Abstract
The drought along with climate variation has become a serious issue for human society and the ecosystem in the arid region like the Soan basin (the main source of water resources for the capital of Pakistan and the Pothohar arid region). The increasing concerns about drought in the study area have brought about the necessity of spatiotemporal analysis and assessment of the linkage between different drought types for an early warning system. Hence, the streamflow drought index (SDI) and standard precipitation index (SPI) were used for the analysis of the spatiotemporal variations in hydrological and meteorological drought, respectively. Furthermore, statistical approaches, including regression analysis, trend analysis using Mann Kendall, and moving average, have been used for investigation of the linkage between these drought types, the significance of the variations, and lag time identification, respectively. The overall analysis indicated an increase in the frequency of both hydrological and meteorological droughts during the last three decades. Moreover, a strong linkage between hydrological and meteorological droughts was found; and this relationship varied on the spatiotemporal scale. Significant variations between hydrological and meteorological droughts also resulted during the past three (3) decades. These discrepancies would be because of different onset and termination times and specific anthropogenic activities in the selected basin for the minimization of hydrological drought. Conclusively, the present study contributes to comprehending the linkage between hydrological and meteorological droughts and, thus, could have a practical use for local water resource management practices at the basin scale.
1. Introduction
Drought is a condition considered as the deficit of water, including surface, ground, or atmospheric water, for a long period [1]. Irrespective of climatic sites, the drought could occur worldwide even in humid and wet environments [2]. Drought is generally classified into meteorological, hydrological, socioeconomic, and agricultural drought [3]. Among these four types of droughts, hydrological is the most important form as sustainable water resources management is heavily dependent on hydro-meteorological information. Various numbers of factors are associated with the onset of hydrological drought, and meteorological drought is one of the main influencing factors. The root cause of drought onset is the deficiency of rainfall across a large area for a very long period and is notated as a meteorological drought [4]. A meteorological drought can develop quickly because it is primarily caused by a lack of precipitation [5], and if the lack of precipitation spreads to specific regions, the meteorological drought can be transformed into a hydrological drought, and then into an agricultural drought. The drought propagation process refers to the transition of different types of droughts.
The relationships between different types of droughts are studied by several authors, for example, [6] resulted that hydrological drought events occurred approximately seven months after meteorological drought events. The streamflow drought can be investigated using meteorological drought information at the annual time scale [7]. The interrelationship between runoff and meteorological drought has also been investigated and it was concluded that the significant dependency of hydrological drought on meteorological drought [8]. The impact of meteorological forcing on hydrological droughts has been computed [9]. A copula-based joint meteorological-hydrological drought index has been used to model the relationship between meteorological and hydrological droughts upstream and downstream of the Kasilian basin [10]. The transmission of meteorological droughts to hydrological droughts and the influence factors have been explored and investigated [11]. The entropy theory was used to create a hybrid drought index that combines hydrological, meteorological, and agricultural data and was used to investigate the drought condition in Northwest China [12]. In literature, the relationships between hydro-meteorological droughts, climatic variables, and human activities were also explored [13,14]. For example, [15] examined the relationship between various hydrologic and meteorological drought indices considering natural and human factors for different basins in the contiguous United States. Similarly, [16,17,18,19] studied the dependence structure between meteorological drought and hydrological drought using different approaches and resulted that the occurring time lag between meteorological and hydrological droughts is critical for sustainable drought management.
Most studies in the literature focused on determining hydro-meteorological drought and drought propagation; however, it remains unexplored. Besides that, the lack of understanding considering hydrological drought response to meteorological drought in different regions raises an unanswered question for basin-scale drought risk management [20]. To find answers to these questions, a comprehensive study of droughts that span multiple geographic areas and last for extended periods is required. Strategic water resources can be implemented more efficiently with accurate water-based information based on regional drought characteristics. Furthermore, given Pakistan’s erratic, scarce, unstable climate and current drought situation [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29], drought propagation information is critical at the regional and national levels, as it can provide the appropriate and consistent information required for efficient water management and drought early warning systems. Drought propagation information can aid in the prevention of significant economic losses as well as decision-making. Early warning systems are estimated to save hundreds of lives, save 2.7 billion Euros in natural disaster losses, and generate billions of supplementary benefits per year in Europe based on the optimization of economic production in the energy and agriculture sectors. In the near past, Pakistan has also experienced recurrent droughts and more severe droughts are anticipated in near future due to climate change [22].
The Soan River is a tributary of Pakistan’s mighty Indus River Basin. It flows from the Murree Mountains into the Indus via the Dhoke Pathan hydrological station. It is the main hydrological unit for the Pothohar arid region of Pakistan. The importance of the Pothohar region cannot be repudiated as the region of Pothohar is rich in agriculture and agriculture is the backbone of the country’s economy [30]. However, there are canal irrigation resources in this area and the crop production depends entirely on rainfall at suitable timings. Pothohar region gets rainfall during both the winter and summer seasons, which is the main source of crop germination, flowering, and maturity. If any of the seasons fail to bring rain, then soil moisture depletes resulting in drought and ultimately significant crop damage. More specifically, the crops in these areas depend on monsoon rains in summer and on western rains in winter. If the summer season fails to bring rains in the area, then it will cause huge crop yield loss in that specific year. Similarly, if the westerly system also fails to bring rains to the area, crops are affected badly, resulting in severe droughts. Historically, this Pothohar region was severely affected by substantial variation in the rainfall and prolonged rain shortage especially from 1999 to 2002 [31]. Hence, the objectives of the present study include the exploration of spatiotemporal evolutions of meteorological and hydrological droughts in the study basin, evaluation of the link between meteorological and hydrological droughts, identifying the lag time, and the investigation of the differences between hydrological and meteorological droughts.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
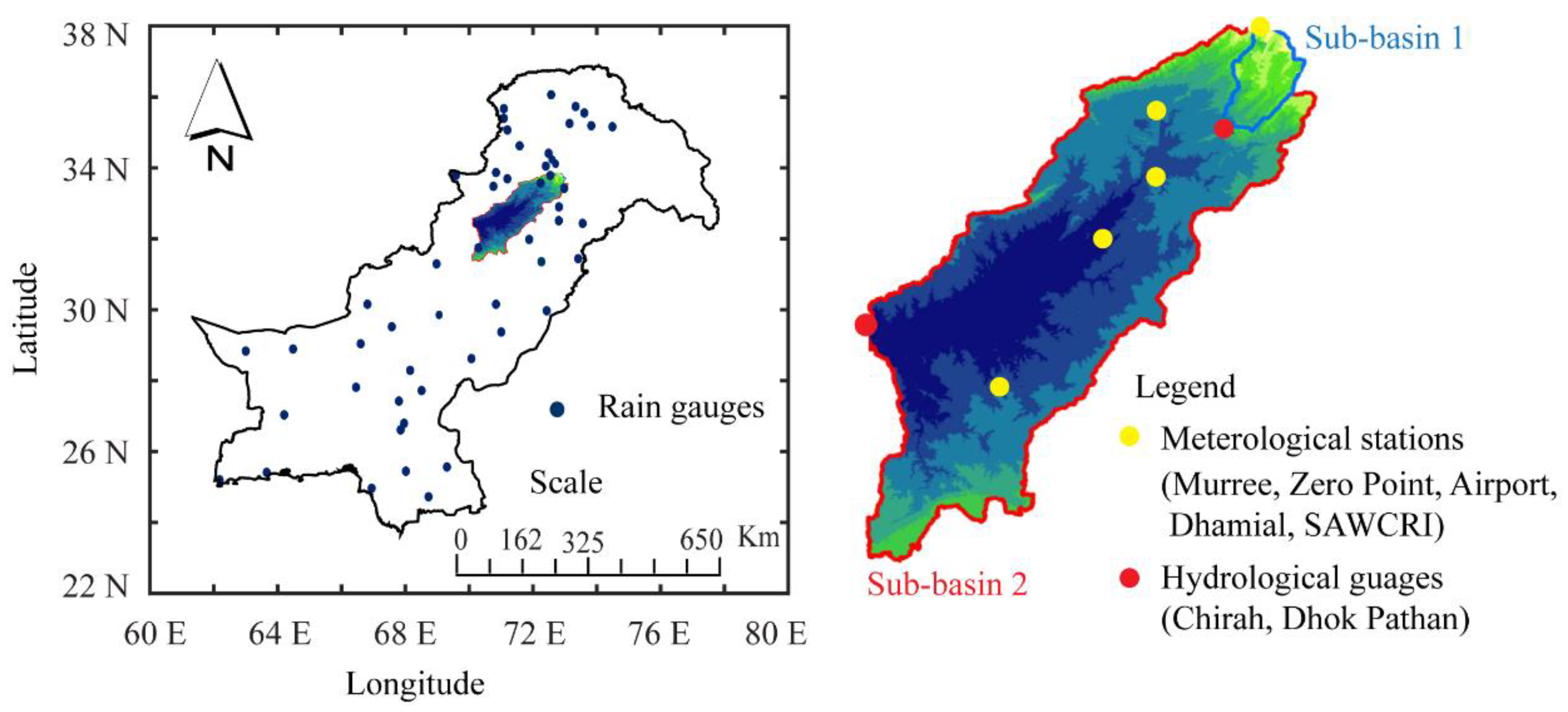
The Soan River, initiating from the Murree highlands, is a major tributary of the Indus River and a key hydrological entity of the Potohar region of Pakistan. The Soan River flows through Chirah and Dhoke Pathan hydrological gauging stations (Figure 1) before being a part of the Indus River. The total drainage area of the Soan River basin is 6842 km2 with an elevation ranging from 265 to 2274 m. The Soan basin is characterized by gentle to the steep slope and monsoon fed streams which generate almost all of the basin flow with mean annual precipitation of 1465 mm, and the mean annual temperature ranges from 8 to 22 °C. The Simly Dam, which spans the Soan River, provides drinking water to Islamabad, Pakistan’s capital, as well as water for irrigation activities in the Pothohar region [32]. Furthermore, for a better understanding and evaluation of the spatial variation of drought, the study area was divided into two sub-basins: Chirah (hereafter sub-basin 1) and Dhoke Pathan (hereafter sub-basin 2). In the current study, monthly precipitation data of five meteorological stations within the basin (Murree, Zero Point, airport, Dhamial, and SAWCRI) from 1983 to 2015 was collected from Pakistan Meteorological Department (PMD). The average value of four stations lying in sub-basin 2 was used to estimate the meteorological drought in sub-basin 2, whereas the data of the remaining one station, i.e., Murree was used for meteorological drought analysis at sub-basin 1. Similarly, the monthly streamflow data of two hydrological gauging stations, i.e., Chirah and Dhoke Pathan was collected from Water and Power Development Authority (WAPDA) for the same period.
