Featured Application
A safe and scalable method is reported for the synthesis of rare earth doped lithium fluorides that allows for much larger bulk syntheses of these materials that would be challenging when using more hazardous reagents.
Abstract
Rare earth doped lithium fluorides are a class of materials with a wide variety of optical applications, but the hazardous reagents used in their synthesis often restrict the amount of product that can be created at one time. In this work, 10%Yb3+:LiLuF4 (Yb:LLF) crystals have been synthesized through a safe and scalable polyethylene glycol (PEG)-assisted hydrothermal method. A combination of X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and photoluminescence (PL) measurements were used to characterize the obtained materials. The influence of reaction temperature, time, fluoride source, and precursor amount on the shape and size of the Yb:LLF crystals are also discussed. Calibrated PL spectra of Yb3+ ions show laser cooling to more than 15 K below room temperature in air and 5 K in deionized water under 1020 nm diode laser excitation measured at a laser power of 50 mW.
1. Introduction
Rare earth lithium fluorides (RELiF4) with a scheelite structure are widely used in various fields such as theranostics [1], long-term in vivo bioimaging [2,3], photothermal therapy [4,5,6], ratiometric temperature sensing [7], transparent volumetric displays [8,9], multi-level anti-counterfeiting applications [10], photocatalysis [11], photovoltaics [12], scintillating materials [13], and refrigeration through laser radiation [14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. These materials also show promise for solid-state laser applications [21].
Recently, it has been demonstrated that low-cost, low-temperature hydrothermal processing can be used to grow YLiF4 [17], NaYF4 [22], KLuF4 [23], and LiLuF4 [24] crystals that are capable of solid-state laser refrigeration. However, the use of ammonium bifluoride inhibits the production of large amounts of these materials due to the danger of hydrofluoric acid formation in solution, which can then form gaseous hydrogen fluoride during the autoclave portion of the synthesis. Using polyethylene glycol (PEG) in place of NH4HF2 helps improve the solubility of lithium ions while also reducing potential hazards posed by the use of ammonium bifluoride and, as a result, makes this method safer and more scalable.
Due to the complexity of hydrothermal systems, various internal and external factors can fundamentally affect the purity, crystal structure, morphology, and physical properties of the obtained materials. For example, it has been shown that LiOH concentration is the key factor responsible for the shape evolution and phase control of RELiF4 nanocrystals at selected temperatures [25]. It has also been shown that the use of EDTA as a chelating agent in the reaction is essential to obtain highly crystalline and smooth Er3+:LiYbF4 microparticles [26]. Most importantly, these hydrothermal materials show more efficient luminescence with further heat treatment. Higher reaction temperatures and prolonged reaction times have been shown to facilitate the formation of more stable LiYbF4 microcrystals [27]. The substitution of Li+ in Na(1--x)LixReF4 not only causes a phase transition but also induces variation in the morphology, size, and luminescent properties of the final microcrystals [28]. Taking these observations into consideration, parameters other than the fluoride source, such as temperature, precursor amount, and reaction length, must be carefully controlled and examined to determine their effect on the final crystal.
In this work, we report a method for PEG-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of Yb3+-doped lithium lutetium fluoride (Yb:LLF) microcrystals and discuss the influence of various factors on the growth of the Yb:LLF microcrystals and their ability to undergo laser refrigeration.
2. Materials and Methods
Synthesis of 10%Yb3+:LiLuF4. The reagents used in this synthesis are identical to those used in a similar synthesis in previous work [24].
