Molecular Basis of Irisin Regulating the Effects of Exercise on Insulin Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biology and Physiology of FNDC5/Irisin
2.1. Summary Profile of FNDC5/Irisin
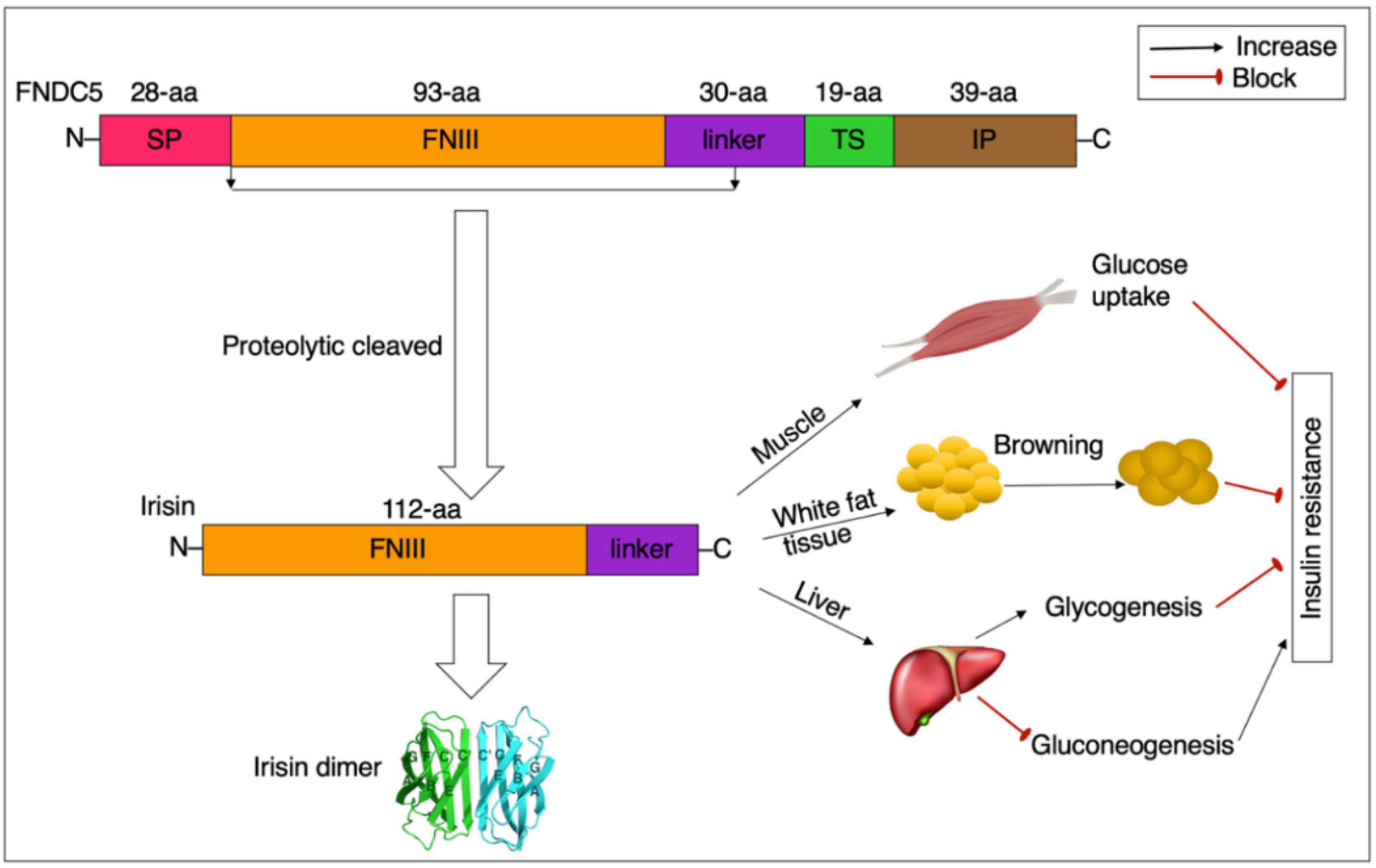
2.2. Consequence, Structure, and Detection of FNDC5/Irisin
2.3. Distribution and Production of FNDC5/Irisin
3. Irisin and Insulin Resistance
3.1. Irisin, Mitochondrial Function, and Insulin Resistance
3.2. Irisin, GLUT4, and Insulin Resistance
3.3. Irisin, Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance
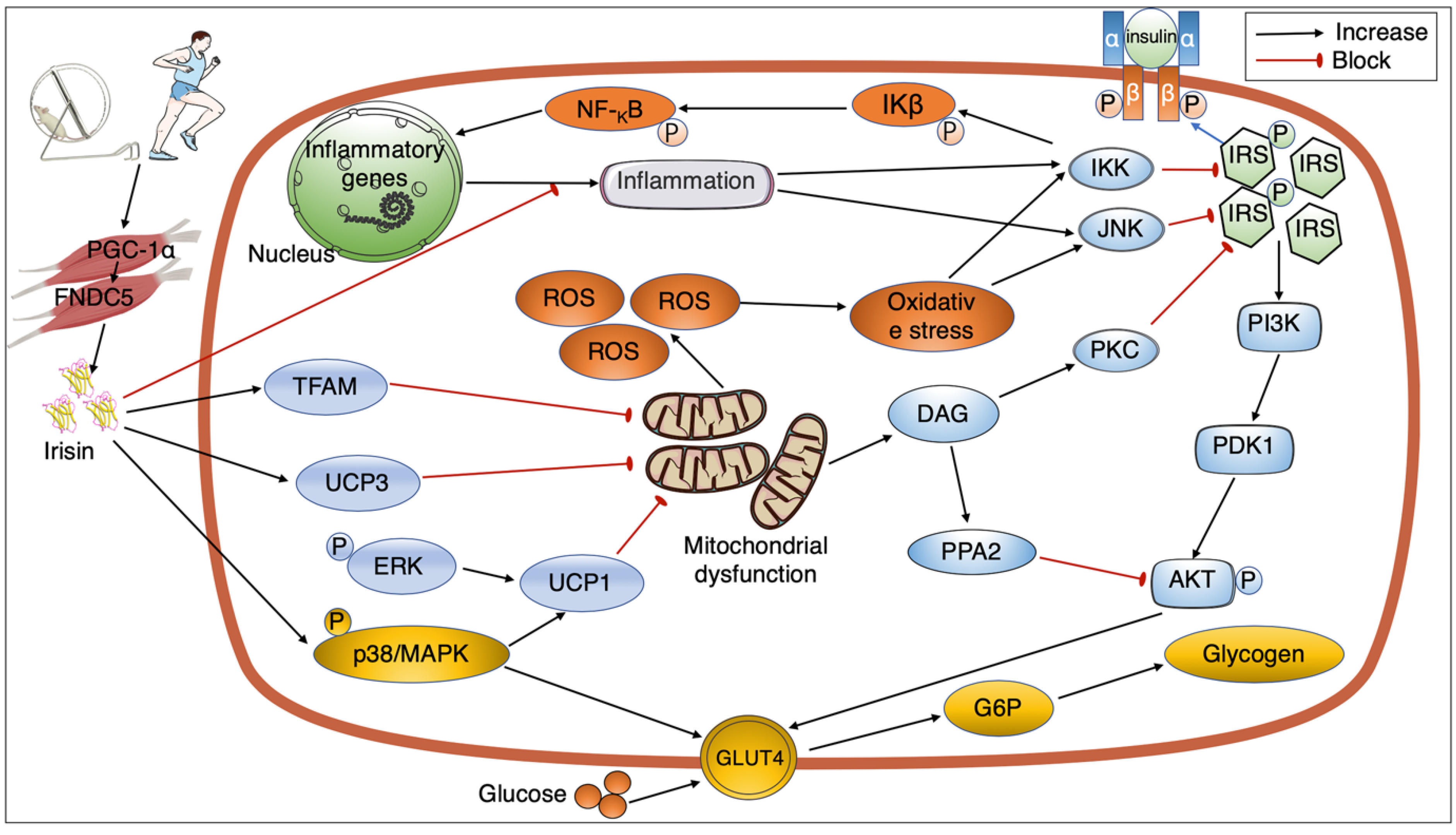
4. Signaling Pathways Mediating the Link between Exercise, Irisin, and Insulin Sensitivity
4.1. Exercise Regulating Irisin Secretion
4.2. GLUT4 and the Interaction between Exercise, Irisin, and Insulin Resistance
4.3. Mitochondrial Action and Interaction between Exercise, Irisin, and Insulin Resistance
4.4. Inflammation and Interaction between Exercise, Irisin, and Insulin Resistance
5. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moller, D.E.; Kaufman, K.D. Metabolic syndrome: A clinical and molecular perspective. Annu. Rev. Med. 2005, 56, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.M.; Olefsky, J.M. The origins and drivers of insulin resistance. Cell 2013, 152, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stumvoll, M.; Goldstein, B.J.; van Haeften, T.W. Type 2 diabetes: Principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet 2005, 365, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Cai, W.; Cai, M.; Xiao, M.; Wang, Z. Influence of the intervention of exercise on obese type II diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Prim. Care Diabetes 2016, 10, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, C.; Pedersen, B.K. The role of exercise-induced myokines in muscle homeostasis and the defense against chronic diseases. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 520258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, N.; Pedersen, B.K. Exercise as a mean to control low-grade systemic inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2008, 2008, 109502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Febbraio, M.A. Muscles, exercise and obesity: Skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, J.; Taylor, J.M. Muscle as a paracrine and endocrine organ. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 34, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Meng, Y.; Li, S.; Donelan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Cui, T.; et al. Irisin stimulates browning of white adipocytes through mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 MAP kinase and ERK MAP kinase signaling. Diabetes 2014, 63, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bostrom, P.; Wu, J.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Korde, A.; Ye, L.; Lo, J.C.; Rasbach, K.A.; Bostrom, E.A.; Choi, J.H.; Long, J.Z.; et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature 2012, 481, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Jia, S. Irisin, an exercise-induced myokine as a metabolic regulator: An updated narrative review. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca-Rivada, A.; Castelao, C.; Senin, L.L.; Landrove, M.O.; Baltar, J.; Belen Crujeiras, A.; Seoane, L.M.; Casanueva, F.F.; Pardo, M. FNDC5/irisin is not only a myokine but also an adipokine. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aydin, S.; Kuloglu, T.; Aydin, S. Copeptin, adropin and irisin concentrations in breast milk and plasma of healthy women and those with gestational diabetes mellitus. Peptides 2013, 47, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, I.Y.M.; Camarillo Romero, E.D.S.; Garduno Garcia, J.J. Irisin a Novel Metabolic Biomarker: Present Knowledge and Future Directions. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 7816806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrer-Martinez, A.; Ruiz-Lozano, P.; Chien, K.R. Mouse PeP: A novel peroxisomal protein linked to myoblast differentiation and development. Dev. Dyn. 2002, 224, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, A.; Malik, N.; Mukhopadhyay, M.; Westphal, H. Frcp1 and Frcp2, two novel fibronectin type III repeat containing genes. Gene 2002, 297, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, M.A.; Chinnam, N.; Ohashi, T.; Shah, R.S.; Erickson, H.P. The structure of irisin reveals a novel intersubunit β-sheet fibronectin type III (FNIII) dimer: Implications for receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 33738–33744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raschke, S.; Elsen, M.; Gassenhuber, H.; Sommerfeld, M.; Schwahn, U.; Brockmann, B.; Jung, R.; Wisloff, U.; Tjonna, A.E.; Raastad, T.; et al. Evidence against a beneficial effect of irisin in humans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albrecht, E.; Norheim, F.; Thiede, B.; Holen, T.; Ohashi, T.; Schering, L.; Lee, S.; Brenmoehl, J.; Thomas, S.; Drevon, C.A.; et al. Irisin-a myth rather than an exercise-inducible myokine. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Wrann, C.D.; Jedrychowski, M.; Vidoni, S.; Kitase, Y.; Nagano, K.; Zhou, C.; Chou, J.; Parkman, V.A.; Novick, S.J.; et al. Irisin Mediates Effects on Bone and Fat via αV Integrin Receptors. Cell 2018, 175, 1756–1768.e1717, Erratum in Cell 2019, 178, 507–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, J.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, T.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Wu, Z.; Lv, Y.; et al. Irisin reverses intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction during intestinal injury via binding to the integrin αVβ5 receptor. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, M.; Tan, J.; Pei, X.; Lu, C.; Xin, Y.; Deng, S.; Zhao, F.; Gao, Y.; Gong, Y. Irisin ameliorates neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis through integrin αVβ5/AMPK signaling pathway after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Mathew, H.; Mantzoros, C.S. Irisin: A true, circulating hormone. Metabolism 2015, 64, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jedrychowski, M.P.; Wrann, C.D.; Paulo, J.A.; Gerber, K.K.; Szpyt, J.; Robinson, M.M.; Nair, K.S.; Gygi, S.P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Detection and Quantitation of Circulating Human Irisin by Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aydin, S.; Kuloglu, T.; Ozercan, M.R.; Albayrak, S.; Aydin, S.; Bakal, U.; Yilmaz, M.; Kalayci, M.; Yardim, M.; Sarac, M.; et al. Irisin immunohistochemistry in gastrointestinal system cancers. Biotech. Histochem. 2016, 91, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, S.L.; Lyu, R.M.; Chen, Y.H.; Chang, J.K.; Luo, J.J.; Dun, N.J. Irisin-immunoreactivity in neural and non-neural cells of the rodent. Neuroscience 2013, 240, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gencer Tarakci, B.; Girgin, A.; Timurkaan, S.; Yalcin, M.H.; Gur, F.M.; Karan, M. Immunohistochemical localization of irisin in skin, eye, and thyroid and pineal glands of the crested porcupine (Hystrix cristata). Biotech. Histochem. 