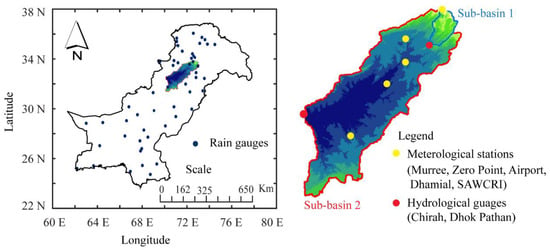
Figure 1.
Location map of the study area.
2.2. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Drought
2.2.1. Meteorological Drought Assessment
For the assessment of meteorological drought, the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) was used due to its effectiveness, applicability, and suitability at different time scales for many case studies, e.g., [28,33,34]. Considering the hydrological year (October to September), SPI was calculated at four different time scales, i.e., SPI-3 (October–December), SPI-6 (October–March), SPI-9 (October–June), and SPI-12 (October–September). Furthermore, for the calculation of SPI at different time scales, the following expression was used for cumulative precipitation .
where corresponds to monthly precipitation, j denotes the particular month of the hydrological year, I indicates the hydrological year, and k reveals the timescale (e.g., SPI-3, k = 1 indicating 3-month time scale October-December, and similarly k = 4 is for October to September).
SPI computation includes fitting distributions to precipitation data and estimating a probability density function (PDF) and cumulative distribution function (CDF). These functions are further transformed into standardized distributions with unit standard deviations and zero means yielding the SPI value using the expression below (Equation (2)). The SPI value could range from <−2 to >+2 [35], whereas the positive value of SPI indicates a wet condition while the negative value represents a drought condition. Moreover, in this study, the drought thresholds were as follows: weak drought (−1.0 ≤ index < 0), moderate drought (−1.49 ≤ index < −1.0), severe drought (−1.99 ≤ index < −1.50), and extreme drought (index ≤ −2).
where and are the standard deviation and average value of the precipitation, respectively.
2.2.2. Hydrological Drought Assessment
The Streamflow Drought Index (SDI) was developed by [36] and is widely used to characterize hydrological drought events. SDI computation also includes fitting distributions to runoff data and estimation of PDF and CDF and then transforming into a standardized distribution, yielding the SDI value [13]. Similarly, the positive SDI value represents wet conditions, while the negative value represents drought conditions. Furthermore, SPI thresholds were adopted for hydrological drought analysis.
where the cumulative runoff for reference period and the is the hydrological year; is the standard deviation and is the mean value of runoff.
The SDI can also be calculated at various time scales, such as one, three, six, and twelve months. For the estimation of SPI-3, SDI-3, SPI-6, SDI-6, SPI-9, SDI-9, SPI-12, and SDI-12, the cumulative sums of precipitation and runoff for 3, 6, 9, and 12-month timescales were used. When calculating SPI-3 and SDI-3, for example, the cumulative sum for October was obtained by adding the following two-month data (November and December) to the October data [20]. SPI-6 and SDI-6 cumulative sums were calculated by adding six months from October to March.
Furthermore, the Mann-Kendall method [37] was used to estimate the trend in SPI-3, SPI-6, SPI-9, and SPI-12 at a significance level of 5% and similarly for SDI values at different time scales.
2.3. Identification of Linkage between Meteorological and Hydrological Drought and Lag Time
A regression analysis is a statistical technique for estimating the magnitude of the effect of any independent time series (hereafter the meteorological drought index) on any dependent time series (hereafter the hydrological drought index) [38]. In particular, regression analysis is used to better understand the relationships between independent and dependent time series. As a result, a linear regression was used to evaluate the relationship and temporal changes in drought. Coefficient of determination (R2), slope, and p-value were calculated for each relationship using the two-tailed t-test, and R2 was used to indicate the best relationship between SDI and SPI [38]. Equation (5) depicts the mathematical expression of regression between any independent and any dependent time. In the current study, several simple linear regression models were developed between SPI and SDI of the same time scale, e.g., SPI-3 versus SDI-3; SPI-6 versus SDI-6; and similarly for other time scales.
where Y is the dependent time series, a is the regression coefficient, X is the independent time series, is the intercept, and is an error term.
Furthermore, in this study, moving average (running average) analysis was performed at multiple time scales to better assess the correlation between SPI and SDI. It is a quite simple statistical analysis tool used as the fluctuation, trend, or lagging indicator. For a given time series and a fixed size subset, the first value of the moving average is calculated by averaging the fixed subset of the given time series. After this, the subset is shifting forward by including the next number and excluding the first number in the subset. For example, Let (X1, t1), (X2, t2),……, (Xn, tn) represents SPI or SDI time series, X1, X2, …, Xn are the values of SPI or SDI; against time periods t1, t2, …, tn, respectively. The first two moving averages of order k (here 2) can be calculated as given in Equations (6) and (7). A similar procedure was adopted up to the nth value.
