Abstract
Finger photo recognition represents a promising touchless technology that offers portable and hygienic authentication solutions in smartphones, eliminating physical contact. Public spaces, such as banks and staff-less stores, benefit from contactless authentication considering the current public health sphere. The user captures the image of their own finger by using the camera integrated in a mobile device. Although recent research has pushed boundaries of finger photo matching, the security of this biometric methodology still represents a concern. Existing systems have been proven to be vulnerable to print attacks by presenting a color paper-printout in front of the camera and photo attacks that consist of displaying the original image in front of the capturing device. This paper aims to improve the performance of finger photo presentation attack detection (PAD) algorithms by investigating deep fusion strategies to combine deep representations obtained from different color spaces. In this work, spoofness is described by combining different color models. The proposed framework integrates multiple convolutional neural networks (CNNs), each trained using patches extracted from a specific color model and centered around minutiae points. Experiments were carried out on a publicly available database of spoofed finger photos obtained from the IIITD Smartphone Finger photo Database with spoof data, including printouts and various display attacks. The results show that deep fusion of the best color models improved the robustness of the PAD system and competed with the state-of-the-art.
1. Introduction
This research promotes the secure adoption of mobile technology in homeland security and across the federal government. Although smartphones have developed into highly portable and accelerated computing devices, there is a growing challenge to secure them properly. Due to lower costs and geographic flexibility, several government services can benefit from using mobile devices. Samsung and German Federal officials have been working on secure storage public credentials, and user-friendly smartphone devices [1]. Samsung has been cooperating with the German Federal Office for Information Security (BSI) to enable secure storage of ID credentials on Galaxy smartphones, which will combine the high-level trust in the physical document with the user-friendliness of smartphones [1]. Furthermore, staff-less stores are predominantly trending where customers are connected via a mobile application for authentication.
Recent advances have shown that finger photos acquired using a basic smartphone camera are promising for authenticating individuals. At FMR = 0.1%, finger photo-to-finger photo matching has achieved an accuracy of 99.66% by fusing four fingers and 85.62% by using individual fingers [2]. Very recently, the contactless finger photo to contact-based fingerprint matching has achieved an Equal Error Rate (EER) less than 1% across multiple datasets and under background and illumination variation [3].
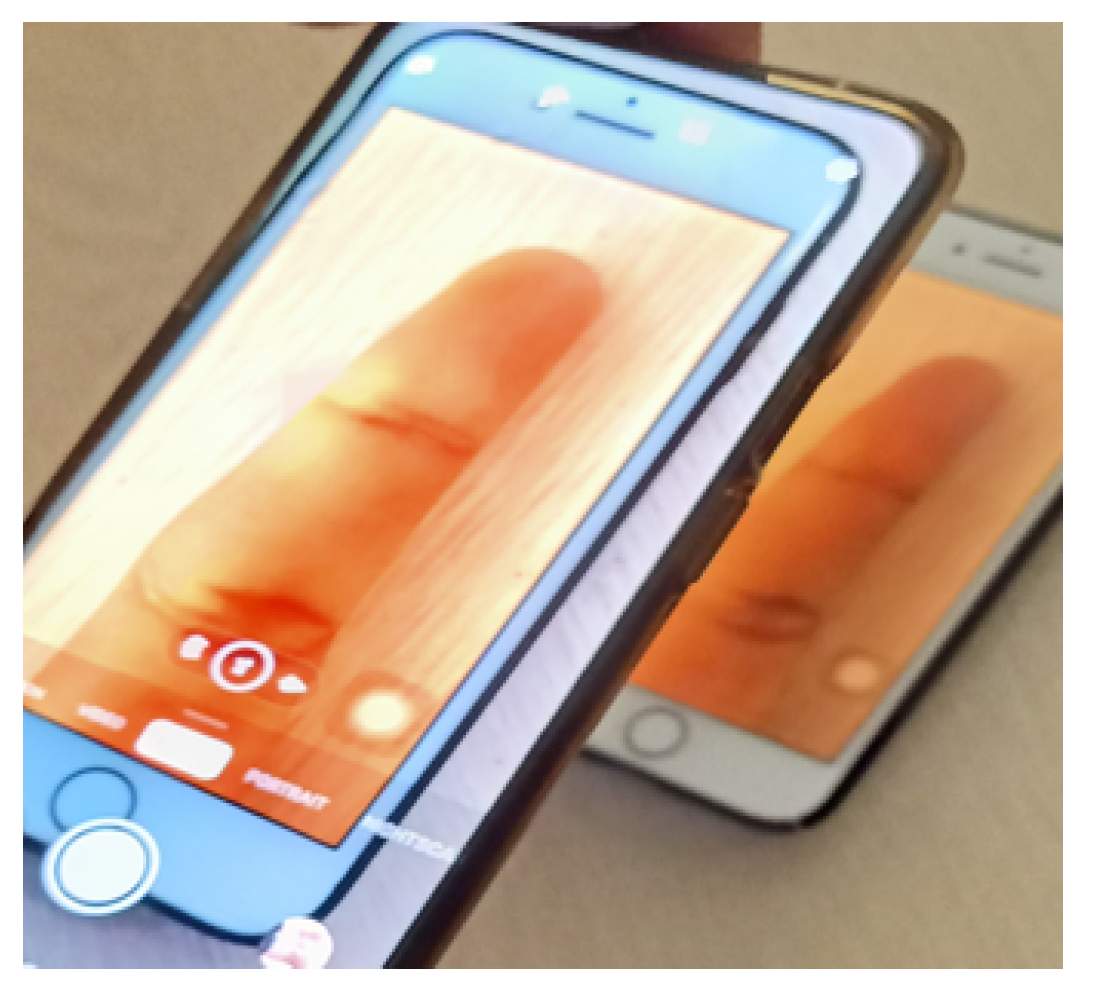
Researchers have also established the vulnerability of finger photo-based systems to presentation attacks (PAs) [4], see an example in Figure 1. The PAs considered in this study are compared with printouts and multiple devices such as iPads and laptops. In mobile devices, the sensor is a component of the architecture that lacks a mechanism for preventing spoofing. Thus, the acquisition sensor requires a Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) module, which classifies biometric samples as being live (non-spoof) or fake (spoof). Only a few research efforts have been made to mitigate this issue. There is an urgent need to build robust PAD modules to classify genuine biometric samples from presentation attacks.
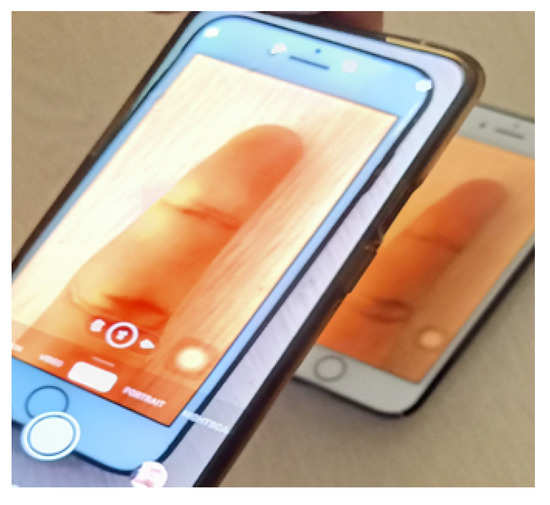

Figure 1.
An example of a finger photo display attack. A finger photo of the genuine identity is displayed by using a smartphone positioned in front of the camera integrated in the mobile to unlock.
