Novel Reversible Comparator Design in Quantum Dot-Cellular Automata with Power Dissipation Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background Materials
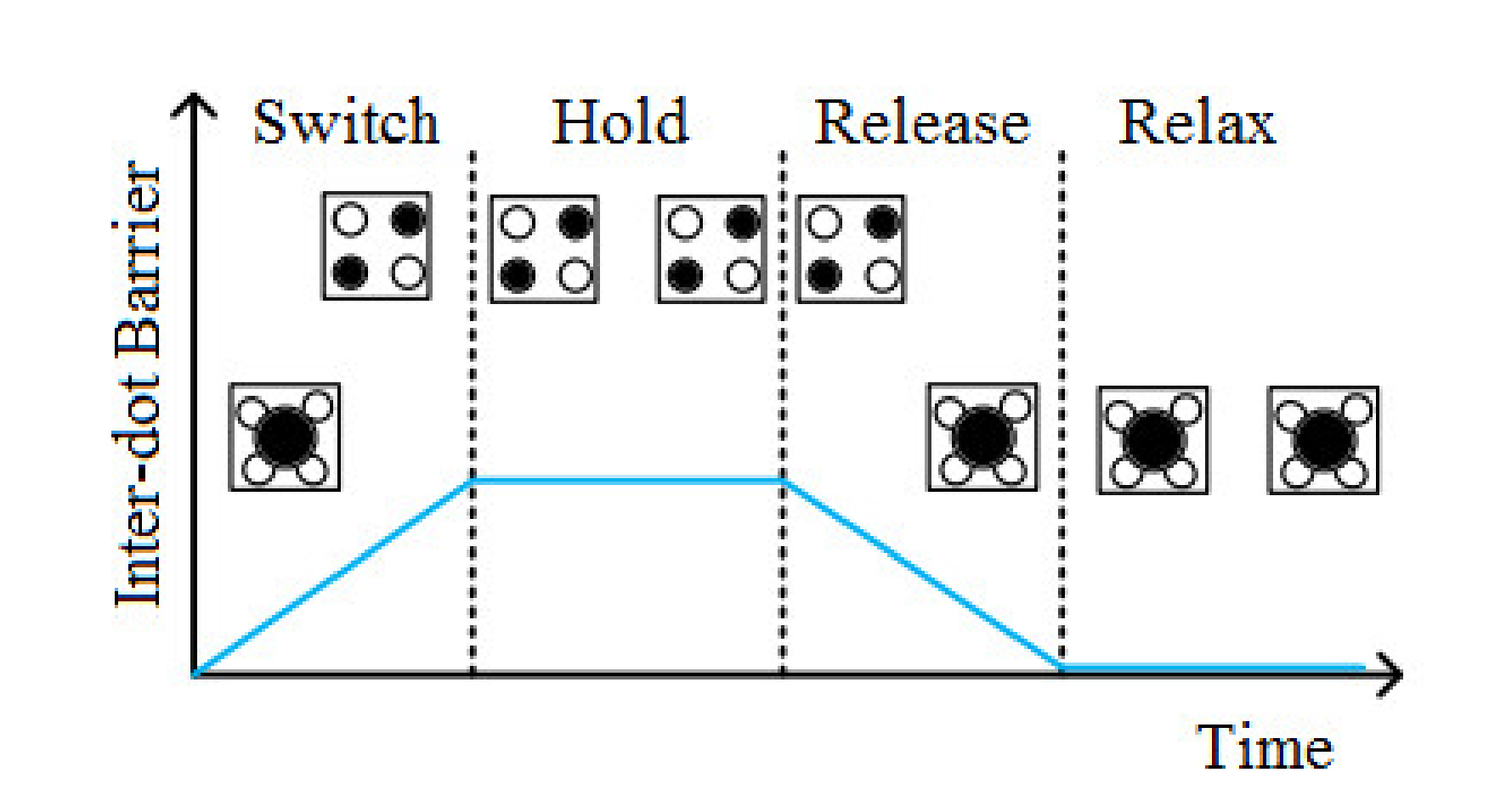
2.1. QCA Basic Terminology
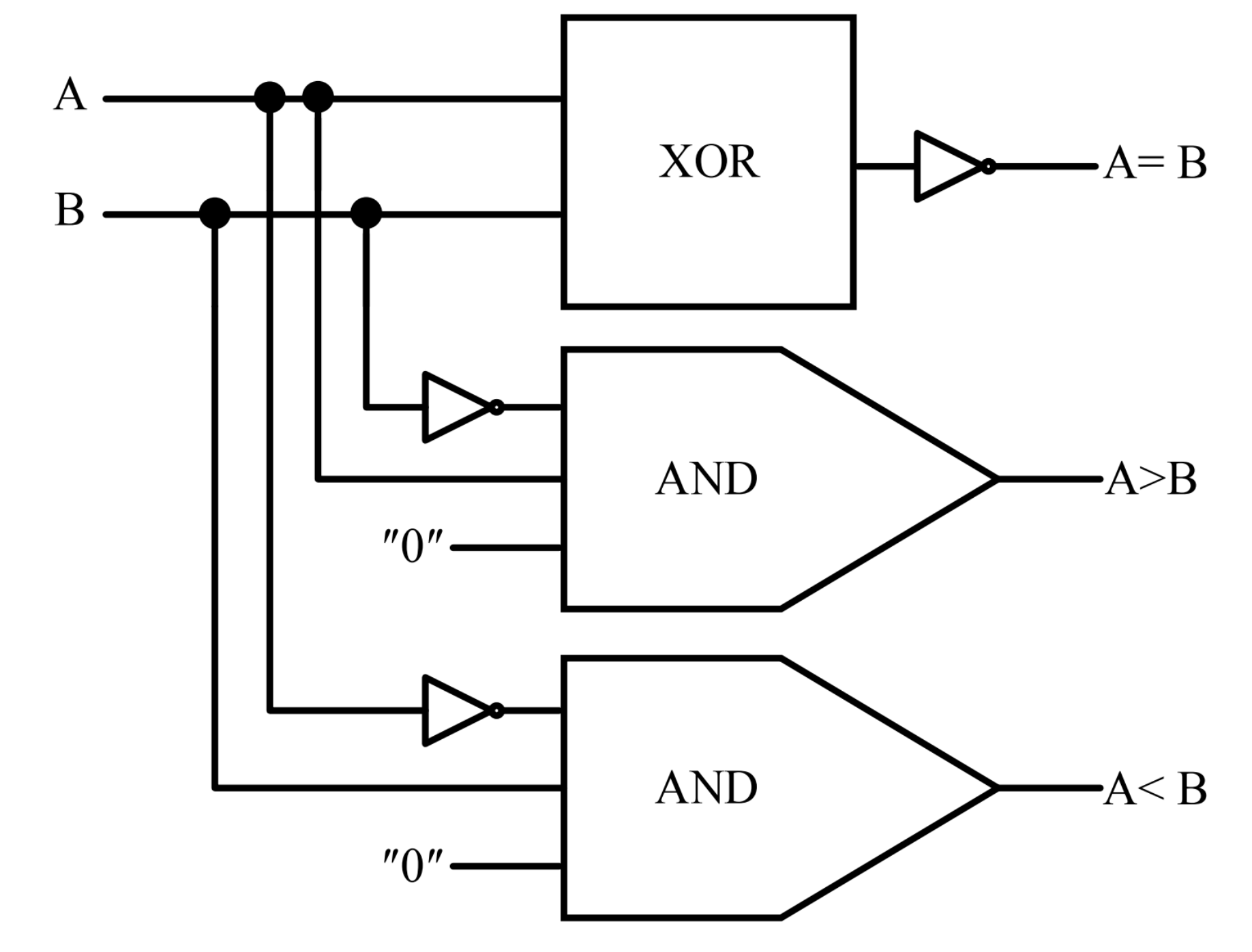
2.2. Comparator
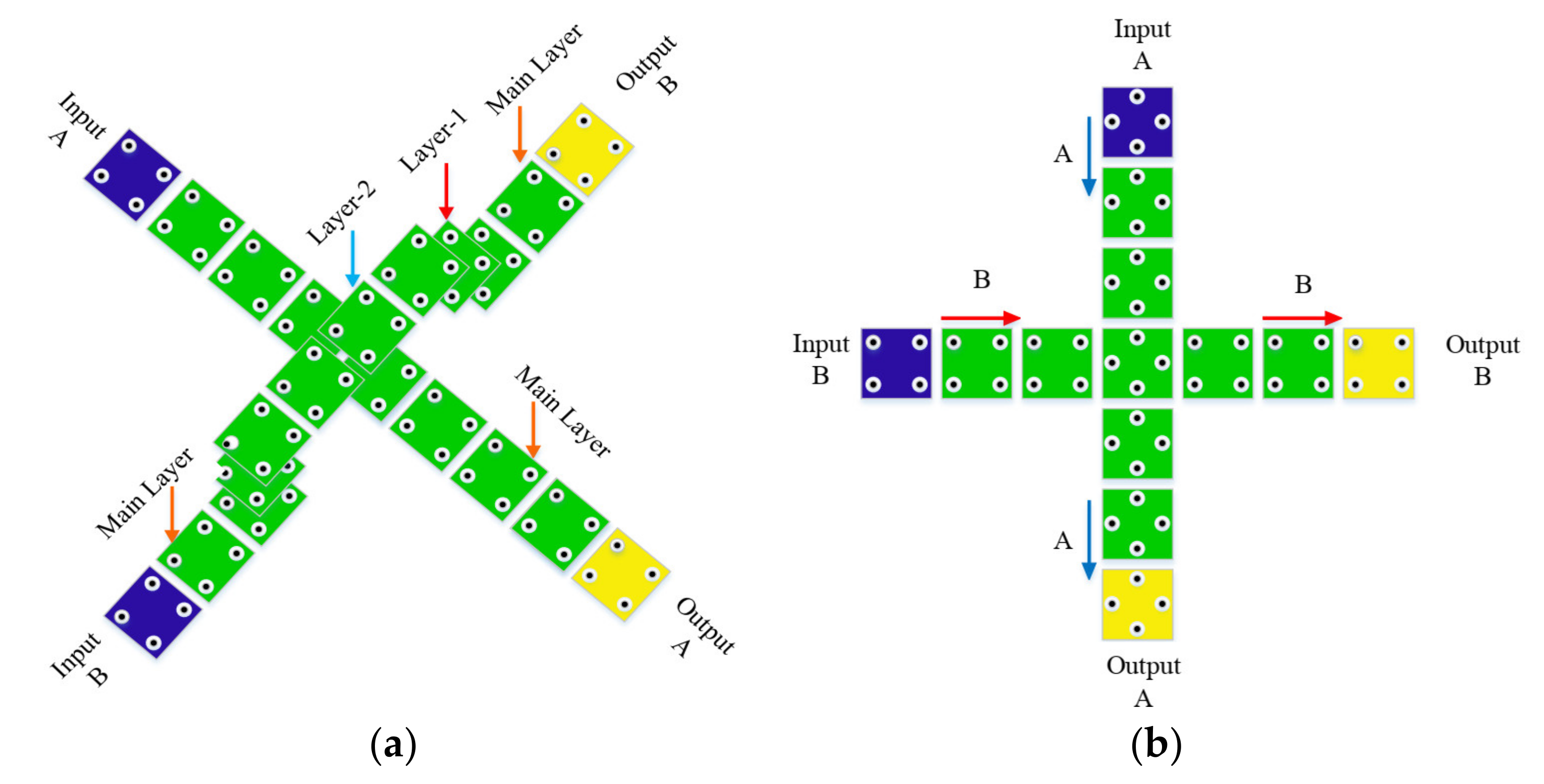
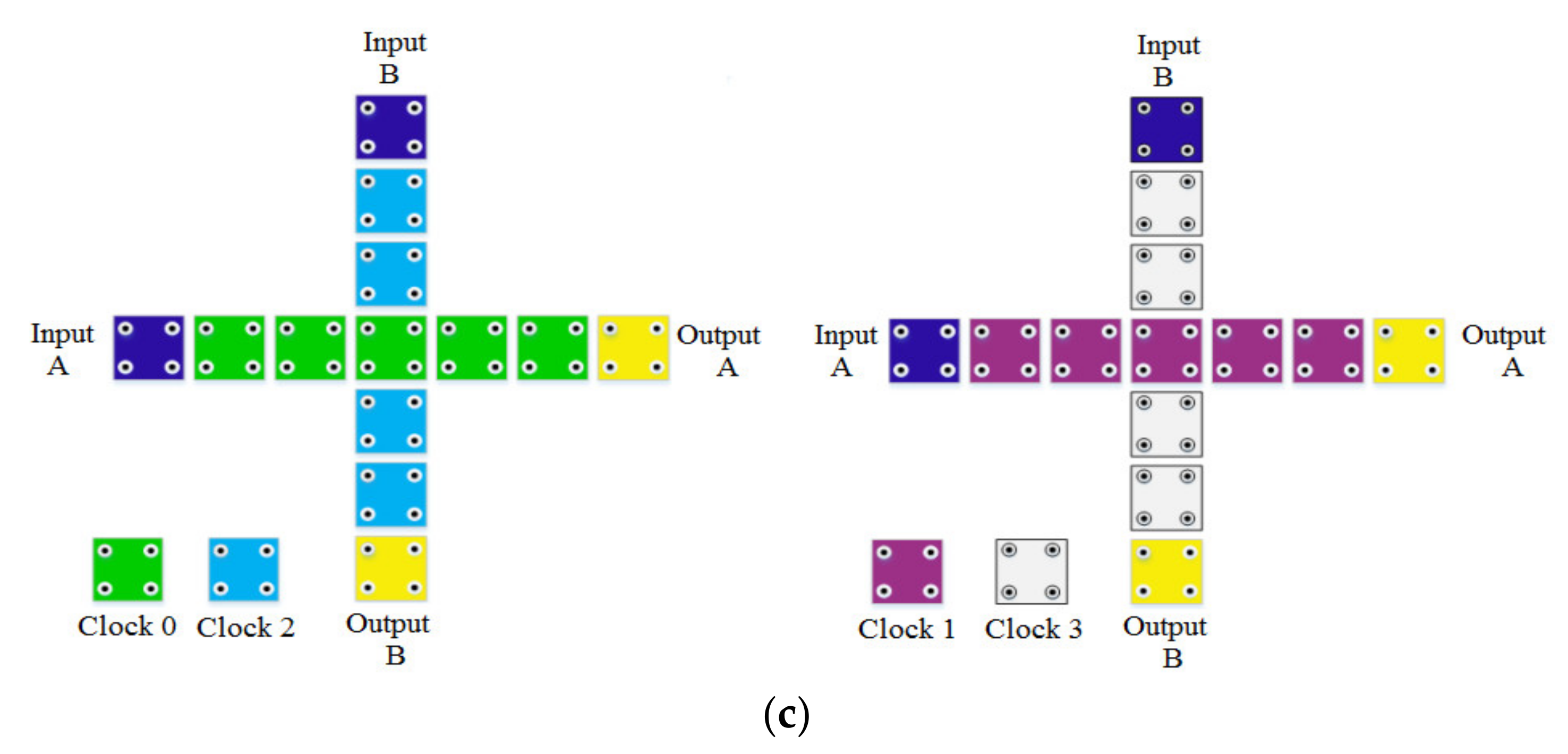
3. The Proposed Circuits
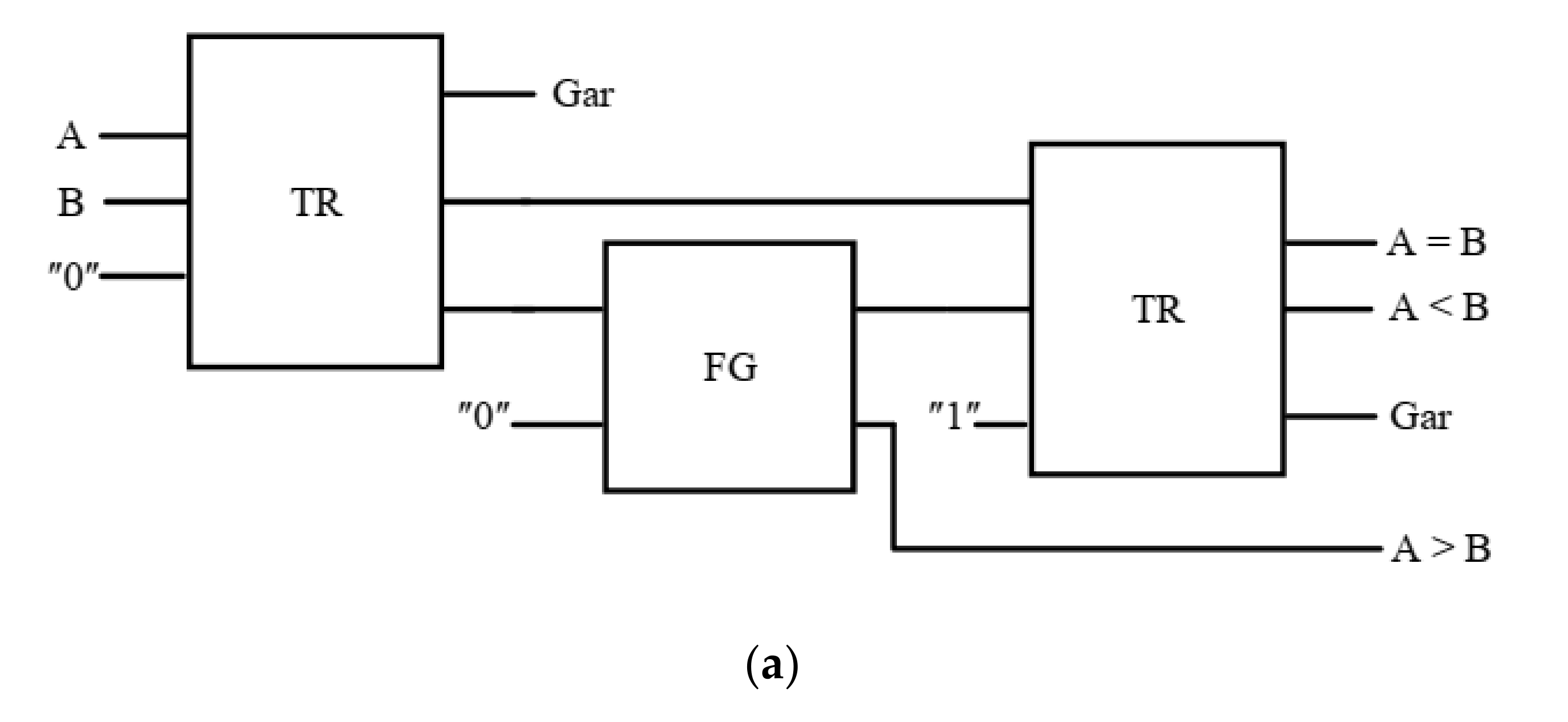
3.1. Reversible Comparator with QCA
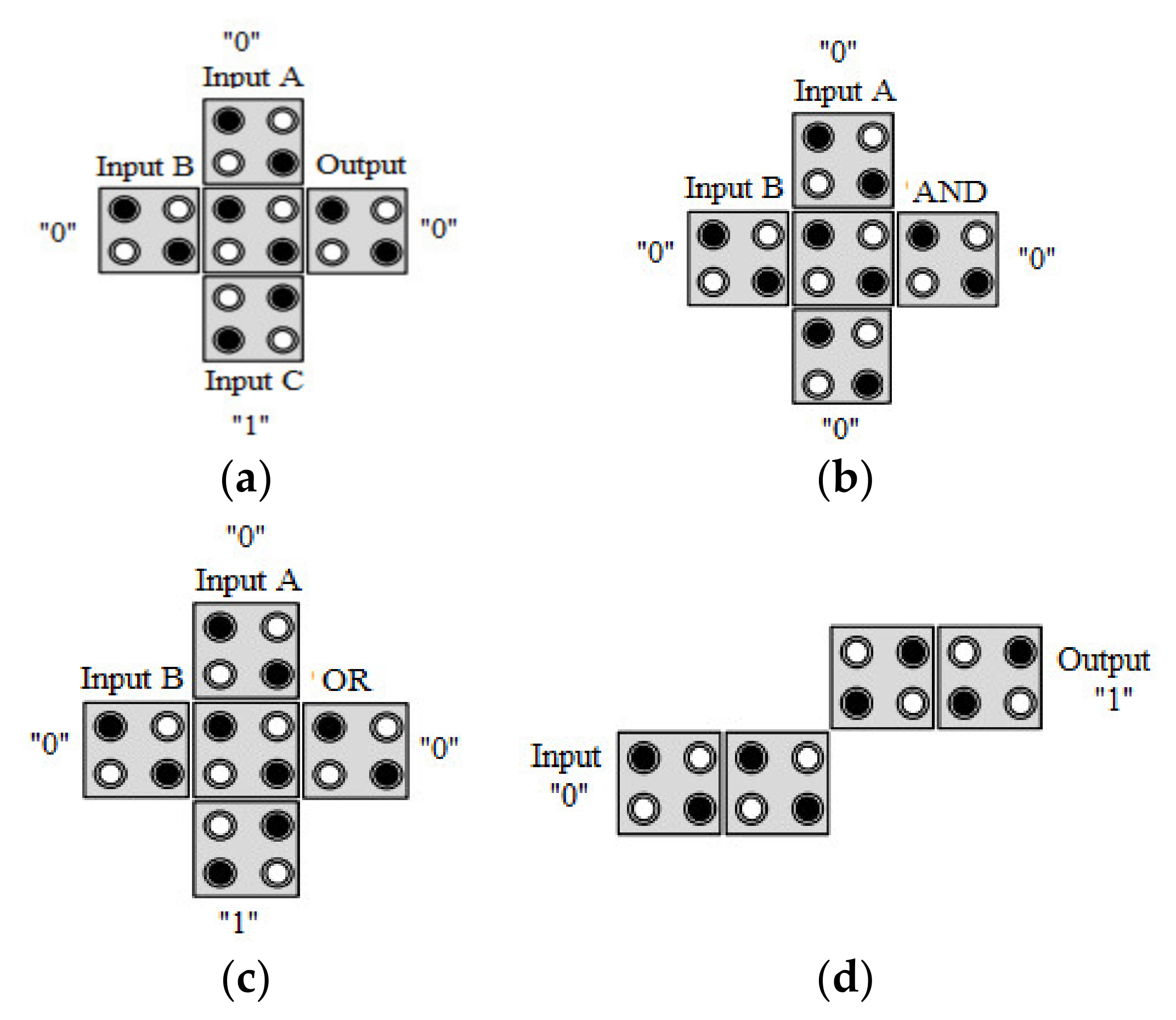
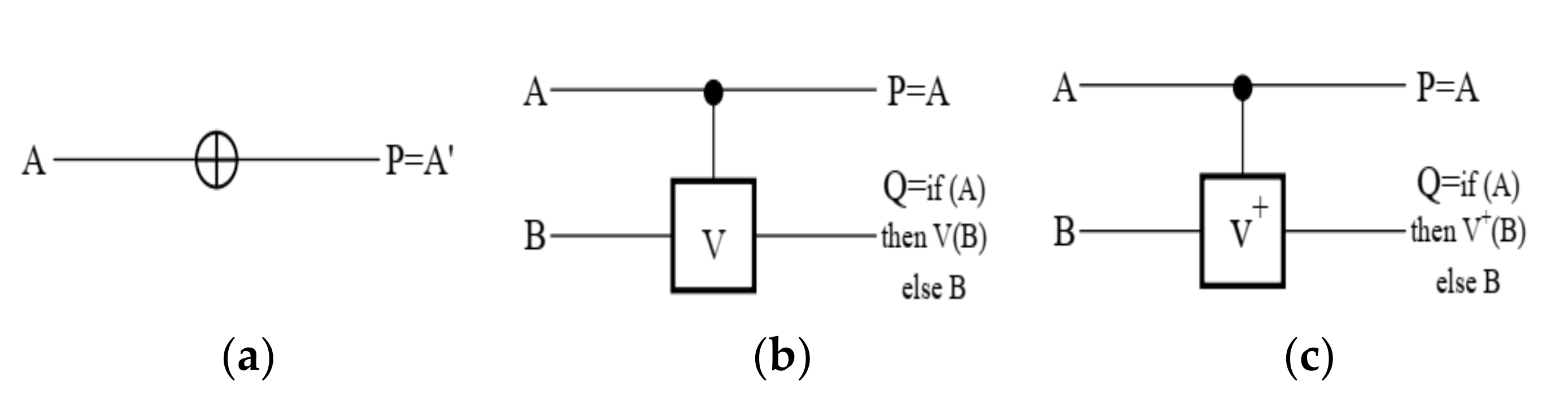
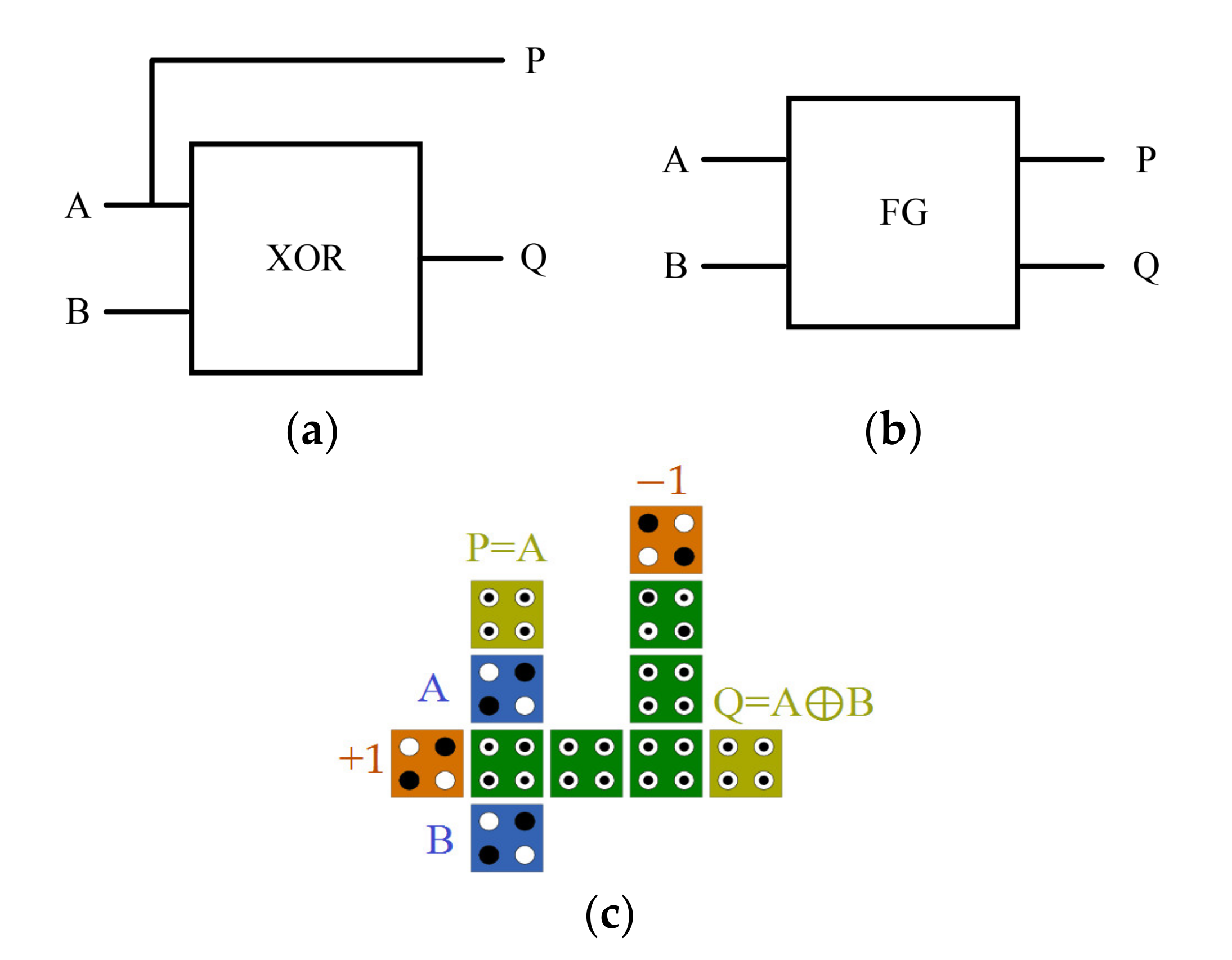
3.2. Design of FG
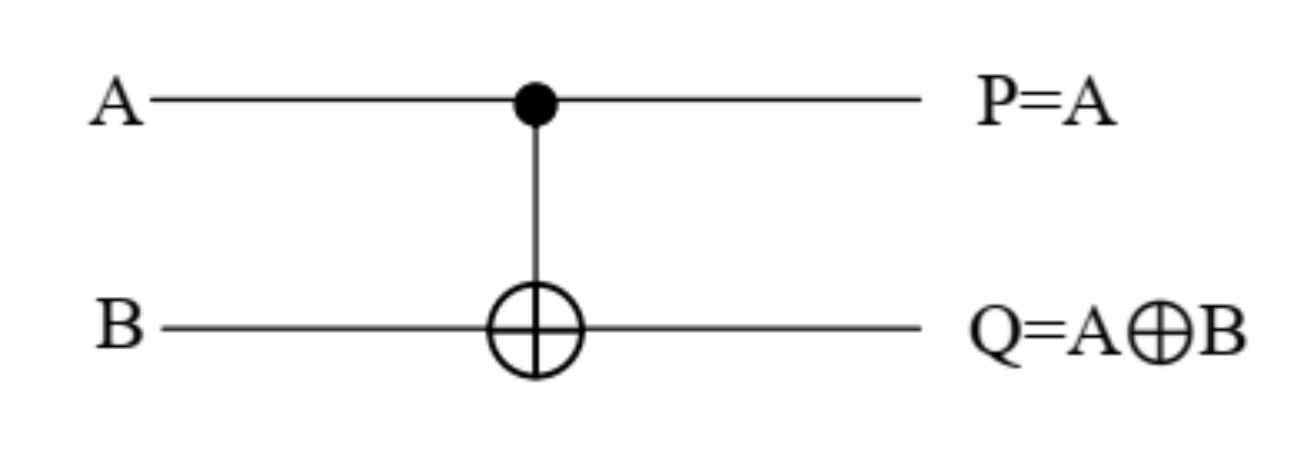
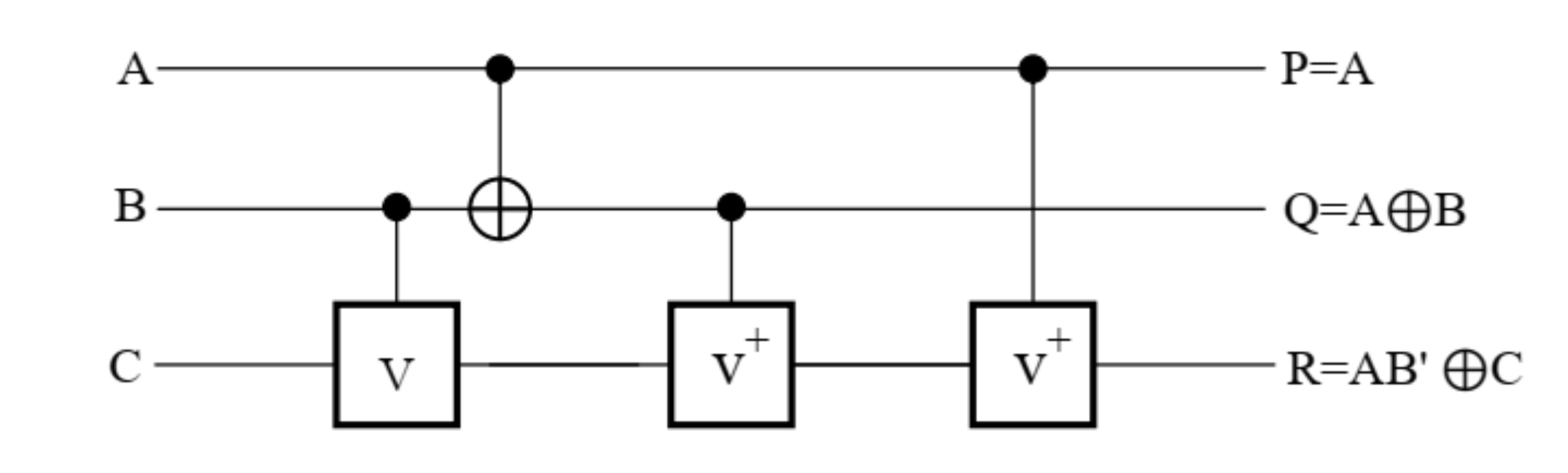
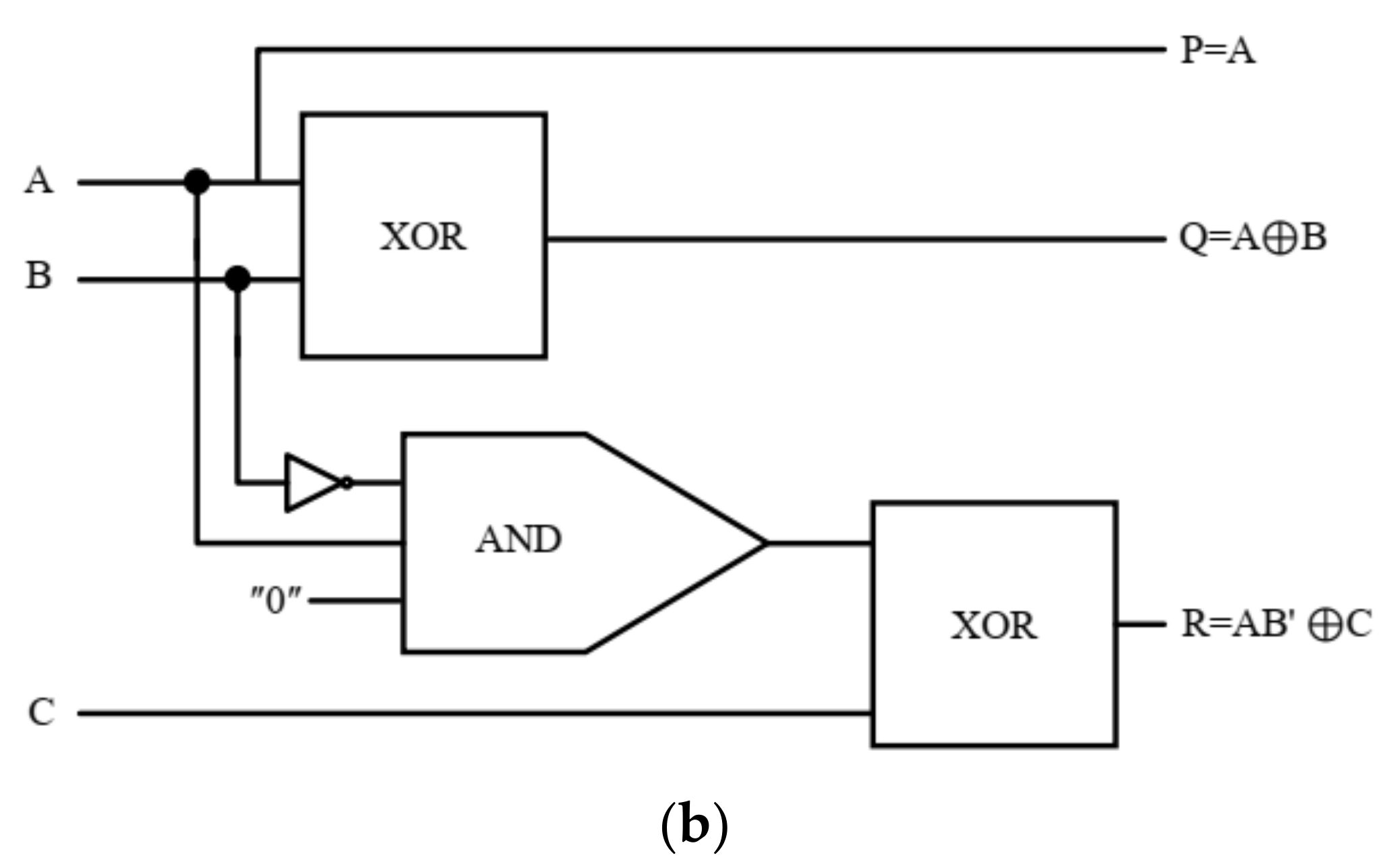
3.3. Design of TR Gate
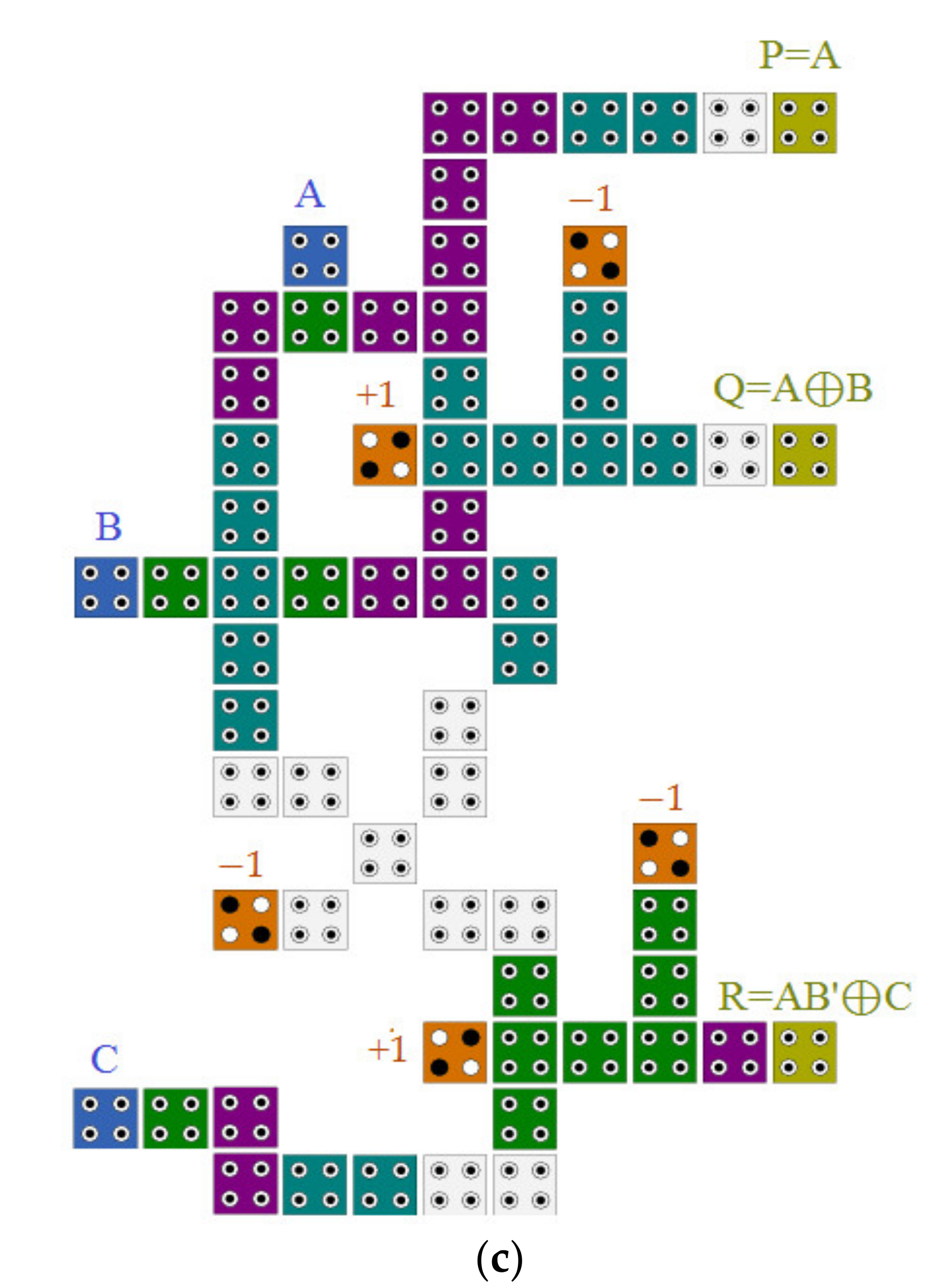
3.4. Design of Reversible 1-Bit Comparator Circuit
4. Performance Evaluation
4.1. Design Results and Discussions
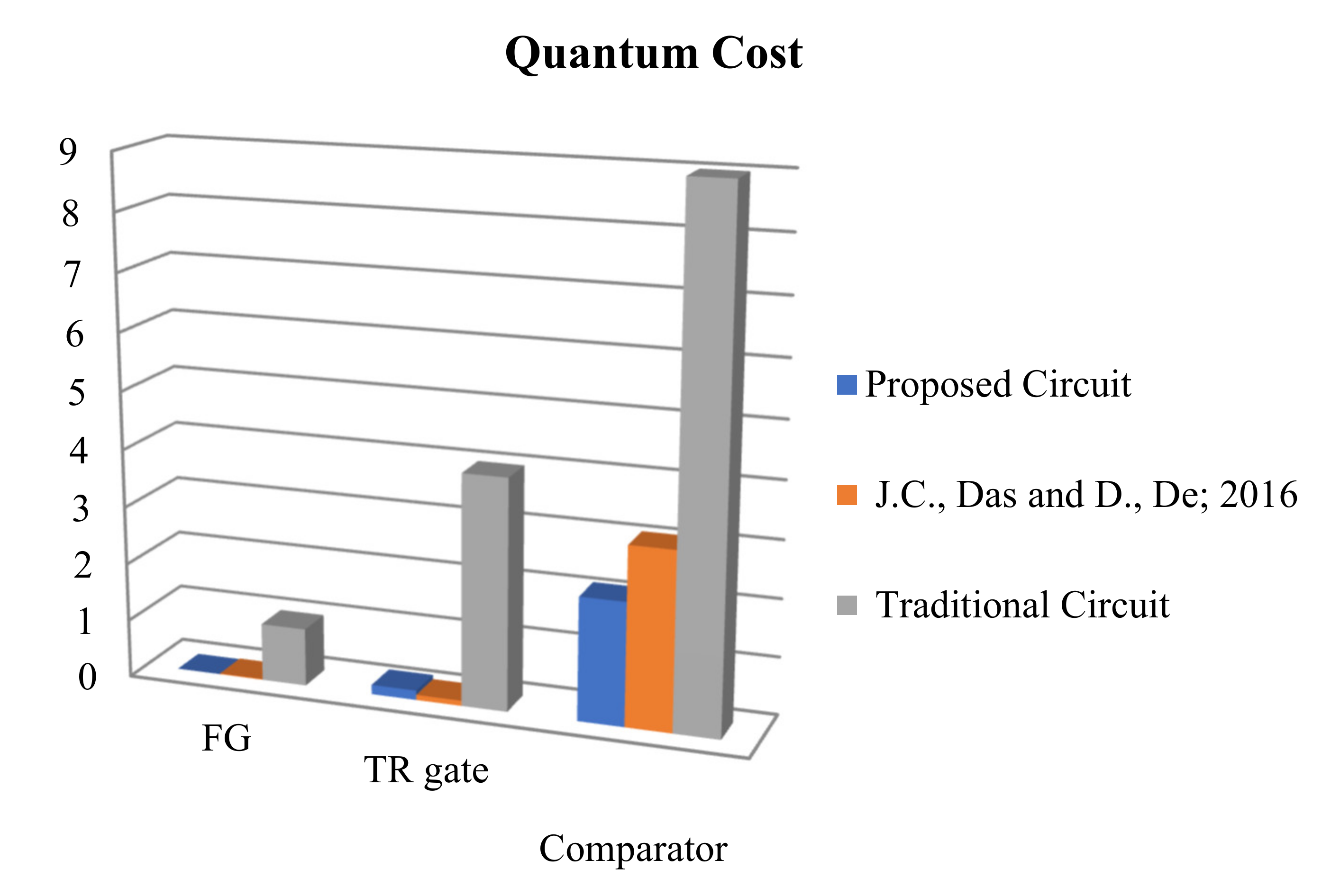
4.2. Results Circuit Cost and Quantum Cost
4.3. Complexity Estimation for the Proposed Circuits
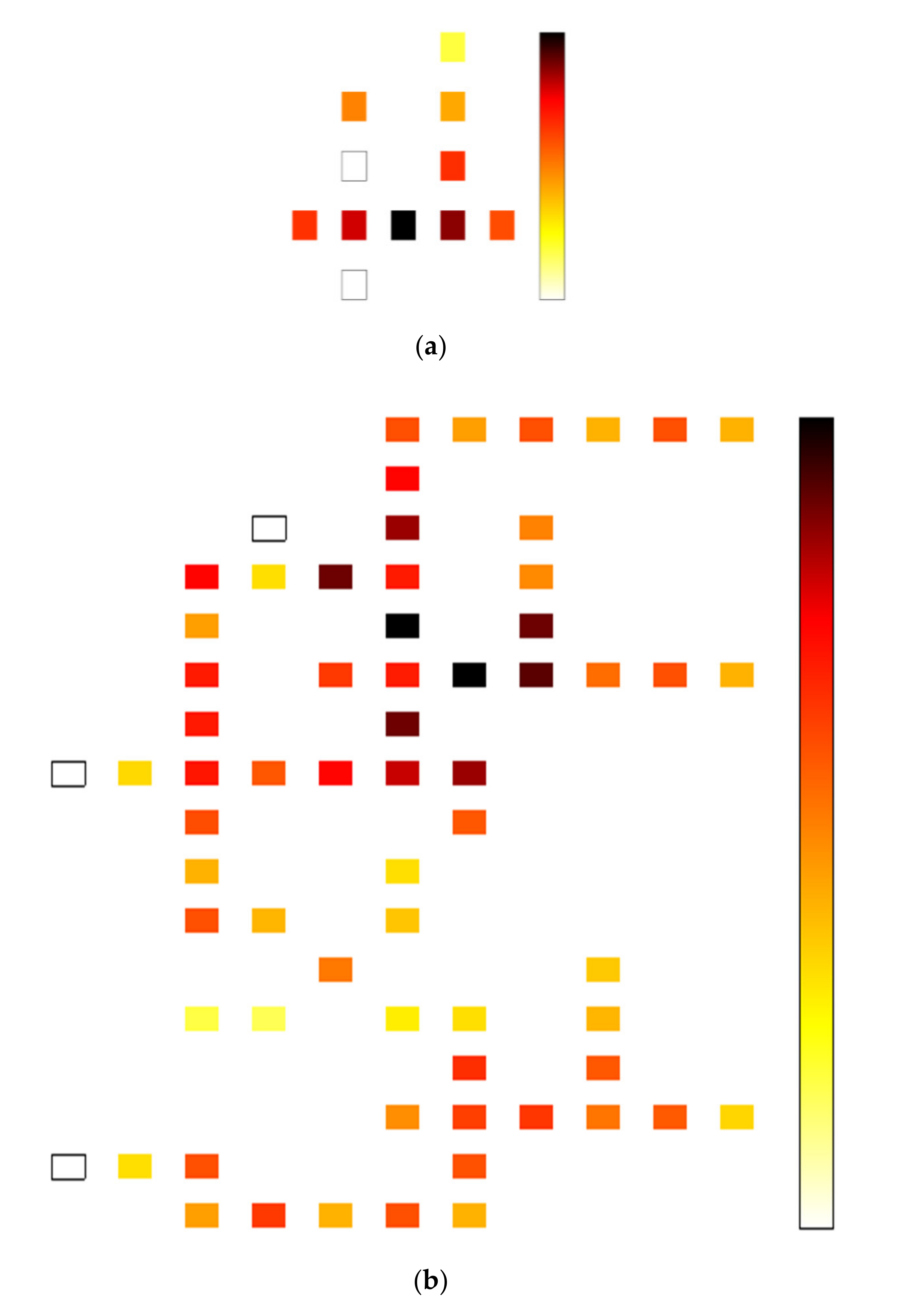
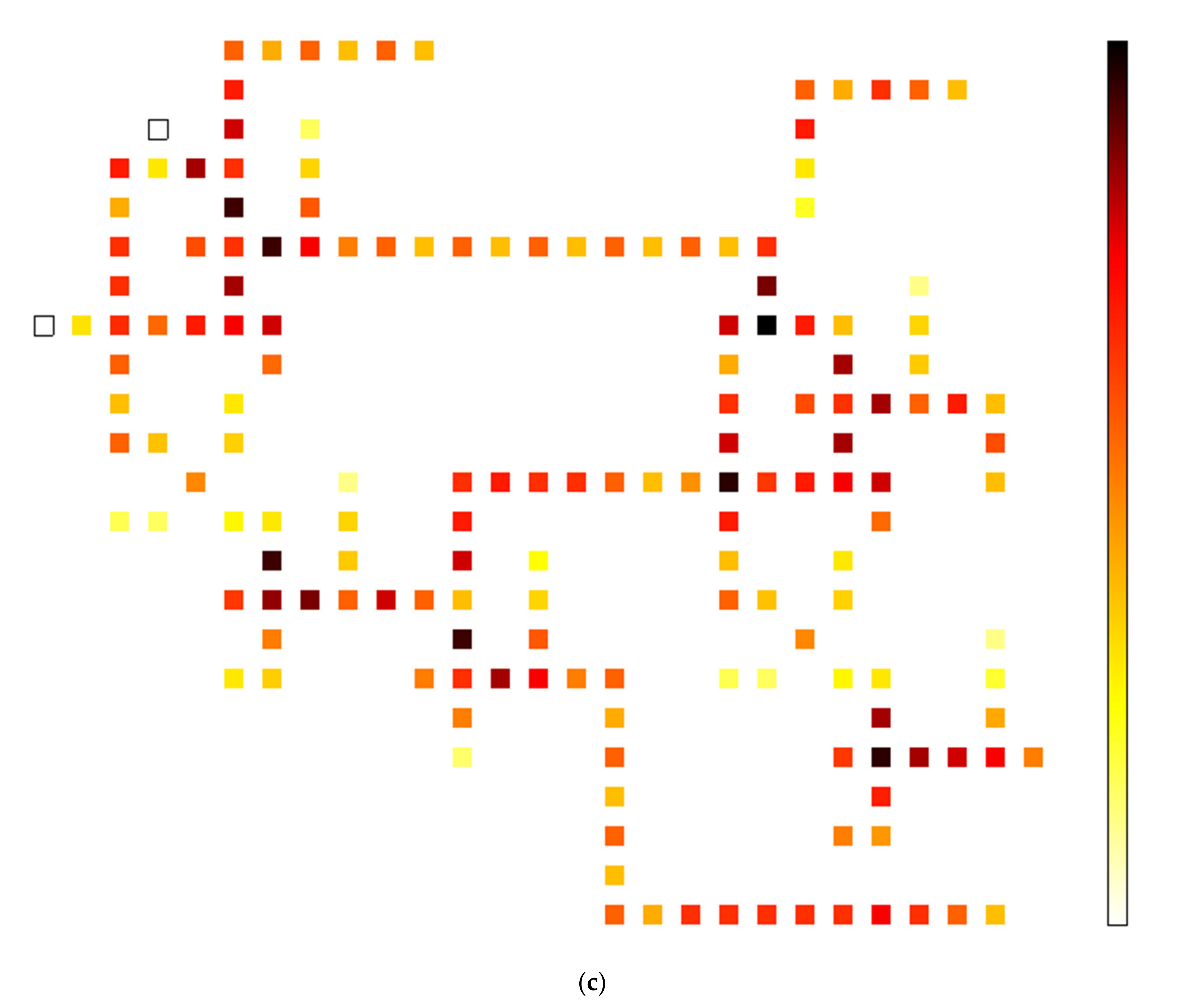
4.4. Energy Dissipation Analysis for the Proposed QCA Layout Circuits
