threshold by high-intensity pumping, the mode volume of the pump beam in the crystal should be minimized. The appropriate pump spot radii in the crystal are 12.2 μm for both the vertical and the horizontal axes, which deviate from the experimental values. Therefore, if the pump spot radii are adjusted to the optimum values, the pump threshold should be much lower than that in this experiment.
2.2. Theory
In the theoretical analysis, we used 4-level laser rate equations with CW pumping, which incorporate the spatial distribution of the pump and laser beams [,,]. First, for simplicity, the incident pump power to the gain medium is nondimensionalized as
and the laser output power is also nondimensionalized as
where the gain medium length is , pump quantum efficiency is , pump photon energy is , laser photon energy is , output coupler transmission is T, total loss of the laser cavity is , laser mode volume in the gain medium is and sum of the localized Boltzmann distribution of the upper and lower laser levels is f.
The optical-to-optical conversion efficiency for the incident pump power is defined by the ratio between the laser output power and incident pump power and is obtained from the ratio between the normalized intracavity laser power and normalized incident pump power derived from Equations (1) and (2) as
where the coupling efficiency between the laser output and intracavity laser powers is defined by
and the atomic quantum efficiency is defined by
The slope efficiency for the incident pump power is also defined by the derivative of the laser output power with respect to the incident pump power and is obtained from Equations (1) and (2) by
where the mode-matching efficiency between the laser and pump beams is defined by the derivative of the normalized intracavity laser power with respect to the normalized pump power by
From Equation (6), it can be seen that the slope efficiency is proportional to the coupling efficiency and mode-matching efficiency , as is well known.
During steady-state laser oscillation, from the condition that the power amplified inside the cavity is equal to the power lost, the relationship between the normalized pump power and the normalized intracavity laser power is obtained by
where the pump distribution function and laser distribution function are normalized by the volume integral inside the gain medium as
These distribution functions and are defined by the spot positions, radii and beam qualities of the pump and laser beams. In the analysis, the pump distribution function was assumed to be a Gaussian beam profile with the same spot position and beam qualities as the experiment. Since the saturation of the pump absorption should disappear when the laser oscillates, the dependence of the pump distribution function on the direction of the beam propagation was assumed to decay exponentially. The absorption coefficient was obtained from the experiment. As for the laser distribution function , it was assumed to be a Gaussian beam profile with the same focusing position as the pump beam and beam qualities of 1.0. Since gain saturation must occur when the laser oscillates, the dependence of the laser distribution function on the direction of the beam propagation was assumed to be constant.
The laser output power and optical-to-optical conversion efficiency as functions of the incident pump power were obtained by using these equations. Therefore, the pump and laser distribution dependence of the laser output power and optical-to-optical conversion efficiency can be obtained from the theory. This means that, more specifically, we can obtain the pump and laser spot radii dependence of the laser output power and optical-to-optical conversion efficiency .
While the normalized intracavity laser power is zero at the pump threshold , the normalized pump threshold is obtained from Equation (8) as
where is the effective mode volume between the pump and laser beams in the gain medium and is defined by
From Equation (9), the pump threshold is obtained as
Equation (12) shows the pump threshold is proportional to the total loss and the effective mode volume , as is well known. The physical parameters of the gain medium, e.g., the emission cross-section of 28 × and the lifetime of 3.2 μs, rely on the material data from []. The crystal length, -ion doping concentration and FOM were identical to those in the experiment (measured by the manufacturer).
The intrinsic residual loss of the laser cavity used in the analysis was 4.0%, which was obtained from the Caird analysis []. The reasons for using the result of the Caird analysis are as follows: In general, there are two known methods for obtaining the intrinsic residual loss of the laser cavity, one by Findlay and Clay [] and the other by Caird []. The Findlay and Clay analysis uses the assumption that the effective mode volume of the pump and laser beams remains unchanged when the pump threshold is changed by changing the cavity loss. The Caird analysis, on the other hand, uses the assumption that changing the coupling efficiency changes the slope efficiency, which in turn changes the laser intensity inside the cavity, but does not change the mode-matching efficiency. As explained below in Section 3, in general, the effect of thermal lensing on beam propagation is often non-negligible under high-intensity pumping. Therefore, the effective mode volume may change significantly depending on the pump power. Hence, changing the output coupler transmittance to change the cavity loss and the pump threshold could also change the effective mode volume. This means that the conditions that satisfy the reliability of the Findlay and Clay analysis may not be maintained. On the other hand, the slope efficiency is almost constant in our experiment, as shown below in Figure 2, even though the beam propagation could vary due to thermal lensing effects. This means that even if the laser intensity in the gain medium could vary due to variation in beam propagation, the mode-matching efficiency remained almost constant. In this case, the laser intensity in the gain medium is changed also by changing the coupling efficiency by changing the output coupler transmittance; however, the mode-matching efficiency is expected to remain almost constant. Namely, in our experiments, the conditions that satisfy the reliability of the Caird analysis are considered to hold, so we used the results of the analysis.