The following synthesis (Figure 1) is a slight modification of previous work [17]. In contrast to the referenced procedure, yttrium nitrate (Lu(NO3)) and ytterbium nitrate (Yb(NO3)) of 99.999% purity were used as purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. The nitrate powders were dissolved in Millipore deionized (DI) water to achieve a stock concentration of the respective nitrates. Additionally, nitric acid (HNO3) and ammonium bifluoride (NH4HF2) were not used in this synthesis. Lithium fluoride (LiF) and polyethylene glycol (PEG, Mn = 4000) were used directly without any purification. For this synthesis, 28.8 mL of 0.5 M Lu(NO3)3 and 3.2 mL of 0.5 M Yb(NO3)3 were mixed with 16 mmol of EDTA and 30 mmol of LiOH in 20 mL of Millipore DI water at 50 °C while stirring for 30 min to form solution A. Subsequently, 64 mmol of LiF were dissolved in 30 mL of 10 wt.% PEG Millipore DI water solution at room temperature while stirring for 1 h to form solution B. Solutions A and B were mixed together while stirring for 30 min to form a homogeneous white suspension, which was transferred to a 2-L Teflon-lined autoclave and heated to 180 °C for 24 h. After the autoclave cooled to room temperature, the Yb:LLF particles were recovered by centrifuging and washing with ethanol and Millipore DI water three times. The final white powder was obtained by calcining at 300 °C for 2 h in air, which was determined to be the ideal temperature for calcination via XRD and SEM (Figures S1 and S2). The theoretical yield was 4.120 g of Yb:LLF. The actual yield was 2.0 g, for a yield percentage of 48.5%
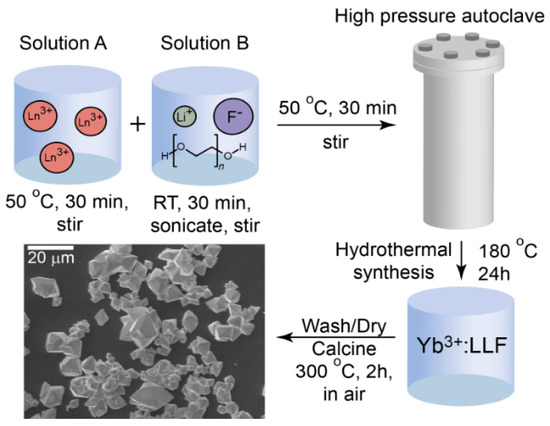
Figure 1.
Schematic of the base PEG-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of Yb:LLF microcrystals.
Multiple variations of this base synthesis were performed to examine the effects of different variables on the crystals. In some experiments, the reagent amounts were reduced by a factor of 4. Other syntheses were performed at temperatures other than 180 °C, including 100, 120, 130, 200, and 220 °C for 24 h. The effect of time on the synthesis was also examined, with data from some syntheses collected at 3 h, 5 h, and 14 h, as well as the standard 24 h time point.
Characterization. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images were taken on an FEI Sirion XL30 SEM at an accelerating voltage of 15 keV. Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns were obtained on the Bruker F8 Focus Powder XRD with Cu K-α (40 kV, 40 mA) irradiation (λ = 0.154 nm). The 2θ angle of the XRD data was 16° to 93°, and the scanning rate was 0.36° s−1. PL spectra were registered following a method outlined in previous work [24].
When collecting photoluminescence spectra, Yb:LLF crystals were attached to optical fibers for the sake of thermal isolation. The crystals were then optically excited in air using a 1020 nm diode laser with irradiances ranging from 0.08 to 1 MW/cm2. Temperatures were calibrated for individual Yb:LLF grains using an optical cryostat. Temperatures were scanned from 300 to 400 K with a low laser irradiance of 0.04 MW/cm2 to minimize any photothermal effects caused by optical excitation. Cold Brownian motion data were collected using a home-built optical trapping setup and following a procedure from previous work [17].
3. Results
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of two different Yb:LLF crystals are shown in Figure 2a. In the first case (Figure 2a), the Yb:LLF crystals have been synthesized through an NH4HF2-assisted hydrothermal method [17,24]. They have a tetragonal bipyramidal morphology with a dominating (101) surface. The Yb:LLF crystals synthesized through the PEG-assisted hydrothermal method (Figure 2b) have two dominating surfaces: (101) and (112), respectively, which was predicted in Littleford’s works [29,30] for a yttrium lithium fluoride (YLF) crystal. Figure S3 also shows the room-temperature FTIR spectra of the Yb:LLF crystals obtained at different conditions. The weak peaks in the FTIR spectra can be attributed to atmospheric water and carbon dioxide adsorbed on the optical elements of the spectrometer and on the samples, and the absence of strong bands in the range of 1000–4000 cm−1 implies that there is no residual PEG and minimal oxyfluorides on the surface of the crystals regardless of synthesis method.
