Evaluation of the User Adaptation in a BCI Game Environment †
Abstract
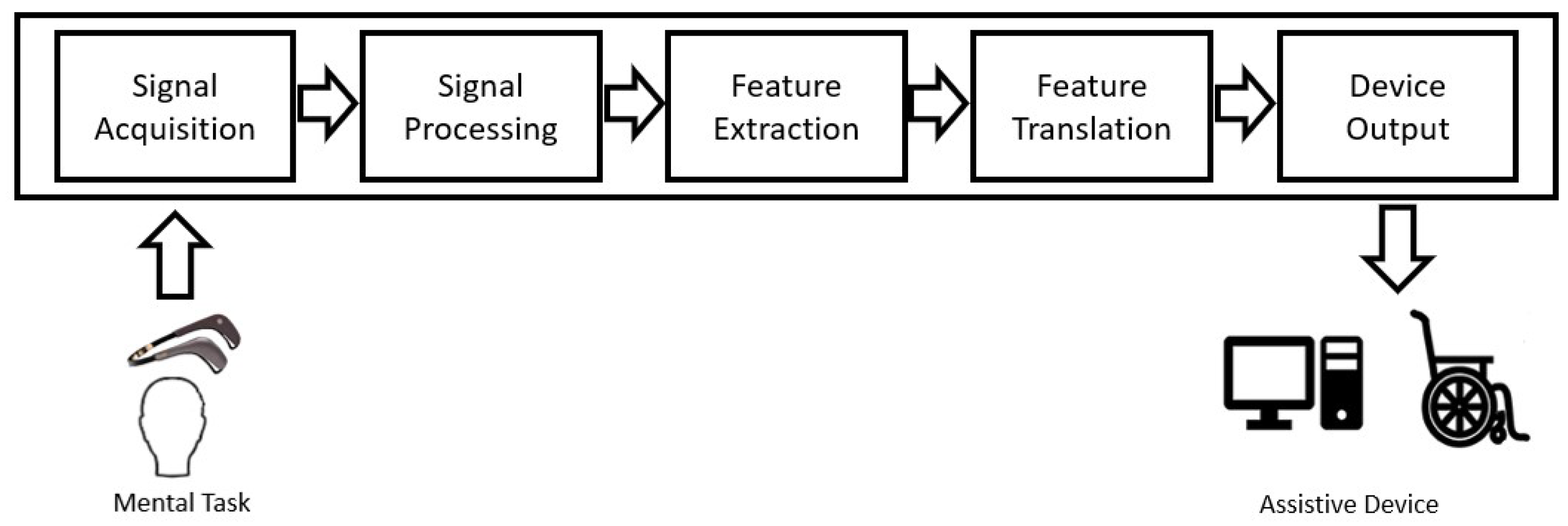
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Signal acquisition;
- (2)
- Signal processing;
- (3)
- Feature extraction;
- (4)
- Feature translation;
- (5)
- Device output.
