Visual Servo Control of the Macro/Micro Manipulator with Base Vibration Suppression and Backlash Compensation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
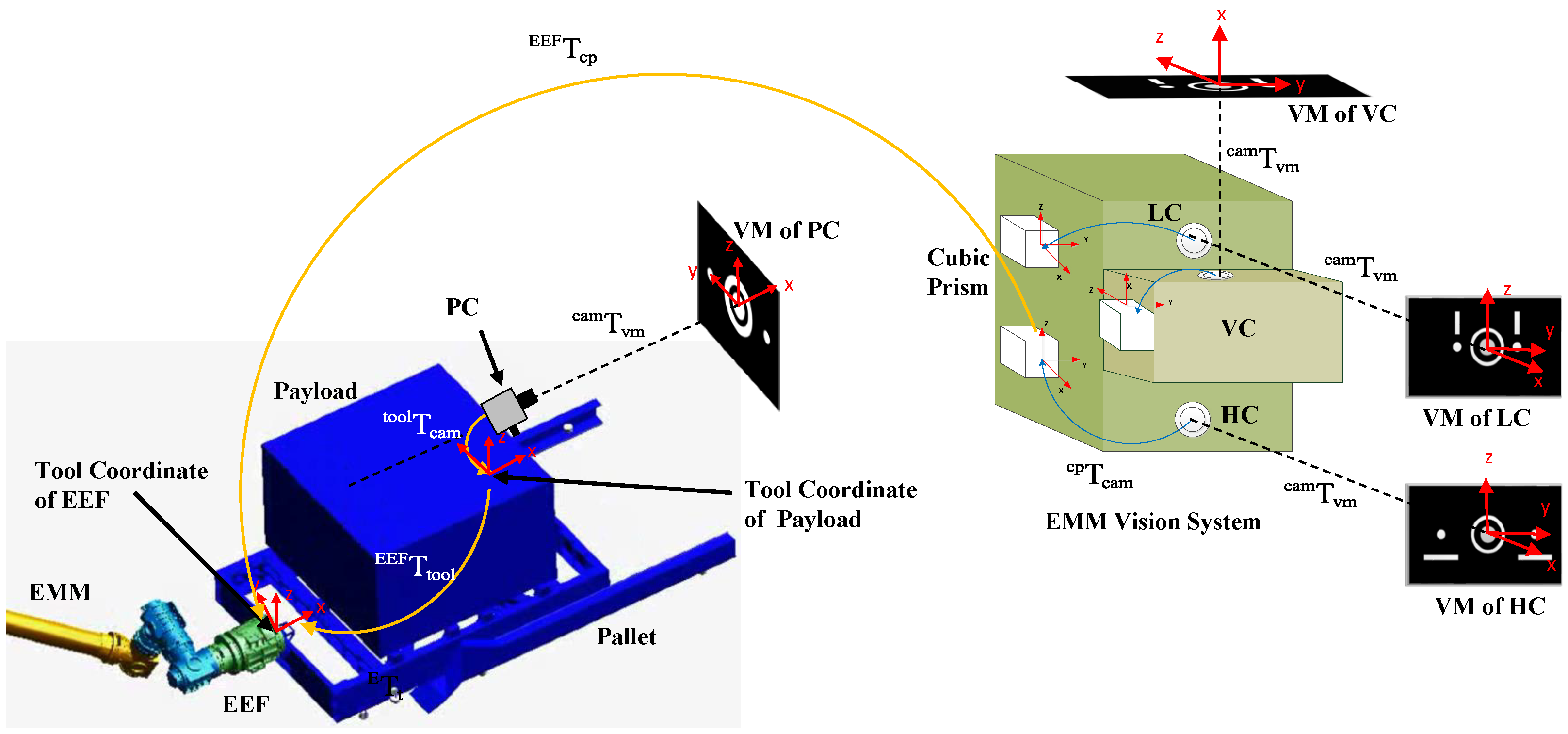
2. Vision-Based Measurement System
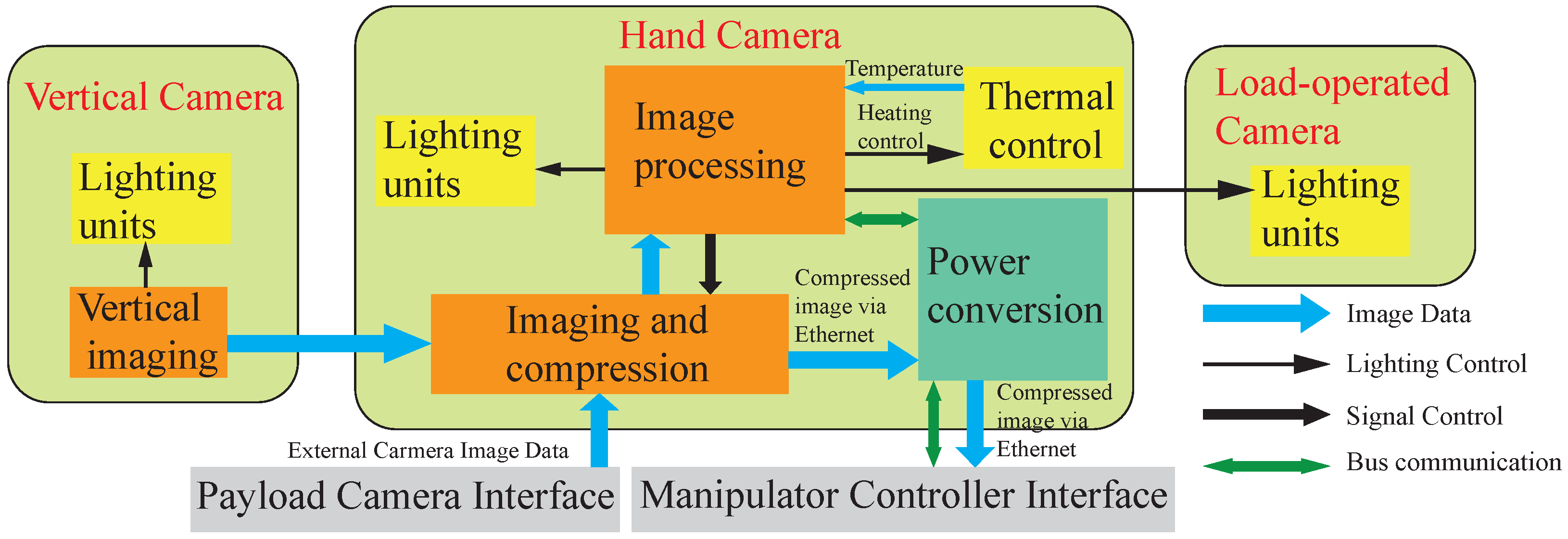
2.1. EMM Vision System
2.2. Measurement of Position and Orientation
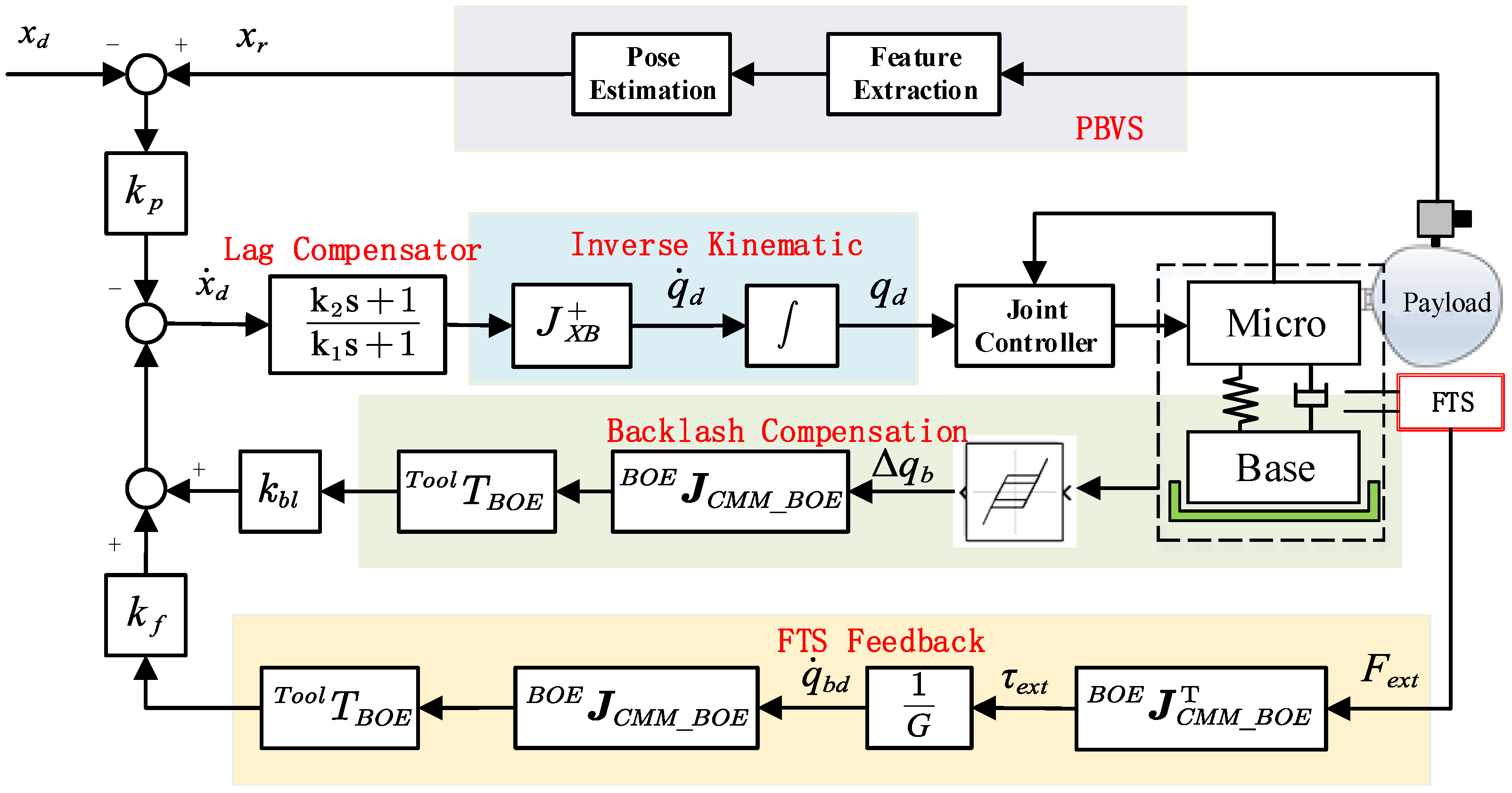
3. Integration of Visual Servo Control
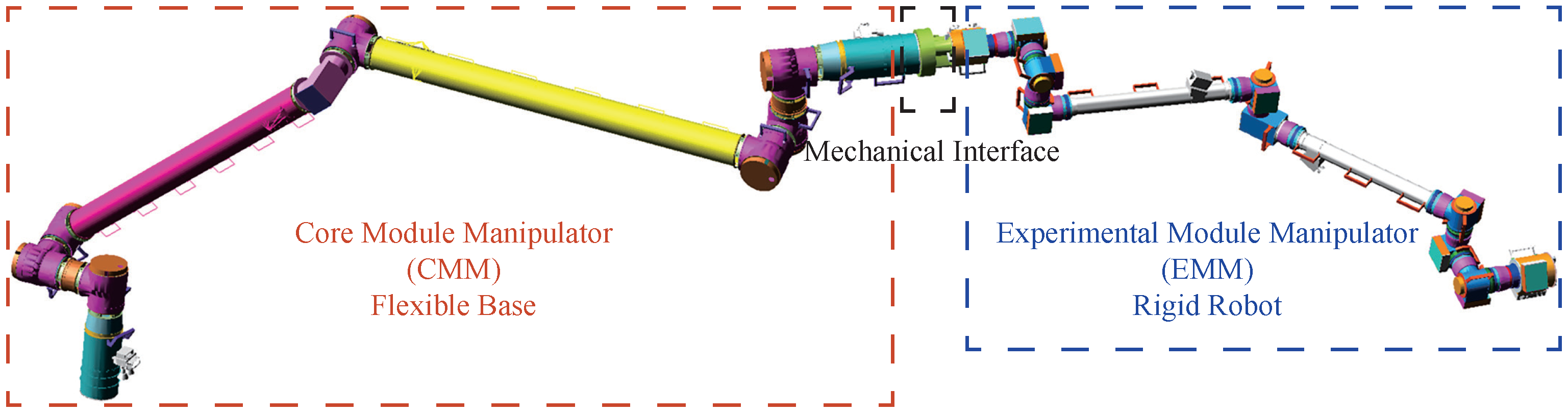
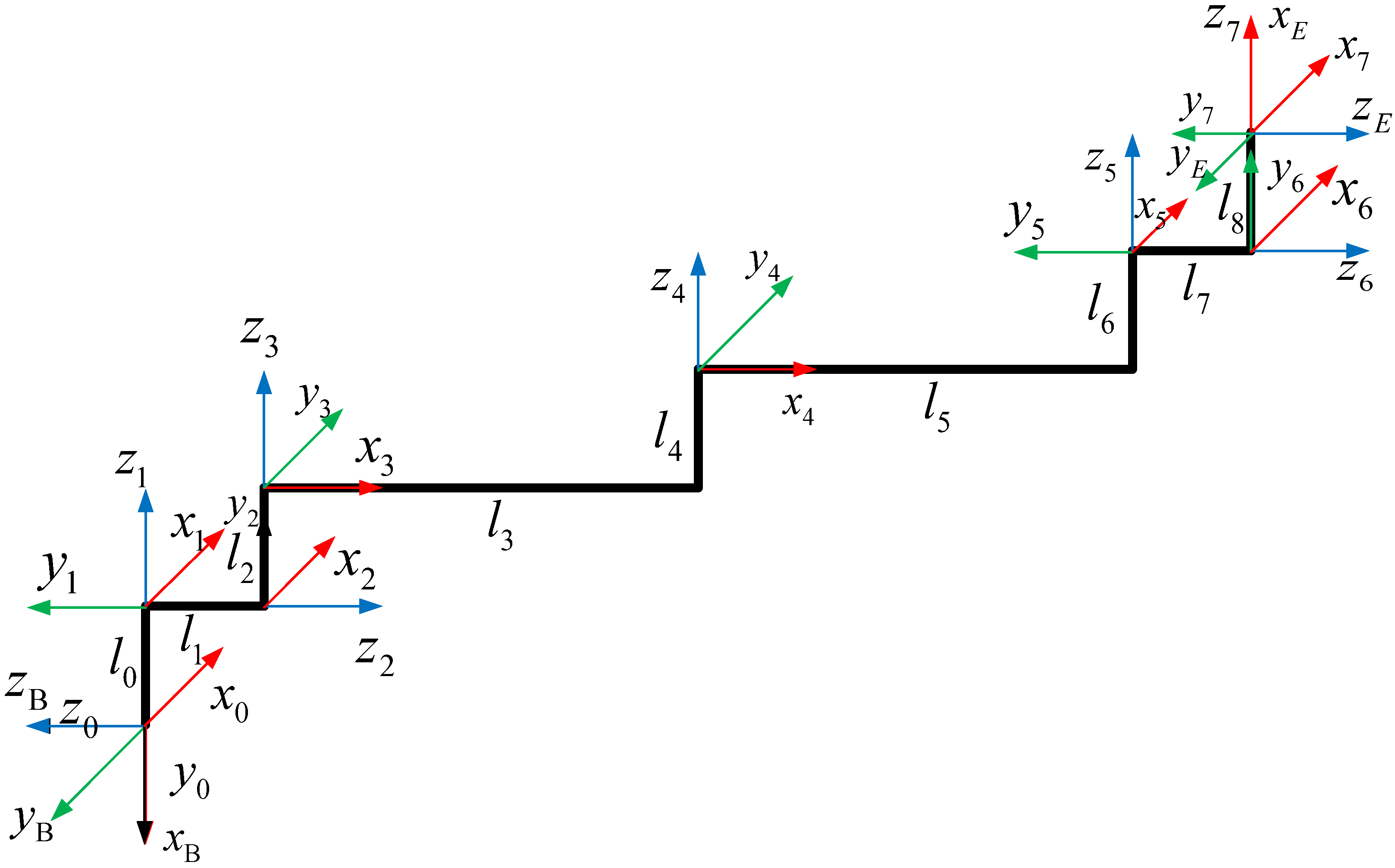
3.1. Model of Macro-Micro Manipulator
3.2. Reaction Force/Torque Feedback Control
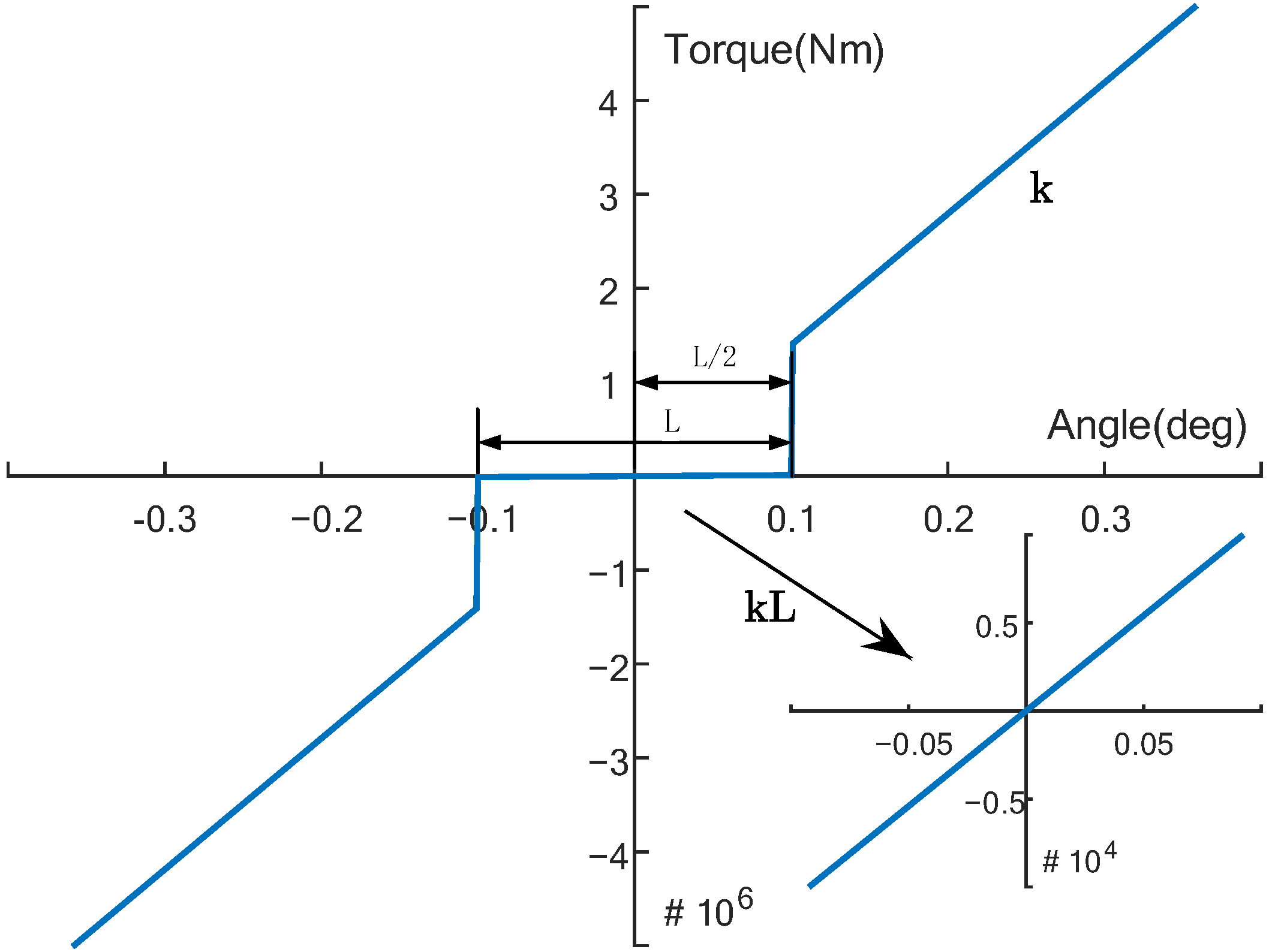
3.3. Base Backlash Compensation
3.4. Integration of a Visual Servo
3.5. Stability Analysis
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Simulation Model
4.2. Simulation Results
5. Experimental Results
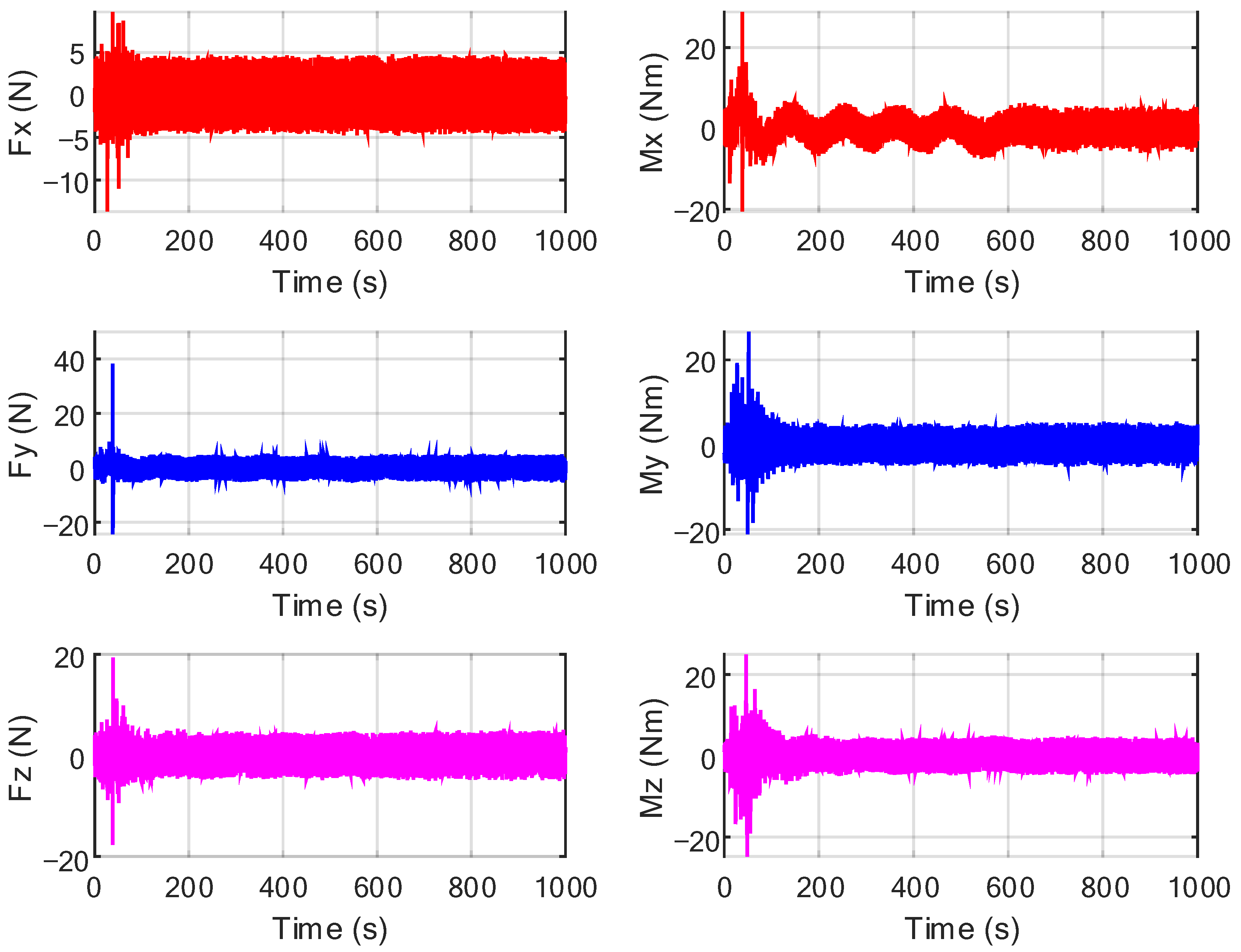
5.1. The Experimental Facility
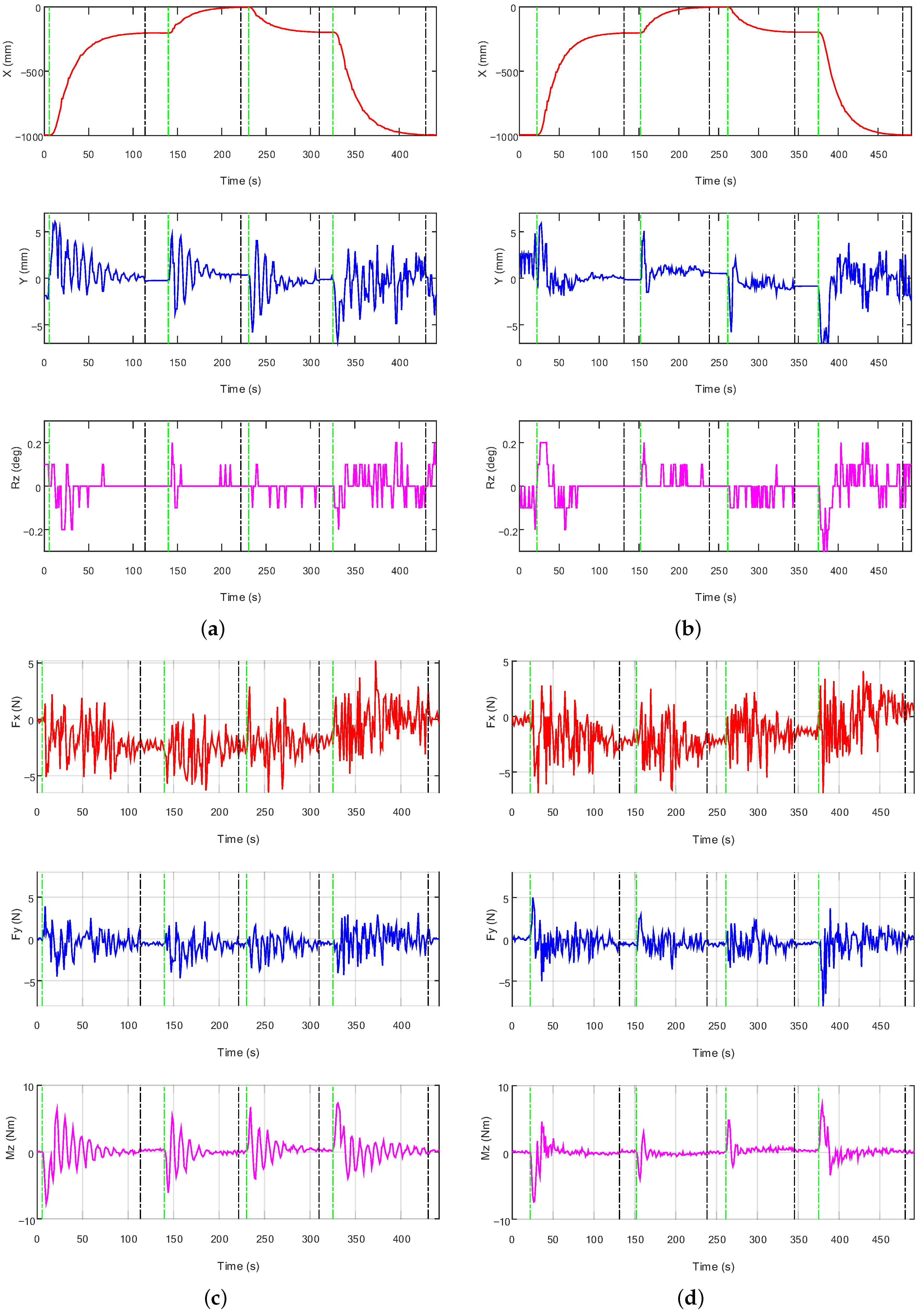
5.2. Visual Servo Control without Payload
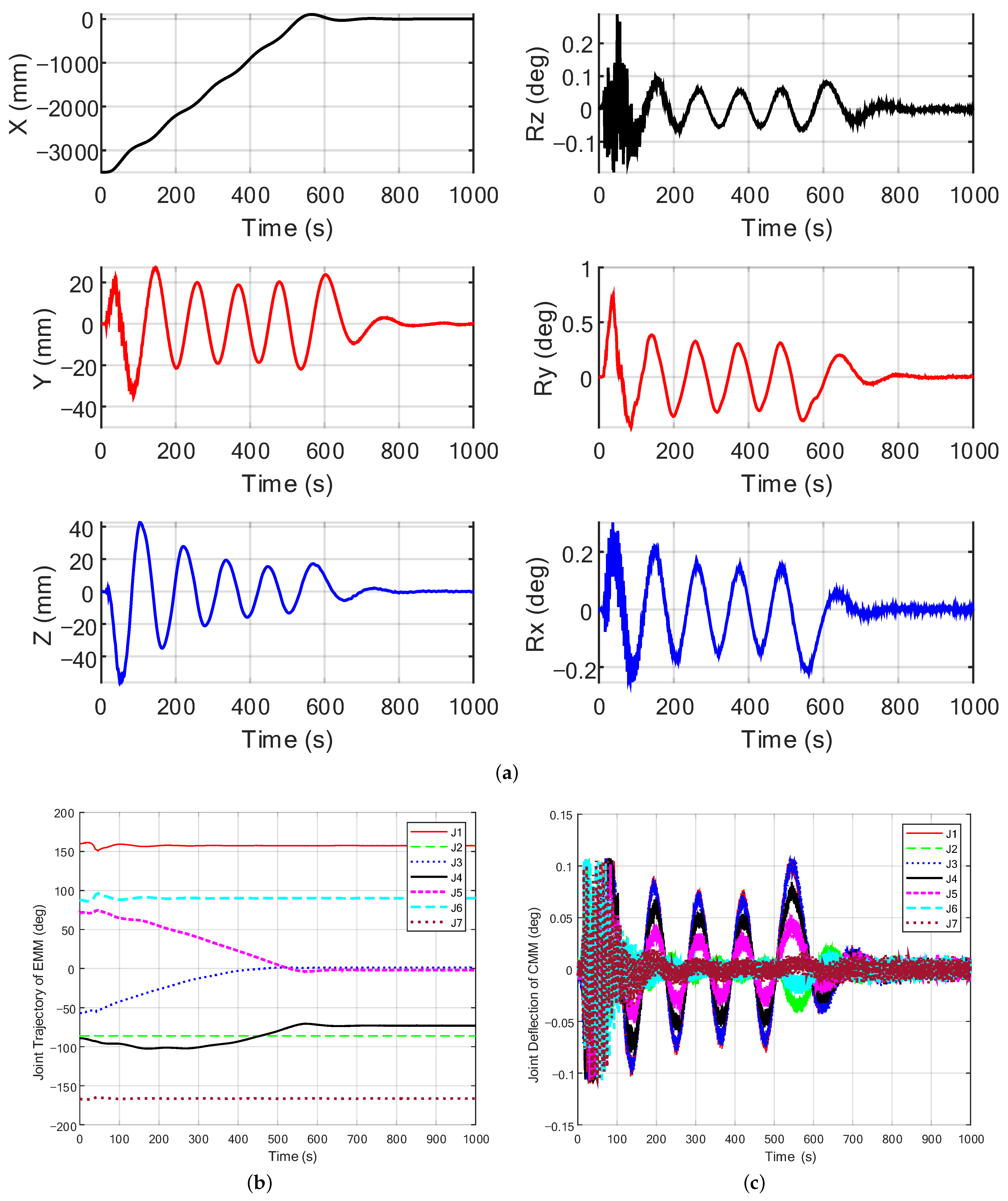
5.3. Visual Servo Control with Large Payload
5.4. Visual Servo Control of MMMS
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FBMS | Flexible base manipulator system |
| PBVS | Position-based visual servo |
| IBVS | Image-based visual servo |
| DOF | Degree of freedom |
| CMM | Core module manipulator |
| EMM | Experimental module manipulator |
| EVA | Extravehicular activities |
| MMMS | Macro/micro manipulator system |
| EEF | End-effector |
| VM | Visual Marker |
| HC | Hand Camera |
| LC | Load-operated Camera |
| VC | Vertical Camera |
| PC | Payload Camera |
| FTS | Six-axis force/torque sensor |
| EVS | Experimental module arm vision system |
| EOC | End of CMM |
| BOE | Base of EMM |
