Heme Dependent Catalase Conditionally Contributes to Oxygen Tolerance of Tetragenococcus halophilus Strains Isolated from Soy Sauce Moromi
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
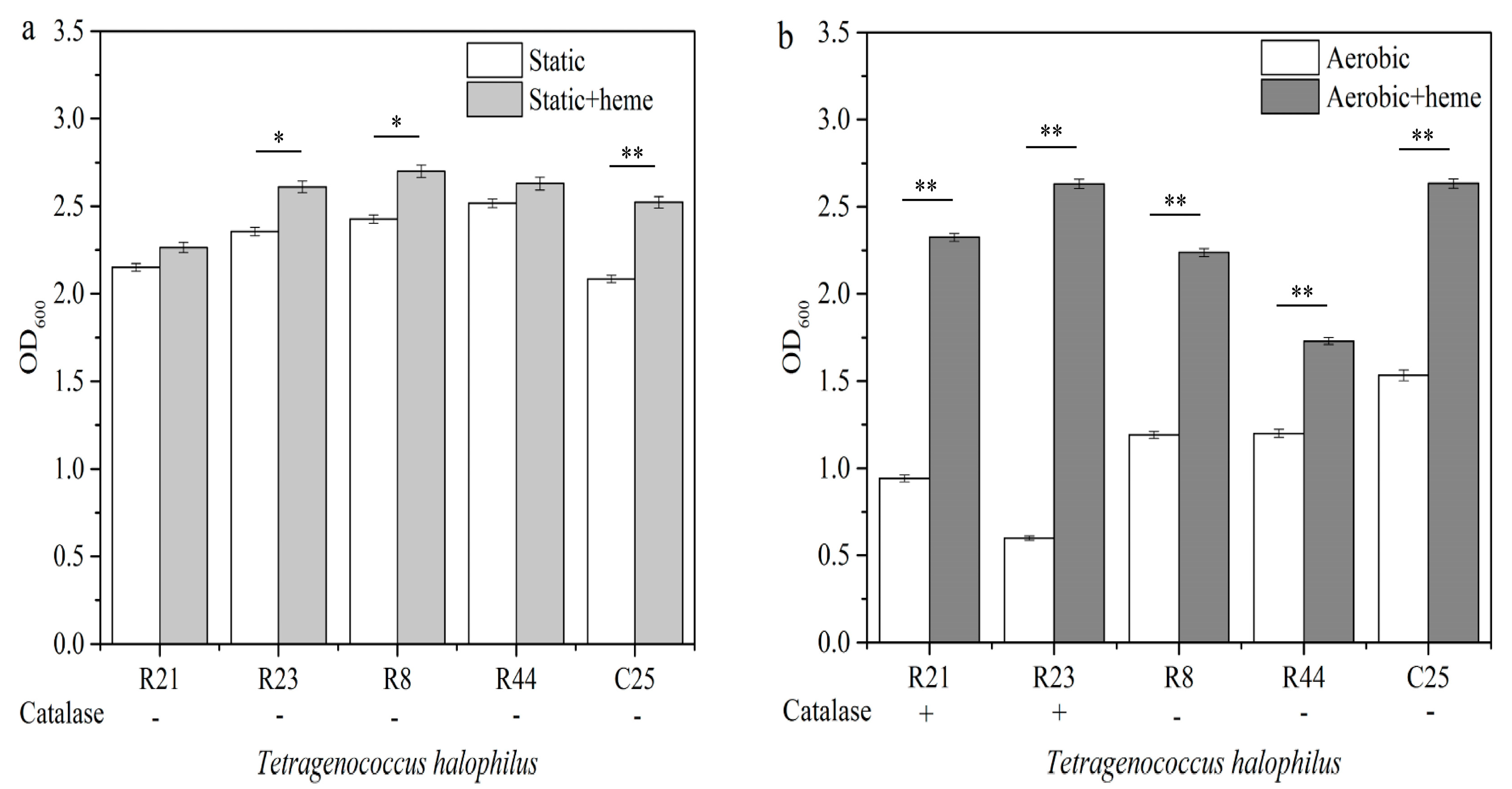
2.2. Detection of Growth of T. halophilus under Different Conditions
2.3. Determination of Antioxidant Enzymes Activities
2.4. H2O2 Challenge Experiment
2.5. Characterization of cat Gene in T. halophilus
2.6. Effect of Catalase Activity on Strain’s Growth
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Tolerance of T. halophilus Strains to Oxidative Stress
3.2. Antioxidant Enzymes Activities Analysis
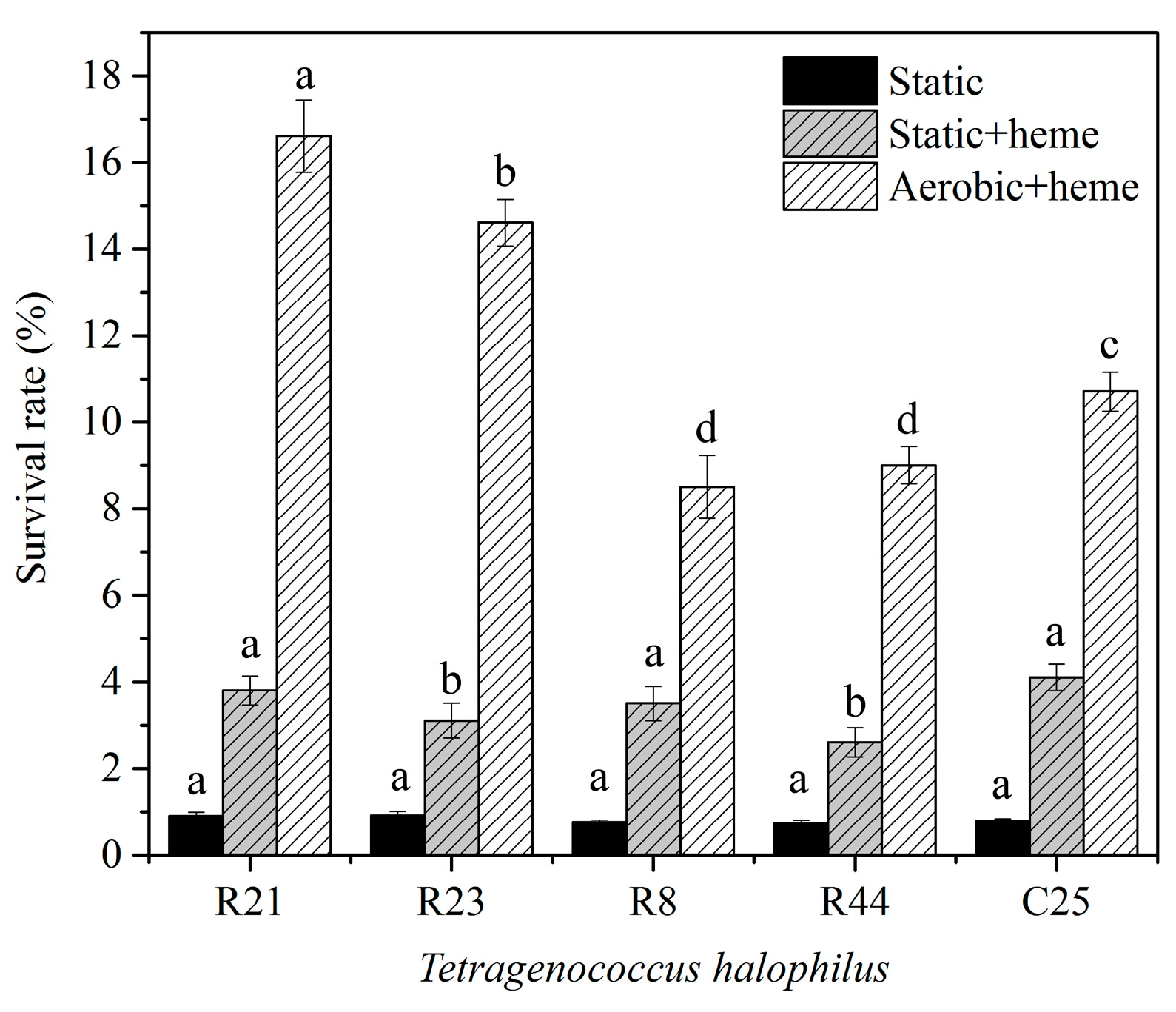
3.3. Resistance of T. halophilus to Hydrogen Peroxide
3.4. Characterization of Catalase Produced by T. halophilus
3.5. The Effect of Catalase on the Growth of T. halophilus Strains
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D. Biochemical changes and microbial community dynamics during spontaneous fermentation of Zhacai, a traditional pickled mustard tuber from China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 347, 109199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodpai, R.; Sanpool, O.; Thanchomnang, T.; Wangwiwatsin, A.; Sadaow, L.; Phupiewkham, W.; Boonroumkaew, P.; Intapan, P.M.; Maleewong, W. Investigating the microbiota of fermented fish products (Pla-ra) from different communities of northeastern Thailand. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devanthi, P.V.P.; Gkatzionis, K. Soy sauce fermentation: Microorganisms, aroma formation, and process modification. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, E.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Huang, Q.; Chen, S.; Ma, H.; Ho, C.T.; Liao, L. Accelerating aroma formation of raw soy sauce using low intensity sonication. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justé, A.; Van, T.S.; Verreth, C.; Cleenwerck, I.; De, V.P.; Lievens, B.; Willems, K.A. Characterization of Tetragenococcus strains from sugar thick juice reveals a novel species, Tetragenococcus osmophilus sp. nov., and divides Tetragenococcus halophilus into two subspecies, T. halophilus subsp. halophilus subsp. nov. and T. halophilus subsp. flandriensis subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, M.D.; Williams, A.M.; Wallbanks, S. The phylogeny of Aerococcus and Pediococcus as determined by 16S rRNA sequence analysis: Description of Tetragenococcus gen. nov. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1990, 58, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udomsil, N.; Rodtong, S.; Tanasupawat, S.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Proteinase-producing halophilic lactic acid bacteria isolated from fish sauce fermentation and their ability to produce volatile compounds. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, D.K. Chapter Two—The role of microorganisms in soy sauce production. In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Gadd, G.M., Sariaslani, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 108, pp. 45–113. [Google Scholar]
