Effects of Slope Angle on Toppling Deformation of Anti-Dip Layered Rock Slopes: A Centrifuge Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
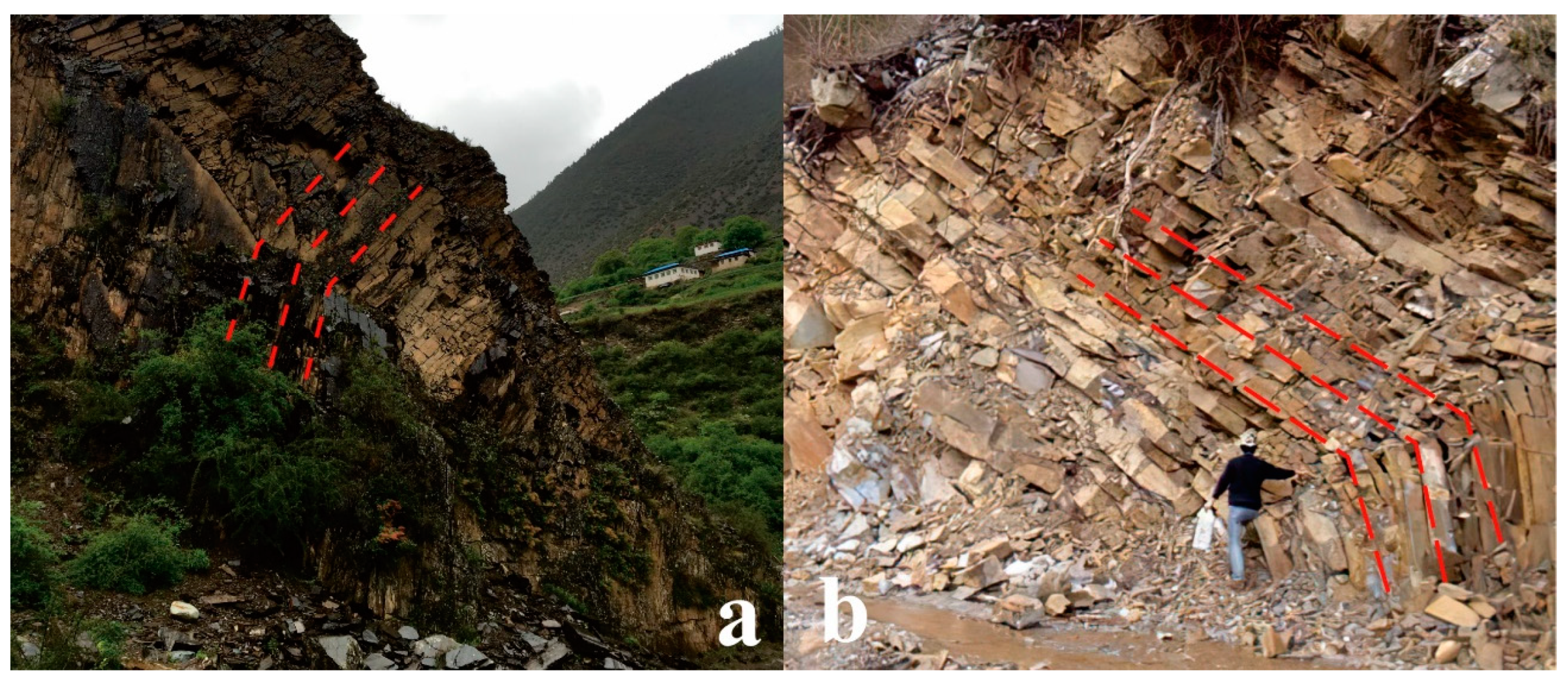
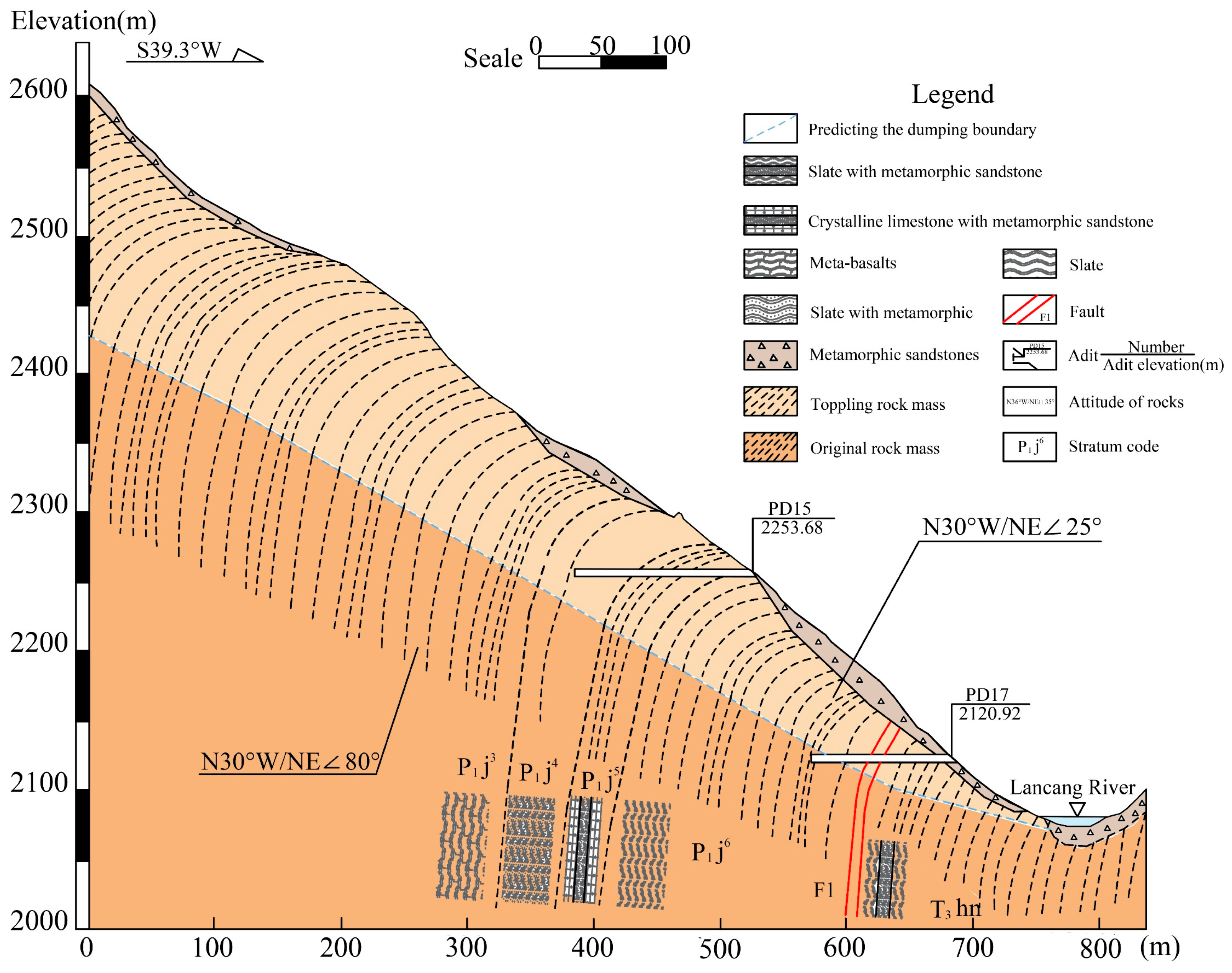
2. Geological Background of the Prototype Slope
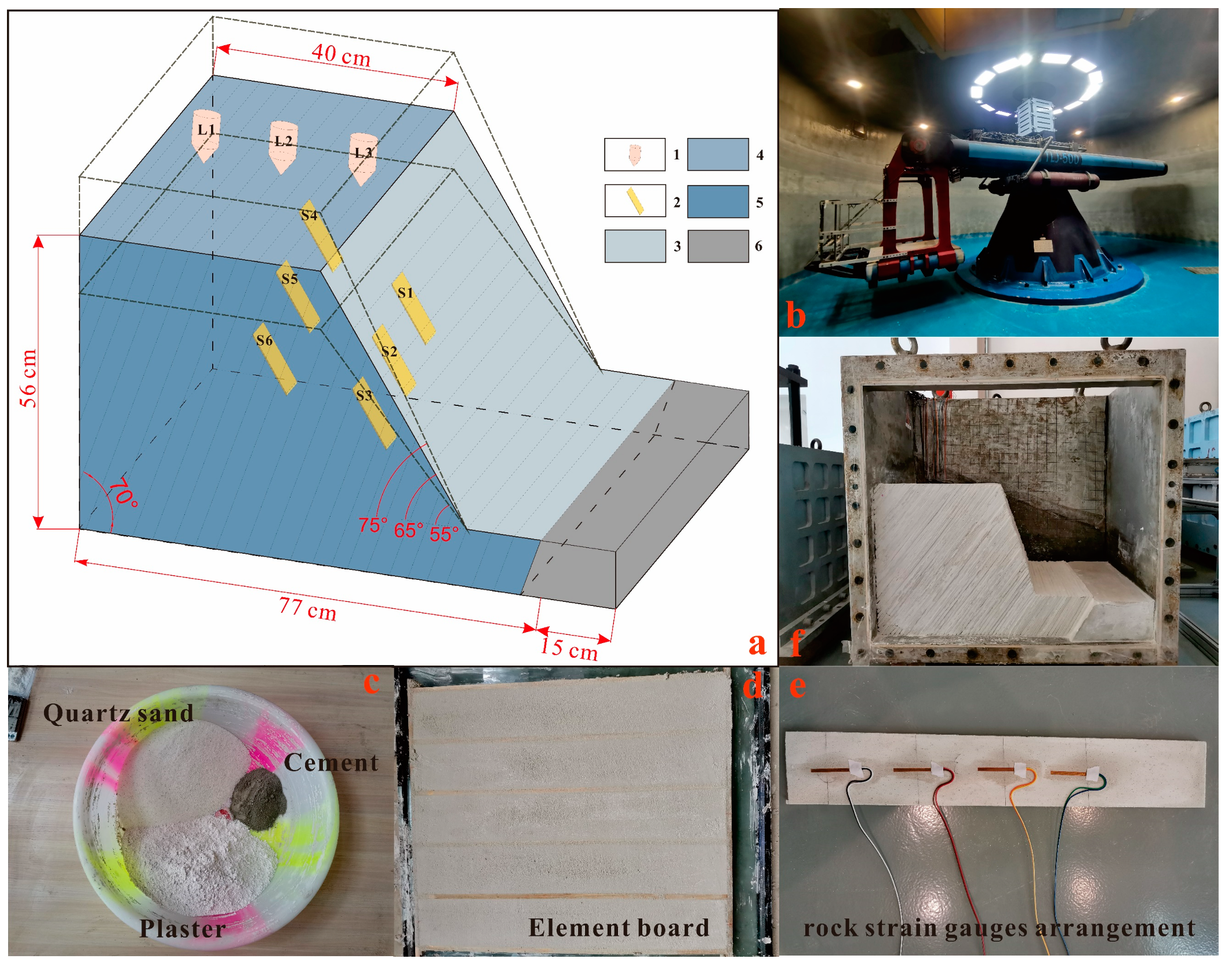
3. Centrifuge Model Design
3.1. Test Equipment
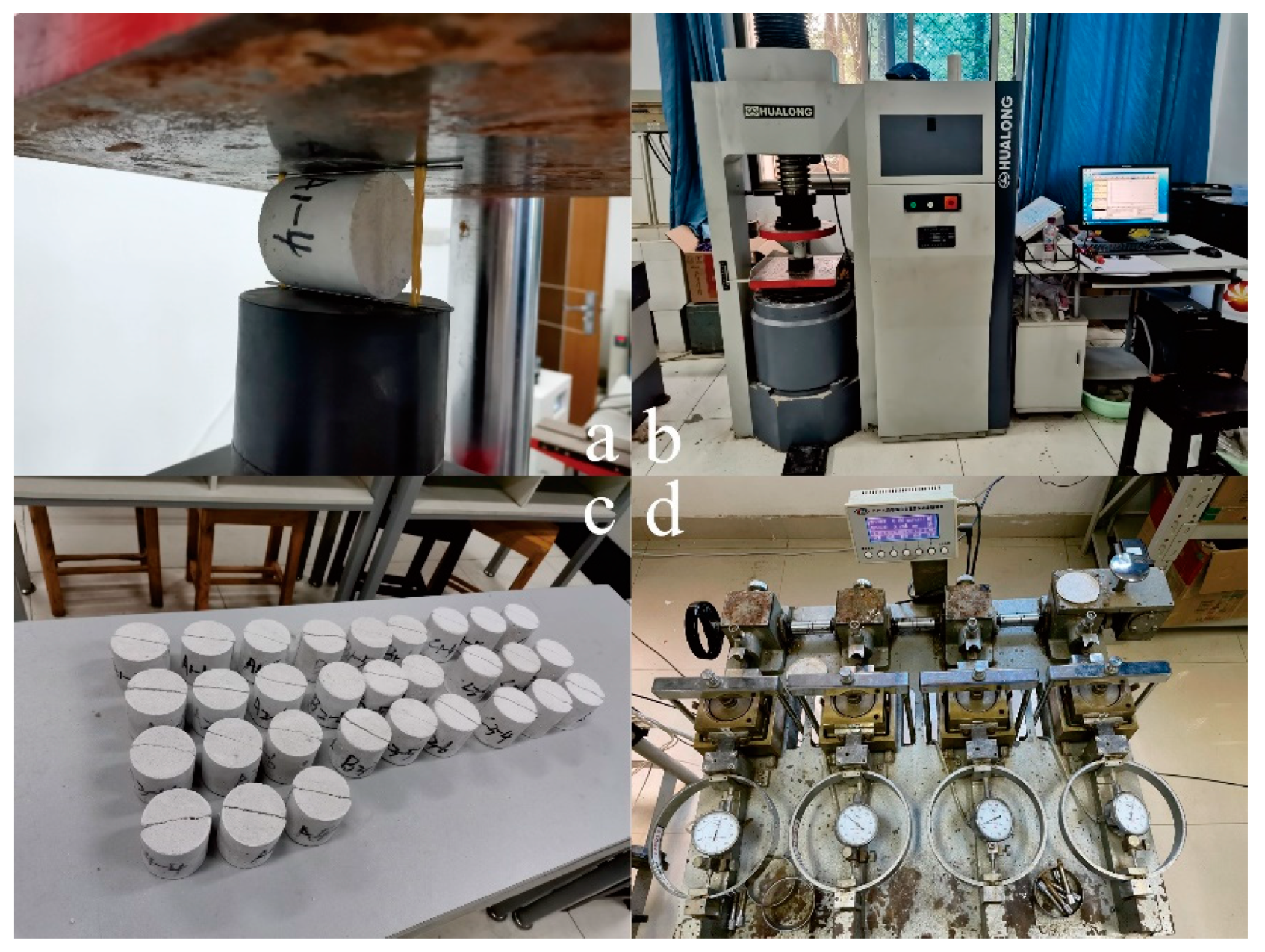
3.2. Model Materials
3.3. Test Model Design
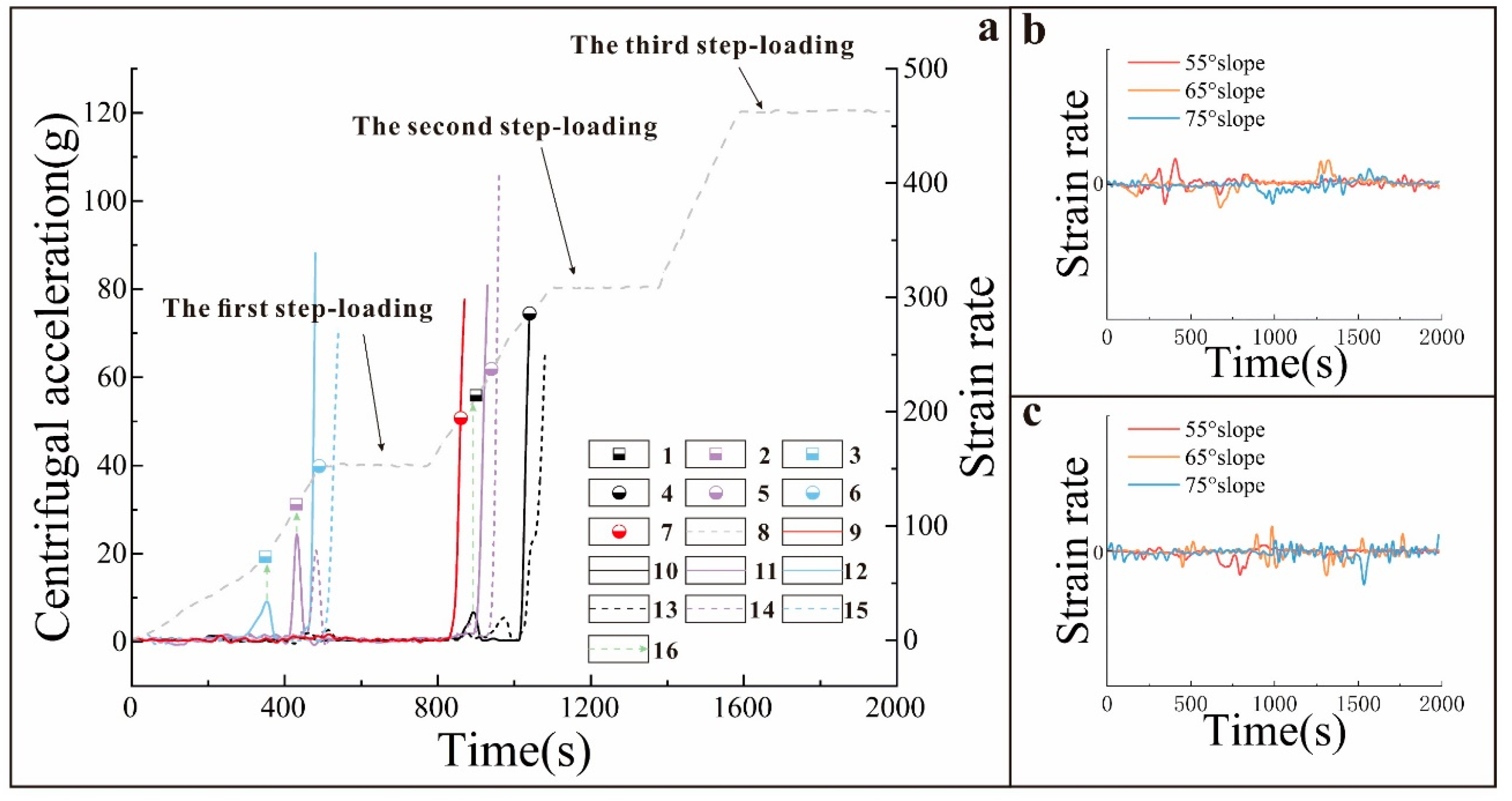
3.4. Scheme of Test Loading
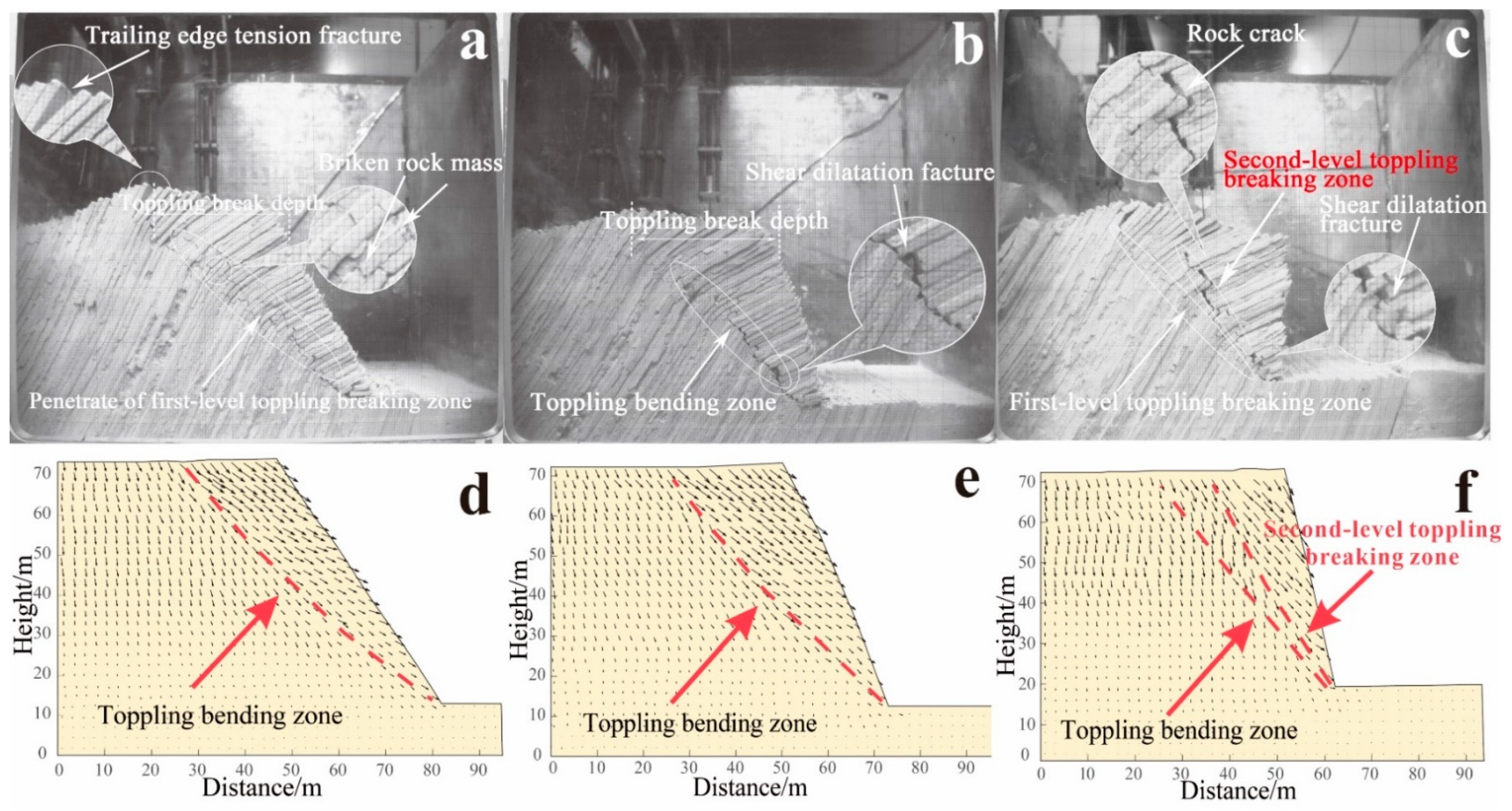
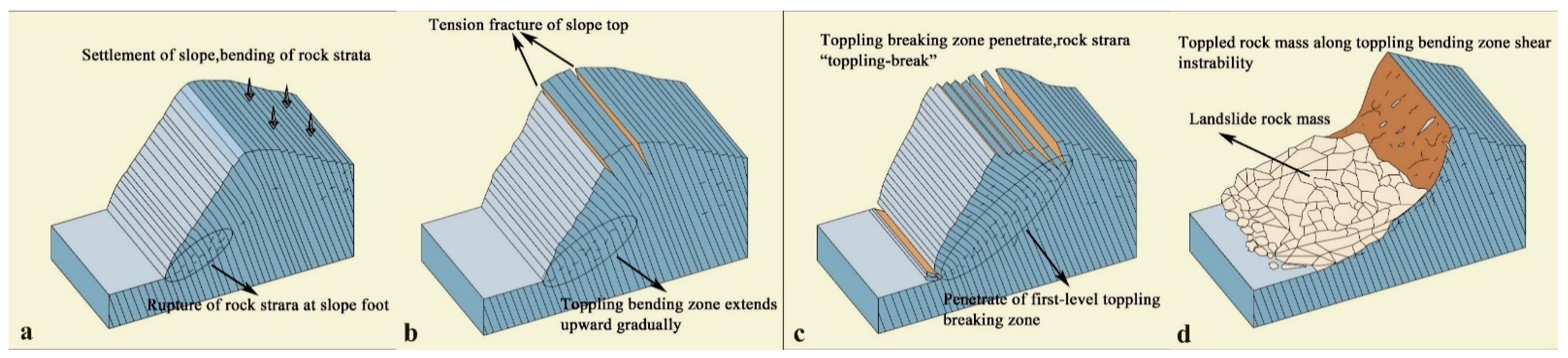
4. Test Phenomena Analysis
4.1. Description of the Test Phenomena
4.2. Analysis of the Test Phenomena
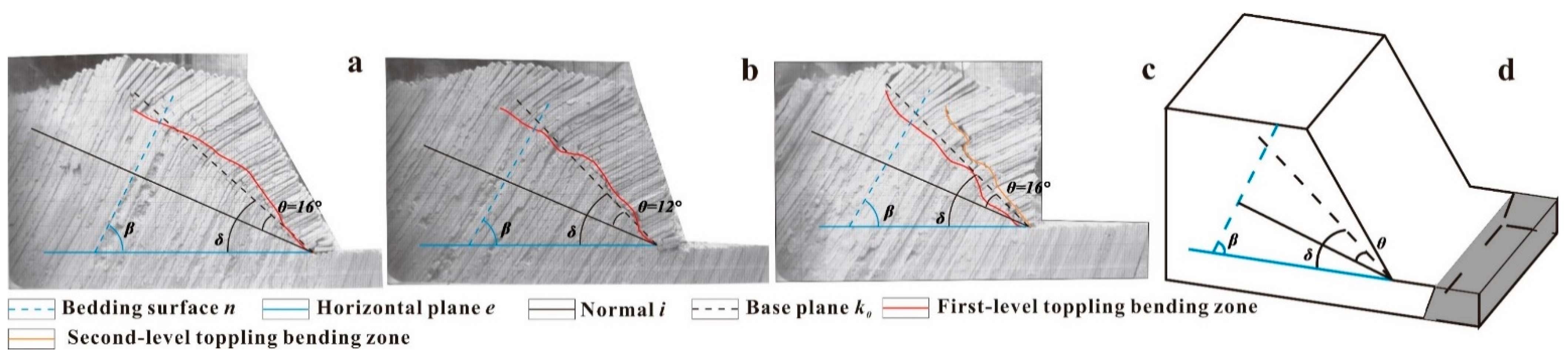
4.2.1. The Depth and Range of the Development of the Toppling-Bending Zone
4.2.2. The Development of the Multi-Level Toppling-Bending Zone
5. Test Data Analysis
5.1. Analysis of Displacement Vector
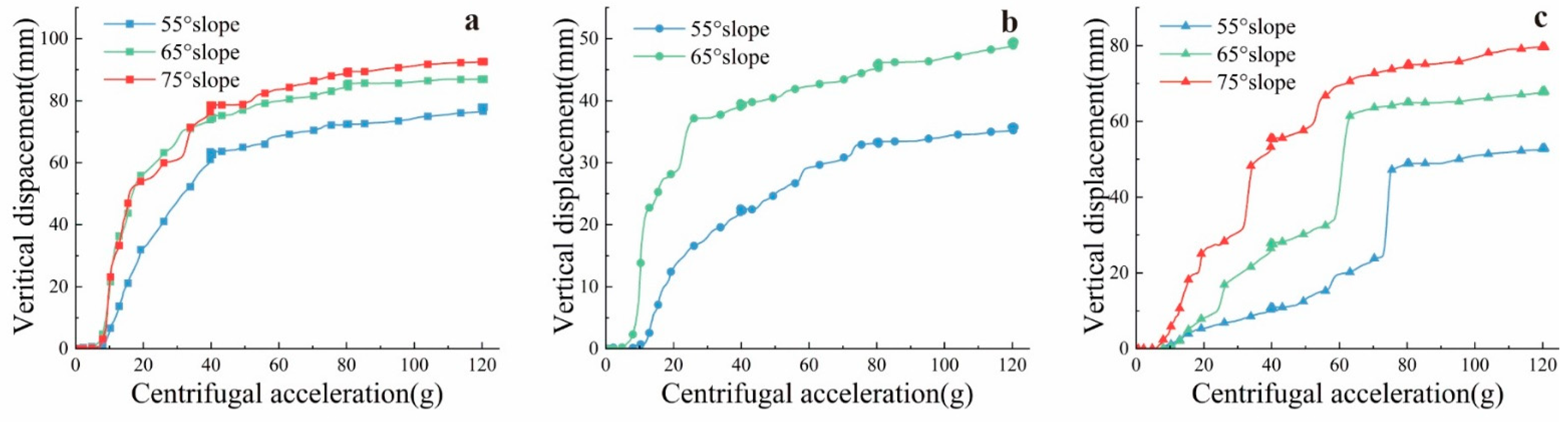
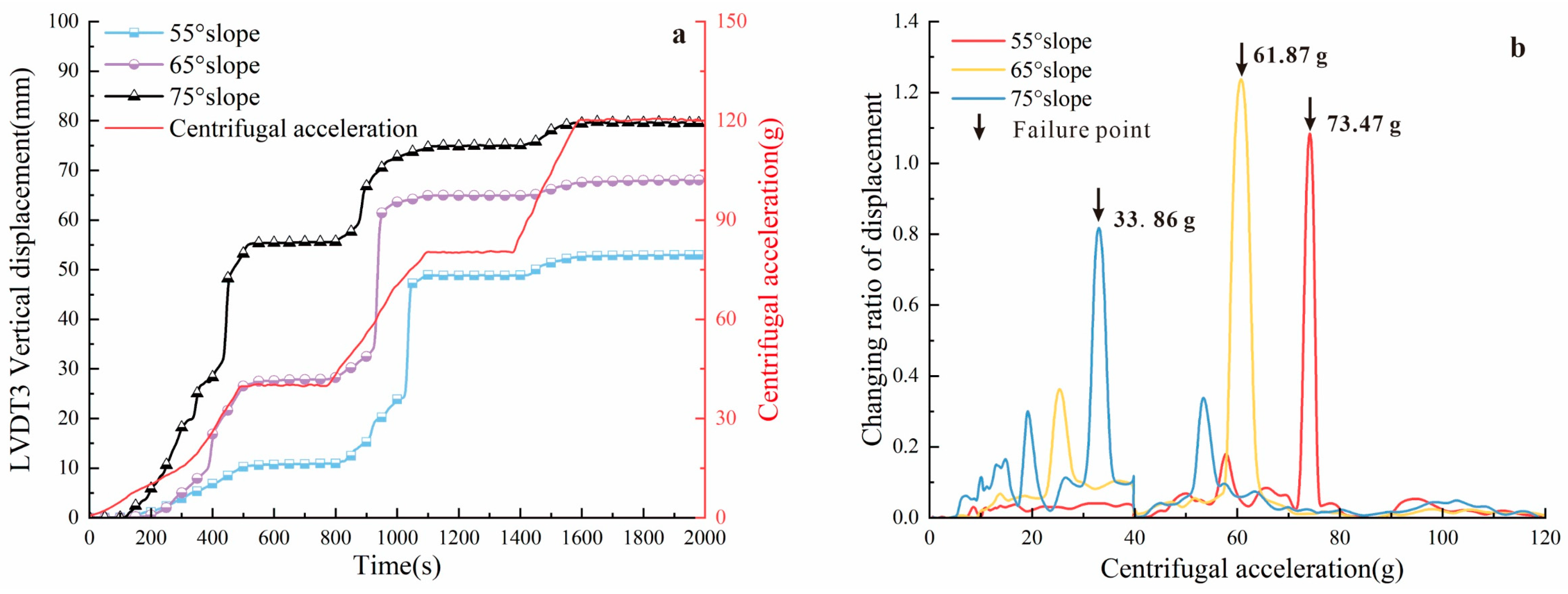
