Laboratory Flame Smoke Detection Based on an Improved YOLOX Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
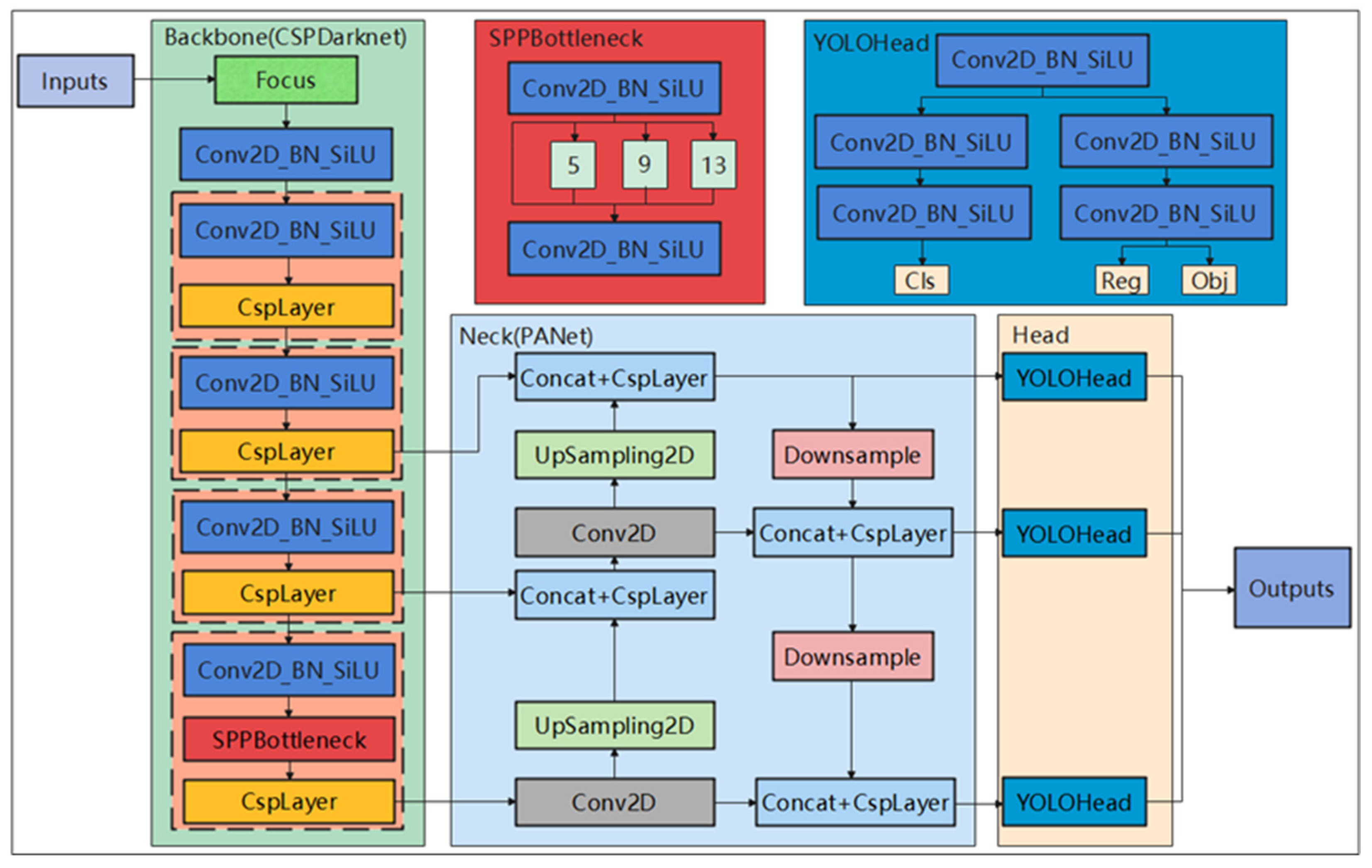
2.1. YOLOX Target Detection Algorithms
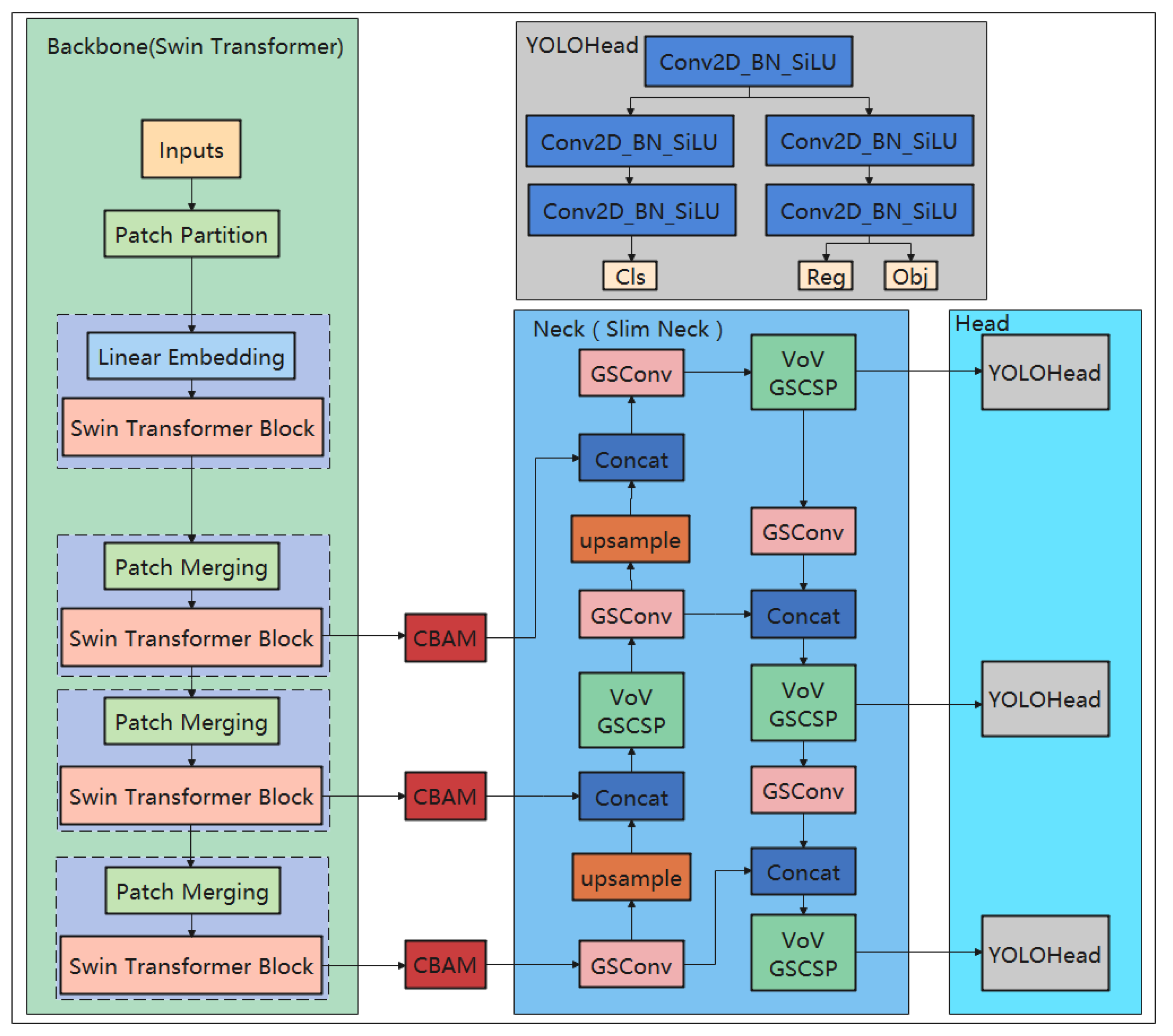
2.2. Model Improvements and Optimization
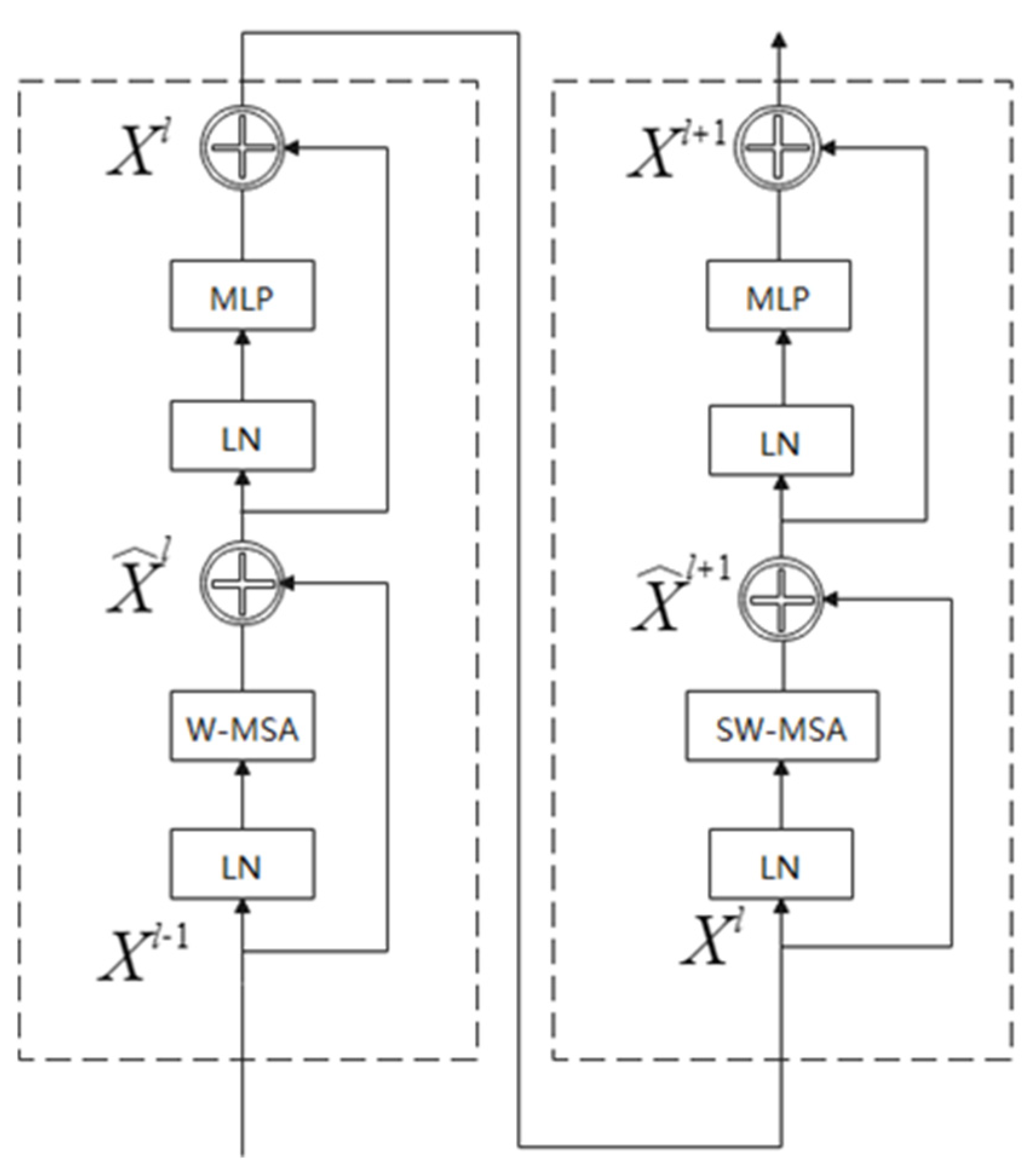
2.3. Swin Transformer
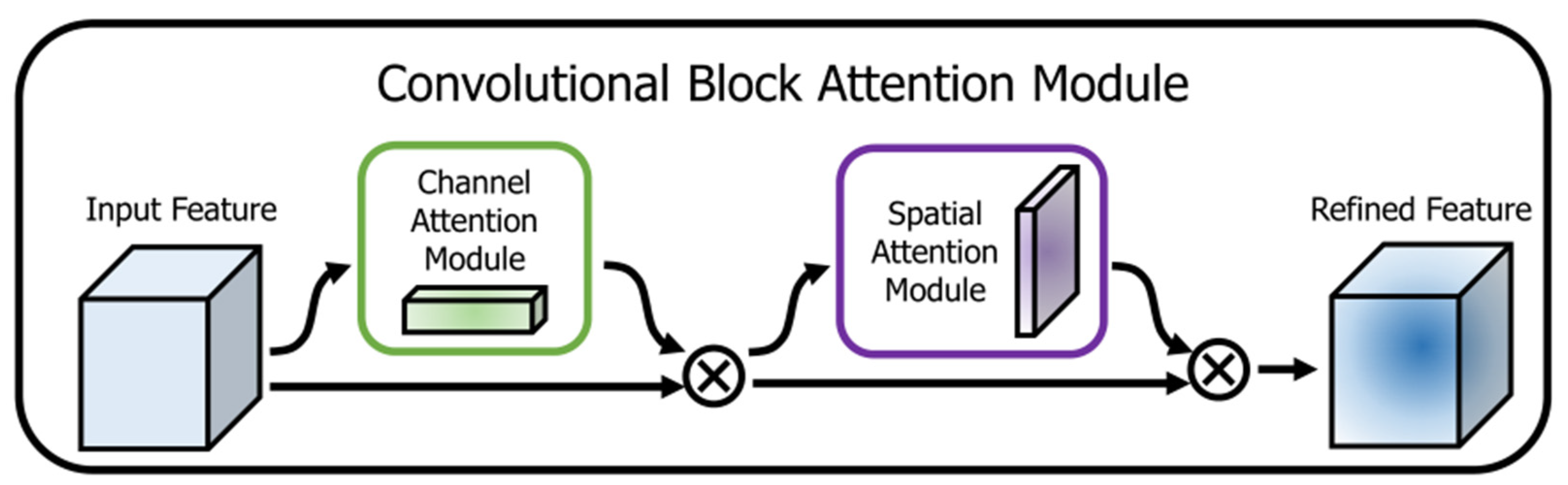
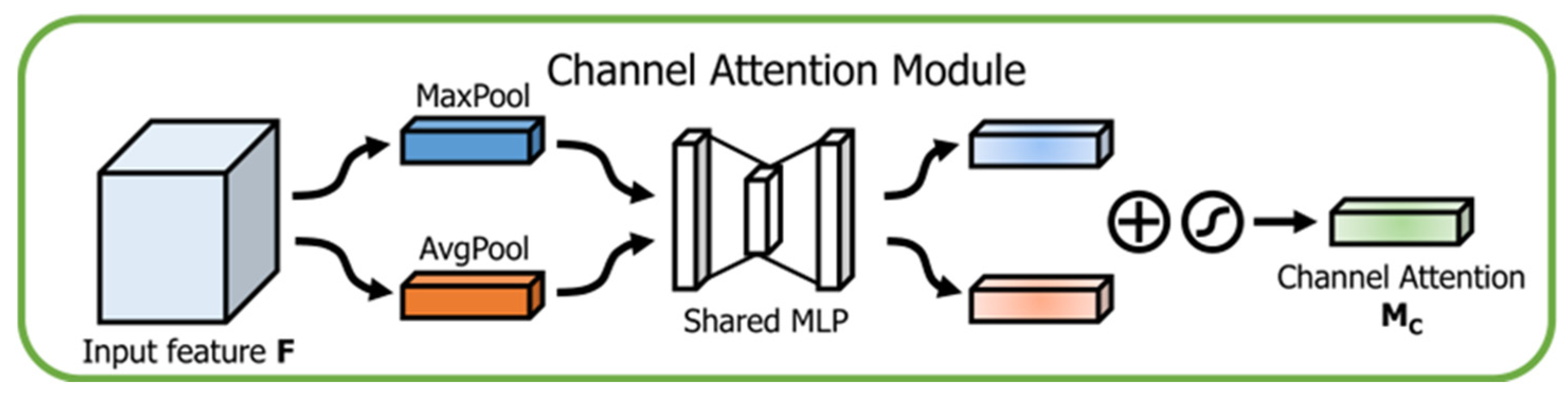
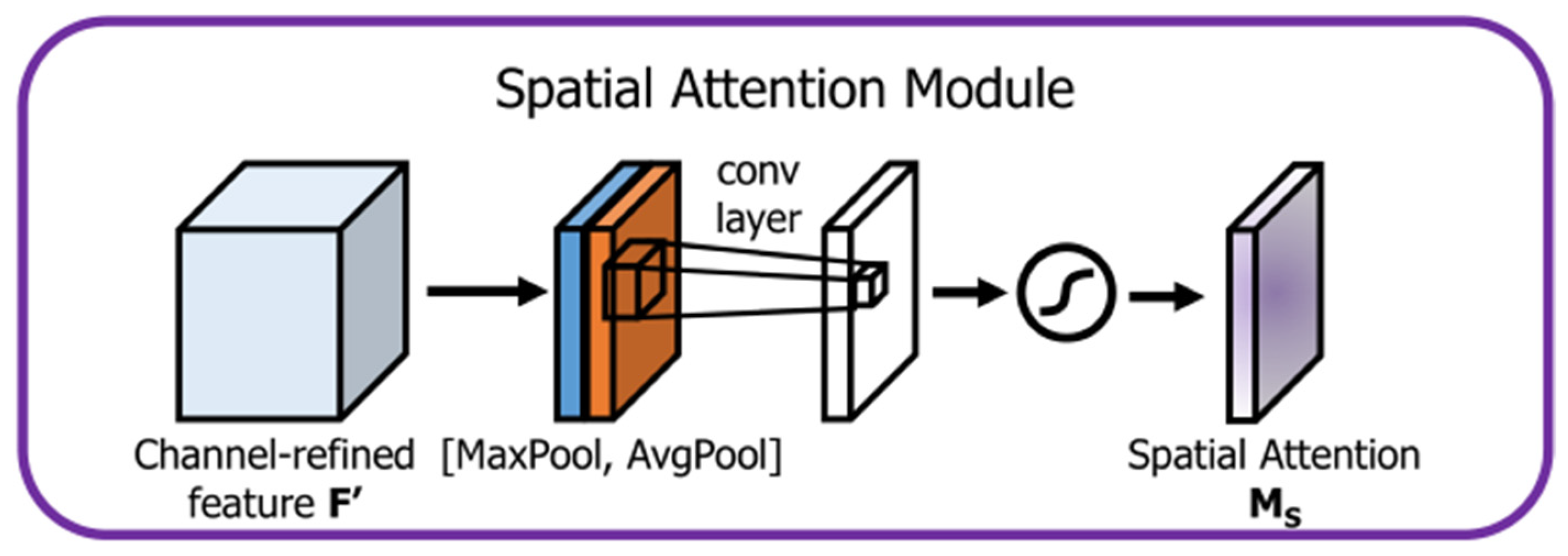
2.4. CBAM Attention Mechanism
2.4.1. Channel Attention Mechanism
2.4.2. Spatial Attention
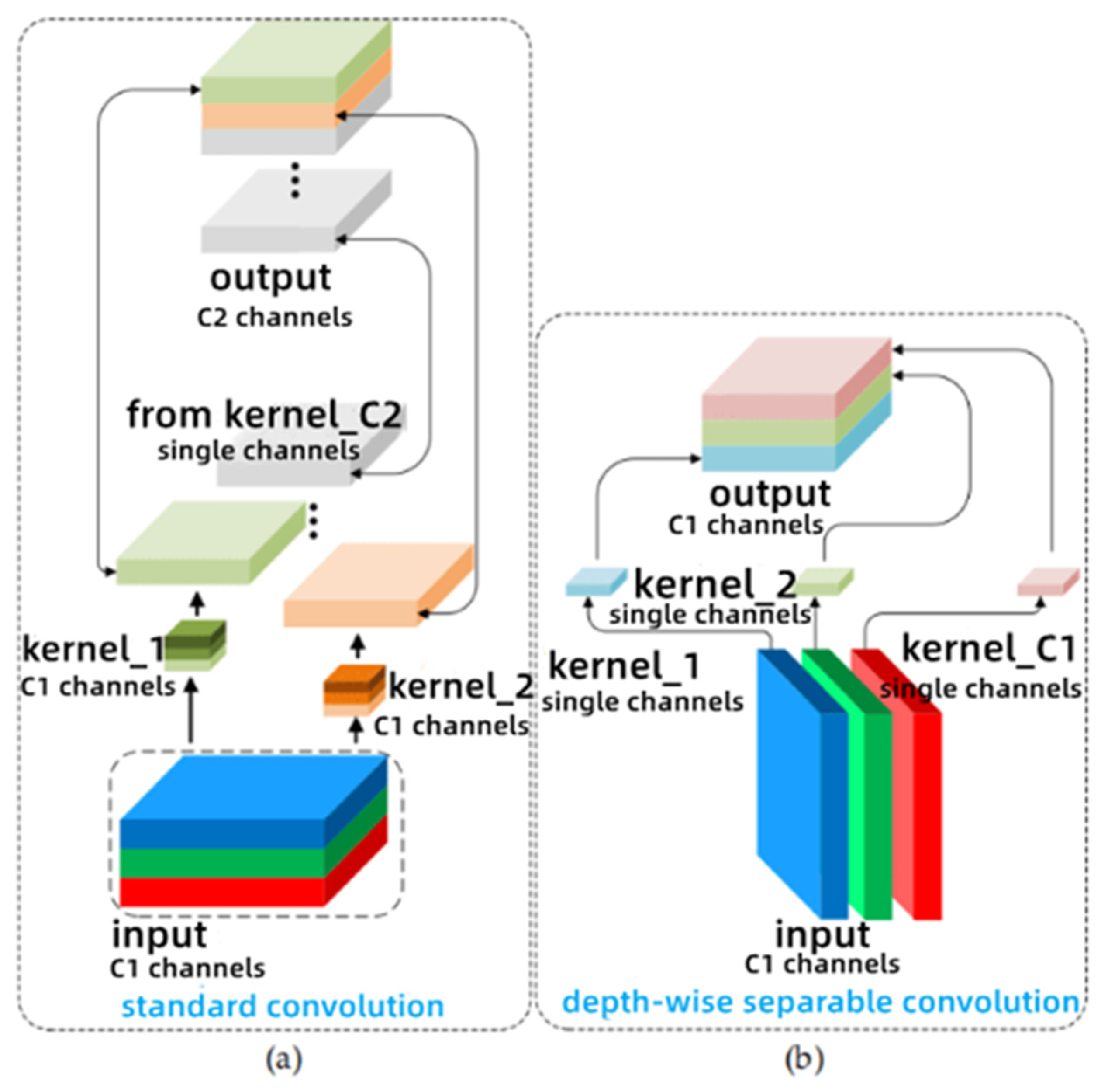
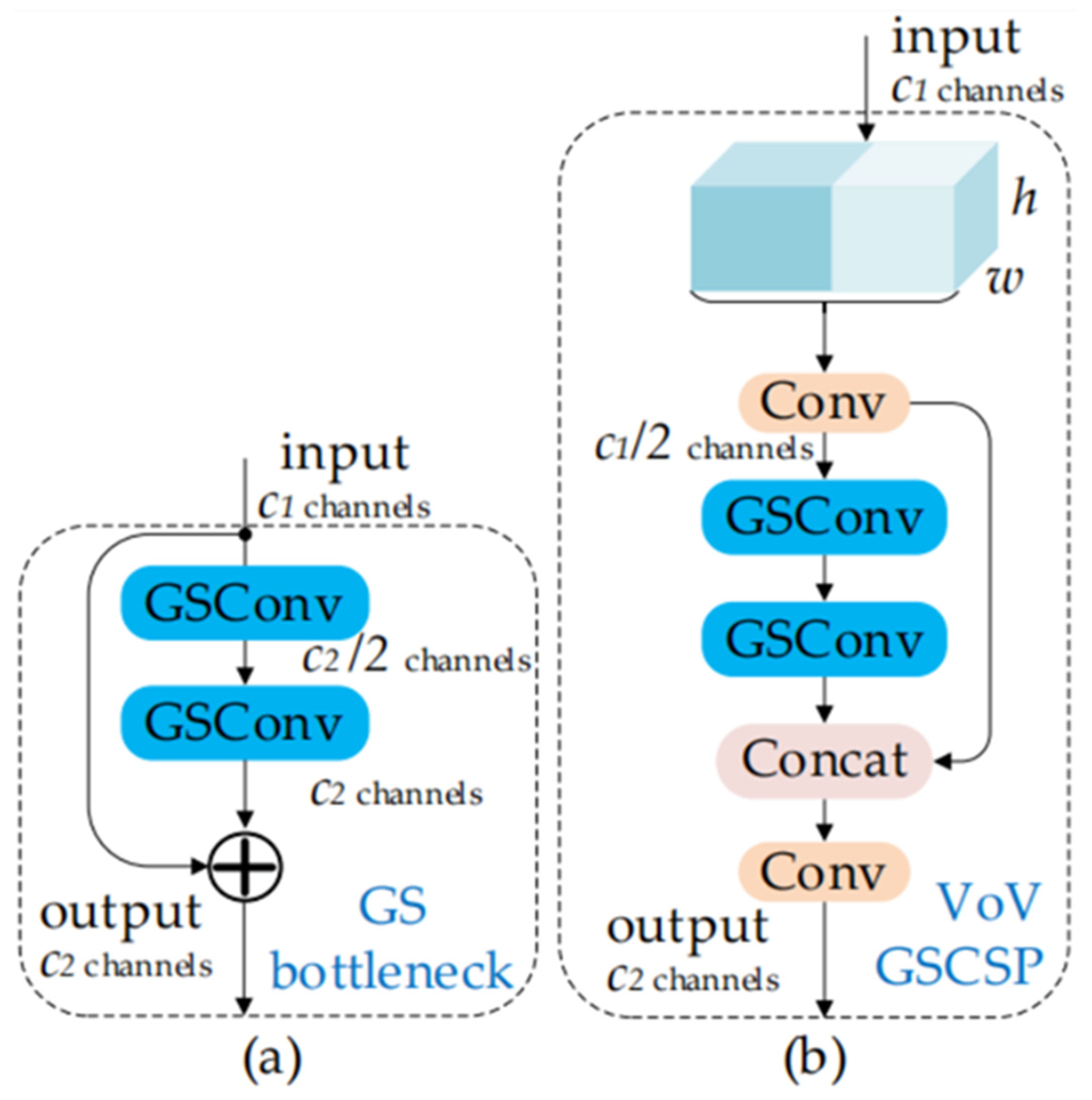
2.5. Slim Neck Module
2.6. Experimental Platform
2.7. Network Training
2.8. Model Evaluation Indicators
3. Results
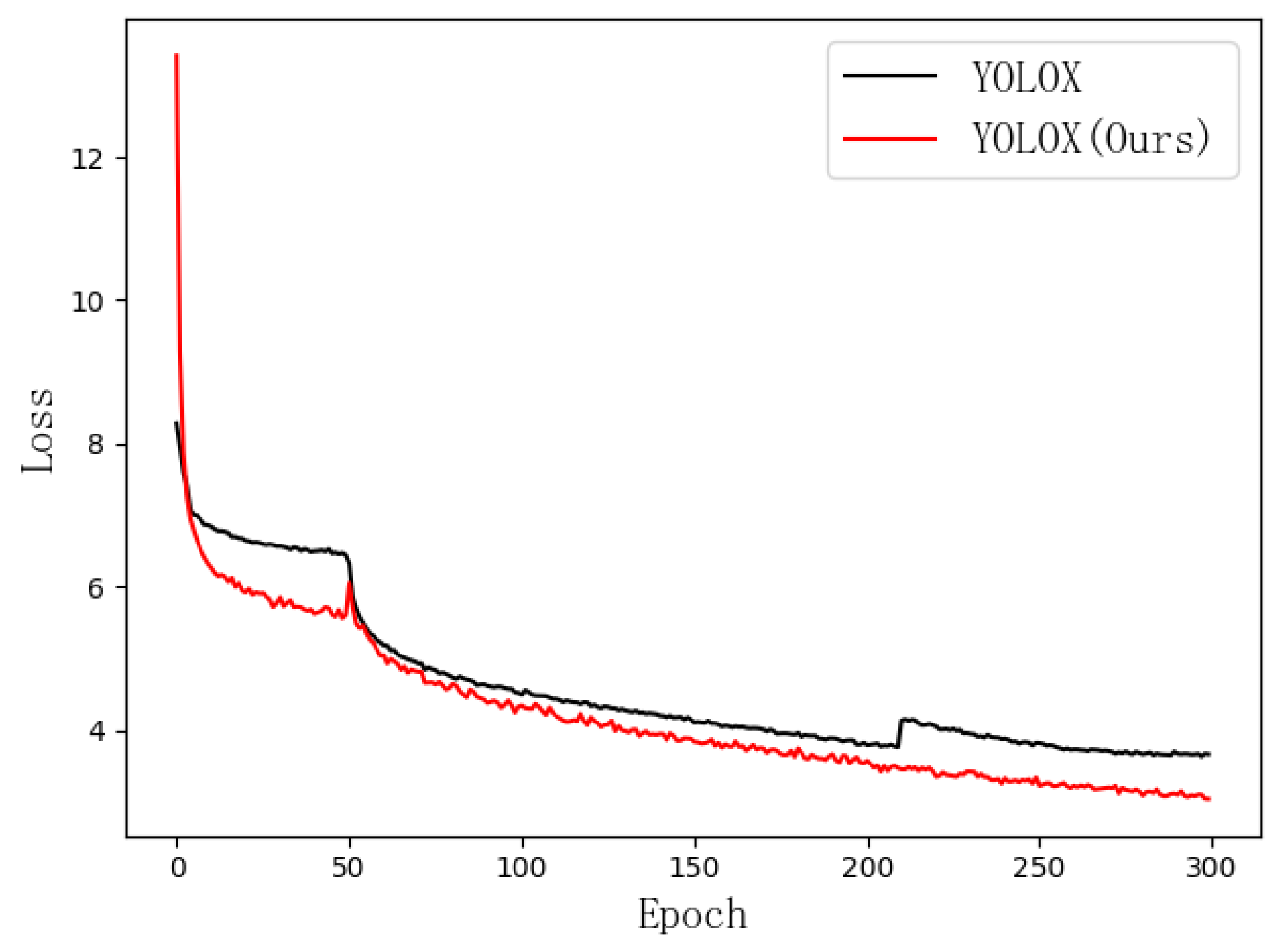
3.1. Ablation Experiments
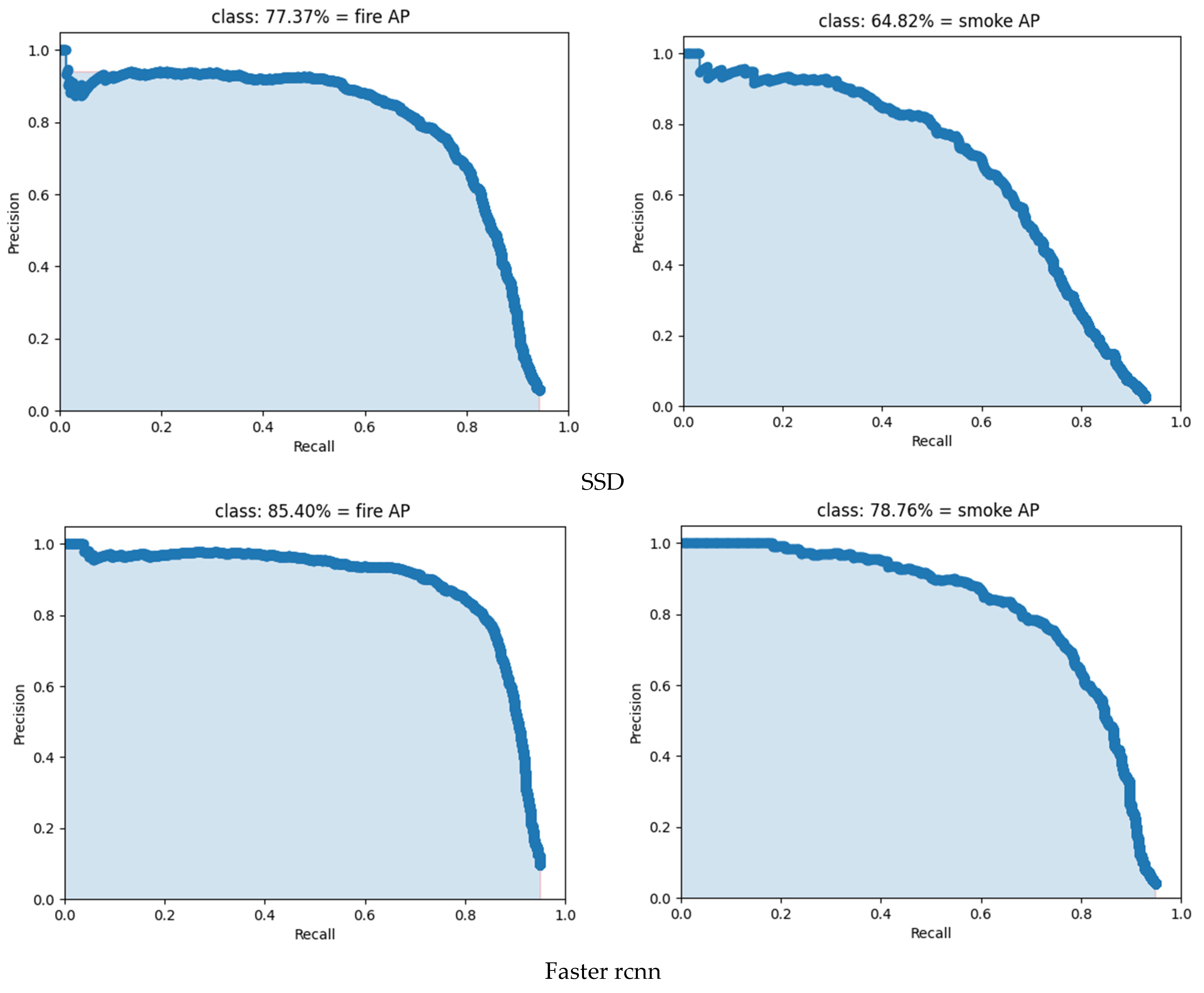
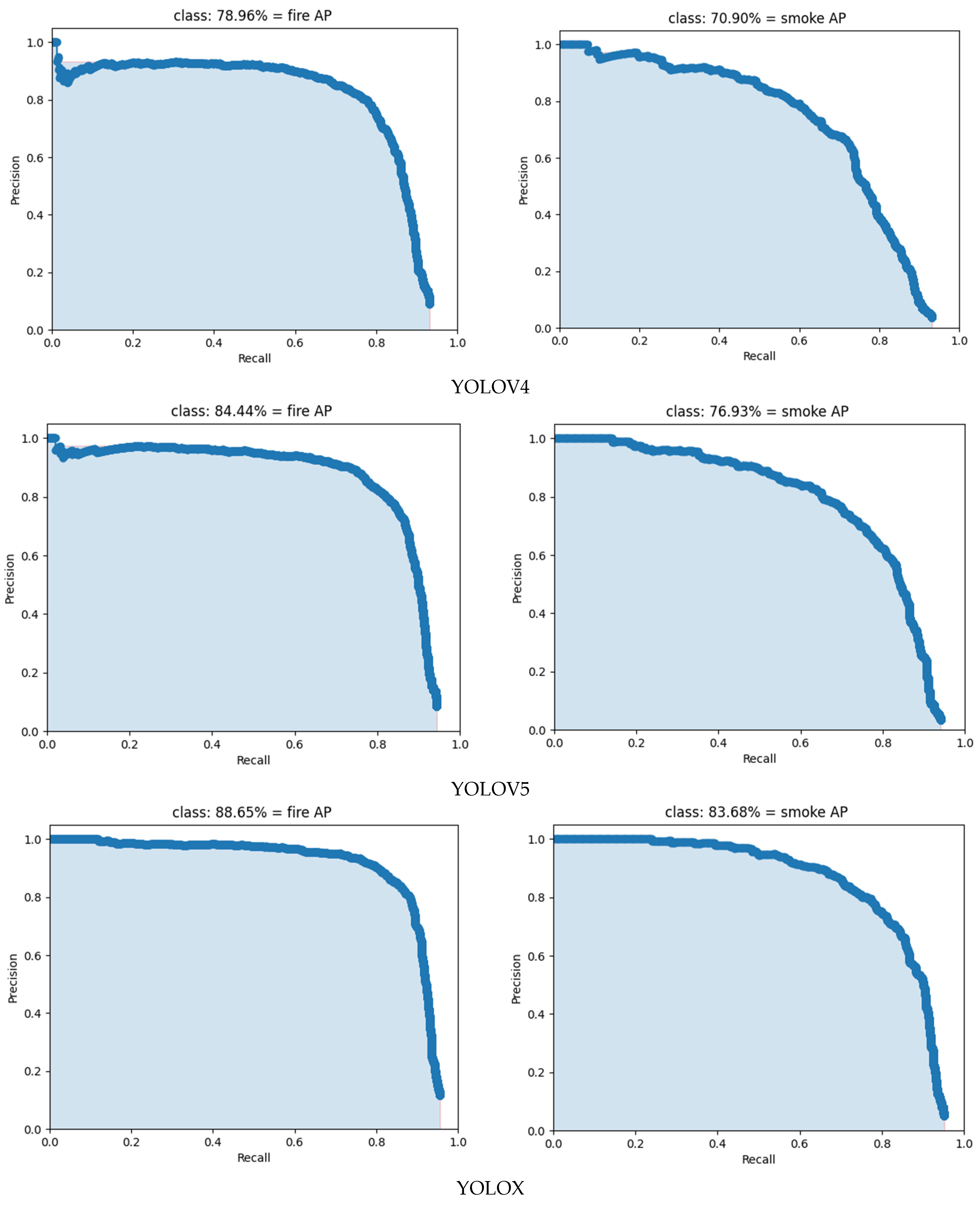