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Droughts
3.1.1. Analysis of Meteorological Drought
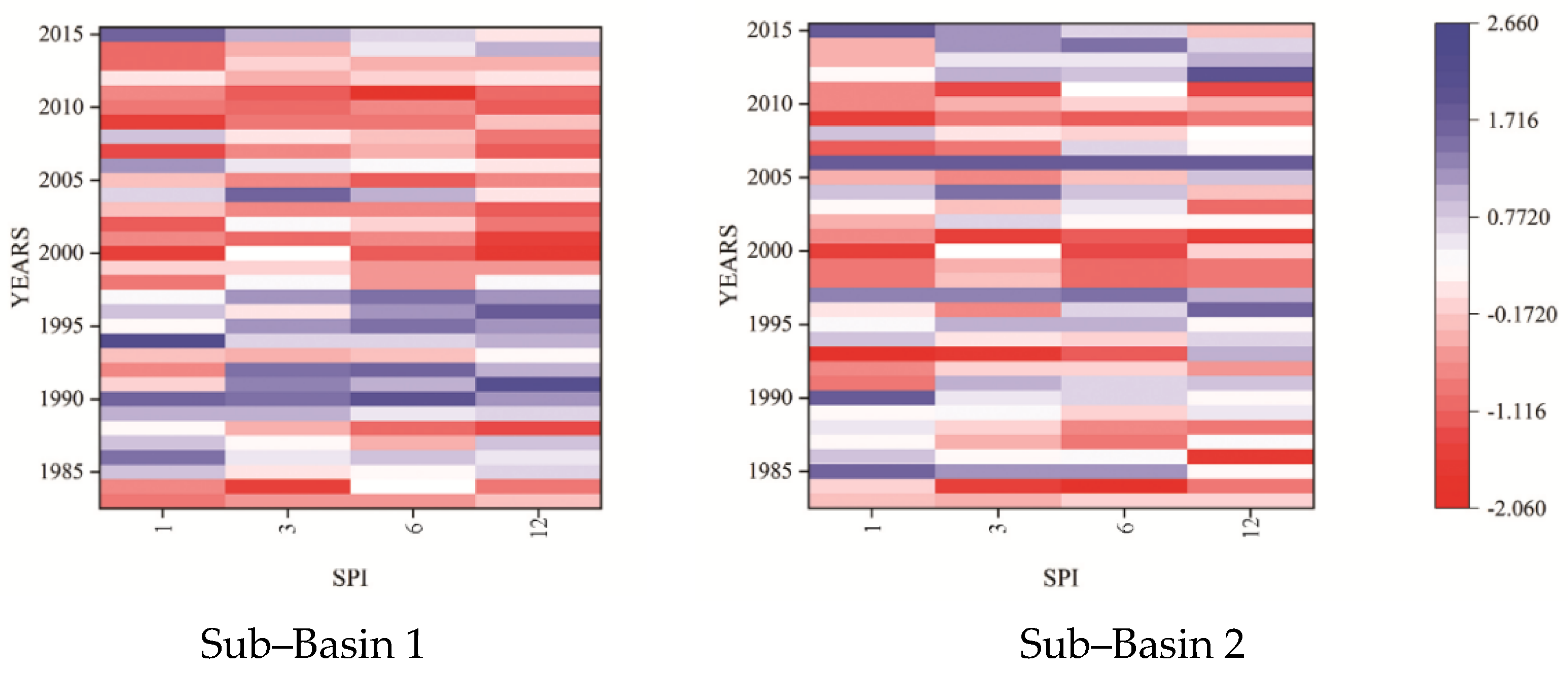
Figure 2 illustrates the meteorological drought index calculated at selected time scales for both sub-basins of the study area. Based on the analysis, it was observed that there was an increase in the frequency of drought after 1998 specifically in the case of sub-basin-1 when SPIs mostly remained negative. These results are in good agreement with the results previously published on droughts in Pakistan [19,20,23,29,39]. The variations in drought between both sub-basins are due to the more relative decrease in precipitation in subbasin-1, compared to sub-basin-2 [30,32]. Moreover, the numbers of drought events were different at different computed time scales. Significant inconsistencies were found when the 3-month time scale was compared with the 6-month time scale, and a comparison between the 6-month and 12-month time scales gave slight variations in results. Results reveal the frequent occurrence of severe drought events at each sub-basin of the study area, and these were more sensitive to short-term drought compared to long-term droughts. According to the results, the recurrence of drought is more frequent and consecutive at 1 to 6 months’ timescale in sub-basin 1 and during the 12-month timescale, there exists a sharp difference between wet and dry episodes. while the sub-basin 2 is found to be more sensitive to drought (mild to severe) at a 1-month timescale as compared to 3, 6, and 12-month timescales. The results also specified that the drought events state varied with the increase in SPI time scales, mostly a declining trend in sub-basin 2. This is due to the reason that computation of 12-month time scale SPI involves the aggregation of total precipitation from October to September and includes both wet and dry seasons. However, the 3-month SPI time scale considers only the sum of three-month precipitation, and the 3-month time scale (March-May) of the study basin was normally a dry season.
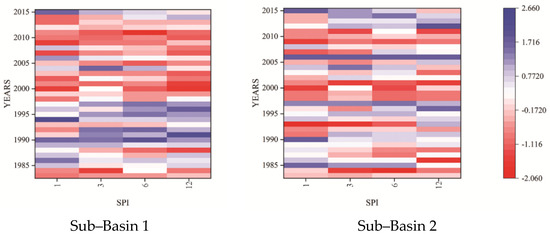
Figure 2.
Temporal variations of meteorological drought periods during 1983–2015 in sub–basins 1 and 2.
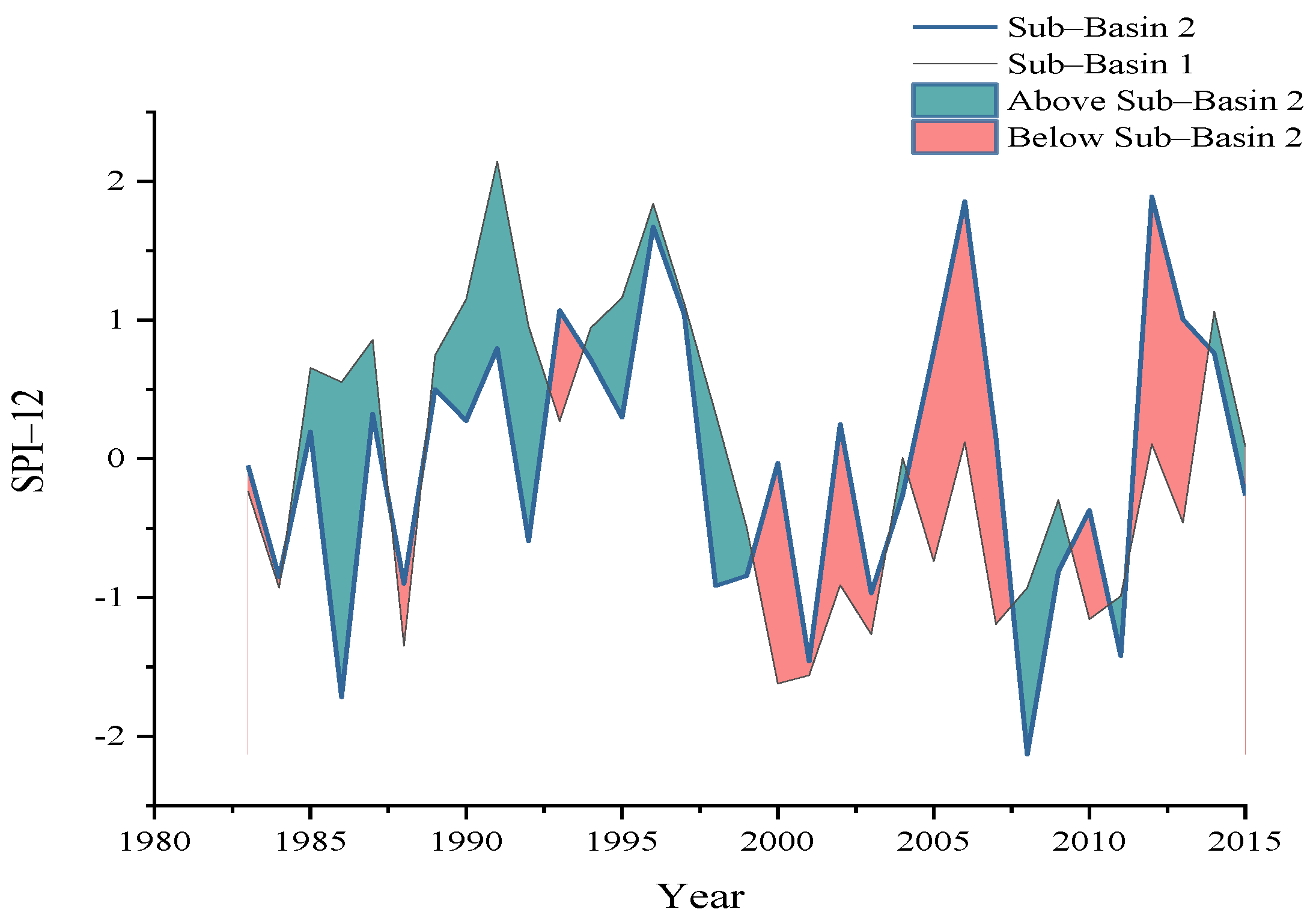
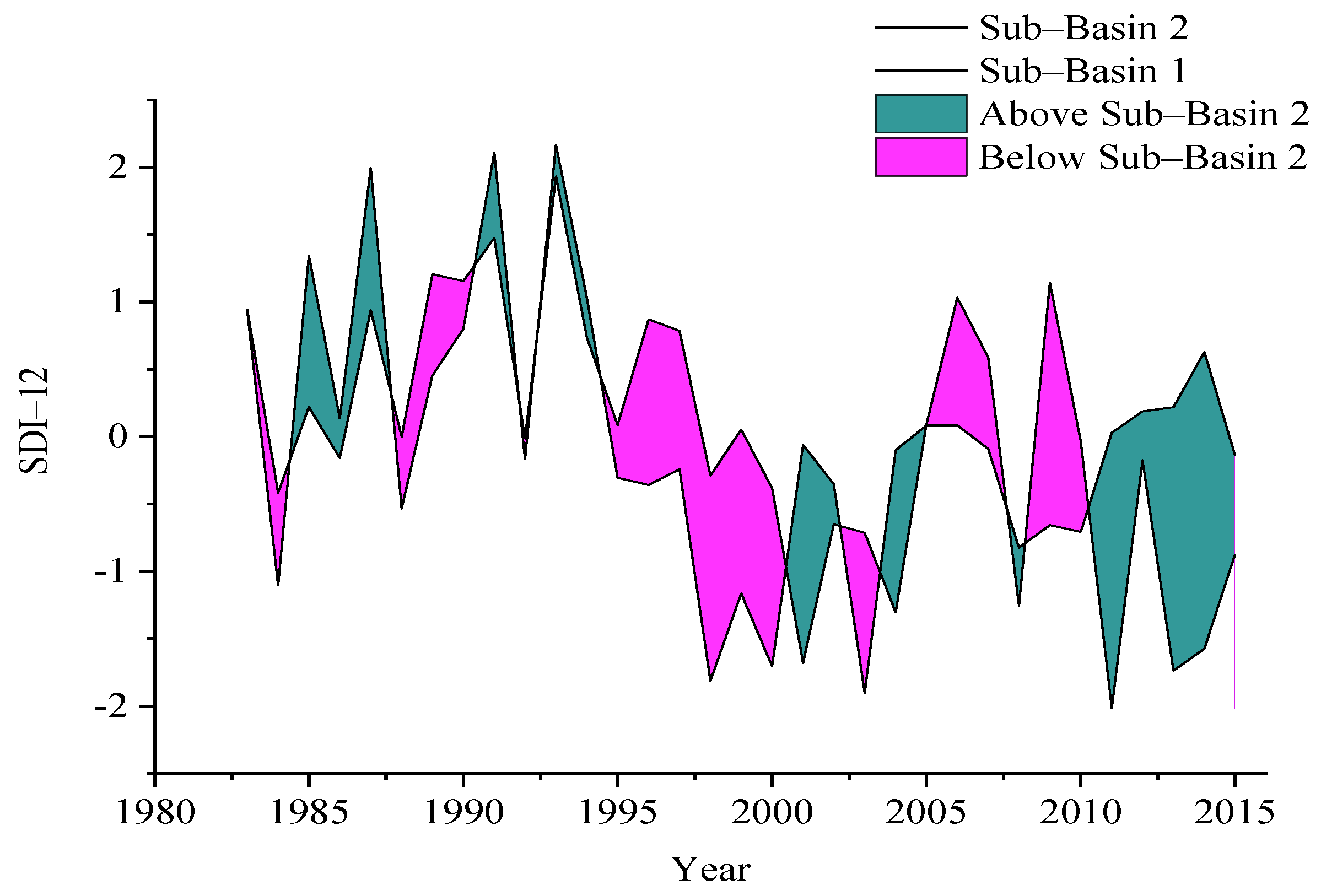
