Potential Application of Hydrocolloid-Based Oleogel and Beeswax Oleogel as Partial Substitutes of Solid Fat in Margarine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Beeswax Oleogel
2.3. Preparation of Hydrocolloid-Based Oleogel
2.4. Preparation of Margarine
2.5. Measurement of Solid Fat Content
2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.7. Rheological Tests
2.7.1. Strain Sweep Test
2.7.2. Frequency Sweep Test
2.7.3. Three Interval Thixotropy Test (3-ITT)
2.8. Spreadability Test
2.9. Color Assessment
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SFC of Margarine
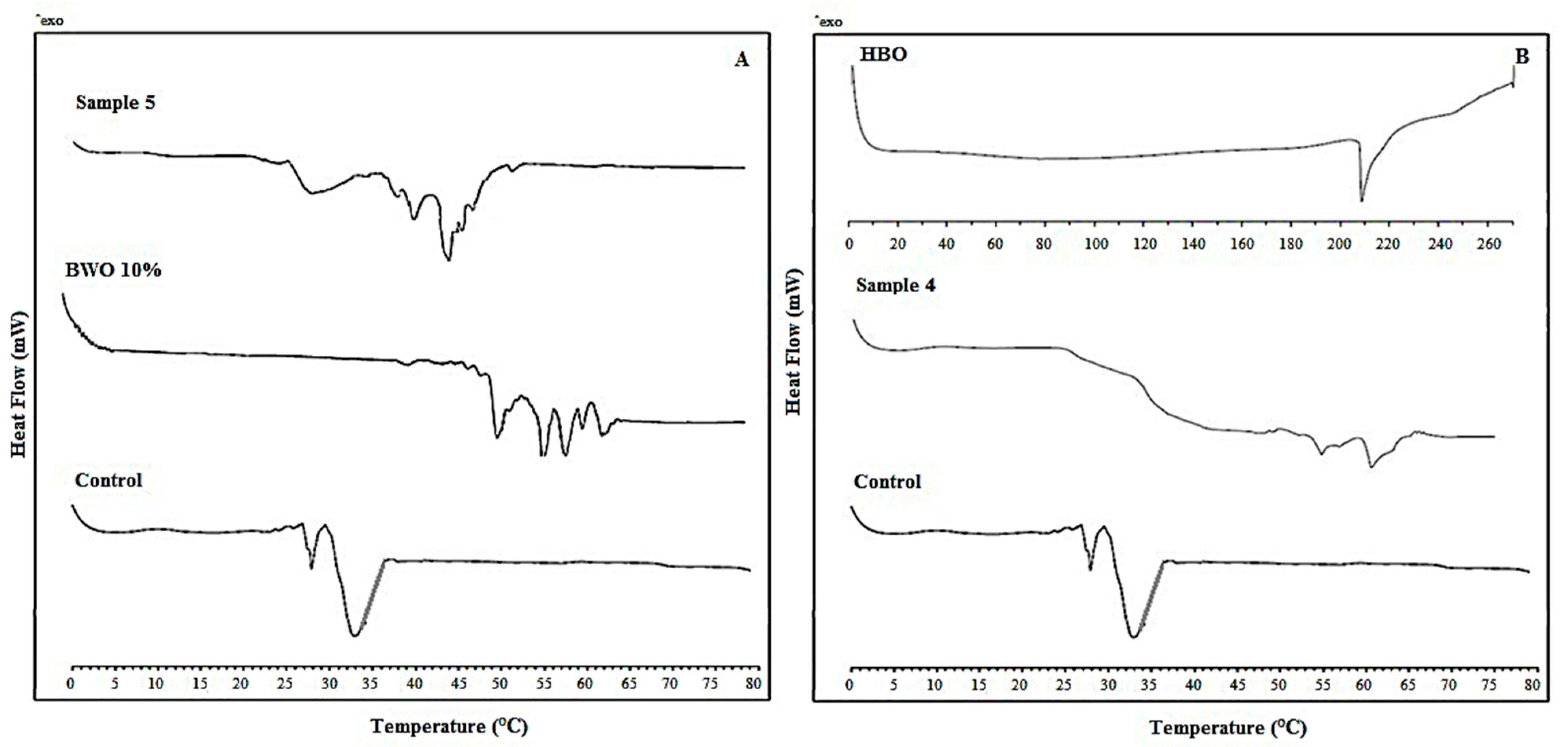
3.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry of Margarine
3.3. Strain Sweep Test of Margarine
3.4. Frequency Sweep Test of Margarine
3.5. Structure Recovery Test of Margarine
3.6. Spreadability Test of Margarine
3.7. Margarine Color
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giacomozzi, A.S.; Palla, C.A.; Carrín, M.E.; Martini, S. Physical Properties of Monoglycerides Oleogels Modified by Concentration, Cooling Rate, and High-Intensity Ultrasound. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2549–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, C.L.; Ng, C.Y.; Hong, W.O.; Wu, T.Y.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Low, L.E.; Kong, P.S.; Chan, E.S. Improving Sustainability of Palm Oil Production by Increasing Oil Extraction Rate: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, T.C.; Martins, A.J.; Pastrana, L.; Pereira, M.C.; Cerqueira, M.A. Oleogel-Based Systems for the Delivery of Bioactive Compounds in Foods. Gels 2021, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanti, R.; Barbut, S.; Marangoni, A.G. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and methylcellulose structured oil as a replacement for shortening in sandwich cookie creams. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Co, E.D.; Marangoni, A.G. Organogels: An Alternative Edible Oil-Structuring Method. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 749–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, D.M. Saturated Fats and Cardiovascular Disease: Interpretations Not as Simple as They Once Were. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1943–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration, HSS. Final Determination Regarding Partially Hydrogenated Oils. Notification; declaratory order; extension of compliance date. Fed. Regist. 2018, 83, 23358–23359. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lim, J.; Lee, J.; Hwang, H.-S.; Lee, S. Utilization of Oleogels as a Replacement for Solid Fat in Aerated Baked Goods: Physicochemical, Rheological, and Tomographic Characterization. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangoni, A.G.; Garti, N. Edible Oleogels: Structure and Health Implications; AOCS: Urbana, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kodali, D.R. Trans Fats Replacement Solutions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, T.J.; Barrera-Arellano, D.; Ribeiro, A.P.B. Oleogel-based emulsions: Concepts, structuring agents, and applications in food. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 2785–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.; Öğütcü, M. Comparative Analysis of Olive Oil Organogels Containing Beeswax and Sunflower Wax with Breakfast Margarine. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, E1732–E1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.; Winkler-Moser, J.K. Properties of margarines prepared from soybean oil oleogels with mixtures of candelilla wax and beeswax. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 3293–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, T.L.T.; Chaves, K.F.; Fernandes, G.D.; Rodrigues, J.B.; Bolini, H.M.A.; Arellano, D.B. Sensory and Technological Evaluation of Margarines with Reduced Saturated Fatty Acid Contents Using Oleogel Technology. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2018, 95, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.-S.; Singh, M.; Bakota, E.L.; Winkler-Moser, J.K.; Kim, S.; Liu, S.X. Margarine from Organogels of Plant Wax and Soybean Oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2013, 90, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, L.; Abdolmaleki, K.; Nayebzadeh, K.; Hosseini, S.M. Oleogel Fabrication Based on Sodium Caseinate, Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose, and Beeswax: Effect of Concentration, Oleogelation Method, and Their Optimization. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2020, 97, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonwai, S.; Luangsasipong, V. Production of Zero-trans Margarines from Blends of Virgin Coconut Oil, Palm Stearin and Palm Oil. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2013, 19, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, T.; Kim, D.A.; Marangoni, A.G. Ethylcellulose Oleogels. In Edible Oleogels; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 295–311. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, A.J.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Fasolin, L.H.; Cunha, R.L.; Vicente, A.A. Beeswax organogels: Influence of gelator concentration and oil type in the gelation process. Food Res. Int. 2016, 84, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavernier, I.; Doan, C.D.; van der Meeren, P.; Heyman, B.; Dewettinck, K. The Potential of Waxes to Alter the Microstructural Properties of Emulsion-Templated Oleogels. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2018, 120, 1700393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibowski, P. Effect of thermal and mechanical factors on rheological properties of high performance inulin gels and spreads. J. Food Eng. 2010, 99, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.; Öğütcü, M. Oleogels as spreadable fat and butter alternatives: Sensory description and consumer perception. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 50259–50267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Akoh, C.C.; Himmelsbach, D.S.; Lee, K.-T. Preparation of Interesterified Plastic Fats from Fats and Oils Free of Trans Fatty Acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4039–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, A.P.B.; Basso, R.C.; Grimaldi, R.; Gioielli, L.A.; Gonçalves, L.A.G. Instrumental Methods for the Evaluation of Interesterified Fats. Food Anal. Methods 2009, 2, 282–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laia, O.; Ghazalia, H.; Cho, F.; Chong, C. Physical and textural properties of an experimental table margarine prepared from lipase-catalysed transesterified palm stearin: Palm kernel olein mixture during storage. Food Chem. 2000, 71, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, C.D.; Patel, A.R.; Tavernier, I.; de Clercq, N.; van Raemdonck, K.; dan de Walle, D.; Delbaere, C.; Dewettinck, K. The feasibility of wax-based oleogel as a potential co-structurant with palm oil in low-saturated fat confectionery fillings. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 1903–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkesen, I.; Mert, B. Utilization of Beeswax Oleogel-Shortening Mixtures in Gluten-Free Bakery Products. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2019, 96, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Rajarethinem, P.S.; Grędowska, A.; Turhan, O.; Lesaffer, A.; de Vos, W.H.; van de Walle, D.; Dewettinck, K. Edible applications of shellac oleogels: Spreads, chocolate paste and cakes. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mert, B.; Demirkesen, I. Evaluation of highly unsaturated oleogels as shortening replacer in a short dough product. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, G.; Akoh, C.C. Enzymatic Synthesis of trans -Free Structured Margarine Fat Analogues Using Stearidonic Acid Soybean and High Stearate Soybean Oils. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Cludts, N.; Bin Sintang, M.D.; Lewille, B.; Lesaffer, A.; Dewettinck, K. Polysaccharide-Based Oleogels Prepared with an Emulsion-Templated Approach. ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 3435–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, X.-W.; Guo, J.; Yin, S.-W.; Yang, X.-Q. Wheat gluten based percolating emulsion gels as simple strategy for structuring liquid oil. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, A.; Bae, W.; Hwang, H.-S.; Lee, H.G.; Lee, S. Evaluation of canola oil oleogels with candelilla wax as an alternative to shortening in baked goods. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, A.I.; Co, E.D.; Marangoni, A.G. Structure and Physical Properties of Plant Wax Crystal Networks and Their Relationship to Oil Binding Capacity. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 885–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghotra, B.S.; Dyal, S.D.; Narine, S.S. Lipid shortenings: A review. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 1015–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, F.; Shan, L.; Wang, X. Influence of lipid composition, crystallization behavior and microstructure on hardness of palm oil-based margarines. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 230, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.H. Edible Oil and Fat Products: Oils and Oil Seeds. In Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, I.K.; Lee, S. Utilization of foam structured hydroxypropyl methylcellulose for oleogels and their application as a solid fat replacer in muffins. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, C.; Giacomozzi, A.; Genovese, D.B.; Carrín, M.E. Multi–objective optimization of high oleic sunflower oil and monoglycerides oleogels: Searching for rheological and textural properties similar to margarine. Food Struct. 2017, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibowski, P.; Zarzycki, P.; Krzepkowska, M. The Rheological and Instrumental Textural Properties of Selected Table Fats. Int. J. Food Prop. 2008, 11, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, B.J.; Wendorff, W.L.; Lindsay, R.C. Effects of Ingredients on the Functionality of Fat-free Process Cheese Spreads. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 822–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangchai, W.; Sangsirimongkolying, R.; Methacanon, P. Feasibility study of margarine substitute based on Gelatin-oil emulsion gel. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2018, 45, 505–514. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, H.; Kim, S.; Winkler-Moser, J.K.; Lee, S.; Liu, S.X. Feasibility of hemp seed oil oleogels structured with natural wax as solid fat replacement in margarine. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 1055–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.; Öğütcü, M. The texture, sensory properties and stability of cookies prepared with wax oleogels. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | SFO% | OL% | PO% | PHPO% | Replacement Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 36 | 0 | 27 | 7 | Control |
| 2 | 36 | 3.50 | 27 | 3.50 | 50% (PHPO) with BWO or HBO |
| 3 | 36 | 5.25 | 27 | 1.75 | 75% (PHPO) with BWO or HBO |
| 4 | 36 | 7 | 27 | 0 | 100% (PHPO) with BWO or HBO |
| 5 | 36 | 13.75 | 20.25 | 0 | 100% (PHPO) and 25% (PO) with BWO or HBO |
| 6 | 36 | 20.50 | 13.50 | 0 | 100% (PHPO) and 50% (PO) with BWO or HBO |
| Sample | 10 °C | 20 °C | 30 °C | 35 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 21.59 ± 0.10 a | 9.75 ± 0.30 a | 4.31 ± 0.10 a | 2.13 ± 0.02 a | |
| BWO | 2 | 18.35 ± 0.00 c | 7.36 ± 0.10 c | 3.93 ± 0.08 b | 2.09 ± 0.00 b |
| 3 | 16.14 ± 0.10 e | 6.11 ± 0.10 d | 3.69 ± 0.09 c | 2.04 ± 0.01 c | |
| 4 | 15.21 ± 0.10 f | 5.51 ± 0.09 e | 3.20 ± 0.10 d | 2.01 ± 0.01 d | |
| 5 | 11.31 ± 0.10 h | 4.31 ± 0.10 f | 2.90 ± 0.06 e | 1.93 ± 0.02 e | |
| 6 | 8.94 ± 0.30 i | 4.01 ± 0.00 g | 2.89 ± 0.04 e | 1.92 ± 0.01 e | |
| HBO | 2 | 20.34 ± 0.10 b | 9.28 ± 0.20 a | 3.85 ± 0.09 bc | 1.80 ± 0.06 f |
| 3 | 17.28 ± 0.30 d | 8.31 ± 0.10 b | 2.97 ± 0.07 e | 1.20 ± 0.03 g | |
| 4 | 13.40 ± 0.20 g | 5.58 ± 0.09 e | 2.84 ± 0.10 e | 1.24 ± 0.03 h | |
| 5 | 3.50 ± 0.20 j | 0.80 ± 0.10 h | 0.00 ± 0.00 f | 0.00 ± 0.00 i | |
| 6 | 0.90 ± 0.08 k | 0.00 ± 0.00 i | 0.00 ± 0.00 f | 0.00 ± 0.00 i | |
| Sample | τy (Pa) | Tan δ | G′ (Pa) | G″ (Pa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 989 ± 3 d | 0.13 ± 0.003 e | 536,432 ± 2354 f | 69,736 ± 2154 f | |
| BWO | 2 | 992 ± 4 de | 0.13 ± 0.001 e | 1,082,967 ± 3895 a | 140,786 ± 1573 c |
| 3 | 990 ± 3 d | 0.14 ± 0.001 d | 912,172 ± 3500 b | 127,704 ± 1322 d | |
| 4 | 997 ± 1 e | 0.13 ± 0.001 e | 909,367 ± 2501 b | 118,218 ± 1215 e | |
| 5 | 1005 ± 3 c | 0.13 ± 0.003 e | 539,775 ± 2684 f | 70,773 ± 1387 f | |
| 6 | 1009 ± 4 bc | 0.15 ± 0.002 c | 375,505 ± 1900 i | 56,326 ± 1224 i | |
| HBO | 2 | 1721 ± 7 a | 0.11 ± 0.006 f | 427,257 ± 1982 h | 46,998 ± 2700 g |
| 3 | 1016 ± 5 b | 0.13 ± 0.005 e | 477,719 ± 3202 g | 62,103 ± 2845 h | |
| 4 | 996 ± 5 ed | 0.13 ± 0.003 e | 547,702 ± 3764 e | 71,201 ± 1935 f | |
| 5 | 610 ± 7 f | 0.33 ± 0.005 b | 684,321 ± 2495 d | 225,826 ± 4590 b | |
| 6 | 563 ± 6 g | 0.45 ± 0.002 a | 708,569 ± 3478 c | 318,856 ± 3348 a | |
| Sample | a (Pa × s/rad) | b | Recovery% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 232,620 ± 2051 h | 0.10 ± 0.01 f | 26.30 ± 1.50 f | |
