Featured Application
The work presents an AI application model of an image recognition algorithm to work with the IRB 1200 robot.
Abstract
This paper presents the application of artificial intelligence applied to image classification according to CNN (Convolutional neutral network) algorithm. Two AI (artificial intelligence) models were submitted for verification. The first was based on mobilenet algorithm, and the second was based on the application of several layers of Convolution, ReLU and Maxpooling. After examining the AI, a solution using image classification was proposed for the IRB1200 robot, which encircles symbols assigned to color saturation on the detected colors. In the introduction, articles were selected that are related to the application of AI in various industries. The second section describes mathematical relationships for algorithms used in the project for image classification. Next, a multi-task control system for a robot is described, which performs specific tasks based on image verification by CNN-based artificial intelligence. The AI model and system handling reading of the image from a camera were submitted for verification, based on the tasks to be performed by the IRB1200 robotic arm based on color recognition. Verification was carried out in the head office of a company called Sii.
1. Introduction
For object and speech recognition, artificial intelligence algorithms are created by writing code that emulates the human brain. Mapping artificial intelligence algorithms refers to defining a deep neural network, which consists of layers of networks that process an image or word for identification. In 2011. Fei-Fei Li and her small team created the ImageNet network [1]. It consisted of 3.2 million tagged images in more than 5000 different categories [2]. As of 2018 the most recognized algorithm is Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), created by Google team. It is one of the most interesting developments in the field of natural language processing (NLP), a sector of artificial intelligence that has been growing particularly rapidly in recent years and concerns speech recognition. Researchers in paper [3] described an interesting solution called SCICERO aimed at solving the problem of generating knowledge graphs (KGs) from article titles and abstracts. In order to skip the authors’ annotation of scientific papers, they proposed a solution to take the input text and generate KGs using NLP, results obtained from the tests of the software, conducted on 6.7 million titles, were very promising.
Use of artificial intelligence in the process of classifying an image, that is, analyzing it based on its actual content, can be carried out in several ways. The best known and one that gives the best results is Convolutional neutral network (CNN), which works by classifying individual pixels and increasing their number as they pass through successive layers of the network [4,5]. Other image classification methods described by A. Voulodimos and others [6] are deep belief networks (DBN), and deep Boltzman machines (DBM) belonging to deep university models using restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM), which is a generative stochastic neural network. Another well-known solution is the Support Vector Machine (SVM), which the authors of article [7] used to build a smart glove with object recognition.
Another task that uses AI is image detection. An example of solutions for high-level and multiscale features used is the so-called deep saliency network [8,9]. It is also worth mentioning the histogram of oriented gradients (HOG), which involves adding local histograms on a dense grid, so there is a lot of interest with it in gait testing. [10,11]. An interesting solution proposed by Redmon et al. [12] is “You Only Look Once” (YOLO), in which object detection is considered as a single problem, where pixels are converted to rectangle coordinates and then class probabilities are assigned. Image segmentation can be divided into three basic categories described as region-based, weakly supervised segregation and fully convolutional network (FCN) [13,14].
Artificial intelligence is not a purely theoretical concept, but it has been used for many years to improve people’s quality of life and health [15,16,17]. It is predicted that, thanks to artificial intelligence, the energy industry can increase its reliability [18], and the employment of people in jobs with a high risk of injury may decrease or disappear altogether [19]. One can also see AI’s strong ties to Industry 4.0, involving continuous monitoring and localization of people, tools and vehicles, and their integration. This is intended to reduce the risk of accidents, increase the quality of products offered and improve the entire supply and production structure [20,21,22].
In the chapters, the authors propose an application of an artificial intelligence algorithm used for image recognition in a validated and verified control system from of an ABB robotic arms.
2. Materials and Methods
When working on artificial intelligence algorithms, it is very important to use the right tools. One of them is the Keras open-source library for creating neural networks, working with TensorFlow [23,24]. The Keras library uses an exponential decay to lower the learning rate as training progresses to achieve better results (tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.ExponentialDecay). TensorFlow was released by Google Brain Team and is among open-source libraries used in machine learning and deep neural networks [25]. To complete the project, the authors of this article used a convolutional neural network (CNN), which can be seamlessly applied by the aforementioned software and is suitable for solving image recognition tasks [26,27,28,29]. Its advantages also include the simplification of multiple steps from TensorFlow, thus reducing the amount of code, as well as processing time [30]. The NPU manufacturer reports that the module is based on solutions proposed by Intel Movidius MyriadTM X and supports kernels computed according to the convolution, pooling and ReLU model.
Assuming that the size of the “Convolution” model at the input has W × W × D (number Equation (1)) and Dout [31], which determines the number of nuclei whose space has size F, spacing S, and padding amount P then the size of output volume of the model is calculated [31,32]:
The second kernel referred (Equation (2)) to as “pooling” can be written mathematically as follows [32]:
Referring to the map variables W × W × D means that the pooling kernel determines the size of the space F and the spacing S.
In addition, ReLU solutions were used, which are based on the function:
Which means that the threshold is set at 0 in this case.
The Mobilenet2 application was used for machine learning. It is typical for image classification. The mathematical notation is proposed by the authors [33] in Equation (4)
where applies to a list of intermediate tensors connected in any node. On the other hand, is the size of the A tensor and is the total amount of memory needed to be stored during operation. Confirmation of validity of the above-described formulas is determined by the authors in this publication as well as papers [32,33].
In addition, the NPU module, according to the manufacturer, uses solutions based on the ONNX recording format, which is currently being developed by Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit platform [34].
With the artificial intelligence model described this way, it was possible to move on to further steps involved in implementing above algorithms, kernels and applications into a workstation located at Sii head office [35].
3. System Configuration
The proposed testbed is the result of a collaboration between Gdynia Maritime University, Siemens and Sii. Particularly suggestive was the article [36] presented at Hanover in 2019, in which the work of a robot, whose actions depended on an artificial intelligence algorithm, was presented for the first time. The purpose of the article is to study CNN models such as mobilenetv2, ReLU, Convultion2D and maxpooling2D with the application of this knowledge based on Industry 4.0. This means selecting the best model according to the TensorFlow environment and implemented to Siemens’ novel approach to the NPU module compatible with the S7-1500 controller. In the presented article, the authors focus on the thread of hardware configuration of the entire system and, above all, on the proposals used by manufacturer of machine learning algorithms closely related to image classification. Launching the testbed consisted of several stages. The first, described below, concerned the configuration under laboratory conditions of the S7-1512C controller with NPU artificial intelligence module, which is a proposal from Siemens, the manufacturer. The second stage concerned verification of artificial intelligence model where, through image detection, the robotic arm was to perform specific tasks. The proposed AI application is the first step to test 2D image recognition algorithms.