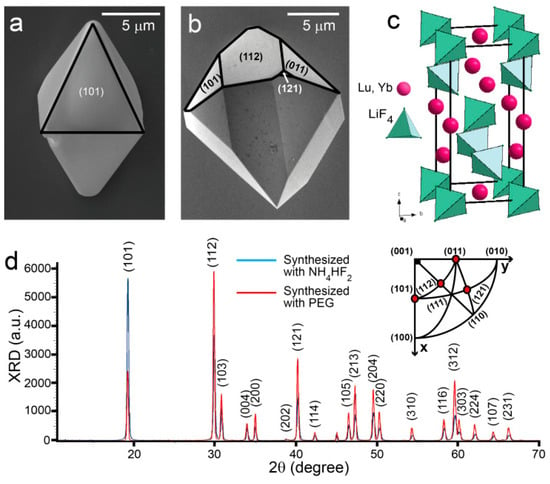
Figure 2.
Characterization of Yb:LLF crystals. Scanning electron microscope images of faceted Yb:LLF particles synthesized with NH4HF2- (a) and PEG-assisted (b) hydrothermal syntheses. Scale bar = 5 μm. Types of facets are indicated in parentheses. (c) Schematic of a Scheelite crystal structure of Yb:LLF with I41/a space group symmetry. (d) Powder XRD pattern of Yb:LLF crystals following NH4HF2- (blue) and PEG-assisted (red) hydrothermal synthesis, indicating a Scheelite crystal structure. Inset: stereographic projections of crystal facets related to the most intensive XRD peaks.
X-ray diffraction analysis confirms that crystals from both syntheses adopt a tetragonal scheelite structure (ICDD number 04-002-3255) with space group I41/a (Figure 2c). Comparison of the two X-ray diffraction spectra of Yb:LLF (Figure 2c) corresponding to NH4HF2- (blue) and PEG-assisted (red) syntheses gives different ratios of I(101):I(112), which correlates with the morphology of the Yb:LLF crystals. Stereographic projections of crystal facets related to the most intensive XRD peaks are shown in Figure 2d (inset) as red circles.
Crystals grown using the base PEG-assisted synthesis described previously were subjected to photoluminescence (PL) measurements to examine the cooling abilities of the crystals grown via this new method. Crystals grown via the base synthesis method were used due to the method’s ability to consistently produce pure single crystals with only one phase. This avoids issues caused by parasitic energy transfer or luminescence quenching due to impurities, maximizing the laser cooling power of the crystals. The PL spectra obtained at different 1020 nm laser powers are shown in Figure 3a. Changes in the ratio of the integrated emission bands R1 and R2 (and their respective intensities in a.u., I1, and I2), which stem from transitions between energy states E6-E1 and E5-E2,3, respectively, are directly correlated to a change in the crystal temperature through a Boltzmann distribution (Figure 3b). Ratiometric spectral measurements were used to calibrate temperature in which ln(I1/I2) varies linearly with 1/T (calibration shown in Figure S4). The decrease in the logarithmic ratio of I1 to I2 with increasing irradiance reflects a decrease in the internal lattice temperature of approximately 15 K below room temperature (Figure 3b). Analogous laser cooling trends (approximately 5 K below room temperature) were observed for individual Yb:LLF grains optically trapped in water (Figure 3c). These values are comparable to cooling temperatures Yb:LLF crystals obtained via the NH4HF2-assisted synthesis. [24] Additionally, these crystals exhibit much greater cooling capability than 5%-Yb doped LLF crystals grown via the Czochralski process but do not cool to the cryogenic temperatures reached by Czochralski-grown Yb:YLF crystals [15,31].
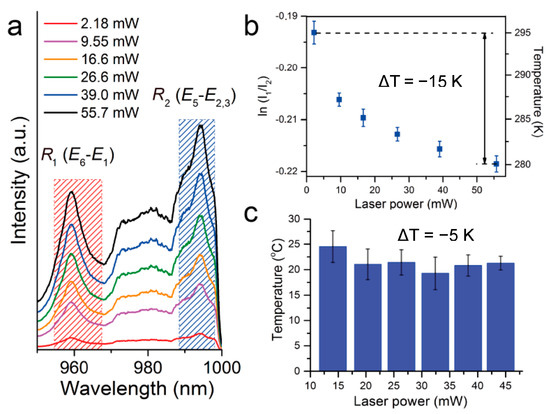
Figure 3.