The proposed research seeks to boost the performance of finger photo PAD using deep fusion strategies by investigating whether the robustness of PADs to different spoofing methods can be enhanced by fusing various color spaces (e.g., HSV, YCbCr). From the image classification literature, it is known that certain classes might be better represented in specific color spaces [5]. Most of the PAs are generated using different hardware inclined toward different color spaces. Color monitors mostly use RGB color space, CMY models for color printout, and HSV, which are the closest to how humans interpret colors, and YCbCr is paired with popular video and digital photography.
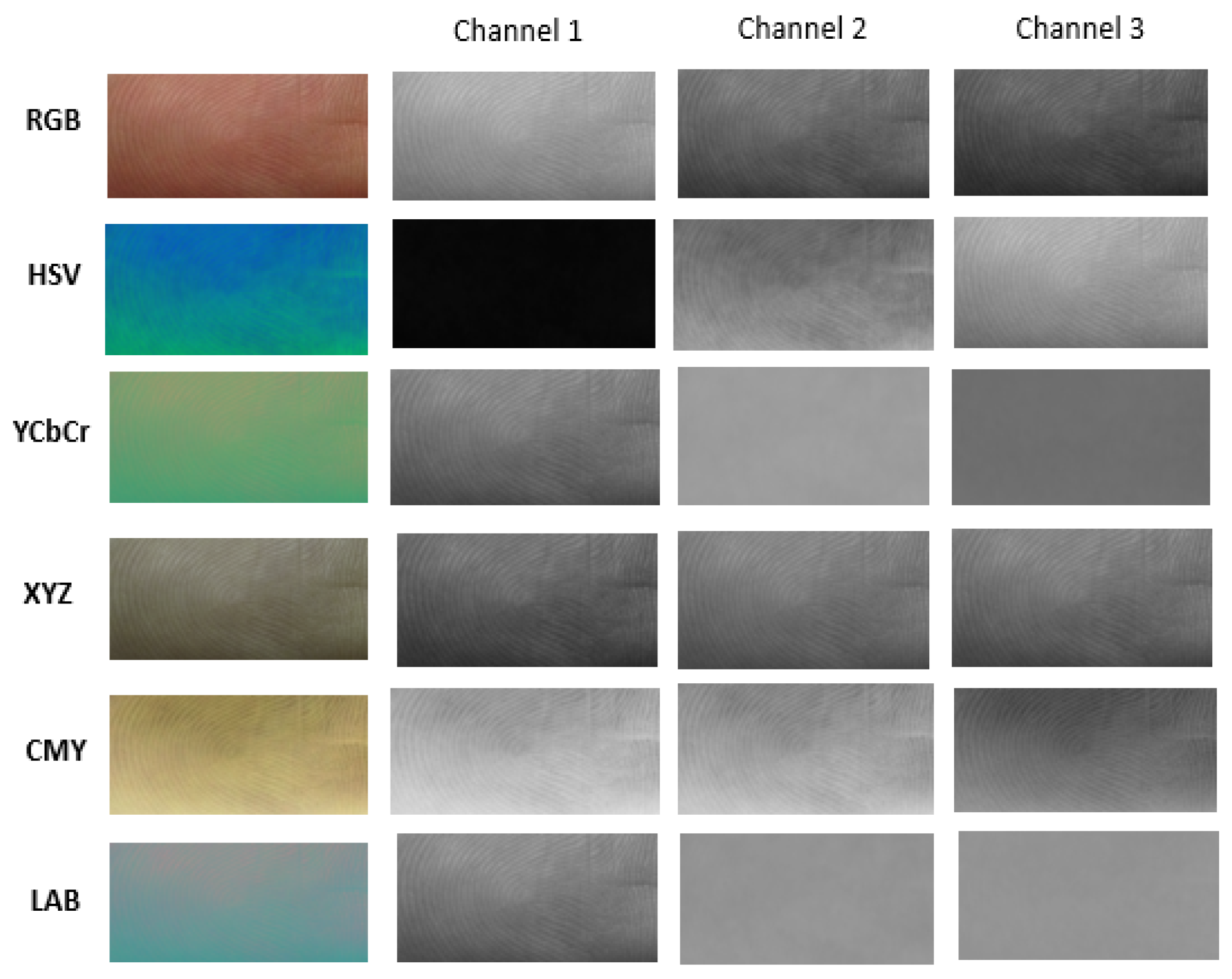
A color space is a specific organization of colors to produce digital color representation [5]. RGB is ideal for image color generation (as in image capture by a color camera), but its use is limited to the color description. Thus, researchers are also investigating transformations of original RGB images into different color spaces, and their impact on accuracy [5]. In RGB, a spoof can only be modeled in terms of percentages of the three primaries composing its color [6]. Differences between live human fingers and display attacks can be better detected using good color descriptors. Choosing an appropriate color space can provide a more robust analysis. Images of the color models used in the proposed study are shown in Figure 2.
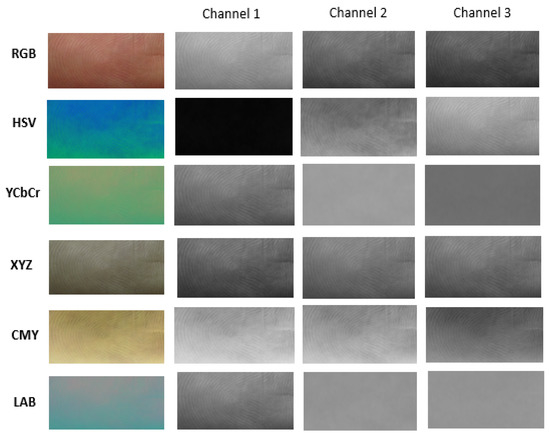
Figure 2.
Examples of finger photo center core patches converted into different color spaces.
Finger photos are featured by qualities such as the color of the skin and ridges of fingerprints; thus, working with various color spaces will help to focus on characteristics that cannot be extracted from RGB images. For example, the color space used in previous work for skin recognition was YCbCr.
Existing PAD algorithms used in finger photo authentication systems are based on texture descriptors, including Local Binary Patterns (LBP), Locally Uniform Comparison Image Descriptor (LUCID), etc., which are processed on RGB images. These approaches might limit the algorithm’s performance since spoofs are extracted only in the RGB color model. Recently, we used appropriate color space liveness detection and found that choosing different color spaces can provide a more robust analysis. This research investigated finger photo patch-based training on a deep learning framework that integrates different color spaces via a late fusion mechanism. The color spaces considered in this work can be derived from RGB, thus the proposed investigation seeks to answer the research question “Is it reasonable to fuse information provided from different color spaces?” more specifically, “Do different color spaces complement each other?”. Then, this study focuses on addressing the problem related to the question “What is an effective fusion strategy to increase the robustness of the finger photo PAD systems?”.
The contribution of this paper is two-fold: (i) carry out a correlation analysis among various color spaces to assess that they complement each other, and (ii) design and evaluate a deep learning framework that integrates different color spaces via late fusion. In the proposed approach, the input RGB finger photo is converted into various color spaces to train various CNNs by using minutia-centered patches. A single fusion layer is built with the input size equivalent to the sum of all the fully connected layers of each best net and the output size equivalent to binary classification (i.e., live or spoof). The last fully connected layers of the most accurate nets are combined through a fusion layer, which yields a global decision. The proposed framework is then compared to the state-of-the-art on a publicly available database.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows: Section 2 reviews research conducted on liveness detection from fingerprints as well as finger photo PAD, Section 3 summarizes the approaches evaluated in this study, Section 4 presents the experimental procedure, Section 5 describes the experimental results, and Section 6 is the conclusions and discusses future work.
