High-Moment FeCo Magnetic Nanoparticles Obtained by Topochemical H2 Reduction of Co-Ferrites
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Co-Ferrite Nanoparticles
2.2. H2 Reduction of Co-Ferrite Nanoparticles
2.3. Samples’ Characterization
2.4. In Situ Study of the Reduction Kinetics
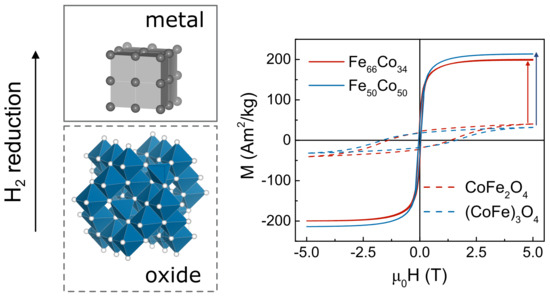
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Desvaux, C.; Amiens, C.; Fejes, P.; Renaud, P.; Respaud, M.; Lecante, P.; Snoeck, E.; Chaudret, B. Multimillimetre-large superlattices of air-stable iron-cobalt nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, G.; Hütten, A. Magnetic nanoparticles: Applications beyond data storage. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 725–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ener, S.; Anagnostopoulou, E.; Dirba, I.; Lacroix, L.M.; Ott, F.; Blon, T.; Piquemal, J.Y.; Skokov, K.P.; Gutfleisch, O.; Viau, G. Consolidation of cobalt nanorods: A new route for rare-earth free nanostructured permanent magnets. Acta Mater. 2018, 145, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huber, D.L. Synthesis, properties, and applications of iron nanoparticles. Small 2005, 1, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Su, D.; Wu, K.; Wang, J. High-moment magnetic nanoparticles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2020, 22, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkaš, B.; De Leeuw, N.H. A perspective on modelling metallic magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine: From monometals to nanoalloys and ligand-protected particles. Materials 2021, 14, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, E. Synthesis, properties and applications of magnetic nanoparticles and nanowires—A brief introduction. Magnetochemistry 2019, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folsom, S.K.; Ivey, D.J.; McNair, F.S.; Siamaki, A.R. Nickel-fe3 o4 magnetic nanoparticles supported on multiwalled carbon nanotubes: Effective catalyst in suzuki cross coupling reactions. Catalysts 2021, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Kenney, M.; Chen, Y.-S.; Zheng, X.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.X.; Gambhir, S.S.; Dai, H.; Rao, J. Carbon-coated FeCo nanoparticles as sensitive magnetic-particle-imaging tracers with photothermal and magnetothermal properties. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherlock, S.P.; Tabakman, S.M.; Xie, L.; Dai, H. Photothermally enhanced drug delivery by ultrasmall multifunctional FeCo/graphitic shell nanocrystals. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seo, W.S.; Lee, J.H.; Sun, X.; Suzuki, Y.; Mann, D.; Liu, Z.; Terashima, M.; Yang, P.C.; McConnell, M.V.; Nishimura, D.G.; et al. FeCo/graphitic-shell nanocrystals as advanced magnetic-resonance-imaging and near-infrared agents. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Xu, Y.H.; Thomas, J.; Wang, J.P. (FeCo)3Si-SiOx core-shell nanoparticles fabricated in the gas phase. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 065701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.H.; Bai, J.; Wang, J.P. High-magnetic-moment multifunctional nanoparticles for nanomedicine applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Laan, G.P.; Beenackers, A.A.C.M. Kinetics and Selectivity of the Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: A Literature Review. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 1999, 41, 255–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Dong, Y.; Yang, W.; Yu, J.; Xu, Z.; Hou, Y. Exchange-coupled fct-FePd/α-Fe nanocomposite magnets converted from Pd/Fe3O4 core/shell nanoparticles. Chem. A Eur. J. 2014, 20, 15197–15202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Sun, S. Chemical Synthesis of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Permanent Magnet Applications. Chem. A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 6757–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados-Miralles, C.; Quesada, A.; Saura-Múzquiz, M.; Andersen, H.L.; Fernández, J.F.; Christensen, M. Expanding the tunability and applicability of exchange-coupled/decoupled magnetic nanocomposites. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, R.S.; Deevi, S.C. Soft magnetic FeCo alloys: Alloy development, processing, and properties. Int. Mater. Rev. 2005, 50, 157–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardos, D.I. Mean Magnetic Moments in bcc Fe–Co Alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1969, 40, 1371–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-De Jesús, F.; Bolarín-Miró, A.M.; Cortés Escobedo, C.A.; Torres-Villaseñor, G.; Vera-Serna, P. Structural Analysis and Magnetic Properties of FeCo Alloys Obtained by Mechanical Alloying. J. Metall. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervikov, A.V. Metal, Metal Composite, and Composited Nanoparticles Obtained by Electrical Explosion of Wires. Nanobiotechnol. Rep. 2021, 16, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Wang, J.P. High-magnetic-moment core-shell-type FeCo-Au/Ag nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Nazrul Islam, M.; Parvatheeswara Rao, B.; Ogawa, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kim, C. One-pot synthesis of high magnetization air-stable FeCo nanoparticles by modified polyol method. Mater. Lett. 2013, 91, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karipoth, P.; Thirumurugan, A.; Justin Joseyphus, R. Synthesis and magnetic properties of flower-like FeCo particles through a one pot polyol process. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 404, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greculeasa, S.G.; Palade, P.; Schinteie, G.; Leca, A.; Dumitrache, F.; Lungu, I.; Prodan, G.; Kuncser, A.; Kuncser, V. Tuning structural and magnetic properties of Fe oxide nanoparticles by specific hydrogenation treatments. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spreitzer, D.; Schenk, J. Reduction of Iron Oxides with Hydrogen—A Review. Steel Res. Int. 2019, 90, 1900108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maltoni, P.; Sarkar, T.; Barucca, G.; Varvaro, G.; Locardi, F.; Peddis, D.; Mathieu, R. Tuning the magnetic properties of hard-soft SrFe12O19/CoFe2O4 nanostructures via composition/interphase coupling. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 5927–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omelyanchik, A.; Salvador, M.; D’orazio, F.; Mameli, V.; Cannas, C.; Fiorani, D.; Musinu, A.; Rivas, M.; Rodionova, V.; Varvaro, G.; et al. Magnetocrystalline and surface anisotropy in cofe2o4 nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirba, I.; Schwöbel, C.A.; Zintler, A.; Komissinskiy, P.; Molina-Luna, L.; Gutfleisch, O. Production of Fe nanoparticles from γ-Fe2O3 by high-pressure hydrogen reduction. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 4777–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylmer, D.; Rowe, M.W. Effects of a strong external magnetic field on the reduction of cobalt and iron oxides: Confirmation. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 78, 2094–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernavsky, P.A.; Kim, N.V.; Andrianov, V.A.; Perfiliev, Y.D.; Novakova, A.A.; Perov, N.S. The influence of an external magnetic field on the dynamics of magnetite reduction with hydrogen. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 15422–15427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannas, C.; Falqui, A.; Musinu, A.; Peddis, D.; Piccaluga, G. CoFe2O4 nanocrystalline powders prepared by citrate-gel methods: Synthesis, structure and magnetic properties. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2006, 8, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omelyanchik, A.; Levada, K.; Pshenichnikov, S.; Abdolrahim, M.; Baricic, M.; Kapitunova, A.; Galieva, A.; Sukhikh, S.; Astakhova, L.; Antipov, S.; et al. Green Synthesis of Co-Zn Spinel Ferrite Nanoparticles: Magnetic and Intrinsic Antimicrobial Properties. Materials 2020, 13, 5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omelyanchik, A.; Singh, G.; Volochaev, M.; Sokolov, A.; Rodionova, V.; Peddis, D. Tunable magnetic properties of Ni-doped CoFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by the sol–gel citrate self-combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 476, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graulis, S.; Chateigner, D.; Downs, R.T.; Yokochi, A.F.T.; Quirós, M.; Lutterotti, L.; Manakova, E.; Butkus, J.; Moeck, P.; Le Bail, A. Crystallography Open Database—An open-access collection of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 726–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzwarth, U.; Gibson, N. The Scherrer equation versus the ‘Debye—Scherrer equation’. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, S.E.; Fellows, B.D.; Mefford, O.T.; Thompson Mefford, O. Best Practices for Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 14159–14169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chernavskii, P.A.; Lunin, B.S.; Zakharyan, R.A.; Pankina, G.V.; Perov, N.S. Experimental setup for investigating topochemical transformations of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Instrum. Exp. Tech. 2014, 57, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaitkus, A.; Merkys, A.; Gražulis, S. Validation of the Crystallography Open Database using the Crystallographic Information Framework. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2021, 54, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.A.S.; Waerenborgh, J.C.; Mendonça, M.H.R.M.; Nunes, M.R.; Costa, F.M. Structural and morphological characterization of FeCo2O4 and CoFe2O4 spinels prepared by a coprecipitation method. Solid State Sci. 2003, 5, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionne, G.F. Magnetic Oxides; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; Volume 8, ISBN 978-1-4419-0053-1. [Google Scholar]
- Demortière, A.; Panissod, P.; Pichon, B.P.; Pourroy, G.; Guillon, D.; Donnio, B.; Bégin-Colin, S. Size-dependent properties of magnetic iron oxide nanocrystals. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omelyanchik, A.; da Silva, F.G.; Gomide, G.; Kozenkov, I.; Depeyrot, J.; Aquino, R.; Campos, A.F.C.; Fiorani, D.; Peddis, D.; Rodionova, V.; et al. Effect of citric acid on the morpho-structural and magnetic properties of ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 883, 160779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobel, M.; Nunes, W.C.; Socolovsky, L.M.; De Biasi, E.; Vargas, J.M.; Denardin, J.C. Superparamagnetism and other magnetic features in granular materials: A review on ideal and real systems. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 2836–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.J.; McNerny, K.L.; Wise, A.T.; Sorescu, M.; McHenry, M.E.; Laughlin, D.E. Observations of oxidation mechanisms and kinetics in faceted FeCo magnetic nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 09A304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishizawa, T.; Ishida, K. The Co−Fe (Cobalt−Iron) system. Bull. Alloy Phase Diagr. 1984, 5, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; Cambrige University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 0521816149. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, K.M. Fundamentals and Applications of Magnetic Materials; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; ISBN 9780199570447. [Google Scholar]





| Sample: | CoFe2O4 | Fe66Co34 | (CoFe)3O4 | Fe50Co50 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| space group | F d −3 m | I m −3 m | F d −3 m | I m −3 m | |
| a, nm | 0.8392(5) | 0.2866(1) | 0.8346(6) | 0.2859(7) | |
| dXRD, nm | 12(1) | 25(6) | 7(1) | 33(8) | |
| MS, Am2/kg | 5 K | 54(2) | 199(4) | 41(2) | 215(4) |
| 300 K | 45(2) | 203(4) | 35(2) | 215(4) | |
| μ0HC, T | 5 K | 1.37(2) | 0.045(3) | 1.63(3) | 0.042(6) |
| 300 K | 0.073(2) | 0.039(1) | 0.068(2) | 0.012(2) | |
| MR/MS | 5 K | 0.37(4) | 0.25(2) | 0.44(4) | 0.16(2) |
| 300 K | 0.14(2) | 0.21(2) | 0.16(2) | 0.12(2) | |
| Toxidation, °C | — | 410(4) | — | 453(2) 496(4) | |
| Treduction, °C | μ0H = 10 mT | 349(5) | — | 357(5) | — |
| μ0H = 0.5 T | 328(5) | 333(5) | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omelyanchik, A.; Varvaro, G.; Maltoni, P.; Rodionova, V.; Murillo, J.-P.M.; Locardi, F.; Ferretti, M.; Sangregorio, C.; Canepa, F.; Chernavsky, P.; et al. High-Moment FeCo Magnetic Nanoparticles Obtained by Topochemical H2 Reduction of Co-Ferrites. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12041899
Omelyanchik A, Varvaro G, Maltoni P, Rodionova V, Murillo J-PM, Locardi F, Ferretti M, Sangregorio C, Canepa F, Chernavsky P, et al. High-Moment FeCo Magnetic Nanoparticles Obtained by Topochemical H2 Reduction of Co-Ferrites. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(4):1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12041899
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmelyanchik, Alexander, Gaspare Varvaro, Pierfrancesco Maltoni, Valeria Rodionova, Jean-Pierre Miranda Murillo, Federico Locardi, Maurizio Ferretti, Claudio Sangregorio, Fabio Canepa, Petr Chernavsky, and et al. 2022. "High-Moment FeCo Magnetic Nanoparticles Obtained by Topochemical H2 Reduction of Co-Ferrites" Applied Sciences 12, no. 4: 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12041899
APA StyleOmelyanchik, A., Varvaro, G., Maltoni, P., Rodionova, V., Murillo, J.-P. M., Locardi, F., Ferretti, M., Sangregorio, C., Canepa, F., Chernavsky, P., Perov, N., & Peddis, D. (2022). High-Moment FeCo Magnetic Nanoparticles Obtained by Topochemical H2 Reduction of Co-Ferrites. Applied Sciences, 12(4), 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12041899