Spatial Heterogeneity of Excess Lung Fluid in Cystic Fibrosis: Generalized, Localized Diffuse, and Localized Presentations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subject Group
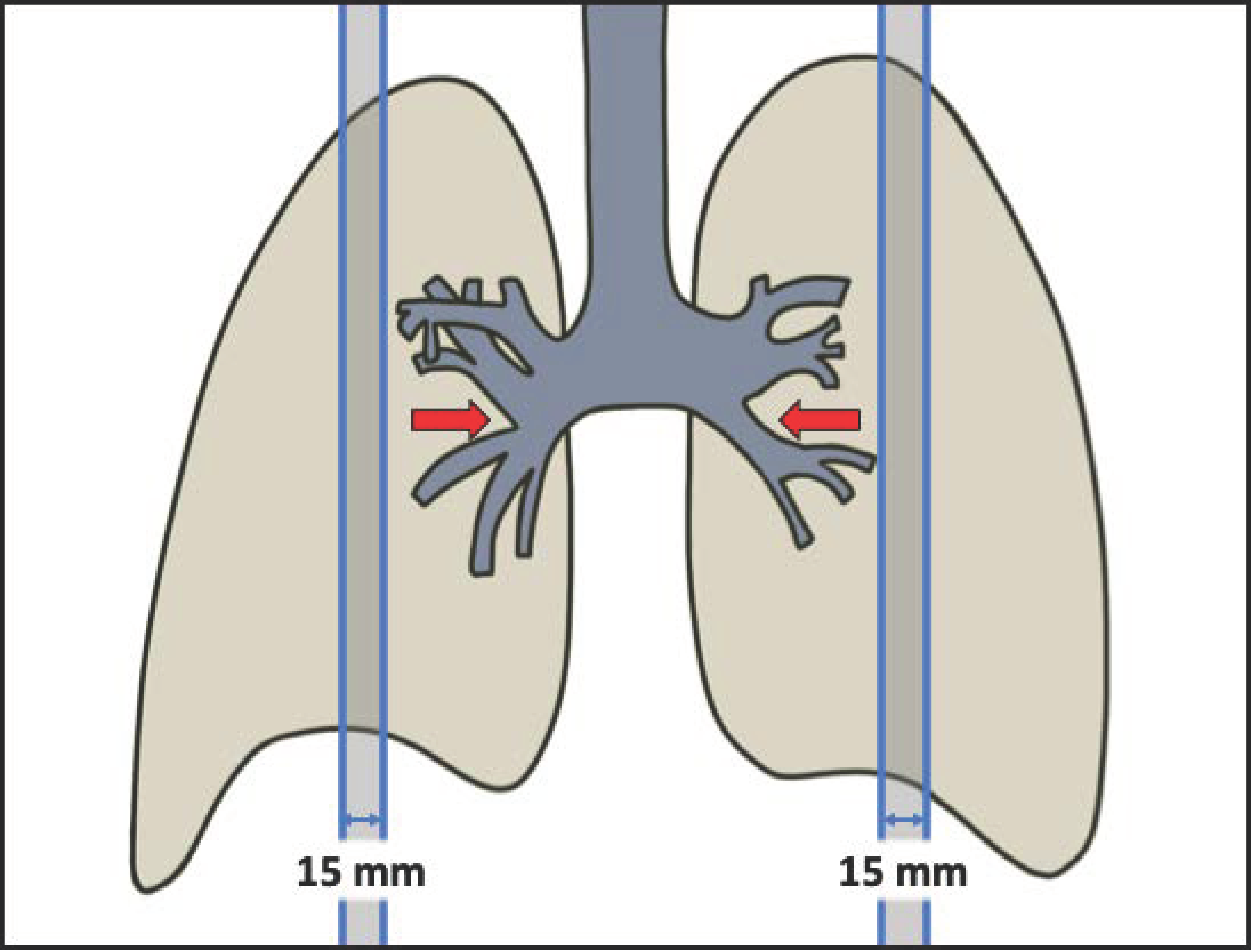
2.2. Image Acquisition
2.3. MR Tissue Density Data
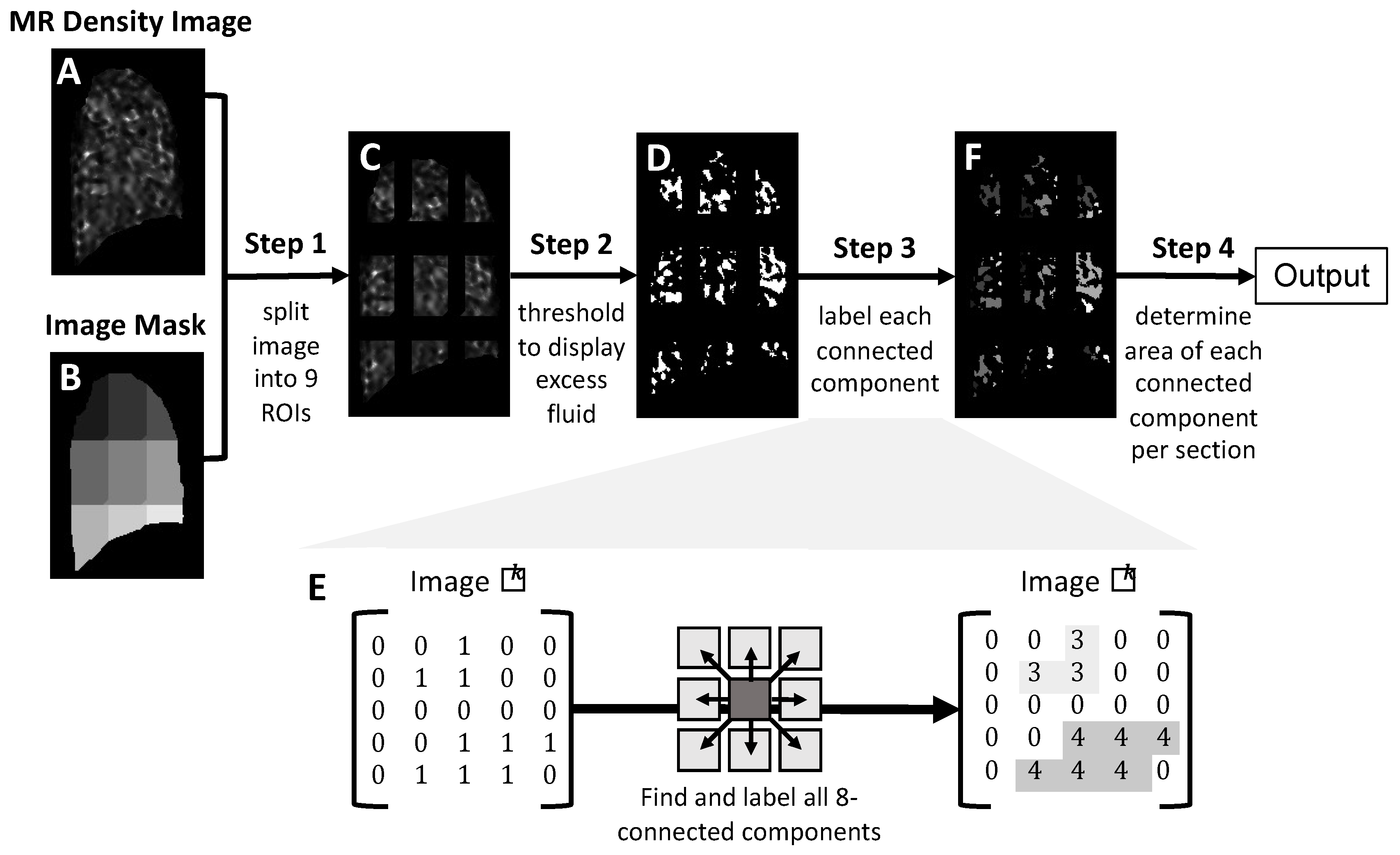
2.4. Image Processing and Analysis for Identification of Excess Lung Fluid in MR Lung Density Images
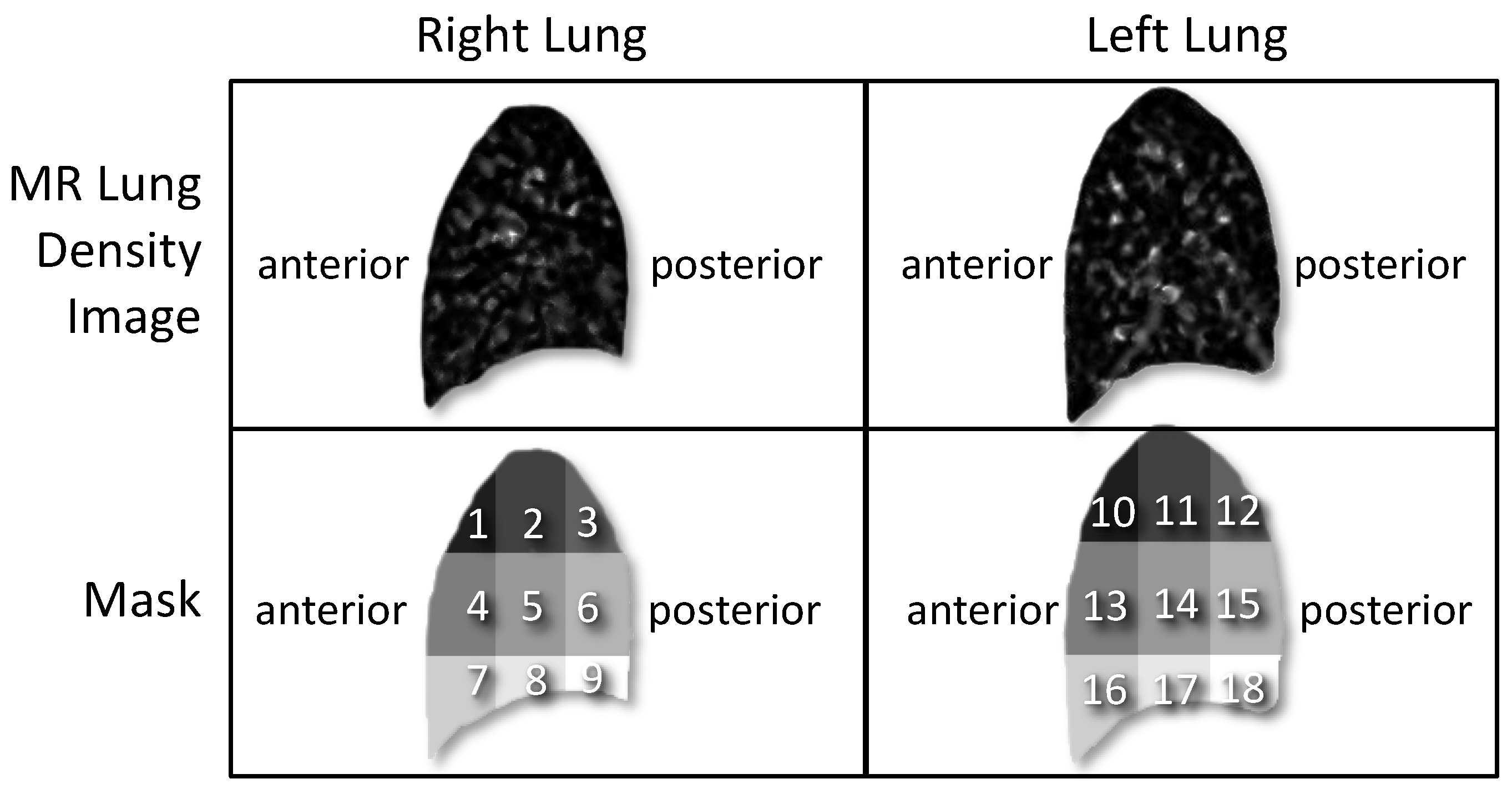
2.4.1. Division of MR Lung Density Image into Nine Regions of Interest (Step 1)
2.4.2. Images Are Thresholded to Identify Excess Lung Fluid (Step 2)
2.4.3. Identification of Connected Components (Step 3)
2.4.4. Quantification of Excess Fluid Collections (Step 4)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
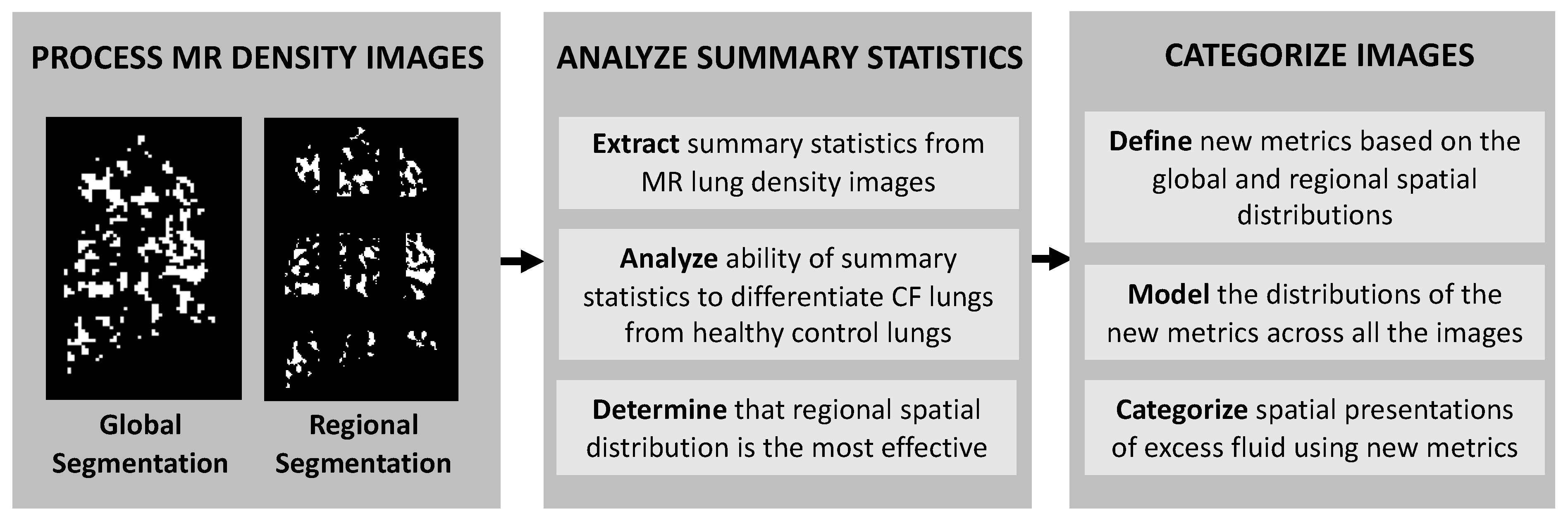
3. Results
3.1. Summary Statistics of Excess Fluid in MR Lung Density Image: CF vs. Control
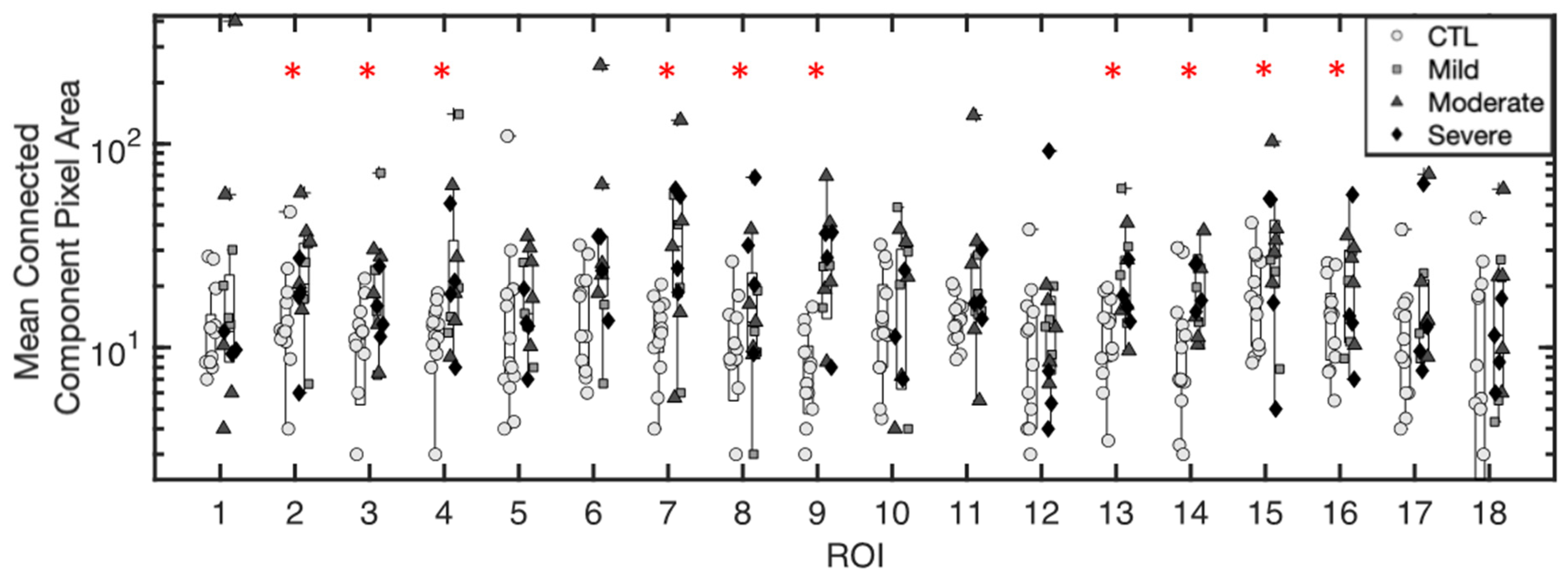
3.1.1. Mean Pixel Area of Excess Fluid Collections
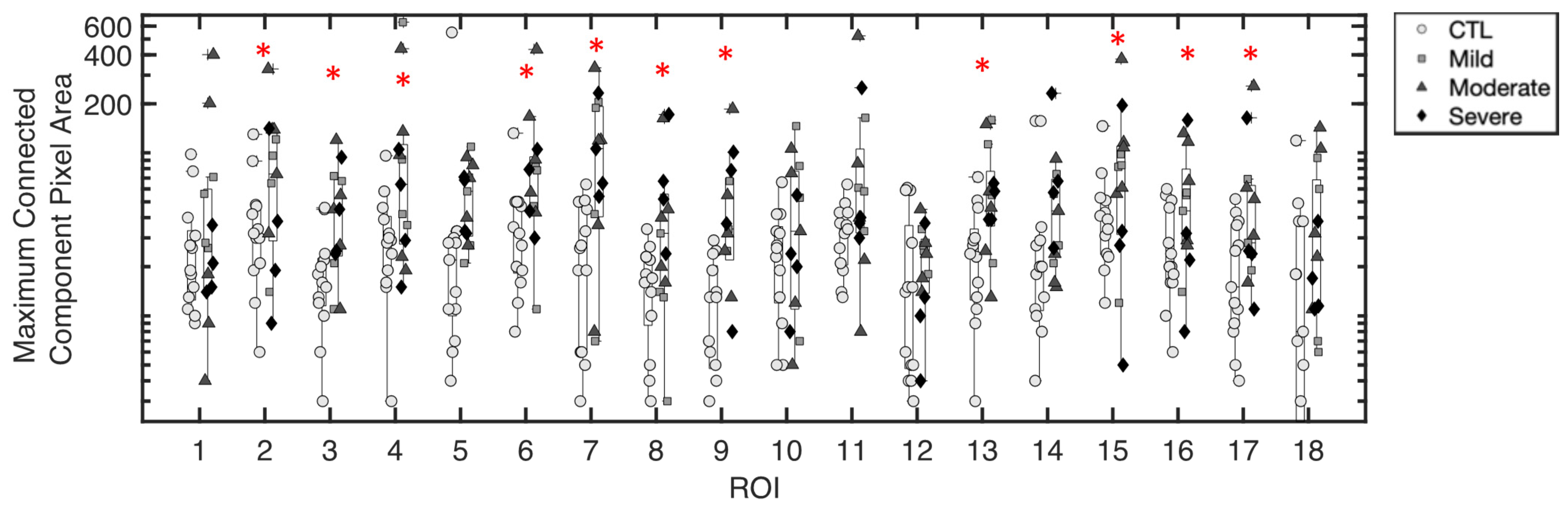
3.1.2. Maximum Pixel Area of Excess Fluid Collections
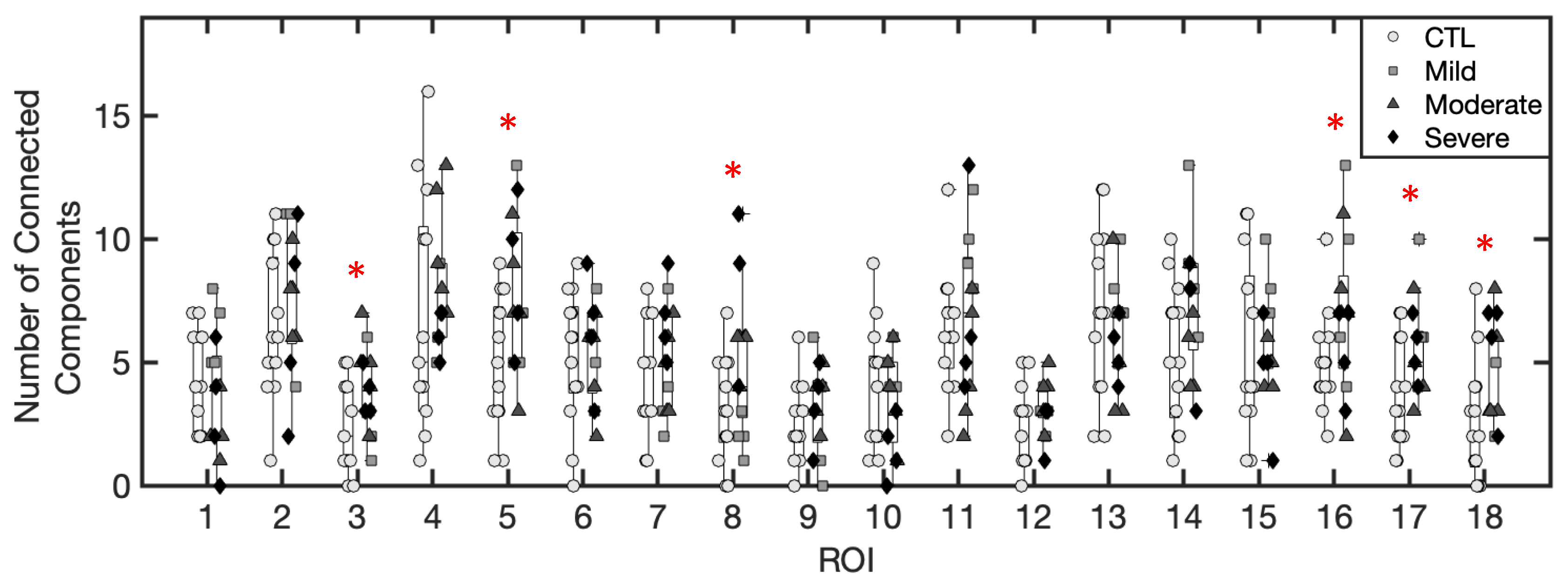
3.1.3. Number of Excess Fluid Collections
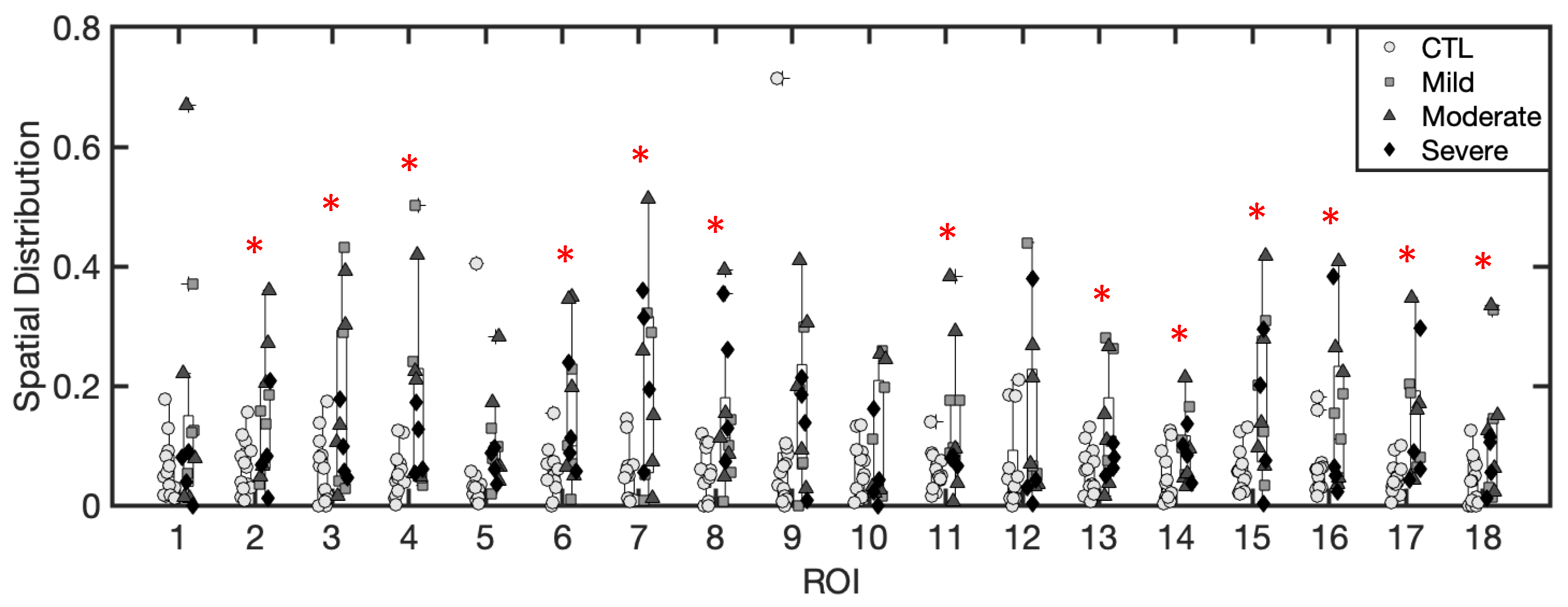
3.1.4. Spatial Distribution of Excess Fluid Collections
3.1.5. Inference of Summary Statistic Importance
3.2. Regional and Global Spatial Distribution of Excess Lung Fluid
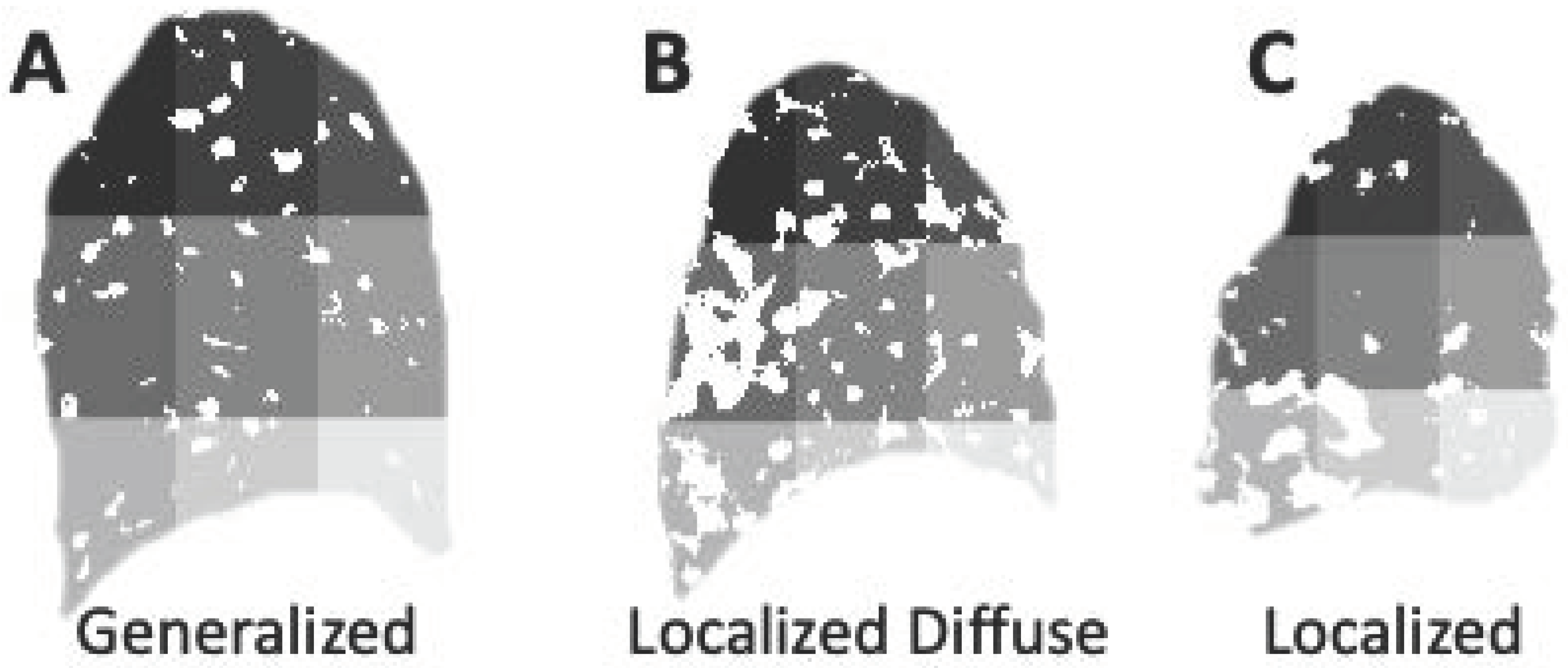
3.3. Categories of the Spatial Presentation of Excess Lung Fluid: Generalized, Localized Diffuse and Localized Presentations
3.3.1. Generalized Spatial Presentation of Excess Lung Fluid
3.3.2. Localized Diffuse Spatial Presentation of Excess Lung Fluid
3.3.3. Localized Spatial Presentation of Excess Lung Fluid