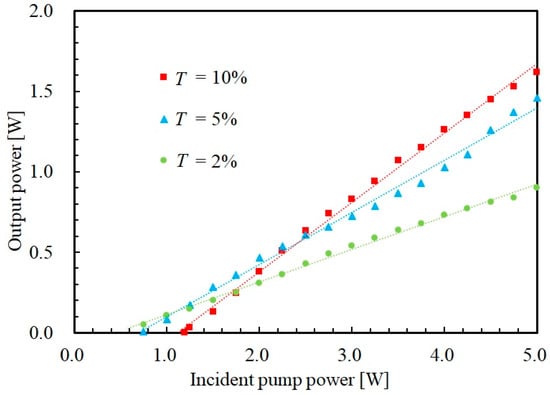
Figure 2.
Laser output power as a function of the incident pump power for various output coupler transmittances (). The dashed lines represent the linear fit of the experimental data.
3. Experimental Results
We measured the Ti:sapphire laser output power for various output coupler transmittances. To obtain the highest output power at the maximum incident pump power of 5.0 W with an output coupler transmittance of 10%, the laser cavity condition was optimized by adjusting the arm angles and and the distances from the crystal and mirrors and , as shown in Figure 1. The laser output beams were measured to have an almost Gaussian beam profile. Figure 2 shows the laser output power as a function of the incident pump power. As shown in Figure 2, these functions representing the input–output characteristics of the laser are almost linear, and this linearity is evident at the output coupler transmittance of 10%. At the output coupler transmittance of 10%, a pump threshold of 1.19 W and maximum output power of 1.62 W were measured. The highest optical-to-optical conversion and slope efficiencies for the incident pump power were 32.4% and 42.5%, respectively, obtained at the maximum pump power.
To increase the laser efficiencies, thermo-optic effects caused by the heat generated during the pumping process [], which affect the beam propagation in the gain medium, should be considered. When considering the Taylor expansion of the thermo-optic distortion of the optical length as a function of distance from the optical axis, the thermal lensing effect is a second-order effect [,]. In other words, thermal lensing is equivalent to an ideal quadratic distribution medium and does not degrade the beam quality of the Hermite–Gaussian mode, which is the eigenmode of the secondary distribution medium [,,,,].
In our experiments, the laser beam radii inside the gain medium where the thermo-optic effect occurs are able to be considered to be less than several tens of micrometers (as mentioned below in Section 4). These radii are small enough that higher-order terms than the second-order term can be neglected. Furthermore, since the laser and pump beams can be regarded as coaxial (if they were not coaxial, the input–output characteristics of the laser would not be almost linear as shown in Figure 2), the system is inversely symmetric with respect to this optical axis, so the odd-order terms in the distance can be ignored. Therefore, in our experiments, the thermo-optic distortion can be approximated by the lowest second order and can be considered as a thermal lensing effect. For reference, this approximation holds true whether the thermo-optic distortion is high or low.
The effect of thermal lenses on the cavity mode is that of varying the beam diameter by changing or shifting the stability region of the cavity. Therefore, thermal lenses affect both the laser cavity and pump modes, but generally the effect on the cavity mode is higher. In general, for the above reasons, thermal lenses could affect the mode-matching efficiency between the laser and the pump beams. The slope efficiency is proportional to the mode-matching efficiency between the laser and the pump beams. Consequently, the thermal lenses could affect the slope efficiency. Therefore, in general, the slope efficiency is not constant when the thermal lens effect varies as the pump power increases.
In our experiment, the maximum pump intensity was approximately , which corresponds to a thermal focusing length of a few millimeters when the gain medium is approximated by a thin lens and the intensity is extremely high in experiments with solid-state lasers, including Ti:sapphire lasers. In general, under these high pumping intensity conditions, the influence of the thermal lens effect on the laser cavity mode is considered to be often high. Nevertheless, the slope efficiency in the experiments was almost constant, as shown in Figure 2. This shows that the mode-matching efficiency was also almost constant. This means that while the effect of thermal lenses on the laser and pump modes could be high, the variation in thermal lenses with varying pump power is considered to have a low effect on the variation of the mode-matching efficiency and therefore to have a low effect on the variation of the slope efficiency as well. Namely, in our experiments, while the thermal lens effects on the laser and pump modes might be high, the thermal lens effect on the mode-matching efficiency is considered to be almost constant. One possible reason for this is that by adjusting the pump focusing position, the arm angles and the distances between the gain medium and the curvature mirrors, we were able to align the laser beam focus to the center of the thermal lens in the gain medium. This may allow us to suppress some variation in the thermal lensing effect on beam propagation and made it relatively easy to align the cavity for higher laser efficiency.