2. Related Work
Existing liveness detection approaches are not explicitly designed for mobile devices and are generally unsuited for portable devices [7,8]. Several software-based methods, including Fourier Transform (FT), Local Binary Patterns (LBP), Binarized Statistical Image Features (BSIF), Local Phase Quantization (LPQ), Weber Local Image Descriptor, or Histograms of Invariant Gradients (HIG), have been investigated for PAD [9,10,11]. Deep learning approaches have also been applied. Menotti et al. learned a suitable CNN architecture that was evaluated by executing linear SVM on the resulting deep representation [12]. Frassetto et al. used a hybrid approach combining CNNs and LBPs with best reported accuracy of 95.2% using 50,000 samples for training from the LivDet 2009, 2011, and 2013 datasets [13].
In 2013, Stein et al. [14] discussed a method to capture multiple finger photos in the smallest time frame. In addition, they implemented an anti-spoofing method that relied on the user’s challenge response to detect spoofs by measuring the light that was reflected from the finger that was exposed to the camera’s LED as well as the position, distance, and sharpness characteristics of the finger. A database of video stream data was built and an overall Equal Error Rate (EER) of 3% on the 37 subjects was reported.
In 2014, Akhtar et al. presented the Mobile Biometric Liveness Detection (MoBio LivDet) approach that analyzes local and global features of biometric images to defend against spoofing [8]. Locally Uniform Comparison Image Descriptor (LUCID), Census Transform Histogram (CENTRIST), and Patterns of Oriented Edge Magnitudes (POEM) were used for being computationally inexpensive and suitable for mobile processors as well as robust to photometric transformations and noise. For fingerprint PAD, the researchers found that LUCID and Local Phase Quantization (LPQ) attained 7.17% and 14.22% Half Total Error Rate (HTER), respectively; while CENTRIST achieved a HTER 2.2% and POEM 3.84%. In this paper, experiments were carried out on sensor-based fingerprint images.
In 2016, Taneja et al. evaluated LBP, DSIFT, and LUCID on a new database of spoofs that they created as an extension of the previously published IIITD Smartphone Finger photo Database built to study matching algorithms [4]. When the complete dataset is considered, the lowest EER reported is 3.7% and achieved using LBP features to train an SVM classifier, followed by DSIFT with EER = 5.37% and LUCID EER = 22.22%.
In 2018, Wasnik et al. discussed an approach based on the convolution of input images at multiple scales through a Frangi filter to obtain Maximum Filter Response (MFR) images that are then processed to extract LBP, HOG, and BSIF features [15]. The performance obtained by SVM trained using these features was Attack Presentation Classification Error Rate (APCER) of 10%, Attack Presentation Classification Error Rate (BPCER) of 1.8% for print picture attacks, 0.0% for display attacks, and 0.66% for replay attacks.
In 2019, Labati et al. discussed the finger photo recognition pipeline, including acquisition from a smartphone, liveness detection, quality assessment, segmentation, enhancement, feature extraction, and matching. The authors concluded that the two main reasons for the low performance of matching are due to heterogeneous smartphone acquisition, uncontrolled illumination, and background conditions’ diversity [16].
Recently, Marasco et al. investigated a methodology that transforms RGB finger photos into various color spaces, which are used to train different CNNs. The approach finds the best deep representation for each color model and combines the corresponding individual outputs. The overall system’s performance combining the top three color spaces achieved an EER of 2.12% [17]. Although multiple color spaces were used on the whole image, there were no experimental validations to prove independence among the color spaces. Simple score-level fusion was used as a mechanism to combine the individual outputs of the CNNs in order to generate a global score for the final decision.
3. Spoofness by Integrating Different Representations of Colors
Since computer images are numbers, their transformations are viewed as new images. For humans, a color object is described by its hue, saturation, and brightness. The brightness component (intensity) in HSV is decoupled from a color image of color-carrying information (hue and saturation). Thus, they represent ideal tools for developing image-processing algorithms based on color descriptions that are natural to humans.
XYZ employs extrapolated X, Y, and Z channels from the R, G, and B channels. Luminance is represented by Y, a channel close to blue by Z, and a mix of non-negative cone response curves by X. LAB is a perceptually uniform color space in which the three channels are L luminance (black to white), A (green to red), and B (blue to yellow). The lightness value, L, defines black at 0 and white at 100. The A axis is oriented in relation to the green–red opponent colors and the blue–yellow opponents are represented on the B axis. The LAB color space is device-independent; thus, its appearance does not depend on the type of screen. CMY is a subtractive color model (colors produced in reflected light) in which cyan, magenta, and yellow pigments are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. Color printers and copiers use a color model based on the cyan, magenta, and yellow colors to deposit color pigments on paper. Printers with a separate black color ribbon or ink are more likely to use the CMYK color model.
3.1. Conversion of RGB Images into Different Color Spaces
The segmented images are then transformed into different color spaces. Below are the reported equations for the conversions. RGB images can be converted to HSV as follows:
Image conversion from RGB supports a modified where Y, , and have the full 8-bit range of [0…255]. Below are the reported equations for the conversion expressed in six decimal digits of precision:
A standardized 3 × 3 matrix describing how to convert RGB into XYZ data.
Converting RGB to LAB requires a reference to the XYZ color space, as illustrated in Equation (5).
Image Conversion from RGB to CMY, CMY is the subtractive colors of RGB. The equation is illustrated in Equation (6):
3.2. Correlation Analysis between Color Spaces
Consider whether it is reasonable to fuse the information provided individually by each color space for an enhanced ability to discriminate between live finger photos and PAs [18]. To provide experimental evidence that different color spaces complement each other, their correlation is investigated. Due to its efficiency in terms of computational requirements at each pixel, in this study, 2D Person’s correlation coefficient (PCC) was used. PCC is a statistical measure of linear correlation strength between two variables X and Y that takes values in the closed interval [−1, +1]. Let X and Y denote the intensities of two images taken in different lighting conditions. A high similarity between them is obtained when corresponding intensities are linearly related [19]. The computational details are illustrated in Equation (7), where is the intensity of the ith pixel of the segmented finger photo image in a given color space, and is the mean. and describe similar quantities but for different color spaces. The correlation is computed for corresponding channels, and the average is then considered.
