A Novel Approach to Detect COVID-19: Enhanced Deep Learning Models with Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Chest X-ray Databases
4. Methodology
4.1. Splitting Datasets
4.2. Image Processing
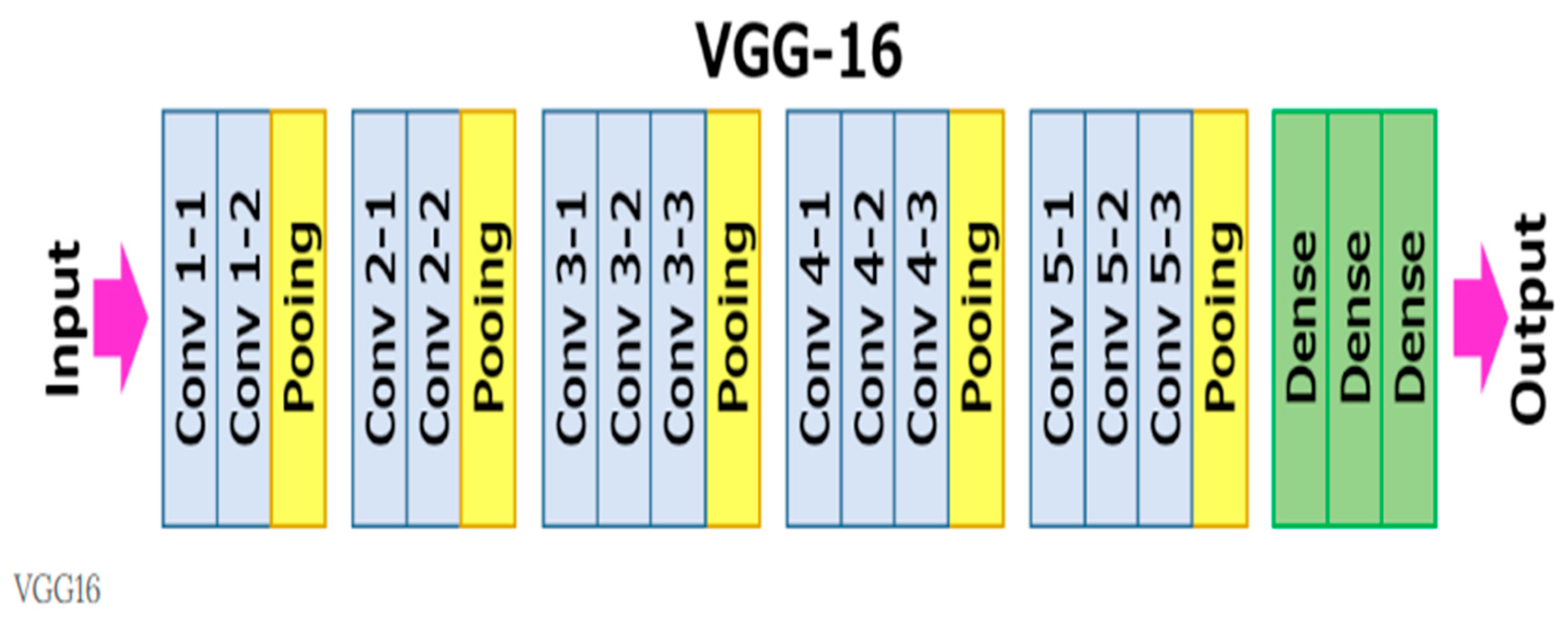
4.3. Proposed Model
4.4. Evaluation Metrics
- TP is the number of correct predictions that an instance is positive,
- FP is the number of incorrect predictions that an instance positive,
- FN is the number of incorrect predictions that an instance is negative, and
- TN is the number of correct predictions that an instance is negative.
