Effect of Raster Angle and Infill Pattern on the In-Plane and Edgewise Flexural Properties of Fused Filament Fabricated Acrylonitrile–Butadiene–Styrene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Printing of Specimens
2.2. Flexural Test
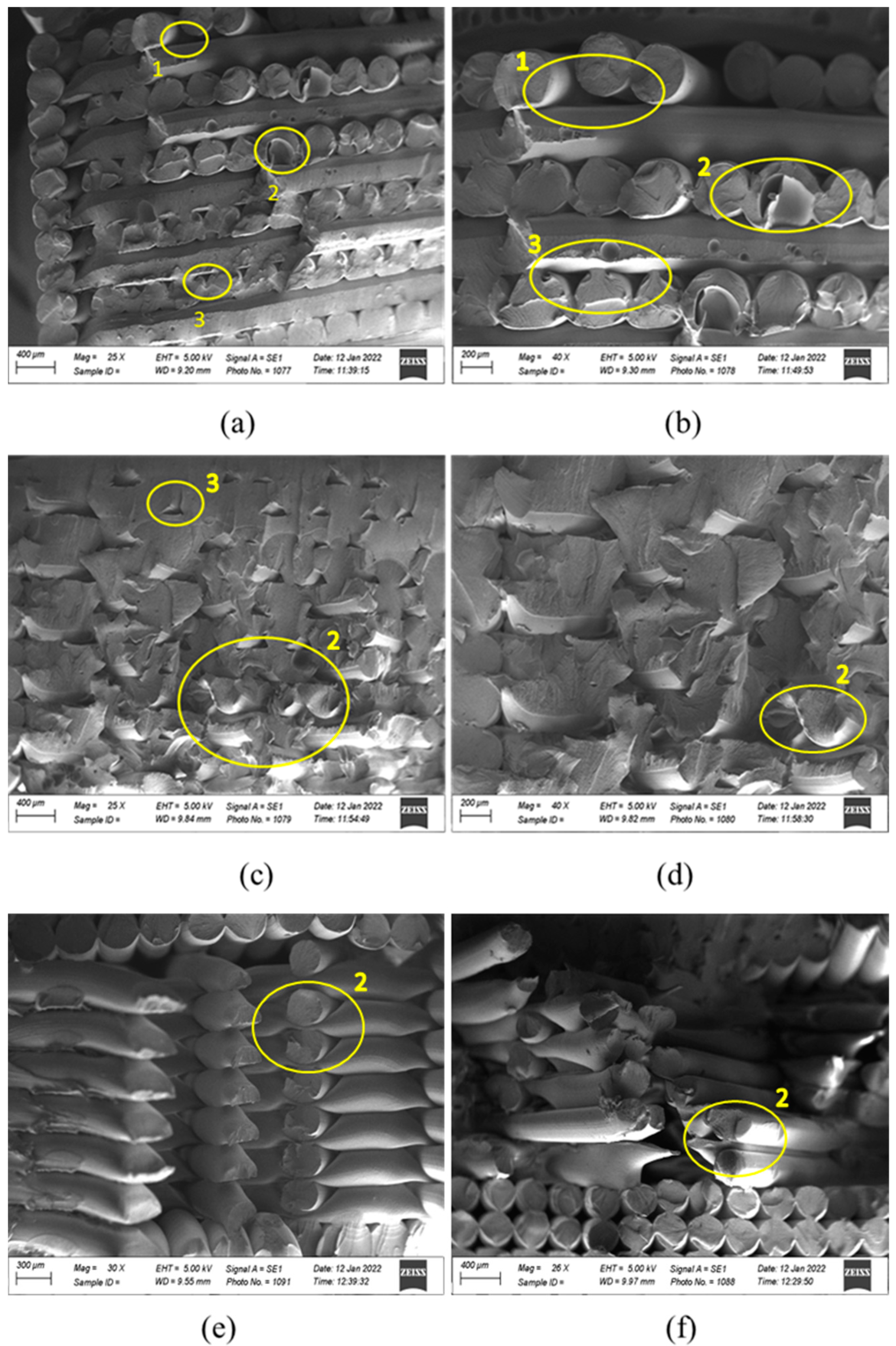
2.3. Fractographic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Raster Angle on Flexural Properties
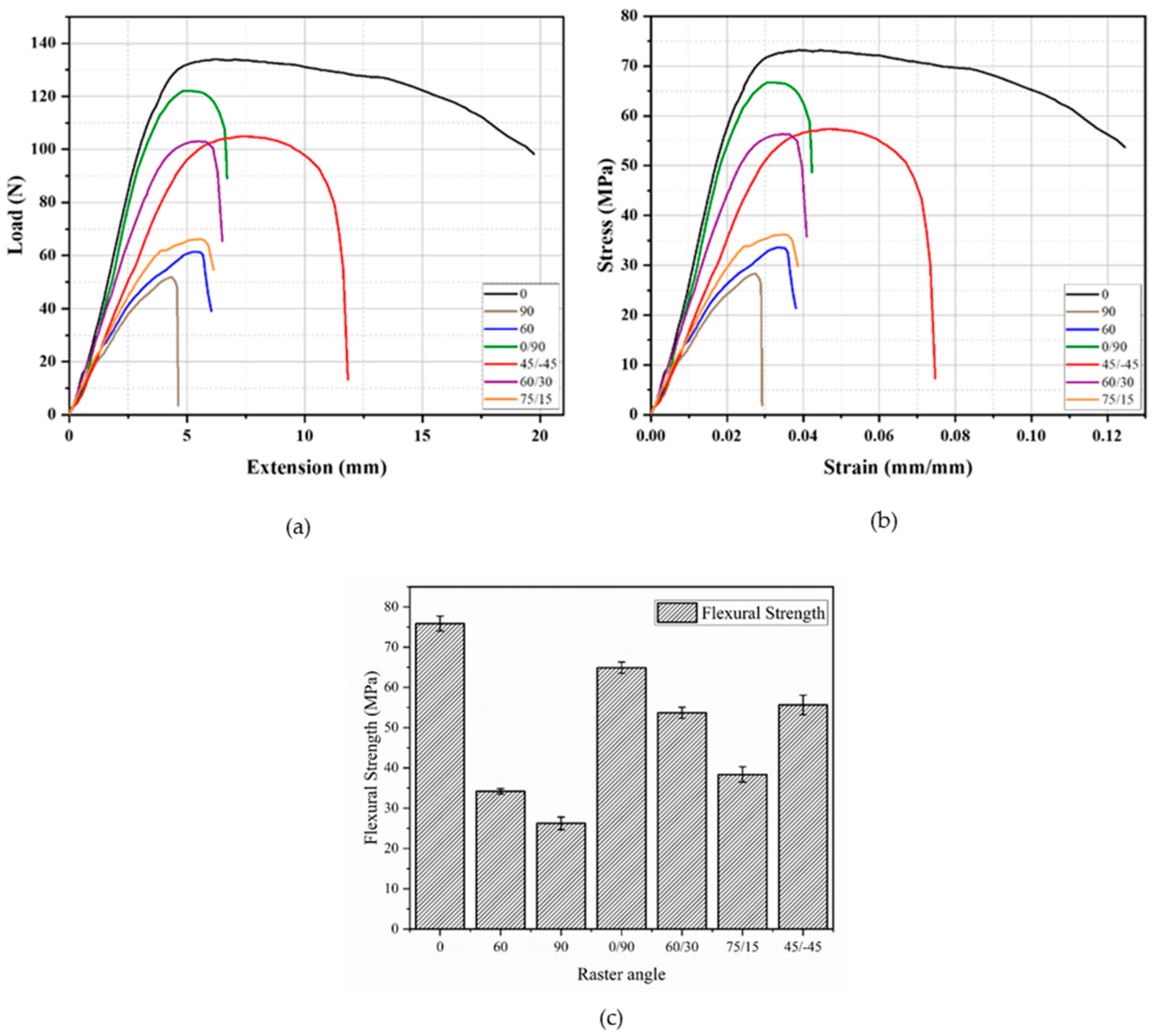
3.1.1. In-Plane Testing
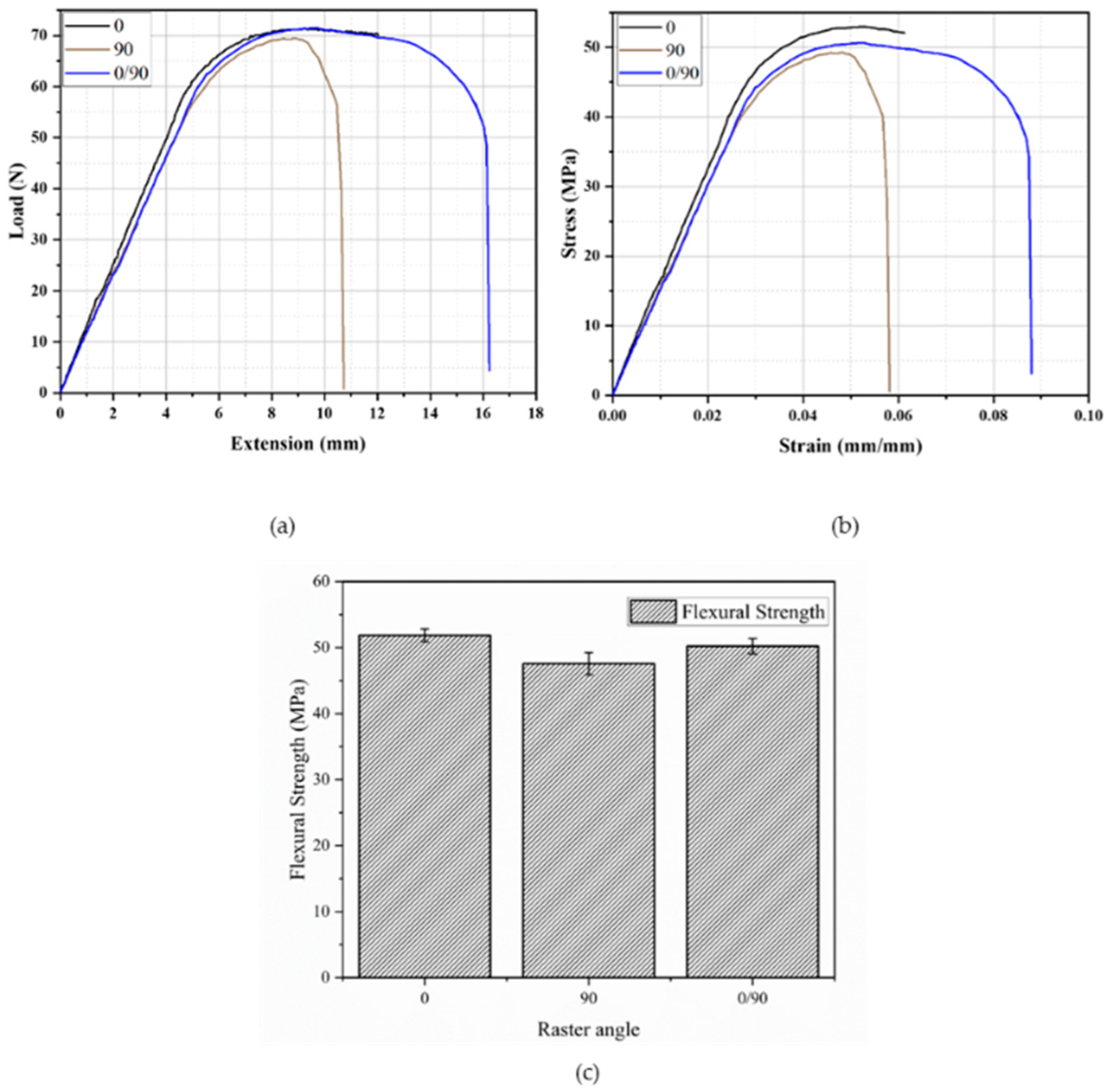
3.1.2. Edgewise Testing
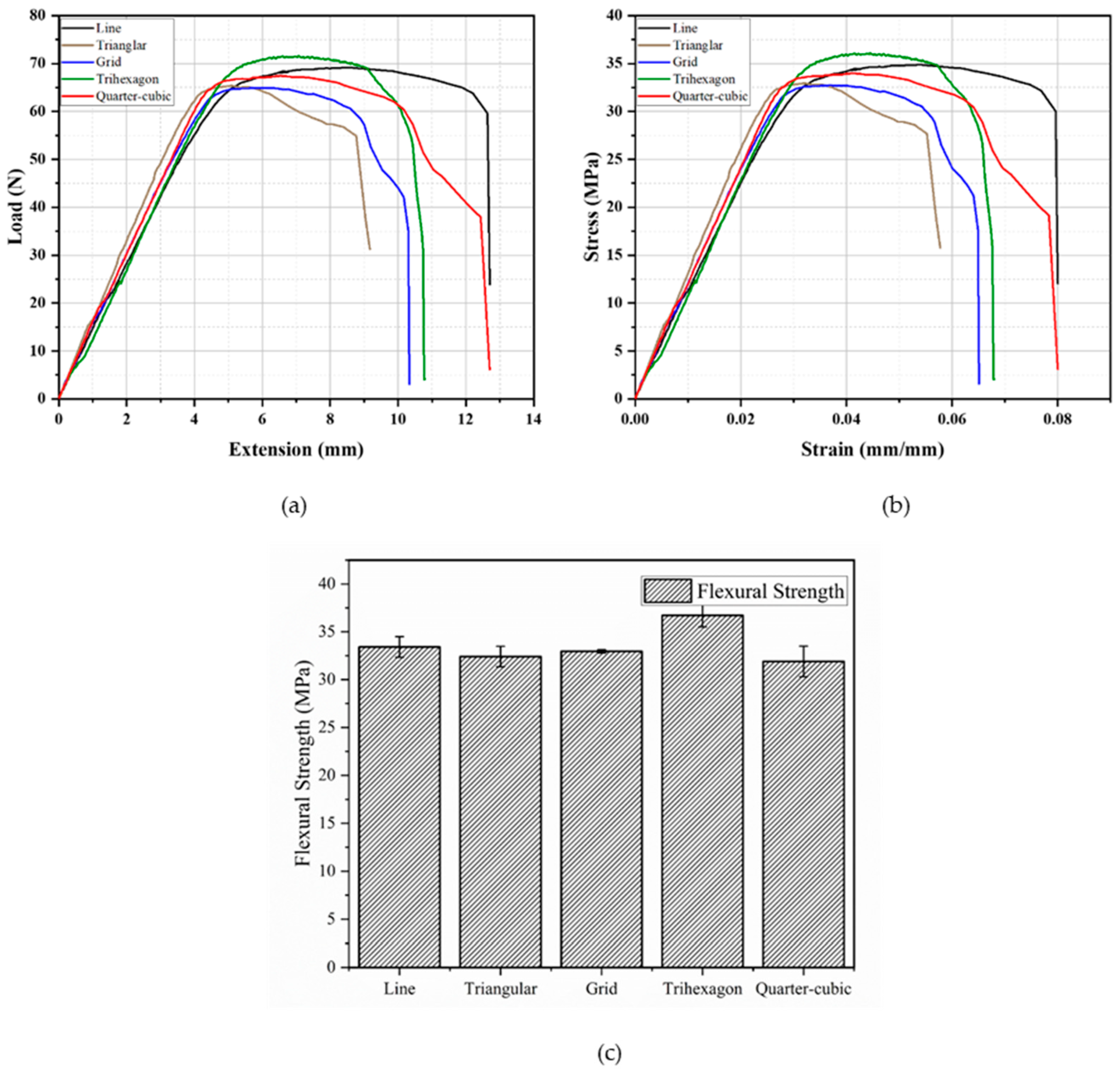
3.2. Effect of Infill Pattern on Flexural Properties
3.2.1. In-Plane Testing
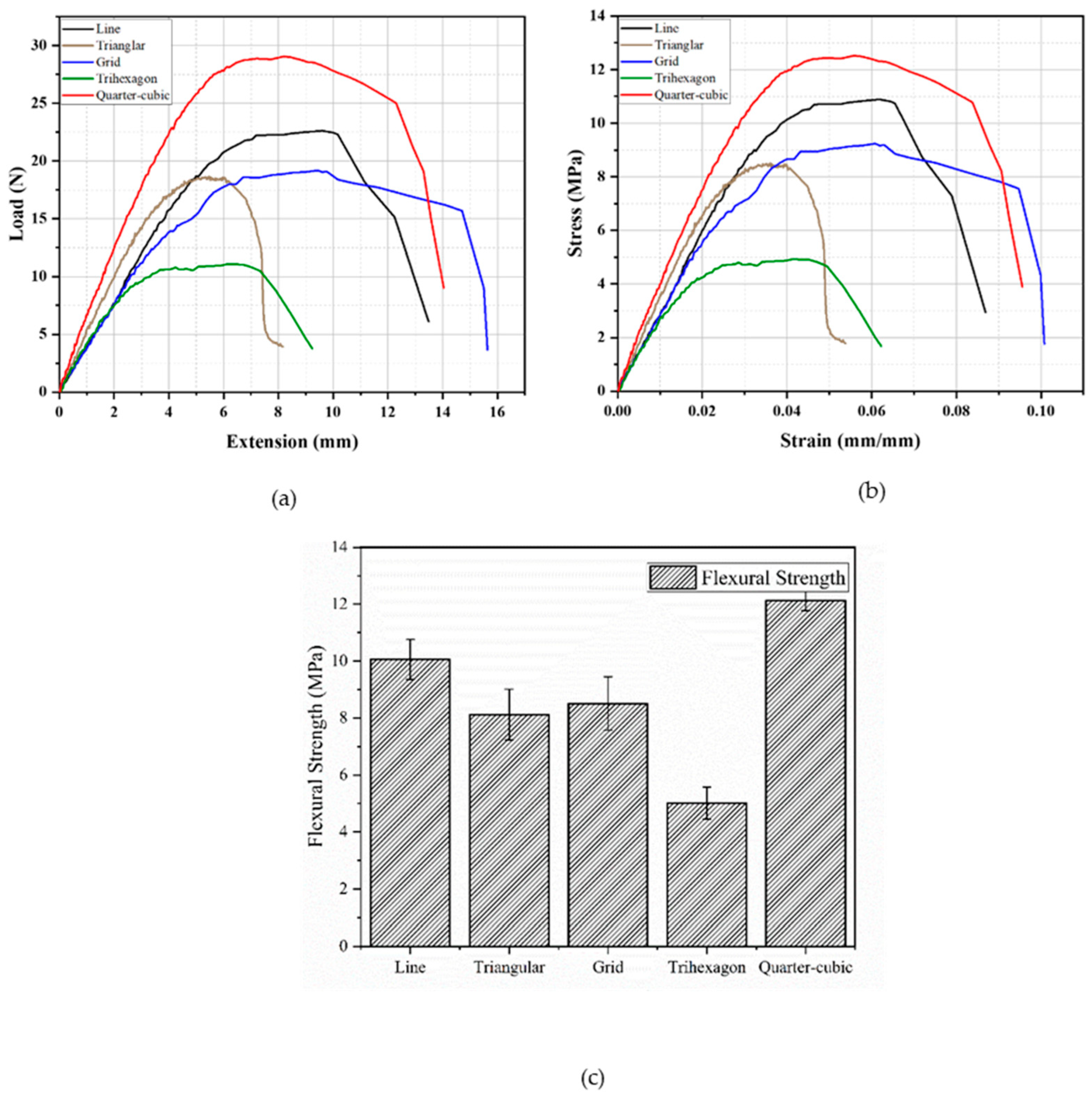
3.2.2. Edgewise Testing
3.2.3. Fractographic Analysis
4. Conclusions
- The samples with 0° raster angle sustained the highest in-plane and edgewise flexural load among all tested raster angles. The increase in the load carrying capacity at 0° was 188% greater than that at 90°;
- 0° raster angle exhibited the highest in-plane/edgewise flexural modulus. In-plane flexural modulus increased by about 148% when the raster angle was changed from 90° to 0°;
- Overall, the edgewise flexural modulus of acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene (ABS) was lower than the in-plane flexural modulus. However, the trend was similar, i.e., the highest edgewise flexural modulus was also obtained for the 0° raster angle;
- For the infill patterns, the percentage difference comparison was used to evaluate the most optimum infill pattern for the flexural loading conditions. This comparison indicated that, for both the flexural load and modulus in both directions, the quarter-cubic pattern was the