Figure 3 illustrates the severity of meteorological drought based on the 12-month time scale for both hydrological sub-basins and the difference in their SPI-12 values during the study period (i.e., 1983–2015). Based on the analysis, it resulted that the years from 1998 to 2004 were the driest years of the selected time series. Moreover, the difference in meteorological drought (SPI-12) severity at both sub-basins represents the notable spatial variations across the Soan river basins. The Mann-Kendall test was also used on SPI-12 to figure out the trend in meteorological drought at sub-basin 1 and sub-basin 2. The analysis showed an increase in meteorological drought severity during the past 33 years, and a significant decreasing trend in SPI–12 values was observed downstream, i.e., sub-basin 2. The Z-value of the Mann-Kendall test was 1.78 at upstream sub-basin 1, and 1.71 at downstream sub-basin 2.
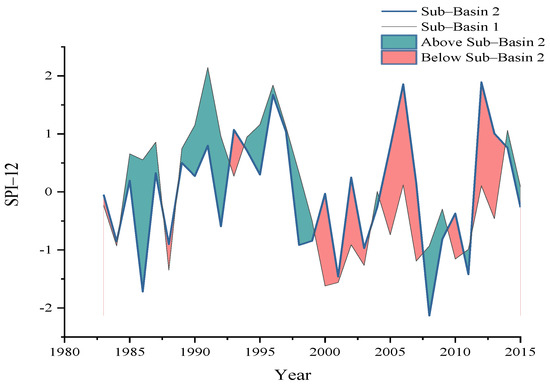
Figure 3.
Difference in meteorological drought (SPI–12) severity at both sub-basins representing the spatial variations across the Soan river basins.
3.1.2. Analysis of Hydrological Droughts
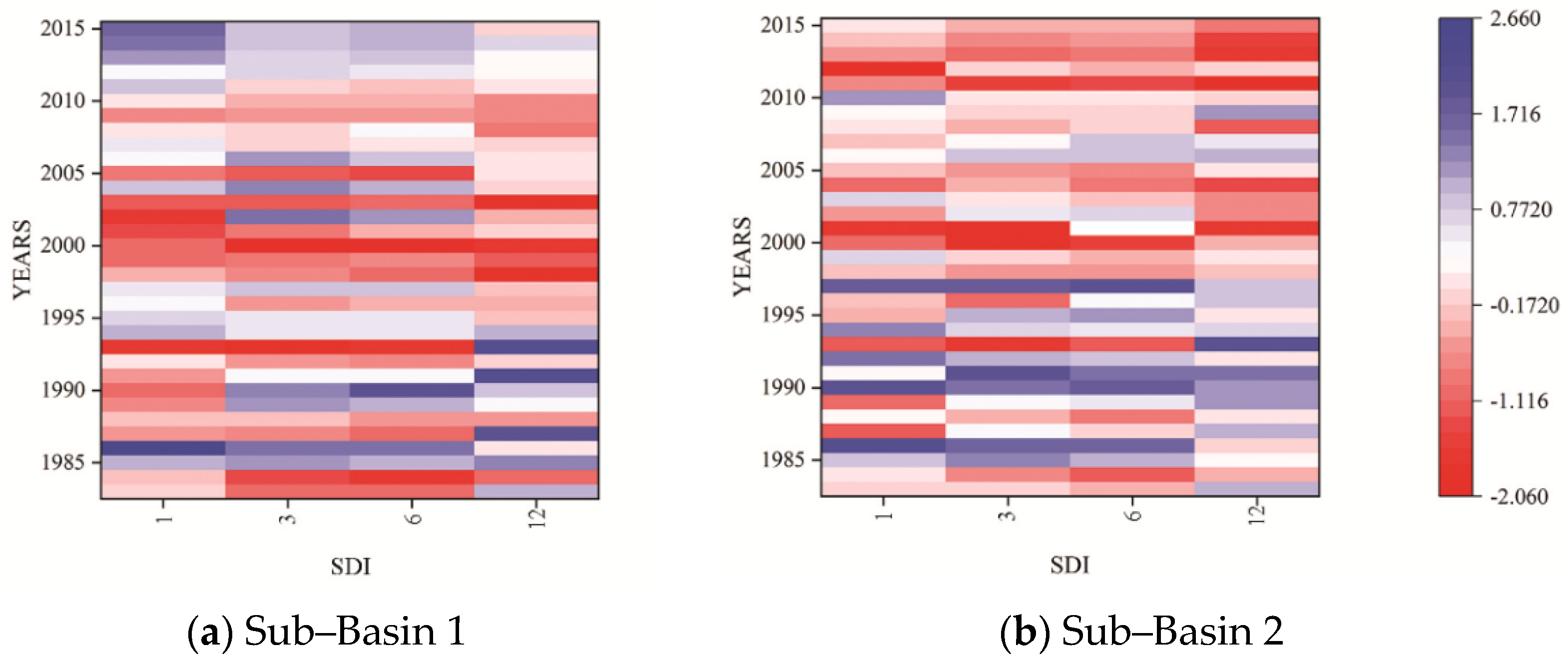
Figure 4 depicts the temporal variations of hydrological drought periods in sub-basins 1 and 2 at different time scales, indicating the occurrence of hydrological drought over the last three decades. Hydrological drought, like meteorological drought, was more sensitive to short-term droughts than long-term droughts. Drought events occurred continuously from 1983 to 2015, with the driest period for the study area being 1998–2004. Drought patches were also randomly observed in 1993, 1998–2004, and 2009. Sub-basin 1 was stressed by hydrological drought, and the number of drought events was high from 1985 to 2004, with a slight wet condition from 2005-to 2015. However, in the case of sub-basin 2, the results showed that the frequency of hydrological drought events was increasing in the basin from 1983 to 2015. Figure 5 shows the illustration of the difference in hydrological drought severity (SDI-12) for two sub-basins and indicates notable variations across the two sub-basin. Furthermore, based on the MK test, a statistically significant trend was observed for downstream sub-basins 2 with a Z-value of 1.83, whereas, upstream sub-basin 1 showed opposite behavior with an insignificant statistical trend. However, there still exists an increasing trend of drought at upstream sub-basin 1.