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.1.1. EEG Headset
3.1.2. BlueMuse
3.1.3. Lab Streaming Layer
3.1.4. OpenViBE
3.2. Methods
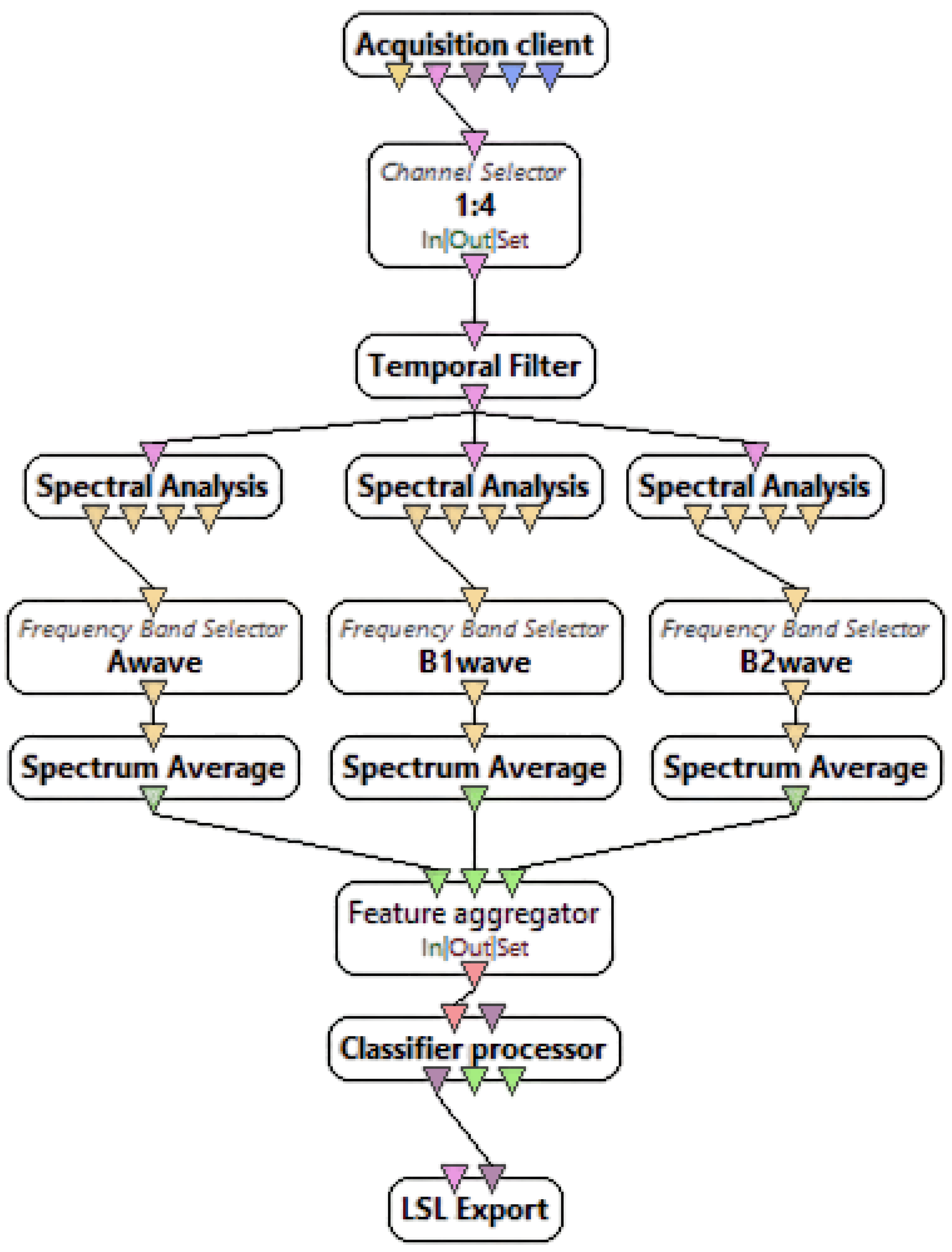
3.2.1. Offline Processing
- (1)
- Alpha waves 8–12 Hz.
- (2)
- Beta low waves 12–20 Hz.
- (3)
- Beta high waves 20–30 Hz.
