Fast Calculation of Acoustic Field Distribution for Ultrasonic Transducers Using Look-Up Table Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
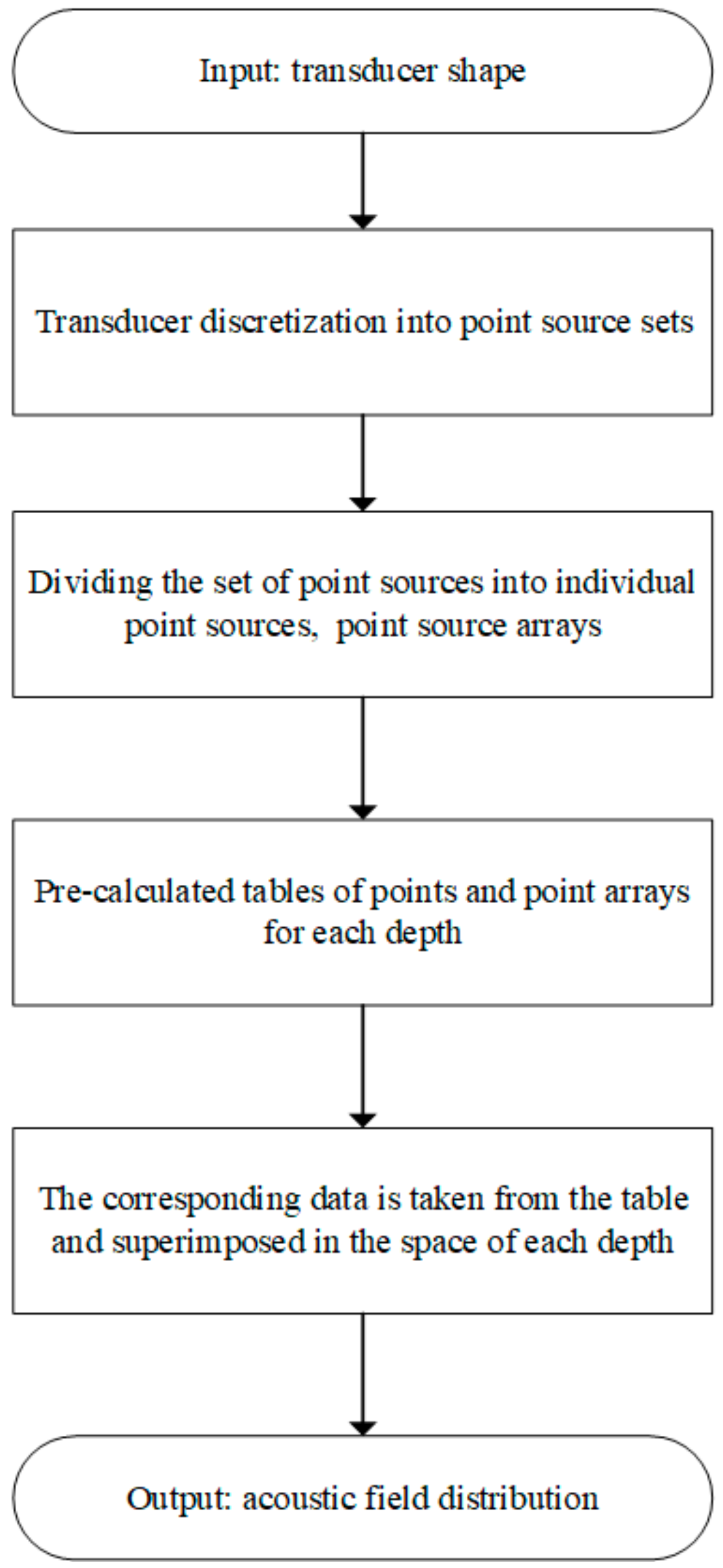
2. Method
2.1. Rayleigh–Sommerfeld Integral Model
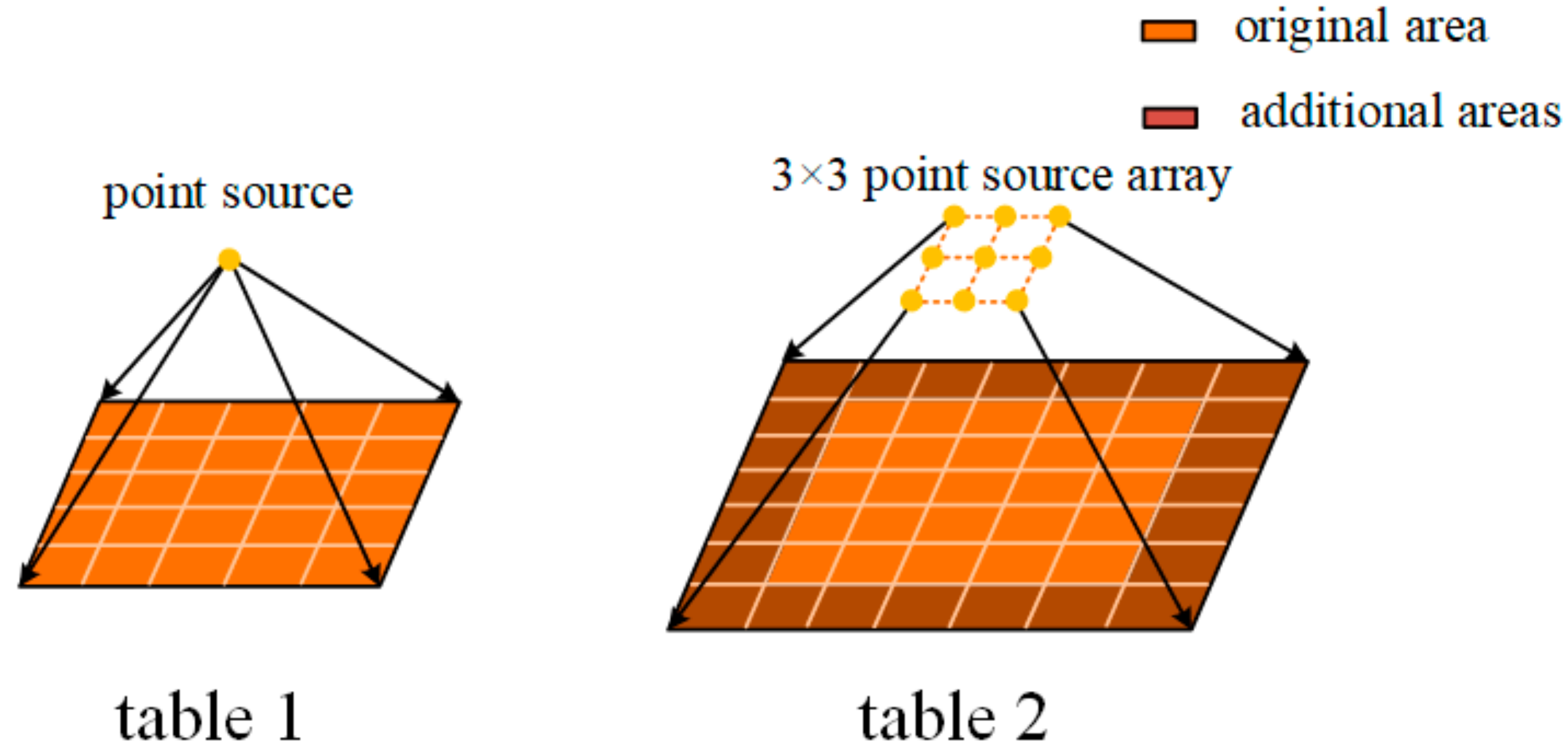
2.2. Acoustic Field Look-Up Table Method
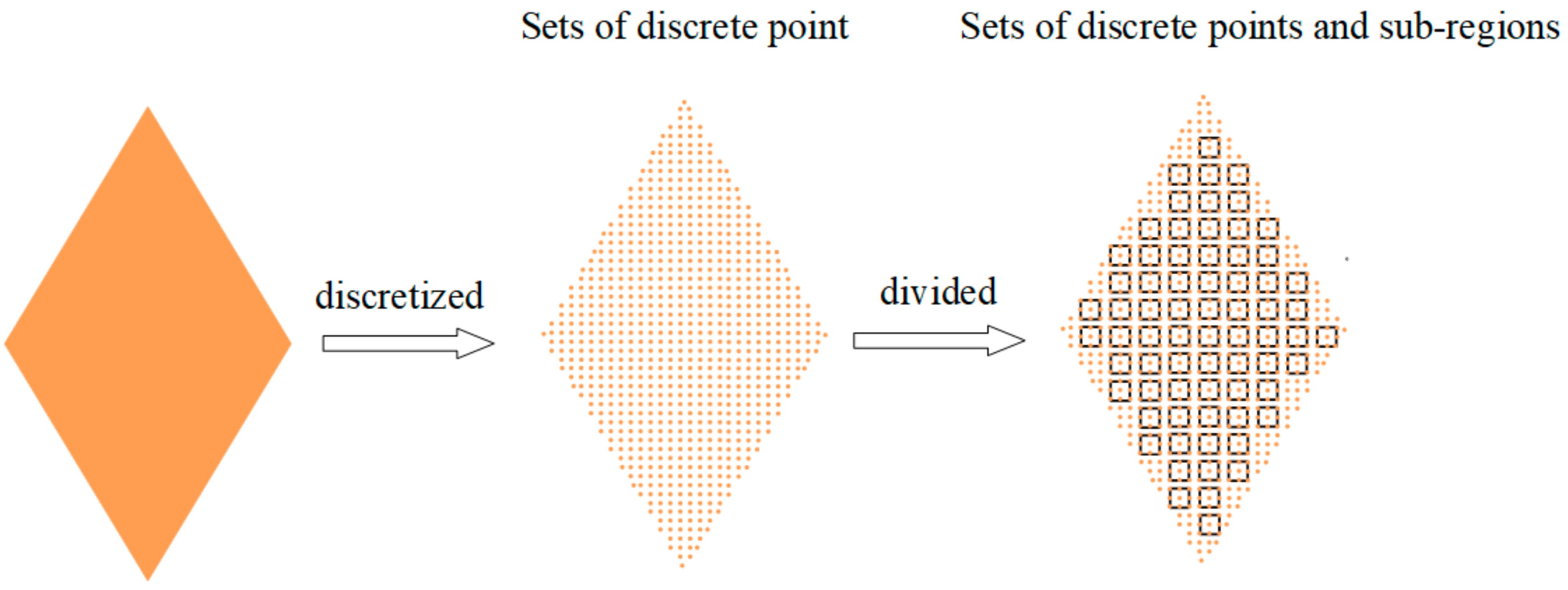
2.3. Acoustic Field Sub-Region Look-Up Table Method
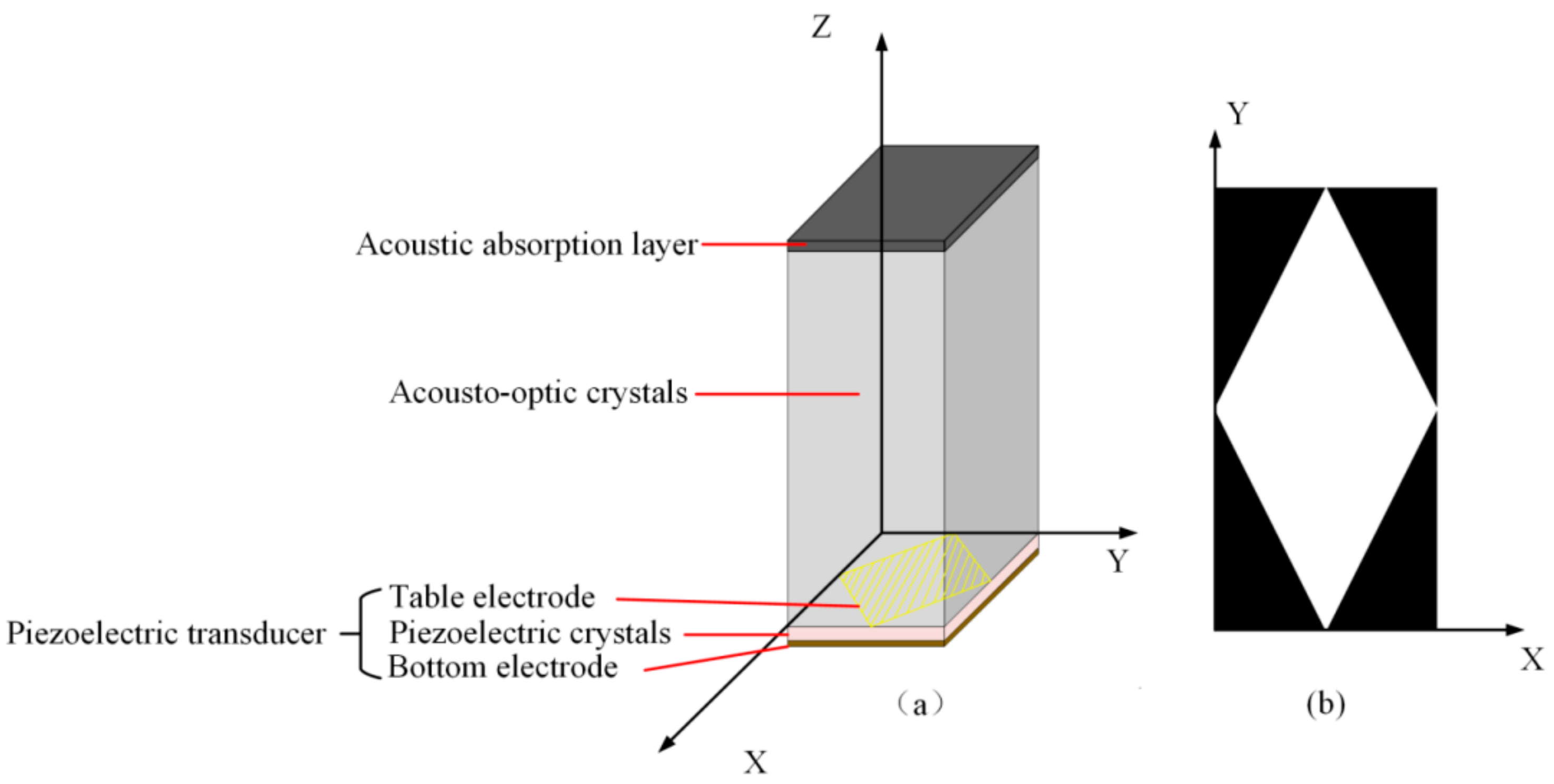
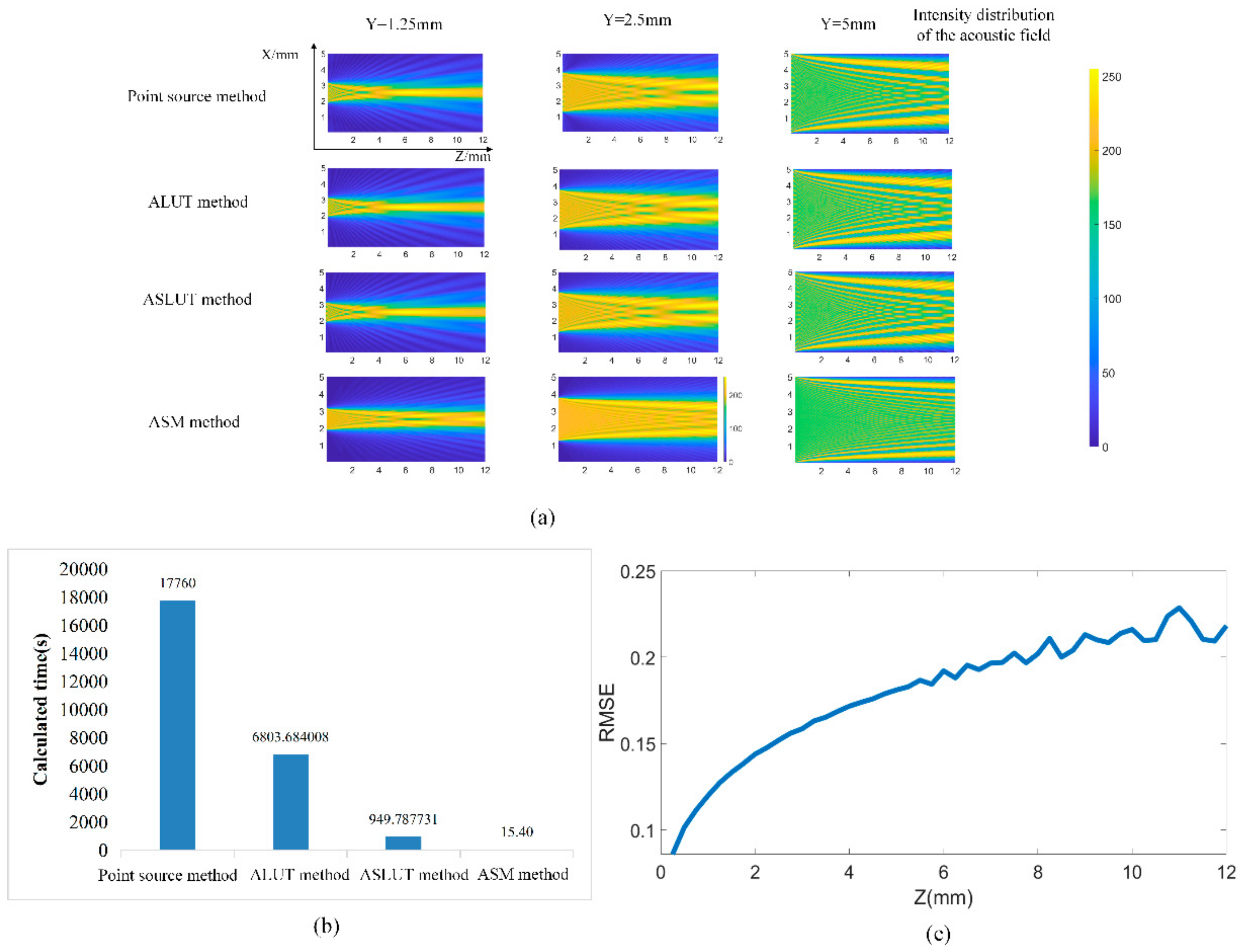
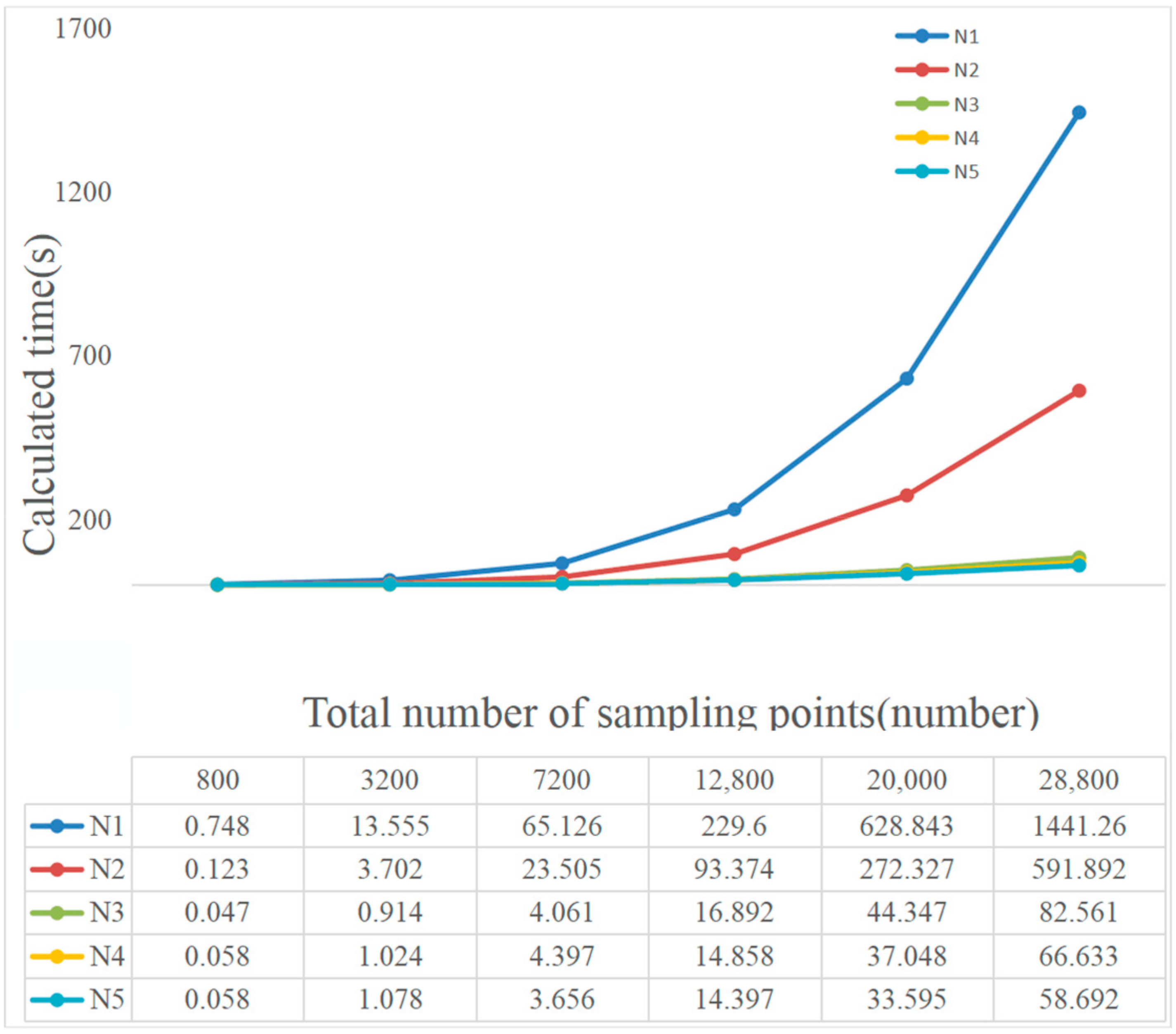
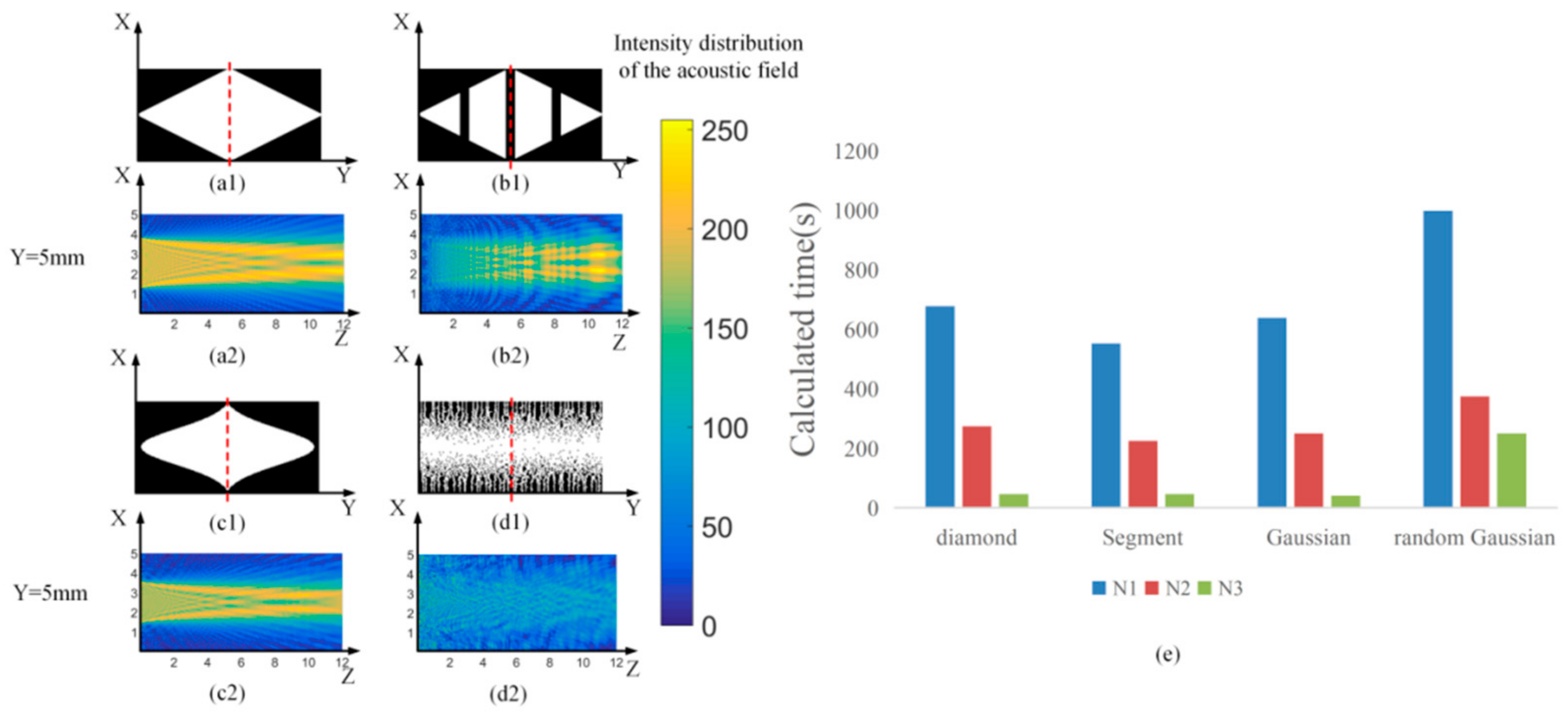
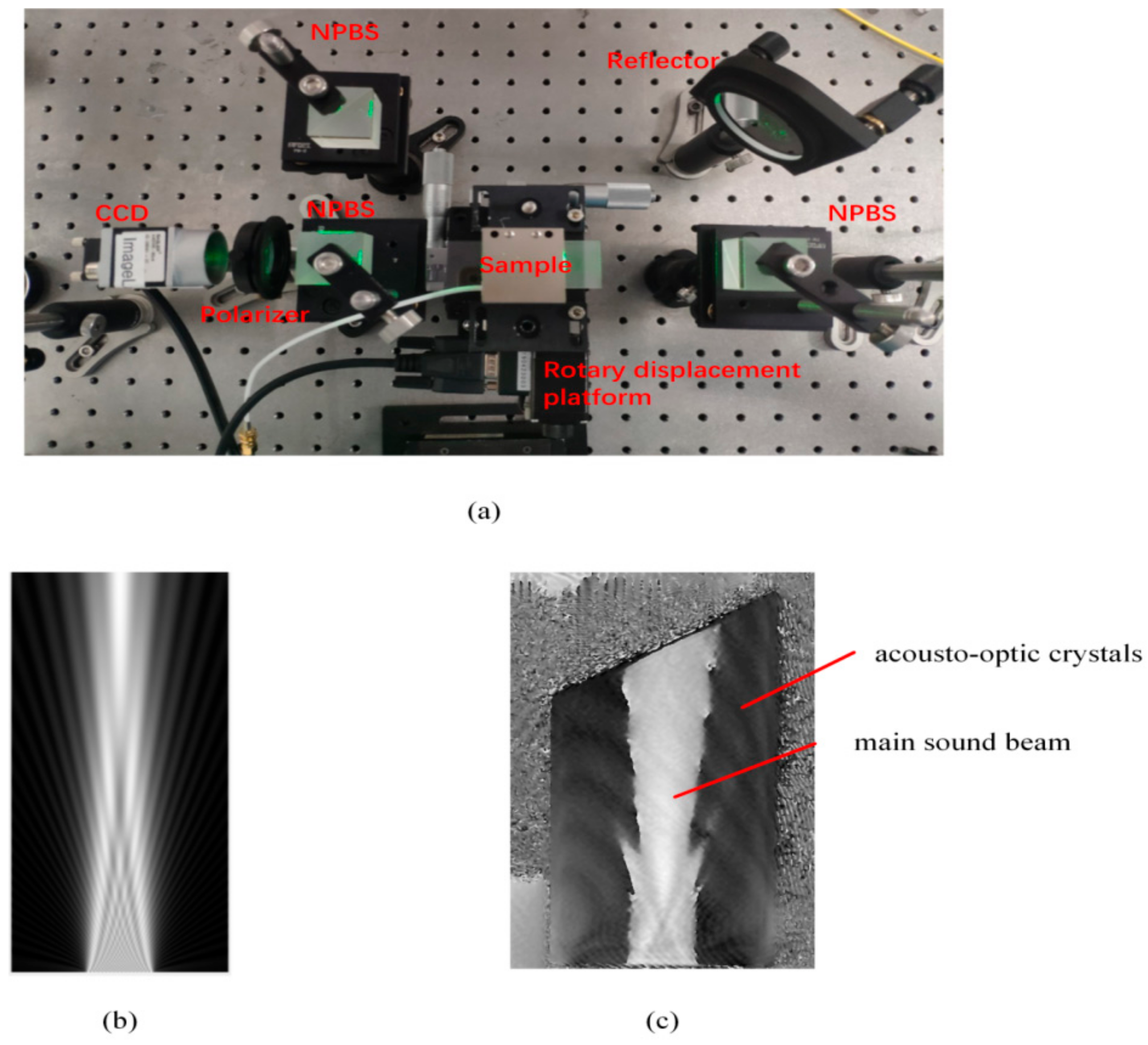
3. Numerical Simulations and Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, Z. Review of Ultrasonic Ranging Methods and Their Current Challenges. Micromachines 2022, 13, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagler, D.; Anzinger, S.; Pfann, E.; Fusco, A.; Bretthauer, C.; Huemer, M. A single ultrasonic transducer fast and robust short-range distance measurement method. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Glasgow, UK, 6–9 October 2019; pp. 2533–2536. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, P.; Kang, J.; Song, T.K. A Pseudo-Dynamic Delay Calculation Using Optimal Zone Segmentation for Ultra-Compact Ultrasound Imaging Systems. Electronics 2019, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.D.; Cavanagh, E.; Dardy, H.D. A numerical procedure for calculating the integrated acoustooptic effect. IEEE Trans. Sonics Ultrason. 1980, 27, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xu, Z.; Li, K.; Lv, G.; Li, X.; Wang, C. Analysis of acoustic near field characteristics in acousto-optic modulator. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2021, 33, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhlova, V.A.; Shmeleva, V.A.; Gavrilov, L.R. Infrared mapping of ultrasound fields generated by medical transducers: Feasibility of determining absolute intensity levels. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laude, V.; Beugnot, J.C.; Sylvestre, T. Special issue on Brillouin scattering and optomechanics. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Piwakowski, B. A time-domain model and experimental validation of the acoustic field radiated by air-coupled transducers. Ultrasonics 2018, 82, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xu, Z.; Ji, K.; Lv, G.; Wang, C.; Li, X. Transducer design of acousto-optic modulators. In Proceedings of the AOPC 2020: Advanced Laser Technology and Application, Beijing, China, 5 November 2020; Volume 11562, pp. 272–280. [Google Scholar]