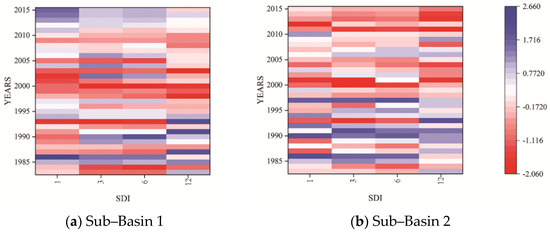
Figure 4.
Temporal variation of hydrological drought periods in sub-basins 1 and 2 at different time scales.
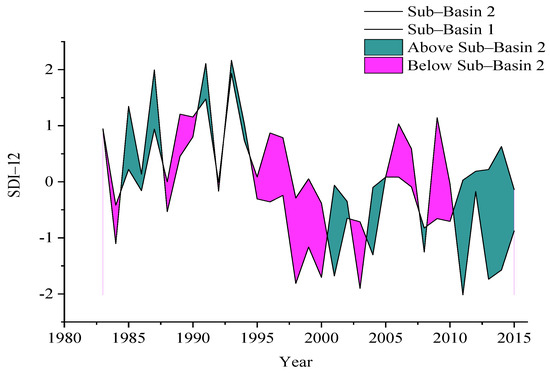
Figure 5.
Difference in Hydrological drought (SDI–12) severity at both sub-basins representing the spatial variations across the Soan river basin.
3.2. Link between Meteorological and Hydrological Droughts
3.2.1. Establishing Regression Function
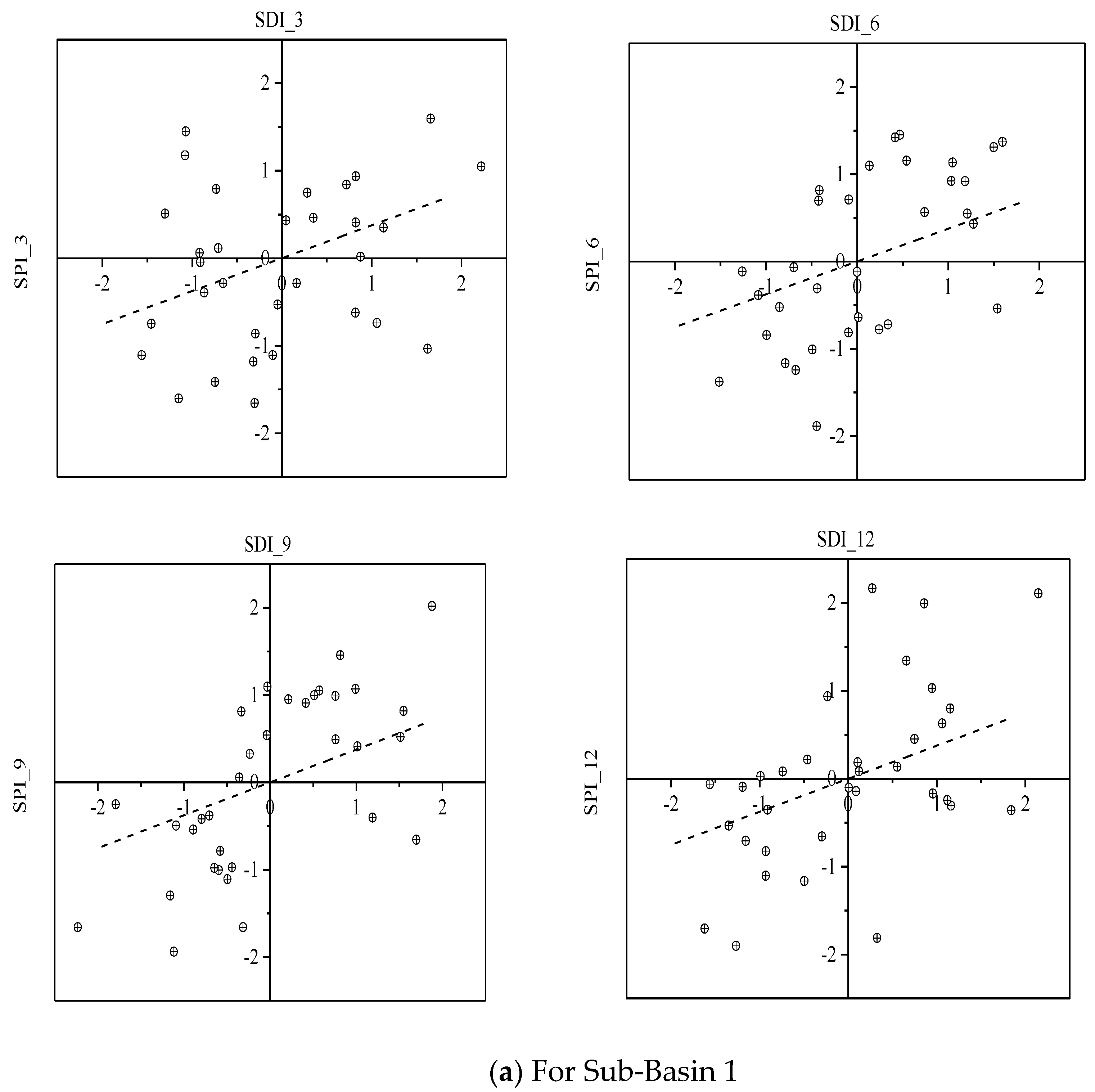
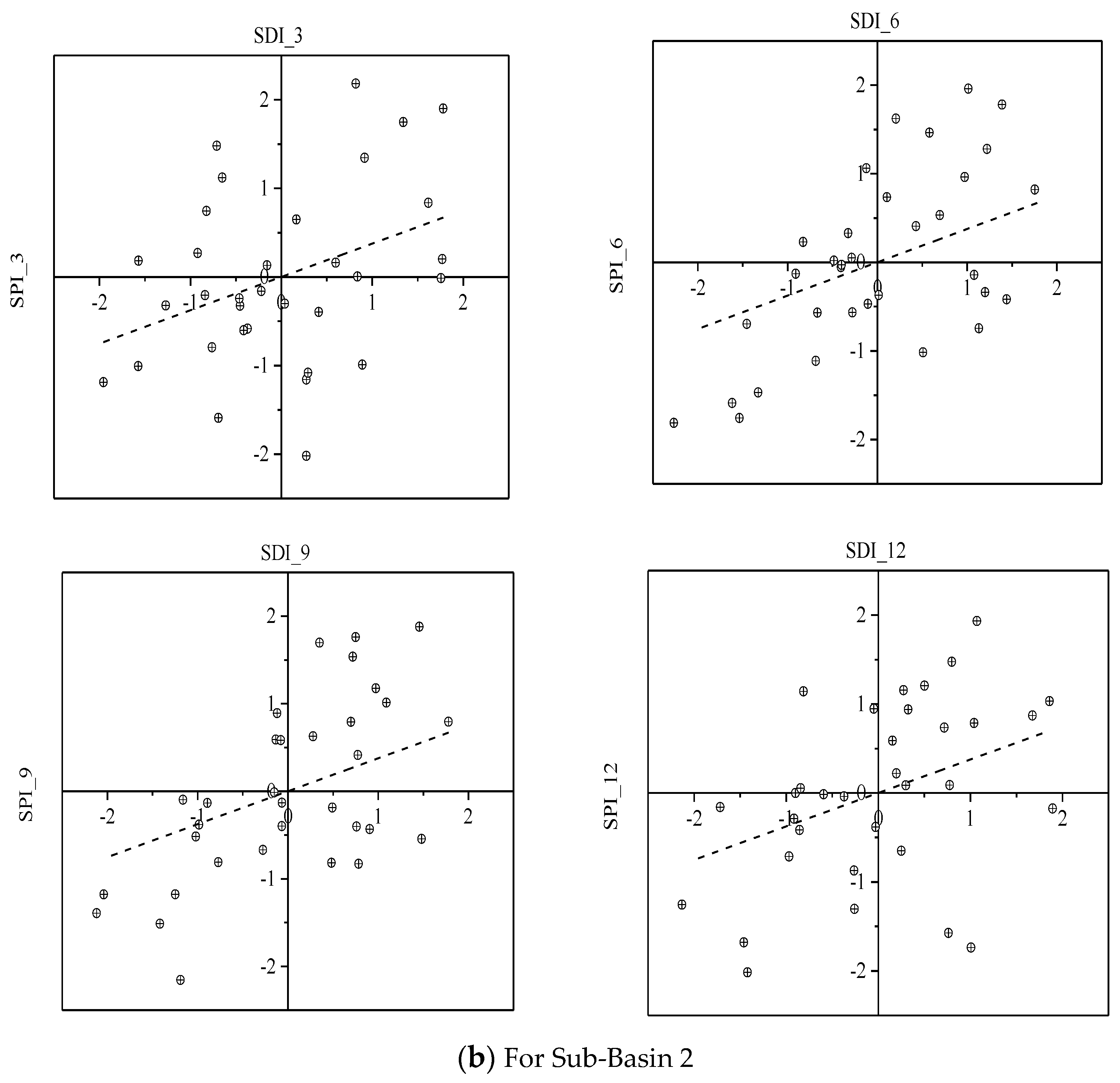
The coefficient of determination (R2) and regression coefficient (a) extracted from linear regression equations (Table 1) showed that a significant relationship existed between SDI and SPI, and it increased up to the 9-month time scale and then decrease in the case of the 12-month time scale. The coefficient of determination (R2) of the 6-months and the 9-month time scale was relatively higher as compared to the other two time scales. Moreover, the correlation of SPI and SDI was higher at upstream sub-basin 1 of the Soan River Basin as compared to downstream. For instance, sub-basin 1 and sub-basin 2 had 0.66 and 0.63 values of R2 based on a 9-month time scale respectively. The regression lines with the related data points are shown in Figure 6 which may be utilized for the prediction of hydrological droughts using the meteorological droughts information.