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison between the Experiment and the Theory
We theoretically analyzed and reproduced the experimental results of the output coupler transmittance of 10%, in which the highest efficiency was obtained, to confirm the reliability of our theoretical analysis described in Section 2.2. In this analysis, we used the same pump parameters as in the experiment: the same pump spot radii, focus positions, beam qualities and pump absorption efficiency at the pump wavelength of 532 nm (obtained in the experiments). First, we calculated the laser spot radii dependence of the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency . Figure 3 shows the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency as a function of the laser spot radii for the vertical and horizontal axes with the output coupler transmittance of 10% at the maximum pump power of 5.0 W. Figure 3 also shows the red dashed contour line that afforded the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 32.4%, which is the highest experimentally obtained efficiency with the output coupler transmittance of 10% at the maximum pump power. As shown in Figure 3, the optimum laser spot radii for the highest optical-to-optical conversion efficiency were 12 μm and 21 μm for the vertical and horizontal axes, respectively. The optimum spot radii were almost the same for other output coupler transmittances. The optimum spot radius in the vertical axis is approximately 20% larger than the pump beam radius in the same axis, and the optimum spot radius in the horizontal axis is approximately 15% larger than the pump beam radius in the same axis. These laser spot radii dependencies of the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency were employed in the theoretical analysis, and the experimental and theoretical results were compared.
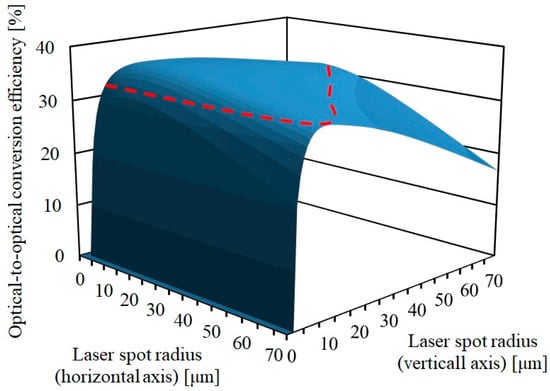
Figure 3.
Optical-to-optical conversion efficiency versus laser spot radii with the output coupler transmittance at the maximum pump power of 5.0 W. The red dashed line is the contour line that afforded the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 32.4%, which is the highest experimentally obtained efficiency with the output coupler transmittance of 10%.
As shown in Figure 3, the spot radii dependence of the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency is relatively low in the high-efficiency region. The comparison between the theory and the experiment in Figure 3 indicates that the laser spot radii in the experiment were considered to deviate extremely from the optimal radii for the highest efficiencies. Nevertheless, in these experiments, higher efficiencies than before have been obtained to the best of our knowledge. This should be another reason why the slope efficiency is almost constant in the experiments, as shown in Figure 2. This means that even if the laser spot radii could vary by variation of thermal lens effects, the variation of slope efficiency is also low in the range of high optical-to-optical conversion efficiencies because of the low variation of optical-to-optical conversion efficiencies in this range.
This low laser spot radii dependence of the efficiency is obtained from the high-intensity pumping. In general, when the output coupler transmittance is optimized to obtain the highest efficiency, the internal cavity laser intensity is lower than that at lower output coupler transmittances. However, under conditions of high-intensity pumping, it is easy to keep the internal cavity laser intensity high even when the output coupler transmittance is set to conditions of optimum coupling efficiency in order to obtain the highest efficiency. As a result, as shown in Figure 3, the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency in the high laser efficiency region did not vary much as the laser spot radii in the gain medium varied, because the induced emission remained strong enough in the high laser efficiency region.
Figure 4 compares the experimental and theoretical dependencies of laser output power on incident pump power. The laser spot radii in the theory in Figure 4 were optimized for the highest optical-to-optical conversion efficiency. These optical-to-optical conversion efficiencies, slope efficiencies and pump thresholds are compared in Table 2. From the theory, with the output coupler transmittance of 10%, the pump threshold was 0.42 W and the maximum output power was 1.89 W at the maximum pump power of 5.0 W. The highest optical-to-optical conversion and slope efficiencies were 37.8% and 41.3%, respectively. The highest optical-to-optical conversion efficiency in the experiment is 5.4% lower than that in the theory, the highest slope efficiency in the experiment is 1.2% higher than that in the theory, and the pump threshold in the experiment is approximately 3 times higher than that in the theory.