3.2.2. Classification
3.2.3. Online Scenario
4. Game Design
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Dataset
5.2. Game Testing
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCI | Brain–computer interface |
| HCI | Human–computer interface |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| EOG | Electrooculography |
| LSL | Lab streaming layer |
| FFT | Fast Fourier transform |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
| MLP | Multi-layer perceptron |
References
- Minguillon, J.; Lopez-Gordo, M.A.; Pelayo, F. Trends in EEG-BCI for daily-life: Requirements for artifact removal. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 31, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiri, R.; Borhani, S.; Sellers, E.W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, X. A comprehensive review of EEG-based brain–computer interface paradigms. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, J.J.; Krusienski, D.J.; Wolpaw, J.R. Brain-computer interfaces in medicine. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Pan, J.; Long, J.; Yu, T.; Wang, F.; Yu, Z.; Wu, W. Multimodal BCIs: Target detection, multidimensional control, and awareness evaluation in patients with disorder of consciousness. Proc. IEEE 2015, 104, 332–352. [Google Scholar]
- Prapas, G.; Glavas, K.; Tzallas, A.T.; Tzimourta, K.D.; Giannakeas, N.; Tsipouras, M.G. Motor Imagery Approach for BCI Game Development. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th South-East Europe Design Automation, Computer Engineering, Computer Networks and Social Media Conference (SEEDA-CECNSM), Ioannina, Greece, 23–25 September 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.L.; Fang, P.H.; Chi, C.Y.; Kuo, C.t.; Liu, M.H.; Hsu, H.M.; Hsieh, C.H.; Liang, S.F.; Hsieh, S.; Yang, C.T. Application of Brain-Computer Interface and Virtual Reality in Advancing Cultural Experience. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), Macau, China, 1–4 December 2020; pp. 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyrl, D.; Kobler, R.J.; Müller-Putz, G.R. On similarities and differences of invasive and non-invasive electrical brain signals in brain-computer interfacing. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2016, 9, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolas-Alonso, L.F.; Gomez-Gil, J. Brain computer interfaces, a review. Sensors 2012, 12, 1211–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldert, S. Invasive vs. non-invasive neuronal signals for brain-machine interfaces: Will one prevail? Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aguiar, S.; Yanez, W.; Benítez, D. Low complexity approach for controlling a robotic arm using the Emotiv EPOC headset. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Autumn Meeting on Power, Electronics and Computing (ROPEC), Zihuatanejo, Mexico, 9–11 November 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Espiritu, N.M.D.; Chen, S.A.C.; Blasa, T.A.C.; Munsayac, F.E.T.; Arenos, R.P.; Baldovino, R.G.; Bugtai, N.T.; Co, H.S. BCI-controlled Smart Wheelchair for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. In Proceedings of the 2019 7th International Conference on Robot Intelligence Technology and Applications (RiTA), Daejeon, Korea, 1–3 November 2019; pp. 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, J.; Ujbanyi, T.; Sziladi, G.; Kovari, A. Speed control of Festo Robotino mobile robot using NeuroSky MindWave EEG headset based brain-computer interface. In Proceedings of the 2016 7th IEEE International Conference on Cognitive Infocommunications (CogInfoCom), Wrocław, Poland, 16–18 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 000251–000256. [Google Scholar]
- Belkacem, A.N.; Lakas, A. A Cooperative EEG-based BCI Control System for Robot–Drone Interaction. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC), Harbin, China, 28 June–2 July 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 297–302. [Google Scholar]
- Mousa, F.A.; El-Khoribi, R.A.; Shoman, M.E. A novel brain computer interface based on principle component analysis. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 82, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanei, S.; Chambers, J.A. EEG Signal Processing; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Xie, Z.; Wang, X. Development of a mind-controlled Android racing game using a brain computer interface (BCI). In Proceedings of the 2014 4th IEEE International Conference on Information Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China, 26–28 April 2014; pp. 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljevic, G.A.M.; Miranda, L.C.d.; Menezes, B.C.d. Mental war: An attention-based single/multiplayer brain-computer interface game. In International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 450–465. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Development of Parkour Game System Using EEG Control. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Symposium on Computer, Consumer and Control (IS3C), Taichung, Taiwan, 6–8 December 2018; pp. 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosca, S.D.; Leba, M. Design of a brain-controlled video game based on a BCI system. In MATEC Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2019; Volume 290, p. 01019. [Google Scholar]
- Alchalcabi, A.E.; Eddin, A.N.; Shirmohammadi, S. More attention, less deficit: Wearable EEG-based serious game for focus improvement. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 5th International Conference on Serious Games and Applications for Health (SeGAH), Perth, WA, USA, 2–4 April 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavas, K.; Prapas, G.; Tzimourta, K.D.; Tzallas, A.T.; Giannakeas, N.; Tsipouras, M.G. Intra-User Analysis Based on Brain-Computer Interface Controlled Game. In Proceedings of the 2022 45th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Virtual, 13–15 July 2022; pp. 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Interaxon’s Muse 2. Available online: https://choosemuse.com/muse-2/ (accessed on 7 October 2022).