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pham, T.D. Classification of COVID-19 chest X-rays with deep learning: New models or fine tuning? Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2020, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, R.; Kamrowski, C.; Langlois, J.; Rozario, P.; Dircks, I.; Grottodden, K.; Martinez, M.; Tee, W.Z.; Sargeant, K.; LaFleur, C.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of Machine Learning Used to Combat COVID-19. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.; Gupta, M.; Taneja, S.; Hemanth, D.J. Deep learning based detection and analysis of COVID-19 on chest X-ray images. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 1690–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, F. DeepCoroNet: A deep LSTM approach for automated detection of COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 103, 107160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethy, P.K.; Behera, S.K.; Ratha, P.K.; Biswas, P. Detection of coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) based on Deep Features and Support Vector Machine. Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2020, 5, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, E.; Hasan, M.; Rahman, A.; Lee, I.; Tamanna, T.; Parvez, M.Z. CoroDet: A deep learning based classification for COVID-19 detection using chest X-ray images. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 142, 110495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varoquaux, G.; Cheplygina, V. Machine learning for medical imaging: Methodological failures and recommendations for the future. NPJ Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narin, A.; Kaya, C.; Pamuk, Z. Department of Biomedical Engineering, Zonguldak Bulent Ecevit University, 67100, Zonguldak, Turkey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.10849. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa, N.E.M.; Taha, M.H.N.; Hassanien, A.E.; Elghamrawy, S. Detection of coronavirus (COVID-19) associated pneumonia based on generative adversarial networks and a fine-tuned deep transfer learning model using chest X-ray dataset. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.01184. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.I.; Shah, J.L.; Bhat, M.M. CoroNet: A deep neural network for detection and diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Sarker, S.; Al Miraj, A.; Nihal, R.A.; Haque, A.K.M.N.; Al Noman, A. Deep Learning–Driven Automated Detection of COVID-19 from Radiography Images: A Comparative Analysis. Cogn. Comput. 2021, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.; Goyal, M.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, A.; Al-Turjman, F.; Pinheiro, P.R. Covidgan: Data augmenta-tion using auxiliary classifier gan for improved COVID-19 detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 91916–91923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.U.; Ozsoz, M.; Serte, S.; Al-Turjman, F.; Yakoi, P.S. Pneumonia Classification Using Deep Learning from Chest X-ray Images During COVID-19. Cogn. Comput. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusakunniran, W.; Borwarnginn, P.; Sutassananon, K.; Tongdee, T.; Saiviroonporn, P.; Karnjanapreechakorn, S.; Siriapisith, T. COVID-19 detection and heatmap generation in chest x-ray images. J. Med Imaging 2021, 8, 14001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.; Varol, S. A Review of Image Segmentation Using MATLAB Environment. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Digital Forensics and Security (ISDFS), Beirut, Lebanon, 1–2 June 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.; Baykara, M. A Comprehensive Review for Emotion Detection Based on EEG Signals: Challenges, Applications, and Open Issues. Trait. Signal 2021, 38, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.; Brifcani, A. Gene Expression Classification Based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 4th Scientific International Conference Najaf (SICN), Al-Najef, Iraq, 29–30 April 2019; pp. 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.K.; Siddhartha, M.; Singh, A. Diagnosis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) from chest X-ray images using modified XceptionNet. Rom. J. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2020, 23, 91–115. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.I.; Tahir, A.A.K. A new image classification system using deep con-volution neural network and modified amsgrad optimizer. J. Duhok Univ. 2019, 22, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Debnath, S.; Roy, R.; Changder, S. Photo classification based on the presence of diagonal line using pre-trained DCNN VGG16. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 22527–22548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, E.; Ruppert, G.; Carvalho, T.; Theophilo, A.; Ramos, F.; de Geus, P. Malicious software classifica-tion using VGG16 deep neural network’s bottleneck features. In Information Technology-New Generations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, J.A.P. To supervise or to self-supervise: A machine learning based comparison on credit supervi-sion. Financ. Innov. 2021, 7, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depren, O.; Kartal, M.T.; Kılıç Depren, S. Recent innovation in benchmark rates (BMR): Evidence from influential factors on Turkish Lira Overnight Reference Interest Rate with machine learning algorithms. Financ. Innov. 2021, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, X.; Kou, G.; Li, T.; Peng, Y. Jie Ke versus AlphaGo: A ranking approach using decision making method for large-scale data with incomplete information. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 265, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.B.; Lim, G.H. Measures of diagnostic accuracy: Sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV. Proc. Singap. Healthc. 2011, 20, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Abdelsamea, M.M.; Gaber, M.M. Classification of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images using DeTraC deep convolutional neural network. Appl. Intell. 2020, 51, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Sandhu, J.K.; Pathak, Y.; Jadhav, S. Chest X-ray scanning based detection of COVID-19 using deepconvolutional neural network. Res. Sq. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchicha, C.; Ammor, O.; Meknassi, M. CVDNet: A novel deep learning architecture for detection of coronavirus (COVID-19) from chest x-ray images. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Mazhar, R.; Kadir, M.A.; Bin Mahbub, Z.; Islam, K.R.; Khan, M.S.; Iqbal, A.; Al Emadi, N.; et al. Can AI Help in Screening Viral and COVID-19 Pneumonia? IEEE Access 2020, 8, 132665–132676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, Z.; Islam, M.; Asraf, A. A combined deep CNN-LSTM network for the detection of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) using X-ray images. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 20, 100412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, U.; Dong, X.; Li, X.; Obiomon, P.; Qian, L. Effective COVID-19 Screening using Chest Radiography Images via Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Multimedia Computing, Networking and Applications (MCNA), Valencia, Spain, 19–22 October 2020; pp. 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Hafeez, A. Covid-resnet: A deep learning framework for screening of covid19 from radio-graphs. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.14395. [Google Scholar]









| Study | Method | No. of Datasets | Classes | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (%) | ||||
| Pham, Tuan [1] | AlexNet, GoogleNet, SqueezeNet | 3 | Two classes | AlexNet 99.14 | AlexNet 98.44 | AlexNet 99.9 |
| GoogleNet 99.70 | GoogleNet 100 | GoogleNet 99.9 | ||||
| SqueezeNet 99.8 | SqueezeNet 100 | SqueezeNet 99.9 | ||||
| Three classes | AlexNet 96.46 | AlexNet 97.35 | AlexNet 96 | |||
| GoogleNet 96.25 | GoogleNet 97.8 | GoogleNet 95.43 | ||||
| SqueezeNet 96.20 | SqueezeNet 98.1 | SqueezeNet 95.35 | ||||
| Asif Iqbal et al. [10] | CoroNet | 2 | Two classes | 99 | 98.6 | - |
| Three classes | 89.6 | 97.5 | - | |||
| Waheed Abdul et al. [12] | CovidGAN | 3 | Two classes | 95 | 90 | 97 |
| Ibrahim Abdullahi et al. [13] | AlexNet | 1 | Two classes | 99.16 | 97.44 | 100 |
| Three classes | 95 | 91.3 | 84.78 | |||
| Kusakunniran et al. [14] | ResNet-101 | 5 | Two classes | 97 | 98 | 98 |
| This study | VGG16 | 3 | Two classes | 99.76 | 100 | 99.68 |
| Three classes | 97.5 | 97.58 | 98.48 |
| Symbol | Database | Normal | COVID-19 | Pneumonia | Lung Opacity | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Db1 | COVID-19 Radiography | 10,192 images | 3616 images | 1345 images | 6012 images | 21,165 images |
| Db2 | COVID-19 + PNEUMONIA + NORMAL Chest X-ray Images | 1802 images | 1626 images | 1800 images | - | 5226 images |
| Db3 | Chest X-ray (COVID-19 & Pneumonia) | 1583 images | 576 images | 4273 images | - | 6432 images |
| Database | Classes | Train | Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Db1 | COVID-19 | 2616 | 824 |
| Normal | 7192 | 1452 | |
| Pneumonia | 945 | 400 | |
| Db2 | COVID-19 | 1140 | 486 |
| Normal | 1262 | 540 | |
| Pneumonia | 1260 | 540 | |
| Db3 | COVID-19 | 460 | 116 |
| Normal | 1266 | 317 | |
| Pneumonia | 3418 | 853 |
| Layer (Type) | Output Shape | Param |
|---|---|---|