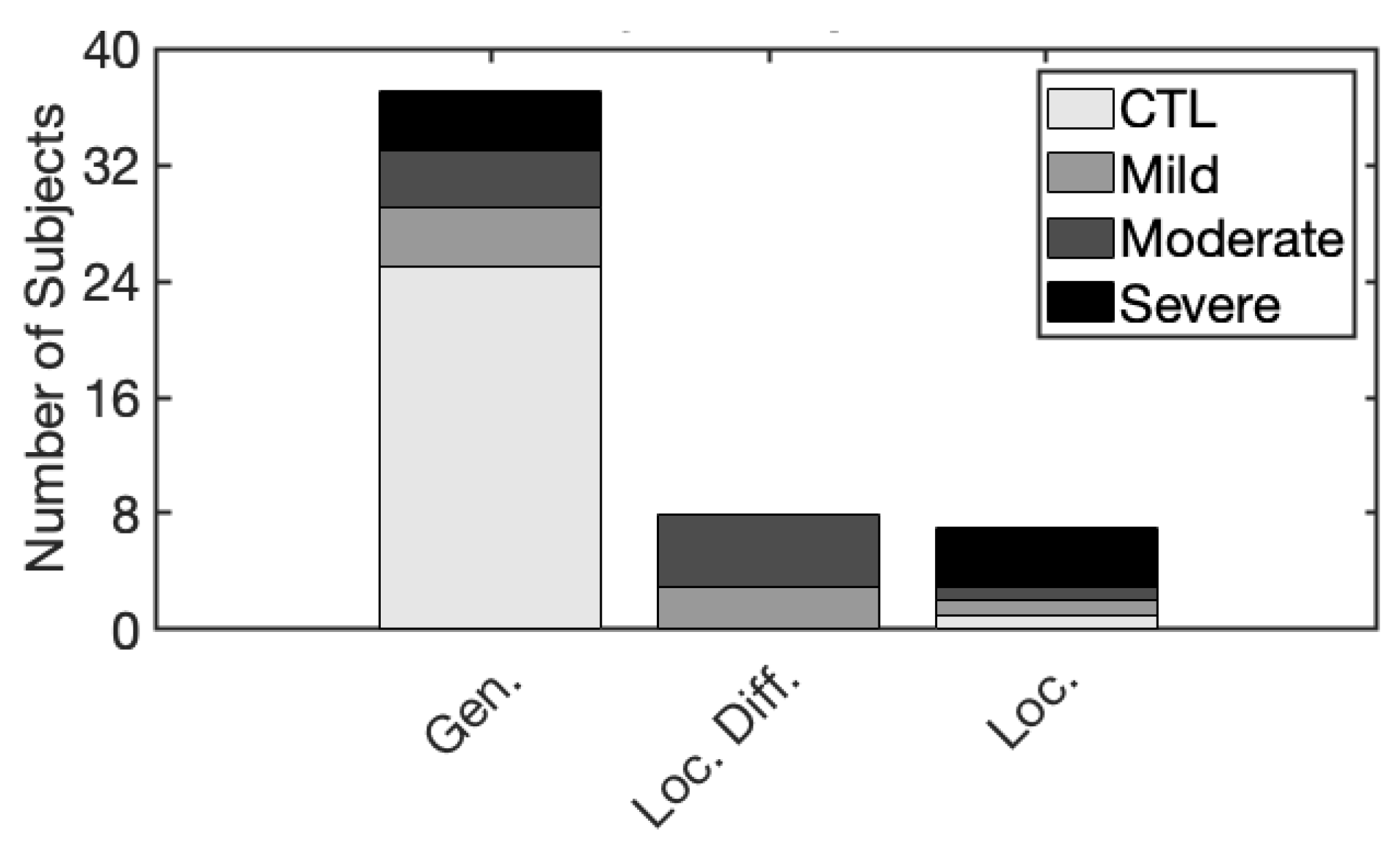
3.3.4. Summary of Spatial Presentation Groups
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramsey, B.W.; Downey, G.P.; Goss, C.H. Update in Cystic Fibrosis 2018. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinton, P.M. Role of epithelial HCO3− transport in mucin secretion: Lessons from cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2010, 299, C1222–C1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chmiel, J.F.; Davis, P.B. State of the art: Why do the lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis become infected and why can’t they clear the infection? Respir. Res. 2003, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horsley, A.; Siddiqui, S. Putting lung function and physiology into perspective: Cystic fibrosis in adults. Respirology 2015, 20, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, A.S.; Kosorok, M.R.; Li, Z.; Broderick, L.S.; Foster, J.L.; Laxova, A.; Bandla, H.; Farrell, P.M. Reproducibility of a scoring system for computed tomography scanning in cystic fibrosis. J. Thorac. Imaging 2006, 21, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutting, G.R. Cystic fibrosis genetics: From molecular understanding to clinical application. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collaco, J.M.; Blackman, S.M.; McGready, J.; Naughton, K.M.; Cutting, G.R. Quantification of the relative contribution of environmental and genetic factors to variation in cystic fibrosis lung function. J. Pediatr. 2010, 157, 802–807.e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verschakelen, J.A.; Van fraeyenhoven, L.; Laureys, G.; Demedts, M.; Baert, A.L. Differences in CT density between dependent and nondependent portions of the lung: Influence of lung volume. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1993, 161, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumcuoglu, E.U.; Long, F.R.; Castile, R.G.; Gurcan, M.N. Image analysis for cystic fibrosis: Computer-assisted airway wall and vessel measurements from low-dose, limited scan lung CT images. J. Digit. Imaging 2013, 26, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonnel, A.S.; Song, S.M.-H.; Kesavarju, K.; Newaskar, M.; Paxton, C.J.; Bloch, D.A.; Moss, R.B.; Robinson, T.E. Quantitative air-trapping analysis in children with mild cystic fibrosis lung disease. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2004, 38, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasfield, D.; Hicks, G.; Soong, S.; Tiller, R.E. The chest roentgenogram in cystic fibrosis: A new scoring system. Pediatrics 1979, 63, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, P.A.; Mayo, J.R.; Golmohammadi, K.; Nakano, Y.; Lequin, M.H.; Tiddens, H.A.; Aldrich, J.; Coxson, H.O.; Sin, D.D. Estimation of cancer mortality associated with repetitive computed tomography scanning. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, W. Radiation doses and risks in chest computed tomography examinations. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2007, 4, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, S.I.; Gappa, M.; Eder, J.; Unsinn, K.M.; Steinkamp, G.; Ellemunter, H. Tracking Lung Clearance Index and chest CT in mild cystic fibrosis lung disease over a period of three years. Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loeve, M.; Lequin, M.H.; de Bruijne, M.; Hartmann, I.J.; Gerbrands, K.; van Straten, M.; Hop, W.C.; Tiddens, H.A. Cystic fibrosis: Are volumetric ultra-low-dose expiratory CT scans sufficient for monitoring related lung disease? Radiology 2009, 253, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, O.J.; Vandeleur, M.; McGarrigle, A.M.; Moore, N.; McWilliams, S.R.; McSweeney, S.E.; O’Neill, M.; Chroinin, M.N.; Maher, M.M. Development of low-dose protocols for thin-section CT assessment of cystic fibrosis in pediatric patients. Radiology 2010, 257, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altes, T.A.; Eichinger, M.; Puderbach, M. Magnetic resonance imaging of the lung in cystic fibrosis. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2007, 4, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichinger, M.; Eichinger, M.; Puderbach, M. Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 32, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichinger, M.; Optazaite, D.E.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Hintze, C.; Biederer, J.; Niemann, A.; Mall, M.A.; Wielpütz, M.O.; Kauczor, H.U.; Puderbach, M. Morphologic and functional scoring of cystic fibrosis lung disease using MRI. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, S.; Puderbach, M.; Fink, C.; Eichinger, M.; Plathow, C.; Teiner, S.; Wiebel, M.; Müller, F.M.; Kauczor, H.U. Assessment of hemodynamic changes in the systemic and pulmonary arterial circulation in patients with cystic fibrosis using phase-contrast MRI. Eur. Radiol. 2005, 15, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puderbach, M.; Eichinger, M.; Gahr, J.; Ley, S.; Tuengerthal, S.; Schmähl, A.; Fink, C.; Plathow, C.; Wiebel, M.; Müller, F.M.; et al. Proton MRI appearance of cystic fibrosis: Comparison to CT. Eur. Radiol. 