- Kowaleski, J. BlueMuse. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/kowalej/BlueMuse (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Kothe, C. Lab Streaming-Layer. 2018. Available online: https://github.com/sccn/labstreaminglayer (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Marsland, S. Machine Learning: An Algorithmic Perspective; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, P.; David, P.E. The Digital Twin Paradigm for Smarter Systems and Environments: The Industry Use Cases; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Menard, M.; Wagstaff, B. Game Development with Unity; Course Technology: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
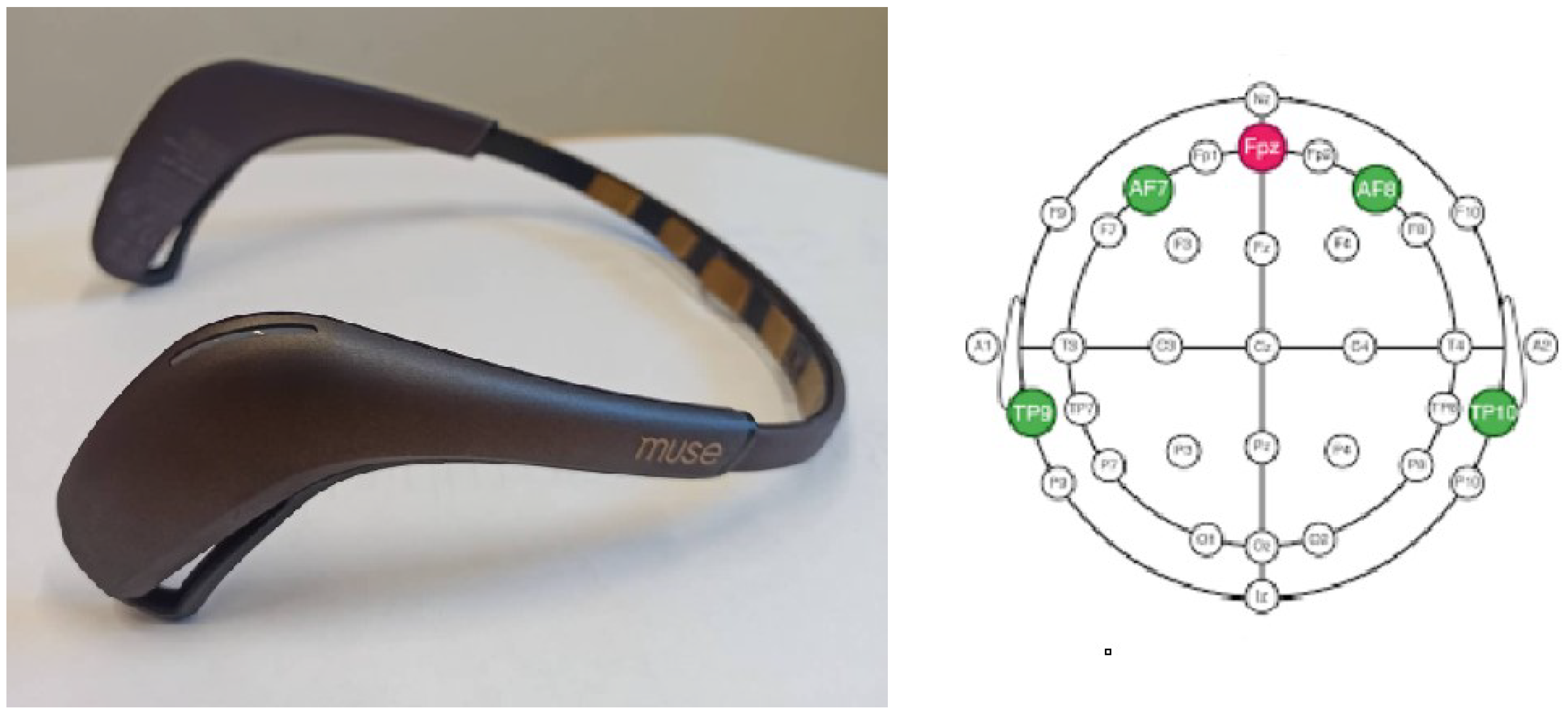



| Device | EEG Electrodes | Sampling Rate | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muse 2 | 4 (AF7, AF8, TP9, TP10) | 256 Hz | 250$ |
| Neurosky MindWave | 1 (FP1) | 512 Hz | 100€ |
| Emotiv Insight | 5 (AF3, AF4, T7, T8) | 128 Hz | 499$ |
| Unicorn Hybrid Black | 8 (Fz, C3, Cz, C4, Pz, PO7, Oz, PO8) | 250 Hz | 990$ |
| Emotiv EPOC+ | 14 (AF3, F7, F3, FC5, T7, P7, O1, O2, P8, T8, FC6, F4, F8, AF4) | 128 Hz | 849$ |
| Subjects | LDA—Blinking | LDA—Eyes Opened | LDA—Overall | Perceptron—Blinking | Perceptron—Eyes Opened | Perceptron—Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 95.20% | 100% | 97.58% | 97.20% | 100% | 98.62% |
| 2 | 99% | 0% | 99.36% | 98.6% | 100% | 99.14% |
| 3 | 99% | 100% | 99.36% | 97.6% | 100% | 98.79% |
| 4 | 97.2% | 100% | 98.62% | 98.3% | 100% | 99.13% |
| 5 | 98.3% | 99.3% | 98.79% | 96.9% | 100% | 98.44% |
| 6 | 98.3% | 100% | 99.3% | 97.6% | 100% | 98.79% |
| 7 | 99% | 100% | 99.48% | 97.9% | 100% | 98.96% |
| 8 | 99% | 100% | 99.48% | 97.2% | 100% | 98.62% |
| 9 | 98.6% | 100% | 99.31% | 97.2% | 100% | 98.62% |
| 10 | 98.6% | 100% | 99.31% | 97.6% | 100% | 98.79% |
| 11 | 98.6% | 100% | 99.31% | 97.2% | 100% | 98.62% |
| 12 | 99% | 100% | 99.48% | 96.9% | 100% | 98.44% |
