Effect of Particle Sizes and Dosages of Rubber Waste on the Mechanical Properties of Rubberized Concrete Composite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
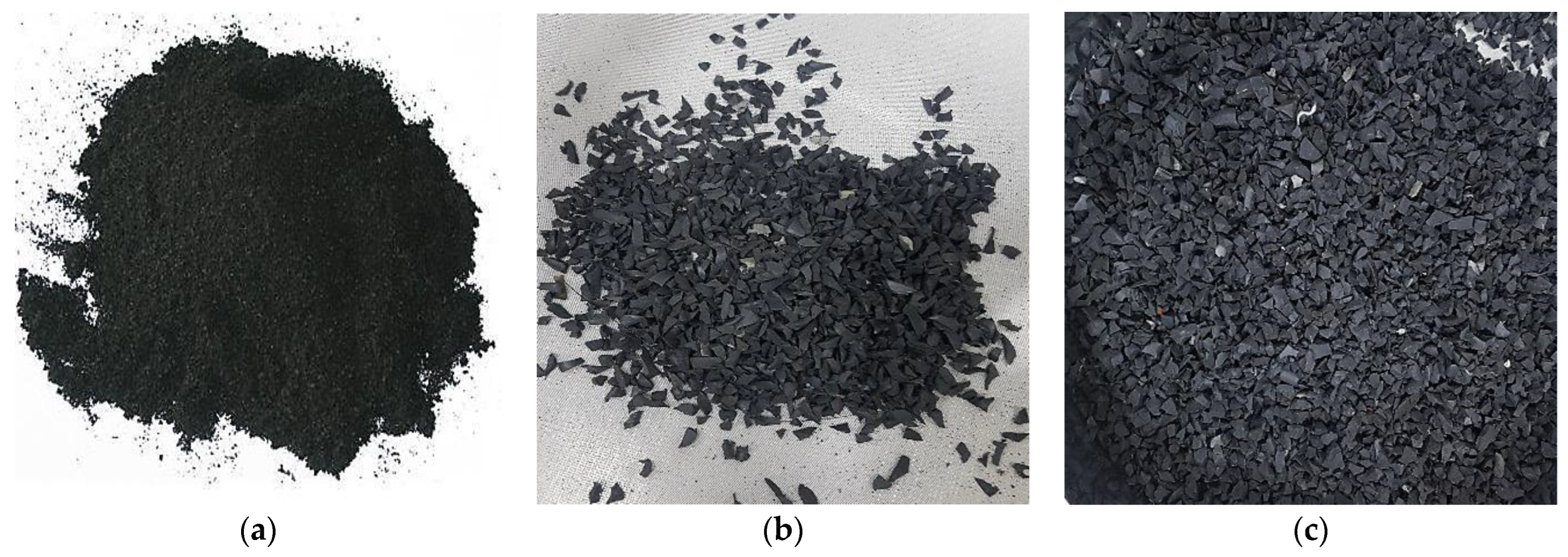
2. Materials and Mixture Proportions
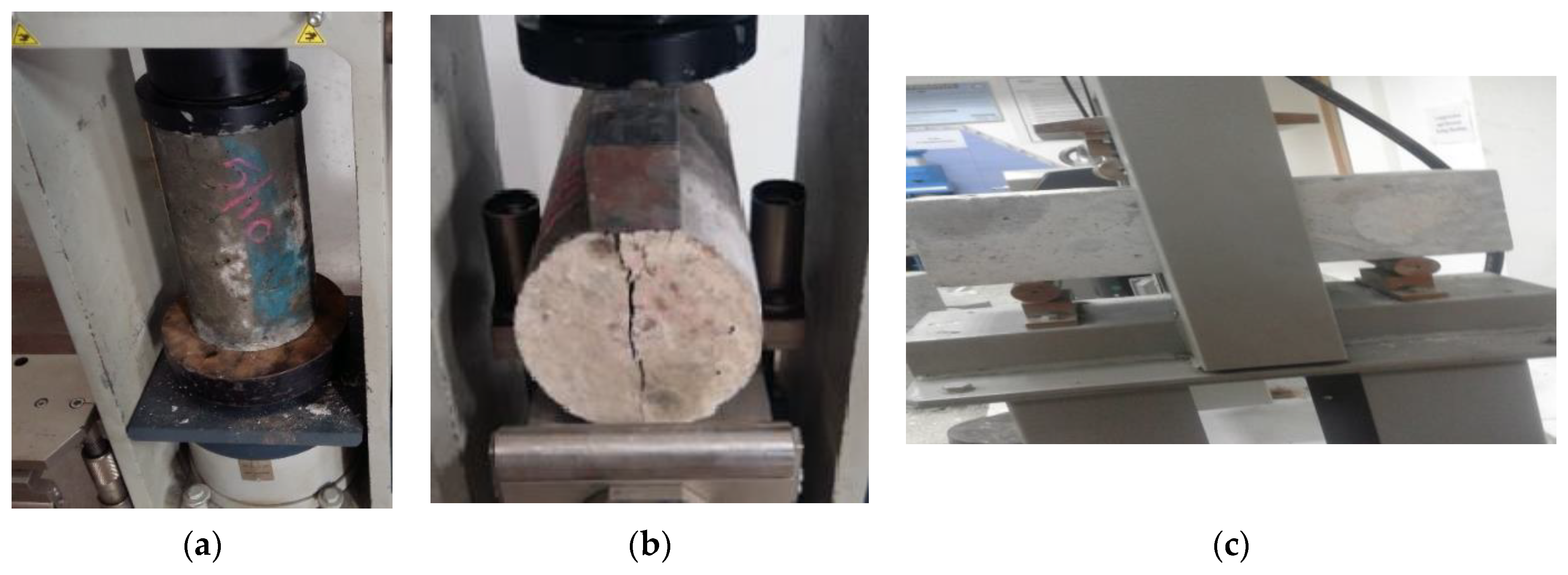
3. Specimen Preparation and Test Methodologies
4. Results and Discussion
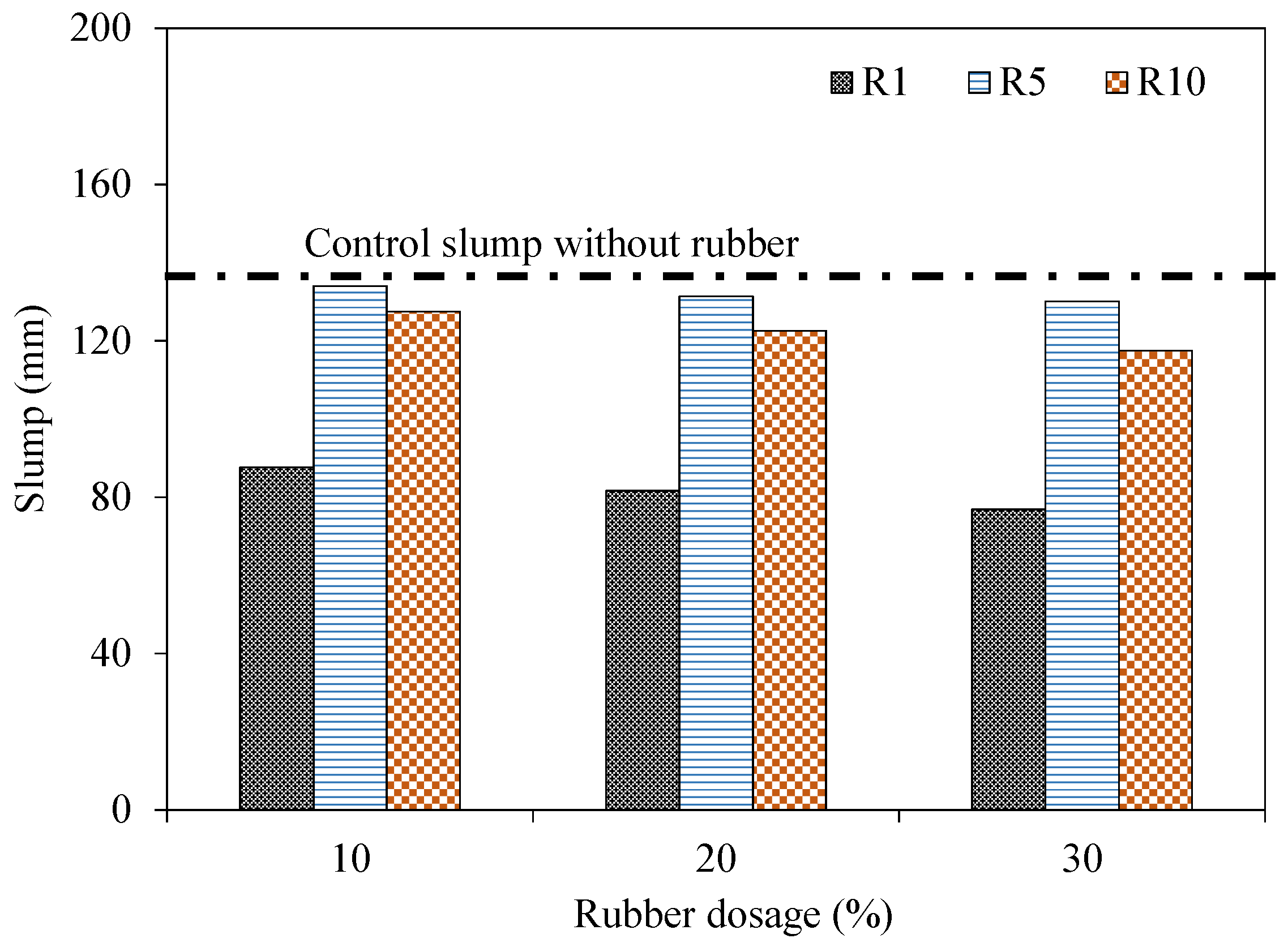
4.1. Slump Flow
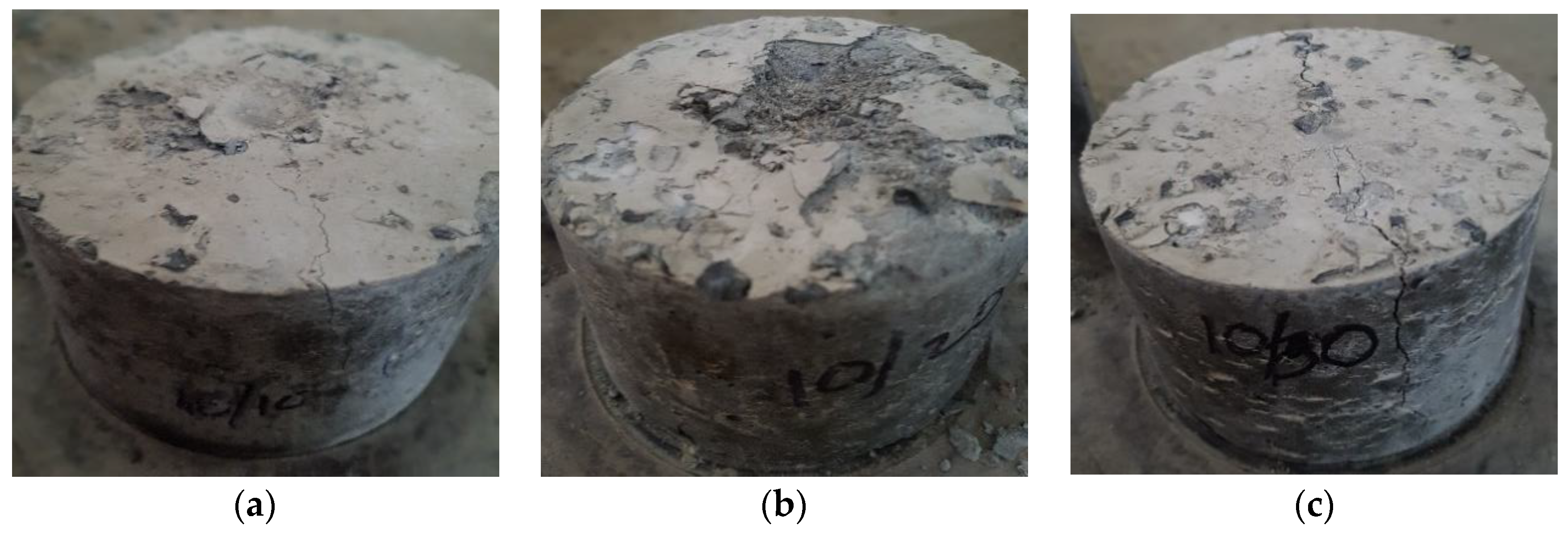
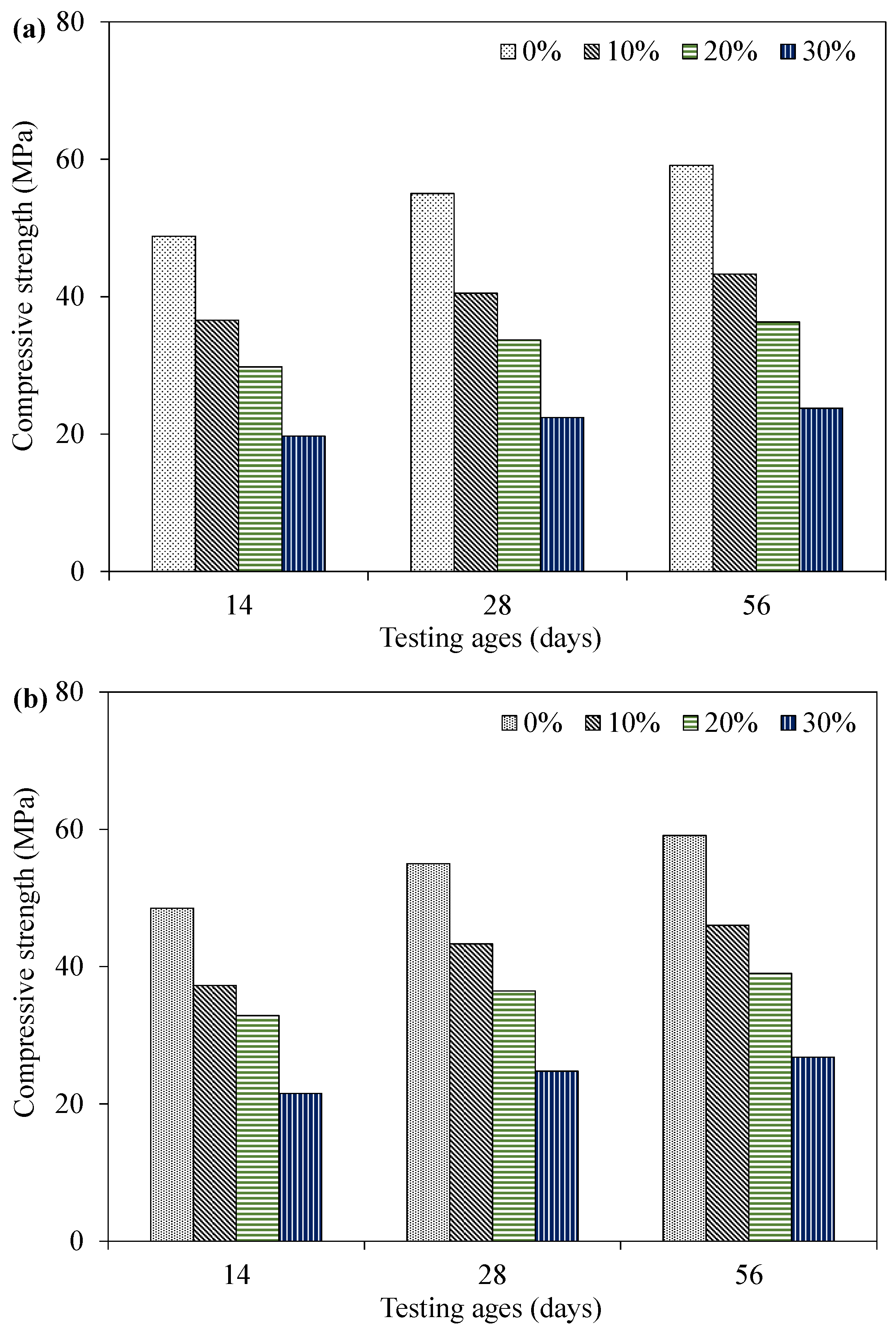
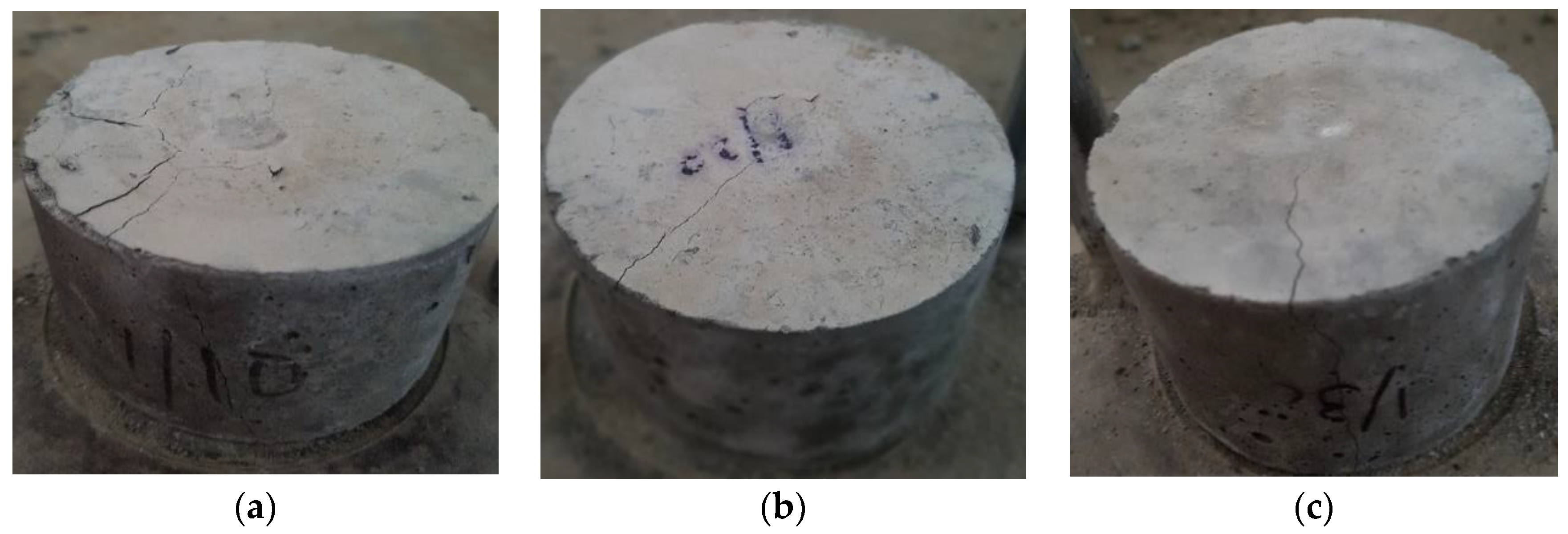
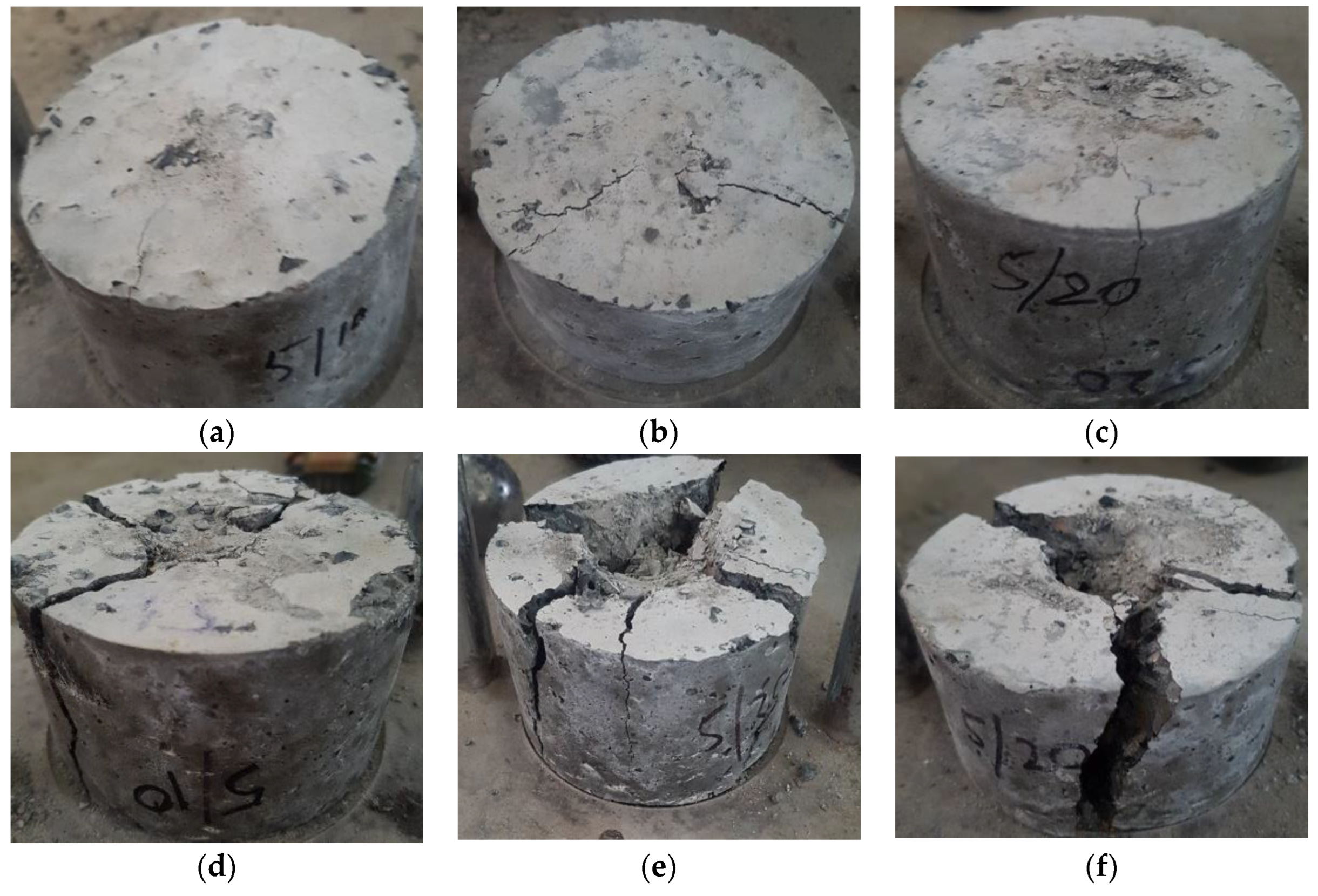
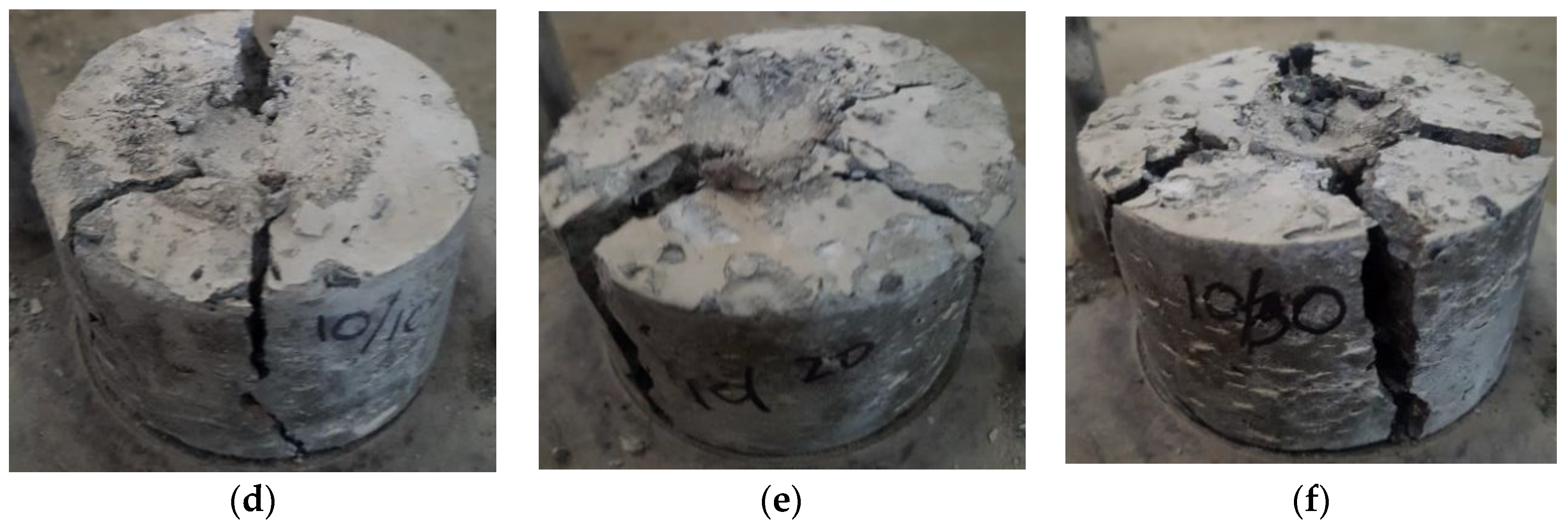
4.2. Compressive Strength
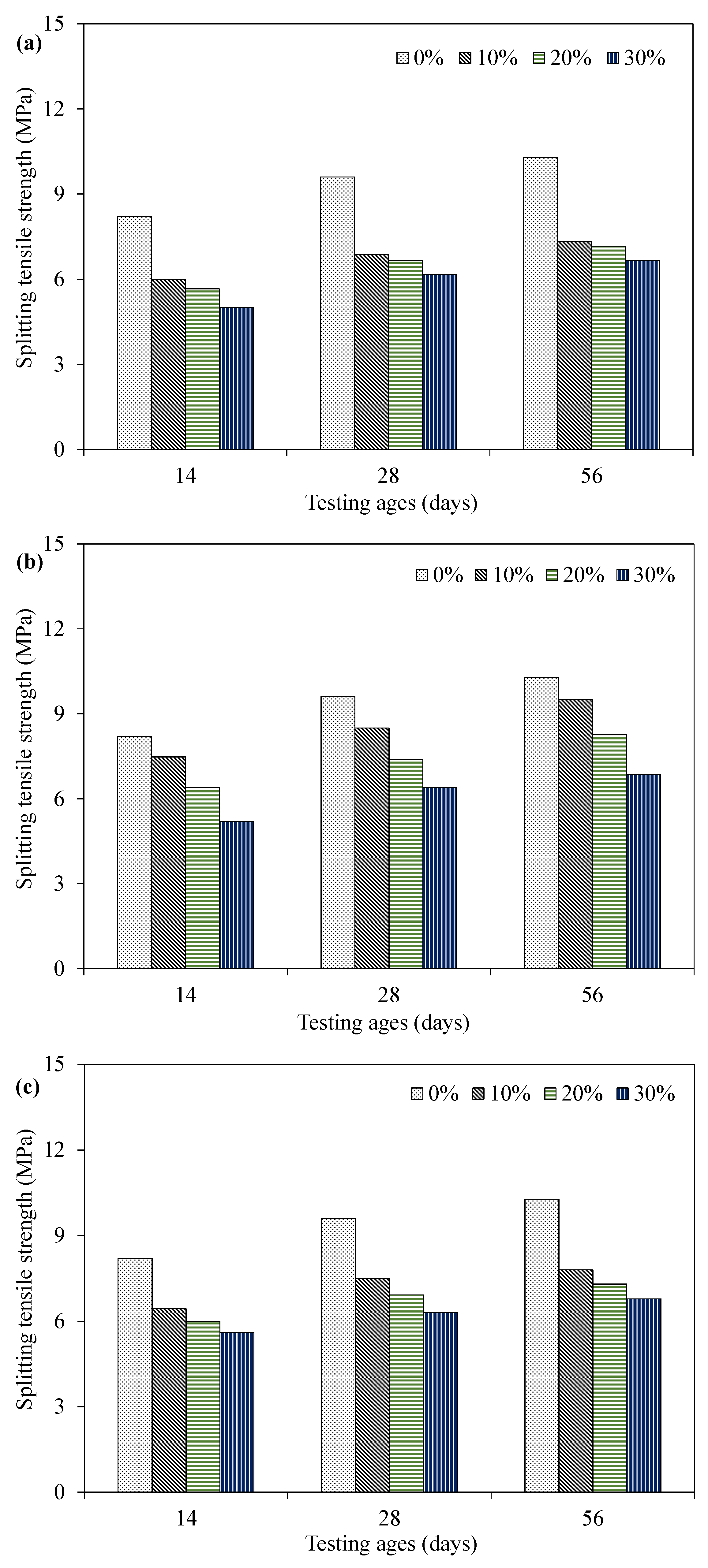
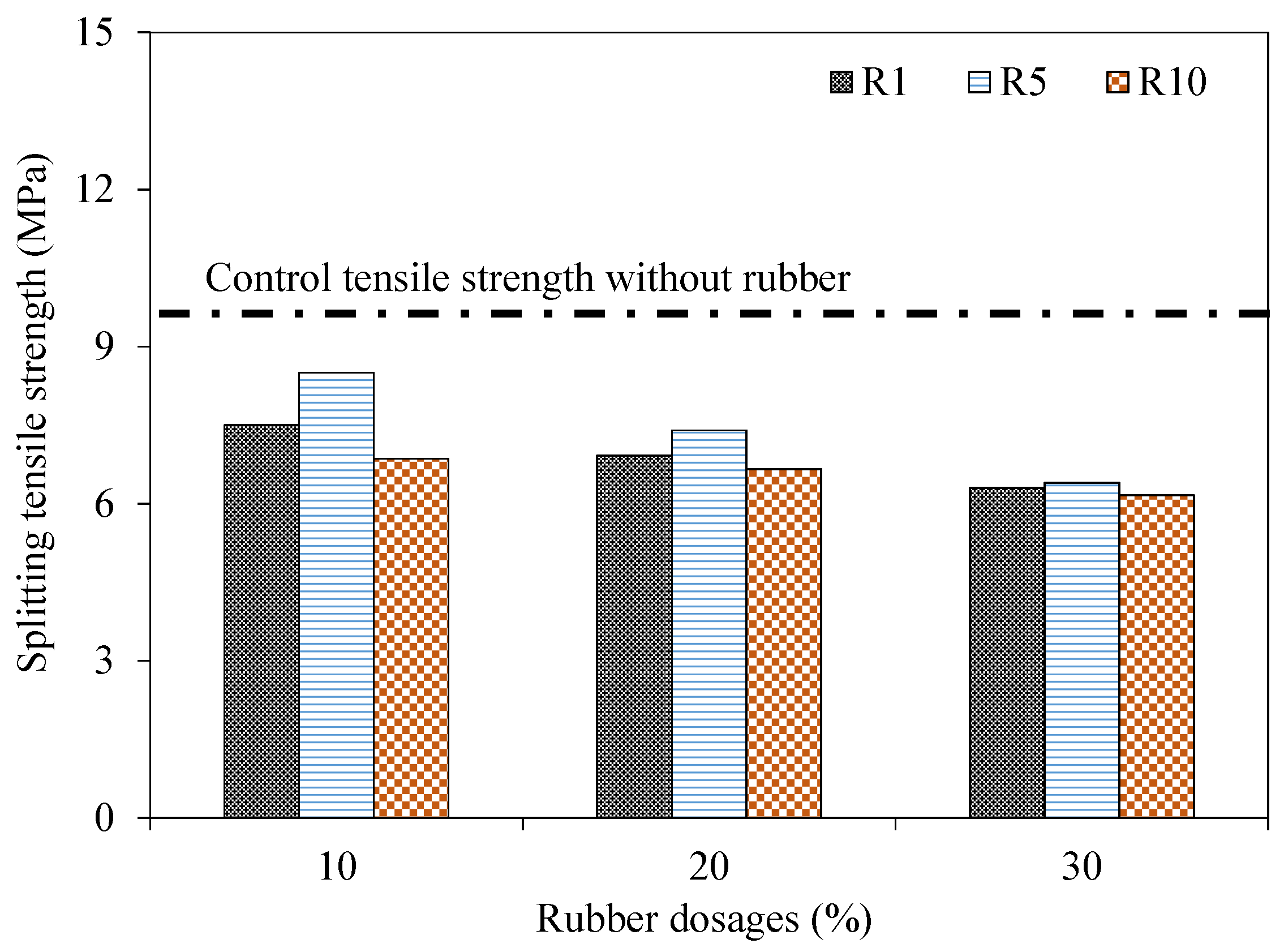
4.3. Splitting Tensile Strength
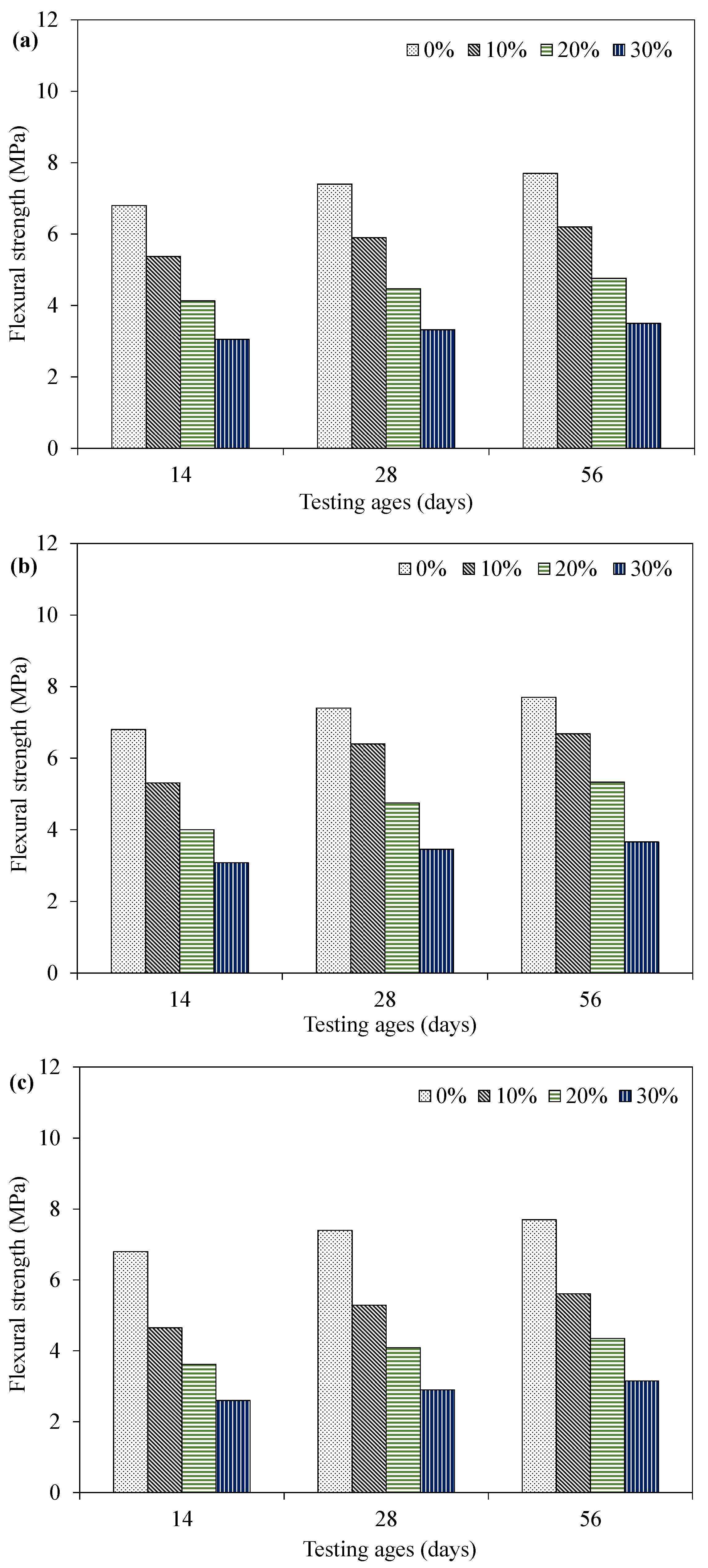
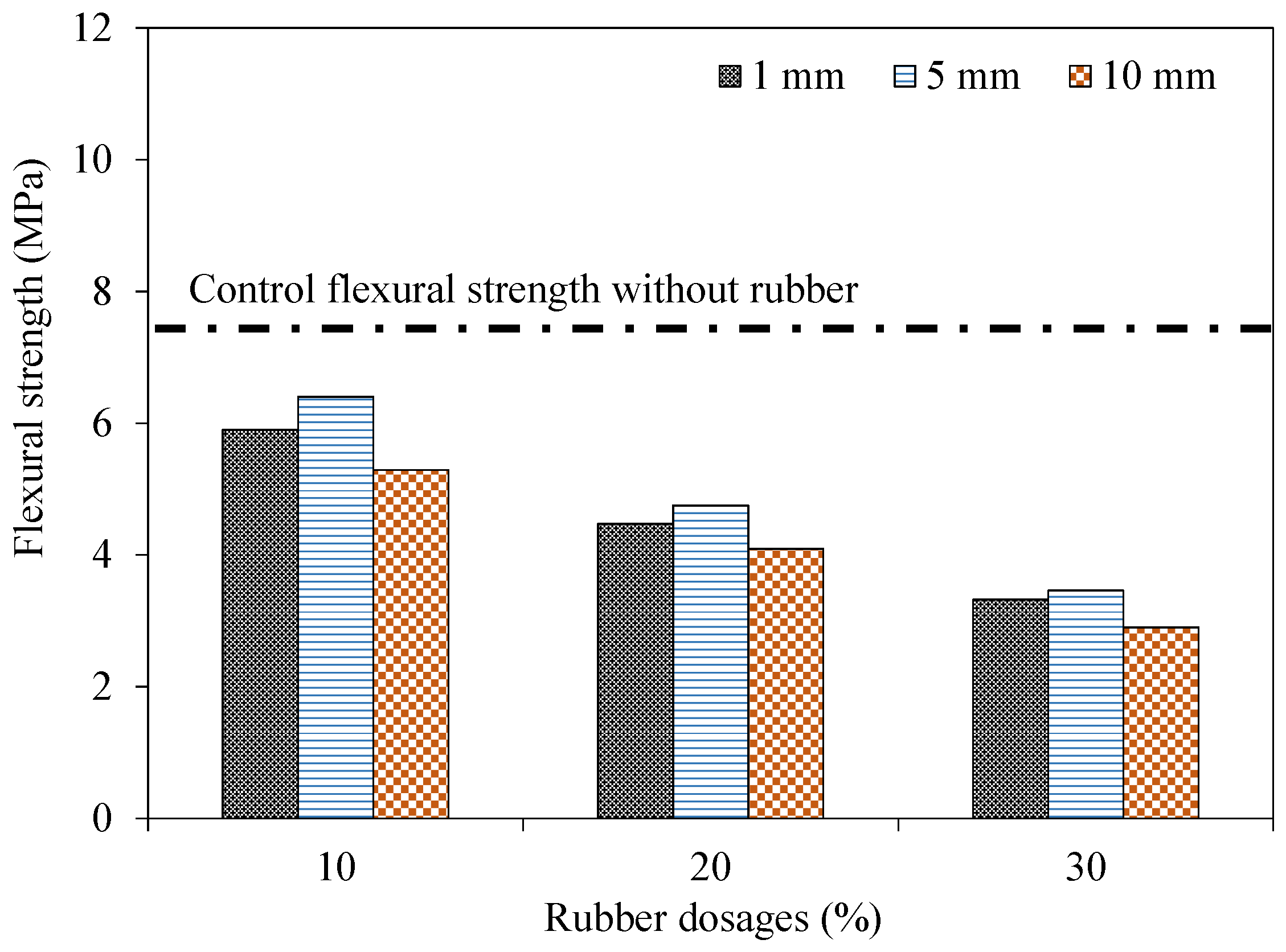
4.4. Flexural Strength
4.5. Impact Resistance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gencel, O.; Kazmi, S.M.S.; Munir, M.J.; Kaplan, G.; Bayraktar, O.Y.; Yarar, D.O.; Karimipour, A.; Ahmad, M.R. Influence of bottom ash and polypropylene fibers on the physico-mechanical, durability and thermal performance of foam concrete: An experimental investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.J.; Kazmi, S.M.S.; Wu, Y.-F.; Patnaikuni, I.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q. Development of a unified model to predict the axial stress–strain behavior of recycled aggregate concrete confined through spiral reinforcement. Eng. Struct. 2020, 218, 110851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.J.; Kazmi, S.M.S.; Khitab, A.; Hassan, M. Utilization of Rice Husk Ash to Mitigate Alkali Silica Reaction in Concrete. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Multi-Disciplinary Conference (IMDC 2016), Gujrat, Pakistan, 19–20 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Murugan, R.B.; Natarajan, C. Experimental study on rubberized concrete. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2015, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Torretta, V.; Rada, E.C.; Ragazzi, M.; Trulli, E.; Istrate, I.A.; Cioca, L.I. Treatment and disposal of tyres: Two EU approaches. A review. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabaniotou, A.A.; Antonio, N.; Stavropoulos, G.N. Sorbent materials for environmental remediation via de polymerization of used tyres. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 56, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmet, E.; Halidun, M.K.; Yildiz, S. An investigation on ITZ microstructure of the concrete containing waste vehicle tire. In Proceedings of the 8th International Fracture Conference, Istanbul, Turkey, 7–9 November 2007; pp. 454–459. [Google Scholar]
- Asutkar, P.; Shinde, P.; Rakesh, P. Study on the behavior of rubber aggregates concrete beams using analytical approach. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 20, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Osama, Y.; Hassanli, R.A.; Julie, E.M. Mechanical performance of FRP-confined and unconfined crumb rubber concrete containing high rubber content. J. Build. Eng. 2017, 11, 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Khatib, Z.K.; Bayomy, F.M. Rubberized Portland cement concrete. ASCE J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 1999, 11, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedroff, D.; Ahmad, S.; Savas, B.Z. Mechanical properties of concrete with ground waste tire rubber. J. Transp. Res. Board 1996, 1532, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldin, N.N.; Senouci, A.B. Rubber-tire particles as concrete aggregate. ASCE J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 1993, 5, 478–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, O.F.; Barluenga, G.; Bollati, M.; Witoszek, B. Static and dynamic behavior of recycled tire rubber-filled concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Huang, B. Recycling of waste tyre rubber in asphalt and Portland cement concrete: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 67, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tayeb, M.M.; Bakar, B.A.; Ismail, H.; Akil, H.M. Impact Resistance of Concrete with Partial Replacements of Sand and Cement by Waste Rubber. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012, 51, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Shinozuka, M. Rubberized concrete: A green structural material with enhanced energy-dissipation capability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 42, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Huo, X.S.; Yuan, Y. Experimental investigation on dynamic properties of rubberized concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldin, N.N.; Senouci, A.B. Measurement and prediction of the strength of rubberized concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1994, 16, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, A.H.; Dawson, A.R.; Thom, N.H. Characterization of rubberized cement bound aggregate mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 105, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.K.; Hassan, A.A.A. Ductility and Cracking Behavior of Reinforced Self-Consolidating Rubberized Concrete Beams. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2016, 29, 04016174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, C.; Ning, L. Experimental research on properties of fresh and hardened rubberized concrete. ASCE J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014, 26, 04014040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghvan, D.; Huynh, H.; Ferrafis, C.F. Workability, mechanical properties and chemical stability of a recycled tire rubber-filled cementations composite. J. Mater. Sci. 1998, 33, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Kuang, C.; Zhang, J.; Hou, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Dong, B. Visual analysis for microscopic cracking propagation of rubberized concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topçu, I.B. The properties of rubberized concretes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataria, R.B.; Wang, Y.C. Mechanical Properties and Durability Performance of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Containing Crumb Rubber. Materials 2022, 15, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, S.; Ahmed, A.; Waheed, A.; Abbass, W.; Yousaf, M.; Shaukat, S.; Alabduljabbar, H.; Awad, Y.A. Recycled Untreated Rubber Waste for Controlling the Alkali–Silica Reaction in Concrete. Materials 2022, 15, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, I.-H.; Lim, H.-J.; Cho, C.-G. Investigation of Strength Properties for Concrete Containing Fine-Rubber Particles Using UPV. Materials 2022, 15, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, P.; Karthikeyan, K.; Subbaram, S.R.; Sudharsan, J.S.; Abid, S.R.; Murali, G.; Vatin, N.I. Experimental and Statistical Investigation to Evaluate Impact Strength Variability and Reliability of Preplaced Aggregate Concrete Containing Crumped Rubber and Fibres. Materials 2022, 15, 5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.R.; Akmal, U.; Khurram, N.; Aslam, F.; Deifalla, A.F. Impact Resistance of Styrene–Butadiene Rubber (SBR) Latex-Modified Fiber-Reinforced Concrete: The Role of Aggregate Size. Materials 2022, 15, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Mo, J.; Wang, Q.; Ho, J.C.M. Crumb rubber as partial replacement for fine aggregate in concrete: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 343, 128049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Fang, Z.; Feng, W.; Liu, F.; Yang, F.; Li, L. Review of dynamic behaviour of rubberised concrete at material and member levels. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 38, 102237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, S.M.S.; Munir, M.J.; Wu, Y.-F. Application of waste tire rubber and recycled aggregates in concrete products: A new compression casting approach. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 167, 105353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Zhou, Z.; Majdi, A.; Alqurashi, M.; Deifalla, A.F. Overview of Concrete Performance Made with Waste Rubber Tires: A Step toward Sustainable Concrete. Materials 2022, 15, 5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C33; Standard Specification for Concrete Aggregates. American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012.
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, H. Influence of Rubber Size on Properties of Crumb Rubber Mortars. Materials 2016, 9, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM C39; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011.
- ASTM C496; Standard Test Method for Splitting Tensile Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM C78; Standard Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete (Using Simple Beam with Third-Point Loading). American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010.
- ACI 544.2R-89; Measurement of Properties of Fiber Reinforced Concrete. American Concrete Institute: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 1989.
- Taha, M.M.R.; El-Dieb, A.S.; El-Wahab, M.A.A.; Abdel-Hameed, M.E. Mechanical, Fracture, and Microstructural Investigations of Rubber Concrete. ASCE J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2008, 20, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunal, B.; Ramana, P.V. Evaluation of mechanical and durability properties of crumb rubber concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 811–817. [Google Scholar]
- Piti, S.; Koshi, T. Expansion under water and drying shrinkage of rubberized concrete mixed with crumb rubber with different size. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 520–526. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Huo, X.S.; Yuan, Y. Strength, modulus of elasticity, and brittleness index of rubberized concrete. ASCE J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2008, 20, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Park, K.B. Analysis of the compressive strength development of concrete considering the interactions between hydration and drying. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 102, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslani, F. Mechanical properties of waste tyre rubber concrete. ASCE J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, E.; Abd-Elmohsen, M.; Anwar, A.M. Impact Resistance of Rubberized Self-Compacting Concrete. Water Sci. 2015, 29, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Compounds | LOI | MgO | SO3 | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | SiO2 | CaO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage | 1.31 | 1.30 | 2.12 | 3.98 | 5.08 | 21.75 | 64.45 |
| Compounds | Values (%) |
|---|---|
| Metal | 0.07 |
| Fiber | 0.55 |
| Water | 0.68 |
| Ash | 0.87 |
| Isoprene | 11.34 |
| Acceton extract | 13.80 |
| Carbon black | 26.20 |
| Rubber hydrocarbon | 45.21 |
| Others | 1.18 |
| Physical Form | Appearance | Ph Value | Relative Density | Viscosity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viscous liquid | Char light brown | 6.7 | 1.2 at 21 °C | 130 cps at 20 °C |
| Mixtures | Cement | Fine Aggregates | Coarse Aggregates | Water | Superplastizer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.00 | 1.51 | 2.56 | 0.35 | 0.01 |
