Silk Bionanocomposites for Organic Dye Absorption and Degradation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Silk Fibroin Extraction
2.3. Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis
2.4. SF-Au NPs Bionanocomposite
2.5. Dye Adsorption
2.6. Adsorption Isotherms
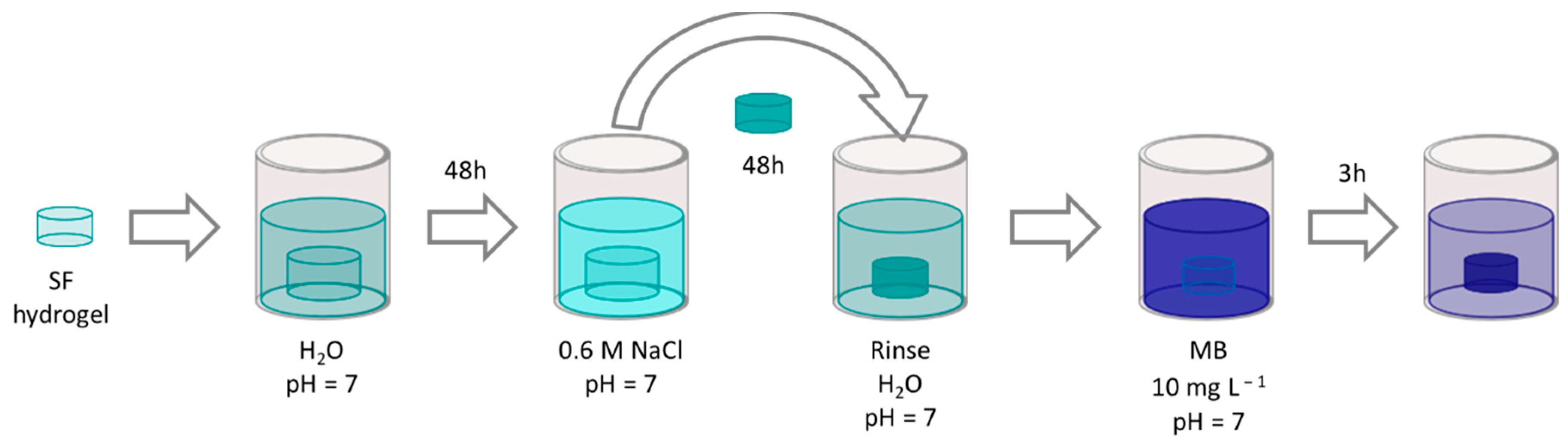
2.7. Materials Pretreatment
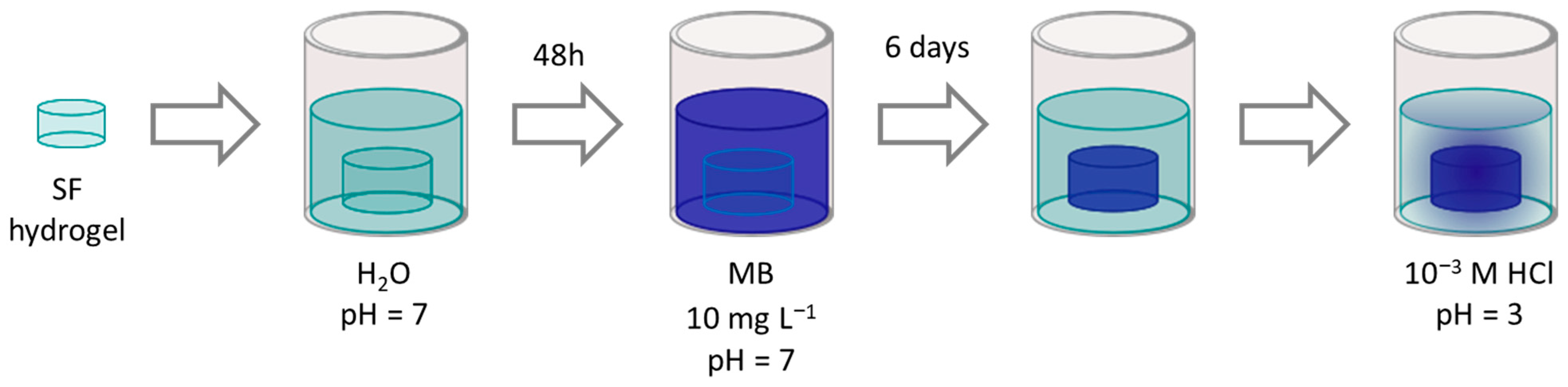
2.8. MB Release
2.9. Catalytic Activity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Silk Fibroin Materials Preparation
3.2. Effect of pH
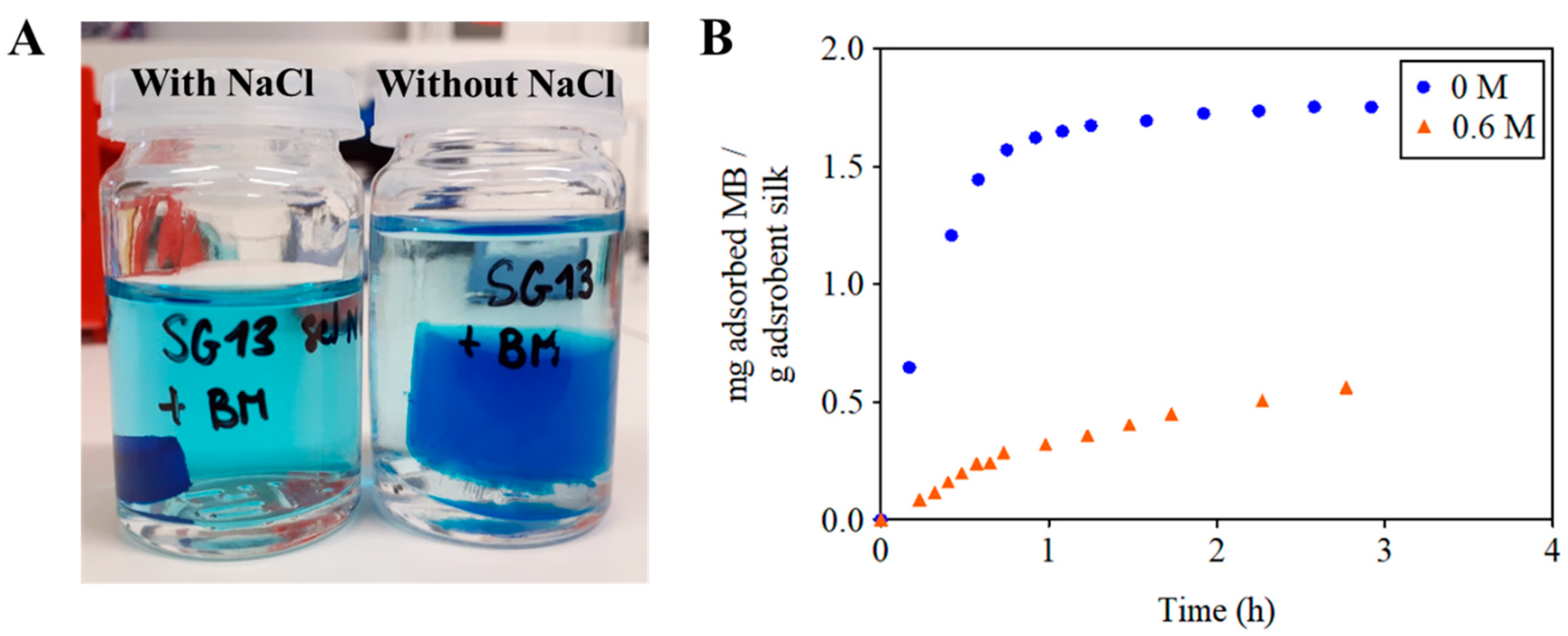
3.3. Influence of the Ionic Strength of the Solution
3.4. Brilliant Blue Adsorption
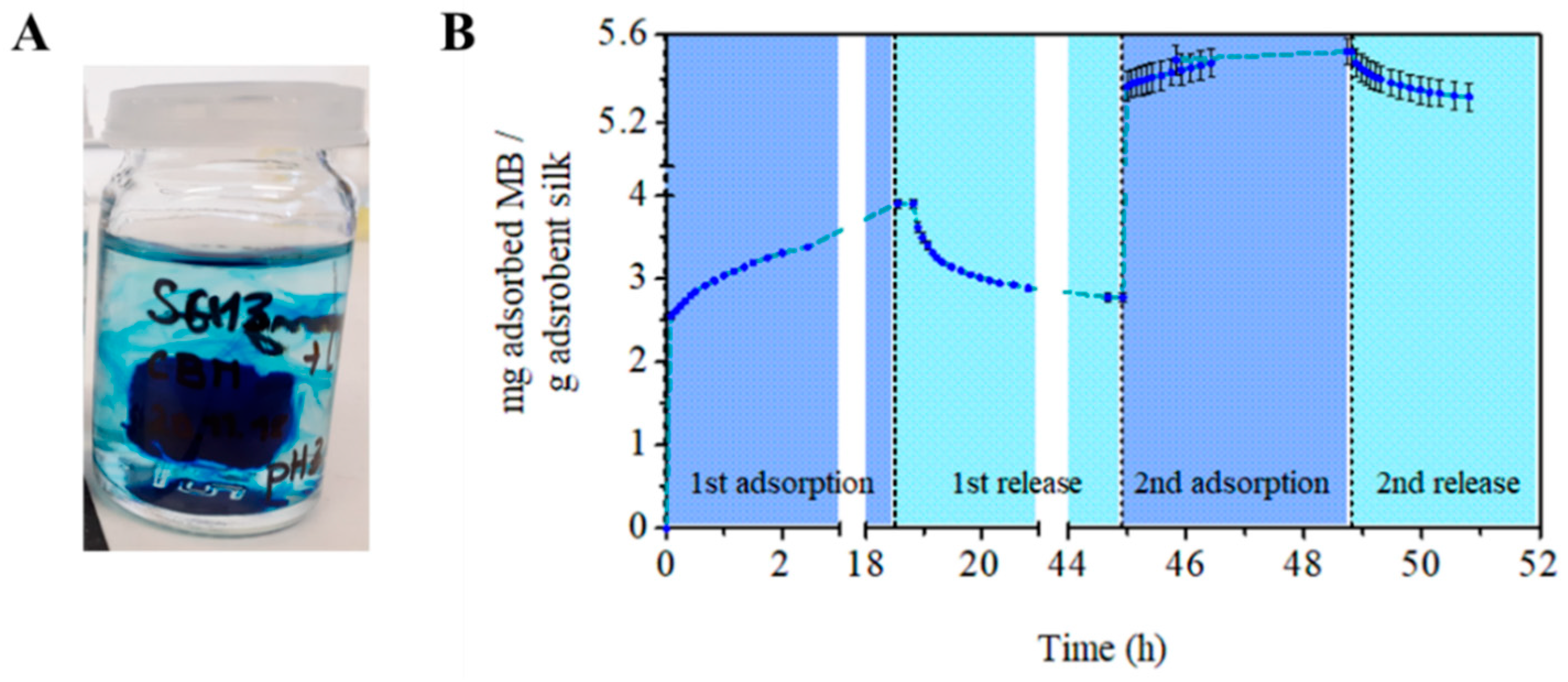
3.5. Adsorbent Regeneration and Recycling
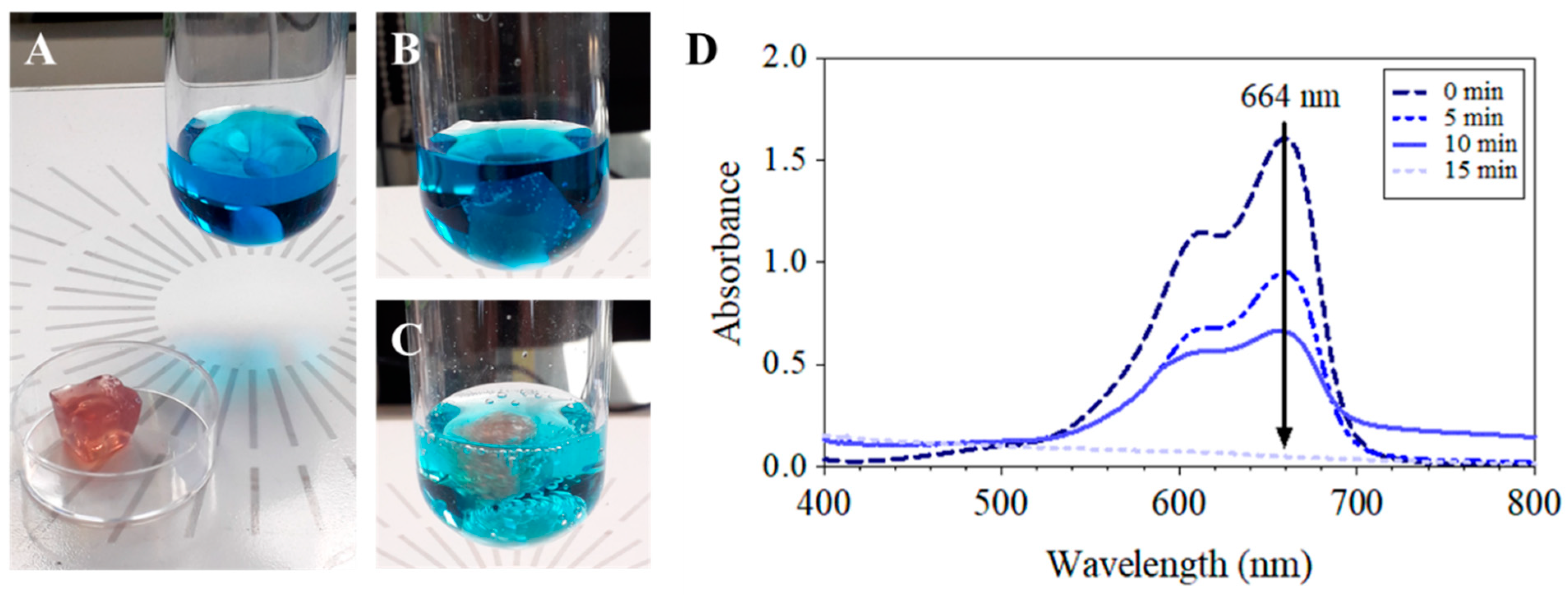
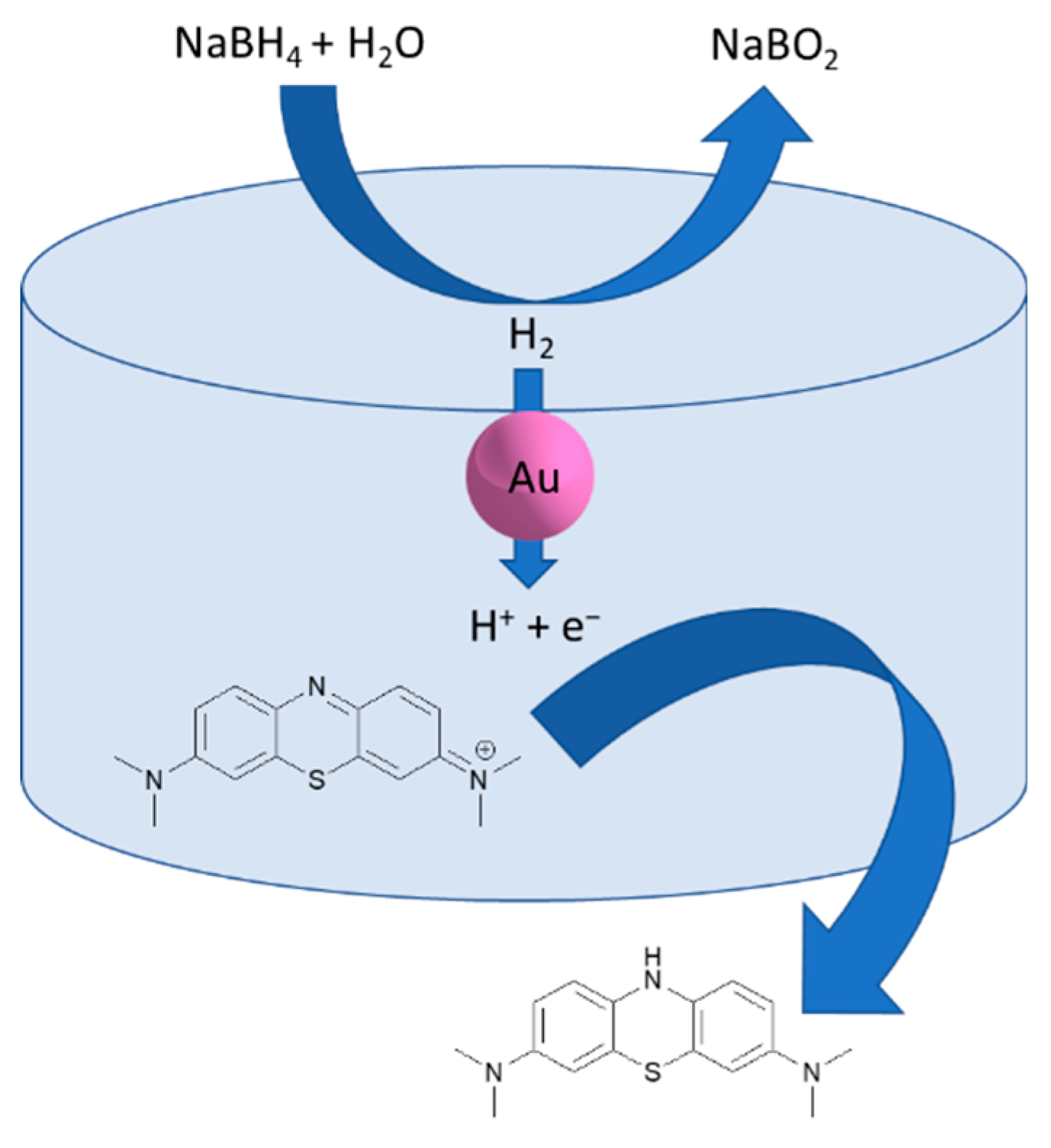
3.6. MB Degradation by a SF-Au NPs Bionanocomposite
3.7. Comparison with Other Materials
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, S.; Malik, A. Toxicity Evaluation of Textile Effluents and Role of Native Soil Bacterium in Biodegradation of a Textile Dye. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4446–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Aragão Umbuzeiro, G.; Freeman, H.S.; Warren, S.H.; de Oliveira, D.P.; Terao, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Claxton, L.D. The Contribution of Azo Dyes to the Mutagenic Activity of the Cristais River. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, Y. Toxicity Assessment of Dye Containing Industrial Effluents by Acute Toxicity Test Using Daphnia Magna. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2011, 27, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, P.; Desai, A.V.; Let, S.; Ghosh, S.K. Advanced Porous Materials for Sensing, Capture and Detoxification of Organic Pollutants toward Water Remediation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7456–7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasulochana, P.; Preethy, V. Comparison on Efficiency of Various Techniques in Treatment of Waste and Sewage Water—A Comprehensive Review. Resour.-Effic. Technol. 