An Adaptive and Bounded Controller for Formation Control of Multi-Agent Systems with Communication Break
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- A definite bounded control law is proposed for anti-saturation control. The nonlinearity caused by maneuvers is considered compared with [24], then a controller with nonlinear parameters is proposed in this paper. Those parameters are designed as functions of states, and the values space of critical parameters is analyzed subsequently. Differing from the use of auxiliary variables in previous literature, parameters of reference are altered adaptively according to the value of inputs, which will be more applicable and easier to be realized.
- (2)
- A nonlinear dynamic programming regulator is proposed for reference with bearings only for some agents encountering breaks. Instead of expected locations change for all agents, we expect to change the expected locations of agents encountering saturation only for sensing measurements. Thus, most parts of the formation won’t be altered if they are not expected to be changed.
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Graph Theory
2.2. Numerical Models and Input Saturation
2.3. Effect of Communication Break
3. Main Results
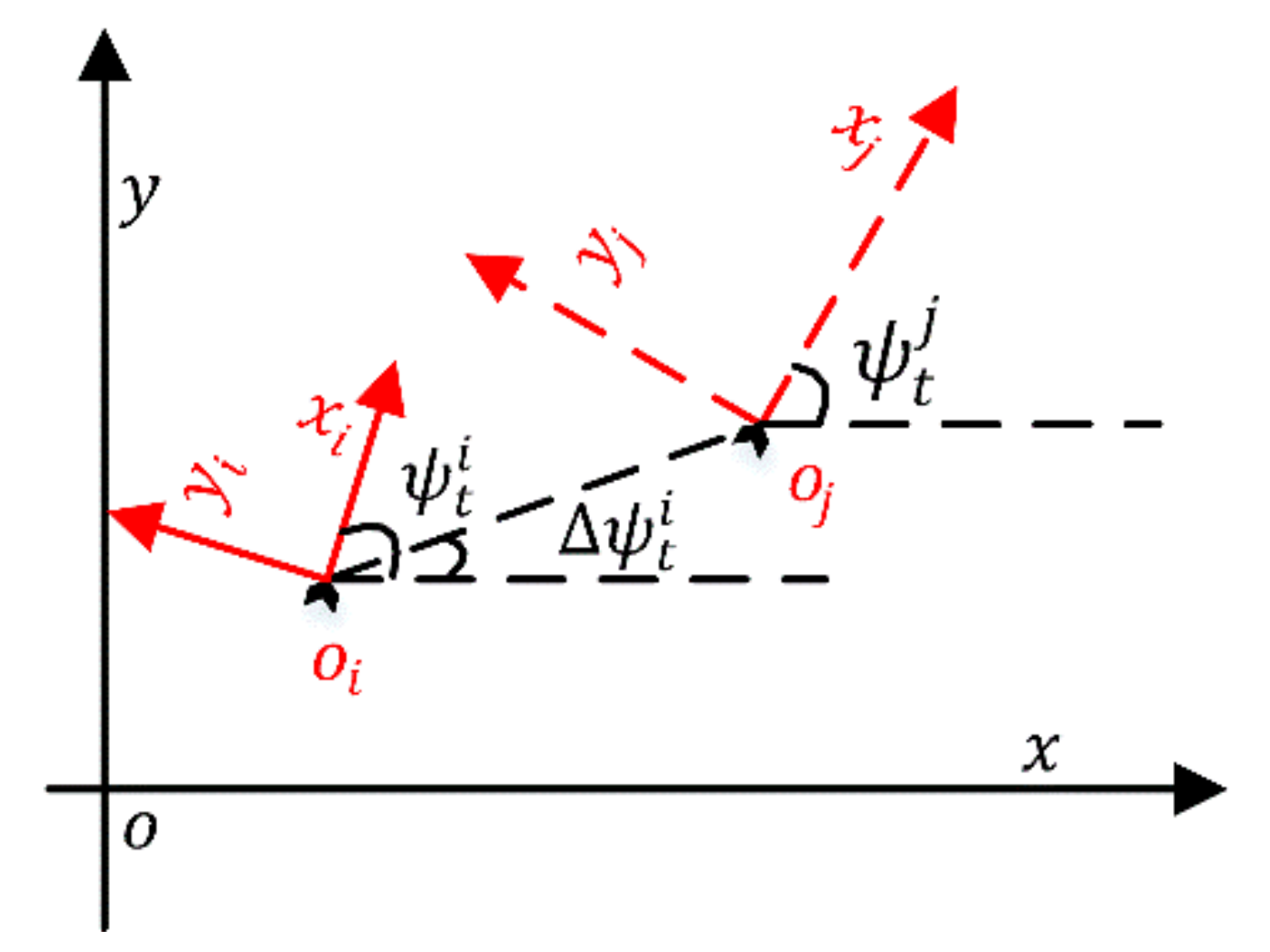
3.1. Reference Information Processing