Laser cooling of Yb:LLF crystals. (a) PL spectra of the Yb:LLF crystal on a SiO2 optical fiber in air under 1020 nm diode laser excitation measured at different irradiances. (b) Cryostat calibration of PL spectra of the Yb:LLF crystal on a SiO2 optical fiber in air under 1020 nm diode laser excitation measured at different irradiances. (c) Laser refrigeration of the Yb:LLF crystal in deionized water measured via cold Brownian motion analysis at different irradiances.
Reducing the concentration of reagents by a factor of four leads to the synthesis of significantly smaller crystals. The low concentration synthesis produced crystals around 5 μm in size, whereas the standard synthesis could produce crystals as large as 20 μm. Although their size is greatly changed, the morphology of the crystals remains the same regardless of the reagent concentration. The (112) plane remains clearly visible on both sets of crystals (Figure S5).
XRD data from a range of experimental temperatures spanning from 100 °C to 200 °C are shown in Figure 4. At lower temperatures, a variety of side products can be seen in the XRD data, including LuF3 and LiLuO2. Unreacted or undissolved LiF can also be seen in many of the XRD patterns. A stable, single phase of Yb:LLF is not reached after 24 h unless the standard reaction temperature of 180 °C or above is used. Additionally, the size of the formed crystals also increases with reaction temperature, which can be seen in SEM images (Figure S6). Reaction time also plays a factor in the generation of a single, stable Yb:LLF phase. At lower time points, the XRD data shows mostly unreacted LiF and little to no evidence of the Yb:LLF crystals. After 14 h, a significant Yb:LLF phase can be seen, and only traces of LiF remain (Figure S7). SEM also shows that increasing the length of the synthesis causes the crystal facets and morphology to be more well-defined and fully formed (Figure S8).
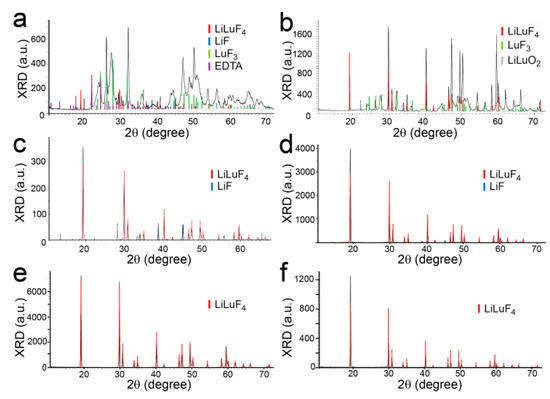
Figure 4.
Powder XRD pattern of crystals following PEG-assisted hydrothermal synthesis at: (a) 100 °C, (b) 120 °C, (c) 130 °C, (d) 150 °C, (e) 180 °C, and (f) 200 °C, for 24 h.
4. Discussion
The fluoride source and inclusion of PEG clearly affect the morphology of the Yb:LLF crystals. The (112) planes seen in all crystals synthesized via the PEG-assisted method indicate that the PEG lowers the surface energy of that plane, changing the Wulff construction of the crystal and allowing it to form during the hydrothermal synthesis. In spite of this additional plane, the stoichiometric 1:1:4 product is formed, as confirmed by XRD. This is of particular interest as other RELiF4 materials, such as NaYF4, do not form a stoichiometric phase. [32] Additionally, this extra plane does not impact the crystals’ cooling abilities, which are comparable to those shown by crystals formed using the ammonium bifluoride synthesis. It can then be concluded that this synthesis method is not only effective, but a safe and scalable alternative to the ammonium bifluoride synthesis when attempting to synthesize large amounts of Yb:LLF crystals. This synthesis generates high amounts of product while avoiding the hazards of hydrofluoric acid formation and hydrogen fluoride gas generation.