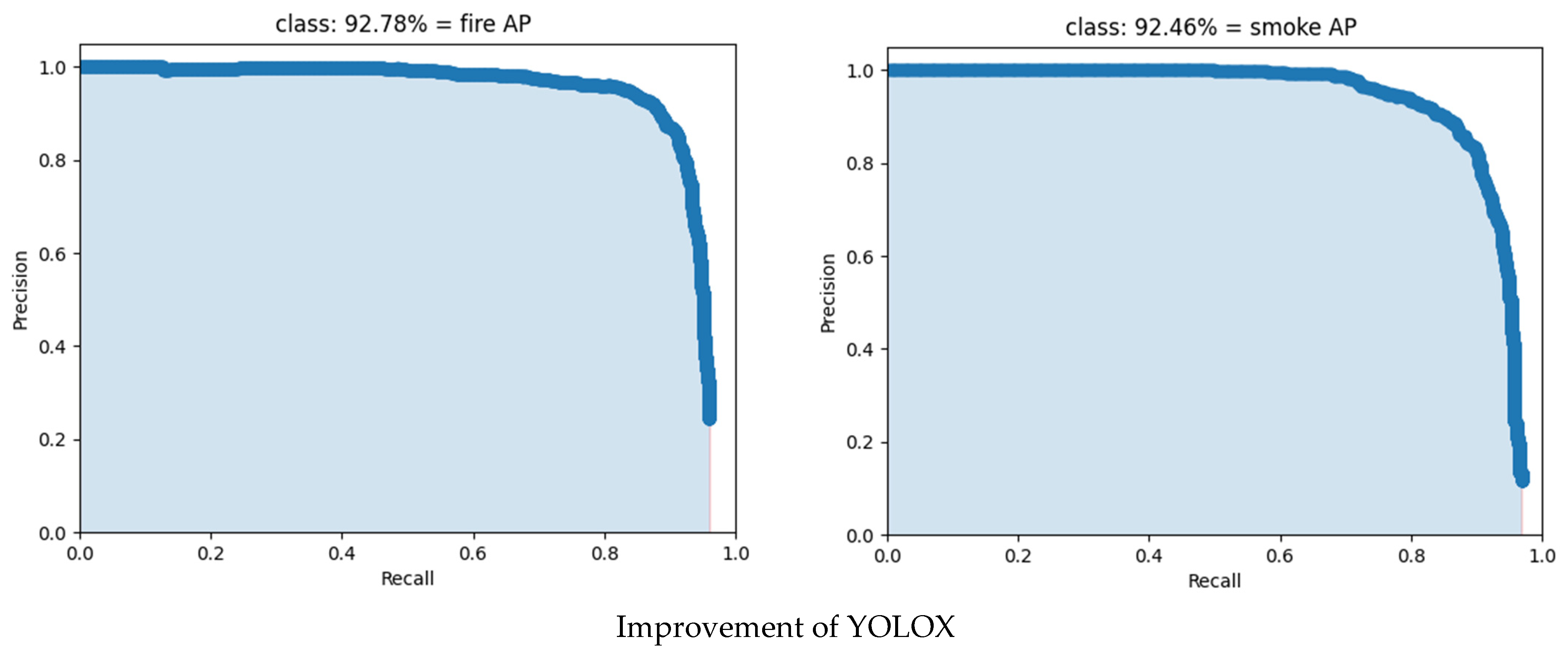
3.2. Analysis of Test Results of Different Models
3.3. Model Detection Effect
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, D.; Meng, K.; Jiang, N.; Li, T.; Liu, S. Analysis of the construction of laboratory safety management system in universities based on information platform. China Insp. Test. 2019, 27, 49–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F. Research and Implementation of Fire Detection Algorithm Based on Deep Learning; Hangzhou University of Electronic Science and Technology: Hangzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Sun, L. A CNN-based lightweight flame detection method for complex scenes. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2021, 34, 415–422. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z. UAV-Based Forest Fire Monitoring and Path Planning Research; Xi’an University of Technology: Xi’an, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D. Research on Deep Learning Method for Forest Fire Detection; Xi’an University of Technology: Xi’an, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S. Research on Video-Based Fire Detection Method for Cruise Ships; Jiangsu University of Science and Technology: Zhenjiang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, H. Improving YOLOv3 for fire detection. Comput. Syst. Appl. 2022, 31, 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Liu, J. Flame image recognition algorithm based on improved Mask R-CNN. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2020, 56, 194–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Sun, J. YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.R.; Ma, W. New exact solutions of Bratu Gelfand model in two dimensions using Lie symmetry analysis. Chin. J. Phys. 2020, 65, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, A.; Sabir, Z.; Altamirano, G.C.; Sadat, R.; Ali, M. RCharacteristics of melting heat transport of blood with time-dependent cross-nanofluid model using Keller–Box and BVP4C method. Eng. Comput. 2022, 38, 3705–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, Hawaii, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Davis, L.S. An analysis of scale invariance in object detection-SNIP. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3578–3587. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Najibi, M.; Davis, L.S. Sniper: Efficient multi-scale training. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.T.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, S.Q.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, L.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06521. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.R. The Method of Lines Analysis of Heat Transfer of Ostwald-de Waele Fluid Generated by a Non-uniform Rotating Disk with a Variable Thickness. J. Appl. Comput. Mech. 2021, 7, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, M.M.; Ali, M.R.; Ma, W. A combined method for simulating MHD convection in square cavities through localized heating by method of line and penalty-artificial compressibility. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2021, 15, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Wei, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Ren, Q. Slim-neck by GSConv: A better design paradigm of detector architectures for autonomous vehicles. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.02424. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Datasets | Total Number of Pictures |