| 13 | 97.9% | 100% | 98.96% | 97.6% | 100% | 98.79% |
| 14 | 97.9% | 100% | 98.96% | 96.9% | 100% | 98.44% |
| 15 | 99% | 100% | 99.48% | 99.7% | 100% | 99.72% |
| 16 | 98.3% | 100% | 99.13% | 96.6% | 100% | 98.27% |
| 17 | 99% | 100% | 99.48% | 97.2% | 100% | 98.62% |
| 18 | 98.3% | 100% | 99.13% | 97.2% | 100% | 98.62% |
| 19 | 97.6% | 99.7% | 98.62% | 96.9% | 100% | 98.44% |
| 20 | 98.3% | 99.3% | 98.79% | 97.2% | 100% | 98.62% |
| 21 | 97.9% | 100% | 98.96% | 97.2% | 100% | 98.62% |
| 22 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 97.6% | 100% | 98.79% |
| 23 | 99% | 100% | 99.48% | 95.2% | 100% | 97.06% |
| 24 | 89.7% | 100% | 94.82% | 97.6% | 100% | 98.79% |
| 25 | 99% | 100% | 99.48% | 99.3% | 100% | 99.65% |
| 26 | 97.9% | 100% | 98.96% | 99.3% | 100% | 99.65% |
| 27 | 98.6% | 100% | 99.31% | 97.6% | 100% | 98.79% |
| 28 | 96.6% | 100% | 98.27% | 97.6% | 100% | 98.79% |
| 29 | 99% | 100% | 99.48% | 97.6% | 100% | 98.79% |
| 30 | 98.6% | 100% | 99.31% | 97.6% | 100% | 98.79% |
| 31 | 92.8% | 100% | 96.37% | 97.2% | 100% | 98.62% |
| 32 | 99% | 100% | 99.48% | 97.2% | 100% | 98.62% |
| 33 | 99% | 100% | 99.48% | 97.9% | 100% | 98.96% |
| 34 | 98.6% | 100% | 99.31% | 97.9% | 100% | 98.96% |
| 35 | 89.7% | 100% | 94.82% | 97.6% | 100% | 98.79% |
| 36 | 95.2% | 100% | 97.58% | 97.2% | 100% | 98.62% |
| 37 | 95.9% | 98.6% | 97.06% | 97.9% | 100% | 98.96% |
| Subjects | Average Score 1 | Average Score 2 | Improvement | Average Overall Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub1 | 45.60 | 53.70 | 8.10% | 49.65 |
| Sub2 | 51.90 | 63.00 | 11.10% | 57.45 |
| Sub3 | 40.50 | 67.50 | 27.00% | 54.00 |
| Sub4 | 46.80 | 63.30 | 16.50% | 55.05 |
| Sub5 | 47.70 | 51.80 | 4.10% | 49.75 |
| Sub6 | 53.70 | 51.40 | −2.30% | 52.55 |
| Sub7 | 41.90 | 56.60 | 14.70% | 49.25 |
| Sub8 | 43.60 | 46.60 | 3.00% | 45.10 |
| Sub9 | 35.80 | 63.30 | 27.50% | 49.55 |
| Sub10 | 48.90 | 47.10 | −1.80% | 48.00 |
| Sub11 | 44.50 | 37.20 | −7.30% | 40.85 |
| Sub12 | 32.60 | 48.00 | 15.40% | 40.30 |