2016, 91, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Kim, D.I.; Choi, J.H.; Heo, Y.R.; Park, S.H. New role of irisin in hepatocytes: The protective effect of hepatic steatosis in vitro. Cell. Signal. 2015, 27, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tastekin, E.; Palabiyik, O.; Ulucam, E.; Uzgur, S.; Karaca, A.; Vardar, S.A.; Yilmaz, A.; Aydogdu, N. The effect of high protein diet and exercise on irisin, eNOS, and iNOS expressions in kidney. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aydin, S.; Kuloglu, T.; Aydin, S.; Kalayci, M.; Yilmaz, M.; Cakmak, T.; Albayrak, S.; Gungor, S.; Colakoglu, N.; Ozercan, I.H. A comprehensive immunohistochemical examination of the distribution of the fat-burning protein irisin in biological tissues. Peptides 2014, 61, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piya, M.K.; Harte, A.L.; Sivakumar, K.; Tripathi, G.; Voyias, P.D.; James, S.; Sabico, S.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Saravanan, P.; Barber, T.M.; et al. The identification of irisin in human cerebrospinal fluid: Influence of adiposity, metabolic markers, and gestational diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E512–E518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakal, U.; Aydin, S.; Sarac, M.; Kuloglu, T.; Kalayci, M.; Artas, G.; Yardim, M.; Kazez, A. Serum, Saliva, and Urine Irisin with and Without Acute Appendicitis and Abdominal Pain. Biochem. Insights 2016, 9, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuloglu, T.; Celik, O.; Aydin, S.; Hanifi Ozercan, I.; Acet, M.; Aydin, Y.; Artas, G.; Turk, A.; Yardim, M.; Ozan, G.; et al. Irisin immunostaining characteristics of breast and ovarian cancer cells. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2016, 62, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huh, J.Y.; Panagiotou, G.; Mougios, V.; Brinkoetter, M.; Vamvini, M.T.; Schneider, B.E.; Mantzoros, C.S. FNDC5 and irisin in humans: I. Predictors of circulating concentrations in serum and plasma and II. mRNA expression and circulating concentrations in response to weight loss and exercise. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1725–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurdiova, T.; Balaz, M.; Vician, M.; Maderova, D.; Vlcek, M.; Valkovic, L.; Srbecky, M.; Imrich, R.; Kyselovicova, O.; Belan, V.; et al. Effects of obesity, diabetes and exercise on Fndc5 gene expression and irisin release in human skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: In vivo and in vitro studies. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 1091–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Ortega, F.; Serrano, M.; Guerra, E.; Pardo, G.; Tinahones, F.; Ricart, W.; Fernandez-Real, J.M. Irisin is expressed and produced by human muscle and adipose tissue in association with obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E769–E778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novelle, M.G.; Contreras, C.; Romero-Pico, A.; Lopez, M.; Dieguez, C. Irisin, two years later. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 746281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.J.; Song, W. Resistance training increases fibroblast growth factor-21 and irisin levels in the skeletal muscle of Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J. Exerc. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 21, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, R.R.; Shockett, P.; Webb, N.D.; Shah, U.; Castracane, V.D. A transient elevated irisin blood concentration in response to prolonged, moderate aerobic exercise in young men and women. Horm. Metab. Res. 2014, 46, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivitz, W.I.; Yorek, M.A. Mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetes: From molecular mechanisms to functional significance and therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 12, 537–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, X.; Shen, Y.; Ni, C.; Ye, J.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ren, Y. Irisin reverses insulin resistance in C2C12 cells via the p38-MAPK-PGC-1α pathway. Peptides 2019, 119, 170120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegelman, B.M. Banting Lecture 2012: Regulation of adipogenesis: Toward new therapeutics for metabolic disease. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansen, J.B.; Kristiansen, K. Regulatory circuits controlling white versus brown adipocyte differentiation. Biochem. J. 2006, 398, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.Q.; Huang, Y.Y.; Gusdon, A.M.; Qu, S. Irisin: A new molecular marker and target in metabolic disorder. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher, F.M.; Kleiner, S.; Douris, N.; Fox, E.C.; Mepani, R.J.; Verdeguer, F.; Wu, J.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Flier, J.S.; Maratos-Flier, E.; et al. FGF21 regulates PGC-1α and browning of white adipose tissues in adaptive thermogenesis. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perakakis, N.; Triantafyllou, G.A.; Fernandez-Real, J.M.; Huh, J.Y.; Park, K.H.; Seufert, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Physiology and role of irisin in glucose homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Xiang, G.; Liu, M.; Mei, W.; Xiang, L.; Dong, J. Irisin protects against endothelial injury and ameliorates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-Null diabetic mice. Atherosclerosis 2015, 243, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Yeh, Y.H.; Chen, W.J.; Lin, K.H. Emerging regulation and function of betatrophin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 23640–23657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaughan, R.A.; Gannon, N.P.; Barberena, M.A.; Garcia-Smith, R.; Bisoffi, M.; Mermier, C.M.; Conn, C.A.; Trujillo, K.A. Characterization of the metabolic effects of irisin on skeletal muscle in vitro. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpulla, R.C. Transcriptional paradigms in mammalian mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 611–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misu, H.; Takamura, T.; Matsuzawa, N.; Shimizu, A.; Ota, T.; Sakurai, M.; Ando, H.; Arai, K.; Yamashita, T.; Honda, M.; et al. Genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately upregulated with fasting hyperglycaemia in livers of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmid, A.I.; Szendroedi, J.; Chmelik, M.; Krssak, M.; Moser, E.; Roden, M. Liver ATP synthesis is lower and relates to insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bi, J.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wei, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; et al. Irisin alleviates liver ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting excessive mitochondrial fission, promoting mitochondrial biogenesis and decreasing oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2019, 20, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, C.