- Rayleigh, L. Theory of Sound; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1965; Volume II, pp. 162–169. [Google Scholar]
- Morse, P.M.; Ingard, U.K. Theoretical Acoustics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Klaseboer, E.; Khoo, B.C.; Chan, D.Y.C. Boundary regularized integral equation formulation of the Helmholtz equation in acoustics. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 140520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, X.; Darbas, M. Generalized Combined Field Integral Equations for the Iterative Solution of the Three-Dimensional Helmholtz Equation. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 2007, 41, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, H.J.; Schmerr, L.W., Jr.; Sedov, A. Generation of the basis sets for multi-Gaussian ultrasonic beam models—An overview. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gang, T. Nonparaxial multi-Gaussian beam models and measurement models for phased array transducers. Ultrasonics 2009, 49, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkup, S.M. Computational solution of the acoustic field surrounding a baffled panel by the Rayleigh integral method. Appl. Math. Model. 1994, 18, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. The use of equivalent source method in computational acoustics. J. Comput. Acoust. 2017, 25, 1630001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmann, G.H.; Song, L.; Fahnline, J.B. A method for computing acoustic fields based on the principle of wave superposition. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 86, 2433–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnekow, M.; Ihlenburg, F.; Grätsch, T. An Efficient Approach to the Simulation of Acoustic Radiation from Large Structures with FEM. J. Theor. Comput. Acoust. 2020, 28, 1950019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaad, J.; Hladky, A.C.; Cugnet, B. Application of the FEM and the BEM to compute the field of a transducer mounted in a rigid baffle (3D case). Ultrasonics 2004, 42, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.G.; Maynard, J.D. Numerical evaluation of the Rayleigh integral for planar radiators using the FFT. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1982, 72, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanishen, P.R.; Benjamin, K.C. Forward and backward projection of acoustic fields using FFT methods. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1982, 71, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, F.P.; Norton, S.J.; Linzer, M. Optical interferometric visualization and computerized reconstruction of ultrasonic fields. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1980, 68, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, H. Sound Field Modeling Method and Key Imaging Technology of an Ultrasonic Phased Array: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Mcgough, R.J. Evaluation of Angular Spectrum Approach for Simulations of Spherically Focused Ultrasound Phased Arrays. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electro/Information Technology, East Lansing, MI, USA, 7–10 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shimobaba, T.; Matsushima, K.; Kakue, T.; Masuda, N.; Ito, T. Scaled angular spectrum method. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 4128–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, A.L.; Sato, A.K.; Silva, A.M., Jr.; Franco, E.E.; Buiochi, F.; Martins, T.C.; Adamowski, J.C.; Tsuzuki, M.S.G. Gpu accelerated acoustic field determination for a continuously excited circular ultrasonic transducer. IFAC-Pap. 2020, 53, 10480–10484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimobaba, T.; Nakayama, H.; Masuda, N.; Ito, T. Rapid calculation algorithm of Fresnel computer-generated-hologram using look-up table and wavefront-recording plane methods for three-dimensional display. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 19504–19509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Xue, G.; Jia, J.; Wang, Y. Accurate compressed look up table method for CGH in 3D holographic display. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 33194–33204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Völz, U. Four-dimensional directivity pattern for fast calculation of the sound field of a phased array transducer. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Dresden, Germany, 7–10 October 2012; pp. 1035–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Lean, H.Q.; Zhou, Y. Acoustic field of phased-array ultrasound transducer with the focus/foci shifting. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2019, 39, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onose, L.; Moraru, L.; Nicolae, M.C. Simulation of Acoustic Fields from Medical Ultrasound Transducers. Rom. J. Biophys. 2009, 19, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Goutzoulis, A.P. Design and Fabrication of Acousto-Optic Devices; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sapozhnikov, O.A.; Tsysar, S.A.; Khokhlova, V.A.; Kreider, w. Acoustic holography as a metrological tool for characterizing medical ultrasound sources and fields. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, 1515–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, M.; Watabe, H.; Tsuchiya, T.; Iwaya, Y. Numerical examination of effects of discretization spacing on accuracy of sound field reproduction. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 2015, 36, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Merthe, D.J. A Sampling Theorem for Computational Diffraction. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.6814. [Google Scholar]
- Pannell, C.N.; Ward, J.D.; Wachman, E.S.; Zhang, B.G.; Reed, M.K. A high-performance passband-agile hyperspectral imager using a large aperture acousto-optic tuneable filter. In Photonic Instrumentation Engineering II; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015; Volume 9369, p. 936906. [Google Scholar]
- Yuanfeng, Z.; Jisheng, Y. Optimization and design of acousto-optic tunable filters. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2005, 7, 1599–1604. [Google Scholar]
- Voloshin, A.; Balakshy, V.; Mantsevich, S. Unpolarized light diffraction in an acoustic field created by a phased array transducer. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Tours, France, 18–21 September 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Tu, K.; Liang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Lv, G. Fast Calculation of Acoustic Field Distribution for Ultrasonic Transducers Using Look-Up Table Method. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8459. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178459
Wu J, Tu K, Liang L, Wang S, Wang Z, Lv G. Fast Calculation of Acoustic Field Distribution for Ultrasonic Transducers Using Look-Up Table Method. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(17):8459. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178459
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Ji, Kefeng Tu, Li Liang, Shuaihua Wang, Zi Wang, and Guoqiang Lv. 2022. "Fast Calculation of Acoustic Field Distribution for Ultrasonic Transducers Using Look-Up Table Method" Applied Sciences 12, no. 17: 8459. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178459
APA StyleWu, J., Tu, K., Liang, L., Wang, S., Wang, Z., & Lv, G. (2022). Fast Calculation of Acoustic Field Distribution for Ultrasonic Transducers Using Look-Up Table Method. Applied Sciences, 12(17), 8459. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178459