3.1. System Configuration—Testbed Description at Sii
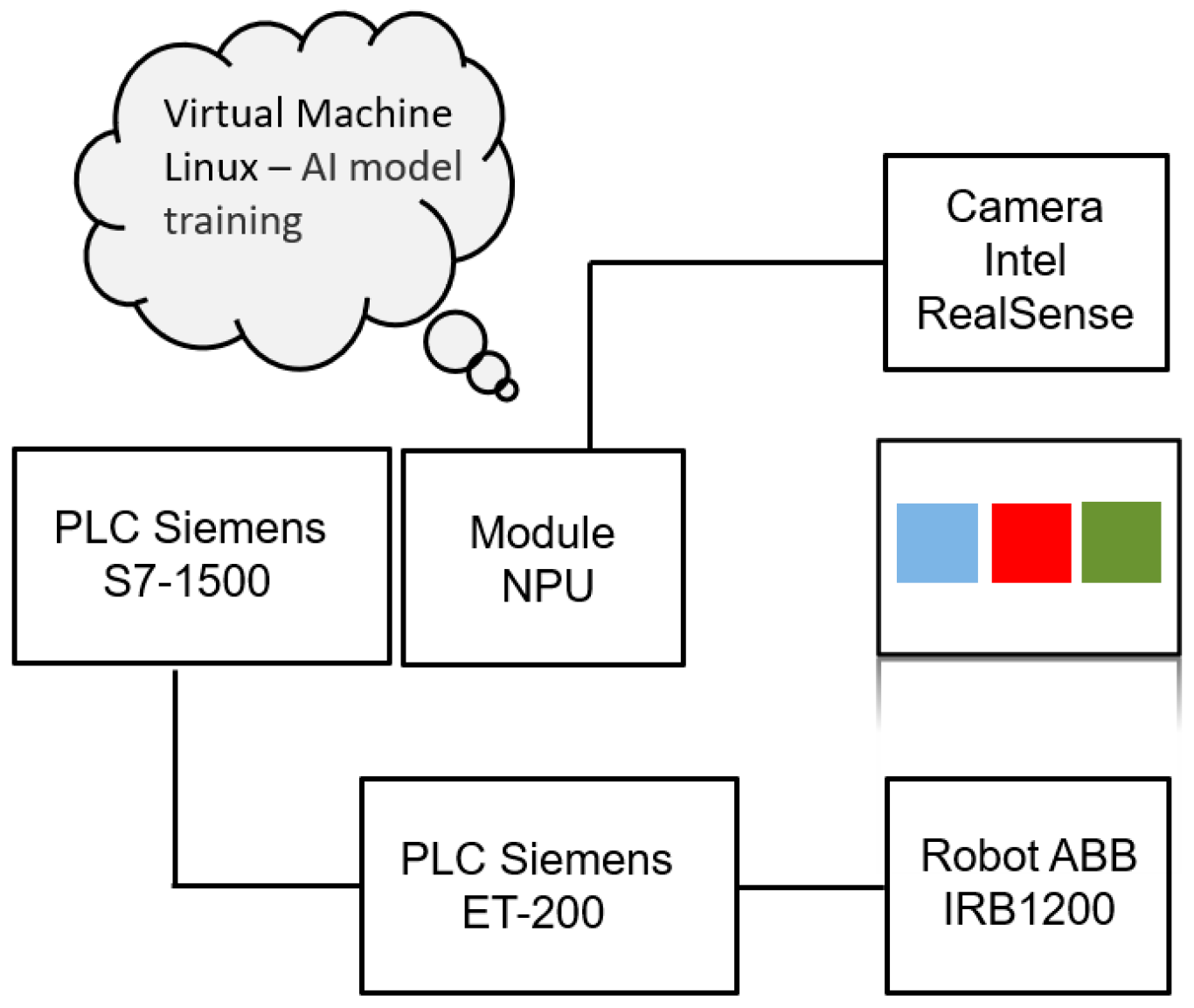
The main goal was to use the robot arm to work so that it would select the appropriate colors suggested by the user. The verification of the robot’s work was to make sure there is an appropriate response to the recognized color. A block diagram is proposed below (Figure 1).
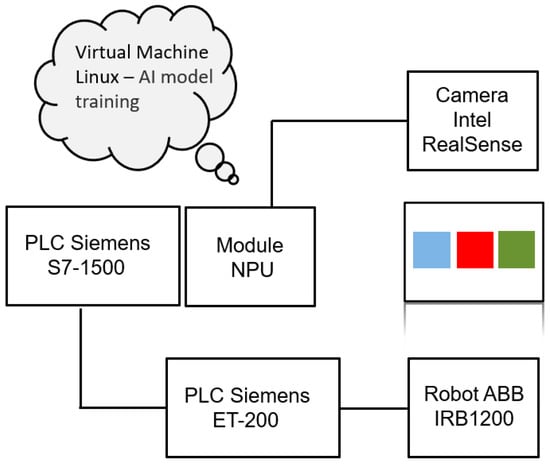
Figure 1.
The implementation system configuration diagram.
It was assumed that the RealSense Camera would be mounted at a specific point in the station and feed the image directly to the NPU module. The color detected by the NPU module is implemented by the program in the PLC. The authors proposed a simple solution that depends on color saturation by programming the robot arm based on the data read from the comparison contact instruction. The IRB1200 robot had to mark the corresponding symbol on the colors with a marker. In the first stage of work described in the schedule, configuration of the controller with the module at the University was performed (to verify data exchange step at the level of the camera, NPU module and controller). Meanwhile, the second stage was to build a control system based on the following components (Figure 2):
- S7-1512C controller with implemented instructions needed to read data from the camera connected directly to the NPU module.
- NPU module (The manufacturer states that the chip contains 16 low-power programmable SHAVE (Streaming Hybrid Architecture Vector Engine) cores and is equipped with a dedicated hardware accelerator for overbuilding deep neural network structures Intel Movidius MyriadTM X).
- ET200S controller and IO device island IM 151-3 PN ST located at Sii head office (the mentioned components are necessary to control the operation of the robot arm).
- Intel RealSense camera tasked with image reading and communicating with the NPU module via USB 3.1.
- ABB robot arm type IRB-1200, which reacts in a certain way to the detected colour.