3.2. Nonlinear Controller Design and Stability Analysis
3.3. Adaptive Rules for Parameters
3.4. Communication Interference Resistance with Sensors
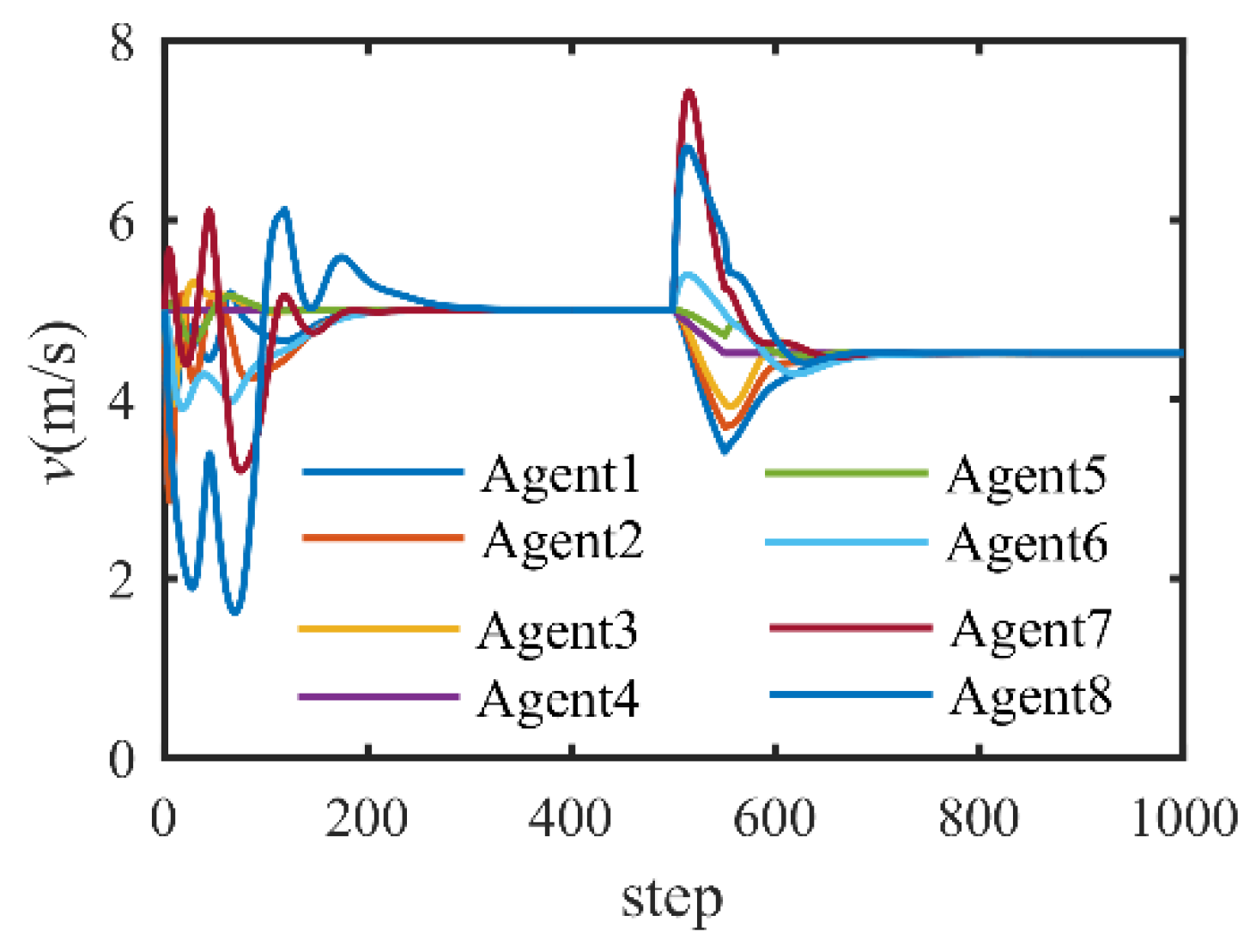
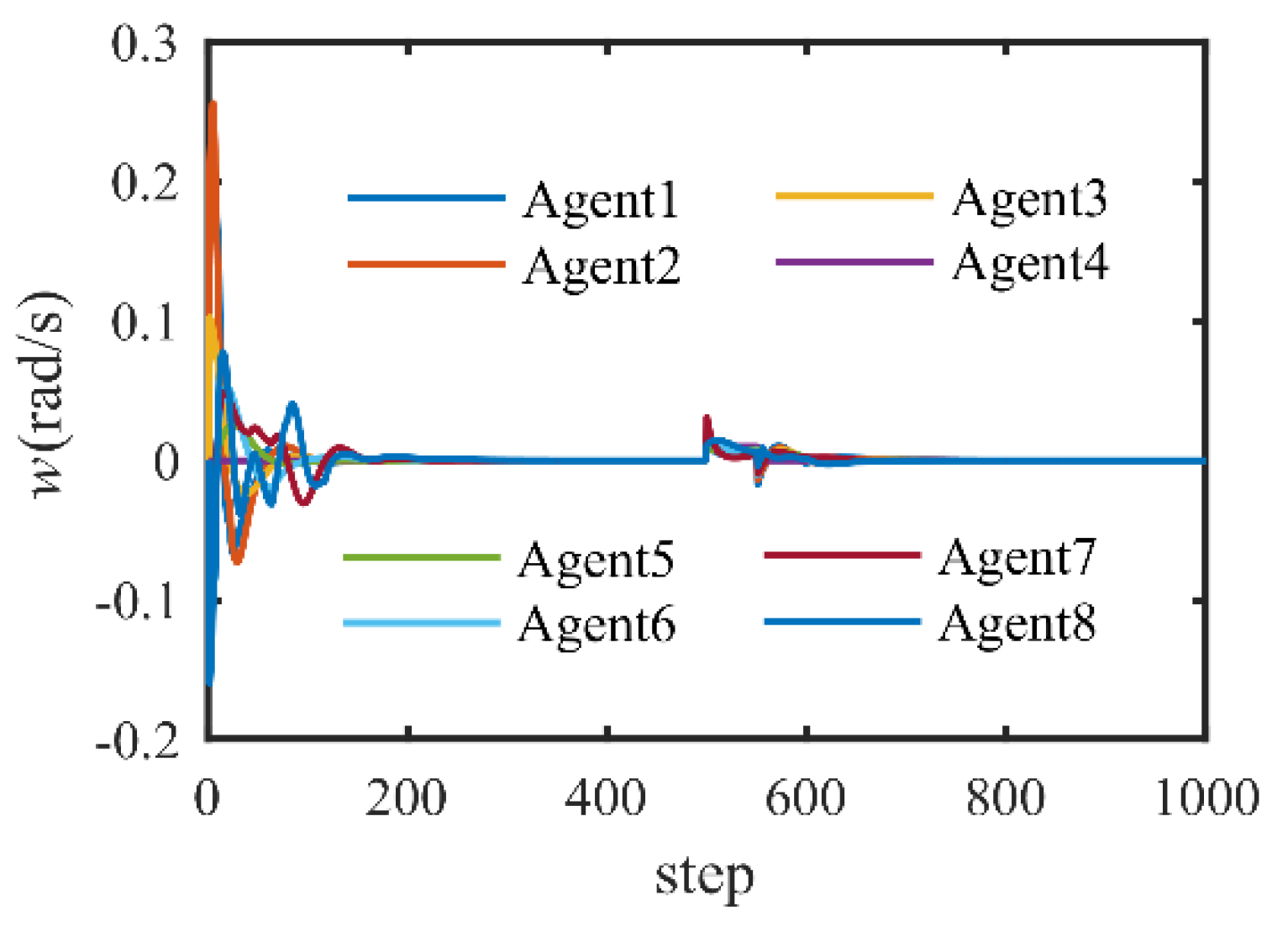
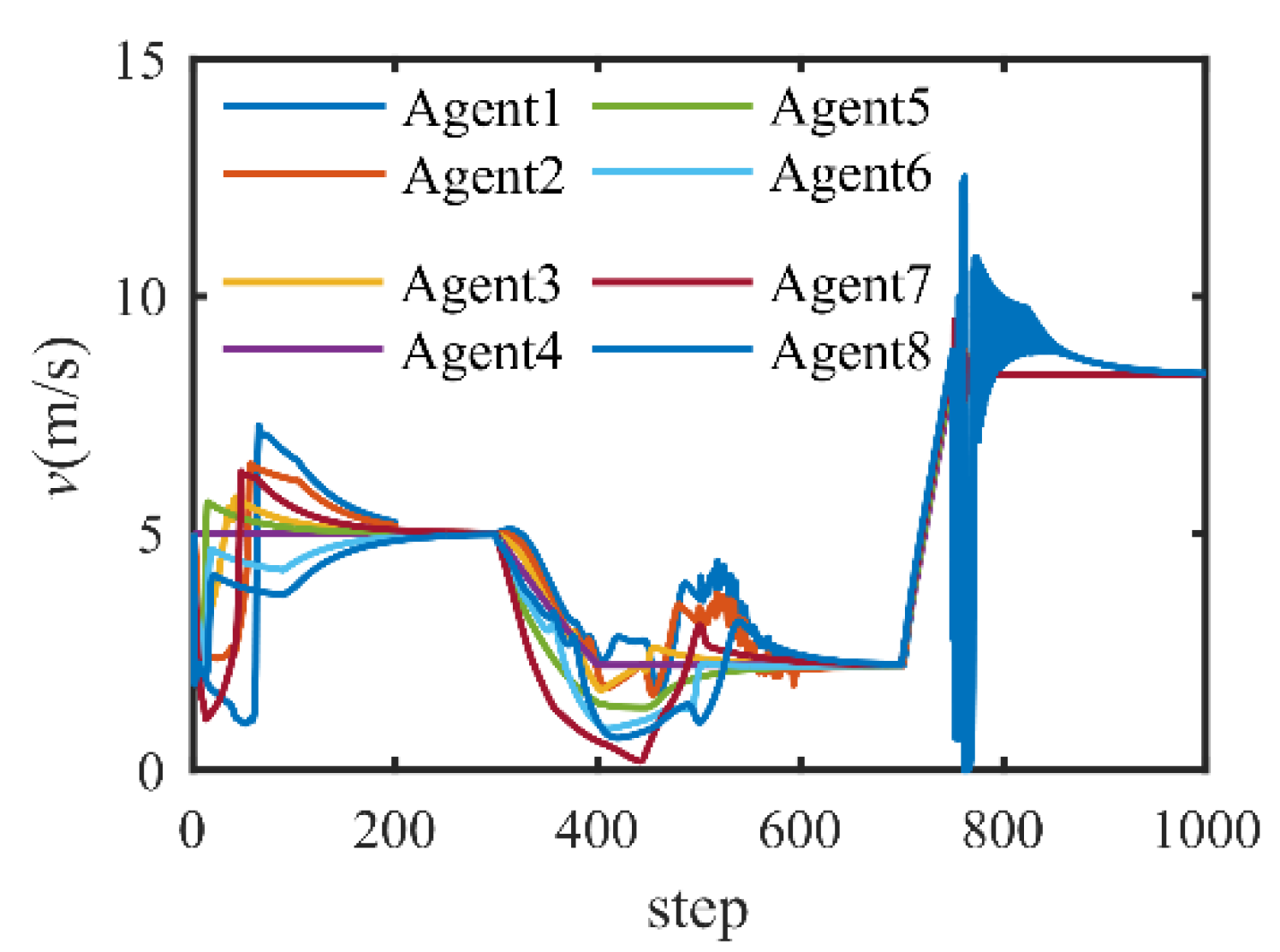
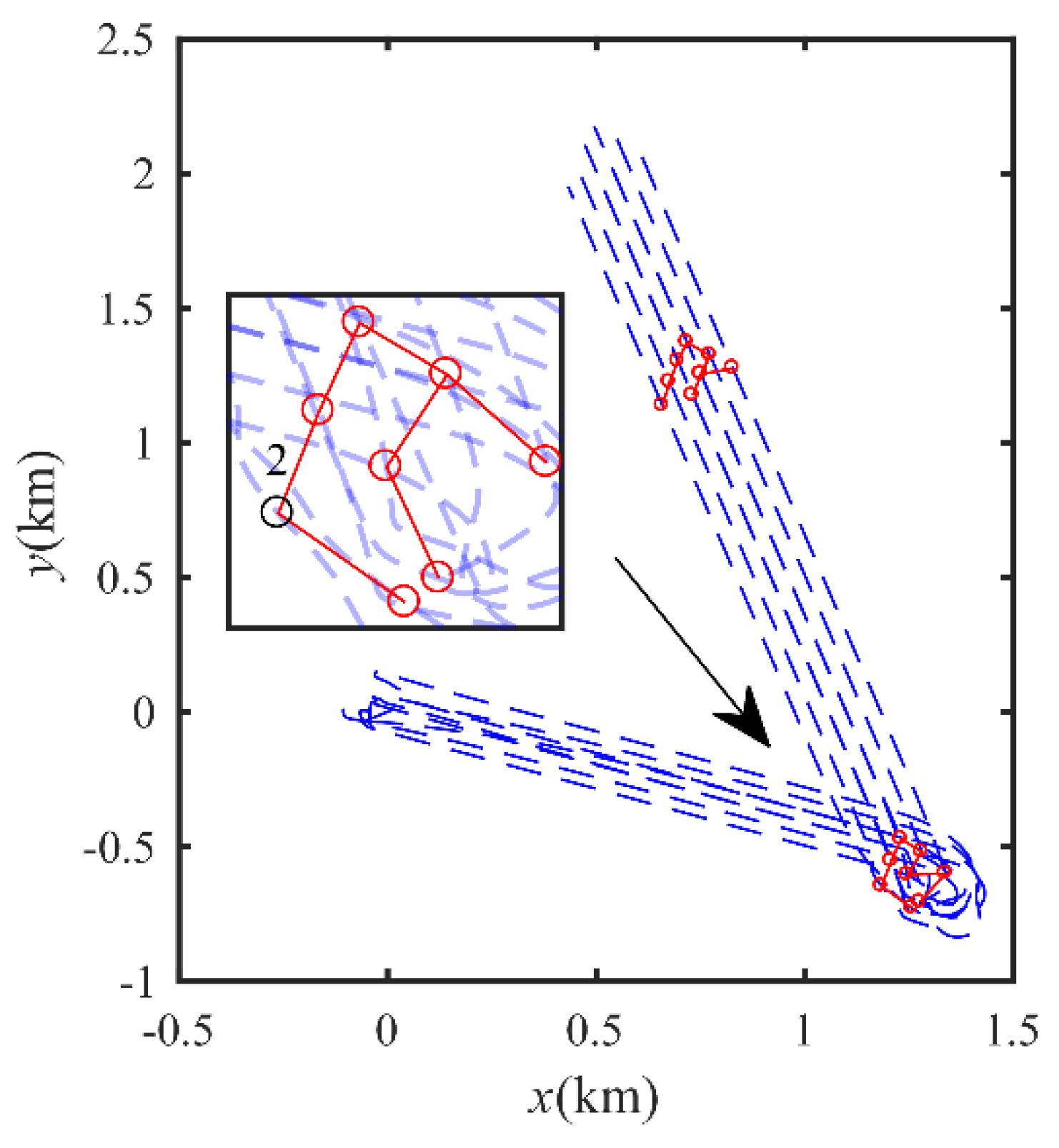
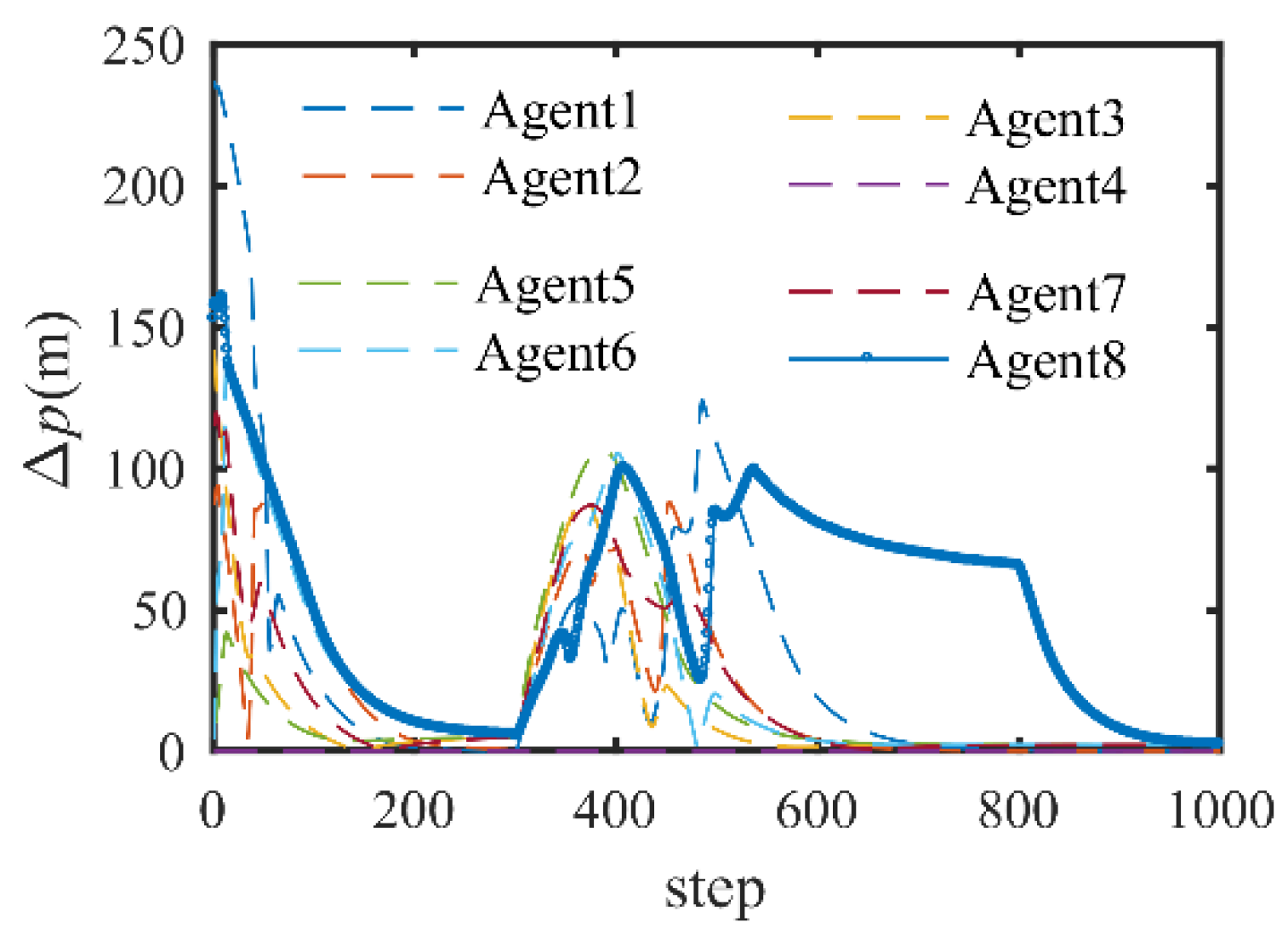
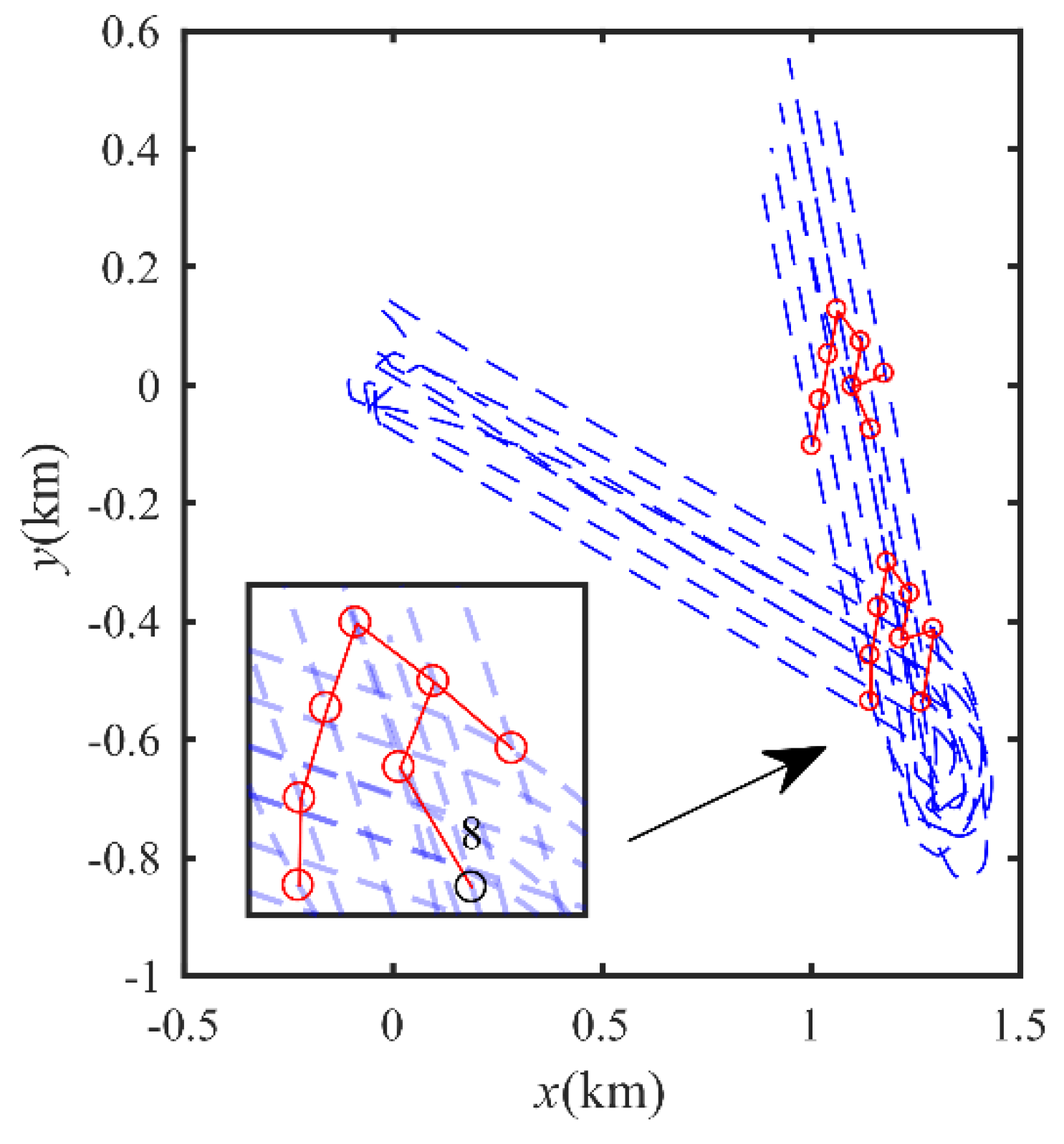
4. Numerical Simulation
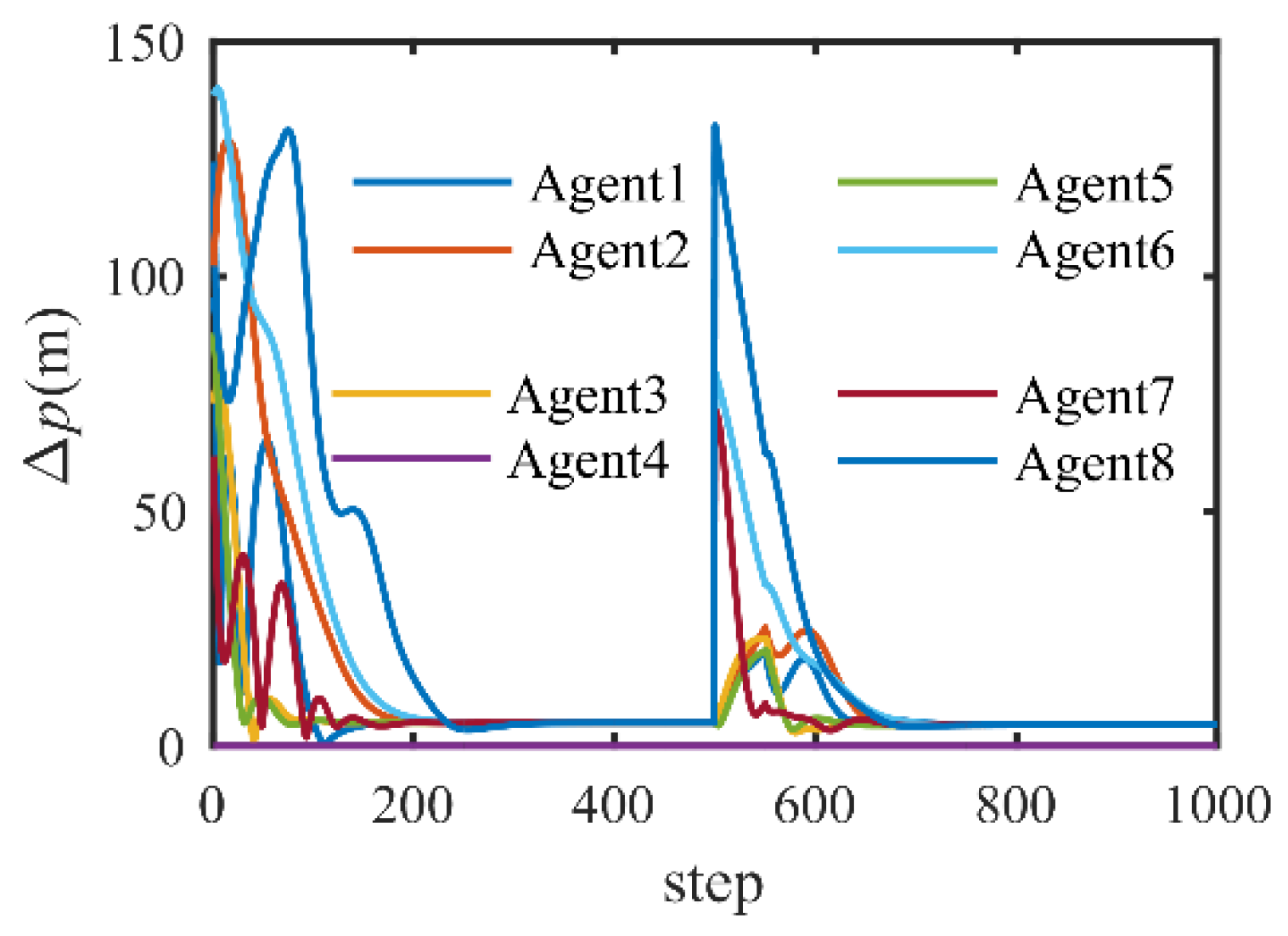
4.1. Leader-Follower Model-Based Formation Control
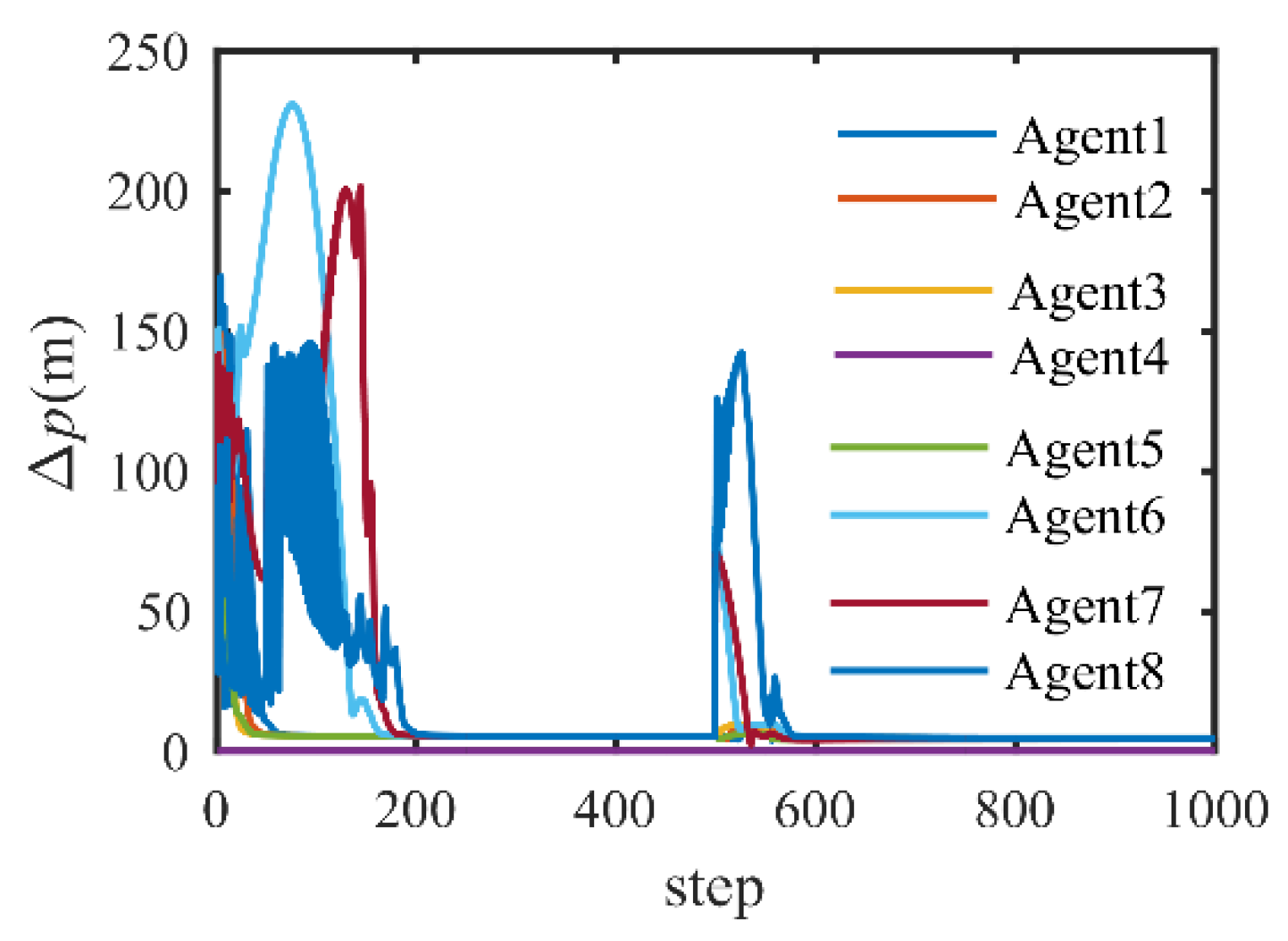
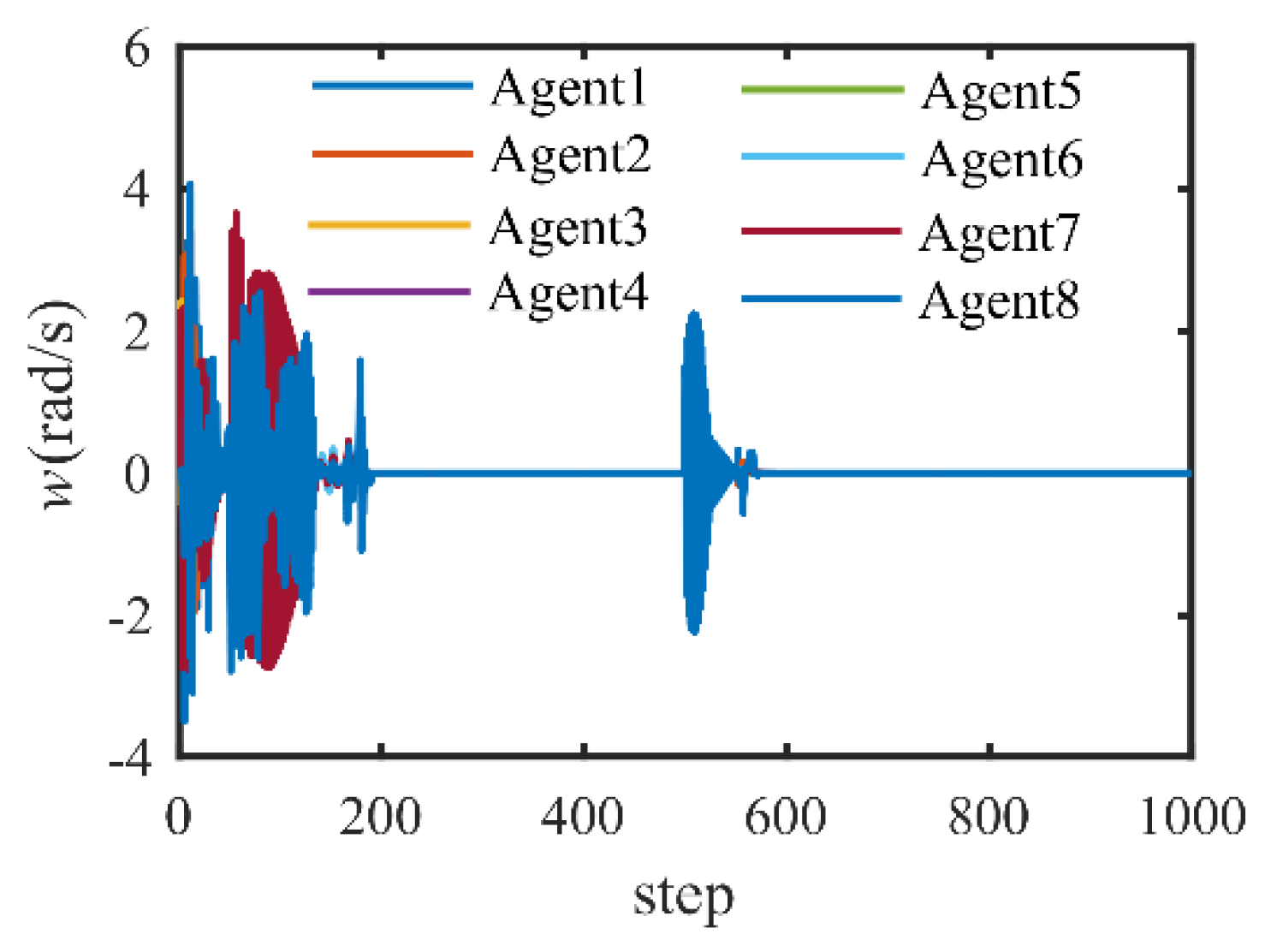
4.2. Formation Control with Communication Break
4.3. Formation Keep with Bearings Only
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gwihan, K.; Minh, H.T.; Hyo-Sung, A. Bearing-only control of directed cycle formations: Almost global convergence and hardware implementation. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2020, 30, 4789–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arijit, S.; Soumya, R.S.; Mangal, K. Nonlinear formation control strategies for agents without relative measurements under heterogeneous networks. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2017, 28, 1653–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiwang, D.; Chao, S.; Guoqiang, H. Time-varying output formation control for linear multi-agent systems with switching topologies. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2016, 26, 3558–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daifeng, Z.; Haibin, D. Switching topology approach for UAV formation based on binary-tree network. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 835–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iman, S.; Khashayar, K. Actuator fault accommodation strategy for a team of multi-agent systems subject to switching topology. Automatica 2015, 62, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JunHao, R.; XiaoFeng, Z. Containment Control of Multi-Agent Systems with Stochastic Multiplicative Noises. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changduo, L.; Mingfeng, G.; Zhiwei, L.; Guang, L.; Feng, L. Predefined-time formation tracking control of networked marine surface vehicles. Control. Eng. Pract. 2021, 107, 104682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhad, M.; Farzad, H.; Mahdi, B.; Marcio, D.Q. Finite-Time Rigidity-Based Formation Maneuvering of Multiagent Systems Using Distributed Finite-Time Velocity Estimators. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 49, 4473–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong, S.P.; Sung, J.Y. Connectivity-maintaining and collision-avoiding performance function approach for robust leader–follower formation control of multiple uncertain underactuated surface vessels. Automatica 2021, 127, 109501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, R.; Farzaneh, A. Motion synchronization in unmanned aircrafts formation control with communication delays. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2013, 18, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.D.; Mohammad, B.M. Communication free leader–follower formation control of unmanned aircraft systems. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 80, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagir, Z.M.; Rustem, A.M. Consensus-based cooperative control of parallel fixed-wing UAV formations via adaptive backstepping. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 106416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, K.; Kamesh, S.; Nicholas, R.G.; Atilla, D.; Frank, L. Distributed backstepping based control of multiple UAV formation flight subject to time delays. IET Control. Theory Appl. 2020, 14, 1628–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, K.D. Bounded and inverse optimal formation stabilization of second-order agents. Automatica 2021, 123, 109367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ShiKai, S.; Yu, P.; Chenglong, H.; Yu, D. Efficient path planning for UAV formation via comprehensively improved particle swarm optimization. ISA Trans. 