| BWO | 2 | 461,400 ± 3212 a | 0.15 ± 0.02 e | 27.40 ± 1.00 f |
| 3 | 422,155 ± 2982 b | 0.18 ± 0.00 c | 30.80 ± 1.90 e | |
| 4 | 403,305 ± 2743 c | 0.23 ± 0.02 b | 31.90 ± 1.30 e | |
| 5 | 239,777 ± 2037 g | 0.40 ± 0.02 a | 44.50 ± 2.80 d | |
| 6 | 188,044 ± 2533 i | 0.47 ± 0.01 a | 51.60 ± 3.30 c | |
| HBO | 2 | 190,940 ± 2264 i | 0.12 ± 0.01 e | 32.60 ± 0.90 e |
| 3 | 235,150 ± 1835 h | 0.13 ± 0.01 e | 45.30 ± 1.70 d | |
| 4 | 275,270 ± 2698 f | 0.13 ± 0.00 e | 56.00 ± 2.20 c | |
| 5 | 377,883 ± 3263 e | 0.17 ± 0.01 ce | 66.00 ± 0.70 b | |
| 6 | 391,442 ± 1988 d | 0.20 ± 0.01 b | 71.50 ± 2.30 a | |
| Sample | Area under the Curve (g × sec) | Hardness (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2643 ± 53 f | 2526 ± 43 f | |
| BWO | 2 | 6190 ± 105 a | 5108 ± 89 a |
| 3 | 6095 ± 123 a | 4904 ± 27 b | |
| 4 | 5508 ± 98 b | 4325 ± 90 c | |
| 5 | 3076 ± 91 e | 2357 ± 32 g | |
| 6 | 2633 ± 66 f | 1651 ± 67 l | |
| HBO | 2 | 1710 ± 32 i | 1609 ± 44 i |
| 3 | 2020 ± 64 h | 2035 ± 58 h | |
| 4 | 2430 ± 12 g | 2314 ± 29 g | |
| 5 | 3600 ± 33 d | 3748 ± 27 e | |
| 6 | 3855 ± 47 c | 4012 ± 51 d | |
| Sample | L* | a* | b* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 88.14 ± 0.03 a | 0.28 ± 0.006 e | 15.37 ± 0.020 k | |
| BWO | 2 | 87.17 ± 0.02 d | 0.28 ± 0.000 e | 16.56 ± 0.006 h |
| 3 | 87.04 ± 0.02 e | 0.28 ± 0.000 e | 17.40 ± 0.006 f | |
| 4 | 86.29 ± 0.03 f | 0.28 ± 0.006 e | 17.42 ± 0.006 e | |
| 5 | 84.01 ± 0.00 h | 0.28 ± 0.006 e | 20.82 ± 0.000 c | |
| 6 | 83.61 ± 0.01 j | 0.28 ± 0.006 e | 21.37 ± 0.006 a | |
| HBO | 2 | 88.04 ± 0.02 b | 0.58 ± 0.006 d | 15.47 ± 0.020 j |
| 3 | 87.69 ± 0.02 c | 0.59 ± 0.006 d | 15.85 ± 0.020 i | |
| 4 | 87.19 ± 0.01 d | 0.61 ± 0.006 c | 17.24 ± 0.020 g | |
| 5 | 84.68 ± 0.02 g | 1.10 ± 0.006 b | 20.45 ± 0.030 d | |
| 6 | 83.96 ± 0.02 i | 1.30 ± 0.006 a | 20.88 ± 0.020 b | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdolmaleki, K.; Alizadeh, L.; Nayebzadeh, K.; Baranowska, H.M.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A. Potential Application of Hydrocolloid-Based Oleogel and Beeswax Oleogel as Partial Substitutes of Solid Fat in Margarine. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12136. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312136
Abdolmaleki K, Alizadeh L, Nayebzadeh K, Baranowska HM, Kowalczewski PŁ, Mousavi Khaneghah A. Potential Application of Hydrocolloid-Based Oleogel and Beeswax Oleogel as Partial Substitutes of Solid Fat in Margarine. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(23):12136. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312136
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdolmaleki, Khadije, Leyla Alizadeh, Kooshan Nayebzadeh, Hanna Maria Baranowska, Przemysław Łukasz Kowalczewski, and Amin Mousavi Khaneghah. 2022. "Potential Application of Hydrocolloid-Based Oleogel and Beeswax Oleogel as Partial Substitutes of Solid Fat in Margarine" Applied Sciences 12, no. 23: 12136. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312136
APA StyleAbdolmaleki, K., Alizadeh, L., Nayebzadeh, K., Baranowska, H. M., Kowalczewski, P. Ł., & Mousavi Khaneghah, A. (2022). Potential Application of Hydrocolloid-Based Oleogel and Beeswax Oleogel as Partial Substitutes of Solid Fat in Margarine. Applied Sciences, 12(23), 12136. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312136