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, G.; Ding, L.; Yang, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Irisin Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury and Improves Mitochondrial Function Through AMPK Pathway in Diabetic Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leto, D.; Saltiel, A.R. Regulation of glucose transport by insulin: Traffic control of GLUT4. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 2001, 414, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.O.; Kim, N.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, H.I.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, J.I.; Oh, Y.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Irisin, a Novel Myokine, Regulates Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Muscle Cells via AMPK. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huh, J.Y.; Mougios, V.; Kabasakalis, A.; Fatouros, I.; Siopi, A.; Douroudos, I.I.; Filippaios, A.; Panagiotou, G.; Park, K.H.; Mantzoros, C.S. Exercise-Induced Irisin Secretion Is Independent of Age or Fitness Level and Increased Irisin May Directly Modulate Muscle Metabolism Through AMPK Activation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E2154–E2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orava, J.; Nuutila, P.; Lidell, M.E.; Oikonen, V.; Noponen, T.; Viljanen, T.; Scheinin, M.; Taittonen, M.; Niemi, T.; Enerback, S.; et al. Different metabolic responses of human brown adipose tissue to activation by cold and insulin. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huh, J.Y.; Dincer, F.; Mesfum, E.; Mantzoros, C.S. Irisin stimulates muscle growth-related genes and regulates adipocyte differentiation and metabolism in humans. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Favelyukis, S.; Nguyen, A.K.; Reichart, D.; Scott, P.A.; Jenn, A.; Liu-Bryan, R.; Glass, C.K.; Neels, J.G.; Olefsky, J.M. A subpopulation of macrophages infiltrates hypertrophic adipose tissue and is activated by free fatty acids via Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 and JNK-dependent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35279–35292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Shargill, N.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-α: Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993, 259, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Chen, N.; Kang, X.; Hu, Y.; Shi, S. Irisin alleviates FFA induced β-cell insulin resistance and inflammatory response through activating PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway. Endocrine 2022, 75, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Dong, Y.; Dong, Y.; Chen, F.; Mitch, W.E.; Zhang, L. Inhibition of myostatin in mice improves insulin sensitivity via irisin-mediated cross talk between muscle and adipose tissues. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 40, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazur-Bialy, A.I.; Pochec, E.; Zarawski, M. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Irisin, Mediator of Physical Activity, Are Connected with TLR4/MyD88 Signaling Pathway Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peraldi, P.; Spiegelman, B. TNF-α and insulin resistance: Summary and future prospects. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1998, 182, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Inflammatory mechanisms in the regulation of insulin resistance. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L.; Yuan, M.; Frantz, D.; Shoelson, S.; White, M.F. SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 block insulin signaling by ubiquitin-mediated degradation of IRS1 and IRS2. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 42394–42398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazur-Bialy, A.I.; Bilski, J.; Pochec, E.; Brzozowski, T. New insight into the direct anti-inflammatory activity of a myokine irisin against proinflammatory activation of adipocytes. Implication for exercise in obesity. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 68, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Shields, K.; Mantzoros, C.S. Irisin: A renaissance in metabolism? Metabolism 2013, 62, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B. BDNF (I)rising from exercise. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, S.W.; Shen, Z.H.; Xu, M.; Yang, C.J.; Li, F.; Feng, Y.B.; Yun, J.T.; Wang, L.; et al. Swimming exercise increases serum irisin level and reduces body fat mass in high-fat-diet fed Wistar rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, M.; Yang, J.; Rao, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Dong, X. Time-Dependent Changes in Increased Levels of Plasma Irisin and Muscle PGC-1α and FNDC5 after Exercise in Mice. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2018, 244, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, E.; Jeong, D.Y.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, S. The Acute Effects of Swimming Exercise on PGC-1α-FNDC5/Irisin-UCP1 Expression in Male C57BL/6J Mice. Metabolites 2021, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsen, M.; Raschke, S.; Eckel, J. Browning of white fat: Does irisin play a role in humans? J. Endocrinol. 2014, 222, R25–R38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norheim, F.; Langleite, T.M.; Hjorth, M.; Holen, T.; Kielland, A.; Stadheim, H.K.; Gulseth, H.L.; Birkeland, K.I.; Jensen, J.; Drevon, C.A. The effects of acute and chronic exercise on PGC-1α, irisin and browning of subcutaneous adipose tissue in humans. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, H.; Slettalokken, G.; Vegge, G.; Hollan, I.; Whist, J.E.; Strand, T.; Ronnestad, B.R.; Ellefsen, S. Irisin in blood increases transiently after single sessions of intense endurance exercise and heavy strength training. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecksteden, A.; Wegmann, M.; Steffen, A.; Kraushaar, J.; Morsch, A.; Ruppenthal, S.; Kaestner, L.; Meyer, T. Irisin and exercise training in humans-results from a randomized controlled training trial. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussey, S.E.; McGee, S.L.; Garnham, A.; McConell, G.K.; Hargreaves, M. Exercise increases skeletal muscle GLUT4 gene expression in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douen, A.G.; Ramlal, T.; Rastogi, S.; Bilan, P.J.; Cartee, G.D.; Vranic, M.; Holloszy, J.O.; Klip, A. Exercise induces recruitment of the “insulin-responsive glucose transporter”. Evidence for distinct intracellular insulin- and exercise-recruitable transporter pools in skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 13427–13430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Selective visualization of GLUT4 storage vesicles and associated Rab proteins using IRAP-pHluorin. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1298, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Saghatelian, A.; Kahn, B.B. GLUT4 Expression in Adipocytes Regulates De Novo Lipogenesis and Levels of a Novel Class of Lipids With Antidiabetic and Anti-inflammatory Effects. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1808–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abel, E.D.; Peroni, O.