2020, 97, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AliNoormohammadi, A.; Mohammad, B.M.; Atena, S. Control of leader-follower formation and path planning of mobile robots using asexual reproduction optimization (ARO). Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 14, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.H.; Anthony, J.M.; Sidney, N.G.; Mohamad, I.; Shahram, Y.; Camille, A.R. Solving multi-UAV dynamic encirclement via model predictive control. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2015, 23, 2251–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.H.; Sidney, N.G.; Shahram, Y. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Formation Using Learning Based Model Predictive Control. Asian J. Control 2018, 20, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qishao, W.; Zhisheng, D.; Yuezu, L.; Qingyun, W.; Guanrong, C. Linear quadratic optimal consensus of discrete-time multi-agent systems with optimal steady state: A distributed model predictive control approach. Automatica 2021, 127, 109505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qishao, W.; Zhisheng, D.; Jingyao, W.; Guanrong, C. LQ Synchronization of Discrete-Time Multi-Agent Systems: A Distributed Optimization Approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2019, 64, 5183–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.L.; Brunet, L.; How, J.P. Consensus-Based Decentralized Auctions for Robust Task Allocation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2009, 25, 912–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiqi, T.; Rita, C.; Tarek, H.; Carlos, S. Formation control of a leader–follower structure in three dimensional space using bearing measurements. Automatica 2021, 128, 109567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanghui, W.; Zhisheng, D.; Wei, R.; Guanrong, C. Distributed consensus of multi-agent systems with general linear node dynamics and intermittent communications. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2014, 24, 2438–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaowen, F.; Jing, P.; Haixiang, W.; Xiaoguang, G. A formation maintenance and reconstruction method of UAV swarm based on distributed control. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 104, 105981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, H.; Mayne, D.Q. Robust receding horizon control of constrained nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1993, 38, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Dai, L.; Liu, K.; Xia, Y.; Johansson, K.H. Robust MPC for tracking constrained unicycle robots with additive disturbances. Automatica 2018, 90, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zongyu, Z.; Lin, T. Distributed robust finite-time nonlinear consensus protocols for multi-agent systems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2016, 47, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenfeng, H.; Xianku, Z.; Guoqing, Z. Adaptive neural finite-time formation control for multiple underactuated vessels with actuator faults. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 222, 108556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florent, L.B.; Tarek, H.; Robert, M.; Claude, S. Observers for Position Estimation Using Bearing and Biased Velocity Information. In Sensing and Control for Autonomous Vehicles; Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 474, pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| 1 | (28.2, 0.7) | (5, 0.6447) | (0, 0) |
| 2 | (49.6, 98.8) | (5, 0.3731) | (0, 0) |
| 3 | (73.8, 31.1) | (5, 0.7681) | (0, 0) |
| 4 | (60.0, 78.2) | (5, 1.2662) | (0, 0) |
| 5 | (11.1, 57.9) | (5, 0.5935) | (0, 0) |
| 6 | (87.0, 69.0) | (5, 0.8136) | (0, 0) |
| 7 | (24.3, 34.3) | (5, 0.1486) | (0, 0) |
| 8 | (54.5, 6.7) | (5, 1.4280) | (0, 0) |
| 1 | (30.3, 81.7) | (5, 2.4997) | (0, 0) |
| 2 | (−31.2, −67.5) | (5, 2.0965) | (0, 0) |
| 3 | (−58.1, −47.2) | (5, 1.4426) | (0, 0) |
| 4 | (−33.5, 28.8) | (5, 5.8818) | (0, 0) |
| 5 | (−104.3, 11.8) | (5, 4.2926) | (0, 0) |
| 6 | (−38.9, 55.0) | (5, 6.0451) | (0, 0) |
| 7 | (−42.8, 0.38) | (5, 2.7519) | (0, 0) |
| 8 | (−46.8, −34.1) | (5, 5.9083) | (0, 0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, Z.; Liu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Xia, J. An Adaptive and Bounded Controller for Formation Control of Multi-Agent Systems with Communication Break. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5602. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12115602
Xiong Z, Liu Z, Luo Y, Xia J. An Adaptive and Bounded Controller for Formation Control of Multi-Agent Systems with Communication Break. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(11):5602. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12115602
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Zhigang, Zhong Liu, Yasong Luo, and Jiawei Xia. 2022. "An Adaptive and Bounded Controller for Formation Control of Multi-Agent Systems with Communication Break" Applied Sciences 12, no. 11: 5602. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12115602
APA StyleXiong, Z., Liu, Z., Luo, Y., & Xia, J. (2022). An Adaptive and Bounded Controller for Formation Control of Multi-Agent Systems with Communication Break. Applied Sciences, 12(11), 5602. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12115602





