Graphene-Based Functional Hybrid Membranes for Antimicrobial Applications: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Properties and Synthesis of Graphene
2.1. Physical and Chemical Properties
2.2. Synthetic Methods
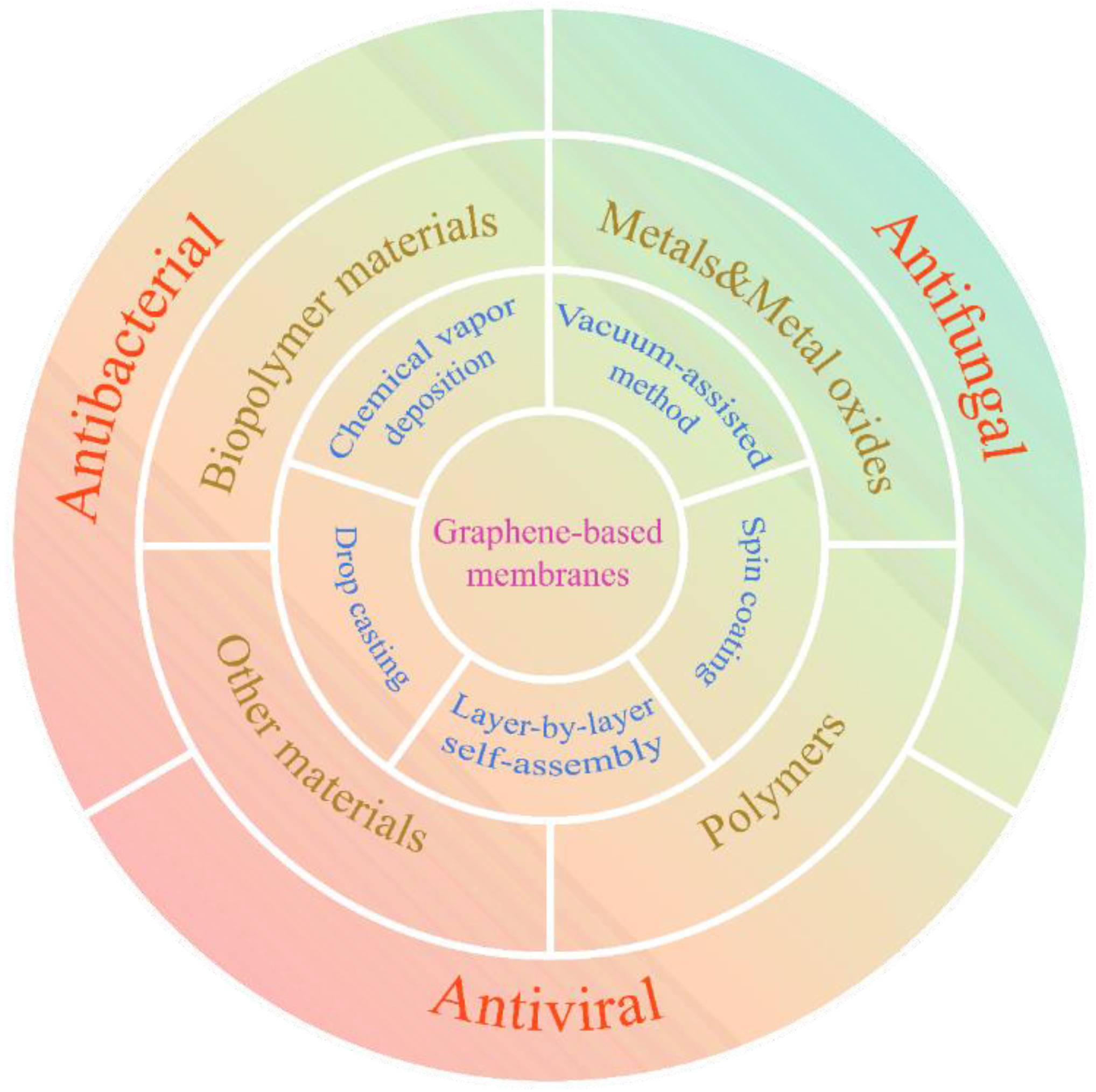
3. Fabrication Techniques of Graphene-Based Membranes
3.1. Chemical Vapor Deposition
3.2. Vacuum Filtration-Assisted Method

3.3. Spin Coating
3.4. Drop Casting
3.5. Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly
4. Functional Tailoring of Graphene-Based Membranes
4.1. Metals and Metal Oxides
4.2. Polymers
4.3. Biopolymers
4.4. Others
5. Antimicrobial Applications
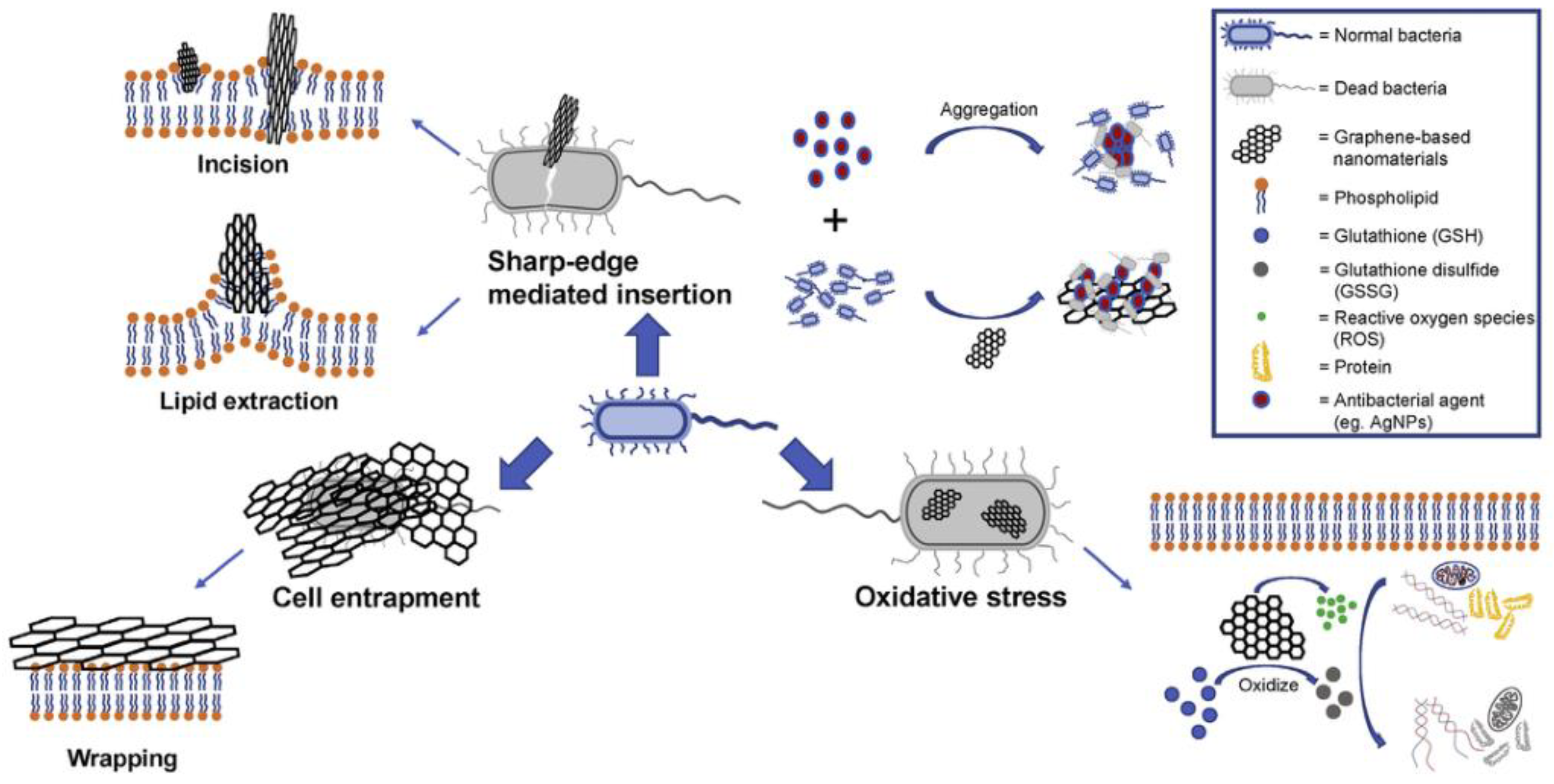
5.1. Antimicrobial Mechanism
5.1.1. Sharp Edge Cutting
5.1.2. Oxidative Stress
5.1.3. Cell Trapping
5.1.4. Parcel Isolation
5.2. Antibacterial Applications
5.3. Antiviral Applications
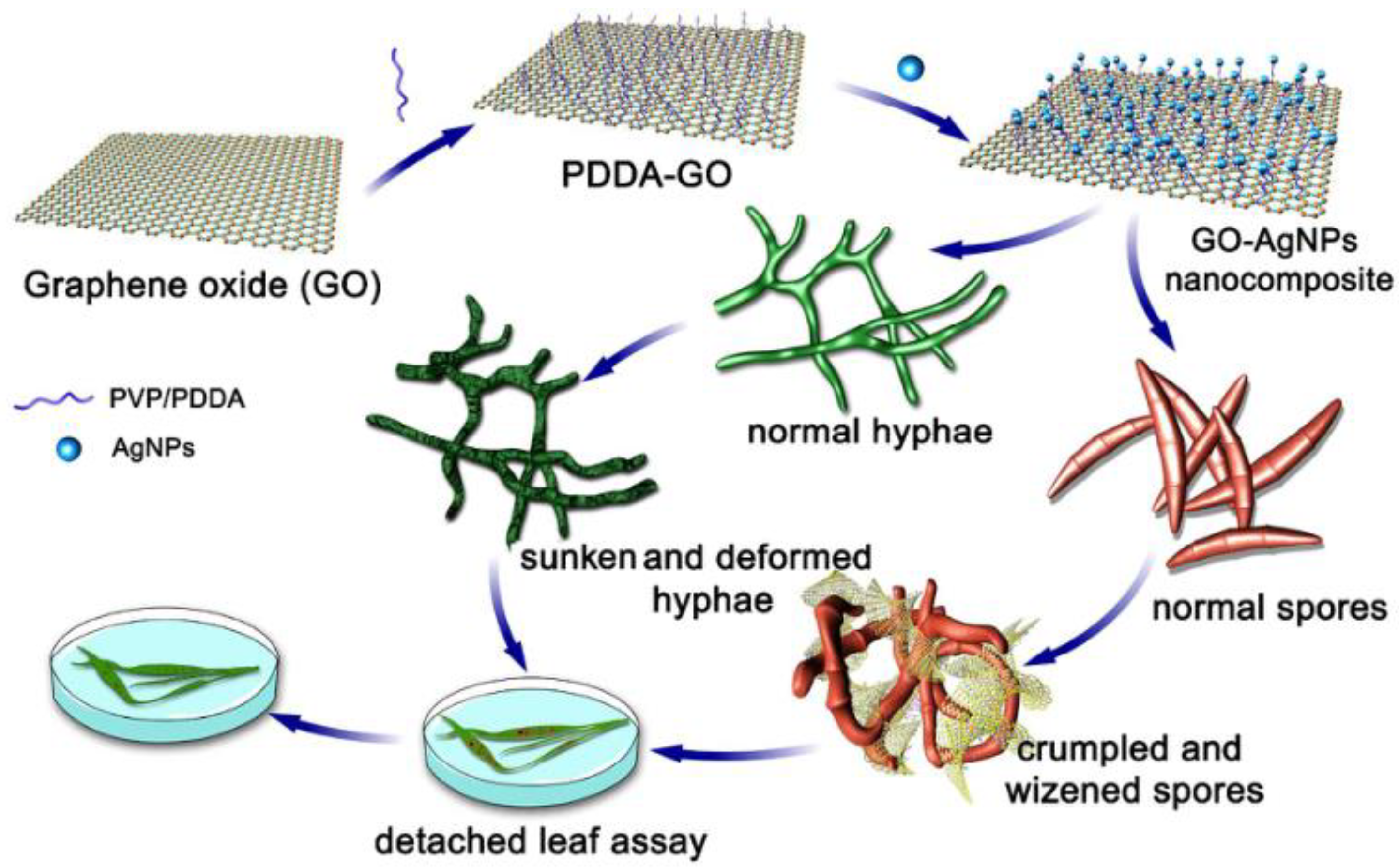
5.4. Antifungal Applications
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fatima, N.; Qazi, U.Y.; Mansha, A.; Bhatti, I.A.; Javaid, R.; Abbas, Q.; Nadeem, N.; Rehan, Z.A.; Noreen, S.; Zahid, M. Recent developments for antimicrobial applications of graphene-based polymeric composites: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 100, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.; Wang, Y.J.; Gao, Y.Y.; Gao, T.Y.; Gao, G. Chemical Insights into Antibacterial N-Halamines. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 4806–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegab, H.M.; ElMekawy, A.; Zou, L.; Mulcahy, D.; Saint, C.P.; Ginic-Markovic, M. The controversial antibacterial activity of graphene-based materials. Carbon 2016, 105, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweileh, W.M. Global research publications on irrational use of antimicrobials: Call for more research to contain antimicrobial resistance. Glob. Health 2021, 17, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Andrade, M.D.; Chata, G.; Rouholiman, D.; Liu, J.; Saltikov, C.; Chen, S. Antibacterial mechanisms of graphene-based composite nanomaterials. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, G.Z.; Liu, B.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wei, G. Two-dimensional material-based functional aerogels for treating hazards in the environment: Synthesis, functional tailoring, applications, and sustainability analysis. Nanoscale Horiz. 2022, 7, 112–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yin, W.; Gao, S.W.; Sun, Y.N.; Xu, P.L.; Wu, S.H.; Kong, H.; Yang, G.Z.; Wei, G. The Combination of Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials with Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Gas Sensors: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Pascual, A.M. Antibacterial Action of Nanoparticle Loaded Nanocomposites Based on Graphene and Its Derivatives: A Mini-Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Zetterlund, P.B. Strategies for reduction of graphene oxide—A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 127018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.T.; Kumar, N.; Krayev, A.; Chaigneau, M. In situ topographical chemical and electrical imaging of carboxyl graphene oxide at the nanoscale. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, Q.; Haidry, A.A.; Yao, Z.J.; He, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, L.C.; Xie, L.J. The critical role of hydroxyl groups in water vapor sensing of graphene oxide. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.Z.; Kong, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhu, D.Z.; Guo, L.; Wei, G. Recent advances in the hybridization of cellulose and carbon nanomaterials: Interactions, structural design, functional tailoring, and applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 279, 118947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ege, D.; Kamali, A.R.; Boccaccini, A.R. Graphene Oxide/Polymer-Based Biomaterials. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1700627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nanda, S.S.; Yi, D.K.; Kim, K. Study of antibacterial mechanism of graphene oxide using Raman spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaragalla, S.; Bhavitha, K.B.; Athanassiou, A. A Review on Graphene Based Materials and Their Antimicrobial Properties. Coatings 2021, 11, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Chen, J.R.; Teng, L.J.; Wang, L.; Zhu, G.L.; Liu, S.; Luo, Z.T.; Shi, X.T.; Wang, Y.J.; Ren, L. The Antibacterial Applications of Graphene and Its Derivatives. Small 2016, 12, 4165–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Dadashpour, M.; Hejazi, M.