Apigenin Promotes Proliferation and Mineralization of Human Osteoblasts and Up-Regulates Osteogenic Markers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
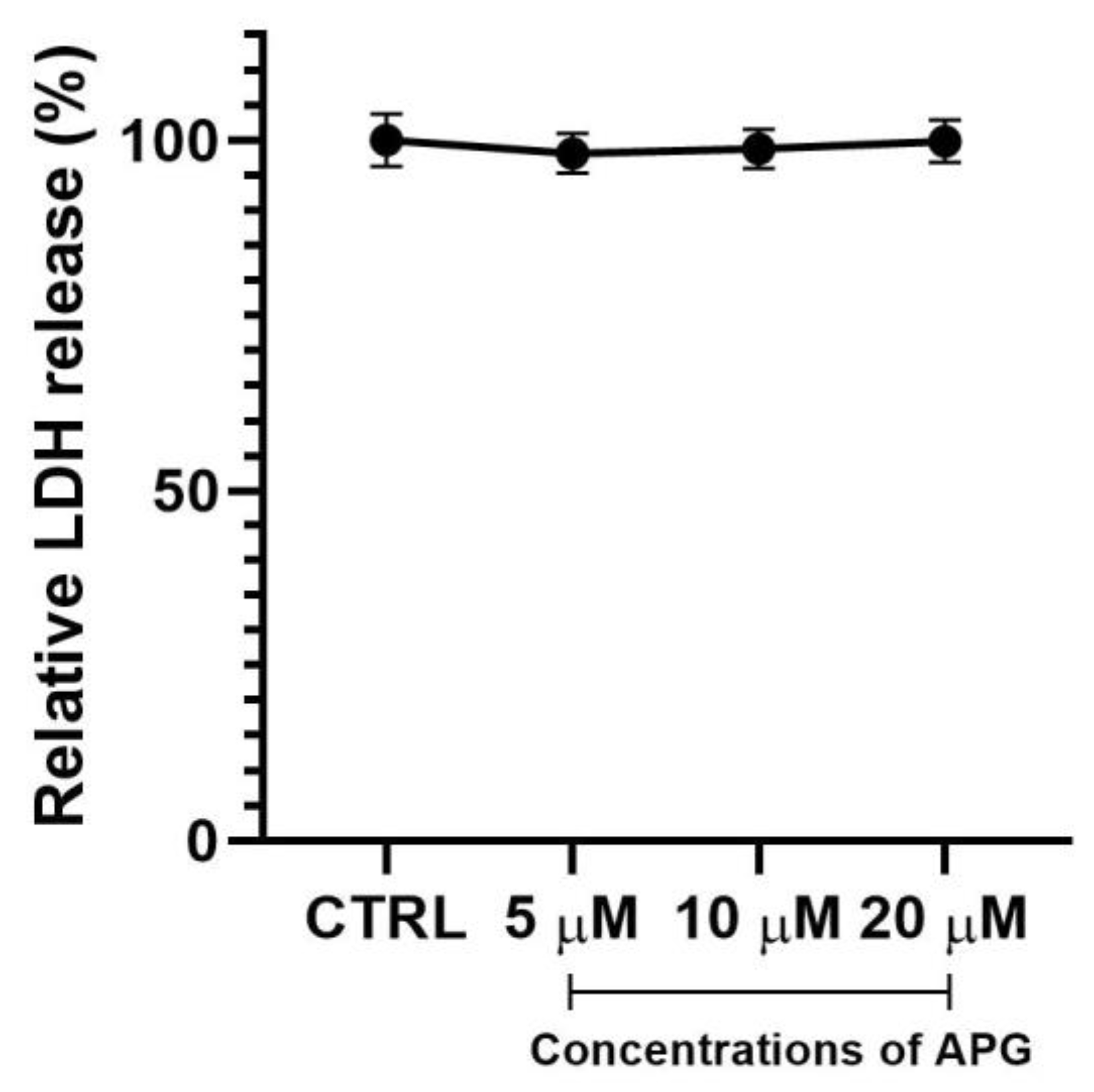
2.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
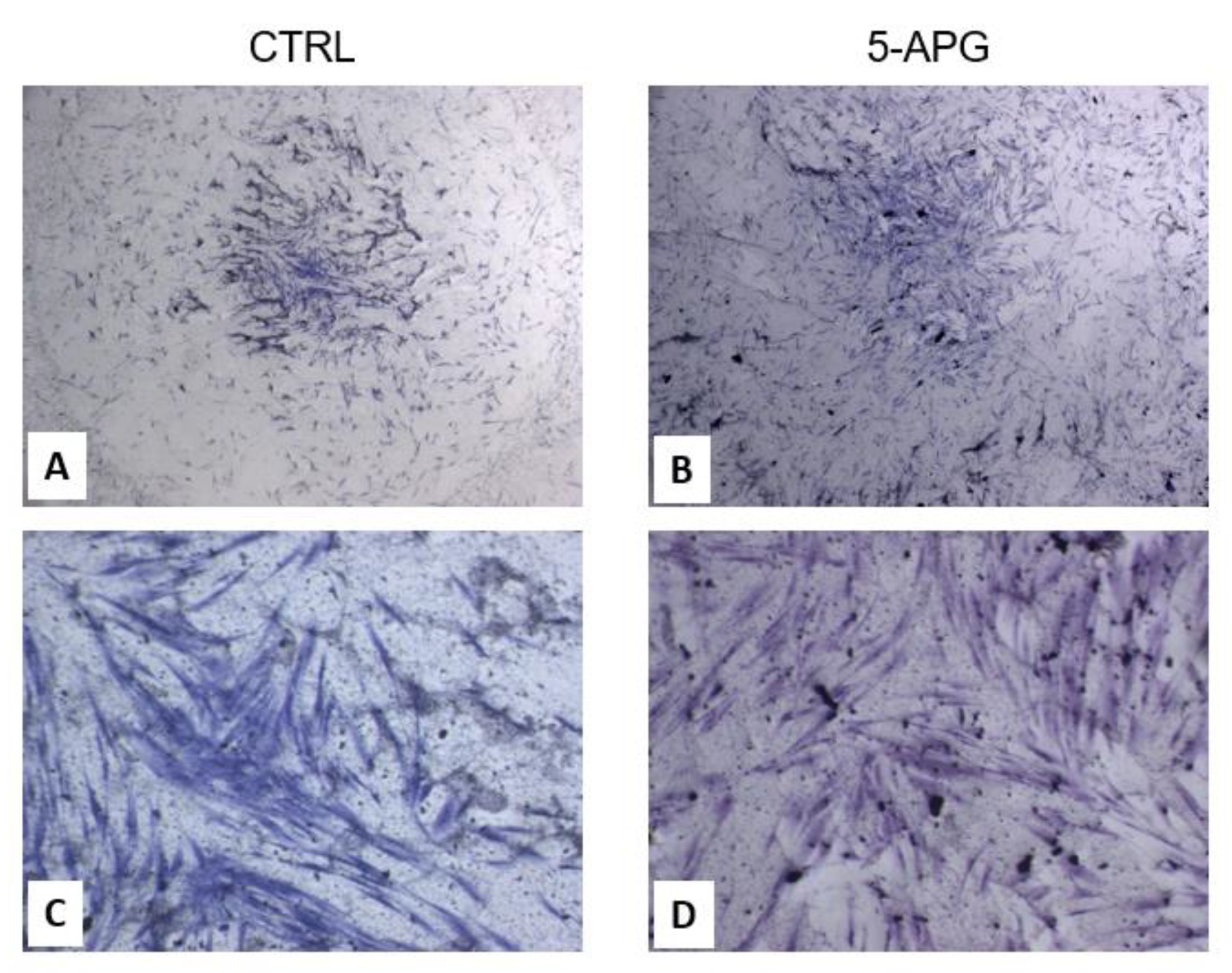
2.4. Toluidine Blue Staining
2.5. Proliferation Assay
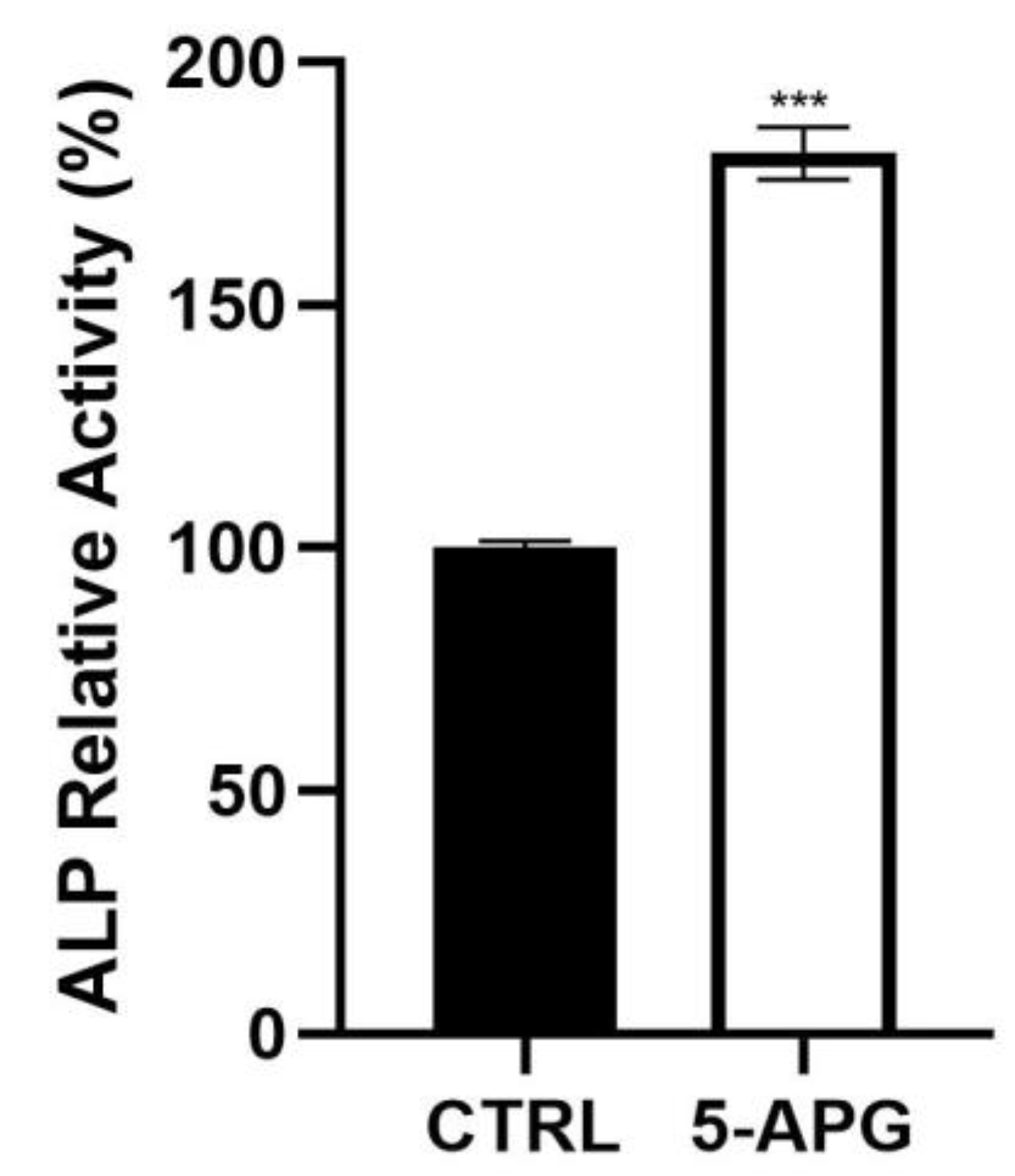
2.6. ALP Assay
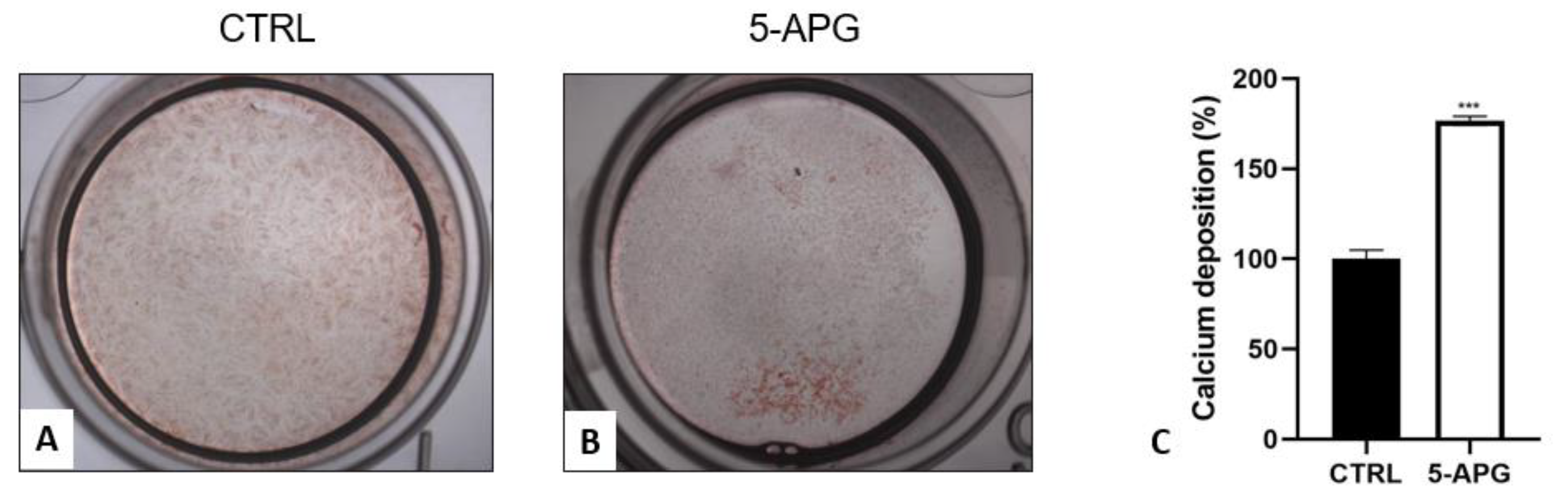
2.7. Alizarin Red Staining and Quantification of Calcium Deposition
2.8. Gene Expression
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Apigenin Showed No Significant Effects on Cell Viability and Morphology of hOBs
3.2. Apigenin Promoted Proliferation of hOBs
3.3. Apigenin Increased ALP Activity
3.4. Apigenin Stimulated Mineral Deposition
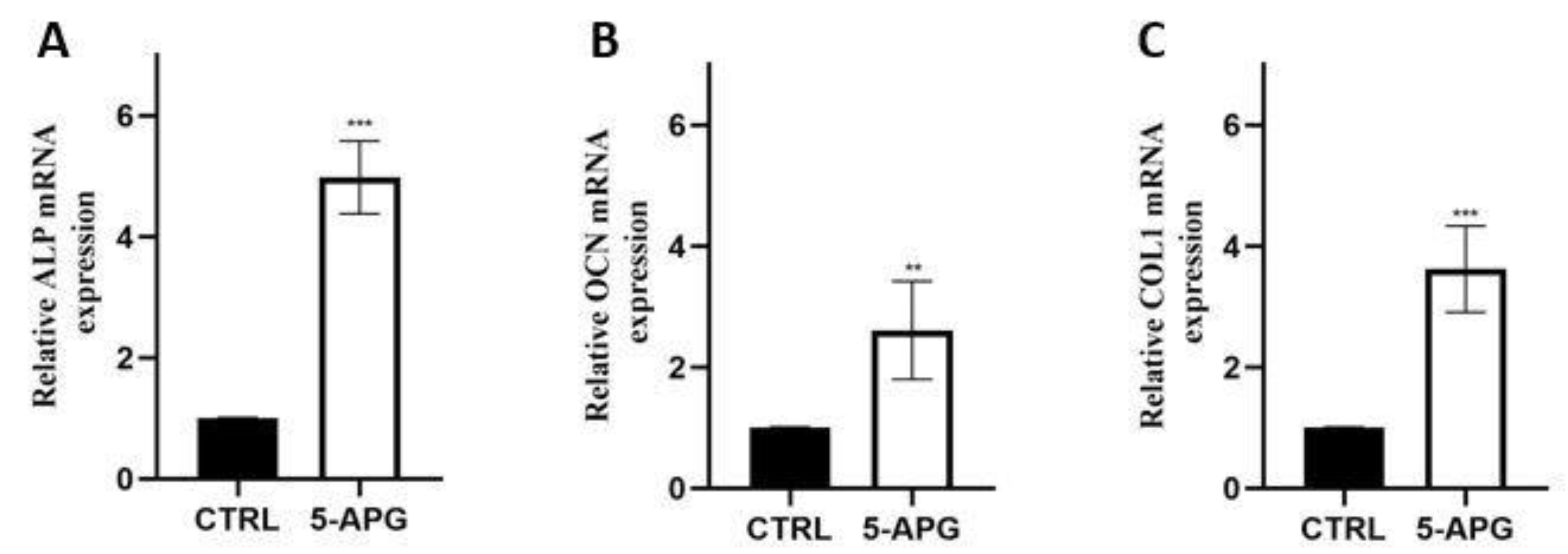
3.5. Apigenin Up-Regulated Mineralization-Related Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abid, R.; Ghazanfar, S.; Farid, A.; Sulaman, S.M.; Idrees, M.; Amen, R.A.; Muzammal, M.; Shahzad, M.K.; Mohamed, M.O.; Khaled, A.A.; et al. Pharmacological Properties of 4′,5,7-Trihydroxyflavone (Apigenin) and Its Impact on Cell Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2022, 27, 4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldanha, E.; Pai, R.J.; George, T.; D’Souza, S.; Adnan, M.; Pais, M.; Naik, T.; D’Souza, R.C.C.; D’Cunha, R.; Shrinath Baliga, M. Health Effects of Various Dietary Agents and Phytochemicals (Therapy of Acute Pancreatitis). Ther. Probiotic Unconv. Foods 2018, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švehlíková, V.; Bennett, R.N.; Mellon, F.A.; Needs, P.W.; Piacente, S.; Kroon, P.A.; Bao, Y. Isolation, Identification and Stability of Acylated Derivatives of Apigenin 7-O-Glucoside from Chamomile (Chamomilla recutita [L.] Rauschert). Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Qi, M.; Li, P.; Zhan, Y.; Shao, H. Apigenin in Cancer Therapy: Anti-Cancer Effects and Mechanisms of Action. Cell Biosci. 