4. The Proposed Finger Photo Color Net (FPCN)
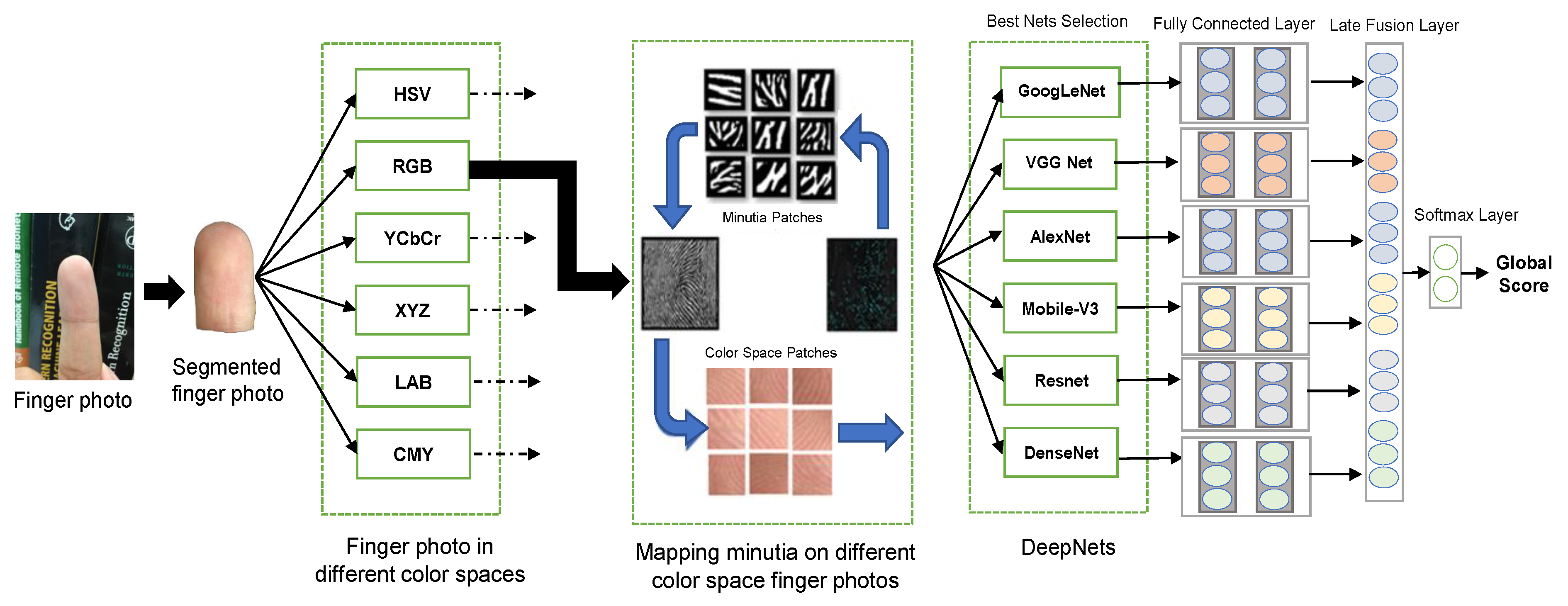
This section discusses the architecture of the proposed deep fusion framework for finger photo anti-spoofing. The input finger photo is segmented using a U-Net segmentation Network based on a pre-trained ResNet-50 as the backbone [20]. The segmented RGB image is converted into multiple color spaces. From the segmented RGB image, minutiae points (i.e., bifurcation and terminal) are also extracted and mapped into the various color spaces. For each color space, a patch image is cropped over the coordinates of minutia points. Furthermore, patches of size 128 × 128 centered around the detected minutia points are generated to capture local texture information for enhancing PAD robustness. Finally, CNNs are individually fine-tuned each on a single color space and the best models are combined using a late fusion strategy, see Figure 3.
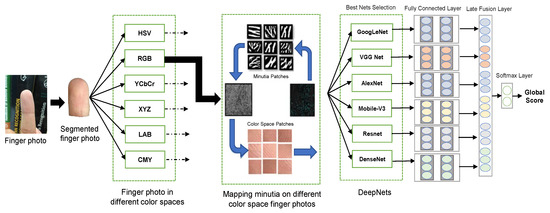
Figure 3.
The finger photo is segmented with respect to the distal phalange and transformed to different color spaces. Patches centered around minutiae points are determined and used to feed different CNNs. Deep fusion is performed on the best-selected color models and an overall global decision is provided.
4.1. Finger Photo Segmentation
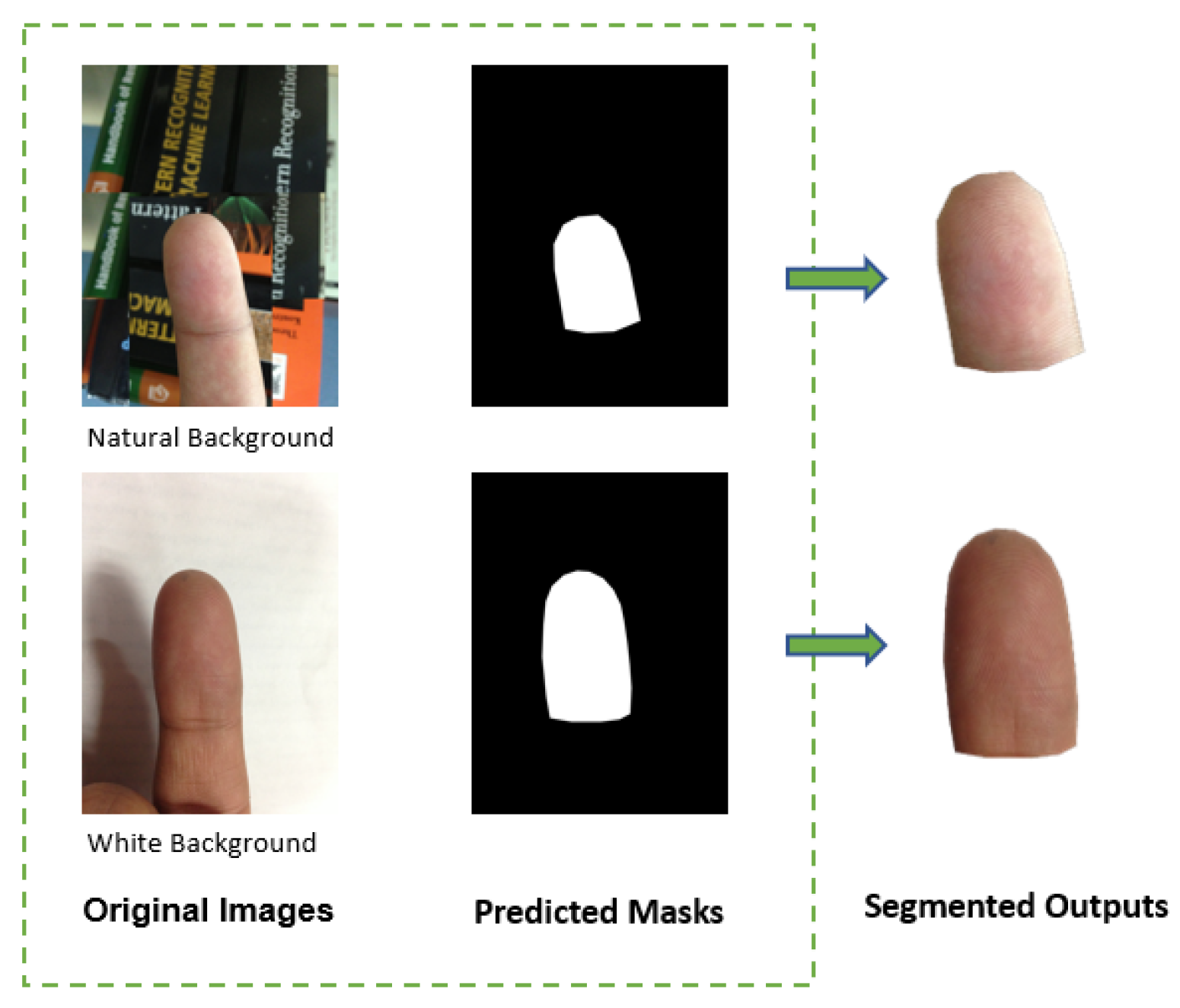
For the IIIT-D finger photo database used in this research, the input finger photo distal phalange (fingertip) is segmented using a U-Net segmentation network [20]. This algorithm has been validated by Grosz et al. on various contactless fingerprint databases with satisfying results [3]. The ground truth was generated using the open-source LabelMe segmentation tool on a subset of 100 live and spoof images from both white and natural backgrounds [20,21]. The ground truth and finger photo images were used to train the U-net model. The trained segmentation model was then applied to the remaining finger photos of the dataset to predict the foreground Figure 4. These binary predictions of size 256 × 256 were expanded to the original size of the finger photo 3264 × 2448 by maintaining the aspect ratio. The Gaussian blur (: 2) is applied to remove the blurriness on the resized binary image. These binary mask predictions are then used to crop the foreground of the entire finger photo image. This process retains the ridges and valleys of the original finger photo image Figure 4.