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Behnam, B.; de la Guardia, M.; Shadjou, N.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. Anti-bacterial activity of graphene oxide as a new weapon nanomaterial to combat multidrug-resistance bacteria. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, K.; Dixit, A.R. A review of the mechanical and thermal properties of graphene and its hybrid polymer nanocomposites for structural applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 5992–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuziel, A.W.; Milowska, K.Z.; Chau, P.L.; Boncel, S.; Koziol, K.K.; Yahya, N.; Payne, M.C. The True Amphipathic Nature of Graphene Flakes: A Versatile 2D Stabilizer. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2000608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Thanh, D.; Duc, D.N.; Thi, T.C.; Phuoc, H.L.; Dai, L.T.; Ngoc, M.P.; Van, C.N. Recent trends in preparation and application of carbon nanotube-graphene hybrid thin films. Adv. Nat. Sci.-Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 033002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Yang, S.H.; Deng, J.P.; Pan, K. Chiral Graphene Hybrid Materials: Structures, Properties, and Chiral Applications. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukowiak, A.; Kedziora, A.; Strek, W. Antimicrobial graphene family materials: Progress, advances, hopes and fears. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 236, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Sun, H.; Qu, X. Antibacterial applications of graphene-based nanomaterials: Recent achievements and challenges. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 105, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadarsini, S.; Mohanty, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Basu, S.; Mishra, M. Graphene and graphene oxide as nanomaterials for medicine and biology application. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2018, 8, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tashan, H.; Khosravi-Darani, K.; Yazdian, F.; Omidi, M.; Sheikhpour, M.; Farahani, M.; Omri, A. Antibacterial Properties of Graphene Based Nanomaterials: An Emphasis on Molecular Mechanisms, Surface Engineering and Size of Sheets. Mini-Rev. Org. Chem. 2019, 16, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbolina, I.; Woods, C.R.; Lozano, N.; Kostarelos, K.; Novoselov, K.S.; Roberts, I.S. Purity of graphene oxide determines its antibacterial activity. 2D Mater. 2016, 3, 025025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.X.; Ping, D.; Dong, X.F. Recent Developments of Graphene Oxide-Based Membranes: A Review. Membranes 2017, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musico, Y.L.F.; Santos, C.M.; Dalida, M.L.P.; Rodrigues, D.F. Surface Modification of Membrane Filters Using Graphene and Graphene Oxide-Based Nanomaterials for Bacterial Inactivation and Removal. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchanapally, R.; Viraka Nellore, B.P.; Sinha, S.S.; Pedraza, F.; Jones, S.J.; Pramanik, A.; Chavva, S.R.; Tchounwou, C.; Shi, Y.; Vangara, A.; et al. Antimicrobial Peptide-Conjugated Graphene Oxide Membrane for Efficient Removal and Effective Killing of Multiple Drug Resistant Bacteria. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 18881–18887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, J.; Ming, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, H.; Yu, B.; Wu, R.; Liu, X.; Bai, Y.; Yang, S.T. Toxicity of graphene oxide to white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, L.; Shi, G. Graphene-based smart materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhi, L. Graphene-Based Transparent Conductive Films: Material Systems, Preparation and Applications. Small Methods 2019, 3, 1800199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, N.; Gao, X.