2017, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.Y.; Sung, B.; Kim, N.D. Role of Induced Programmed Cell Death in the Chemopreventive Potential of Apigenin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Núñez, L.; Lozano, M.L.; Palomo, M.; Martínez, C.; Vicente, V.; Castillo, J.; Benavente-García, O.; Diaz-Ricart, M.; Escolar, G.; Rivera, J. Apigenin Inhibits Platelet Adhesion and Thrombus Formation and Synergizes with Aspirin in the Suppression of the Arachidonic Acid Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2970–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Venditti, A.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Kręgiel, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B.; Novellino, E.; et al. The Therapeutic Potential of Apigenin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezai-Zadeh, K.; Ehrhart, J.; Bai, Y.; Sanberg, P.R.; Bickford, P.; Tan, J.; Douglas, R.D. Apigenin and Luteolin Modulate Microglial Activation via Inhibition of STAT1-Induced CD40 Expression. J. Neuroinflamm. 2008, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, L.; Shen, T.; Ji, L.; Zhao, X.; Si, C.L.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, G. Apigenin-7-O-β-D-Glucuronide Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammation through the Inactivation of AP-1 and MAPK Signaling Pathways in RAW 264.7 Macrophages and Protects Mice against Endotoxin Shock. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1002–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, S.; Umeda, D.; Maeda, N.; Fujimura, Y.; Yamada, K.; Tachibana, H. Dietary Apigenin Suppresses IgE and Inflammatory Cytokines Production in C57BL/6N Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 5203–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, H. Protective Roles of Apigenin Against Cardiometabolic Diseases: A Systematic Review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 875826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Huang, C.; Yang, C.; Jiang, T.; Su, J.; Chen, M.; Fatima, S.; Gong, R.; Hu, X.; Bian, Z.; et al. Apigenin Inhibits STAT3/CD36 Signaling Axis and Reduces Visceral Obesity. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Fujimori, K. Antiadipogenic Effect of Dietary Apigenin through Activation of AMPK in 3T3-L1 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 13346–13352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Cai, S.; Wang, O.; Ji, B. Synergistic Interactions of Apigenin, Naringin, Quercetin and Emodin on Inhibition of 3T3-L1 Preadipocyte Differentiation and Pancreas Lipase Activity. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 10, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solini, A.; Suvan, J.; Santini, E.; Gennai, S.; Seghieri, M.; Masi, S.; Petrini, M.; D’Aiuto, F.; Graziani, F. Periodontitis Affects Glucoregulatory Hormones in Severely Obese Individuals. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R. Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Sun, W.; Xing, Y.; Xiu, Z.; Zhuang, C.; Dong, Y. Dietary Flavonoids and Acarbose Synergistically Inhibit α-Glucosidase and Lower Postprandial Blood Glucose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8319–8330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.N.; Dutta, R.K.; Maharjan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lim, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-J.; Cho, D.-H.; So, H.-S.; Choe, S.-K.; Park, R. Catalase Inhibition Induces Pexophagy through ROS Accumulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 501, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Qin, W.; Wu, F.; Wang, S.; Pan, C.; Wang, L.; Zeng, B.; Ma, S.; Liang, J. Apigenin and Naringenin Regulate Glucose and Lipid Metabolism, and Ameliorate Vascular Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 773, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina Prats, P.; Gómez Garcia, F.; Martinez Diaz, F.; Amaral Mendes, R.; Lopez-Jornet, P. The Therapeutic Effects of Apigenin and Dexamethasone on 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Oral Mucositis—A Pilot Study Using a Syrian Hamster Model. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2017, 46, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, D.; Garavello, W.; Rigolio, R.; Pignataro, L.; Gaini, R.; Nicolini, G. Apigenin Impairs Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth in Vitro Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvan, S.; Manoharan, S.; Baskaran, N.; Anusuya, C.; Karthikeyan, S.; Prabhakar, M.M. Chemopreventive Potential of Apigenin in 7,12-Dimethylbenz(a)Anthracene Induced Experimental Oral Carcinogenesis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, P.; Jagadeesan, R.; Sekaran, S.; Dhanasekaran, A.; Vimalraj, S. Flavonoids: Classification, Function, and Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Bone Remodelling. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.A.; Ha, S.K.; Kang, T.H.; Oh, M.S.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.Y. Protective Effect of Apigenin on Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss in Rats. Life Sci. 2008, 82, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.F.; Shao, J.; Shi, C.J.; Li, Z.P.; Fu, W.M.; Zhang, J.F. Apigenin Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Accelerates Bone Fracture Healing via Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 320, E760–E771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandatori, D.; Penolazzi, L.; Pelusi, L.; Lambertini, E.; Michelucci, F.; Porreca, A.; Cerritelli, P.; Pipino, C.; di Iorio, A.; Bruni, D.; et al. Three-Dimensional Co-Culture System of Human Osteoblasts and Osteoclast Precursors from Osteoporotic Patients as an Innovative Model to Study the Role of Nutrients: Focus on Vitamin K2. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Lion, J.M.; Mentaverri, R.; Ricupero, D.A.; Kamel, S.; Romero, J.R.; Chattopadhyay, N. Attenuation of Osteoclastogenesis and Osteoclast Function by Apigenin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.W. Protective Effect of Apigenin against Oxidative Stress-Induced Damage in Osteoblastic Cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, Y.P.; Yeon, C.Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, E.S.; Sung, S.; Pokharel, E.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, S.Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Sohn, W.J.; et al. Facilitating Reparative Dentin Formation Using Apigenin Local Delivery in the Exposed Pulp Cavity. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Ortiz, G.; Neiva, R.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Rudek, I.; Benavides, E.; Wang, H.L. Analysis of the Influence of Residual Alveolar Bone Height on Sinus Augmentation Outcomes. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bathla, S.C.; Fry, R.R.; Majumdar, K. Maxillary Sinus Augmentation. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2018, 22, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierfelice, T.V.; D’amico, E.; Iezzi, G.; Piattelli, A.; di Pietro, N.; D’arcangelo, C.; Comuzzi, L.; Petrini, M. Nanoporous Titanium Enriched with Calcium and Phosphorus Promotes Human Oral Osteoblast Bioactivity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Yao, F.; Xue, Q.; Fan, H.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y. Inhibitory Effects against α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase of the Flavonoids-Rich Extract from Scutellaria Baicalensis Shoots and Interpretation of Structure–Activity Relationship of Its Eight Flavonoids by a Refined Assign-Score Method. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilani-Jaziri, S.; Mustapha, N.; Mokdad-Bzeouich, I.; el Gueder, D.; Ghedira, K.; Ghedira-Chekir, L. Flavones Induce Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Effects by Activating Cellular Anti-Oxidant Activity: A Structure-Activity Relationship Study. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 6571–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouache, A.; Zabaiou, N.; de Joussineau, C.; Morel, L.; Silvente-Poirot, S.; Namsi, A.; Lizard, G.; Poirot, M.; Makishima, M.; Baron, S.; et al. Flavonoids Differentially Modulate Liver X Receptors Activity—Structure-Function Relationship Analysis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 190, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkett, D.J. Pharmacokinetics Made Easy 10 Pharmacodynamics—The Concentration-Effect Relationship. Aust. Prescr. 1995, 18, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Mishra, S.K.; Noel, S.; Sharma, S.; Rath, S.K. Acute Exposure of Apigenin Induces Hepatotoxicity in Swiss Mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, N.; Naniwa, K.; Yamada, T.; Osawa, T.; Nakamura, Y. Dietary Flavonoid Apigenin Is a Potential Inducer of Intracellular Oxidative Stress: The Role in the Interruptive Apoptotic Signal. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 466, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; Manzano-Moreno, F.J.; Illescas-Montes, R.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; de Luna-Bertos, E.; Ruiz, C.; García-Martínez, O. Bone Protective Effect of Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds by Modulating Osteoblast Gene Expression. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Lin, M.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Gao, B.; Gan, H.; Yang, Z.; Lin, X.; Liao, L.; Yang, M. Icariin Promotes Bone Formation via the BMP-2/Smad4 Signal Transduction Pathway in the HFOB 1.19 Human Osteoblastic Cell Line. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Zhu, L.; Chen, O.; Wang, X. Flavonoid Compound Icariin Enhances BMP-2 Induced Differentiation and Signalling by Targeting to Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) in SAMP6 Osteoblasts. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawadi, G.; Vayssière, B.; Dunn, F.; Baron, R.; Roman-Roman, S. BMP-2 Controls Alkaline Phosphatase Expression and Osteoblast Mineralization by a Wnt Autocrine Loop. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2003, 18, 1842–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movassagh, E.Z.; Vatanparast, H. Current Evidence on the Association of Dietary Patterns and Bone Health: A Scoping Review. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayaka, H.B.; Londonkar, R.L.; Umesh, M.K.; Tukappa, A. Antibacterial Attributes of Apigenin, Isolated from Portulaca Oleracea L. Int. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 2014, 175851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczak, A.; Ożarowski, M.; Karpiński, T.M. Antibacterial Activity of Some Flavonoids and Organic Acids Widely Distributed in Plants. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qiao, H.; Lv, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Hou, Y.; Tan, R.; Li, E. Apigenin Inhibits Enterovirus-71 Infection by Disrupting Viral RNA Association with Trans-Acting Factors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, C.; Ohno, M.; Otsuka, M.; Kishikawa, T.; Goto, K.; Muroyama, R.; Kato, N.; Yoshikawa, T.; Takata, A.; Koike, K. The Flavonoid Apigenin Inhibits Hepatitis C Virus Replication by Decreasing Mature MicroRNA122 Levels. Virology 2014, 462–463, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Li, H.; Shu, R.; Chen, H.; Zhao, L.; Song, Z.; Zhou, W. Mesoporous Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Loaded with Recombinant-Human Amelogenin Could Enhance Antibacterial Effect and Promote Periodontal Regeneration. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.K.; Chin, K.Y.; Ima-Nirwana, S. Quercetin as an Agent for Protecting the Bone: A Review of the Current Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozhat, Z.; Heydarzadeh, S.; Memariani, Z.; Ahmadi, A. Chemoprotective and Chemosensitizing Effects of Apigenin on Cancer Therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| ALP OCN COL1 | AATGAGTGAGTGACCATCCTGG TCAGCCAACTCGTCACAGTC AGTCAGAGTGAGGACAGTGAATTG | GCACCCCAAGACCTGCTTTAT GGCGCTACCTGTATCAATGG CACATCACACCAGGAAGTGC |
| βACT | CCAGAGGCGTACAGGGATAG | GAGAAGATGACCCAGGACTCTC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Amico, E.; Pierfelice, T.V.; Iezzi, G.; Di Pietro, N.; Lepore, S.; Lorusso, F.; Scarano, A.; Pandolfi, A.; Piattelli, A.; Petrini, M. Apigenin Promotes Proliferation and Mineralization of Human Osteoblasts and Up-Regulates Osteogenic Markers. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8510. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178510
D’Amico E, Pierfelice TV, Iezzi G, Di Pietro N, Lepore S, Lorusso F, Scarano A, Pandolfi A, Piattelli A, Petrini M. Apigenin Promotes Proliferation and Mineralization of Human Osteoblasts and Up-Regulates Osteogenic Markers. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(17):8510. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178510
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Amico, Emira, Tania Vanessa Pierfelice, Giovanna Iezzi, Natalia Di Pietro, Stefania Lepore, Felice Lorusso, Antonio Scarano, Assunta Pandolfi, Adriano Piattelli, and Morena Petrini. 2022. "Apigenin Promotes Proliferation and Mineralization of Human Osteoblasts and Up-Regulates Osteogenic Markers" Applied Sciences 12, no. 17: 8510. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178510
APA StyleD’Amico, E., Pierfelice, T. V., Iezzi, G., Di Pietro, N., Lepore, S., Lorusso, F., Scarano, A., Pandolfi, A., Piattelli, A., & Petrini, M. (2022). Apigenin Promotes Proliferation and Mineralization of Human Osteoblasts and Up-Regulates Osteogenic Markers. Applied Sciences, 12(17), 8510. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178510