| Properties | Rubber Contents | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 10% | 20% | 30% | |
| Slump (mm) | 136 | 88 | 81 | 76 |
| Compressive strength (MPa) | 55.1 | 40.5 | 33.7 | 22.4 |
| Splitting tensile strength (MPa) | 9.6 | 7.5 | 6.9 | 6.3 |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 7.4 | 5.9 | 4.4 | 3.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbas, S.; Fatima, A.; Kazmi, S.M.S.; Munir, M.J.; Ali, S.; Rizvi, M.A. Effect of Particle Sizes and Dosages of Rubber Waste on the Mechanical Properties of Rubberized Concrete Composite. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8460. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178460
Abbas S, Fatima A, Kazmi SMS, Munir MJ, Ali S, Rizvi MA. Effect of Particle Sizes and Dosages of Rubber Waste on the Mechanical Properties of Rubberized Concrete Composite. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(17):8460. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178460
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbas, Safeer, Ayesha Fatima, Syed Minhaj Saleem Kazmi, Muhammad Junaid Munir, Shahid Ali, and Mujasim Ali Rizvi. 2022. "Effect of Particle Sizes and Dosages of Rubber Waste on the Mechanical Properties of Rubberized Concrete Composite" Applied Sciences 12, no. 17: 8460. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178460
APA StyleAbbas, S., Fatima, A., Kazmi, S. M. S., Munir, M. J., Ali, S., & Rizvi, M. A. (2022). Effect of Particle Sizes and Dosages of Rubber Waste on the Mechanical Properties of Rubberized Concrete Composite. Applied Sciences, 12(17), 8460. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178460