| BMM | Base of the macro-micro manipulator |
References
- Waldron, K.; Schmiedeler, J. Kinematics. In Springer Handbook of Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 1423–1461. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. An overview of the space robotics progress in China. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and Automation in Space (i-SAIRAS 2014), Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–19 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sharon, A.; Hogan, N.; Hardt, D.E. The Macro/Micro Manipulator: An Improved Architecture for Robot Control. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 1993, 10, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laryssa, P.; Lindsay, E.; Layi, O.; Marius, O.; Nara, K.; Aris, L.; Ed, T. International space station robotics: A comparative study of ERA, JEMRMS and MSS. In Proceedings of the 7th ESA Workshop on Advanced Space Technologies for Robotics and Automation, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 19–21 November 2002; pp. 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, N.; Wakabayashi, Y. JEMRMS design features and topics from testing. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and Automation in Space (iSAIRAS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 18–22 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi, Y.; Morimoto, H.; Satoh, N.; Hayashi, M.; Aiko, Y.; Suzuki, M. Performance of Japanese robotic arms of the international space station. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2002, 35, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flandin, G.; Chaumette, F.; Marchand, E. Eye-in-Hand/Eye-to-Hand Cooperation for Visual Servoing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 April 2000; pp. 2741–2746. [Google Scholar]