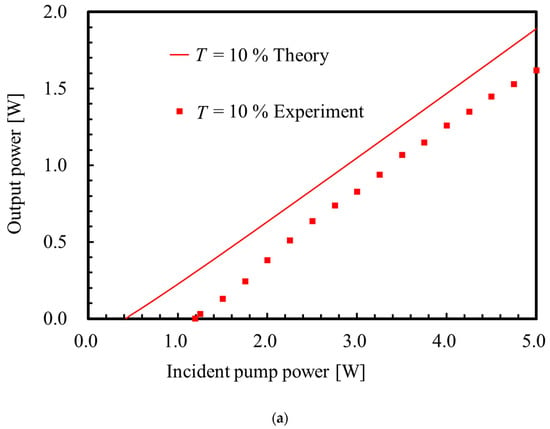
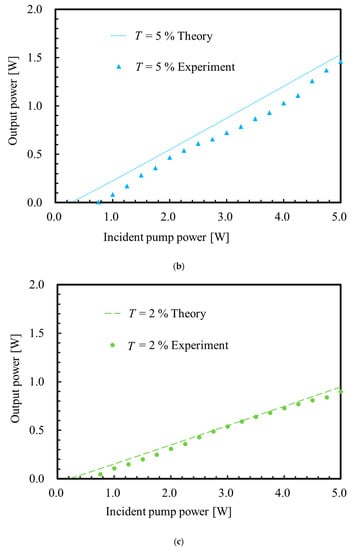
Figure 4.
Experimental and theoretical laser output powers as functions of the incident pump power. (a) The output coupler transmittance . The red squares show the experimental results and the red solid line shows the theoretical results. (b) The output coupler transmittance . The blue squares show experimental results and the blue dotted line shows theoretical results. (c) The output coupler transmittance . The green circles show the experimental results and the green dashed line shows the theoretical results.

Table 2.
Comparison of the experiment and the theory of the highest optical-to-optical conversion efficiencies () and the corresponding slope efficiencies () and pump thresholds ().
In general, the slope efficiency is proportional to the coupling efficiency inside and outside the laser cavity, and the mode-matching efficiency between the laser and the pump beam and the pump threshold is proportional to the total cavity loss and the effective mode volume of the laser and pump beam. Therefore, there was a high probability that the mode-matching efficiency is almost appropriate for the highest efficiencies, however, the effective mode volume in the experiment was approximately 3 times larger than the optimum volume. The reason for the difference between the experimental effective mode volume and the theoretical optimum effective mode volume may be due to the deviation of the laser spot radius from the optimum value for high efficiency, as shown in Figure 3. These results mean that it is possible that the efficiencies can be further improved by lowering the pump threshold by a factor of 3 through optimization of the laser spot radii.
Figure 5 shows the laser output powers as functions of the incident pump power using the contour line region laser spot radii in Figure 3 with the output coupler transmittance of 10%. As shown in Figure 5, the pump threshold and slope efficiency vary depending on the laser spot radii. The reason for the variation, even though the highest optical-to-optical conversion efficiencies at the maximum pump power of 5.0 W were the same, is that the effective mode volume and mode-matching efficiency vary with the laser spot radii. In the contour line region where the laser spot radii vary, the highest slope efficiency is 42.1% and the lowest slope efficiency is 40.2%. The maximum pump threshold is 1.16 W and the minimum pump threshold is 0.98 W. In the contour range, the variation in the threshold and slope efficiency, i.e., the variation in the effective mode volume and mode-matching efficiency, is smaller than that in the case of laser-diode pumping []. This is because the pump intensity in this SHG laser pumping experiment is extremely high compared to its laser diode pumping case and consequently the laser intensity inside the cavity is also high.
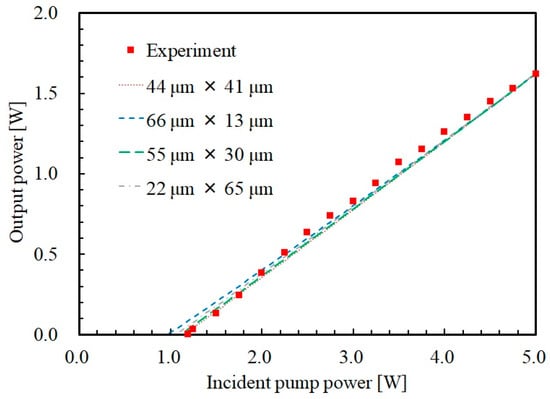
Figure 5.
Experimental and theoretical output powers as functions of the incident pump power with the output coupler transmittance . The red squares show the experimental results. The lines show theoretical results with the laser spot radii (vertical × horizontal axes). The black dotted line, the blue fine dashed line, the green dashed line and the gray single-dashed line correspond to the results for vertical and horizontal laser spot radii of 44 μm and 41 μm, 66 μm and 13 μm, 55 μm and 30 μm and 22 μm and 65 μm, respectively.
Furthermore, Figure 5 shows that the experimental results reproduced using the theoretical analysis under appropriate laser spot radii were selected. The laser spot radii at the same slope efficiency as in the experiment were 44 μm on the vertical axis and 41 μm on the horizontal axis. In this case, the theoretical pump threshold was also almost the same as in the experiment, as shown in Figure 5. Therefore, this laser spot radius condition is considered to be the best reproduction of the experimental results. These laser spot radii obtained from these comparisons are approximately 3.7 times larger on the vertical axis and 2.0 times larger on the horizontal axis than the optimal laser spot radii for the highest optical-to-optical conversion efficiency.