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Gao, C. A review of graphene-based separation membrane: Materials, characteristics, preparation and applications. Desalination 2018, 437, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranford, S.W.; Buehler, M.J. Packing efficiency and accessible surface area of crumpled graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 205451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Jia, L.; Mo, S.; Liu, Z. Ultrahigh specific surface area of graphene for eliminating subcooling of water. Appl. Energy 2014, 130, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Abidi, N.; Cabrales, L. Wettability and surface free energy of graphene films. Langmuir 2009, 25, 11078–11081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, P.C.; Borges, I.; Pinto, A.M.; Magalhães, F.D.; Gonçalves, I.C. Fabrication and antimicrobial performance of surfaces integrating graphene-based materials. Carbon 2018, 132, 709–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, D.G.; Kinloch, I.A.; Young, R.J. Mechanical properties of graphene and graphene-based nanocomposites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 90, 75–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, R.C.; Suter, J.L.; Coveney, P.V. Micromechanical exfoliation of graphene on the atomistic scale. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 5716–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, J.; Yi, D.; Niu, J.; Wu, M.; Lin, L.; Yin, R.; Li, M.; Zhou, J.; et al. Ultrafast epitaxial growth of metre-sized single-crystal graphene on industrial Cu foil. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Piner, R.D.; Kohlhaas, K.A.; Kleinhammes, A.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 2007, 45, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, K.K.H.; Huang, H.H.; Joshi, R.K.; Yoshimura, M. Chemical reduction of graphene oxide using green reductants. Carbon 2017, 119, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guex, L.G.; Sacchi, B.; Peuvot, K.F.; Andersson, R.L.; Pourrahimi, A.M.; Strom, V.; Farris, S.; Olsson, R.T. Experimental review: Chemical reduction of graphene oxide (GO) to reduced graphene oxide (rGO) by aqueous chemistry. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 9562–9571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhol, P.; Yadav, S.; Altaee, A.; Saxena, M.; Misra, P.K.; Samal, A.K. Graphene-Based Membranes for Water and Wastewater Treatment: A Review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 3274–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, M.; Bai, B. Molecular simulations on graphene-based membranes. Carbon 2019, 153, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Aamir, M.; Thebo, K.H.; Akhtar, J. Laminar Graphene Oxide Membranes Towards Selective Ionic and Molecular Separations: Challenges and Progress. Chem. Rec. 2020, 20, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Li, D. Graphene-based transparent conductive films with enhanced transmittance and conductivity by introducing antireflection nanostructure. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 325, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, G.Z.; Liu, B.; Kong, H.; Xiong, Z.; Guo, L.; Wei, G. Biomineralization of ZrO2 nanoparticles on graphene oxide-supported peptide/cellulose binary nanofibrous membranes for high-performance removal of fluoride ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskoro, F.; Wong, C.-B.; Kumar, S.R.; Chang, C.-W.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, D.W.; Lue, S.J. Graphene oxide-cation interaction: Inter-layer spacing and zeta potential changes in response to various salt solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, J.; Chung, T.-S. Layer-by-layer construction of graphene oxide (GO) framework composite membranes for highly efficient heavy metal removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 515, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayande, A.B.; Obaid, M.; Kim, I.S. Antimicrobial mechanism of reduced graphene oxide-copper oxide (rGO-CuO) nanocomposite films: The case of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, K.; Liu, G.; Matsuyama, H.; Jin, W. Graphene-based membranes for pervaporation processes. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Yoon, H.W.; Yoon, S.M.; Yoo, B.M.; Ahn, B.K.; Cho, Y.H.; Shin, H.J.; Yang, H.; Paik, U.; Kwon, S.; et al. Selective gas transport through few-layered graphene and graphene oxide membranes. Science 2013, 342, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chi, C.; Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Qian, Y.; Hu, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhao, D. Facile Preparation of Graphene Oxide Membranes for Gas Separation. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 2921–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, M.; De-La-Pinta, I.; Quindos, G.; Fernandez, M.J.; Fernandez, M.D. Synthesis, Physical, Mechanical and Antibacterial Properties of Nanocomposites Based on Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanoparticles. Polymers 2020, 12, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbari, A.; Sheath, P.; Martin, S.T.; Shinde, D.B.; Shaibani, M.; Banerjee, P.C.; Tkacz, R.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Majumder, M. Large-area graphene-based nanofiltration membranes by shear alignment of discotic nematic liquid crystals of graphene oxide. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Shen, S.; Xiao, L.; Jin, J.; Zhao, J.; Che, Q. Constructing multilayered membranes with layer-by-layer self-assembly technique based on graphene oxide for anhydrous proton exchange membranes. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 122, 109362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wan, D.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Stable LBL self-assembly coating porous membrane with 3D heterostructure for enhanced water treatment under visible light irradiation. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Bian, W.; Ji, S. Layer-by-layer self-assembly of polycation/GO nanofiltration membrane with enhanced stability and fouling resistance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 160, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, V.B.; Lau, K.-t.; Hui, D.; Bhattacharyya, D. Graphene-based materials and their composites: A review on production, applications and product limitations. Compos. Part B 2018, 142, 200–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Meng, F. Recent advances in graphene-based films for electromagnetic interference shielding: Review and future prospects. Carbon 2021, 180, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Graphene family nanomaterials (GFNs)—promising materials for antimicrobial coating and film: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, F. Anti-bacterial properties of ultrafiltration membrane modified by graphene oxide with nano-silver particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 484, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Gao, B.; Wang, Y.; Jin, B.; Yue, Q.; Wang, Z. Antibacterial thin film nanocomposite reverse osmosis membrane by doping silver phosphate loaded graphene oxide quantum dots in polyamide layer. Desalination 2019, 464, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Uliana, A.A.; Tian, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Volodin, A.; Simoens, K.; Yuan, S.; Li, J.; et al. Mussel-Inspired Architecture of High-Flux Loose Nanofiltration Membrane Functionalized with Antibacterial Reduced Graphene Oxide-Copper Nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28990–29001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadikhah, H.; Naderi Kalali, E.; Khodi, S.; Xu, X.; Agathopoulos, S. Multifunctional Thin-Film Nanofiltration Membrane Incorporated with Reduced Graphene Oxide@TiO2@Ag Nanocomposites for High Desalination Performance, Dye Retention, and Antibacterial Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 23535–23545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lv, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Y.; Yang, F. Highly antifouling and antibacterial performance of poly (vinylidene fluoride) ultrafiltration membranes blending with copper oxide and graphene oxide nanofillers for effective wastewater treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 505, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Z. Polyethylenimine-functionalized graphene oxide as an efficient gene delivery vector. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Yang, X.; Shi, X.; Tan, X.; Peng, R.