Table 1.
Results of Regression modeling developed between SDI on SPI.
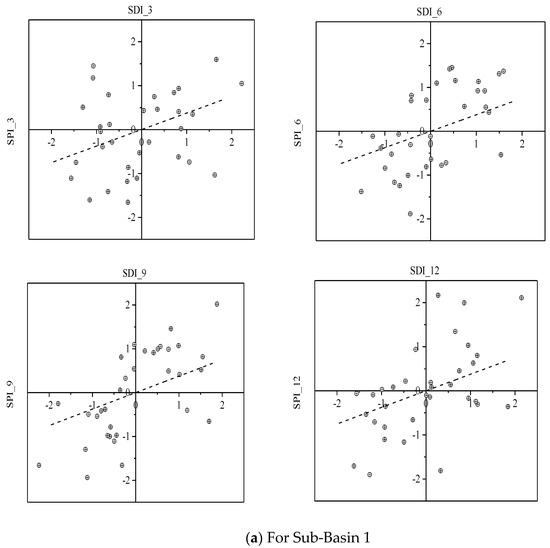
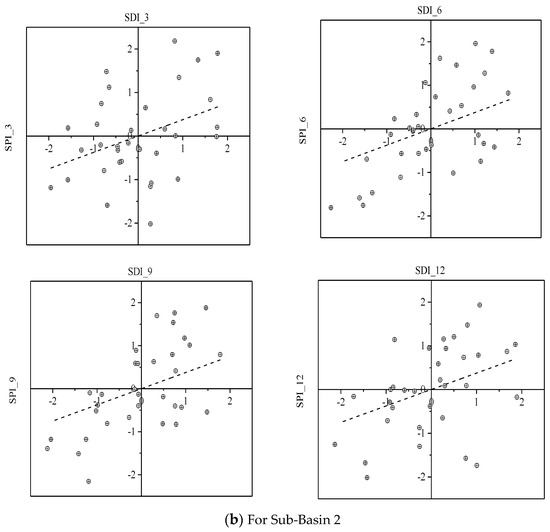
Figure 6.
The linear relationship between SDI and SPI at the four selected time scales.
3.2.2. Moving Average Analysis and Lag Time Identification
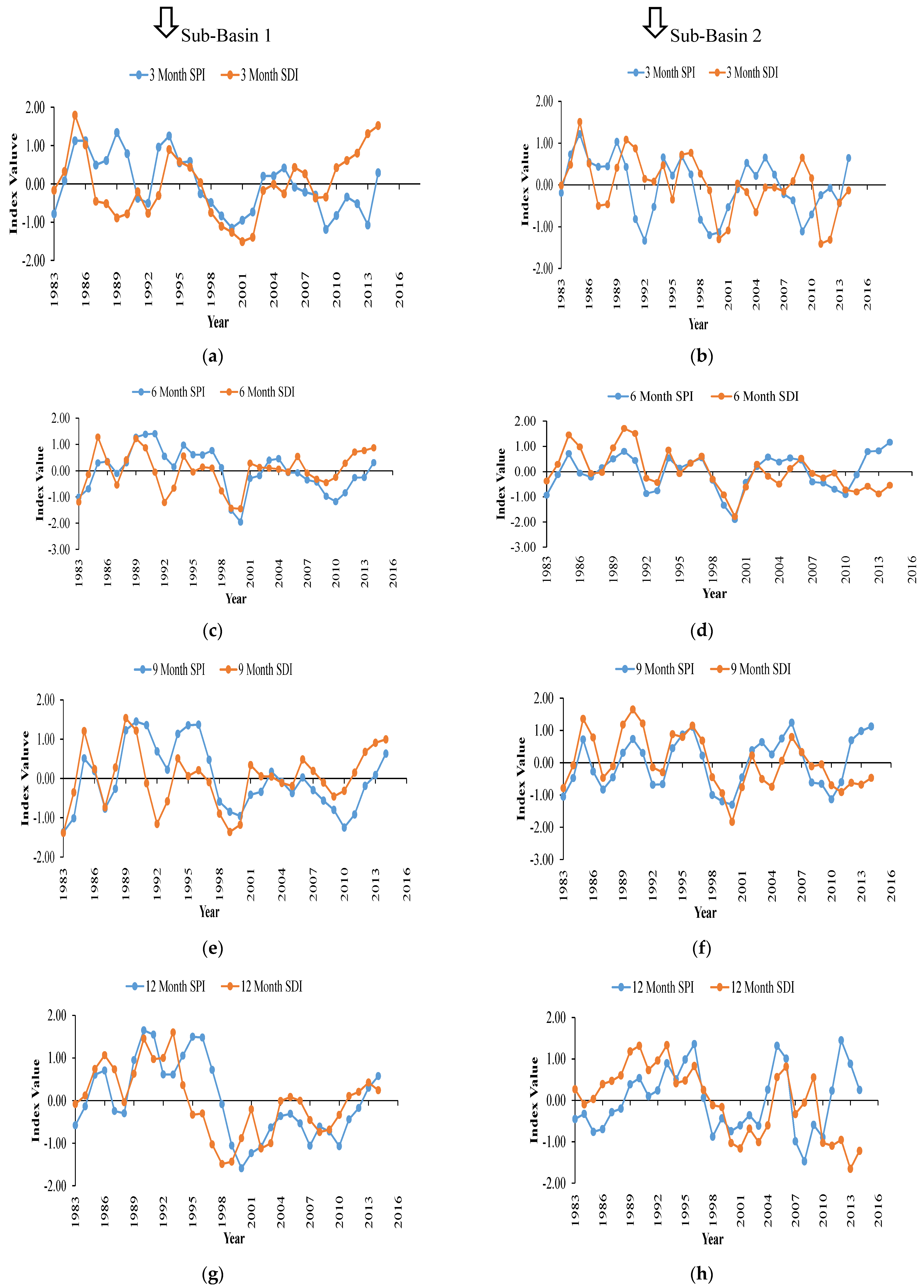
A moving average analysis was performed at multiple time scales to better assess the correlation between SPI and SDI, see Figure 7. Results show that the variations of SPI and SDI were quite comparable; however, the differences between them do exist. In general, a strong correlation was observed between SPI and SDI at the upstream sub-basin 1, i.e., CC = 0.66. Overall based on the correlation analysis with different lag times, it was observed that at both sub-basins, the SDI was 1 month lagging behind SPI at 3-month and 12-month time scales and 2 months lagging for 6–month and 9-month time scales. This period of lagging time was in accordance with the prior study [7].
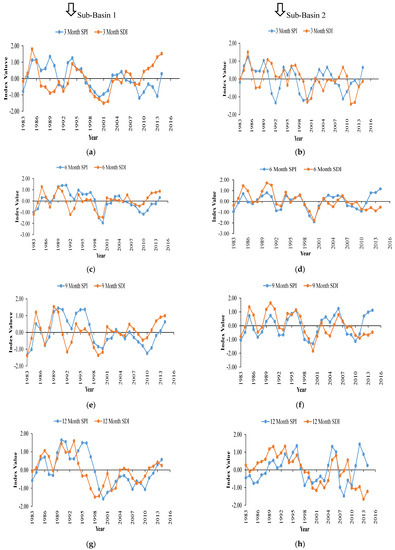
Figure 7.