optimum choice for components such as structural components subjected to bi-directional flexural loading conditions. This is because the quarter-cubic pattern outperformed the tri-hexagon pattern by 89% and 37% in terms of flexural load and modulus, respectively;
- The difference in the properties in the two directions for every parameter indicates that the additive manufacturing processes, especially the FFF process, cause a significant degree of anisotropy in the fabricated components. Hence, this study was of fundamental importance to serve as a guideline where AM for the design of structural components subjected to flexural loading conditions is utilized.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vafadar, A.; Guzzomi, F.; Rassau, A.; Hayward, K. Advances in Metal Additive Manufacturing: A Review of Common Processes, Industrial Applications, and Current Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohar, S.; Hussain, G.; Ilyas, M.; Ali, A. Performance of 3D printed topologically optimized novel auxetic structures under compressive loading: Experimental and FE analyses. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.W.; Hussain, G.; Al-Ghamdi, K.A.; Altaf, K. Mechanical properties of an additive manufactured CF-PLA/ABS hybrid composite sheet. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2019, 34, 1577–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, N.; Siddiqi, M.; Muhammad, R. Thermal simulation of grain during selective laser melting process in 3D metal printing. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2020, 39, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/ASTM 52900:2015; Additive Manufacturing-General Principles-Terminologies. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/69669.html (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Gohar, S.; Hussain, G.; Ali, A.; Ahmad, H. Mechanical performance of honeycomb sandwich structures built by FDM printing technique. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Hussain, G.; Gohar, S.; Ali, A.; Alkahtani, M. Impact Toughness of Hybrid Carbon Fiber-PLA/ABS Laminar Composite Produced through Fused Filament Fabrication. Polymers 2021, 13, 3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaal, M.; Anas, M.; Rastogi, H.; Bhardwaj, N.; Rahaman, A. Effect of FDM process parameters on mechanical properties of 3D-printed carbon fibre–PLA composite. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 6, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, I.J.; Sevvel, P.; Gunasekaran, J. A review on the various processing parameters in FDM. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, R.; Raghuraman, S. Experimental analysis on density, micro-hardness, surface roughness and processing time of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) through Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) using Box Behnken Design (BBD). Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 27, 102353. [Google Scholar]
- Ramezani Dana, H.; El Mansori, M.; Barrat, M.; Seck, C. Tensile behavior of additively manufactured carbon fiber reinforced polyamide-6 composites. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2022, 61, 624–641. [Google Scholar]
- Balderrama-Armendariz, C.O.; MacDonald, E.; Espalin, D.; Cortes-Saenz, D.; Wicker, R.; Maldonado-Macias, A. Torsion analysis of the anisotropic behavior of FDM technology. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azammi, A.N.; Ilyas, R.; Sapuan, S.; Ibrahim, R.; Atikah, M.; Asrofi, M.; Atiqah, A. Characterization studies of biopolymeric matrix and cellulose fibres based composites related to functionalized fibre-matrix interface. In Interfaces in Particle and Fibre Reinforced Composites; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2020; pp. 29–93. [Google Scholar]
- Byberg, K.I.; Gebisa, A.W.; Lemu, H.G. Mechanical properties of ULTEM 9085 material processed by fused deposition modeling. Polym. Test. 2018, 72, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplun, B.W.; Zhou, R.; Jones, K.W.; Dunn, M.L.; Yakacki, C.M. Influence of orientation on mechanical properties for high-performance fused filament fabricated ultem 9085 and electro-statically dissipative polyetherketoneketone. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motaparti, K.P.; Taylor, G.; Leu, M.C.; Chandrashekhara, K.; Castle, J.; Matlack, M. Experimental investigation of effects of build parameters on flexural properties in fused deposition modelling parts. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2017, 12, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.; Wang, X.; Mason, L.; Leu, M.C.; Chandrashekhara, K.; Schniepp, T.; Jones, R. Flexural behavior of additively manufactured Ultem 1010: Experiment and simulation. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2018, 24, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Geng, P.; Li, G.