- Devanthi, P.V.P.; Linforth, R.; Onyeaka, H.; Gkatzionis, K. Effects of co-inoculation and sequential inoculation of Tetragenococcus halophilus and Zygosaccharomyces rouxii on soy sauce fermentation. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Zhou, R.; Jin, Y.; Huang, J.; Wu, C. Effect of co-culture with Tetragenococcus halophilus on the physiological characterization and transcription profiling of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Huang, J.; Liang, R.; Wu, C.; Zhou, R. Comparing the differences of characteristic flavour between natural maturation and starter culture for Mucor-type Douchi. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.H.; Chun, B.H.; Jeong, S.E.; Jeon, C.O. Tetragenococcus halophilus MJ4 as a starter culture for repressing biogenic amine (cadaverine) formation during saeu-jeot (salted shrimp) fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2019, 82, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Huang, J.; Jin, Y.; Wu, C.; Shen, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, R. Aflatoxin B1 degradation by salt tolerant Tetragenococcus halophilus CGMCC 3792. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 121, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, J.H.; Chen, Q.; Wang, H.; Kong, B.H. Physiological, morphological and antioxidant responses of Pediococcus pentosaceus R1 and Lactobacillus fermentum R6 isolated from harbin dry sausages to oxidative stress. Foods 2021, 10, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, S.; Saruwatari, K.; Higashi, C.; Tsuruno, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Nakayama, J.; Sonomoto, K. In vivo and in vitro complementation study comparing the function of DnaK chaperone systems from halophilic lactic acid bacterium Tetragenococcus halophilus and Escherichia coli. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugimoto, S.; Yoshida, H.; Mizunoe, Y.; Tsuruno, K.; Nakayama, J.; Sonomoto, K. Structural and functional conversion of molecular chaperone ClpB from the gram-positive halophilic lactic acid bacterium Tetragenococcus halophilus mediated by ATP and stress. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 8070–8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Liang, H.; Yan, J.; Luo, L. The molecular mechanism and post-transcriptional regulation characteristic of Tetragenococcus halophilus acclimation to osmotic stress revealed by quantitative proteomics. J. Proteom. 2017, 168, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, H.; Le Marrec, C.; Blanco, C.; Jebbar, M. Glycine betaine, carnitine, and choline enhance salinity tolerance and prevent the accumulation of sodium to a level inhibiting growth of Tetragenococcus halophila. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denich, T.J.; Beaudette, L.A.; Lee, H.; Trevors, J.T. Effect of selected environmental and physico-chemical factors on bacterial cytoplasmic membranes. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2003, 52, 149–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.S.; Seeras, A.; Sanchezmaldonado, A.F.; Zhang, C.; Su, M.S.; Gänzle, M.G. Glutamine, glutamate, and arginine-based acid resistance in Lactobacillus reuteri. Food Microbiol. 