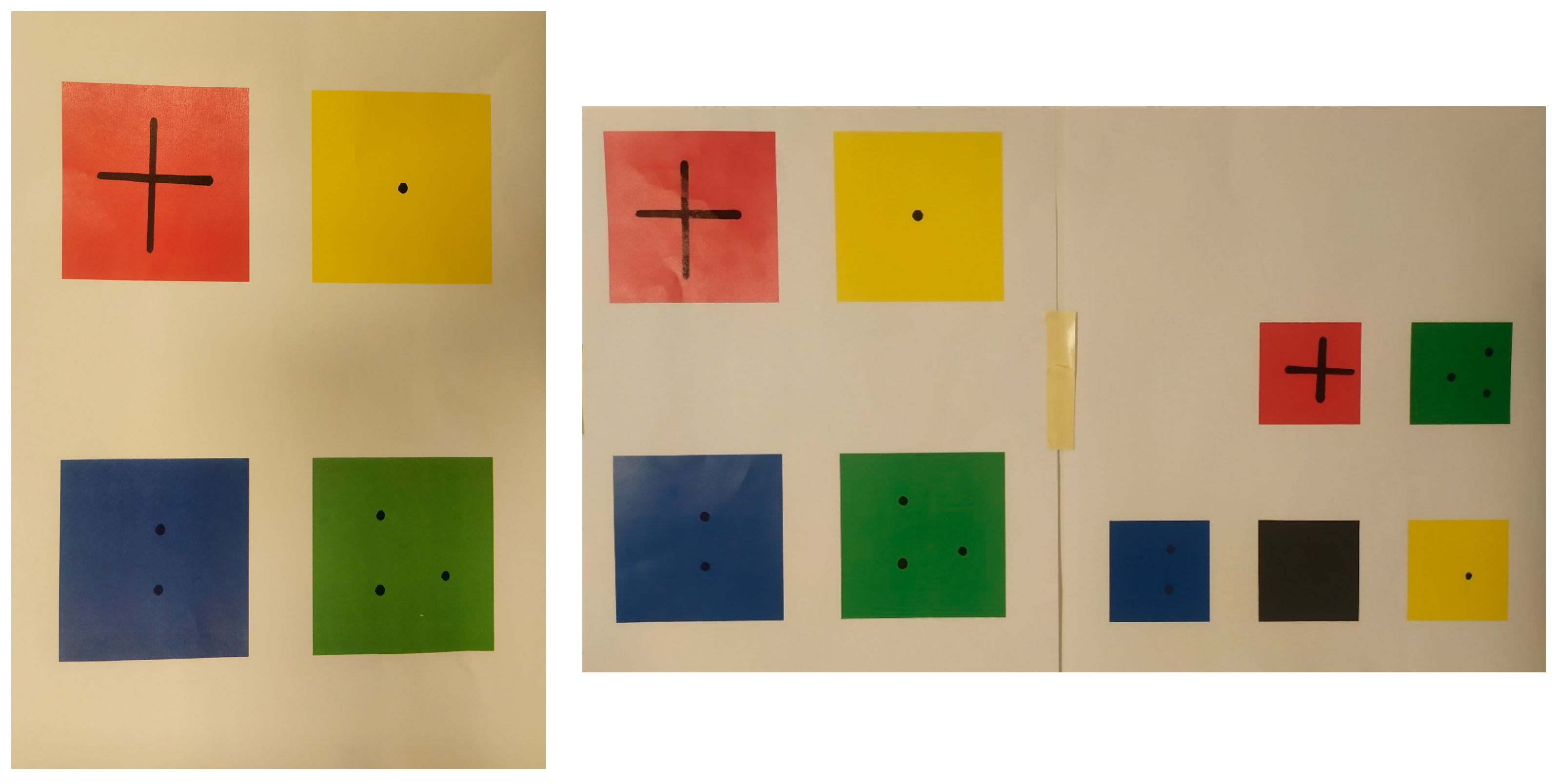
- Workspace: the AI model learned the colored square boxes on a white background, so for most effective testing of the network, colors were printed on a white sheet of paper.
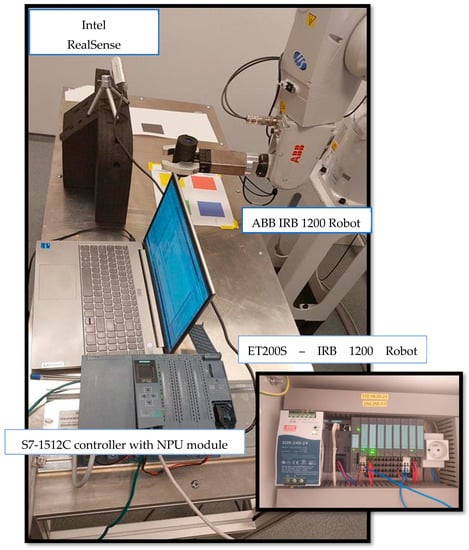

Figure 2.
The testbed—an image recognition system based on two Siemens controllers, Intel RealSense camera, NPU module and IRB1200 robot.
Figure 2.
The testbed—an image recognition system based on two Siemens controllers, Intel RealSense camera, NPU module and IRB1200 robot.

3.2. NLP Study—Image Recognition
For the study of colors, the following were chosen: basic RGB colors (Red; Green; Blue), which from the computer level are the farthest apart, black, which according to the program is the absence of colors, and yellow, which is a mixture of red and green. All colors were placed as squares on a white background.
In the course of the work, it was found that various external factors such as lighting or print quality could adversely affect the recognition of the image from NPU, and before that from Intel RealSense camera. In order to avoid reading the color incorrectly, five different shades, shown in Table 1, were used for the artificial neural network to learn a given color.

Table 1.
The five introduced colors with five different shades each.
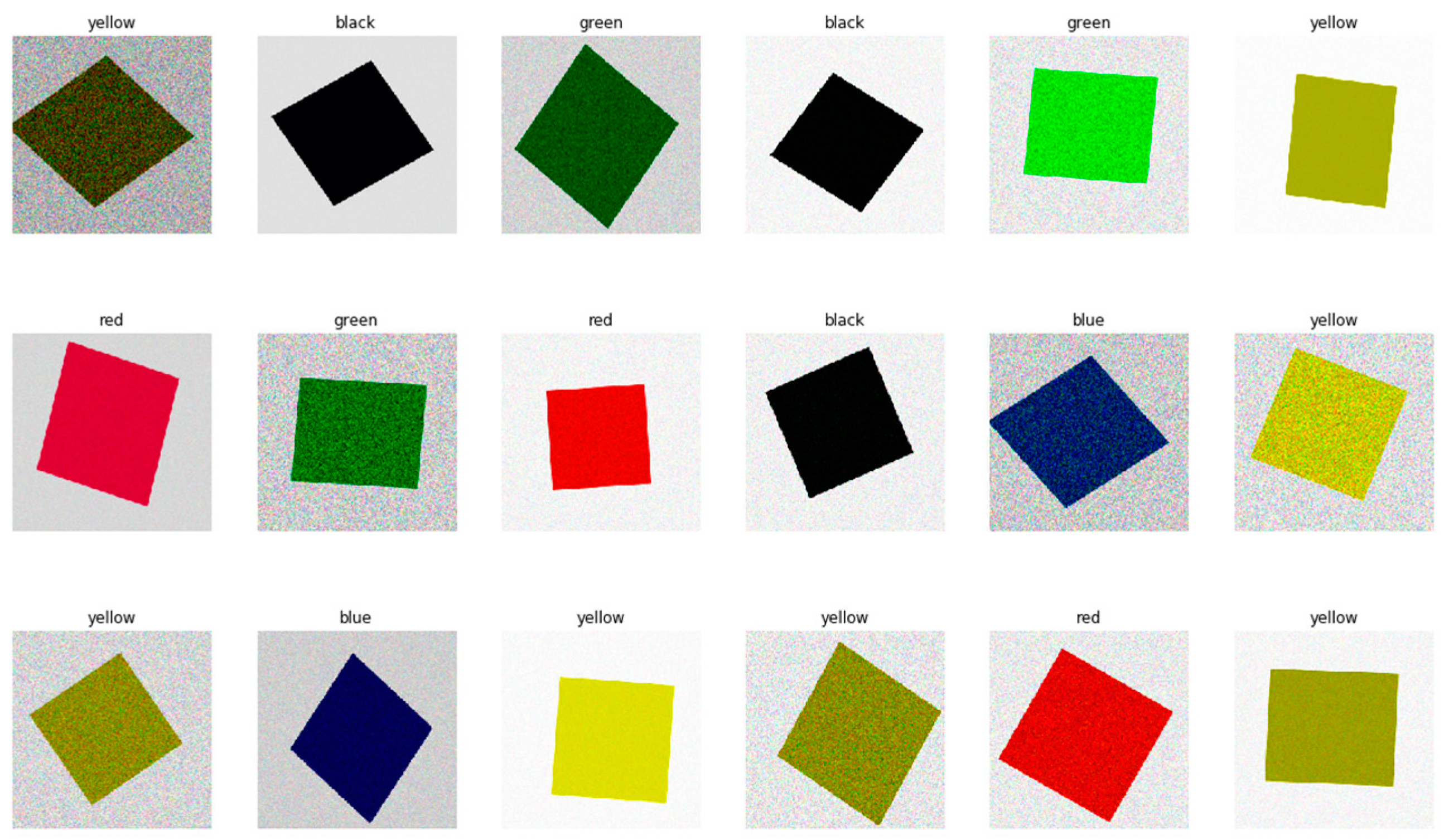
Using the TensorFlow library, an augmented training base was generated. The mobilenet_v2 generator (tf.keras.applications.mobilenet_v2.preprocess_input) was used. In this step, the original images were transformed many times, adding noise or changing their rotation. Below is a set of sample training data produced by the generator (Figure 3).