2016, 2, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, I.; Hafner, C.; Schneider, K. Mutagenicity of Different Textile Dye Products in Salmonella Typhimurium and Mouse Lymphoma Cells. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagenesis 2004, 561, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lellis, B.; Fávaro-Polonio, C.Z.; Pamphile, J.A.; Polonio, J.C. Effects of Textile Dyes on Health and the Environment and Bioremediation Potential of Living Organisms. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019, 3, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Kaolinite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2002, 20, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Jeevanantham, S.; Karishma, S.; Tajsabreen, B.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; Reshma, B. Effective Water/Wastewater Treatment Methodologies for Toxic Pollutants Removal: Processes and Applications towards Sustainable Development. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Nazari, M.; Kabiri, B.; Hosseini, S.H.; Bennett, C. Preparation of Porous Graphene Oxide/Hydrogel Nanocomposites and Their Ability for Efficient Adsorption of Methylene Blue. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 10430–10437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ning, H.; Hu, N.; Huang, K.; Weng, S.; Wu, X.; Wu, L.; Liu, J.; Alamusi. Preparation and Characterization of Graphene Oxide/Silk Fibroin Hybrid Aerogel for Dye and Heavy Metal Adsorption. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 163, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Qin, Z.; Huang, W.; Cao, S.; Kaplan, D.L.; Buehler, M.J. Design and Function of Biomimetic Multilayer Water Purification Membranes. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1601939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Yang, H.; Xu, W. Effective Removal of Dyes from Aqueous Solution Using Ultrafine Silk Fibroin Powder. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Min, K.; Jo, M.; Kim, S. Ultra-Thin, Conformal, and Hydratable Color-Absorbers Using Silk Protein Hydrogel. Opt. Mater. 