| conv2d_10 | (None, 150, 150, 128) | 3584 |
| batch normalization | (None, 150, 150, 128) | 512 |
| conv2d_11 | (None, 150, 150, 128) | 147,584 |
| batch normalization | (None, 150, 150, 128) | 512 |
| max_pooling2d | (None, 75, 75, 128) | 0 |
| dropout_6 | (None, 75, 75, 128) | 0 |
| conv2d_12 | (None, 75, 75, 256) | 295,168 |
| batch normalization | (None, 75, 75, 256) | 1024 |
| conv2d_13 | (None, 75, 75, 256) | 590,080 |
| batch normalization | (None, 75, 75, 256) | 1024 |
| max_pooling2d_6 | (None, 37, 37, 256) | 0 |
| dropout_7 | (None, 37, 37, 256) | 0 |
| conv2d_14 | (None, 37, 37, 512) | 1,180,160 |
| batch normalization | (None, 37, 37, 512) | 2048 |
| conv2d_15 | (None, 37, 37, 512) | 2,359,808 |
| batch normalization | (None, 37, 37, 512) | 2048 |
| max_pooling2d_7 | (None, 18, 18, 512) | 0 |
| dropout_8 | (None, 18, 18, 512) | 0 |
| conv2d_16 | (None, 18, 18, 512) | 2,359,808 |
| batch normalization | (None, 18, 18, 512) | 2048 |
| conv2d_17 | (None, 18, 18, 512) | 2,359,808 |
| batch normalization | (None, 18, 18, 512) | 2048 |
| max_pooling2d_8 | (None, 9, 9, 512) | 0 |
| dropout_9 | (None, 9, 9, 512) | 0 |
| conv2d_18 | (None, 9, 9, 1024) | 4,719,616 |
| batch normalization | (None, 9, 9, 1024) | 4096 |
| conv2d_19 | (None, 9, 9, 1024) | 9,438,208 |
| batch normalization | (None, 9, 9, 1024) | 4096 |
| max_pooling2d_9 | (None, 4, 4, 1024) | 0 |
| dropout_10 | (None, 4, 4, 1024) | 0 |
| flatten_1 (Flatten) | (None, 16,384) | 0 |
| dense_4 (Dense) | (None, 1024) | 16,778,240 |
| dense_5 (Dense) | (None, 512) | 524,800 |
| dense_6 (Dense) | (None, 256) | 131,328 |
| dropout_11 (Dropout) | (None, 256) | 0 |
| dense_7 (Dense) | (None, 3) | 771 |
| Total params: 40,908,419 | ||
| Trainable params: 40,898,691 | ||
| Non-trainable params: 9728 | ||
| Experimental Parameters | Setting |
|---|---|
| Image size | 100 × 100 × 3 |
| Batch size | 8 |
| Epoch | 100 |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| momentum | 0.9 |
| Learning rate (LR) | 0.001 |
| Loss | Binary = binary cross entropy Multiple = Categorical cross entropy |
| Validation split | 0.2 |
| Dataset | Model | Classes | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB1 | VGG16 | Binary | 97 | 90.85 | 98.3 |
| Multi | 95.14 | 93.60 | 94.76 | ||
| DB2 | VGG16 | Binary | 98.73 | 98.18 | 99.10 |
| Multi | 97.50 | 97.58 | 98.48 | ||
| Db3 | VGG16 | Binary | 99.76 | 100 | 99.68 |
| Multi | 96.50 | 96.30 | 97.30 |
| Model | Model | Classes | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB1 | VGG16 | Normal | 98% | 98% | 98% |
| COVID | 94% | 91% | 92% | ||
| DB2 | VGG16 | Normal | 98% | 99% | 99% |
| COVID | 99% | 98% | 98% | ||
| DB3 | VGG16 | Normal | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| COVID | 99% | 100% | 100% |
| Study | Method | Classes | Acc. (%) | COVIDacc. (%) | Sensitive (%) | Specificity (%) | Total Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Ouchicha, 2020) [29] | CVDNet | 2 | 96.69 | 97.2 | - | - | 2905 |
| (Chowdhury, 2020) [30] | DenseNet201 | 2 | 99.70 | 99.3 | 99.70 | 99.55 | 3487 |
| (Yadav, 2020) [28] | VGG16 | 2 | 99.35 | 98.41 | 99.5 | 98.41 | 15,000 |
| This study | VGG16 | 2 | 99.76 | 100 | 100 | 99.68 | 6432 |
| (Islam, 2020) [31] | CNN-LSTM | 3 | 99.4 | 99.2 | 99.3 | 99.2 | 4575 |
| (Chowdhury, 2020) [30] | DenseNet201 | 3 | 97.74 | 96.7 | 96.61 | 98.31 | 3487 |
| (Victor, 2020) [32] | CNN, ResNet | 3 | 87.99 | - | - | - | 13,800 |
| (Yadav, 2020) [28] | VGG16 | 3 | 98.84 | 96.82 | 98.71 | 99 | 15,000 |
| (Khan, 2020) [10] | CoroNet | 3 | 95 | - | 97.5 | 96.9 | 2424 |
| This study | VGG16 | 3 | 97.5 | 98.14 | 97.58 | 98.48 | 15,153 |
| (Farooq, 2020) [33] | ResNet50 | 4 | 96.2 | 100 | - | - | 5941 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramadhan, A.A.; Baykara, M. A Novel Approach to Detect COVID-19: Enhanced Deep Learning Models with Convolutional Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9325. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189325
Ramadhan AA, Baykara M. A Novel Approach to Detect COVID-19: Enhanced Deep Learning Models with Convolutional Neural Networks. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(18):9325. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189325
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamadhan, Awf A., and Muhammet Baykara. 2022. "A Novel Approach to Detect COVID-19: Enhanced Deep Learning Models with Convolutional Neural Networks" Applied Sciences 12, no. 18: 9325. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189325
APA StyleRamadhan, A. A., & Baykara, M. (2022). A Novel Approach to Detect COVID-19: Enhanced Deep Learning Models with Convolutional Neural Networks. Applied Sciences, 12(18), 9325. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189325