2014, 42, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Ren, C.; Xu, Y.; Kivisaar, M. GlnR negatively regulates glutamate-dependent acid resistance in Lactobacillus brevis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02615–e02619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianniello, R.G.; Zotta, T.; Matera, A.; Genovese, F.; Parente, E.; Ricciardi, A. Investigation of factors affecting aerobic and respiratory growth in the oxygen-tolerant strain Lactobacillus casei N87. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.; Wang, J. Oxidative stress tolerance and antioxidant capacity of lactic acid bacteria as probiotic: A systematic review. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1801944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, H. Antioxidant properties of wine lactic acid bacteria: Oenococcus oeni. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5189–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Yen, C. Antioxidative ability of lactic acid bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Du, G.; Fang, F. Classification and characteristics of Tetragenococcus halophilus derived from moromi. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2018, 58, 1826–1838. [Google Scholar]
- Maehly, A.C.; Chance, B. The assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods Biochem. Anal. 1954, 1, 357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gürtler, M.; Gänzle, M.G.; Wolf, G.; Hammes, W.P. Physiological diversity among strains of Tetragenococcus halophilus. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 21, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matés, J.M. Effects of antioxidant enzymes in the molecular control of reactive oxygen species toxicology. Toxicology 2000, 153, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.W.; Heo, S.; Lee, J.H. Safety assessment of Tetragenococcus halophilus isolates from doenjang, a Korean high-salt-fermented soybean paste. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juste, A.; Lievens, B.; Frans, I.; Marsh, T.L.; Klingeberg, M.; Michiels, C.W.; Willems, K.A. Genetic and physiological diversity of Tetragenococcus halophilus strains isolated from sugar- and salt-rich environments. Microbiology 2008, 154, 2600–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Liu, C.; He, G.; Huang, J.; Zhou, R. Characterization of a multiple-stress tolerance Tetragenococcus halophilus and application as starter culture in Chinese horsebean-chili-paste manufacture for quality improvement. Food Sci. Technol. Int. Tokyo 2013, 19, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Si, L.; Meng, X.; Luo, L. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals novel genes and regulatory mechanisms of Tetragenococcus halophilus in response to salt stress. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 42, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staerck, C.; Gastebois, A.; Vandeputte, P.; Calenda, A.; Larcher, G.; Gillmann, L.; Papon, N.; Bouchara, J.P.; Fleury, M.J.J. Microbial antioxidant defense enzymes. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 110, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhsler, M.; Leitsch, D.; Mbouaka, A.L.; Wekerle, M.; Walochnik, J. Transcriptional changes of proteins of the thioredoxin and glutathione systems in Acanthamoeba spp. under oxidative stress—An RNA approach. Parasite 2022, 29, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikanyika, M.; Aragão, D.; McDevitt, C.A.; Maher, M.J. The structure and activity of the glutathione reductase from Streptococcus pneumoniae. Acta Crystallogr. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 2019, 75, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Benlekbir, S.; Venkatakrishnan, P.; Wang, Y.H.; Hong, S.J.; Hosler, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Rubinstein, J.L.; Gennis, R.B. Structure of the alternative complex III in a supercomplex with cytochrome oxidase. Nature 2018, 557, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwalkar, A.; Kailasapathy, K.; Hourigan, J.; Peiris, P.; Arumugaswamy, R. An improved method for the determination of NADH oxidase in the presence of NADH peroxidase in lactic acid bacteria. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2003, 52, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanasombat, S.; Treebavonkusol, P.; Kittisrisopit, S.; Jaichalad, T.; Phunpruch, S.; Kootmas, A.; Nualsri, I. Lactic acid bacteria isolated from raw and fermented pork products: Identification and characterization of catalase-producing Pediococcus pentosaceus. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.B.; Garrigues, C.; Tuphile, K.; Brun, C.; Vido, K.; Bennedsen, M.; Møllgaard, H.; Gaudu, P.; Gruss, A. Impact of aeration and heme-activated respiration on Lactococcus lactis gene expression: Identification of a heme-responsive operon. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 4903–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Strain | R23 | R21 | C25 | R44 | R8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalase activity | + | + | − | − | − |
| Interruption of cat gene | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Du, G.; Fang, F. Heme Dependent Catalase Conditionally Contributes to Oxygen Tolerance of Tetragenococcus halophilus Strains Isolated from Soy Sauce Moromi. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168039
Li J, Wang B, Chen J, Du G, Fang F. Heme Dependent Catalase Conditionally Contributes to Oxygen Tolerance of Tetragenococcus halophilus Strains Isolated from Soy Sauce Moromi. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(16):8039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168039
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jialian, Bo Wang, Jian Chen, Guocheng Du, and Fang Fang. 2022. "Heme Dependent Catalase Conditionally Contributes to Oxygen Tolerance of Tetragenococcus halophilus Strains Isolated from Soy Sauce Moromi" Applied Sciences 12, no. 16: 8039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168039
APA StyleLi, J., Wang, B., Chen, J., Du, G., & Fang, F. (2022). Heme Dependent Catalase Conditionally Contributes to Oxygen Tolerance of Tetragenococcus halophilus Strains Isolated from Soy Sauce Moromi. Applied Sciences, 12(16), 8039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168039