2018, 80, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Cheng, X.; Deng, G.; Li, D.; Lu, X. Silk Fibroin/Polyethylenimine Functional Hydrogel for Metal Ion Adsorption and Upcycling Utilization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Abe, S.; Ito, S.; Abe, T. Silk Fibroin Fiber for Selective Palladium Adsorption: Kinetic, Isothermal and Thermodynamic Properties. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, P.M.; Naebe, M.; Wang, X.; Kandasubramanian, B. Progress in Silk Materials for Integrated Water Treatments: Fabrication, Modification and Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 437–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, G.H.; Diaz, F.; Jakuba, C.; Calabro, T.; Horan, R.L.; Chen, J.; Lu, H.; Richmond, J.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk-Based Biomaterials. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, D.; Tokareva, O.; Rim, N.G.; Wong, J.Y.; Kaplan, D.L.; Buehler, M.J. Silk-Its Mysteries, How It Is Made, and How It Is Used. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, K.; Schlatter, G.; Hébraud, A.; Marin, F.; Testelin, S.; Dakpé, S.; Devauchelle, B.; Egles, C. A Multi-Layered Nerve Guidance Conduit Design Adapted to Facilitate Surgical Implantation. Health Sci. Rep. 2018, 1, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Ding, F.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Gu, X. Biocompatibility Evaluation of Silk Fibroin with Peripheral Nerve Tissues and Cells in Vitro. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-García, L.; Marí-Buyé, N.; Barios, J.A.; Madurga, R.; Elices, M.; Pérez-Rigueiro, J.; Ramos, M.; Guinea, G.V.; González-Nieto, D. Safety and Tolerability of Silk Fibroin Hydrogels Implanted into the Mouse Brain. Acta Biomater. 2016, 45, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, S.C. Silk Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belda Marín, C.; Fitzpatrick, V.; Kaplan, D.L.; Landoulsi, J.; Guénin, E.; Egles, C. Silk Polymers and Nanoparticles: A Powerful Combination for the Design of Versatile Biomaterials. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 604398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Gou, J.; Zhang, L.; Duan, S.; Li, C. A Silk Fibroin Based Green Nano-Filter for Air Filtration. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 8181–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueman, H.E.; Sriskantha, A.; Qu, Y.; Rapson, T.D.; Sutherland, T.D. Modification of Honeybee Silk by the Addition of Antimicrobial Agents. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 4456–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgan, C.C.; Han, Y.S.; Trueman, H.; Jackson, C.J.; Sutherland, T.D.; Rapson, T.D. Phosphorescent Oxygen-Sensing and Singlet Oxygen Production by a Biosynthetic Silk. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 39530–39533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ania, C.O.; Menéndez, J.A.; Parra, J.B.; Pis, J.J. Microwave-Induced Regeneration of Activated Carbons Polluted with Phenol. A Comparison with Conventional Thermal Regeneration. In Carbon; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 42, pp. 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, N.; Lai, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, X. Tannic Acid Functionalized Graphene Hydrogel for Entrapping Gold Nanoparticles with High Catalytic Performance toward Dye Reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Su, J.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Functional Clay Supported Bimetallic NZVI/Pd Nanoparticles Used for Removal of Methyl Orange from Aqueous Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Long, J.; Mao, Z.; Qiu, T.; Wu, Q.; Chen, X. Synthesis of Pt3Ni Microspheres with High Performance for Rapid Degradation of Organic Dyes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaja, M.; Paulkumar, K.; Baburaja, M.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Gnanajobitha, G.; Malarkodi, C.; Sivakavinesan, M.; Annadurai, G. Degradation of Methylene Blue Using Biologically Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2014, 2014, 742346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso-Martín, I.; Moretti, E.; Talon, A.; Storaro, L.