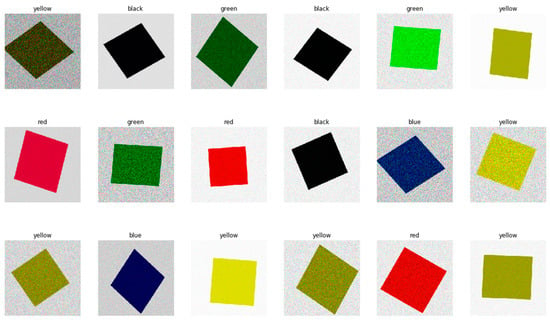
Figure 3.
Training base. Samples produced using TensorFlow library.
Next, a pure artificial neural network model was produced and training parameters were set, such as learning patience (in the absence of performance improvement in the given number of epochs, selecting the best model before that number) and the number of epochs. With a total of 125 images in the original database, the learning algorithm generally works quickly and needs 5 s per epoch.
The final step of data preparation was to increase the number of images in order to teach the artificial neural network even more effectively. The five shades of each color were duplicated several times, reaching a total of 25 samples per color. After that, it was transferred to a virtual machine so that a folder of photos could be connected to the learning algorithm. Each color has its own folder, which translates into classes in the artificial neural network model.
Two artificial intelligence models have been designed. The first a regular one based on Mobilenet layer (tf.keras.applications.mobilenet.preprocess_input). The neural network model was subjected to 10 tests (10 epochs). The following diagram (Figure 4) represents the network model based on Mobilenet layer—Model 1.
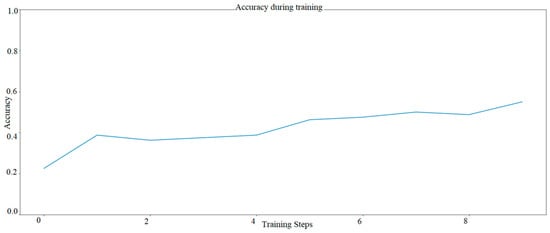
Figure 4.
Learning progress of the AI model with Mobilenet layer—Model One AI. The graph was developed based on TensorFlow library.
The second model (Figure 5) includes activation functions such as ReLU, Convultion2D and maxpooling2D layer, dropout layer—Model 2. Both models were compared for 20 image samples.
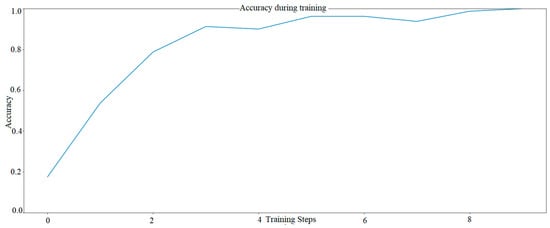
Figure 5.
The learning progress of AI model with several solutions proposed by Siemens—Model two AI. The graph was developed based on TensorFlow library.
It was observed that for model 2 with a small number of colors (the model was taught for only 5 shades), the progress of teaching is visible very quickly and already in the fifth epoch the efficiency is about 97%, in the tenth epoch the efficiency is 100%. Model 1 based on the mobilenet layer was at 60%, according to the authors, this did not meet expectations. Especially since this color recognition task was not difficult. The above-mentioned trials determined that it was decided to carry out further research based on Model 2, which after 9 epochs had already reached 100% efficiency.
4. Results
The research results will be divided into two parts. The first part is about the results obtained during machine learning based on CNN and AI Model 2. The second part is based on the presentation of work of the entire testbed. The result of implementation was to be the response of the robot, controlled by artificial intelligence, to the image read by Intel RealSense camera, implemented into the NPU module. The design assumptions are as follows:
- Part 1: Artificial intelligence model (reading from Intel RealSense camera) recognizes colors: yellow, blue, green, red, black
- Part 2: The IRB 1200 robot, after recognizing the colors, reacts in a specific way described in Table 2.
 Table 2. Reaction of the robot assigned to the read color, to mark the corresponding symbol on the detected color using a marker pen.
Table 2. Reaction of the robot assigned to the read color, to mark the corresponding symbol on the detected color using a marker pen.
4.1. Results Part 1—AI
The effectiveness of the chosen artificial intelligence model (Model 2) can also be tested by performing an inference, that is, feeding several images from the original database and asking the model to make a prediction about colors.