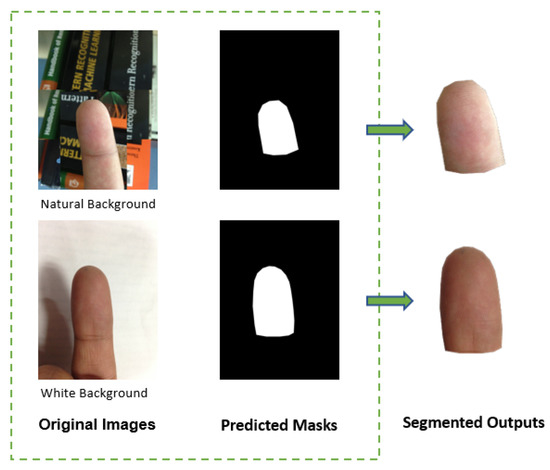
Figure 4.
Examples of predicted output masks by using the U-Net framework.
4.2. Finger Photo Enhancement and Generation of Patches
A fingerprint enhancement algorithm is applied to improve the clarity of ridge and valley structures [22]. A bank of Gabor filters is used as band-pass filters to remove noise while preserving the ridge/valley structures. These filters are tuned to the orientation and frequency of the ridge configurations. The general Gabor filter function is reported in Equation (8), where and f are the orientation and frequency of the filter, and and are the space constants of the Gaussian envelope along the x and y axes. For the enhancement, the segmented finger photos are converted into grey-scale images and then normalized to estimate the orientation and frequency parameters.
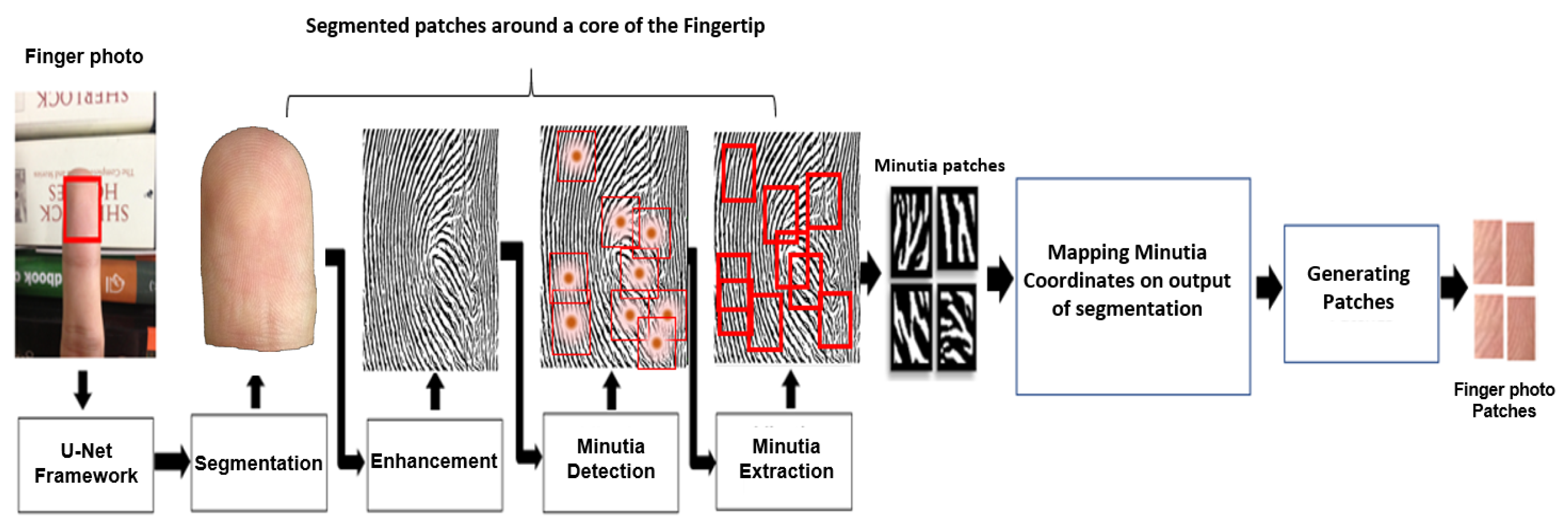
The enhanced images are binarized and further processed via ridge thinning to convert them into skeletonized images [23]. The ridge ending and bifurcation minutiae points are extracted by scanning the local neighborhood of each pixel in the ridge-thinned image using a 3 × 3 window; then, the crossing number (CN) is computed [23]. CN is half of the sum of the differences between pairs of neighboring pixels and ; see Equation (9). The coordinates of the minutia points extracted from the ROI of the finger photos are simultaneously mapped into the various color spaces used in this study. For each color space, a patch image is cropped over the coordinates of minutia points; see Figure 5.
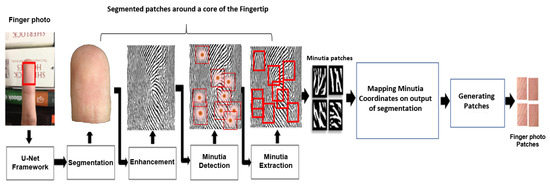
Figure 5.
Architecture illustrating image segmentation, enhancement and minutia points extraction.
4.3. The Deep Fusion Layer
Late fusion is a deep feature-level fusion strategy in which multiple CNNs, each trained on a particular color space, are integrated to obtain a global decision [24]. After fine-tuning the pre-trained models, the parameters are frozen, and the last layer of each CNN (i.e., the SoftMax) is removed. A single customized SoftMax layer is built by concatenating the deep features generated by each CNN. The overall model is then fine-tuned again. In this study, various pre-trained CNNs are considered, including AlexNet, VGGNet, ResNet, GoogLeNet, MobileNetV3, and DenseNet-121 [25,26,27,28]. Table 1 shows the notations used in this research.

Table 1.
Notations.
4.4. Statistical Test for Comparing Classification Algorithms
To compare the proposed approach to various color space-based binary classification methods, this research applies the paired non-parametric McNemar’s statistical test [29,30,31]. The scores output of the classifiers do not follow a normal distribution and the live/spoof group samples are paired. This test analyzes whether two models disagree in the same way (or not). It is not commenting on whether one model is more accurate or error-prone than another. The McNemar’s test statistic is calculated as follows:
where Yes/No represents the number of test instances correctly classified by Model 1 but incorrectly classified by Model 2, and No/Yes represents the number of test instances incorrectly classified by Model 1 but correctly classified by Model 2. The test determines whether there is a statistically significant difference in these counts. The null hypothesis () of the test is that the two classifiers disagree in similar ways, see Equation (11). If the null hypothesis is rejected, it suggests that our models disagree in significantly different ways. Furthermore, McNemar’s test provides a distribution with one degree of freedom. The higher value indicates the significant difference of our models.