Of course, these results do not mean that the laser spot radii were fixed at these values even if the pump power was varied in the experiment. For example, as shown in Figure 5, the deviation of the theory from the experiment is small even when the laser spot radius is 55 μm on the vertical axis and 30 μm on the horizontal axis. This is because of the fact that the laser spot radii dependence of the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency is lower in the region of high optical-to-optical conversion efficiency because of the high-intensity pumping, as mentioned before and shown in Figure 3. In other words, these results show that the input–output characteristics of the experiment can be obtained by varying the laser spot radii within these ranges.
4.2. Theoretical Analysis for Higher Efficiency
As explained above, our theory was in good agreement with the experimental results, and the discrepancy between the theoretical and experimental results was explained by the difference in the laser spot radii. In other words, we succeeded in confirming the reliability of our theory. From these results, we are able to provide a reliable theoretical analysis of how to further improve the efficiency of SHG laser-pumped CW Ti:sapphire lasers through optimization by high-intensity pumping. This analysis was conducted under the same crystal conditions and beam qualities as above. The pump spot radii, which were chosen to minimize the effective mode volume for high-intensity pumping, were 12.2 μm for both the vertical and horizontal axes. The pump absorption efficiencies were selected to be 90.5% for the single-pass pumping, the same as in the experiment, and 99.1% for the double-pass pumping. The intrinsic residual losses were selected to be 4.0%, the same as that obtained in the experiment, and 8.0%, twice as high as that obtained in the experiment. The reason for assuming twice as much loss as in the experiment is to include loss due to the insertion of wavelength-selective elements and mode-locking. In general, these losses can be kept within the range of assumed loss values with sufficient adjustments. The maximum pump powers were selected to be 10.0 W, the maximum output power of Spectra-Physics Millennia Pro, and 25.0 W, the maximum output power of Spectra-Physics Millennia eV [].
Figure 6 compares the input–output characteristics for single-pass pumping and double-pass pumping under these conditions, and Table 3 compares the corresponding highest efficiencies. In Figure 6a, the intrinsic residual loss of the laser cavity is 4.0%, and we optimized the output coupler transmittance and the laser spot radii to improve the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency at the maximum pump power of 10.0 W. An output coupler transmittance of 31.0% was selected for the single-pass pumping, and 32.6% was selected for the double-pass pumping. The laser spot radii were selected to be 14 μm for both the vertical and horizontal axes for both pumping conditions. For the single-pass pumping, the highest optical-to-optical conversion and slope efficiencies were obtained at the maximum pump power and were 46.5% and 51.1%, respectively. For the double-pass pumping, the highest optical-to-optical conversion and slope efficiencies were increased over those for single-pass pumping, at 51.2% and 57.4%, respectively.
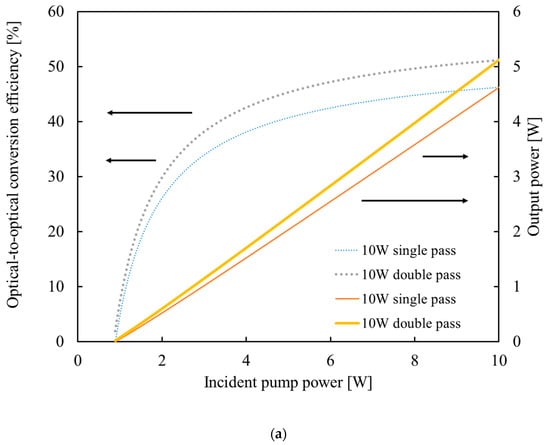
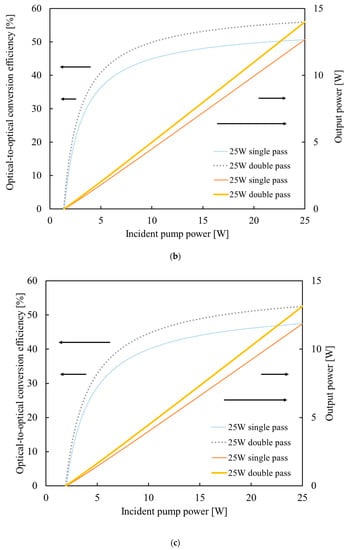
Figure 6.
Theoretical laser output powers and optical-to-optical conversion efficiencies as functions of the incident pump power. The thin blue dotted lines and thin red solid lines show the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency and output power for single-pass pumping, respectively. The bold gray dotted lines and bold orange solid lines show the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency and output power for double-pass pumping. The pump spot radii were optimized to obtain the minimum mode volume of the pump beam, which was 12.2 μm in both the vertical and horizontal directions. The laser spot radii were also optimized to obtain the highest optical-to-optical conversion efficiency at the maximum pump powers, which were 14 μm in both the vertical and horizontal directions. The optimization conditions for (a) were 10 W maximum pump power and 4.0% intrinsic residual loss, for (b) were 25 W maximum pump power and 4.0% intrinsic residual loss and for (c) were 25 W maximum pump power and 8.0% intrinsic residual loss.