5.2. Analysis of Displacement Data
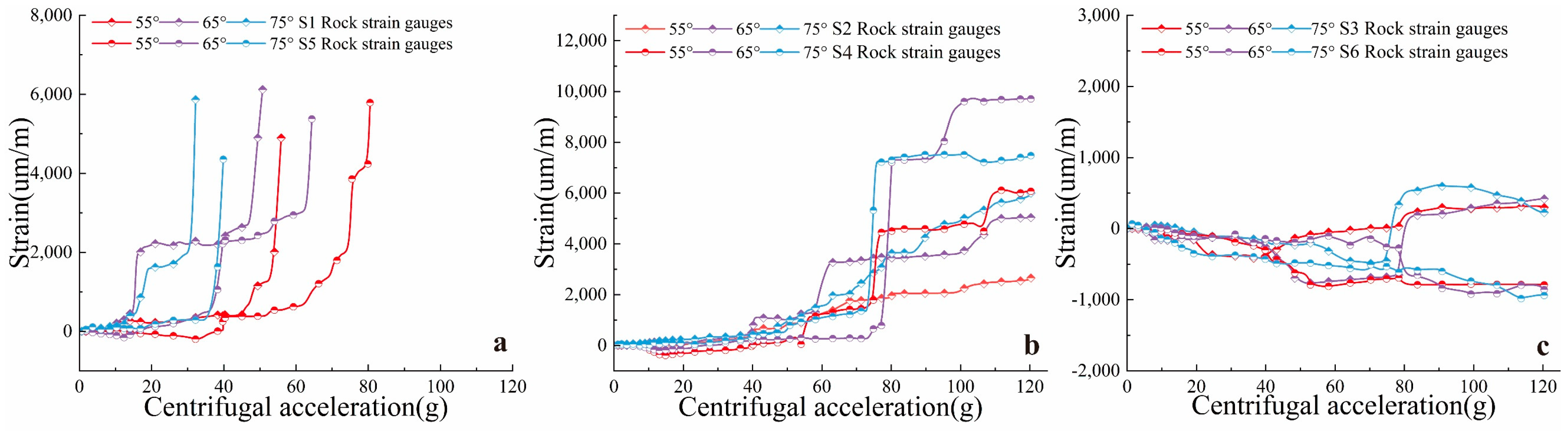
5.3. Analysis of the Strain Data
6. Discussion
6.1. The Position of the Toppling-Bending Zone
6.2. Analysis of Disaster Patterns
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Su, A.; Liu, Q.; Xiang, W.; Yeh, H.F.; Xiong, C.; Zou, Z.; Zhong, C.; Liu, J.; Cao, S. Three-dimensional analyses of the sliding surface distribution in the Huangtupo No. 1 riverside sliding mass in the Three Gorges Reservoir area of China. Landslides 2018, 15, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Schweizer, D.; Liu, Q.; Su, A.; Hu, X.; Blum, P. Three-dimensional landslide evolution model at the Yangtze River. Eng. Geol. 2021, 292, 106275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, E.; Bray, J. Rock Slope Engineering, 3rd ed.; Institution of Mining and Metallurgy: London, UK, 1981; pp. 257–270. Available online: https://books.google.com/books?id=R0NZDwAAQBAJ&lpg=PP1&dq=Rock%20slope%20engineering&lr&hl=zh-CN&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q=Rock%20slope%20engineering&f=false (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Huang, R.Q.; Li, Y.S. The implication and evaluation of toppling failure in engineering geology practice. J. Eng. Geol. 2017, 25, 1165–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Rock slope deformation mechanism in the Cihaxia Hydropower Station, Northwest China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2015, 74, 942–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, S.L.; Hungr, O. Large-scale brittle and ductile toppling of rock slopes. Can. Geotech. J. 2002, 39, 773–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moo-Young, T.; Myers, B. Centrifuge simulation of the consolidation characteristics of capped marine sediment beds. Eng. Geol. 2003, 70, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, J.; Woo, S.I. Analysis of Horizontal Earth Pressure Acting on Box Culverts through Centrifuge Model Test. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapogianni, E.; Laue, J. Experimental Investigation of Reinforced Soil Slopes in a Geotechnical Centrifuge, with the Use of Optical Fibre Sensors. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2017, 35, 585–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Chen, Z.Y. Centrifuge Modeling of Rock Slopes Susceptible to Block Toppling. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2007, 40, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzo’ubi, A.K.; Martin, C.D. Influence of tensile strength on toppling failure in centrifuge tests. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2010, 47, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, G. Centrifuge modelling of clay slope with montmorillonite weak layer under rainfall conditions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 50, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewoolkar, M.M.; Goddery, T. Centrifuge Modeling for Undergraduate Geotechnical Engineering Instruction. GTJ 2003, 26, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, I.; Woo, S.K. Analysis of Vertical Earth Pressure Acting on Box Culverts through Centrifuge Model Test. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Zhang, J. Earthquake loading response of a slope with an inclined weak intercalated layer using centrifuge modeling. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 4439–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idinger, G.; Aklil, W. Centrifuge model test on the face stability of shallow tunnel. Acta Geotech. 2011, 6, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adhikary, D.P.; Dyskin, A.V. A study of the mechanism of flexural toppling failure of rock slopes. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 1997, 30, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, D.P.; Dyskin, A.V. Numerical modelling of the flexural deformation of foliated rock slopes. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1996, 33, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, C. Centrifuge modeling of layered rock slopes susceptible to block-flexure toppling failure. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 3815–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonika, A.; Abdoun, T.; Sasanakul, I. Centrifuge tests on liquefaction potential and slope stability of mine tailings. Int. J. Phys. Model. Geotech. 2018, 19, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Wang, Q.L. Centrifuge model test study on key hazard-inducing factors of deep toppling deformation and disaster patterns of counter-tilt layered rock slopes. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2019, 38, 1954–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.E. Toppling—A Fundamental Failure Mode in Discontinuous Materials—Description and Analysis. In Proceedings of the Geo-Congress 2013, San Diego, CA, USA, 3–7 March 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.E.; Bray, J.W. Toppling of Rock Slopes, 1st ed.; American Society of Civil Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 201–234. Available online: https://cedb.asce.org/CEDBsearch/record.jsp?dockey=0265503 (accessed on 13 December 2021).