Given the selection of a significance level (), the p-value (p) calculated by the test can be interpreted as follows:
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Dataset
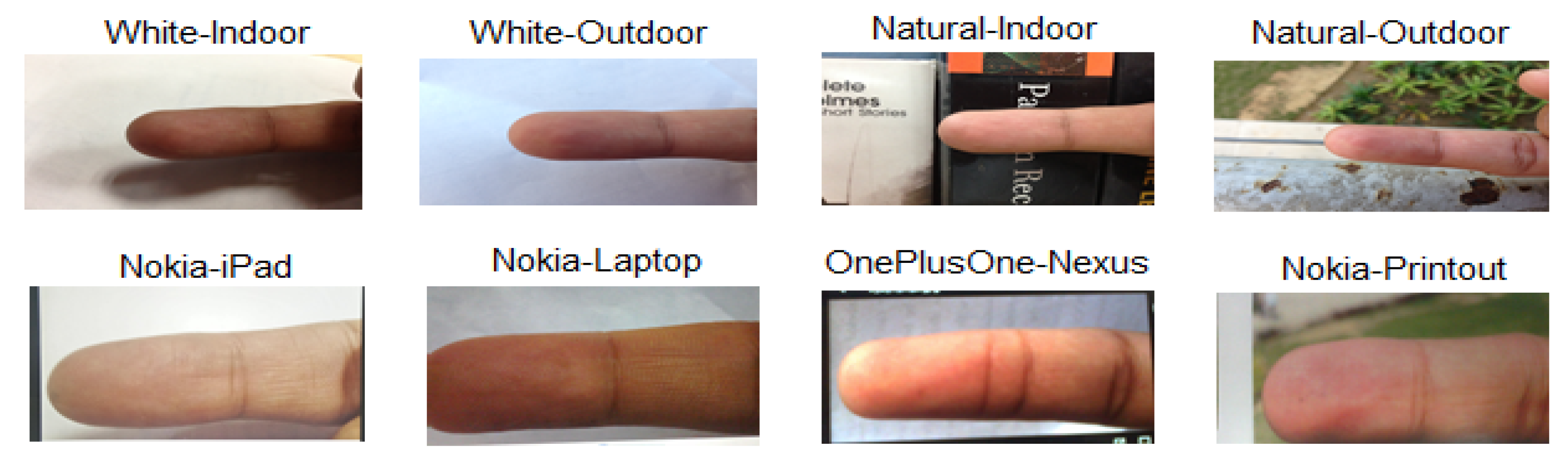
The experiments were carried out using the IIITD smartphone finger photo database, which is the only publicly available database with both live and spoof finger photos [4,32]. Samples pertain to 64 individuals featured by two different backgrounds, under both controlled and uncontrolled illumination. Examples are shown in Figure 6. The data used in this study consist of 12,288 finger photo images (4096 live and 8192 spoof).
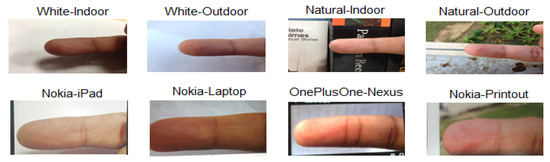
Figure 6.
Examples of finger photos acquired from live human fingers with white and natural background as well as of display spoof attacks.
A total of 400,000 minutia patches were extracted from the dataset. For each image, 30 patches centered around a minutia point were randomly selected for training. For training each CNN, finger photos need to be downsized to the input shape of the model, which results in a loss of texture features. This issue can be mitigated by using patches that conserve texture information at a local region. Thus, the proposed approach is based on training the deep networks using patches centered at the minutia points, which lets the model learn the salient texture information at local regions resulting in enhanced PAD robustness.
128 × 128 patches centered around the minutia points are extracted. These patches are resized to 224 × 224 to train the CNNs under study and to 227 × 227 to train the AlexNet. The resizing strategy uses area interpolation that retains the aspect ratio to prevent any feature loss [3,33]
5.2. Evaluation Procedure
To assess the proposed framework, the performance metrics defined in the ISO/IEC 30107-3 standard on biometric presentation attack detection were referenced, partly related to testing and reporting performance metrics for evaluating biometric presentation attacks. The assessment scheme is reported below:
- Attack Presentation Classification Error Rate (APCER): Proportion of attack presentations incorrectly classified as normal presentations, i.e., false acceptance of spoof samples.
- Normal Presentation Classification Error Rate (NPCER): Proportion of normal presentations incorrectly classified as attack presentations, i.e., false rejection of live samples.
- Equal Error Rate (EER): The intersection point of the percentage of normal presentation classification error rate and attack presentation classification error rate.
- Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves to assess the accuracy.
The proposed framework is trained on both natural and white backgrounds in different lighting conditions (i.e., Indoor and Outdoor). The data were partitioned into 50% training, 20% validation, and 30% testing sets with subjects mutually exclusive.
The experiments were carried out using Argo Cluster at George Mason University [34]. Argo Cluster is a high-performance batch computing resource provided to all the students and faculty of George Mason University. It was assembled in 2013, which has 75 compute nodes totaling 1496 cores and over 8 TB of memory. The cluster is managed by two head nodes, Argo-1 and Argo-2, which is assigned to the user in a round-robin fashion upon login. Sixty-nine compute nodes have dual Intel processors with 64 to 512 GB RAM. There are six GPU compute nodes powered by V100 GPUs with 28 core CPUs, 32 GB onboard memory per GPU750 GB to 1.5 TB RAM per node, equipped with specialized libraries for Pytorch, which were used for this research.
5.3. Results
The experimental results related to the correlation analysis demonstrate that the color spaces considered in this study complement each other. Pearson correlation confirms that the color spaces to be fused are uncorrelated. From Table 2, it is clear that HSV and LAB images exhibit a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.015 and −0.031, respectively, which suggests no correlation. Furthermore, RGB and CMY images are negatively correlated. The general trend found from this analysis supports the initial hypothesis that color spaces provide enough diversity to be exploited in a fusion strategy.

Table 2.
Pearson correlation between color spaces.
Table 3 illustrates the EER% of the CNNs under study when individually fine-tuned on a single color space. Findings support the initial hypothesis about the diversity in the information provided by various color spaces, which can enhance the performance of the overall system. The lowest EER of 0.96% is achieved by the MobileNet-V3 trained using HSV images. Further, 1.39% and 1.84% are the EER achieved by YCbCr and CMY, respectively. ResNet-18 and ResNet-34 perform well with RGB, YCbCr, and CMY color spaces. ResNet34 reached an EER of 1.19% using HSV.

Table 3.
Performance of the individual color spaces in terms of EER%.
Table 4 compares CNN models individually trained by using all color spaces as well as only by using RHY, the proposed late fusion framework, and the state-of-the-art. Results are reported in terms of EER%, average accuracy after repeating each experiment three times, standard deviation, F1, and 10-fold cross-validation. Individual CNNs trained on all color spaces (e.g., RHYLXC) generally do not exhibit competitive results. In particular, ResNet-34 and Densenet-121 achieved an EER of 6.12% and 6.38%. When trained on RHY, Densenet-121 and Resnet-34 achieved an EER of 3.01% and 3.54%.

Table 4.
Comparison of the Proposed Approach to the State-of-the-art in terms of EER%.
By using the proposed late fusion strategy, the combination RHYC achieved an EER of 0.841%. Late fusion with selected best net models outperformed the current state-of-the-art.