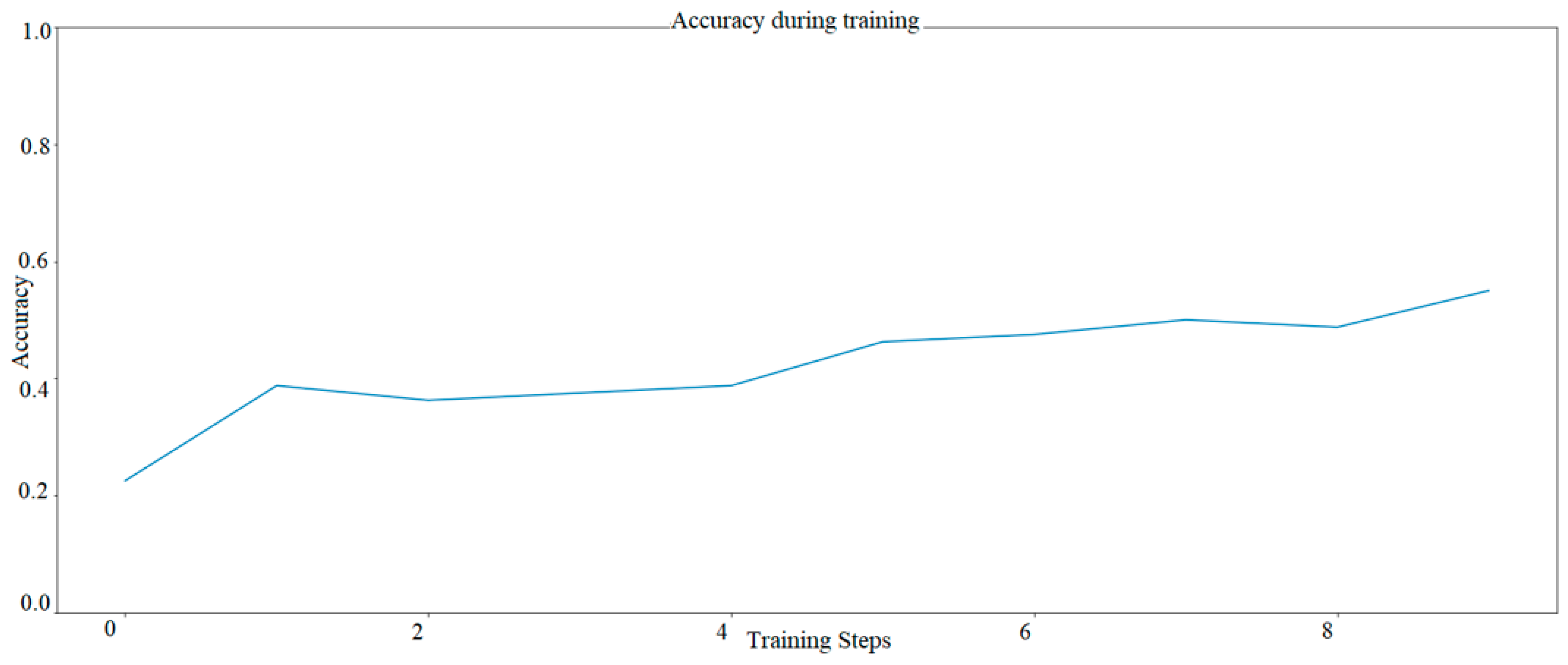
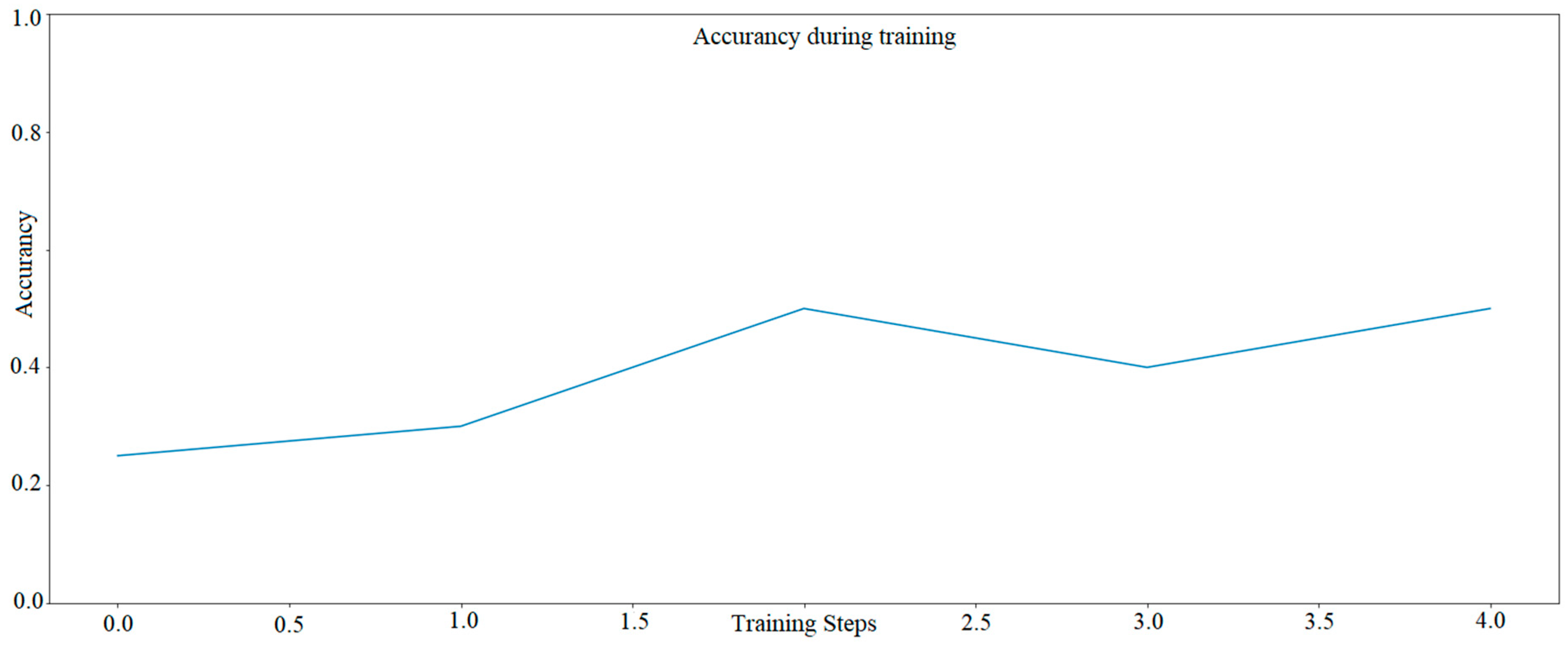
A trial in TensorFlow for five epochs was also performed for Model 2 (graph). The analysis results with an efficiency of about 45% are shown in Figure 6.
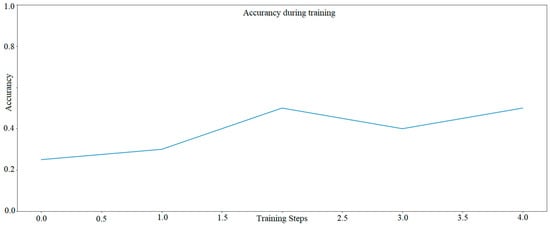
Figure 6.
The learning progress of AI model with several solutions proposed by Siemens—Model two AI only 5 epochs. The graph was developed based on TensorFlow library.