2007, 17, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawhai, M.H.; Nash, M.P.; Lin, C.L.; Hoffman, E.A. Supine and prone differences in regional lung density and pleural pressure gradients in the human lung with constant shape. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holverda, S.; Theilmann, R.J.; Sá, R.C.; Arai, T.J.; Hall, E.T.; Dubowitz, D.J.; Prisk, G.K.; Hopkins, S.R. Measuring Lung Water: Ex Vivo Validation of Multi-image Gradient Echo MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 34, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mansoor, A.; Bagci, U.; Foster, B.; Xu, Z.; Papadakis, G.Z.; Folio, L.R.; Udupa, J.K.; Mollura, D.J. Segmentation and Image Analysis of Abnormal Lungs at CT: Current Approaches, Challenges, and Future Trends. Radiographics 2015, 35, 1056–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hankinson, J.L.; Odencrantz, J.R.; Fedan, K.B. Spirometric reference values from a sample of the general U.S. population. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theilmann, R.J.; Arai, T.J.; Samiee, A.; Dubowitz, D.J.; Hopkins, S.R.; Buxton, R.B.; Prisk, G.K. Quantitative MRI measurement of lung density must account for the change in T(2) (*) with lung inflation. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 30, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asadi, A.K.; Sá, R.C.; Kim, N.H.; Theilmann, R.J.; Hopkins, S.R.; Buxton, R.B.; Prisk, G.K. Inhaled nitric oxide alters the distribution of blood flow in the healthy human lung, suggesting active hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in normoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 118, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glassner, A.S. (Ed.) Graphics Gems; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Clancy, J.P.; Mall, M.A.; Dřevínek, P.; Lands, L.C.; McKone, E.F.; Polineni, D.; Ramsey, B.W.; Taylor-Cousar, J.L.; Tullis, E.; Vermeulen, F.; et al. CFTR modulator theratyping: Current status, gaps and future directions. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2019, 18, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Condren, M.E.; Bradshaw, M.D. Ivacaftor: A novel gene-based therapeutic approach for cystic fibrosis. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 18, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Boeck, K.; Amaral, M.D. Progress in therapies for cystic fibrosis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijerman, H.G.M.; Cotton, C.U.; Donaldson, S.H.; Solomon, G.M.; VanDevanter, D.R.; Boyle, M.P.; Gentzsch, M.; Nick, J.A.; Illek, B.; Wallenburg, J.C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of the elexacaftor plus tezacaftor plus ivacaftor combination regimen in people with cystic fibrosis homozygous for the F508del mutation: A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1940–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, P.G.; Mall, M.A.; Dřevínek, P.; Lands, L.C.; McKone, E.F.; Polineni, D.; Ramsey, B.W.; Taylor-Cousar, J.L.; Tullis, E.; Vermeulen, F.; et al. Elexacaftor–Tezacaftor–Ivacaftor for Cystic Firosis with a Single Phe508del Allele. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drug Approvals and Databases. Orkambi. 2015. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/development-approval-process-drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases (accessed on 11 May 2020).