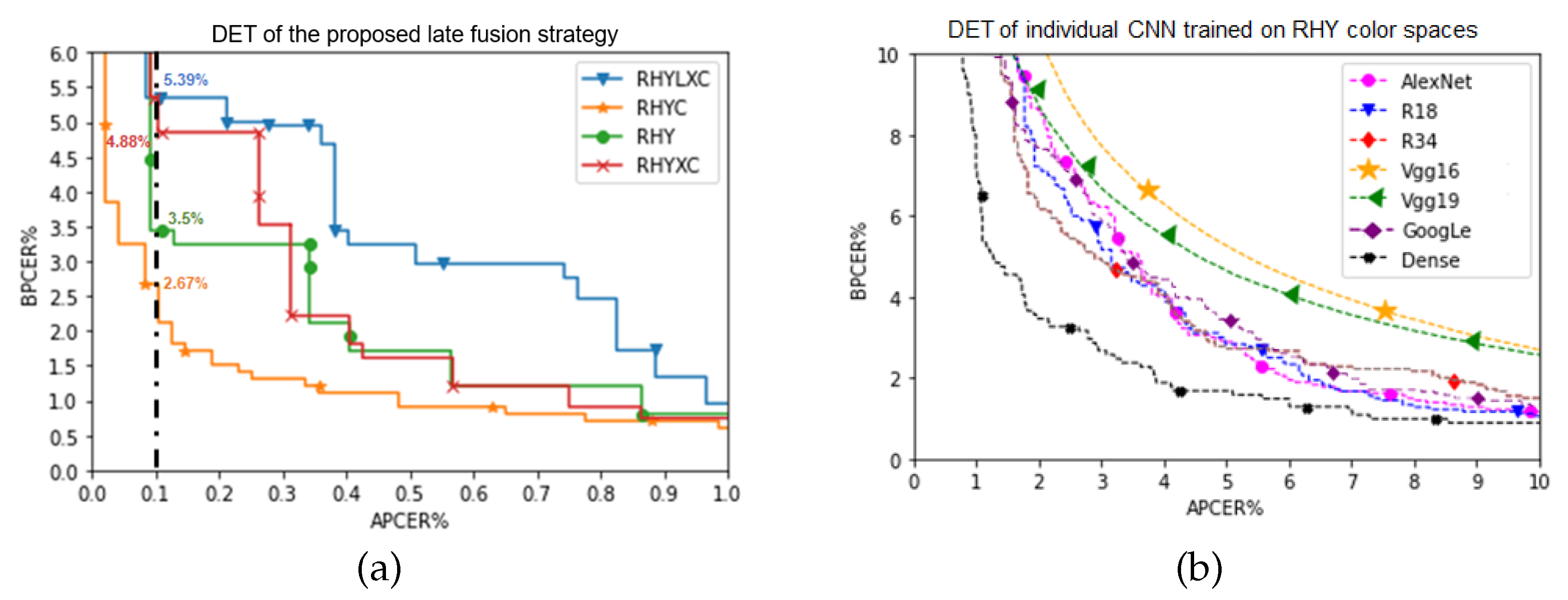
Figure 7a shows the DET curve of the proposed late fusion strategy. RHYXC and RHY achieved an EER of 0.961%, with BPCER of 4.88% at APCER = 0.1%, and 0.864% with BPCER of 3.5% at APCER = 0.1%, respectively. The lowest EER of 0.841% is obtained by RHYC with BPCER of 2.67% at APCER = 0.1%. Figure 7b shows the DET curve of individual CNNs trained on RHY color spaces.
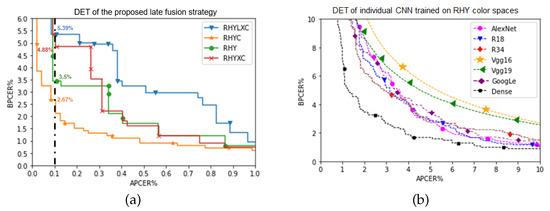
Figure 7.
(a) DET Curves illustrate the performance of late fusion on the overall system. (b) DET Curves illustrate the RHY finger photo patches trained on individual CNN.
Estimating the liveness of RGB finger photos acquired with a smartphone under unstable illumination conditions is a complex task. Results suggest that characteristics of indoor and outdoor brightness conditions that were not captured by RGB can be captured by a combination of V and Y components in the HSV and YCbCr color spaces, respectively. Spoof finger photos displayed by a certain device, thus featured by certain saturation levels can be effectively represented by the HSV representation. CMY is the subtractive color of RGB, i.e., brighter colors in RGB color space are darker in CMY. This property is useful for discriminating printout attacks since most printouts are captured on white paper, which is a reflective (bright) material.
The time efficiency of the proposed PAD system was also computed. Time efficiency indicates the time required by the system to be executed on the available resources [35,36]. It is defined as the elapsed time from the moment the input data is captured until the decision is output [37]. The deep fusion module operating on six patches (one patch per color space) provides a global decision in 485 milliseconds. The total time efficiency when the fusion model provides a global decision by sequentially testing on five patches per subject is 2.6 s computed as 5 × 485 ms added to the time to execute a majority voting. Additionally, the segmentation process with UNet takes 632 ms, while enhancement, minutia detection, and minutia patch extraction take a total of 14.35 s.
Mcnemar’s Test
The research performed a statistical test for a meaningful interpretation and comparison of the PAD methods analyzed in this study and their statistical differences. Table 5 reports McNemar’s test between the late fusion models. The results clearly show that the p-value is less than the significance value, i.e., 5%. our research also reports the with 1 degree of freedom for all the late fusion models. Results suggest that the p-value is less than the significance level, which shows that the null hypothesis can be rejected. This means the fusion models have different performances when tested on the same dataset.

Table 5.
McNemar’s test.
From Table 5, the p-result suggests that RHYC and RHYXC have a of 4.2 and p-value of 0.041, which is very close to the significance value (). Although, when compared with other fusion models, the p-value is < 1% and has a large value. This shows that our model’s performances are diverse. We can also observe that the values of RHYC and RHY are 35.53 and 35.15 compared with RHYLXC. This suggests that the performance of RHYC and RHY fusion models significantly differs from RHYLXC.
6. Conclusions
Finger photo technology can be used as a viable approach for touchless authentication in mobile devices. However, it is vital to understand the implications of spoofing attempts on finger photo recognition. The proposed research provides a mechanism for defense against finger photo spoofing. Different CNNs are trained individually using various color spaces and then integrated via deep fusion. Finger photo patches were used to train the deep networks to conserve texture information in a local region. Results demonstrate the superiority after combining different color spaces compared to the state-of-the-art. Findings show that when late fusion is performed, the scheme that integrates RHYC results in an EER of 0.841%. This supports the hypothesis that different color spaces complement each other, and combining the information provided by each of them can aid spoof representation and thus PAD. The proposed study is constrained by the limited publicly available finger photos spoof database with 64 subjects. Furthermore, the existing IIIT-D database device used for the acquisition of live and spoof samples was not of similar specification. Therefore, our future efforts will focus on creating a larger database for spoof finger photos using the same capture device for live and spoof. This will allow us to generalize our current framework. We will also explore methodologies such as activation maps to explain the deep models obtained in this work.
Author Contributions
Methodology, E.M.; software, A.V.; validation, E.M., A.V.; formal analysis, E.M., A.V.; investigation, E.M., A.V.; writing—original draft preparation, E.M.; writing—review and editing, E.M., A.V.; visualization, E.M., A.V.; supervision, E.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Marasco was partially supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) under award CNS-1822094.