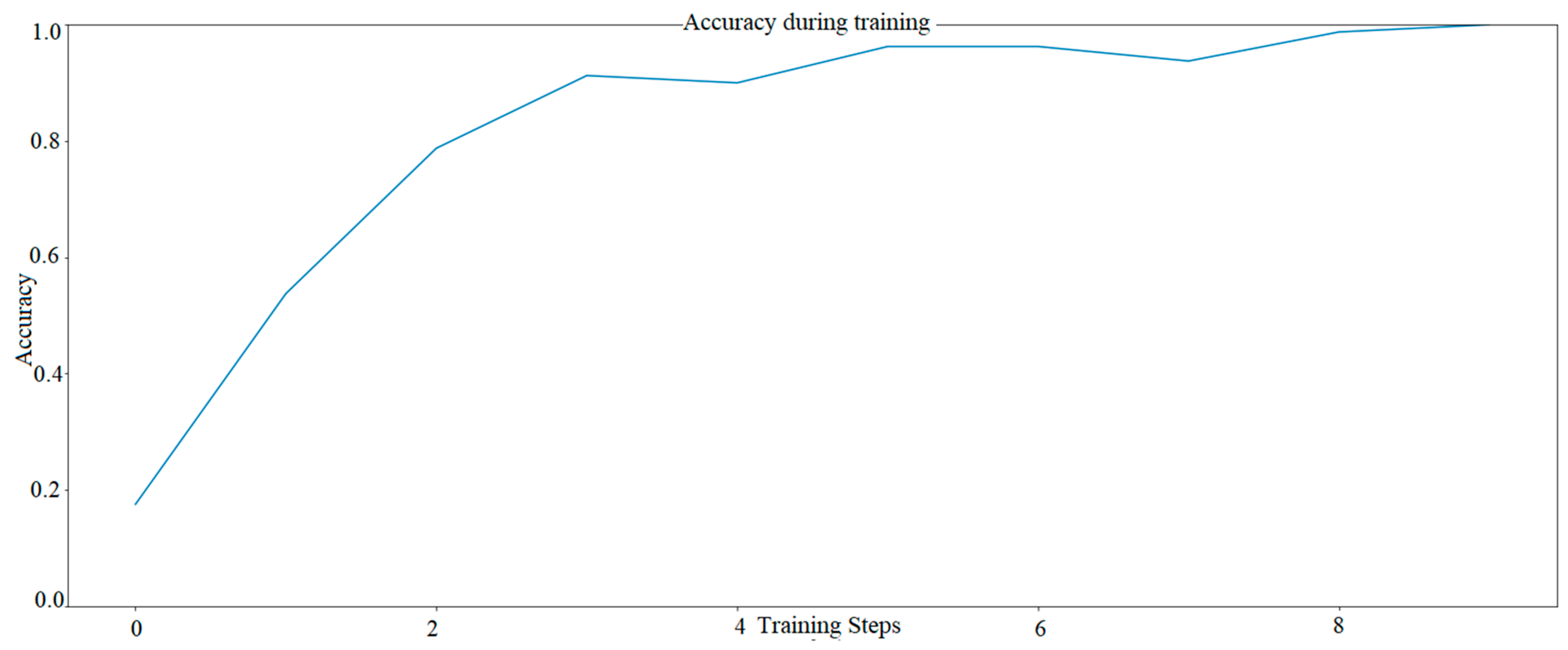
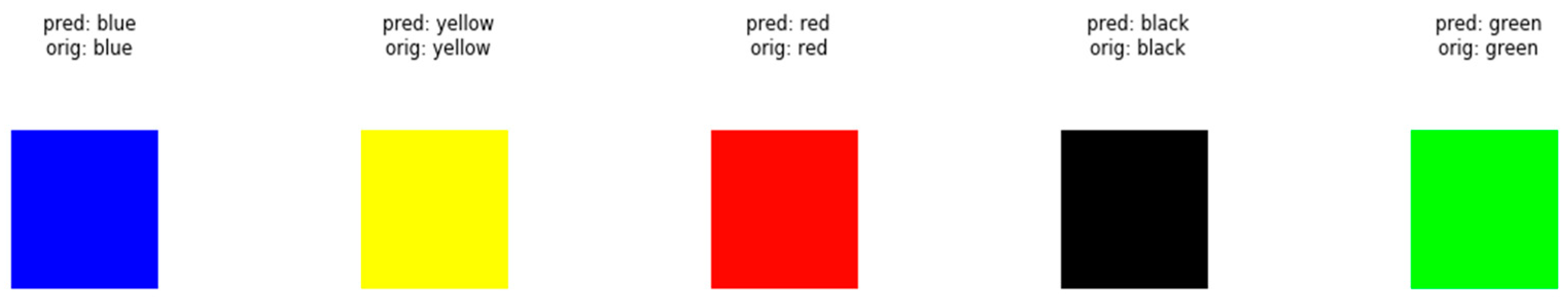
The effect can be seen in the screenshot below. In this case, “pred” is the model’s prediction, and “orig” is the actual color (Figure 7—5 epochs, Figure 8—10 epochs).

Figure 7.
The effectiveness of inference for 5 epochs.

Figure 8.
The effectiveness of inference for 10 epochs.
4.2. Results Part 2—Testbed
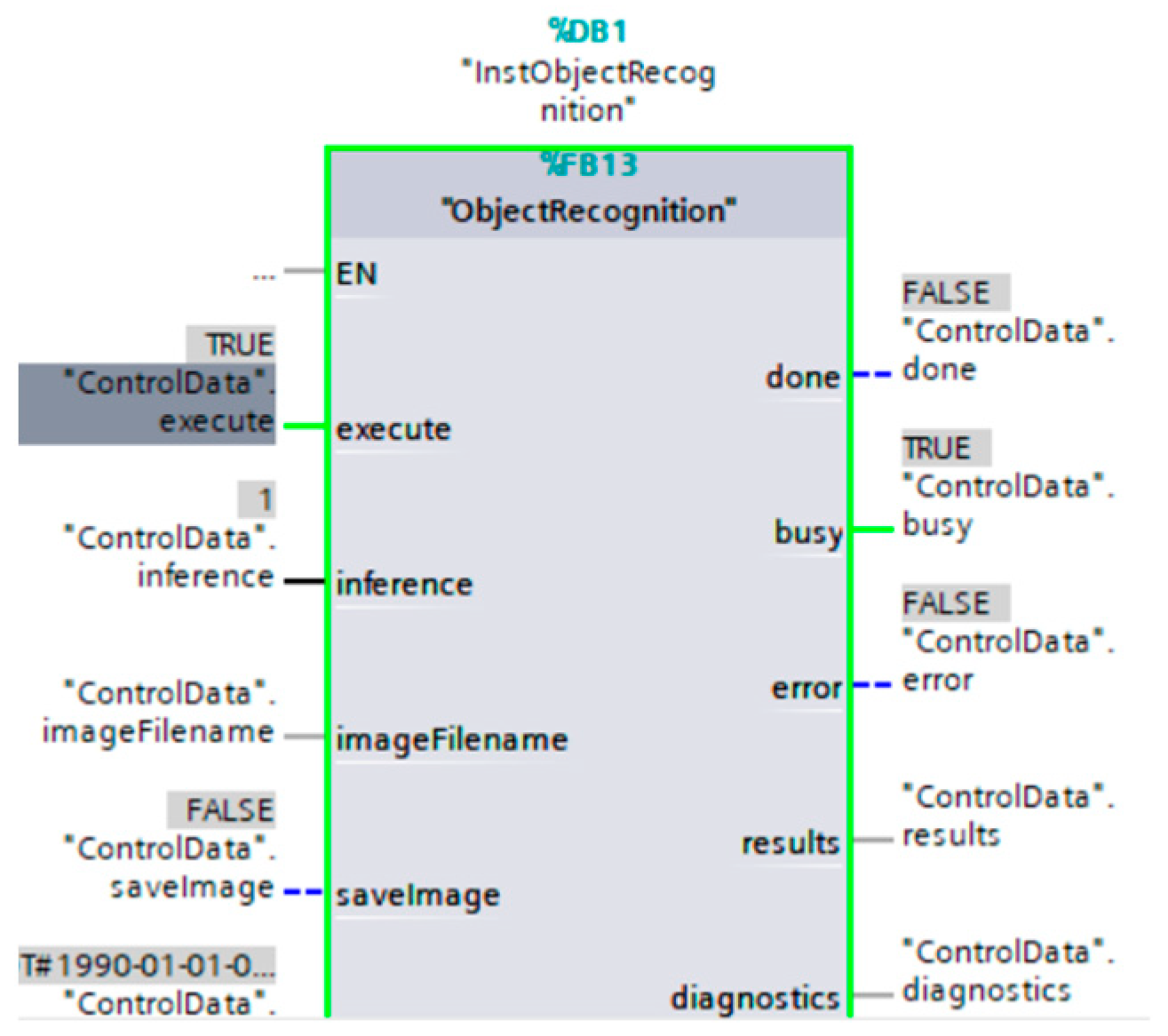
Part two deals with the operation of the IRB1200 robotic arm, which depends on several important steps. The artificial intelligence is trained in an algorithm written in Phyton language in a virtual machine on Linux. It is necessary for it to be on a different disk from the control system, in this case TIA Portal (Figure 9).