Table 3.
Comparison of the highest optical-to-optical conversion efficiencies () and the corresponding slope efficiencies () and coupling efficiencies () under the optimization conditions of the maximum pump power, intrinsic residual loss and pumping pass (single or double).
In Figure 6b, the intrinsic residual loss is 4.0%, the same in Figure 6a, but we optimized at the higher maximum pump power of 25.0 W. We selected an output coupler transmittance of 51.3% for the single-pass pumping and 53.9% for the double-pass pumping. The highest optical-to-optical conversion and slope efficiencies were increased over those optimized at the maximum pump power of 10.0 W in Figure 6a. For single-pass pumping, the highest optical-to-optical conversion and slope efficiencies were 50.7% and 54.2%, respectively. For the double-pass pumping, the highest optical-to-optical conversion and slope efficiencies were increased at 55.9% and 59.6%, respectively.
In Figure 6c, the intrinsic residual loss is 8.0%, twice as high as that in Figure 6a,b, and we optimized at the maximum pump power of 25.0 W, the same in Figure 6b. We selected an output coupler transmittance of 70.3% for the single-pass pumping and 73.9% for the double-pass pumping. In Figure 6c, the highest efficiencies were of course reduced compared to those in Figure 6b because the intrinsic residual loss is twice as high as that in Figure 6b, but the reductions were limited to approximately 3%. The reason for the limitation of the reduction in the efficiencies is the high pump intensity. For the single-pass pumping, the highest optical-to-optical conversion and slope efficiencies were 47.5% and 52.1%, respectively. For the double-pass pumping, the highest optical-to-optical conversion and slope efficiencies were increased over those for single-pass pumping, at 52.5% and 57.4%, respectively. These efficiencies are higher than those optimized at the maximum pump power of 10.0 W with the intrinsic residual loss of 4.0% in Figure 6a.
The reasons why the highest efficiencies at the intrinsic residual loss of 8.0% in Figure 6c are higher than the highest efficiencies at the intrinsic residual loss of 4.0% shown in Figure 6a are as follows: First, the intrinsic residual loss of 8.0% in Figure 6c is twice the intrinsic residual loss of 4.0% in Figure 6a. In contrast, the maximum pump power of 25.0 W for the optimization condition in Figure 6c is 2.5 times the maximum pump power of 10.0 W for the optimization condition in Figure 6a. As indicated previously, in the analysis in Figure 6, the unsaturated gain is proportional to the pump power because the pump beam propagation is fixed. Thus, the ratio of the unsaturated gain of the optimization condition of 2.5 is higher than the ratio of the intrinsic residual loss of 2.0, so the highest efficiencies in Figure 6c are higher than the highest efficiencies in Figure 6a.
As shown in Table 3, high-intensity pumping resulted in optimum coupling efficiencies of approximately 90% or higher, even at high loss conditions of 4.0% to 8.0%, and these high coupling efficiencies are one of the reasons for very high efficiencies. These high optical-to-optical conversion and slope efficiencies are obtained from the theory that has been confirmed reliable as explained above. Optimum pump and laser spot radii are easily obtained by adjusting the focusing optics and controlling the stability region of the cavity. Furthermore, as explained in Section 4.1, in high-intensity pumping, it is easy to increase the laser intensity inside the resonator at the optimum coupling efficiency, so that even if the spot radii deviate from the optimum values, the efficiencies decrease only in a range of a few percent, as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 5. In other words, these efficiencies are sufficiently feasible experimentally because they are values obtained from our reliable theory, including the reduction in efficiency due to deviations from optimal conditions.
In general, insertion loss of wavelength-selective elements such as birefringent filters and Fabry–Perot etalons and loss due to SESAM and Kerr lens mode-locking for ultrashort pulse generation can be easily reduced to a few percent or less. Therefore, the efficiencies of wavelength-tunable lasers, narrowband lasers and ultrashort pulse lasers can be increased to the efficiencies shown in Figure 6 and Table 3. High-intensity pumping can also improve the efficiency of laser-diode-pumped Ti:sapphire lasers []. Hence, high-intensity pumping is one of the most effective techniques to increase the efficiency of wavelength-tunable, narrowband and ultrashort pulse lasers in which all components can be easily commercially available. For example, without the use of complex and expensive injection seeding, it is possible to achieve narrowband lasers with efficiencies in excess of 50% and output powers as high as 10 W or more. These results can be used to improve the utility of wavelength-tunable, narrowband and ultrashort pulse lasers by increasing their reliability and lowering their price, which have been issues with these lasers.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, by high-intensity pumping, we experimentally demonstrated a high-efficiency SHG laser-pumped CW Ti:sapphire laser in which all components, including a high-loss Ti:sapphire crystal, are easily commercially available. The optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 32.4% and the slope efficiency of 42.5% were obtained by single-pass pumping at the maximum pump power of 5.0 W. Furthermore, we have succeeded in confirming the reliability of our theoretical analysis by theoretically reproducing the experimental results for further improvement of the efficiency of Ti:sapphire lasers. Based on our reliable theory, even with a high intrinsic residual loss of 4.0%, the highest optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 55.9% and slope efficiency of 59.6% were obtained by increasing the maximum pump power to 25.0 W and double-pass pumping.