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J. Influence of layer thickness and raster angle on the mechanical properties of 3D-printed PEEK and a comparative mechanical study between PEEK and ABS. Materials 2015, 8, 5834–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgun, I.; Ertan, R. Experimental investigation of FDM process for improvement of mechanical properties and production cost. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2014, 20, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Kumar, K.N.; Ibrahim, A.J.; Anandu, K.; Gurudhevan, R. Impact of fused deposition process parameter (infill pattern) on the strength of PETG part. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 27, 1801–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Siddiqui, B.A.; Fahad, M.; Khan, M.A. Evaluation of the effect of infill pattern on mechanical stregnth of additively manufactured specimen. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Fekete, I.; Ronkay, F.; Lendvai, L. Highly toughened blends of poly (lactic acid)(PLA) and natural rubber (NR) for FDM-based 3D printing applications: The effect of composition and infill pattern. Polym. Test. 2021, 99, 107205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grbović, A.; Kastratović, G.; Sedmak, A.; Balać, I.; Popović, M.D. Fatigue crack paths in light aircraft wing spars. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 123, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Yokozeki, T.; Arizono, H.; Tamayama, M. Fundamental Study on Adaptive Wing Structure for Control of Wing Load Distribution. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Aeronaut. Space Sci. Aerosp. Technol. Jpn. 2017, 15, a83–a88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D790-02; Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2002.