Compared to the fluoride source, the temperature and length of the reaction do not significantly impact crystal morphology but, instead, are key factors in forming a pure and highly crystalline Yb:LLF phase, as well as impacting the size of the crystals formed. The number of precursors remaining in solution at shorter time points, specifically undissolved or unreacted LiF, could be eliminated by allowing the reaction to proceed for longer times, further improving the yield of the reaction. The size of the crystals can also be controlled by the concentration of precursors in an aqueous solution. By combining the size control demonstrated by changing the reaction temperature and the size control demonstrated by the precursor concentrations, it could be possible to finely control the size of the crystals.
5. Conclusions
Yb:LLF crystals with a scheelite structure (space group I41/a) have been synthesized through a safe and scalable PEG-assisted hydrothermal approach. We show that size and morphology can be finely controlled by changing reaction conditions such as temperature, time, fluoride source, and precursor amount. The results show that higher temperature and prolonged reaction time facilitate the formation of more stable LiLuF4 crystals. The substitution of PEG for NH4HF2 changes the morphology of the product, as shown by the appearance of crystal facets (101) and (112) in the PEG-assisted crystals. The average size of the crystals can be controlled by the concentration of precursors in an aqueous solution. We demonstrate solid-state laser refrigeration of the Yb:LLF crystals using a focused near-infrared laser excitation source (λ = 1020 nm). A calibrated ratiometric Boltzmann analysis of the Yb3+ luminescence reveals laser cooling in air by more than 15 K below room temperature and in water by more than 5 K below room temperature.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app12020774/s1, Figure S1: Scanning electron microscope images of crystals following PEG-assisted hydrothermal synthesis at: (a) 100 °C (scale bar is 1 μm), (b) 120 °C (scale bar is 1 μm), (c) 130 °C (scale bar is 1 μm), (d) 180 °C (scale bar is 2 μm), (e) 200 °C (scale bar is 2 μm) and (f) 220 °C (scale bar is 5 μm), for 24 h, Figure S2: Powder XRD pattern of crystals following PEG-assisted hydrothermal synthesis at 130 °C for: (a) 3 h, (b) 5 h, (c) 14 h, (d) 24 h, Figure S3: Scanning electron microscope images of crystals following PEG-assisted hydrothermal synthesis at 130 °C for: (a) 3 h (scale bar is 1 μm), (b) 5 h (500 nm), (c) 14 h (1 μm), (d) 24 h (1 μm), Figure S4: Temperature-calibrated PL spectra of Yb3+:LLF, Figure S5: ATR-FTIR spectra of Yb3+:LLF synthesized under following conditions: (a) at 130 °C for 14 h; (b) at 150 °C for 5 h; (c) at 200 °C for 24 h; (d) at 200 °C for 72 h; (e) at 220 °C for 5 h; (f) at 220 °C for 48 h, Figure S6: Powder XRD pattern of crystals following PEG-assisted hydrothermal synthesis at 220 °C for 2 h (a) without calcination and calcination at: (b) 300 °C, (c) 500 °C, (d) 600 °C, Figure S7: Scanning electron microscope images of crystals following PEG-assisted hydrothermal synthesis at 220 °C for 2 h (a) without calcination and calcination at: (b) 300 °C, (c) 500 °C h, (d) 600 °C. Scale bar is 1 μm, Figure S8: Scanning electron microscope images of LLF crystals following PEG-assisted hydrothermal synthesis at 200 °C for 24 h. (a) RE nitrate precursor amount is 4 mmol. Scale bar is 5 μm. (b) RE nitrate precursor amount is 16 mmol. Scale bar is 20 μm.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.A.D. and P.J.P.; methodology, E.A.D. and P.J.P.; software, E.A.D., A.P. and X.X.; validation, R.E.G.; formal analysis, E.A.D., A.P. and X.X.; investigation, E.A.D., A.P., X.X. and R.E.G.; resources, P.J.P.; data curation, E.A.D., X.X., A.P. and R.E.G.; writing—original draft preparation, E.A.D.; writing—review and editing, E.A.D., A.P., X.X., R.E.G. and P.J.P.; visualization, E.A.D., A.P. and X.X.; supervision, E.A.D. and P.J.P.; project administration, E.A.D. and P.J.P.; funding acquisition, P.J.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