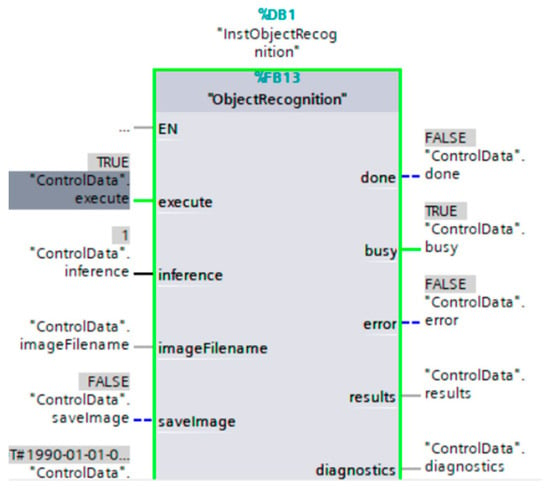
Figure 9.
Part of the program written in TIA Portal to read data from the camera and run the interference parameter (“ControlData” interference), which in this case concerns image classification (according to the learned AI model). The green color is evidence of the operation of the controller in the given calculation process.
After the AI model is produced according to manufacturer’s steps [37], it needs to be written on the card and implemented into the NPU module. The image is continuously read by the camera. After proper interpretation of the code, the trajectory of robotic arm dependent on detected color is designed. The table below shows dependence of the symbol drawn by robot arm using a marker pen to the read color.
Two trials were conducted (Figure 10), with the first board placing four colored rectangles on a card. The second trial involves the recognition of five colored rectangles, with the assumption that the robot will not respond to black color. The tests were carried out on two boards with colored boxes, the rectangles were randomly inserted on the board (Figure 10).

Figure 10.
The proof of task competition. Testbed—sample 1, Testbed—sample 2.
The verification of the results obtained from implementation work at Sii is posted at: image archive [38]. A video of implementation work at Sii including the work of the robotic arm is posted at [39].
5. Discussion
The tests carried out provide evidence that a simple task can be performed by the IRB1200 robotic arm, whose work depends on the read image and, above all, on the learned model of the neural network, which is capable of discerning 5 colors.
The results of AI model, shown in Figure 7, mean that in the first case, the number of epochs (i.e., successive generations of the neural network, where each successive generation tries to select the best selection features from the previous one) is reduced to five, and its efficiency (i.e., the percentage of correct predictions) ranges from 25% to 50%. The results show that with such a small number, the artificial neural network will not manage to learn to correctly recognize colors that share common features. In this case, yellow, which is a mixture of green and red. Hence, it can be seen that seeing a significant level of color (according to the RGB color scale) green or red in a given image, the network recognizes the color as yellow.
In contrast, the second model (Figure 8) was taught twice for ten epochs, which resulted in improved results. In the first approach the efficiency reached about 80%, and with the second approach the results rose to values between 95% and 100%. It can be observed that increasing the number of epochs significantly improves the prediction results of the artificial neural network. Similar effects occur with an increased number of training images and an even higher number of repetitions. Increasing the number of repetitions, as well as increasing the number of images in the training base, significantly improves the results of the artificial neural network models.
Figure 10 shows the results of the robot. As can be seen, the system correctly recognized the colors by placing the appropriate symbols on them according to the data in Table 2. The results presented are for the classification of the image read by the Intel RealSense camera and the learned artificial intelligence model for image classification.
6. Conclusions
The results obtained concern the designed image classification model for the neural network, including the configuration and programming of the IRB 1200 robot arm control system using a Siemens family controller. The implementation was carried out at Sii head office.
During the research, two AI models were analyzed finally a model containing several layers was selected. The layer used was maxpooling2D version (2,2), which changes the depth of the layer volume while keeping the same number of slices. The maxpooling operation is performed separately in each slice [40]. In addition, the size maxpooling is (2,2), convolution kernel size id (3,3) and number of convolutional filters is 32. The AI model includes a “dropout” layer, which speeds up learning by preventing over-fitting, among other things [41]. Based on the results of two different models (Model 1 (Figure 4) and model 2 (Figure 5)) based on the same data set, it can be seen that the number of epochs significantly affects the effectiveness of the artificial neural network.
The purpose of the paper was to study CNN models such as mobilenetv2, ReLU, Convultion2D and maxpooling2D with the application of this knowledge based on Industry 4.0. The verification of the AI model is supported by the TensorFlow environment. The study showed that it is possible to implement AI for Siemens’ novel approach to a Siemens family controller-compatible NPU module. This is a very interesting application of machine learning theoretical considerations to industrial solutions.