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Ariano, G.M.; Perinotti, P. Quantum cellular automata and free quantum field theory. Front. Phys. 2017, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, J.C.; De, D. Reversible comparator design using quantum dot-cellular automata. IETE J. Res. 2016, 62, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapliyal, H.; Ranganathan, N. Reversible logic-based concurrently testable latches for molecular QCA. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2010, 9, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nower, N.; Chowdhury, A.R. Design and analysis of a compact reversible ternary systolic array. Int. J. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2011, 3, 8905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmand, M.M.; Soryani, M.; Navi, K. Coplanar wire crossing in quantum cellular automata using a ternary cell. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2013, 7, 26372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.C.; Debnath, B.; De, D. Image steganography using quantum-dot cellular automata. Quantum Matter 2015, 4, 50417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahabi, M.; Lyakhov, P.; Bahar, A.N. Design and Implementation of Novel Efficient Full Adder/Subtractor Circuits Based on Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata Technology. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lent, C.S.; Tougaw, P.D. A device architecture for computing with quantum dots. Proc. IEEE 1997, 85, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lent, C.S.; Tougaw, P.D. Lines of interacting quantum-dot cells: A binary wire. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 74, 6227–6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vahabi, M.; Bahar, A.N.; Otsuki, A.; Wahid, K.A. Ultra-Low-Cost Design of Ripple Carry Adder to Design Nanoelectronics in QCA Nanotechnology. Electronics 2022, 11, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landauer, R. Irreversibility and heat generation in the computing process. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1961, 5, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.H. Logical reversibility of computation. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1973, 17, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gin, A.; Tougaw, P.D.; Williams, S. An alternative geometry for quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 8281–8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walus, K.; Jullien, G.A. Design tools for an emerging soc technology: Quantum-dot cellular automata. Proc. IEEE 2006, 94, 1225–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.-H.; Jeon, J.-C.; Yoo, K.-Y. Wire-crossing technique on quantum-dot cellular automata, in NGCIT2013, the 2nd International Conference on Next Generation Computer and Information Technology. Comput. Sci. 2013, 27, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Vahabi, M.; Lyakhov, P.; Bahar, A.N.; Wahid, K.A. Design and Implementation of New Coplanar FA Circuits without NOT Gate and Based on Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata Technology. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 12157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.C.; De, D. Reversible half-adder design using QCA. In Quantum Matter; American Scientific Publishers: Valencia, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Das, K.; De, D. Characterization, test and logic synthesis of novel conservative & reversible logic gates for QCA. Int. J. Nanosci. 2010, 9, 20114. [Google Scholar]
- Thapliyal, H.; Ranganathan, N.; Kotiyal, S. Design of testable reversible sequential circuits. IEEE Trans. 2013, 21, 12019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, B.; Roozbeh, A.; Zare, J. Design of low power comparator using DG gate. Circuits Syst. Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thapliyal, H.; Ranganathan, N. Design of efficient reversible binary subtractors based on a new reversible gate. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI, Washington, DC, USA, 13–15 May 2009; p. 22934. [Google Scholar]
- Moallem, P.; Ehsanpour, M. A novel design of reversible multiplier circuit. Int. J. Eng. 2013, 26, 57786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Srivastava, S.; Lu, L.; O’Neill, M.; Swartzlander, E.E. Are QCA cryptographic circuits resistant to power analysis attack? IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2012, 11, 123951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Asthana, A.; Bhanja, S.; Sarkar, S. QCAPro-an error-power estimation tool for QCA circuit design. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium of Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 15–18 May 2011. [Google Scholar]