Even at the higher intrinsic residual loss of 8.0%, the highest optical-to-optical conversion and slope efficiencies were reduced to only approximately 3%. In general, insertion loss of wavelength-selective elements and loss due to mode-locking for ultrashort pulse generation can be easily reduced to a few percent or less. It was also theoretically confirmed that even if the conditions deviated from the optimum conditions for the highest efficiency, the decrease in efficiency would be on the order of a few percent. Therefore, the efficiency of wavelength-tunable, narrowband and ultrashort-pulsed Ti:sapphire lasers, in which all elements are easily commercially available, can be increased to well over half the quantum limit by high-intensity pumping. These results can be used to improve the utility of wavelength-tunable, narrowband and ultrashort pulse lasers and will lead to a transformation in their application fields from basic to practical.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.K.; data curation, T.K.; formal analysis, T.K.; funding acquisition, S.K.; investigation, T.K. and S.K.; methodology, S.K.; project administration, S.K.; resources, S.K.; software, T.K. and S.K.; supervision, S.K.; validation, T.K. and S.K.; visualization, S.K. and T.K.; writing—original draft, S.K. and T.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
A part of this research was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP25390123, JP21K04924; AMADA CO., LTD. (AF-2018223-B3); and the joint research project of the Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University (under contract subject “2016B1-KAWATO-1”).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Keisuke Hayashi for the experiments, Shinichi Matubara for providing the Ti:sapphire crystal and optical elements, Masashi Shibata, Toshiya Kato, Hiroki Goto, and Kazufumi Ueshima for the theoretical analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflict of interest to declare.
References
- Moulton, P.F. Ti-doped sapphire: Tunable solid-state laser. Opt. Photonics News 1982, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, P.F. Spectroscopic and laser characteristics of Ti:Al2O3. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1986, 3, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zipfel, W.; Shear, J.B.; Williams, R.M.; Webb, W.W. Multiphoton fluorescence excitation: New spectral windows for biological nonlinear microscopy. Appl. Phys. 1996, 93, 10763–10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartels, A. Ultrahigh-resolution ophthalmic optical coherence tomography. Opt. Lett. 1999, 46, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drexler, W.; Morgner, U.; Ghanta, R.K.; Kärtner, F.K.; Schumand, J.S.; Fujimoto, J.G. Ultrahigh-resolution ophthalmic optical coherence tomography. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, D.E.; Kean, P.N.; Sibbett, W. 60-fsec pulse generation from a self-mode-locked Ti:sapphire laser. Opt. Lett. 1991, 16, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, S.; Binhammer, T.; Harth, A.; Kim, J.; Ell, R.; Kärtner, F.X.; Morgner, U. Controlled waveforms on the single-cycle scale from a femtosecond oscillator. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 9739–9745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boquillon, J.P.; Musset, O. Flashlamp-pumped Ti:Sapphire laser: Influence of the rod figure of merit and Ti3+ concentration. Appl. Phys. 1994, 59, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.; Finch, A.; Rines, D.M.; Rines, G.A.; Moulton, P.F. Low-threshold, cw, all-solid-state Ti:A12O3 laser. Opt. Lett. 1991, 16, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.F.; Esterowitz, L.; Rosenblatt, G.H.; Kokta, M.; Peressini, D. Improved Ti:sapphire laser performance with new high figure of merit crystals. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1994, 30, 2612–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, G.K.; Kumar, S.C.; Devi, K.; Ebrahim-Zadeh, M. High-power, continuous-wave Ti:sapphire laser pumped by fiber-laser green source at 532 nm. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2011, 50, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanetake, T.; Hayashi, K.; Kadoya, H.; Inayoshi, S.; Kataoka, S.; Sugiki, F.; Nakajima, N.; Kobayashi, R.; Kawato, S. High efficiency continuous-wave Ti:sapphire laser. In Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, OSA Technical Digest (Online), San Jose, CA, USA, 13–18 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, M.; Kawashima, T.; Yamashita, M.; Kawato, S. Theoretical analysis of a high efficiency blue-laser-diode-pumped Ti:sapphire laser by high intensity pumping. Laser Phys. Lett. 2021, 18, 105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Ogawa, H.; Ohae, C.; Katsuragawa, M. 10 W injection-locked single-frequency continuous-wave titanium:sapphire laser. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 6927–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3900S, Spectra Physics. Available online: https://www.spectra-physics.com/en/f/3900s-ti-sapphire-laser (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- HEM® Ti:Sapphire Laser Optics Are Renowned for Their High Quality, Demanded by the World’s Top Ultrafast Laser Laboratories, GT Advanced Technologies. Available online: https://gtat.com/products/ti-sapphire/?utm_source=pocket_mylist (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Ti:Sapphire, Crytur. Available online: https://www.crytur.cz/materials/tisapphire/ (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Ti:sapphire Crystals, Optogama. Available online: https://4lasers.com/en/components/crystals/laser-crystals/ti-sapphire-crystals (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Ti:Sapphire, Castech. Available online: https://www.castech.com/product/Ti%3ASapphire---Titanium-Doped-Sapphire-99.html (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Ti:Sapphire Crystals, Newlight Photonics. Available online: https://www.newlightphotonics.com/Laser-Crystals/Ti-doped-Sapphire-Crystals (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Ti:SAPPHIRE Crystal, Altechna. Available online: https://www.altechna.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/ti-sapphire-white-paper-a4-05.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Ti:Sapphire Laser Crystals. The Roditi International Corporation Ltd. Available online: https://www.roditi.com/Laser/Ti_Sapphire.html (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Ti:Sapphire Crystals, Eksma Optics. Available online: https://eksmaoptics.com/nonlinear-and-laser-crystals/laser-crystals/ti-sapphire-crystals/ (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Ti:Sapphire Crystal, Opt City. Available online: https://www.optocity.com/TiSapphire.htm (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Ti:Sapphire, Crylink. Available online: https://www.laser-crylink.com/laser-products/laser-crystal/titanium-sapphire-crystal/ (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Products, Union Carbide Corporation. Available online: https://www.unioncarbide.com/products.html (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Matsubara, S.; Ueda, T.; Takamido, T.; Kawato, S.; Kobayashi, T. Nearly quantum-efficiency limited oscillation of Yb:YAG laser at room temperature. In Proceedings of the Advanced Solid-State Photonics; Technical Digest, Vienna, Austria, 6–9 February 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara, S.; Ueda, T.; Kawato, S.; Kobayashi, T. Highly efficient continuous-wave laser oscillation in microchip Yb:YAG laser at room temperature. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 46, L132–L134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, S.; Ueda, T.; Inoue, M.; Tanaka, M.; Otani, K.; Kawato, S.; Kobayashi, T. High efficiency cavity dumped operation of Yb:YAG laser at room temperature. In Proceedings of the Advanced Solid-State Photonics; Technical Digest, Incline Village, NV, USA, 20 January–1 February 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Takama, M.; Matsubara, S.; Ueda, T.; Inoue, M.; Tanaka, M.; Otani, K.; Kawato, S.; Kobayashi, T. Highly efficient nanosecond-pulse Yb:YAG laser. Smart Process. Technol. 2007, 2, 281–283. [Google Scholar]
- Nishio, M.; Maruko, A.; Inoue, M.; Takama, M.; Matsubara, S.; Okunishi, H.; Kato, K.; Kyomoto, K.; Yoshida, T.; Shimabayashi, K.; et al. High-efficiency cavity-dumped micro-chip Yb:YAG laser. In Proceedings of the SPIE 9238, Pacific Rim Laser Damage 2014: Optical Materials for High-Power Lasers, 92380K (22 September 2014), Yokohama, Japan, 22–24 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kubodera, K.; Otsuka, K. Single-transverse-mode LiNdP4O12 slab waveguide laser. J. Appl. Phys. 1979, 50, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, T.Y.; Byer, R.L. Medeling and CW Operation of a Quasi-Three-Level 946 nm Nd:YAG Laser. IEEE J. Quantum. Electron. 1987, 23, 605–612. [Google Scholar]
- Risk, W.P. Modeling of longitudinally pumped solid-state lasers. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1988, 5, 1412–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koechner, W. Solid State Laser Engineering, 5th ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Caird, J.A.; Payne, S.A.; Staver, P.R.; Ramponi, A.J.; Chase, L.L. Quantum electronic properties of the Na3Ga2Li3F12:Cr3+ laser. IEEE J. Quantum. Electron. 1988, 24, 1077–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, D.; Clay, R.A. Measument of internal losses in 4-level lasers. Phys. Lett. 1966, 20, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.D.; Osterink, L.M. Thermal effects in a Nd:YAG laser. J. Appl. Phys. 1970, 41, 3656–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koechner, W. Thermal lensing in a Nd:YAG laser rod. Appl. Opt. 1970, 9, 2548–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Innocenzi, M.E.; Yura, H.T.; Fincher, C.L.; Fields, R.A. Thermal modeling of continuous-wave end pumped solid-state lasers. Appl. Phys. 1990, 56, 1831–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millenia eV, Spectra Physics. Available online: https://www.spectra-physics.com/en/f/millennia-ev-cw-dpss-laser (accessed on 19 March 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).