- Chaumette, F.; Hutchinson, S. Visual Servo Control. I. Basic Approaches. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2006, 13, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Liu, H.; Xie, Z.; Ni, F. Structure Design of an End-Effector for the Chinese Space Station Experimental Module Manipulator. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and Automation in Space, Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–19 June 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, W.; Hulls, C.; Bell, G. Relative end-effector control using cartesian position-based visual servoing. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1996, 12, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Janabi-Sharifi, F.; Wilson, W. Stability and robustness of visual servoing methods. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Washington, DC, USA, 11–15 May 2002; pp. 1604–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Singer, N.C.; Seering, W.P. Preshaping command inputs to reduce system vibration. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 1990, 112, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, H.; Konoue, K.; Matunaga, S.; Ueno, H.; Oda, M. Input Shaping Experiment for Damping Vibration in Manual Operation of a Large Robotic Arm. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, and Automation in Space, Munich, Germany, 5–8 September 2005; pp. 537–542. [Google Scholar]
- Cannon, D.; Magee, D.; Book, W.J.; Lew, J.Y. Experimental Study on Micro/Macro Manipulator Vibration Control. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 22–28 April 1996; Volume 3, pp. 2549–2554. [Google Scholar]
- Damaren, C.J. Approximate Inverse Dynamics and Passive Feedback for Flexible Manipulators with Large Payloads. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1996, 12, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christoforou, E.G.; Damaren, C.J. A passivity-based control case study of flexible-link manipulators. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; pp. 1005–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Stieber, M.E.; Mckay, M.; Vukovich, G. Vision-Based Sensing and Control for Space Robotics Applications. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1999, 48, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lew, J.Y.; Moon, S.M. A Simple Active Damping Control for Compliant Base Manipulators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2001, 6, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, L.E.; Book, W.J. Inertial Vibration Damping Control of a Flexible Base Manipulator. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2003, 8, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Book, W.J.; Lee, S.H. Vibration Control of A Large Flexible Manipulator by A Small Robotic Arm. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 21–23 June 1989; pp. 1377–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Bascetta, L.; Rocco, P. Task Space Visual Servoing of Eye-in-Hand Flexible Manipulators. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM 2003), Kobe, Japan, 20–24 July 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1442–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Bascetta, L.; Rocco, P. Tip Position Control of Flexible Manipulators through Visual Servoing. In Proceeding of the 6th International Conference on Dynamics and Control of Systems and Structures in Space, Liguria, Italy, 17–21 July 2004; pp. 673–682. [Google Scholar]