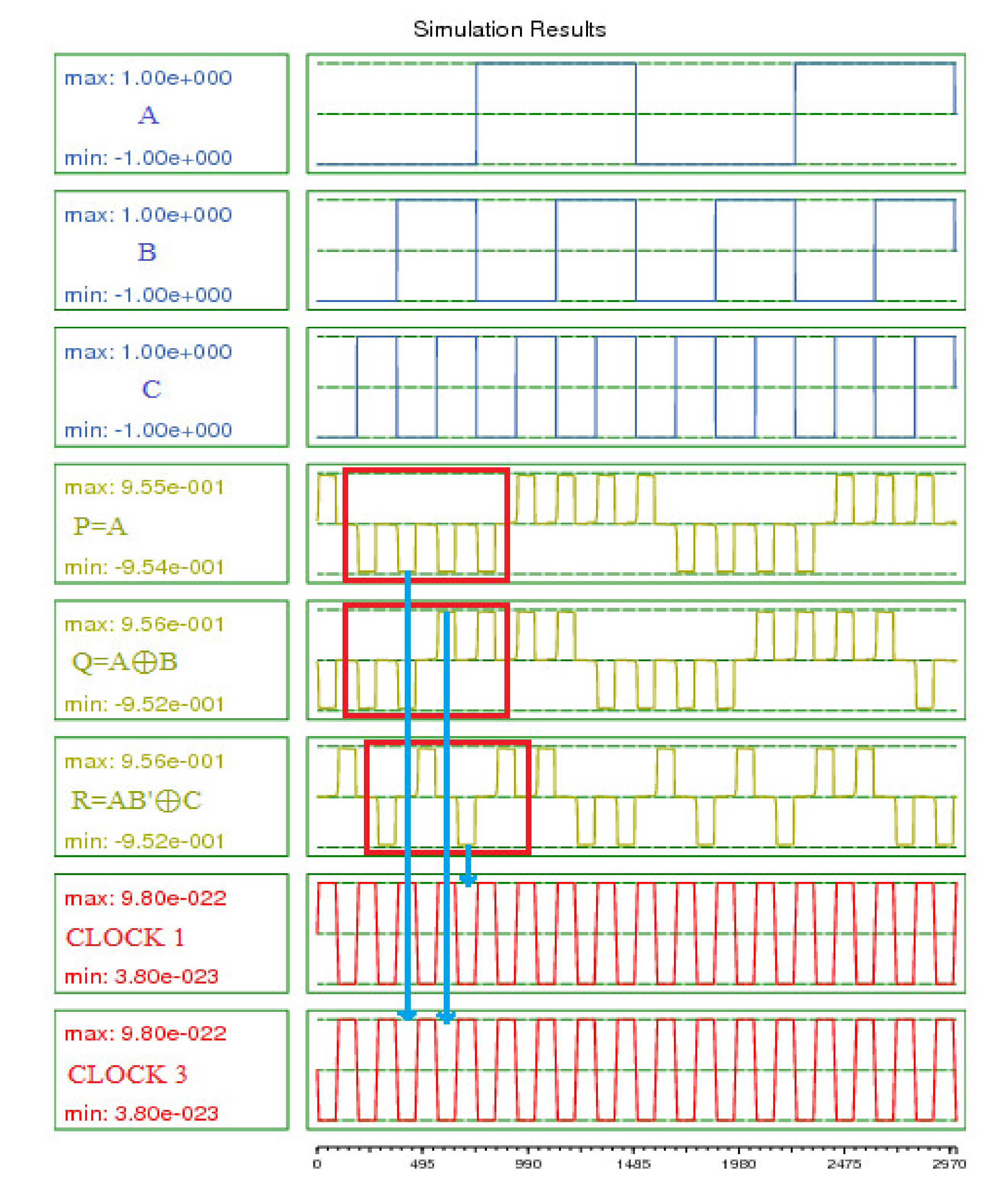

| Input | Output | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | A > B | A < B | A = B |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Input | Output | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | P | Q |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Input | Output | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | P | Q | R |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Cell width | 18 nm |
| Cell height | 18 nm |
| Relative permittivity | 12.9 |
| Dot diameter | 5 nm |
| Number of samples | 12,800 |
| Convergence tolerance | 0.001 |
| Clock high | 9.8 × 10−22 J |
| Clock low | 3.8 × 10−23 J |
| Clock amplitude factor | 2 |
| Radius of effect | 65 nm |
| Layer separation | 11.5 nm |
| Maximum iteration per sample | 100 |
| Proposed Reversible Circuits | Area (µm2) | Latency (clock) | Cost (Area × Latency2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FG | 0.010 | 0.25 | 0.0006 |
| TR gate | 0.073 | 1.50 | 0.164 |
| 1-bit comparator | 0.237 | 3.0 | 2.133 |
| Proposed Reversible Circuits | Circuit Cost | Quantum Cost |
|---|---|---|
| FG | 1 | |
| TR gate | 4 | |
| 1-bit comparator | 9 |