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Infantes-Molina, A. Au and AuCu Nanoparticles Supported on SBA-15 Ordered Mesoporous Titania-Silica as Catalysts for Methylene Blue Photodegradation. Materials 2018, 11, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, R.; Najeeb, J.; Sattar, A.; Naseem, K.; Irfan, A.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Farooqi, Z.H. Chemical Reduction of Methylene Blue in the Presence of Nanocatalysts: A Critical Review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 749–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najahi-Missaoui, W.; Arnold, R.D.; Cummings, B.S. Safe Nanoparticles: Are We There Yet? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnovale, C.; Bryant, G.; Shukla, R.; Bansal, V. Identifying Trends in Gold Nanoparticle Toxicity and Uptake: Size, Shape, Capping Ligand, and Biological Corona. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufaure, R.; Buendia, R.; Motte, L.; Hardouin, J.; Lalatonne, Y.; Guénin, E. Versatile “Click” Synthesis of 1-Hydroxy-1,1-Methylenebisphosphonic Acids with Thioalkoxy Substituents for the Preparation of Stable Gold Nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 12153–12158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, D.N.; Preda, R.C.; Yücel, T.; Wang, X.; Lovett, M.L.; Kaplan, D.L. Materials Fabrication from Bombyx Mori Silk Fibroin. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1612–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belda Marín, C.; Egles, C.; Humblot, V.; Lalatonne, Y.; Motte, L.; Landoulsi, J.; Guénin, E. Gold, Silver, and Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Incorporation into Silk Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: Elaboration, Structure, and Properties. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 2358–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partlow, B.P.; Hanna, C.W.; Rnjak-Kovacina, J.; Moreau, J.E.; Applegate, M.B.; Burke, K.A.; Marelli, B.; Mitropoulos, A.N.; Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. Highly Tunable Elastomeric Silk Biomaterials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4615–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perju, M.M.; Dinu, M.V.; Dragan, E.S. Sorption of Methylene Blue onto Ionic Composite Hydrogels Based on Polyacrylamide and Dextran Sulfate: Kinetics, Isotherms, and Thermodynamics. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, C.M.C.; Bueno, P.V.A.; Matsushita, A.F.Y.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C.; Durães, L.; Murtinho, D.M.B.; Valente, A.J.M. Synthesis, Characterization and Sorption Studies of Aromatic Compounds by Hydrogels of Chitosan Blended with β-Cyclodextrin- and PVA-Functionalized Pectin. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 14609–14622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, F.; Akbar, J.; Iqbal, S.; Noreen, S.; Bukhari, S.N.A. Study of Isothermal, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Parameters for Adsorption of Cadmium: An Overview of Linear and Nonlinear Approach and Error Analysis. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daryabeigi Zand, A.; Rabiee Abyaneh, M. Adsorption of Lead, Manganese, and Copper onto Biochar in Landfill Leachate: Implication of Non-Linear Regression Analysis. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2020, 30, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, V.; Chakma, S. Advances in the Preparation of Hydrogel for Wastewater Treatment: A Concise Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putro, J.N.; Kurniawan, A.; Ismadji, S.; Ju, Y.H. Nanocellulose Based Biosorbents for Wastewater Treatment: Study of Isotherm, Kinetic, Thermodynamic and Reusability. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2017, 8, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Chen, T.; Yi, H.; Rao, F.; Song, S. Removal of Methylene Blue from Water with Montmorillonite Nanosheets/Chitosan Hydrogels as Adsorbent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 448, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, C.W.P.; Bini, E.; Hensman, J.; Knight, D.P.; Lewis, R.V.; Kaplan, D.L. Role of PH and Charge on Silk Protein Assembly in Insects and Spiders. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2006, 82, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.; Sabzi, M.; Fattahi, A.; Arkan, E. Electrospun Silk Fibroin/PAN Double-Layer Nanofibrous Membranes Containing Polyaniline/TiO2 Nanoparticles for Anionic Dye Removal. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Yang, X.; Xu, X. Wet Chemical Method for Synthesizing 3D Graphene/Gold Nanocomposite: Catalytic Reduction of Methylene Blue. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2017, 88, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, E.R.; Rodríguez, E.L.; Beas, C.R.; Plascencia-Villa, G.; Palomares, R.A.I. Study of Methylene Blue Degradation by Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized within Natural Zeolites. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 9541683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.; Shi, F.; Deng, Y. Nano-Gold Catalysis in Fine Chemical Synthesis. In Chemical Reviews; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 2467–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Dominguez, N.; Ahsan, M.A.; Dominguez-Cisneros, H.; Zuniga, P.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Noveron, J.C. Sodium Rhodizonate Induced Formation of Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Cellulose Fibers for Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and Organic Dyes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4185–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapuram, B.R.; Alle, M.; Dadigala, R.; Dasari, A.; Maragoni, V.; Guttena, V. Catalytic Reduction of Methylene Blue and Congo Red Dyes Using Green Synthesized Gold Nanoparticles Capped by Salmalia Malabarica Gum. Int. Nano Lett. 2015, 5, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukhele, E.J.; Khutlane, J.T.; Báthori, N.B.; Malgas-Enus, R. Reduction and Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions via Recyclable Magnetic Gold Nanomaterials. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 31, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocher, V.; Siaugue, J.M.; Cabuil, V.; Bee, A. Removal of Organic Dyes by Magnetic Alginate Beads. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šekuljica, N.; Prlainović, N.; Stefanović, A.B.; Žuža, M.G.; Čičkarić, D.Z.; Mijin, D.; Knezevic-Jugovic, Z.D. Decolorization of Anthraquinonic Dyes from Textile Effluent Using Horseradish Peroxidase: Optimization and Kinetic Study. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 371625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