- Bascetta, L.; Rocco, P. End-Point Vibration Sensing of Planar Flexible Manipulators through Visual Servoing. Mechatronics 2006, 16, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascetta, L.; Rocco, P. Two-Time Scale Visual Servoing of Eye-in-Hand Flexible Manipulators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2006, 22, 818–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Konno, A.; Uchiyama, M. A Vision-Based Endpoint Trajectory and Vibration Control for Flexible Manipulators. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Roma, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; pp. 3427–3432. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, W. Visual Servoing of a Flexible Aerial Refueling Boom With an Eye-in-Hand Camera. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 51, 6282–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.A.; Dubowsky, S.; Pisoni, A.C. Vibration Control of Deployment Structures’ Long-Reach Space Manipulators: The P-PED Method. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 22–28 April 1996; Volume 3, pp. 2498–2504. [Google Scholar]
- Nenchev, D.N.; Yoshida, K.; Vichitkulsawat, P.; Uchiyama, M. Reaction null-space control of flexible structure mounted manipulator systems. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1999, 15, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Moallem, M. Optimal Reaction Control for the Flexible Base Redundant Manipulator System. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Dali, China, 6–8 December 2019; pp. 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, C.; Kim, H.; Lee, D. Experimental Evaluation of Passivity-Based Control of Manipulator-Stage System on Flexible Beam. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence, Jeju, Korea, 28 June–1 July 2017; pp. 465–466. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, F.; Garofalo, G.; Ott, C. Vibration Control for Manipulators on a Translationally Flexible Base. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 4451–4457. [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo, G.; Beck, F.; Klodmann, J.; Ott, C. On the control of translationally flexible base manipulators. In Proceedings of the 2020 European Control Conference (ECC), St. Petersburg, Russia, 12–15 May 2020; pp. 867–874. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zou, T.; Jin, M.; Liu, H. Design and Optimization of a Novel Six-Axis Force/Torque Sensor for Space Robot. Measurement 2015, 65, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, G.; Dubowsky, S. The Precise Control of Manipulators with Joint Friction: A Base Force/Torque Sensor Method. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 22–28 April 1996; Volume 1, pp. 360–365. [Google Scholar]
- Geffard, F.; Andriot, C.; Micaelli, A.; Morel, G. On the Use of a Base Force/Torque Sensor in Teleoperation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 April 2000; Volume 3, pp. 2677–2683. [Google Scholar]
- Ott, C.; Nakamura, Y. Base Force/Torque Sensing for Position Based Cartesian Impedance Control. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and System, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009; pp. 3244–3250. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, F.; Tang, L.N.; Xu, J.F.