- Akhoundi, B.; Behravesh, A.H. Effect of filling pattern on the tensile and flexural mechanical properties of FDM 3D printed products. Exp. Mech. 2019, 59, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
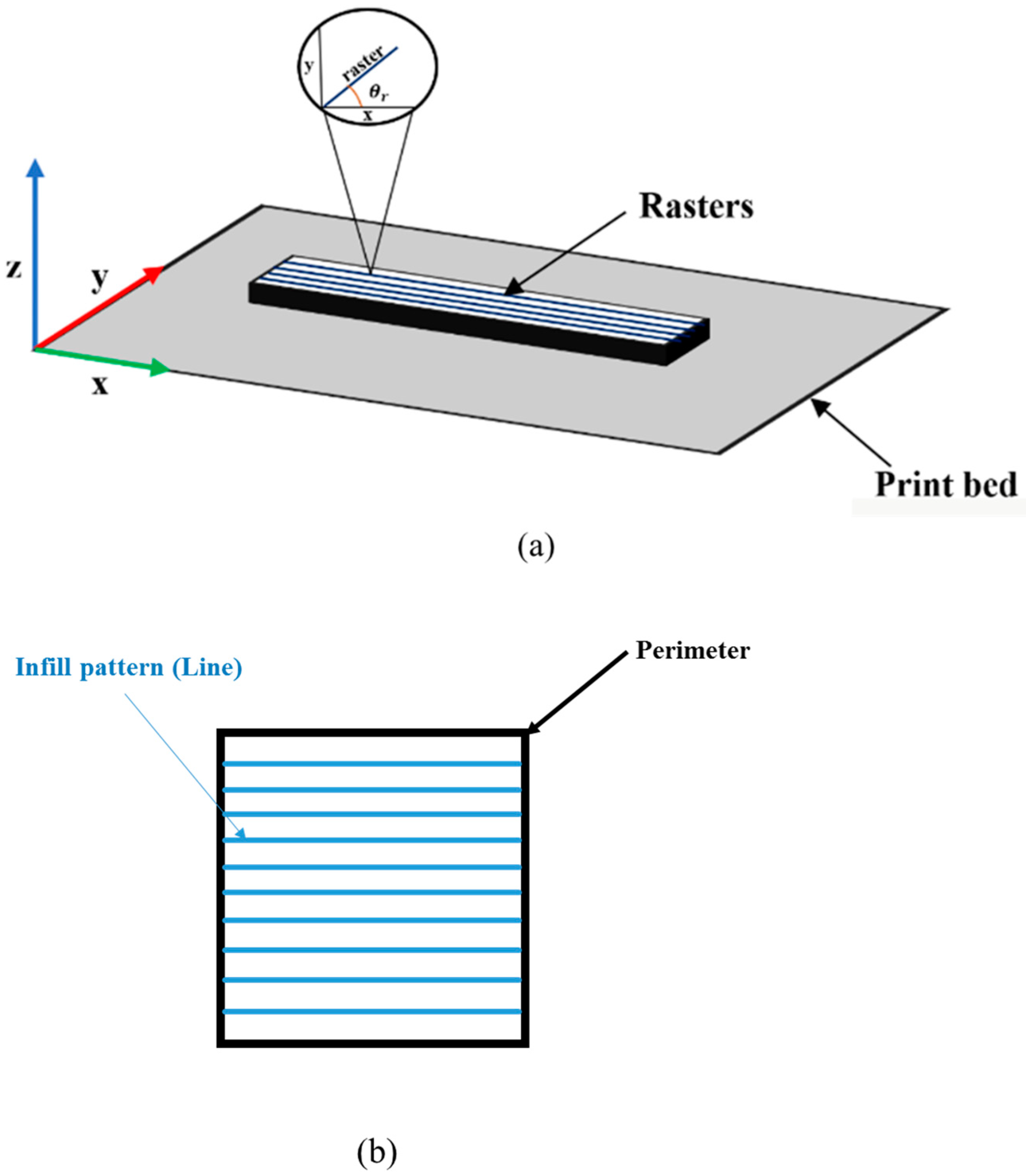



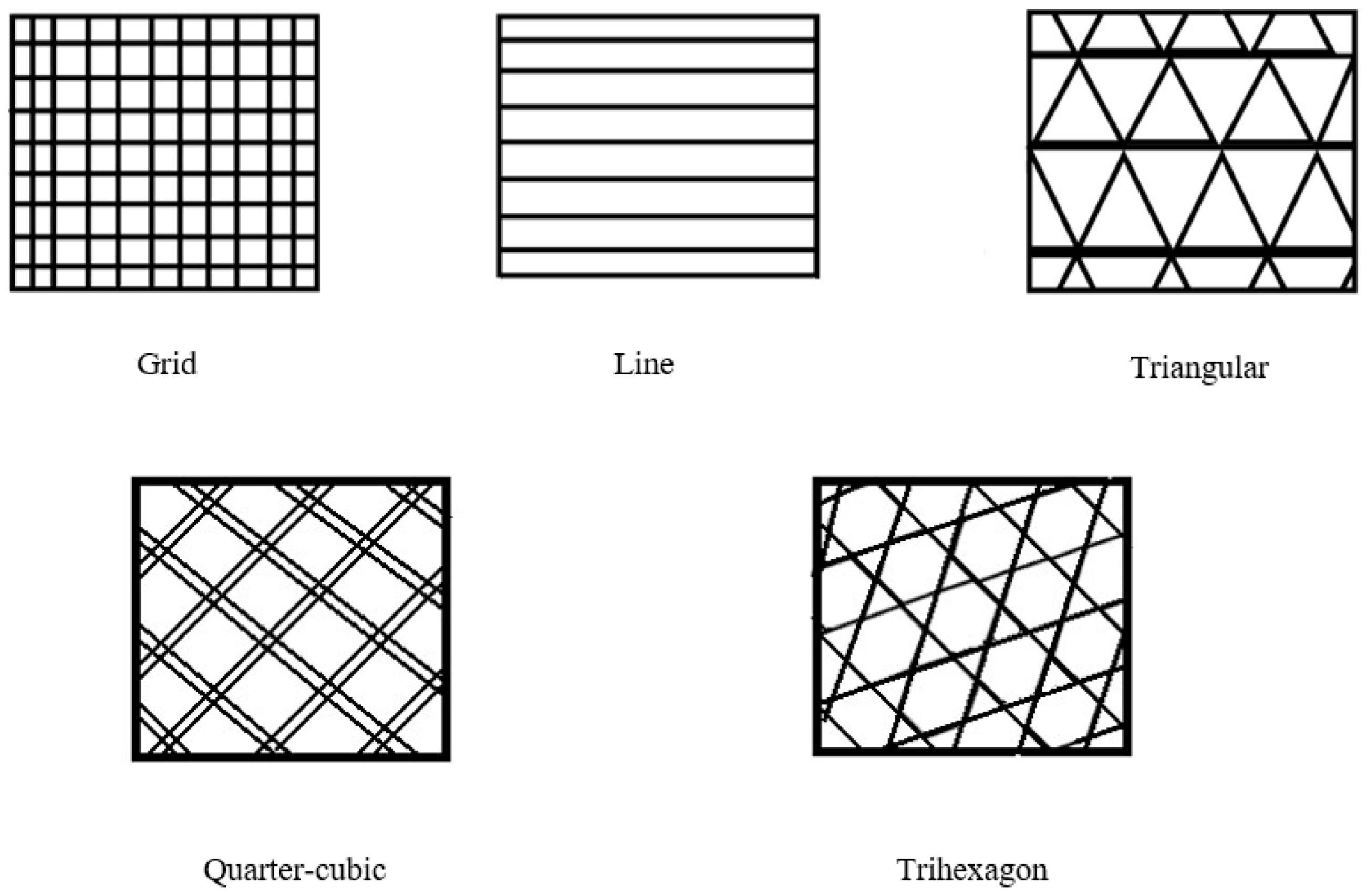


| Process Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Nozzle diameter (mm) | 0.4 |
| Layer height (mm) | 0.3 |
| Chamber Temperature (C) | 28 |
| Nozzle temperature (C) | 250 |
| Bed temperature (C) | 100 |
| Printing speed (mm/s) | 60 |
| Number of bottom layers with 100% infill density (for infill pattern evaluation) | 3 |
| Number of top layers 100% infill density (for infill pattern evaluation) | 3 |
| Number of layers inner layers contributing to 60% infill density (for infill pattern evaluation) * | 8 |
| Raster Angle (°) | Max. Flexural Load (N) | Flexural Modulus (Gpa) | Flexural Strength (Mpa) | Fracture Strain (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 138.42 ± 3.19 | 3.2 ± 0.01 | 75.87 ± 1.88 | Fracture did not occur |
| 60 | 62.52 ± 1.26 | 1.56 ± 0.02 | 34.19 ± 0.67 | 3.59 ± 0.03 |
| 90 | 48.02 ± 2.87 | 1.29 ± 0.08 | 26.24 ± 1.57 | 2.97 ± 0.29 |
| 0/90 | 119.10 ± 2.60 | 2.80 ± 0.14 | 64.90 ± 1.40 | 3.49 ± 0.34 |
| 45/−45 | 101.56 ± 2.61 | 1.87 ± 0.41 | 55.64 ± 1.38 | 5.68 ± 0.13 |
| 60/30 | 98.22 ± 3.45 | 2.14 ± 0.12 | 53.69 ± 1.91 | 3.82 ± 0.12 |
| 75/15 | 70.34 ± 4.66 | 1.70 ± 0.02 | 38.37 ± 2.41 | 3.76 ± 0.12 |