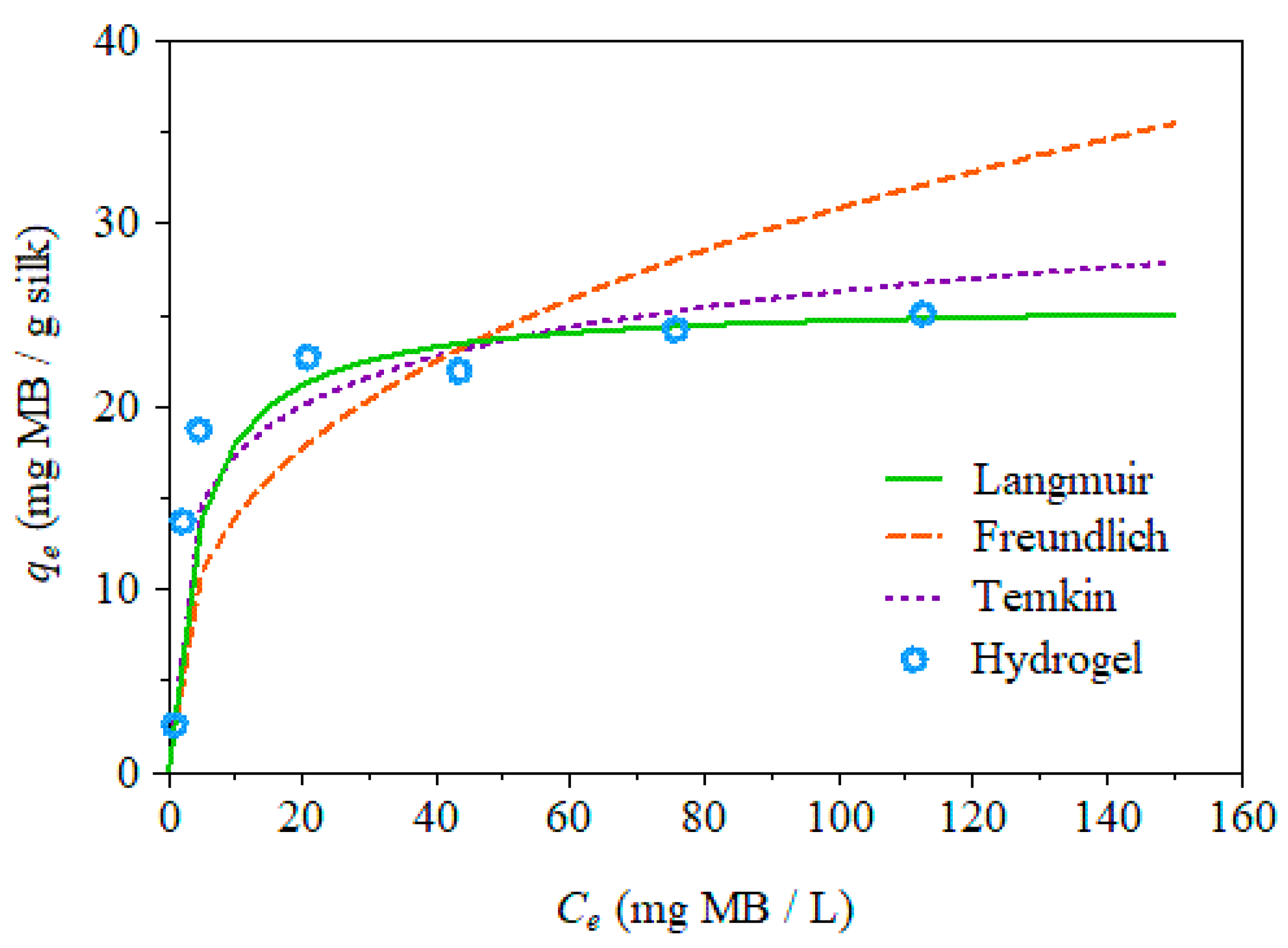


| Langmuir | Freundlich | Temkin | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm | KL | R2 | 1/n | KF | R2 | bT | KT | R2 |
| 25.77 | 0.23 | 0.996 | 0.34 | 6.33 | 0.624 | 638.29 | 8.75 | 0.8223 |
| Material | Mode of Action | Maximum Capacity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| SF hydrogel | Adsorption | 25.77 mg g−1 | This work |
| Silk-graphene oxide aerogel | 1322.71 mg g−1 | [11] | |
| Graphene oxide hydrogel | 714.29 mg g−1 | [10] | |
| Alginate beads-magnetic NPs-activated carbon | 18.23 mg g−1 | [56] | |
| Polyacrylamide dextran sulfate hydrogels | 19.145 mg g−1 | [41] | |
| Exfoliated montmorillonite nanosheets-chitosan | 530 mg g−1 | [47] | |
| SF-Au NPs hydrogel | Chemical reduction | This work | |
| Graphene-tanic acid-Au NPs hydrogel | [29] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belda Marín, C.; Egles, C.; Landoulsi, J.; Guénin, E. Silk Bionanocomposites for Organic Dye Absorption and Degradation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9152. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189152
Belda Marín C, Egles C, Landoulsi J, Guénin E. Silk Bionanocomposites for Organic Dye Absorption and Degradation. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(18):9152. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189152
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelda Marín, Cristina, Christophe Egles, Jessem Landoulsi, and Erwann Guénin. 2022. "Silk Bionanocomposites for Organic Dye Absorption and Degradation" Applied Sciences 12, no. 18: 9152. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189152
APA StyleBelda Marín, C., Egles, C., Landoulsi, J., & Guénin, E. (2022). Silk Bionanocomposites for Organic Dye Absorption and Degradation. Applied Sciences, 12(18), 9152. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189152