Moving average analysis for lag time identification between SPI and SDI at sub-basins 1 and 2 for different time scales. (a,b) 3 months, (c,d) 6 months, (e,f) 9 months, (g,h) 12 months.
4. Discussion
Climate change includes the variations in the behavior of climatic parameters, e.g., precipitation, evapotranspiration, etc. [40]. Whereas anthropogenic activities include land-use/land cover changes, irrigation area expansion, increased water diversion, water conservation practices, etc. During the last decades, the Soan basin experienced precipitation and runoff variation (with a change point in 1998 [30]) due to both climate change and anthropogenic activities [30,32]. Based on the drought analysis performed in the current study, notable variations between SPI and SDI values were found over the past three decades. It could be mainly because of major changes in agricultural land, forest, settlement, water bodies, and bare land in addition to natural climate variability [41].
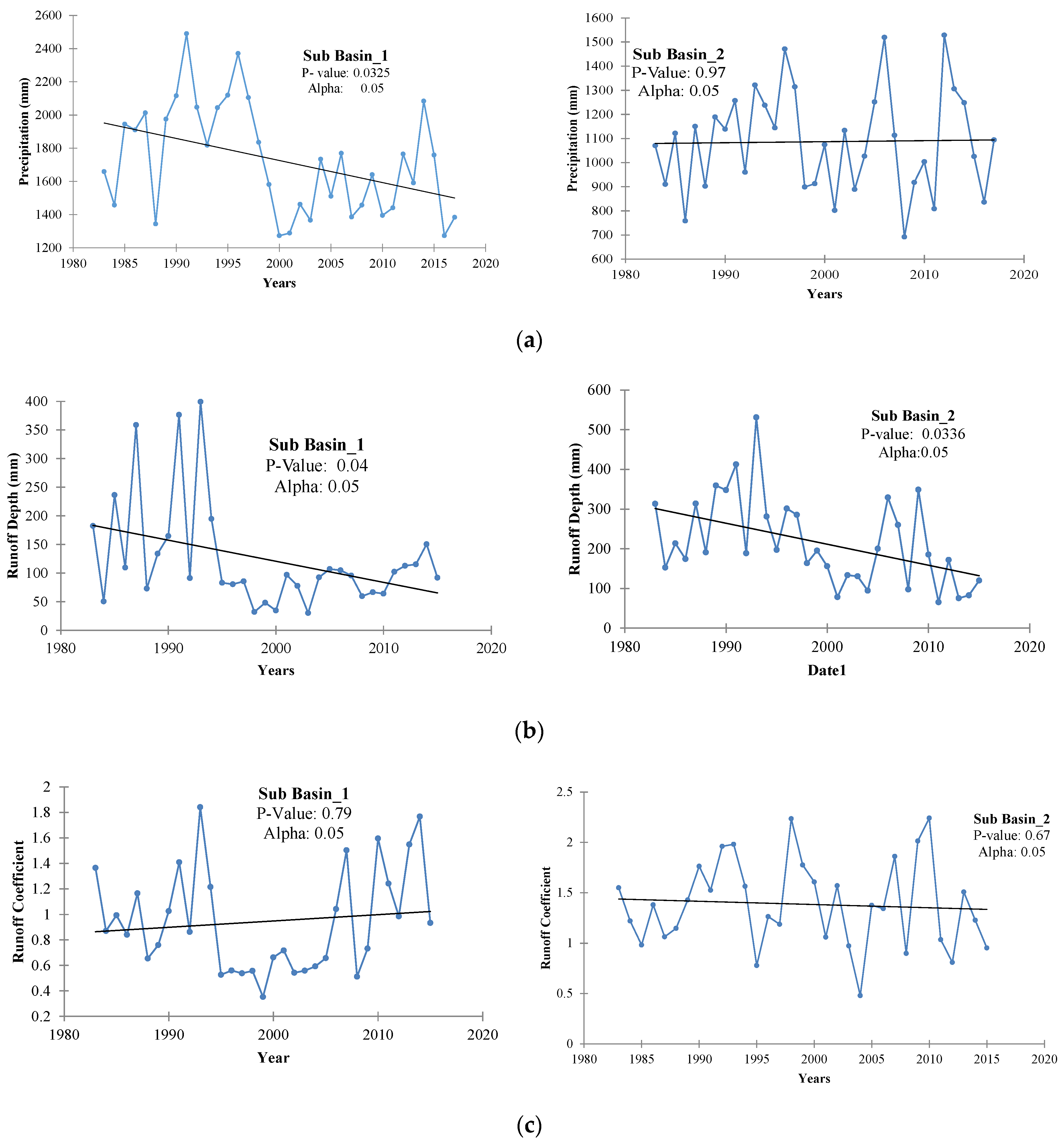
To further justify, a trend analysis of precipitation, runoff, and runoff coefficient had been performed. The analysis resulted, in the case of sub-basin 1 a declining trend in precipitation was observed during the years 1983–2015, as shown in Figure 8a. For instance, the average annual precipitation decreased from 1983–1997 (1950 mm) to 1998–2015 (1570.50 mm). This decline in precipitation was significant in sub-basin 1, while little variation (no significant trend) was found in the case of sub-basin 2 with an average value of 1115 mm and 1065 mm for 1983–1997 and 1998–2015 respectively. For sub-basin 1, the annual runoff depth had a decreasing trend (i.e., an average of 174.44 mm for 1983–1997, and 84.00 mm for 1998–2015) during the study period (left panel Figure 8b) and, the runoff coefficient had no significant trend (left panel Figure 8c). Similarly, in the case of sub-basin 2, runoff depth has a decreasing trend, while runoff coefficient has no significant trend as the p-value is greater than alpha. The variations in the trend direction of runoff, and runoff coefficient in the case of sub-basins 1 and 2 could be mainly due to land-use changes, e.g., 71 km2 and 1611 km2 increase in agriculture land was observed in sub-basins 1 and 2 respectively from 1983–1997 to 1998–2015 [30].
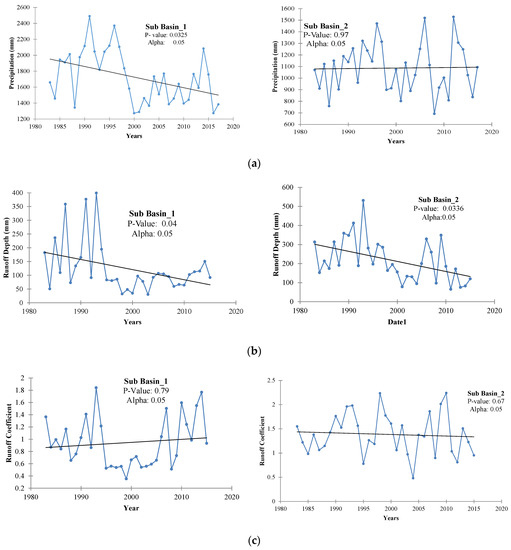
Figure 8.
Temporal Variation of (a) Precipitation, (b) Runoff depth, and (c) Runoff Coefficient at sub-basin 1 and 2.
Moreover, the higher decreasing rate in runoff compared to precipitation and change point showed the possible effect of anthropogenic activities [32]. It was anticipated because of a significant increase in the intensity of crops and the construction of large numbers of small dams from 1998- onward [27]. These significant variations were also anticipated due to the significant number of development projects under the Government of Punjab, Pakistan, which comprises the development of ponds and mini-dams for rainwater harvesting and to increase the intensity of agriculture. The initiative of these developments was to increase the storage for crop and drinking purposes, which might have caused the increase in evaporation, and water use for the growing population, ultimately decrease in surface runoff and increasing in probability of drought occurrence. In addition to that, a reservoir could decrease the frequency, duration, and severity of drought events downstream of the dam, and irrigation practices can primarily influence hydrological droughts by consuming streamflow and groundwater, which typically results in a decrease in streamflow and groundwater levels [16,42]. Hence, the Simly reservoir operation, as well as seasonal irrigation practices, could have an impact on the statistical relationship among drought indices.
The difference in SPI and SDI trends could be due to evapotranspiration or lag time between rainfall and runoff, which could predict the propagation of meteorological to hydrological droughts. Drought propagation may also be influenced by basin characteristics such as soil moisture, land use, and the relationships between streamflow and groundwater. A time lag was used to perform cross-correlation between SPI and SDI, which acknowledged the sequence between SPI and SDI and demonstrated that meteorological drought events could be used to predict hydrological droughts in relatively small watersheds with less anthropogenic activities.