| Rock Similarity Index | Density (g/cm3) | Elastic Modulus (MPa) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Cohesion (kPa) | Internal Fiction Angle (°) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prototype | Metamorphic sandstone | 2.42 | 3000 | 15 | 1.75 | / | / |
| Interlayer bonding | / | / | / | / | 35 | 16 | |
| Model | Metamorphic sandstone | 2.38 | 2800 | 14.8 | 1.84 | / | / |
| Interlayer bonding | / | / | / | / | 34.5 | 15.8 | |
| Slope Angle | Vertical Displacement Change Value (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LVDT1 | LVDT2 | LVDT3 | |
| 55° | 77 | 35 | 52 |
| 65° | 87 | 49 | 68 |
| 75° | 92 | / | 79 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, D.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, H.; Liu, F.; Chen, Q.; Wu, Z. Effects of Slope Angle on Toppling Deformation of Anti-Dip Layered Rock Slopes: A Centrifuge Study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5084. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105084
Zheng D, Zhou H, Zhou H, Liu F, Chen Q, Wu Z. Effects of Slope Angle on Toppling Deformation of Anti-Dip Layered Rock Slopes: A Centrifuge Study. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(10):5084. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105084
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Da, Hongke Zhou, Hang Zhou, Fangzhou Liu, Qiang Chen, and Zhanglei Wu. 2022. "Effects of Slope Angle on Toppling Deformation of Anti-Dip Layered Rock Slopes: A Centrifuge Study" Applied Sciences 12, no. 10: 5084. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105084
APA StyleZheng, D., Zhou, H., Zhou, H., Liu, F., Chen, Q., & Wu, Z. (2022). Effects of Slope Angle on Toppling Deformation of Anti-Dip Layered Rock Slopes: A Centrifuge Study. Applied Sciences, 12(10), 5084. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12105084