Data Availability Statement
The two databases used in this study are IIITD Smartphone Finger-Selfie Database V2 and the Spoofed Fingerphoto Database 1. The link to IIITD Smartphone Finger-Selfie Database V2 is http://iab-rubric.org/index.php/spfd2, last accessed on 26 September 2022. and; 2. The link to Spoofed Finger photo Database is http://iab-rubric.org/index.php/spoofed-fingerphoto-database photo database, last accessed on 26 September 2022.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| PA | presentation attack |
| PAD | presentation attack detection |
| CNN | convolutional neural network |
| PCC | person’s correlation coefficient |
| ROI | region of interest |
| CN | crossing number |
| LUCID | locally uniform comparison image descriptor |
| BSIF | Binarized Statistical Image Features |
| LBP | local binary patterns |
| LPQ | Local Phase Quantization |
| HIG | Histograms of Invariant Gradients |
| FT | Fourier Transform |
| CENTRIST | Census Transform Histogram |
| POEM | Patterns of Oriented Edge Magnitudes |
| MFR | Maximum Filter Response |
| DSIFT | dense scale invariant feature transform |
| APCER | attack presentation classification error rate |
| NPCER | normal presentation classification error rate |
| HTER | Half Total Error Rate |
| EER | equal error rate |
| RHYXLC | RGB, HSV, YCbCr, LAB, XYZ, CMY |
| RHYXC | RGB, HSV, YCbCr, XYZ, CMY |
| RHYC | RGB, HSV, YCbCr, CMY |
| RHYLX | RGB, HSV, YCbCr, LAB, XYZ |
| RHYL | RGB, HSV, LAB, YCbCr |
| RHY | RGB, HSV, YCbCr |
References
- Avisian. German National Digital ID is Going Mobile. 2020. Available online: https://www.secureidnews.com/news-item/german-national-digital-id-is-going-mobile/ (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Deb, D.; Chugh, T.; Engelsma, J.; Cao, K.; Nain, N.; Kendall, J.; Jain, A. Matching Fingerphotos to Slap Fingerprint Images. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.08122. [Google Scholar]
- Grosz, S.; Engelsma, J.; Liu, E.; Jain, A. C2CL: Contact to contactless fingerprint matching. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 17, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, A.; Tayal, A.; Malhorta, A.; Sankaran, A.; Vatsa, M.; Singh, R. Fingerphoto spoofing in mobile devices: A preliminary study. In Proceedings of the IEEE 8th International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Niagara Falls, NY, USA, 1–6 September 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, S.; Yuan, C. ColorNet: Investigating the Importance of Color Spaces for Image Classification. In Computer Vision—ACCV 2018, Proceedings of the 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, 2–6 December 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 11364, pp. 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lukac, R.; Plataniotis, K. Color Image Processing: Methods and Applications; Image Processing Series; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Marasco, E.; Ross, A. A Survey on Antispoofing Schemes for Fingerprint Recognition Systems. ACM Comput. Surv. 2014, 47, 28:1–28:36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, Z.; Micheloni, C.; Piciarelli, C.; Foresti, G.L. MoBio_LivDet: Mobile Biometric liveness Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), Seoul, Korea, 26–29 August 2014; pp. 187–192. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Shi, P. Fake Finger Detection Based on Thin-Plate Spline Distortion Model. Adv. Biom. 2007, 11, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghiani, L.; Hadid, A.; Marcialis, G.; Roli, F. Fingerprint Liveness Detection using Binarized Statistical Image Features. In Proceedings of the IEEE Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Arlington, VA, USA, 29 September–2 October 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschlich, C.; Marasco, E.; Yang, A.; Cukic, B. Fingerprint Liveness Detection Based on Histograms of Invariant Gradients. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Clearwater, FL, USA, 29 September–2 October 2014; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menotti, D.; Chiachia, G.; Allan, A.; Robson, S.; Pedrini, H.; Xavier, F.; Rocha, A. Deep Representations for Iris, Face, and Fingerprint Spoofing Detection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 864–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frassetto, N.; Nogueira, R.; Lotufo, R.; Machado, R. Evaluating Software-based Fingerprint Liveness Detection using Convolutional Networks and Local Binary Patterns. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Biometric Measurements and Systems for Security and Medical Applications (BIOMS), Rome, Italy, 17 October 2014; pp. 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, C.; Bouatou, V.; Busch, C. Video-Based Fingerphoto Recognition with Anti-Spoofing Techniques with Smartphone Cameras. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference of the BIOSIG Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), Darmstadt, Germany, 4–6 September 2013; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wasnik, P.; Ramachandra, R.; Raja, K.; Busch, C. Presentation Attack Detection for Smartphone Based Fingerphoto Recognition Using Second Order Local Structures. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Signal-Image Technology &Internet-Based Systems (SITIS), Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, 26–29 November 2018; pp. 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labati, D.; Genovese, A.; Piuri, V.; Scotti, F. A Scheme for Fingerphoto Recognition in Smartphones. In Advances in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marasco, E.; Vurity, A.; Otham, A. Deep Color Spaces for Fingerphoto Presentation Attack Detection in Mobile Devices. In Computer Vision and Image Processing; CVIP 2021; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 1567, pp. 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, J.; Nicewander, A. Thirteen Ways to Look at the Correlation Coefficient. Am. Stat. 1988, 42, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshtasby, A. Similarity and Dissimilarity Measures. In Image Registration: Principles, Tools and Methods; Springer: London, UK, 2012; pp. 7–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wada, K. Labelme: Image polygonal annotation with python. Github Repos. 2016. Available online: https://github.com/wkentaro/labelme (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Hong, L.; Wan, Y.; Jain, A. Fingerprint image enhancement: Algorithm and performance evaluation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Więcław, Ł. A minutiae-based matching algorithms in fingerprint recognition systems. J. Med. Inform. Technol. 2009, 13, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zerman, E.; Rana, A.; Smolic, A. Colornet-Estimating Colorfulness in Natural Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 3791–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chen, B.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Tan, M.; Chu, G.; Vasudevan, V.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puuronen, S.; Terziyan, V.; Tsymbal, A. A dynamic integration algorithm for an ensemble of classifiers. Found. Intell. Syst. 1999, 1609, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietterich, T. Approximate Statistical Tests for Comparing Supervised Classification Learning Algorithms. Neural Comput. 1998, 10, 1895–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brownlee, J. Machine Learning Mastery. 2019. Available online: https://machinelearningmastery.com/mcnemars-test-for-machine-learning/ (accessed on 26 September 2022).
- Sankaran, A.; Malhotra, A.; Mittal, A.; Vatsa, M.; Singh, R. On Smartphone Camera based Fingerphoto Authentication. In Proceedings of the IEEE 7th International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Arlington, VA, USA, September 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, T.; Cao, K.; Jain, A. Fingerprint Spoof Buster: Use of Minutiae-Centered Patches. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 2190–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George Mason Computing Resources. Available online: https://orc.gmu.edu/resources/computing-systems/computing-resources/ (accessed on 28 June 2022).
- Marasco, E.; Albanese, M.; Patibandla, V.; Vurity, A.; Sriram, S. Biometric Multi-factor Authentication: On the Usability of the FingerPIN Scheme. Wiley Secur. Priv. J. 2022, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L. Time Efficiency. 2019. Available online: https://jcsites.juniata.edu/faculty/rhodes/cs2/ch12a.htm#Defns (accessed on 26 September 2022).
- Time Complexity: How to Measure the Efficiency of Algorithms. 2019. Available online: https://www.kdnuggets.com/2020/06/time-complexity-measure-efficiency-algorithms.html (accessed on 26 September 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).