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.W. A Review of the End-Effector of Large Space Manipulator with Capabilities of Misalignment Tolerance and Soft Capture. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2016, 59, 1621–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wang, N. Review of Research on the Chinese Space Station Robots. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications, Shenyang, China, 8–11 August 2019; pp. 423–430. [Google Scholar]
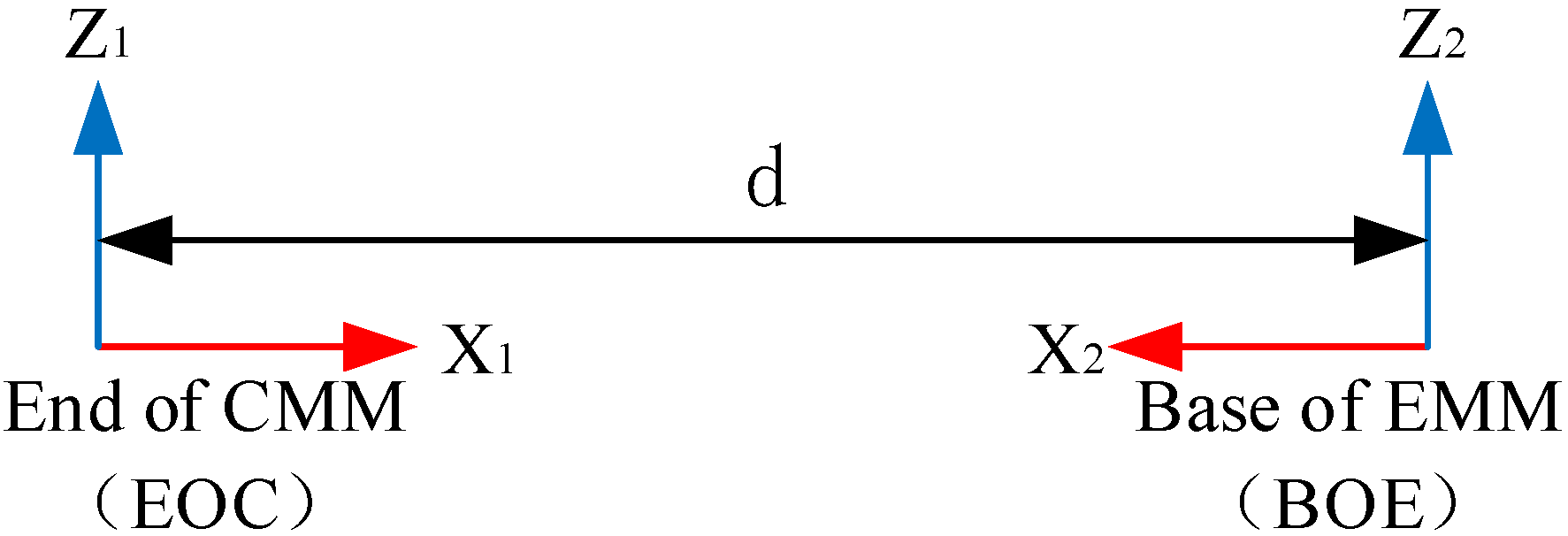




| Base | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90 |
| 1 | 0 | 90 | 0 | |
| 2 | 0 | −90 | 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | −90 | −90 | |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 5 | 0 | 90 | ||
| 6 | 0 | 90 | 0 | |
| 7 | 0 | −90 | 0 | |
| End | 0 | 90 | 0 | 90 |
| Manipulator | CMM | EMM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stiffness (Nm/rad) | Damping (Nms/rad) | Stiffness (Nm/rad) | Damping (Nms/rad) | |
| kL | 19 | 3 | 210 | |
| k | 3183 | |||
| Manipulator | Property | Mass (kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMM | Joint 1 | 59.5 | 4.322 | 1.438 | 4.121 |
| Joint 2 | 53.6 | 2.468 | 1.329 | 2.267 | |
| Link 1 | 108.4 | 2.782 | 384.756 | 384.327 | |
| Link 2 | 98.7 | 4.527 | 341.956 | 339.871 | |
| Joint 6 | 53.6 | 2.468 | 1.329 | 2.267 | |
| Joint 7 | 53.5 | 4.322 | 1.438 | 4.120 | |
| EEF | 100.5 | 3.347 | 9.731 | 9.833 | |
| EMM | Joint 1 | 31.7 | 0.366 | 0.366 | 0.332 |
| Joint 2 | 31.7 | 0.366 | 0.366 | 0.332 | |
| Link 1 | 74.7 | 0.881 | 70.702 | 70.554 | |
| Link 2 | 57.5 | 0.730 | 45.040 | 44.918 | |
| Joint 6 | 31.7 | 0.366 | 0.332 | 0.355 | |
| Joint 7 | 31.7 | 0.366 | 0.334 | 0.358 | |
| EEF | 28.9 | 0.52 | 0.527 | 0.421 | |