It has been proven that 5 colors can be verified on the proposed AI model and the robot can be taught to respond to a specific color. Verification of these results on a real robot at Sii makes it possible to verify other models for image detection. The testbed has a lot of potential, due to the multidimensionality that is now part of Industry 4.0.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.R., N.P. and K.K.; methodology, M.R.; software, K.K.; validation, M.R., N.P. and K.K.; formal analysis, M.R.; investigation, M.R. and K.K.; resources, N.P.; data curation, N.P.; writing—original draft preparation, M.R.; writing—review and editing, N.P.; visualization, M.R.; supervision, M.R.; project administration, M.R.; funding acquisition, M.R., N.P. and K.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The project was financed within the framework of the program by Ministry of Science and Higher Education called “Regionalna Inicjatywa Doskonalosci” in the years 2019–2022, project number 006/RID/2018/19, and the sum of financing was 11,870,000 PLN.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available for request.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks for providing the IRB1200 robotic arm to the company “Sii” headquartered in Gdansk, Poland, and to the company “Siemens”—headquartered in Warsaw—for providing documentation for the NPU module. Subsidized by the Poland Minister of Education and Science with funds from the state budget as part of the program “Student Scientific Circles create innovations”. SKN/SP/495972/2021.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savva, M.; Kong, N.; Chhajta, A.; Fei-Fei, L.; Agrawala, M.; Heer, J. Revision: Automated classification, analysis and redesign of chart images. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 16–19 October 2011; pp. 393–402. [Google Scholar]
- Dessí, D.; Osborne, F.; Recupero, D.R.; Buscaldi, D.; Motta, E. SCICERO: A deep learning and NLP approach for generating scientific knowledge graphs in the computer science domain. Knowl. Based Syst. 2022, 258, 109945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. GradientBased Learning Applied to Document Recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.R.; Pandey, M.; Rautaray, S. Application of deep learning for object detection. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 132, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A.; Protopapadakis, E. Deep Learning for Computer Vision: A Brief Review. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 13, 7068349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.T.; Chee, P.S.; Lim, E.H.; Lim, C.C. Artificial intelligence (AI)-driven smart glove for object recognition application. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 64, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, H.; Ruan, X.; Yang, M.H. Deep Networks for Saliency Detection via Local Estimation and Global Search. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Juan, PR, USA, 17–19 June 1997; pp. 3183–3192. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, B.; Ye, W.; Zheng, J.; Chai, Q.; Yao, Y. RETRACTED: Deep network for visual saliency prediction by encoding image composition. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2018, 55, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Meng, Z.; Nojiri, N.; Iwahori, Y.; Meng, L.; Tomiyama, H. A HOG-SVM Based Fall Detection IoT System for Elderly Persons Using Deep Sensor. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 147, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Srivastava, S.; Arora, K.; Bareja, S. Improved Gait Recognition Using Gradient Histogram Gaussian Image. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 58, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Işın, A.; Direkoğlu, C.; Şah, M. Review of MRI-based Brain Tumor Image Segmentation Using Deep Learning Methods. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 102, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, I.; Yan, J.; Abbas, Q.; Shaheed, K.; Riaz, A.B.; Wahid, A.; Khan, M.W.J.; Szczuko, P. Medical image segmentation using deep semantic-based methods: A review of techniques, applications and emerging trends. Inf. Fusion 2023, 90, 316–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontiwachwuthikul, P.; Chan, C.W.; Zeng, F.; Liang, Z.; Sema, T.; Chao, M. Recent progress and new developments of applications of artificial intelligence (AI), knowledge-based systems (KBS), and Machine Learning (ML) in the petroleum industry. Spec. Issue Artif. Intell. Pet. J. 2020, 6, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Xiang, Y.; Lin, D.; Yan, A.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Lai, W.; Wu, X.; Wan, C.; et al. Standardization of collection, storage, annotation, and management of data related to medical artificial intelligence. Intell. Med. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Hegde, S.; Ajila, V.; Zhu, W.; Zeng, C. Review of the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Early Diagnosis and Prevention of Oral Cancer. Asia-Pac. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2022, 9, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Zhang, D.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dai, N.; Song, Y.; Chen, H. Artificial intelligence in sustainable energy industry: Status Quo, challenges and opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abioye, S.O.; Oyedele, L.O.; Akanbi, L.; Ajayi, A.; Delgado, J.M.D.; Akinade, O.O.; Ahmed, A. Artificial intelligence in the construction industry: A review of present status, opportunities and future challenges. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 103299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Qiao, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, P. Data-driven AI emergency planning in process industry. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2022, 76, 104740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewiadomski, P.; Stachowiak, A.; Pawlak, N. Knowledge on IT Tools Based on AI Maturity-Industry 4.0 Perspective. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 39, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpulainen, S.; Terziyan, V. Artificial General Intelligence vs. Industry 4.0: Do They Need Each Other. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 200, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, L.; Ma, R.; RaviChandran, N.; Lanzillotta, M. hyper-sinh: An accurate and reliable function from shallow to deep learning in TensorFlow and Keras. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2021, 6, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat, E.; Juanes, R. SciANN: A Keras/TensorFlow wrapper for scientific computations and physics-informed deep learning using artificial neural networks. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 373, 113552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PS Janardhanan. Project repositories for machine learning with TensorFlow. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 171, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Michele, A.; Colin, V.; Santika, D.D. MobileNet Convolutional Neural Networks and Support Vector Machines for Palmprint Recognition. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 157, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbel, J.J.; Siddiq, U.H.; Zarnekow, R. Towards Virtual 3D Asset Price Prediction Based on Machine Learning. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2022, 17, 924–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, P.; Baglio, S.; Fortuna, L.; Manganaro, G. Self-organization in a two-layer CNN. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 1998, 45, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, I.; Mazahir, A.; Fatima, A.; Ashraf, I. Internal defects detection and classification in hollow cylindrical surfaces using single shot detection and MobileNet. Measurement 2022, 202, 111836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Company Mathworks: Introduction CNN. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/videos/introduction-to-deep-learning-what-are-convolutional-neural-networks--1489512765771.html (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Explained Convolutional-Neural-Networks. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/convolutional-neural-networks-explained-9cc5188c4939 (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Juan, PR, USA, 17–19 June 1997; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Information about Openvino. Available online: https://docs.openvino.ai/2020.1/_docs_MO_DG_prepare_model_convert_model_Convert_Model_From_TensorFlow.html (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Company Whos Starter Work System. Available online: https://sii.pl/ (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Solowjow, E.; Ugalde, I.; Shahapurkar, Y.; Aparicio, J.; Mahler, J.; Satish, V.; Goldberg, K.; Claussen., H. Industrial robot grasping with deep learning using a programmable logic controller (plc). In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 16th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), online, 20–21 August 2020; pp. 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Siemens Module NPU. Available online: https://new.siemens.com/global/en/products/automation/systems/industrial/plc/simatic-s7-1500/simatic-s7-1500-tm-npu.html (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- Picture Result on Page. Available online: https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100049758506515 (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Video Run Robot IRB1200 with NPU and Camera. Available online: https://pl-pl.facebook.com/people/Ko%C5%82o-Naukowe-HMI/100049758506515/ (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Zocca, V.; Spacagna, G.; Slater, D.; Roelants, P. Deep learning. Uczenie głębokie z językiem Python. In Sztuczna Inteligencja Neuronowe; Helion Energy: Everett, WA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).