| Sub13 | 46.75 | 48.90 | 2.15% | 47.80 |
| Sub14 | 35.60 | 46.40 | 10.80% | 41.00 |
| Sub15 | 66.20 | 60.90 | −5.30% | 63.55 |
| Sub16 | 57.30 | 64.80 | 7.50% | 61.05 |
| Sub17 | 64.20 | 69.50 | 5.30% | 66.85 |
| Sub18 | 56.60 | 59.70 | 3.10% | 58.15 |
| Sub19 | 38.90 | 57.30 | 18.40% | 48.10 |
| Sub20 | 50.80 | 60.10 | 9.30% | 55.45 |
| Sub21 | 30.20 | 40.60 | 10.40% | 35.40 |
| Sub22 | 27.40 | 22.60 | −4.80% | 25.00 |
| Sub23 | 66.80 | 50.80 | −16.00% | 58.80 |
| Sub24 | 57.60 | 64.30 | 6.70% | 60.95 |
| Sub25 | 63.50 | 62.20 | −1.30% | 62.85 |
| Sub26 | 34.00 | 41.70 | 7.70% | 37.85 |
| Sub27 | 41.00 | 53.10 | 12.10% | 47.05 |
| Sub28 | 51.20 | 54.10 | 2.90% | 52.65 |
| Sub29 | 49.00 | 65.00 | 16.00% | 57.00 |
| Sub30 | 62.90 | 60.70 | −2.20% | 61.80 |
| Sub31 | 55.90 | 63.80 | 7.90% | 59.85 |
| Sub32 | 59.60 | 64.30 | 4.70% | 61.95 |
| Sub33 | 52.20 | 64.30 | 12.10% | 58.25 |
| Sub34 | 64.30 | 68.50 | 4.20% | 66.40 |
| Sub35 | 53.10 | 64.60 | 11.50% | 58.85 |
| Sub36 | 53.80 | 66.10 | 12.30% | 59.85 |
| Sub37 | 28.20 | 59.20 | 31.00% | 43.7 |
| Subjects | Average Score 1 | Average Score 2 | Improvement | Average Overall Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub2 | 65.20 | 77.40 | 8.13% | 71.30 |
| Sub4 | 61.60 | 78.40 | 11.20% | 70.00 |
| Sub15 | 62.60 | 83.30 | 13.8% | 72.95 |
| Sub16 | 96.60 | 71.20 | −16.93% | 83.90 |
| Sub17 | 68.40 | 73.20 | 3.20% | 70.80 |
| Sub18 | 67.10 | 55.50 | −7.73% | 61.30 |
| Sub20 | 43.20 | 58.90 | 10.46% | 51.05 |
| Sub23 | 61.30 | 65.20 | 2.60% | 63.25 |
| Sub24 | 82.10 | 84.30 | 1.46% | 83.20 |
| Sub25 | 84.45 | 78.55 | −3.93% | 81.50 |
| Sub29 | 73.20 | 70.00 | −2.13% | 71.60 |
| Sub30 | 77.90 | 58.10 | −13.20% | 68.00 |
| Sub31 | 70.20 | 64.20 | −4.00% | 67.20 |
| Sub32 | 72.00 | 103.80 | 21.20% | 87.90 |
| Sub33 | 51.40 | 61.10 | 6.46% | 56.25 |
| Sub34 | 61.20 | 74.30 | 8.73% | 67.75 |
| Sub35 | 69.40 | 67.80 | −1.06% | 68.60 |
| Sub36 | 71.50 | 68.10 | −2.26% | 69.80 |