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, Y.B.; Boss, O.; Hadro, E.; Minnemann, T.; Shulman, G.I.; Kahn, B.B. Adipose-selective targeting of the GLUT4 gene impairs insulin action in muscle and liver. Nature 2001, 409, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sone, H.; Suzuki, H.; Takahashi, A.; Yamada, N. Disease model: Hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance. Part A-targeted disruption of insulin signaling or glucose transport. Trends Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenbit, A.E.; Tsao, T.S.; Li, J.; Burcelin, R.; Geenen, D.L.; Factor, S.M.; Houseknecht, K.; Katz, E.B.; Charron, M.J. GLUT4 heterozygous knockout mice develop muscle insulin resistance and diabetes. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati-Ahmadabad, S.; Rostamkhani, F.; Meftahi, G.H.; Shirvani, H. Comparative effects of high-intensity interval training and moderate-intensity continuous training on soleus muscle fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5, myonectin and glucose transporter type 4 gene expressions: A study on the diabetic rat model. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 6123–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, H.M.; Che, H.; Qin, Y.; Yang, F.; Meng, S.Y.; Li, X.G.; Bai, Y.L.; Wang, L.H. Coriolus versicolor aqueous extract ameliorates insulin resistance with PI3K/Akt and p38 MAPK signaling pathways involved in diabetic skeletal muscle. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Zhao, X.; Cao, R.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, D.Q.; Wang, R. Irisin improves insulin resistance by inhibiting autophagy through the PI3K/Akt pathway in H9c2 cells. Gene 2021, 769, 145209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de las Heras, N.; Klett-Mingo, M.; Ballesteros, S.; Martín-Fernández, B.; Escribano, Ó.; Blanco-Rivero, J.; Balfagón, G.; Hribal, M.L.; Benito, M.; Lahera, V.; et al. Chronic Exercise Improves Mitochondrial Function and Insulin Sensitivity in Brown Adipose Tissue. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, L.; From, A.; Seaquist, E. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance: The interplay of local lipid excess and mitochondrial dysfunction. Metabolism 2010, 59, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dela, F.; Helge, J.W. Insulin resistance and mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms for insulin resistance: Common threads and missing links. Cell 2012, 148, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebastian, D.; Hernandez-Alvarez, M.I.; Segales, J.; Sorianello, E.; Munoz, J.P.; Sala, D.; Waget, A.; Liesa, M.; Paz, J.C.; Gopalacharyulu, P.; et al. Mitofusin 2 (Mfn2) links mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum function with insulin signaling and is essential for normal glucose homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5523–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Atkin, S.L.; Sahebkar, A. A review of the molecular mechanisms of hyperglycemia-induced free radical generation leading to oxidative stress. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 1300–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Wang, P.; Chen, Q.; Li, C. Exercise enhances mitochondrial fission and mitophagy to improve myopathy following critical limb ischemia in elderly mice via the PGC1a/FNDC5/irisin pathway. Skelet. Muscle 2020, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.T.; Zhang, L.; Dubielecka, P.M.; Zhuang, S.; Qin, G.; Chin, Y.E.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, T.C. Irisin Improves Myocardial Performance and Attenuates Insulin Resistance in Spontaneous Mutation (Leprdb) Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.