| Raster Angle (o) | Max. Flexural Load (N) | Flexural Modulus (GPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Fracture Strain (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 73.2 ± 1.36 | 1.61 ± 0.01 | 51.9 ± 0.97 | Fracture did not occur |
| 90 | 67.1 ± 2.37 | 1.51 ± 0.02 | 47.6 ± 1.68 | 5.8 ± 0.18 |
| 0/90 | 70.9 ± 1.64 | 1.53 ± 0.04 | 50.2 ± 1.16 | 7.6 ± 0.35 |
| Pattern | Max. Flexural Load (N) | Flexural Modulus (GPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Fracture Strain (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line | 62.7 ± 2.14 | 1.06 ± 0.01 | 33.4 ± 1.08 | 7.36 ± 0.60 |
| Triangular | 64.3 ± 2.12 | 1.26 ± 0.04 | 32.4 ± 1.07 | 4.95 ± 0.40 |
| Grid | 65.3 ± 0.32 | 1.21 ± 0.02 | 33.0 ± 0.16 | 5.95 ± 0.69 |
| Tri-hexagon | 69.0 ± 2.77 | 1.23 ± 0.03 | 36.7 ± 1.22 | 5.99 ± 0.35 |
| Quarter-cubic | 63.3 ± 3.19 | 1.17 ± 0.03 | 31.9 ± 1.60 | 6.03 ± 0.51 |
| Pattern | Max. Flexural Load (N) | Flexural Modulus (GPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Fracture Strain (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line | 22.6 ± 1.25 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 10.1 ± 0.70 | 6.7 ± 0.1 |
| Triangular | 18.9 ± 1.74 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 8.12 ± 0.89 | 4.8 ± 0.1 |
| Grid | 19.2 ± 1.52 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 8.51 ± 0.94 | 9.4 ± 1.2 |
| Tri-hexagon | 11.1 ± 0.90 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 5.01 ± 0.56 | 5.0 ± 0.1 |