| Authors | Subjects | EEG Device | Mental Commands | Reps per Subj | Evaluation Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wu et al. [16] | 5 | NeuroSky Mindset | 2 | 1 | Avg mean meditation (49.4) |
| Vasiljevic et al. [17] | 24 | NeuroSky MindWave | 1 | - | Avg attention single player (53.49); avg attention multiplayer (52.42) |
| Rosca et al. [19] | 3 | Emotiv Insight | 2 | 1 | Not presented |
| Wang et al. [18] | 5 | NeuroSky MindWave Mobile | 2 | 1 | Avg maximum attention 1 (73.6) Avg maximum attention 2 (76.4) Avg maximum meditation 1 (51) Avg maximum meditation 2 (47.4) Game duration 1 (34.6 s) Game duration 2 (30.2 s) |
| Alchalabi et al. [20] | 4 | Emotiv Epoc+ | 2 | 2 | Avg focus (0.38), Avg stress (0.49) Avg relaxation (0.32) Avg excitement (0.25) Avg engagement (0.65) |
| This work | 37 | Muse 2 Headband | 2 | 20 | Classification accuracy (98.75%) Game score 1 (52.70/100) Game score 2 (70.35/150) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glavas, K.; Prapas, G.; Tzimourta, K.D.; Giannakeas, N.; Tsipouras, M.G. Evaluation of the User Adaptation in a BCI Game Environment. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12722. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412722
Glavas K, Prapas G, Tzimourta KD, Giannakeas N, Tsipouras MG. Evaluation of the User Adaptation in a BCI Game Environment. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(24):12722. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412722
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlavas, Kosmas, Georgios Prapas, Katerina D. Tzimourta, Nikolaos Giannakeas, and Markos G. Tsipouras. 2022. "Evaluation of the User Adaptation in a BCI Game Environment" Applied Sciences 12, no. 24: 12722. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412722
APA StyleGlavas, K., Prapas, G., Tzimourta, K. D., Giannakeas, N., & Tsipouras, M. G. (2022). Evaluation of the User Adaptation in a BCI Game Environment. Applied Sciences, 12(24), 12722. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412722