E.A.D., R.E.G. and P.J.P. acknowledge support from the National Science Foundation through the UW Molecular Engineering Materials Center, a Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (DMR-1719797). A.P., X.X. and P.J.P. acknowledge financial support from the MURI:MARBLe project under the auspices of the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (Award No. FA9550-16-1-0362). Part of this work was conducted at the Molecular Analysis Facility, a National Nanotech-ology Coordinated Infrastructure site at the University of Washington, which is supported in part by the National Science Foundation (grant ECC-1542101).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Mikhail Kosobokov (N.D. Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry of the Russian Academy of Sciences) for his useful recommendations for hydrothermal synthesis of the Yb:LLF crystals.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Skripka, A.; Karabanovas, V.; Jarockyte, G.; Marin, R.; Tam, V.; Cerruti, M.; Rotomskis, R.; Vetrone, F. Decoupling theranostics with rare earth doped nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, S.; Tu, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, H.; Li, R.; Ma, E.; Huang, M.; Chen, X. Lanthanide-doped LiLuF4 upconversion nanoprobes for the detection of disease biomarkers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1252–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.-S.; Zhang, P.-Z.; Sun, L.-D.; Shi, S.; Chen, N.-X.; Dong, H.; Zheng, X.-Y.; Li, L.-M.; Yan, C.-H. Ultralow-power near-infrared excited neodymium-doped nanoparticles for long-term in vivo bioimaging. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 4660–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboi, T.; Shimamura, K. Temperature sensitive near-infrared luminescence of Er3+ ions in LiYF4. Phys. Status Solidi C 2011, 8, 2833–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skripka, A.; Morinvil, A.; Matulionyte, M.; Cheng, T.; Vetrone, F. Advancing neodymium single-band nanothermometry. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 11322–11330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, M.S.; Rojas-Gutierrez, P.A.; Busko, D.; Howard, I.A.; Frenzel, F.; Würth, C.; Resch-Genger, U.; Richards, B.S.; Turshatov, A.; Capobianco, J.A.; et al. Absolute upconversion quantum yields of blue-emitting LiYF4:Yb3+, Tm3+ upconverting nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 22556–22562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, P.; Zheng, W.; Tu, D.; Shang, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, R.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X. Unraveling the electronic structures of neodymium in LiLuF4 nanocrystals for ratiometric temperature sensing. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1802282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.; Kyhm, J.-H.; Hong, A.-R.; Song, J.D.; Lee, K.; Ko, H.; Jang, H.S. Multicolor tunable upconversion luminescence from sensitized seed-mediated grown LiGdF4:Yb, Tm-based core/triple-shell nanophosphors for transparent displays. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 8457–8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Won, Y.-H.; Jang, H.S. A strategy to enhance Eu3+ emission from LiYF4:Eu nanophosphors and green-to-orange multicolor tunable, transparent nanophosphor-polymer composites. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, W.; Wang, R.; Han, Q.; Dong, J.; Yan, L.; Zheng, H. Tuning red upconversion emission in single LiYF4:Yb3+/Ho3+ microparticle. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 2349–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Marin, R.; Skripka, A.; Vetrone, F. Small and bright lithium-based upconverting nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12890–12899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, W.; Song, H.; Chen, C.; Xia, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Cui, S.; Dai, Q.; Zhang, J. Highly efficient LiYF4:Yb3+, Er3+ upconversion single crystal under solar cell spectrum excitation and photovoltaic application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 9071–9079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, V.; Naccache, R.; Vetrone, F.; Capobianco, J.A. Sensitized Ce3+ and Gd3+ ultraviolet emissions by Tm3+ in colloidal LiYF4 nanocrystals. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2009, 15, 9660–9663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seletskiy, D.V.; Melgaard, S.D.; Bigotta, S.; Di Lieto, A.; Tonelli, M.; Sheik-Bahae, M. Laser cooling of solids to cryogenic temperatures. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgaard, S.D.; Seletskiy, D.V.; Di Lieto, A.; Tonelli, M.; Sheik-Bahae, M. Optical refrigeration to 119 K, below national institute of standards and technology cryogenic temperature. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahman, A.A.; Barker, P. Laser refrigeration, alignment and rotation of levitated Yb3+:YLF nanocrystals. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roder, P.B.; Smith, B.E.; Zhou, X.; Crane, M.J.; Pauzauskie, P.J. Laser refrigeration of hydrothermal nanocrystals in physiological media. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15024–15029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, X.; Pant, A.; Davis, E.J.; Pauzauskie, P.J. Design of a radiation-balanced fiber laser via optically active composite cladding materials. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2019, 36, 3307–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, A.; Xia, X.; Davis, E.J.; Pauzauskie, P.J. Solid-state laser refrigeration of a composite semiconductor Yb:YLiF4 optomechanical resonator. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Pant, A.; Ganas, A.S.; Jelezko, F.; Pauzauskie, P.J. Quantum point defects for solid-state laser refrigeration. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 1905406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasyukevich, A.S.; Mandrik, A.V.; Kuleshov, N.V.; Gordeev, E.Y.; Korableva, S.L.; Naumov, A.K.; Semashko, V.V.; Popov, P.A. Spectral kinetic properties of Yb3+:Na4Y6F22 and Yb3+:LiLuF4 crystals. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2007, 74, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Smith, B.E.; Roder, P.B.; Pauzauskie, P.J. Laser refrigeration of ytterbium-doped sodium–yttrium–fluoride nanowires. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8658–8662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Pant, A.; Zhou, X.; Dobretsova, E.A.; Bard, A.B.; Lim, M.B.; Roh, J.Y.D.; Gamelin, D.R.; Pauzauskie, P.J. Hydrothermal synthesis and solid-state laser refrigeration of ytterbium-doped potassium-lutetium-fluoride (KLF) microcrystals. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 4417–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobretsova, E.A.; Xia, X.; Pant, A.; Lim, M.B.; De Siena, M.C.; Boldyrev, K.N.; Molchanova, A.D.; Novikova, N.N.; Klimin, S.A.; Popova, M.N. Hydrothermal synthesis of Yb3+: LuLiF4 microcrystals and laser refrigeration of Yb3+: LuLiF4/silicon-nitride composite nanostructures. Laser Photonics Rev. 2021, 15, 2100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yan, B. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of LiREF4 (RE = Y, Tb−Lu) nanocrystals and their core−shell nanostructures. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 6834–6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Huang, W.; Ni, Y.; Xu, Z. Hydrothermal synthesis and luminescence properties of octahedral LiYbF4:Er3+ microcrystals. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Lu, C.; Jiang, C.; Jin, J.; Ding, M.; Ni, Y.; Xu, Z. Rare earth doped LiYbF4 phosphors with controlled morphologies: Hydrothermal synthesis and luminescent properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 2012, 47, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Ning, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.; Lai, X.; Zhong, C.; Wang, C.; Bi, J.; et al. Na(1-x)Lix(Gd0.39Y0.39Yb0.2Er0.02)f4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) solid solution microcrystals: Li/Na ratio-induced transition of crystalline phase and morphology and their enhanced upconversion emission. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 6581–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littleford, T.E.; Jackson, R.A.; Read, M.S.D. An atomistic simulation study of the effect of dopants on the morphology of YLiF4. Phys. Status Solidi C 2013, 10, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littleford, T.E.; Jackson, R.A.; Read, M.S. An atomistic surface simulation study predicting morphologies and segregation in yttrium lithium fluoride. Surf. Sci. 2012, 606, 1550–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzurra, V.; Giovanni, C.; Alberto Di, L.; Arlete, C.; Hans, P.J.; Mauro, T. Investigation of yb-doped LiLuF4 single crystals for optical cooling. Opt. Eng. 2016, 56, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, P.P.; Aleksandrov, V.B.; Bondareva, O.S.; Buchinskaya, I.I.; Val’Kovskii, M.D.; Sobolev, B.P. Concentration dependences of the unit-cell parameters of nonstoichiometric fluorite-type Na0.5−xR0.5+xF2+2x phases (R = rare-earth elements). Crystallogr. Rep. 2001, 46, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).