| Proposed Reversible Circuits | Area (µm2) | Cell Count | Delay (Clock) | Cost (Area × Latency2) | Power (W) | PDP (Ws) (Power × Latency) | Crossover Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FG [2] | 0.023 | 37 | 0.75 | 0.013 | 23.23 × 10−10 | 17.42 × 10−22 | Multi-Layer |
| TR gate [2] | 0.090 | 122 | 1.0 | 0.090 | 73.86 × 10−10 | 73.86 × 10−22 | Multi-Layer |
| 1-bit comparator [2] | 0.343 | 319 | 3.0 | 3.087 | 161.8 × 10−10 | 485.4 × 10−22 | Multi-Layer |
| Proposed FG | 0.010 | 11 | 0.25 | 0.0006 | 11.47 × 10−10 | 2.867 × 10−22 | Coplanar |
| Proposed TR gate | 0.073 | 64 | 1.5 | 0.164 | 27.56 × 10−10 | 41.34 × 10−22 | Coplanar |
| Proposed 1-bit comparator | 0.237 | 165 | 3.0 | 2.133 | 58.32 × 10−10 | 174.96 × 10−22 | Coplanar |
| Proposed Reversible Circuits | Avg Leakage Energy (meV) | Avg Switching Energy (meV) | Avg Energy Diss (meV) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 EK | 1 EK | 1.5 EK | 0.5 EK | 1 EK | 1.5 EK | 0.5 EK | 1 EK | 1.5 EK | |
| FG | 3.78 | 10.42 | 17.82 | 10.54 | 9.22 | 7.98 | 14.32 | 19.64 | 25.80 |
| TR gate | 21.42 | 63.10 | 110.65 | 89.03 | 76.12 | 64.38 | 110.45 | 139.22 | 175.03 |
| 1-bit comparator | 53.82 | 162.65 | 287.96 | 267.05 | 230.20 | 195.15 | 320.87 | 392.85 | 483.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vahabi, M.; Lyakhov, P.; Bahar, A.N.; Otsuki, A.; Wahid, K.A. Novel Reversible Comparator Design in Quantum Dot-Cellular Automata with Power Dissipation Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7846. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157846
Vahabi M, Lyakhov P, Bahar AN, Otsuki A, Wahid KA. Novel Reversible Comparator Design in Quantum Dot-Cellular Automata with Power Dissipation Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(15):7846. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157846
Chicago/Turabian StyleVahabi, Mohsen, Pavel Lyakhov, Ali Newaz Bahar, Akira Otsuki, and Khan A. Wahid. 2022. "Novel Reversible Comparator Design in Quantum Dot-Cellular Automata with Power Dissipation Analysis" Applied Sciences 12, no. 15: 7846. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157846
APA StyleVahabi, M., Lyakhov, P., Bahar, A. N., Otsuki, A., & Wahid, K. A. (2022). Novel Reversible Comparator Design in Quantum Dot-Cellular Automata with Power Dissipation Analysis. Applied Sciences, 12(15), 7846. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12157846