|---|---|
| Training sets | 4000 |
| Validation Sets | 500 |
| Test Sets | 500 |
| Total | 5000 |
| Methods | Swin-Transformer | CBAM | Slim Neck | Loss Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOX | × | × | × | 3.66 |
| Improvement1 | ✓ | × | × | 3.05 |
| Improvement2 | × | ✓ | × | 3.60 |
| Improvement3 | × | × | ✓ | 3.49 |
| Improvement4 | ✓ | ✓ | × | 2.94 |
| Improvement5 | ✓ | × | ✓ | 2.88 |
| Improvement6 | ✓ | ✓ | × | 2.91 |
| Improvement7 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 2.72 |
| Methods | Swin-Transformer | CBAM | Slim Neck | mAPtest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOX | × | × | × | 86.17% |
| Improvement1 | ✓ | × | × | 90.52% |
| Improvement2 | × | ✓ | × | 87.13% |
| Improvement3 | × | × | ✓ | 86.30% |
| Improvement4 | ✓ | ✓ | × | 91.48% |
| Improvement5 | ✓ | × | ✓ | 90.72% |
| Improvement6 | ✓ | ✓ | × | 91.48% |
| Improvement7 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 92.26% |
| Models | fireF1 | smokeF1 | fireP | smokeP | fireR | smokeR | fireAP | smokeAP | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSD | 74% | 61% | 85.05% | 81.40% | 65.29% | 48.99% | 77.37% | 64.82% | 71.09% |
| Faster R-CNN | 82% | 74% | 86.28% | 81.32% | 77.85% | 67.89% | 85.40% | 78.76% | 82.08% |
| YOLOv4 | 76% | 67% | 87.20% | 80.99% | 67.80% | 57.06% | 78.96% | 70.90% | 74.93% |
| YOLOv5 | 81% | 71% | 87.13% | 83.83% | 76.50% | 61.83% | 84.44% | 76.93% | 80.68% |
| YOLOX | 85% | 77% | 87.52% | 81.80% | 82.42% | 73.39% | 88.65% | 83.68% | 86.17% |
| Improvement YOLOX | 89% | 87% | 90.99% | 87.78% | 87.89% | 86.97% | 92.78% | 92.46% | 92.26% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, M.; Xu, L.; Yang, Y.; Cao, M.; Yang, J. Laboratory Flame Smoke Detection Based on an Improved YOLOX Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12876. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412876
Luo M, Xu L, Yang Y, Cao M, Yang J. Laboratory Flame Smoke Detection Based on an Improved YOLOX Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(24):12876. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412876
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Maolin, Linghua Xu, Yongliang Yang, Min Cao, and Jing Yang. 2022. "Laboratory Flame Smoke Detection Based on an Improved YOLOX Algorithm" Applied Sciences 12, no. 24: 12876. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412876
APA StyleLuo, M., Xu, L., Yang, Y., Cao, M., & Yang, J. (2022). Laboratory Flame Smoke Detection Based on an Improved YOLOX Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 12(24), 12876. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412876