- Drug Approvals and Databases. Symdeko 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/development-approval-process-drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases (accessed on 11 May 2020).
- Drug Approvals and Databases. Trikafta. 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/development-approval-process-drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases (accessed on 11 May 2020).
- Chassagnon, G.; Hubert, D.; Fajac, I.; Burgel, P.R.; Revel, M.P. Long-term computed tomographic changes in cystic fibrosis patients treated with ivacaftor. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoare, S.; McEvoy, S.; McCarthy, C.J.; Kilcoyne, A.; Brady, D.; Gibney, B.; Gallagher, C.G.; McKone, E.F.; Dodd, J.D. Ivacaftor Imaging Response in Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D., Jr.; Long, F.R.; McCoy, K.S.; Sheikh, S.I. Improvement in bronchiectasis on CT imaging in a pediatric patient with cystic fibrosis on ivacaftor therapy. Respiration 2014, 88, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, S.I.; Long, F.R.; McCoy, K.S.; Johnson, T.; Ryan-Wenger, N.A.; Hayes, D., Jr. Computed tomography correlates with improvement with ivacaftor in cystic fibrosis patients with G551D mutation. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2015, 14, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Xue, P.; Li, N.; Zhao, P.; Xu, Z.; Ji, H.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, W.; Dong, E. Fusion of 3D lung CT and serum biomarkers for diagnosis of multiple pathological types on pulmonary nodules. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 210, 106381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, S.L.F.; Humphries, S.M.; Wells, A.U.; Brown, K.K. Imaging research in fibrotic lung disease; applying deep learning to unsolved problems. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassagnon, G.; Zacharaki, E.I.; Bommart, S.; Burgel, P.R.; Chiron, R.; Dangeard, S.; Paragios, N.; Martin, C.; Revel, M.P. Quantification of Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease with Radiomics-based CT Scores. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elicker, B.M.; Sohn, J.H. Radiomics and Computerized Analysis of CT Images: Looking Forward. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayal, S.; Dubost, F.; Tiddens, H.A.W.M.; de Bruijine, M. Spectral Data Augmentation Techniques to Quantify Lung Pathology from CT-Images. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Iowa City, IA, USA, 3–7 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado, F.; Moua, T.; Rajagopalan, S.; Karwoski, R.A.; Raghunath, S.; Decker, P.A.; Hartman, T.E.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Robb, R.A.; Ryu, J.H. Automated quantification of radiological patterns predicts survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walsh, S.L.F.; Calandriello, L.; Silva, M.; Sverzellati, N. Deep learning for classifying fibrotic lung disease on high-resolution computed tomography: A case-cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluimer, I.; Schilham, A.; Prokop, M.; van Ginneken, B. Computer analysis of computed tomography scans of the lung: A survey. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2006, 25, 385–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermejo-Peláez, D.; Ash, S.Y.; Washko, G.R.; San José Estépar, R.; Ledesma-Carbayo, M.J. Classification of Interstitial Lung Abnormality Patterns with an Ensemble of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marques, F.; Bubost, F.; Kemmer-van de Corput, M.; Tiddens, H.A.W.; de Bruijne, M. Quantification of lung abnormalities in cystic fibrosis using deep networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.07991. [Google Scholar]
- Izonin, I.; Tkachenko, R.; Fedushko, S.; Koziy, D.; Zub, K.; Vovk, O. RBF-Based Input Doubling Method for Small Medical Data Processing; Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Aghasafari, P.; George, U.; Pidaparti, R. A review of inflammatory mechanism in airway diseases. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Range of R Values | R Category | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.18 | R1 | 0.1 | S1 |
| 0.35 | R2 | 0.19 | S2 |