5. Conclusions
This study concludes that the frequency of both hydrological and meteorological droughts increased in the Soan River Basin during the study period. At various time scales, Sub-basin 1 was subjected to more frequent meteorological moderate drought and hydrological drought events. The current study was also designed to investigate the relationship between meteorological and hydrological drought events and SPI and SDI by developing a simple linear function between them. The results of a linear regression between SPI and SDI show an increase in regression coefficients with increasing time scale and became stronger until the ninth month. Climate change and anthropogenic activities (i.e., land use/land cover changes) are the main reasons that cause the variations between these two types of droughts. Moreover, the hydrological drought events commonly lagged 1–3 months (subject to the time scale and sub-basin) from the meteorological drought events. The dissimilarities between these two types of droughts became larger due to climatic variation and might be due to human activities as well. Conclusively, this study provided drought propagation and the basis for long-term drought forecasting and, thus, can be employed for early warning water resources management and as an extension of this current study can be to assess the climate change impacts on hydrological drought at the basin scale.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.N.S. and M.W.; methodology, M.A. and A.A.; software, M.A.; validation, M.W., J.E.L. and M.A.; formal analysis, I.A. and A.A.; investigation, F.u.H.; data curation, A.N.S. and M.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.E.L.; funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education of the Republic of Korea and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2020S1A5B8103910).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data is provided in the form of tables and figures.
Acknowledgments
The Authors appreciate the NRPU-HEC projects.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dai, A. Drought under Global Warming: A Review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Loon, A.F.; Stahl, K.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Clark, J.; Rangecroft, S.; Wanders, N.; Gleeson, T.; Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Hannaford, J. Drought in a Human-Modified World: Reframing Drought Definitions, Understanding, and Analysis Approaches. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 3631–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilhite, D.A. Drought as a Natural Hazard. In Droughts; Routledge: London, UK, 2021; p. 33. [Google Scholar]
- Vidal, J.-P.; Martin, E.; Franchistéguy, L.; Habets, F.; Soubeyroux, J.-M.; Blanchard, M.; Baillon, M. Multilevel and Multiscale Drought Reanalysis over France with the Safran-Isba-Modcou Hydrometeorological Suite. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 459–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, E.; Bier, G.; Van Lanen, H.A.J.; Torfs, P. Propagation and Spatial Distribution of Drought in a Groundwater Catchment. J. Hydrol. 2006, 321, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edossa, D.C.; Babel, M.S.; Das Gupta, A. Drought Analysis in the Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 1441–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, A.A.; Khalili, D.; Kamgar-Haghighi, A.A.; Zand-Parsa, S. Utilization of Time-Based Meteorological Droughts to Investigate Occurrence of Streamflow Droughts. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 4287–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslinger, K.; Koffler, D.; Schöner, W.; Laaha, G. Exploring the Link between Meteorological Drought and Streamflow: Effects of Climate-catchment Interaction. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 2468–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jörg-Hess, S.; Griessinger, N.; Zappa, M. Probabilistic Forecasts of Snow Water Equivalent and Runoff in Mountainous Areas. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 2169–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghalizadeh, M.; Ghameshlou, A.N.; Bazrafshan, J.; Bazrafshan, O. A Copula-Based Joint Meteorological–Hydrological Drought Index in a Humid Region (Kasilian Basin, North Iran). Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, P.; Huang, Q.; Leng, G.; Hou, B.; Ma, L. The Propagation from Meteorological to Hydrological Drought and Its Potential Influence Factors. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhou, L.; Huang, S. A Hybrid Drought Index Combining Meteorological, Hydrological, and Agricultural Information Based on the Entropy Weight Theory. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, V.; Algin, H.M. Meteorological and Hydrological Drought Analysis of the Seyhan− Ceyhan River Basins, Turkey. Meteorol. Appl. 2017, 24, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Leng, G.; Liu, S. A Nonparametric Multivariate Standardized Drought Index for Characterizing Socioeconomic Drought: A Case Study in the Heihe River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijdeman, E.; Barker, L.J.; Svoboda, M.D.; Stahl, K. Natural and Human Influences on the Link between Meteorological and Hydrological Drought Indices for a Large Set of Catchments in the Contiguous United States. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 6005–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Gao, L.; Yao, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M. Response of Hydrological Drought to Meteorological Drought under the Influence of Large Reservoir. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 2197142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, G.; Van Lanen, H.A.J.; Torfs, P. Probabilistic Analysis of Hydrological Drought Characteristics Using Meteorological Drought. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sattar, M.N.; Lee, J.-Y.; Shin, J.-Y.; Kim, T.-W. Probabilistic Characteristics of Drought Propagation from Meteorological to Hydrological Drought in South Korea. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 2439–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Waseem, M.; Ullah, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, J. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Meteorological and Hydrological Droughts and Their Propagations. Water 2021, 13, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Khurshid, T.; Abbas, A.; Ahmad, I.; Javed, Z. Impact of Meteorological Drought on Agriculture Production at Different Scales in Punjab, Pakistan. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2022, 13, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Harun, S.B.; Wang, X. Characterization of Seasonal Droughts in Balochistan Province, Pakistan. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.M. Drought Management and Prevention in Pakistan. In Proceedings of the COMSATS 1st Meeting on Water Resources in the South: Present Scenario and Future Prospects, Islamabad, Pakistan, 1–2 November 2001; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Nawaz, N. Impacts of Climate Variability and Change on Seasonal Drought Characteristics of Pakistan. Atmos. Res. 2018, 214, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Wang, X.; Nawaz, N.; Khan, N. Spatiotemporal Changes in Aridity of Pakistan during 1901–2016. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 3081–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahid, M.; Rasul, G. Frequency of Extreme Temperature and Precipitation Events in Pakistan 1965–2009. Sci. Int. 2011, 23, 313–319. [Google Scholar]
- Usman, M.; Nichol, J.E. A Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Rainfall and Drought Monitoring in the Tharparkar Region of Pakistan. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adnan, S.; Ullah, K.; Gao, S.; Khosa, A.H.; Wang, Z. Shifting of Agro-climatic Zones, Their Drought Vulnerability, and Precipitation and Temperature Trends in Pakistan. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Ringler, C.; Zhu, T.; Waqas, A. Droughts in Pakistan: A Spatiotemporal Variability Analysis Using the Standardized Precipitation Index. Water Int. 2013, 38, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Azam, M.; Rehman, S.U.; Waseem, M.; Anjum, M.N.; Afzal, A.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Mehtab, M.; Latif, M.; Ahmed, R. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Drought Characteristics across Pakistan. Paddy Water Environ. 2022, 20, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Cong, Z.; Zhang, D. Understanding the Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Streamflow: A Case Study of the Soan River Basin, Pakistan. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 134, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Khalid, S.; Schreck, E.; Xiong, T.; Niazi, N.K. Foliar Heavy Metal Uptake, Toxicity and Detoxification in Plants: A Comparison of Foliar and Root Metal Uptake. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 325, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muhammad, W.; Muhammad, S.; Khan, N.M.; Si, C. Hydrological Drought Indexing Approach in Response to Climate and Anthropogenic Activities. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 141, 1401–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, C.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal Drought Analysis by the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) and Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI) in Sichuan Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Yang, D.; Lei, H.; Xu, K.; Xu, X. Comparative Analysis of Drought Based on Precipitation and Soil Moisture Indices in Haihe Basin of North China during the Period of 1960–2010. J. Hydrol. 2015, 526, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Lü, H.; Wang, W.; Fu, G. From Meteorological Droughts to Hydrological Droughts: A Case Study of the Weihe River Basin, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbantis, I.; Tsakiris, G. Assessment of Hydrological Drought Revisited. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 881–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Ahmad, I.; Mujtaba, A.; Tayyab, M.; Si, C.; Lü, H.; Dong, X. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Precipitation in Southwest Arid-Agriculture Zones of Pakistan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waseem, M.; Ajmal, M.; Kim, T.-W. Improving the Flow Duration Curve Predictability at Ungauged Sites Using a Constrained Hydrologic Regression Technique. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 20, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Ajmal, M.; Ahmad, I.; Khan, N.M.; Azam, M.; Sarwar, M.K. Projected Drought Pattern under Climate Change Scenario Using Multivariate Analysis. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Johanson, C.M.; Warren, S.G.; Seidel, D.J. Contribution of Stratospheric Cooling to Satellite-Inferred Tropospheric Temperature Trends. Nature 2004, 429, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, F.; Mu, X.; Yan, H.; Zhao, G. An Assessment of Human versus Climatic Impacts on Jing River Basin, Loess Plateau, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 478739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Yao, H.; Gao, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M. Non-Linear Relationship of Hydrological Drought Responding to Meteorological Drought and Impact of a Large Reservoir. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).