| Quarter-cubic | 29.0 ± 1.01 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 12.1 ± 0.36 | 8.3 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qayyum, H.; Hussain, G.; Sulaiman, M.; Hassan, M.; Ali, A.; Muhammad, R.; Wei, H.; Shehbaz, T.; Aamir, M.; Altaf, K. Effect of Raster Angle and Infill Pattern on the In-Plane and Edgewise Flexural Properties of Fused Filament Fabricated Acrylonitrile–Butadiene–Styrene. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12690. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412690
Qayyum H, Hussain G, Sulaiman M, Hassan M, Ali A, Muhammad R, Wei H, Shehbaz T, Aamir M, Altaf K. Effect of Raster Angle and Infill Pattern on the In-Plane and Edgewise Flexural Properties of Fused Filament Fabricated Acrylonitrile–Butadiene–Styrene. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(24):12690. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412690
Chicago/Turabian StyleQayyum, Hamza, Ghulam Hussain, Muhammad Sulaiman, Malik Hassan, Aaqib Ali, Riaz Muhammad, Hongyu Wei, Tauheed Shehbaz, Muhammad Aamir, and Khurram Altaf. 2022. "Effect of Raster Angle and Infill Pattern on the In-Plane and Edgewise Flexural Properties of Fused Filament Fabricated Acrylonitrile–Butadiene–Styrene" Applied Sciences 12, no. 24: 12690. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412690
APA StyleQayyum, H., Hussain, G., Sulaiman, M., Hassan, M., Ali, A., Muhammad, R., Wei, H., Shehbaz, T., Aamir, M., & Altaf, K. (2022). Effect of Raster Angle and Infill Pattern on the In-Plane and Edgewise Flexural Properties of Fused Filament Fabricated Acrylonitrile–Butadiene–Styrene. Applied Sciences, 12(24), 12690. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412690