| 0.35 | R3 | 0.19 | S3 |
| Spatial Presentation | R Category | |
|---|---|---|
| Generalized | R1, R2, R3 | S1 |
| R1 | S2 | |
| Localized Diffuse | R2, R3 | S3 |
| Localized | R2, R3 | S2 |
| Sample | Sex | Age | FEV1 [%pred] | Disease | Right Lung | Left Lung | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | Spatial Presentation | Focality Region | R | Spatial Presentation | Focality Region | |||||||
| CTL 6 | M | 31 | 107 | Control | 0.02 | 0.06 | Generalized | - | 0.05 | 0.11 | Generalized | - |
| CTL 7 | F | 19 | 105 | Control | 0.05 | 0.10 | Generalized | - | 0.06 | 0.12 | Generalized | - |
| CTL 9 | F | 44 | 105 | Control | 0.06 | 0.08 | Generalized | - | 0.03 | 0.05 | Generalized | - |
| CTL 11 | M | 58 | 103 | Control | 0.06 | 0.13 | Generalized | - | 0.02 | 0.09 | Generalized | - |
| CF 1 | M | 23 | 103 | Mild | 0.03 | 0.07 | Generalized | - | 0.05 | 0.08 | Generalized | - |
| CTL 2 | F | 42 | 102 | Control | 0.05 | 0.71 | Generalized | - | 0.05 | 0.09 | Generalized | - |
| CTL 10 | M | 41 | 102 | Control | 0.01 | 0.03 | Generalized | - | 0.01 | 0.03 | Generalized | - |
| CF 2 | F | 37 | 99 | Mild | 0.09 | 0.16 | Generalized | - | 0.11 | 0.15 | Generalized | - |
| CTL1 | M | 23 | 96 | Control | 0.07 | 0.09 | Generalized | - | 0.05 | 0.07 | Generalized | - |
| CTL 12 | M | 22 | 96 | Control | 0.13 | 0.39 | Localized | 5 | 0.04 | 0.08 | Generalized | - |
| CTL 13 | M | 26 | 95 | Control | 0.02 | 0.05 | Generalized | - | 0.03 | 0.06 | Generalized | - |
| CTL 8 | F | 30 | 93 | Control | 0.06 | 0.04 | Generalized | - | 0.06 | 0.18 | Generalized | - |
| CTL 3 | F | 29 | 92 | Control | 0.07 | 0.13 | Generalized | - | 0.09 | 0.14 | Generalized | - |
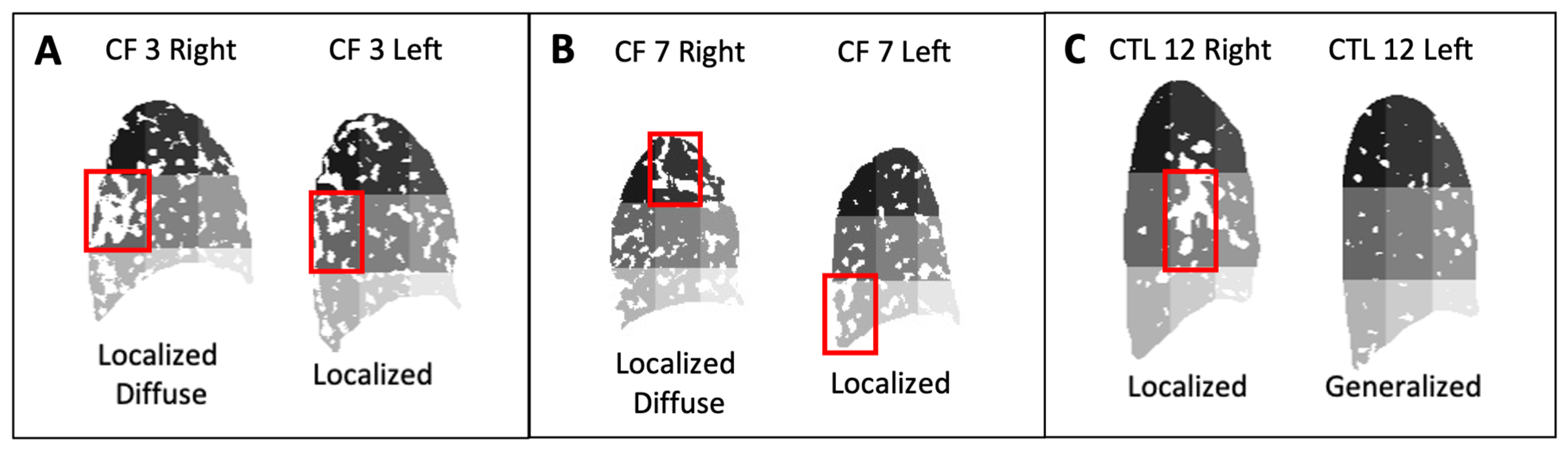
| CF 3 | F | 29 | 89 | Mild | 0.22 | 0.40 | Loc. Diff. | 4 | 0.18 | 0.25 | Localized | 13 |
| CTL 4 | F | 29 | 85 | Control | 0.10 | 0.16 | Generalized | - | 0.11 | 0.14 | Generalized | - |
| CTL 5 | M | 21 | 84 | Control | 0.04 | 0.06 | Generalized | - | 0.09 | 0.11 | Generalized | - |
| CF 4 | F | 29 | 80 | Mild | 0.22 | 0.38 | Loc. Diff. | 7 | 0.21 | 0.36 | Loc. Diff. | 13 |
| CF 6 | M | 32 | 58 | Moderate | 0.05 | 0.07 | Generalized | - | 0.04 | 0.09 | Generalized | - |
| CF 7 | F | 19 | 58 | Moderate | 0.20 | 0.33 | Loc. Diff. | 2 | 0.14 | 0.26 | Localized | 16 |
| CF 8 | F | 30 | 58 | Moderate | 0.39 | 0.53 | Loc. Diff. | 4 | 0.28 | 0.27 | Loc. Diff. | 11 |
| CF 5 | M | 21 | 56 | Moderate | 0.06 | 0.09 | Generalized | - | 0.04 | 0.03 | Generalized | - |
| CF 9 | F | 41 | 56 | Moderate | 0.21 | 0.23 | Loc. Diff. | 6 | 0.22 | 0.36 | Loc. Diff. | 16 |
| CF 13 | M | 25 | 46 | Severe | 0.09 | 0.19 | Generalized | - | 0.09 | 0.18 | Generalized | - |
| CF 12 | M | 24 | 32 | Severe | 0.16 | 0.35 | Localized | 7 | 0.14 | 0.38 | Localized | 15 |
| CF 11 | M | 60 | 25 | Severe | 0.18 | 0.32 | Localized | 7 | 0.14 | 0.35 | Localized | 16 |
| CF 10 | M | 54 | 20 | Severe | 0.06 | 0.07 | Generalized | - | 0.05 | 0.10 | Generalized | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schwartz, A.V.; Lee, A.N.; Theilmann, R.J.; George, U.Z. Spatial Heterogeneity of Excess Lung Fluid in Cystic Fibrosis: Generalized, Localized Diffuse, and Localized Presentations. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10647. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010647
Schwartz AV, Lee AN, Theilmann RJ, George UZ. Spatial Heterogeneity of Excess Lung Fluid in Cystic Fibrosis: Generalized, Localized Diffuse, and Localized Presentations. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(20):10647. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010647
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwartz, Ashley V., Amanda N. Lee, Rebecca J. Theilmann, and Uduak Z. George. 2022. "Spatial Heterogeneity of Excess Lung Fluid in Cystic Fibrosis: Generalized, Localized Diffuse, and Localized Presentations" Applied Sciences 12, no. 20: 10647. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010647
APA StyleSchwartz, A. V., Lee, A. N., Theilmann, R. J., & George, U. Z. (2022). Spatial Heterogeneity of Excess Lung Fluid in Cystic Fibrosis: Generalized, Localized Diffuse, and Localized Presentations. Applied Sciences, 12(20), 10647. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122010647