| Payload | – | 3000 | 722.5 | 1160 | 1062.5 |
| Cases | Vibration Control | Max Visual Errors | Vibration Periods | Total VS Time (s) | Torque of FTS (Nm) | Stability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X (mm) | Y (mm) | Rz (deg) | ||||||
| Without payload | No | 0 | 7 | 0.2 | 8 | 374 | 7.7 | Yes |
| Yes | 0 | 6 | 0.3 | 1 | 386 | 7.4 | Yes | |
| 1500 kg payload | No | 12 | 77 | 0.7 | 4 | 530 | 18 | No |
| Yes | 0 | 77 | 0.8 | 1 | 406 | 13.5 | Yes | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cao, B.; Liu, H. Visual Servo Control of the Macro/Micro Manipulator with Base Vibration Suppression and Backlash Compensation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8386. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168386
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Xie Z, Liu Y, Cao B, Liu H. Visual Servo Control of the Macro/Micro Manipulator with Base Vibration Suppression and Backlash Compensation. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(16):8386. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168386
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yaowen, Yechao Liu, Zongwu Xie, Yang Liu, Baoshi Cao, and Hong Liu. 2022. "Visual Servo Control of the Macro/Micro Manipulator with Base Vibration Suppression and Backlash Compensation" Applied Sciences 12, no. 16: 8386. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168386
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liu, Y., Xie, Z., Liu, Y., Cao, B., & Liu, H. (2022). Visual Servo Control of the Macro/Micro Manipulator with Base Vibration Suppression and Backlash Compensation. Applied Sciences, 12(16), 8386. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168386