-C.; Xie, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tran, T.D.N.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; George, E.V.; Zhuang, H.; Zhang, P.; Kandel, A.; et al. Irisin Controls Growth, Intracellular Ca2+ Signals, and Mitochondrial Thermogenesis in Cardiomyoblasts. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisi, J.; Ghaedi, K.; Rajabi, H.; Marandi, S.M. Can Resistance Exercise Alter Irisin Levels and Expression Profiles of FNDC5 and UCP1 in Rats? Asian J. Sports Med. 2016, 7, e35205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, F.; Bock, P.M.; Motta, M.T.; Helal, L. Biochemical and Molecular Mechanisms of Glucose Uptake Stimulated by Physical Exercise in Insulin Resistance State: Role of Inflammation. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2019, 113, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, R.L.; Jeon, J.Y.; Liu, F.-F.; Maratos-Flier, E. Voluntary exercise improves insulin sensitivity and adipose tissue inflammation in diet-induced obese mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E586–E594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tataranni, P.A.; Ortega, E. A burning question: Does an adipokine-induced activation of the immune system mediate the effect of overnutrition on type 2 diabetes? Diabetes 2005, 54, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuki, T.; Horai, R.; Sudo, K.; Iwakura, Y. IL-1 plays an important role in lipid metabolism by regulating insulin levels under physiological conditions. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kopp, H.P.; Kopp, C.W.; Festa, A.; Krzyzanowska, K.; Kriwanek, S.; Minar, E.; Roka, R.; Schernthaner, G. Impact of weight loss on inflammatory proteins and their association with the insulin resistance syndrome in morbidly obese patients. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klover, P.J.; Clementi, A.H.; Mooney, R.A. Interleukin-6 depletion selectively improves hepatic insulin action in obesity. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3417–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Sahar, N.E.; Javaid, H.M.A.; Pak, E.S.; Liang, G.; Wang, Y.; Ha, H.; Huh, J.Y. Exercise-Induced Irisin Decreases Inflammation and Improves NAFLD by Competitive Binding with MD2. Cells 2021, 10, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, B.; Wang, Y.; Cui, W.; Peng, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, R. Molecular Basis of Irisin Regulating the Effects of Exercise on Insulin Resistance. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5837. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125837
Lin J, Liu X, Zhou Y, Zhu B, Wang Y, Cui W, Peng Y, Wang B, Zhao C, Zhao R. Molecular Basis of Irisin Regulating the Effects of Exercise on Insulin Resistance. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(12):5837. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125837
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Junjie, Xu Liu, Yalan Zhou, Baishu Zhu, Yuanxin Wang, Wei Cui, Yan Peng, Bin Wang, Chen Zhao, and Renqing Zhao. 2022. "Molecular Basis of Irisin Regulating the Effects of Exercise on Insulin Resistance" Applied Sciences 12, no. 12: 5837. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125837
APA StyleLin, J., Liu, X., Zhou, Y., Zhu, B., Wang, Y., Cui, W., Peng, Y., Wang, B., Zhao, C., & Zhao, R. (2022). Molecular Basis of Irisin Regulating the Effects of Exercise on Insulin Resistance. Applied Sciences, 12(12), 5837. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125837