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z. Polyethylene glycol and polyethylenimine dual-functionalized nano-graphene oxide for photothermally enhanced gene delivery. Small 2013, 9, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Dong, C.; Dong, H.; Shen, A.; Xia, W.; Cai, X.; Song, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Shi, D. Engineered redox-responsive PEG detachment mechanism in PEGylated nano-graphene oxide for intracellular drug delivery. Small 2012, 8, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.; Huang, D.; Liu, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhong, H. Synergistic effect of chemo-photothermal therapy using PEGylated graphene oxide. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8555–8561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
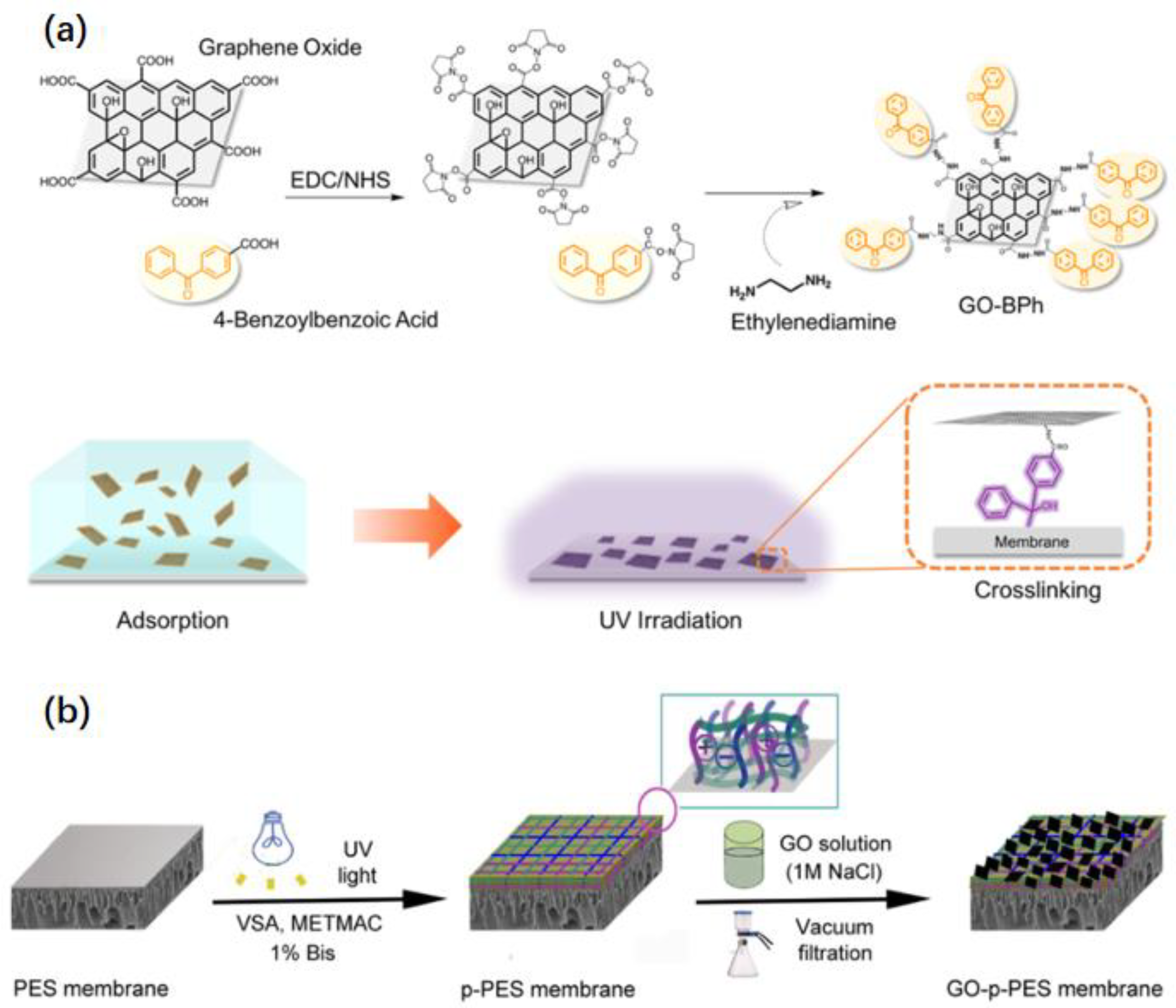
- Lim, M.-Y.; Choi, Y.-S.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Shin, H.; Kim, J.-J.; Shin, D.M.; Lee, J.-C. Cross-linked graphene oxide membrane having high ion selectivity and antibacterial activity prepared using tannic acid-functionalized graphene oxide and polyethyleneimine. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 521, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; An, J.; Fu, H.; Wu, X.; Pang, C.; Gao, H. Construction of an Antibacterial Membrane Based on Dopamine and Polyethylenimine Cross-Linked Graphene Oxide. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 2732–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneda, M.; Lu, X.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, X.; Bernstein, R.; Zhang, W.; Kimura, K.; Elimelech, M. Photografting Graphene Oxide to Inert Membrane Materials to Impart Antibacterial Activity. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Shi, Z.Q.; Cheng, C.; Lu, H.Q.; Zhou, M.; Sun, S.D.; Zhao, C.S. Graphene oxide and sulfonated polyanion co-doped hydrogel films for dual-layered membranes with superior hemocompatibility and antibacterial activity. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Cheng, W.; Ziemann, E.; Be’er, A.; Lu, X.; Elimelech, M.; Bernstein, R. Functionalization of ultrafiltration membrane with polyampholyte hydrogel and graphene oxide to achieve dual antifouling and antibacterial properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, D.Z.; Zhang, J.M.; Wei, G. Metal-organic frameworks functionalized with nucleic acids and amino acids for structure- and function-specific applications: A tutorial review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, C.D.; Mangadlao, J.; Fan, J.; De Leon, A.; Delgado-Ospina, J.; Rojas, J.G.; Rodrigues, D.F.; Advincula, R. Chitosan Cross-Linked Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Films with Antimicrobial Activity for Application in Food Industry. Macromol. Symp. 2017, 374, 1600114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmugam, A.; Vikraman, D.; Park, H.J.; Kim, H.S. One-Pot Facile Methodology to Synthesize Chitosan-ZnO-Graphene Oxide Hybrid Composites for Better Dye Adsorption and Antibacterial Activity. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sreeprasad, T.S.; Maliyekkal, M.S.; Deepti, K.; Chaudhari, K.; Xavier, P.L.; Pradeep, T. Transparent, luminescent, antibacterial and patternable film forming composites of graphene oxide/reduced graphene oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2643–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.Y.; Hu, X.H.; Zhang, Y.W.; Wahid, F.; Chu, L.Q.; Jia, S.R.; Zhong, C. Development and antibacterial activities of bacterial cellulose/graphene oxide-CuO nanocomposite films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-M.; Chang, Y.-C.; Cheng, L.-C.; Liu, C.-H.; Chang, S.C.; Hsien, T.-Y.; Wang, D.-M.; Hsieh, H.-J. Preparation of graphene-embedded hydroxypropyl cellulose/chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofiber membranes as wound dressings with enhanced antibacterial properties. Cellulose 2020, 27, 2651–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Li, F.; Hu, K.D.; Xue, J.; Pan, X.F.; He, T.; Dong, L.; Wang, X.Y.; Wu, Y.D.; Song, Y.H.; et al. Nacre-mimic Reinforced Ag@reduced Graphene Oxide-Sodium Alginate Composite Film for Wound Healing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geng, H.; Dai, J.; Li, J.; Di, Z.; Liu, X. Antibacterial ability and hemocompatibility of graphene functionalized germanium. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dhanasekar, M.; Jenefer, V.; Nambiar, R.B.; Babu, S.G.; Selvam, S.P.; Neppolian, B.; Bhat, S.V. Ambient light antimicrobial activity of reduced graphene oxide supported metal doped TiO2 nanoparticles and their PVA based polymer nanocomposite films. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 97, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Van der Bruggen, B. Graphene-based antimicrobial polymeric membranes: A review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 6776–6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Kang, Z.; Wang, R.; Xu, B.; Nie, X.; Fan, L.; Zhang, F.; Du, X.; Feng, S.; Sun, D. Exploring the sandwich antibacterial membranes based on UiO-66/graphene oxide for forward osmosis performance. Carbon 2019, 144, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Akram, S.; Rashid, A.; Rehan, Z.A.; Javed, T.; Shabbir, R.; Hessien, M.M.; El-Sayed, M.E. Investigating the Antibacterial Activity of Polymeric Membranes Fabricated with Aminated Graphene Oxide. Membranes 2021, 11, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ruan, H.; Guo, C.; Liao, J.; Shen, J.; Gao, C. Thin-film nanocomposite reverse osmosis membranes with enhanced antibacterial resistance by incorporating p-aminophenol-modified graphene oxide. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 234, 116017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
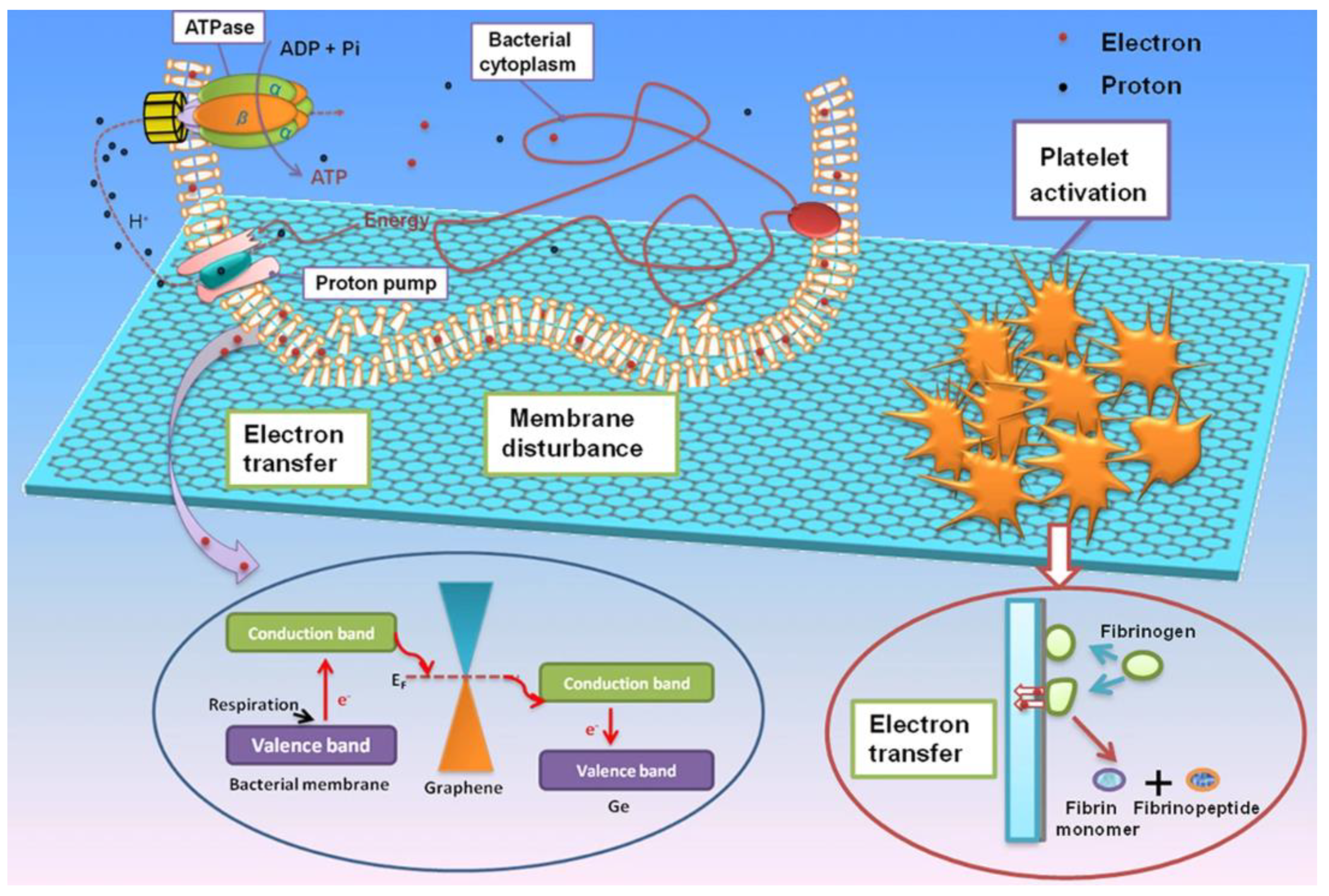
- Li, J.; Wang, G.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, X.; Di, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Antibacterial activity of large-area monolayer graphene film manipulated by charge transfer. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, M.Y.; Xie, Y.; Yu, C.H.; Chen, G.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, T.; Peng, Q. Graphene-based nanomaterials: The promising active agents for antibiotics-independent antibacterial applications. J. Control. Release 2019, 307, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, V.T.H.; Truong, V.K.; Quinn, M.D.J.; Notley, S.M.; Guo, Y.C.; Baulin, V.A.; Al Kobaisi, M.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Graphene Induces Formation of Pores That Kill Spherical and Rod-Shaped Bacteria. Acs Nano 2015, 9, 8458–8467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Toxicity of Graphene and Graphene Oxide Nanowalls Against Bacteria. Acs Nano 2010, 4, 5731–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marković, Z.M.; Jovanović, S.P.; Mašković, P.Z.; Danko, M.; Mičušík, M.; Pavlović, V.B.; Milivojević, D.D.; Kleinová, A.; Špitalský, Z.; Todorović Marković, B.M. Photo-induced antibacterial activity of four graphene based nanomaterials on a wide range of bacteria. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 31337–31347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Dayem, A.A.; Eppakayala, V.; Kim, J.H. Oxidative stress-mediated antibacterial activity of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5901–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.B.; Zeng, T.H.; Hofmann, M.; Burcombe, E.; Wei, J.; Jiang, R.R.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial Activity of Graphite, Graphite Oxide, Graphene Oxide, and Reduced Graphene Oxide: Membrane and Oxidative Stress. Acs Nano 2011, 5, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, F.; de Faria, A.F.; Nejati, S.; Elimelech, M. Antimicrobial Properties of Graphene Oxide Nanosheets: Why Size Matters. Acs Nano 2015, 9, 7226–7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.N.; Peng, H.; Wang, X.P.; Shao, F.; Yuan, Z.D.; Han, H.Y. Graphene oxide exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against bacterial phytopathogens and fungal conidia by intertwining and membrane perturbation. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1879–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellata, M. Human and avian extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli: Infections, zoonotic risks, and antibiotic resistance trends. Foodbrone Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 916–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costalonga, M.; Herzberg, M.C. The oral microbiome and the immunobiology of periodontal disease and caries. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 162, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krzysciak, W.; Jurczak, A.; Koscielniak, D.; Bystrowska, B.; Skalniak, A. The virulence of Streptococcus mutans and the ability to form biofilms. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hebecker, B.; Naglik, J.R.; Hube, B.; Jacobsen, I.D. Pathogenicity mechanisms and host response during oral Candida albicans infections. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. 2014, 12, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bentzmann, S.; Plesiat, P. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa opportunistic pathogen and human infections. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.N.; Clegg, S. Klebsiella pneumoniae and type 3 fimbriae: Nosocomial infection, regulation and biofilm formation. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gart, E.V.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Welsh, T.H., Jr.; Alaniz, R.C.; Randel, R.D.; Lawhon, S.D. Salmonella Typhimurium and Multidirectional Communication in the Gut. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, B.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, G.; Gong, J.; Chang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Antibacterial properties and mechanism of graphene oxide-silver nanocomposites as bactericidal agents for water disinfection. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 604, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahan, H.E.; Wei, L.; Goh, K.; Liu, Z.; Birer, O.; Dehghani, F.; Xu, C.; Wei, J.; Chen, Y. Bacterial physiology is a key modulator of the antibacterial activity of graphene oxide. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17181–17189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregnocchi, A.; Zanni, E.; Uccelletti, D.; Marra, F.; Cavallini, D.; De Angelis, F.; De Bellis, G.; Bossu, M.; Ierardo, G.; Polimeni, A.; et al. Graphene-based dental adhesive with anti-biofilm activity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Marsh, K.L.; McVerry, B.T.; Hoek, E.M.; Kaner, R.B. Low-Fouling Antibacterial Reverse Osmosis Membranes via Surface Grafting of Graphene Oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14334–14338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Ziemann, E.; Be’er, A.; Bashouti, M.Y.; Elimelech, M.; Bernstein, R. One-step sonochemical synthesis of a reduced graphene oxide–ZnO nanocomposite with antibacterial and antibiofouling properties. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 3080–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Geng, C.; Huang, P. Preparation of a hydrophilic and antibacterial dual function ultrafiltration membrane with quaternized graphene oxide as a modifier. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 562, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najjar, A.; Sabri, S.; Al-Gaashani, R.; Kochkodan, V.; Atieh, M. Enhanced Fouling Resistance and Antibacterial Properties of Novel Graphene Oxide-Arabic Gum Polyethersulfone Membranes. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, C.; Shen, C.; Meng, Q. Guanidyl-functionalized graphene/polysulfone mixed matrix ultrafiltration membrane with superior permselective, antifouling and antibacterial properties for water treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 540, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, H.; Gao, B.; Wang, Z. Antibacterial Thin-Film Nanocomposite Membranes Incorporated with Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles for Reverse Osmosis Application. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 8724–8734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, M.; Yadav, A.K.; Chauhan, V.; Singh, N.; Kumar, S.; Das, A.; Yadav, V.; Mandal, A.; Tiwari, J.K.; Siddiqui, H.; et al. Facile development of graphene-based air filters mounted on a 3D printed mask for COVID-19. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Dev. 2021, 6, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, F.; Cirone, M.; Relucenti, M.; Santarelli, R.; Gaeta, A.; Mussi, V.; De Simone, S.; Zicari, A.; Mardente, S. Antiviral Filtering Capacity of GO-Coated Textiles. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Sharma, C.P.; Thamaraiselvan, C.; Pisharody, L.; Powell, C.D.; Arnusch, C.J. Low-Voltage Bacterial and Viral Killing Using Laser-Induced Graphene-Coated Non-woven Air Filters. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 59373–59380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das Jana, I.; Kumbhakar, P.; Banerjee, S.; Gowda, C.C.; Kedia, N.; Kuila, S.K.; Banerjee, S.; Das, N.C.; Das, A.K.; Manna, I.; et al. Copper Nanoparticle–Graphene Composite-Based Transparent Surface Coating with Antiviral Activity against Influenza Virus. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 4, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, S.; Etxeberria, A.; Mocholi, V.; Rekondo, A.; Grande, H.; Labidi, J. Effect of combining cellulose nanocrystals and graphene nanoplatelets on the properties of poly(lactic acid) based films. Express Polym. Lett. 2018, 12, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Jacobsen, J.; Larsen, S.W.; Genina, N.; van de Weert, M.; Mullertz, A.; Nielsen, H.M.; Mu, H. Graphene oxide as a functional excipient in buccal films for delivery of clotrimazole: Effect of molecular interactions on drug release and antifungal activity in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontarek-Castro, E.; Rybarczyk, M.K.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; Morales-Jiménez, M.; Barragán-Huerta, B.; Lieder, M. Characterization of PVDF/Graphene Nanocomposite Membranes for Water Desalination with Enhanced Antifungal Activity. Water 2021, 13, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sun, L.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, Z.; Shao, K.; Li, T.; Hu, C.; Han, H. Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanocomposite: Novel Agricultural Antifungal Agent against Fusarium graminearum for Crop Disease Prevention. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24057–24070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| GMBs | Pathogens | Comments | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| GNPs | Streptococcus mutans | Inhibit adhesion and growth | [108] |
| GO-RO | Escherichia coli | Reduced water permeability, reduced salt selectivity, reduced pollution | [109] |
| rGO-Zno-PES | Escherichia coli Serratia marcescens Bacillus subtilis | Inhibit biofilm growth | [110] |
| QGO | Escherichia coli | Hydrophilic, antibacterial and mechanical properties are significantly enhanced | [111] |
| GO-AG-PES | Escherichia coli Bacillus subtilis | Superior antibacterial effect | [112] |
| GFG/PSF | Escherichia coli Staphylococcus aureus | Good antibacterial activity, long duration | [113] |
| TFN-GOQD/Ag200 | Escherichia coli Staphylococcus aureus | Significant bactericidal power | [114] |
| fG-PP | SARS-CoV-2 | Good inhibition effect | [115] |
| GO-textile | HHV-6A | Prevent cell infection, has antiviral properties | [116] |
| LIG-PI | Pseudomonas aeruginosa T4 virus | Inactivation of a large number of bacteria and viruses | [117] |
| Cu-Gr | Influenza virus | Virus particles are inactivated, slowing infection | [118] |
| PLA-CNC/GR | Aspergillus niger | High antifungal activity | [119] |
| CS/alginate/GO/clotrimazole | Oral candidiasis | GO can be used as a functional excipient for delivery of antifungal drugs. | [120] |
| PVDF/G | Curvuria | High inhibition rate | [121] |
| GO/AgNP | graminearum | High antibacterial activity and inhibit pathogen infection | [122] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Kong, H.; Yang, G.; Zhu, D.; Luan, X.; He, P.; Wei, G. Graphene-Based Functional Hybrid Membranes for Antimicrobial Applications: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4834. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12104834
Zhang X, Kong H, Yang G, Zhu D, Luan X, He P, Wei G. Graphene-Based Functional Hybrid Membranes for Antimicrobial Applications: A Review. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(10):4834. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12104834
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaoting, Hao Kong, Guozheng Yang, Danzhu Zhu, Xin Luan, Peng He, and Gang Wei. 2022. "Graphene-Based Functional Hybrid Membranes for Antimicrobial Applications: A Review" Applied Sciences 12, no. 10: 4834. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12104834
APA StyleZhang, X., Kong, H., Yang, G., Zhu, D., Luan, X., He, P., & Wei, G. (2022). Graphene-Based Functional Hybrid Membranes for Antimicrobial Applications: A Review. Applied Sciences, 12(10), 4834. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12104834







